check engine MITSUBISHI GALANT 1989 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1989, Model line: GALANT, Model: MITSUBISHI GALANT 1989Pages: 1273, PDF Size: 37.62 MB
Page 236 of 1273
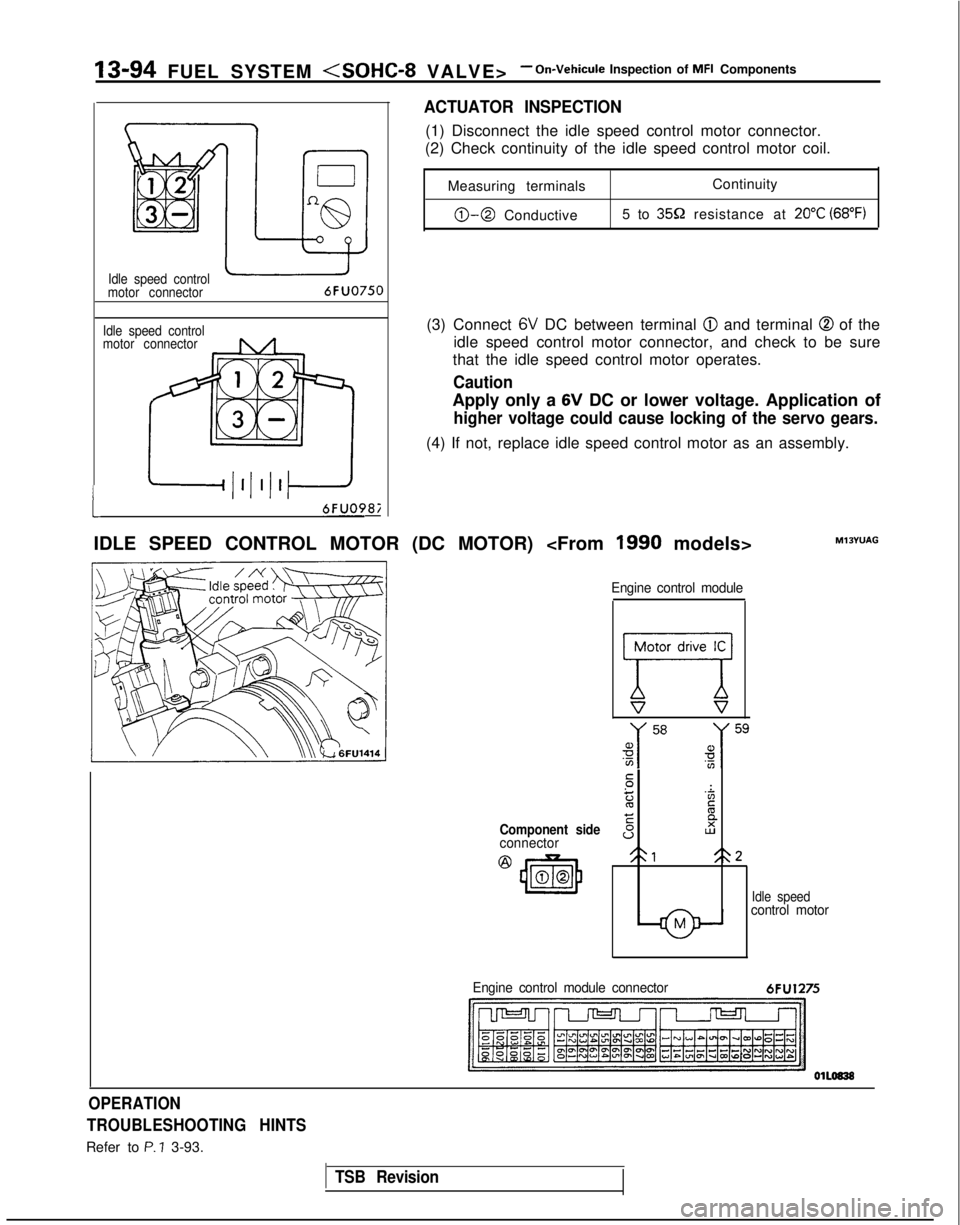
13-94 FUEL SYSTEM
1
Idle speed control
motor connector
Idle speed control
motor connector6FUO750
6FUO9&
ACTUATOR INSPECTION
(1) Disconnect the idle speed control motor connector.
(2) Check continuity of the idle speed control motor coil.
Measuring terminals Continuity
0-0 Conductive
5 to 359 resistance at 20°C (68°F)
(3) Connect 6V DC between terminal @I and terminal @ of the
idle speed control motor connector, and check to be sure
that the idle speed control motor operates.
Caution
Apply only a 6V DC or lower voltage. Application of
higher voltage could cause locking of the servo gears.
(4) If not, replace idle speed control motor as an assembly.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL MOTOR (DC MOTOR)
Component sideconnector
@
43m00
Engine control module
77V s
.-:
z'Zc
EE
sI2
21<\2
Idle speedcontrol motor
MlOYUAG
Engine control module connector
6FU1275
OPERATION
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Refer to P. ? 3-93.
TSB Revision
Page 237 of 1273
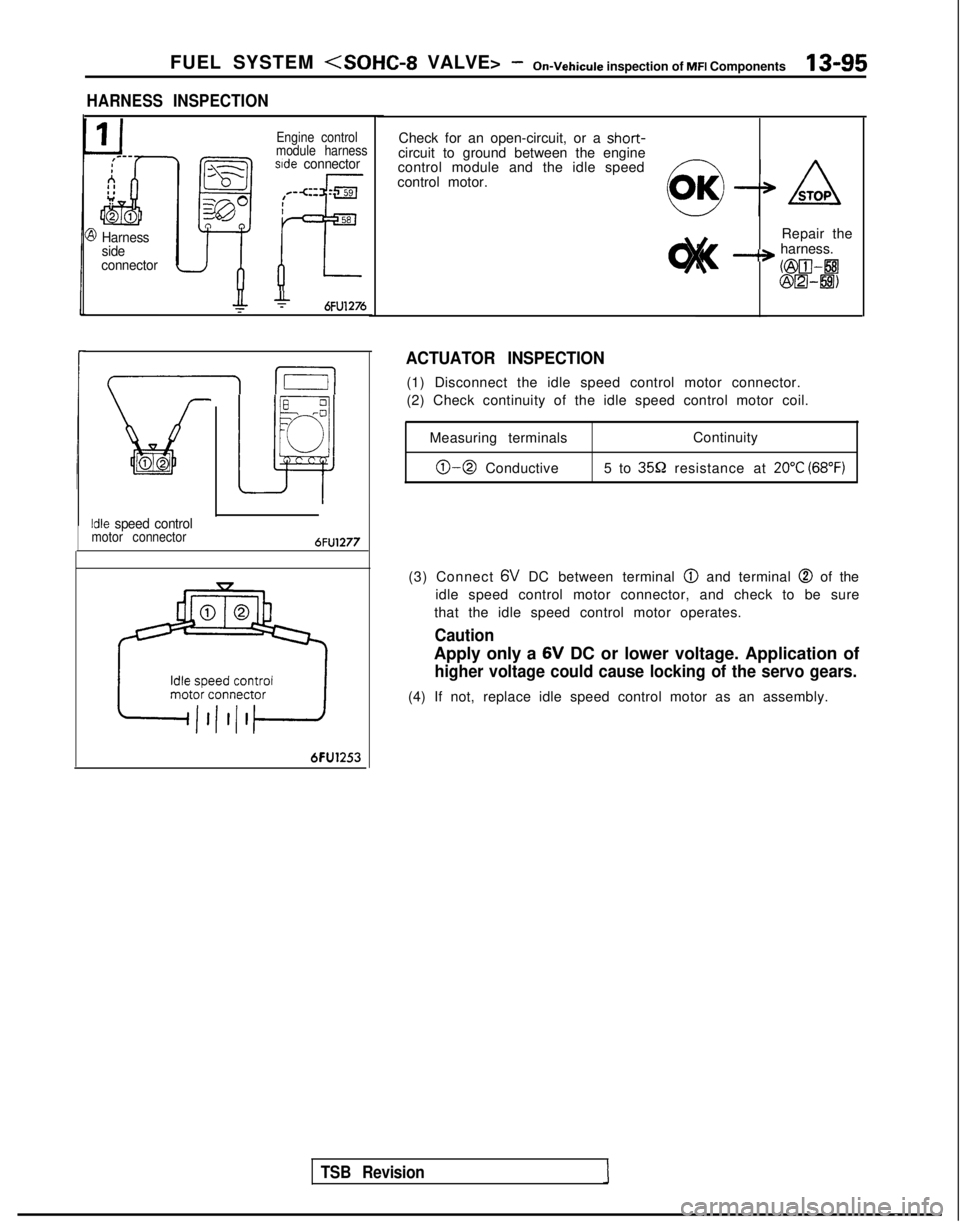
FUEL SYSTEM
HARNESS INSPECTION
3 Harness
side
connector
Engine control
module harness
sde connector
+6FU1276
I I
Lit02
Idle speed controlmotor connector6FU1277
6FU1253
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground between the engine
control module and the idle speed
control motor.
Repair the
-+ harness.
OZGII-8@m-8)
TSB Revision
ACTUATOR INSPECTION
(1) Disconnect the idle speed control motor connector.
(2) Check continuity of the idle speed control motor coil.Measuring terminals Continuity
0-0 Conductive
5 to 3552 resistance at 20°C (68°F)
(3) Connect 6V
DC between terminal @
and terminal @ of the
idle speed control motor connector, and check to be sure
that the idle speed control motor operates.
Caution
Apply only a 6V
DC or lower voltage. Application of
higher voltage could cause locking of the servo gears.
(4) If not, replace idle speed control motor as an assembly.
Page 238 of 1273
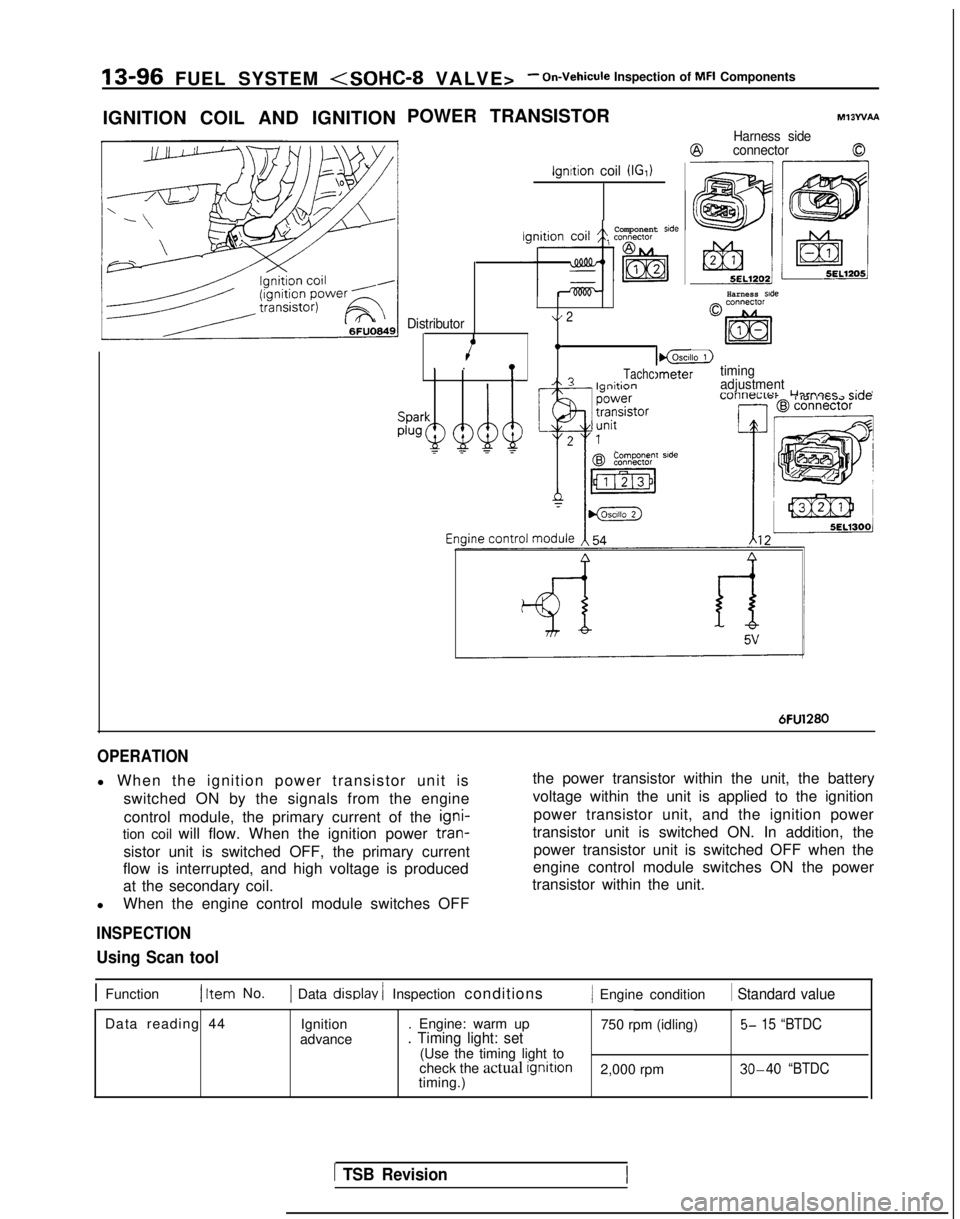
13-96 FUEL SYSTEM
IGNITION COIL AND IGNITION POWER TRANSISTOR
ignition coil (IGI)
Ml3WAA
Harness side
@connector0
Harness side
Component side
Distributor\/ 2
4.I_lgnltion. .!
I@LZ)
TachcImetertimingA? I--:*:^^adjustment-_
Lllrnacr
r;rlnI 101 i IG.72 Jl”F
Componenr side
6FU1280
OPERATION
l When the ignition power transistor unit is
switched ON by the signals from the engine
control module, the primary current of the igni-
tion coil will flow. When the ignition power tran-
sistor unit is switched OFF, the primary current
flow is interrupted, and high voltage is produced
at the secondary coil.
l When the engine control module switches OFF
INSPECTION
the power transistor within the unit, the battery
voltage within the unit is applied to the ignition
power transistor unit, and the ignition power
transistor unit is switched ON. In addition, the power transistor unit is switched OFF when the
engine control module switches ON the power
transistor within the unit.
Using Scan tool
1 Function1 Item No.1 Data display / Inspection conditions/ Engine condition 1 Standard value
Data reading 44
Ignition
advance . Engine: warm up
750 rpm (idling)5- 15 “BTDC. Timing light: set(Use the timing light to
check the actual ignition
2,000 rpm 30-40 “BTDCtiming.)
1 TSB Revision
Page 239 of 1273
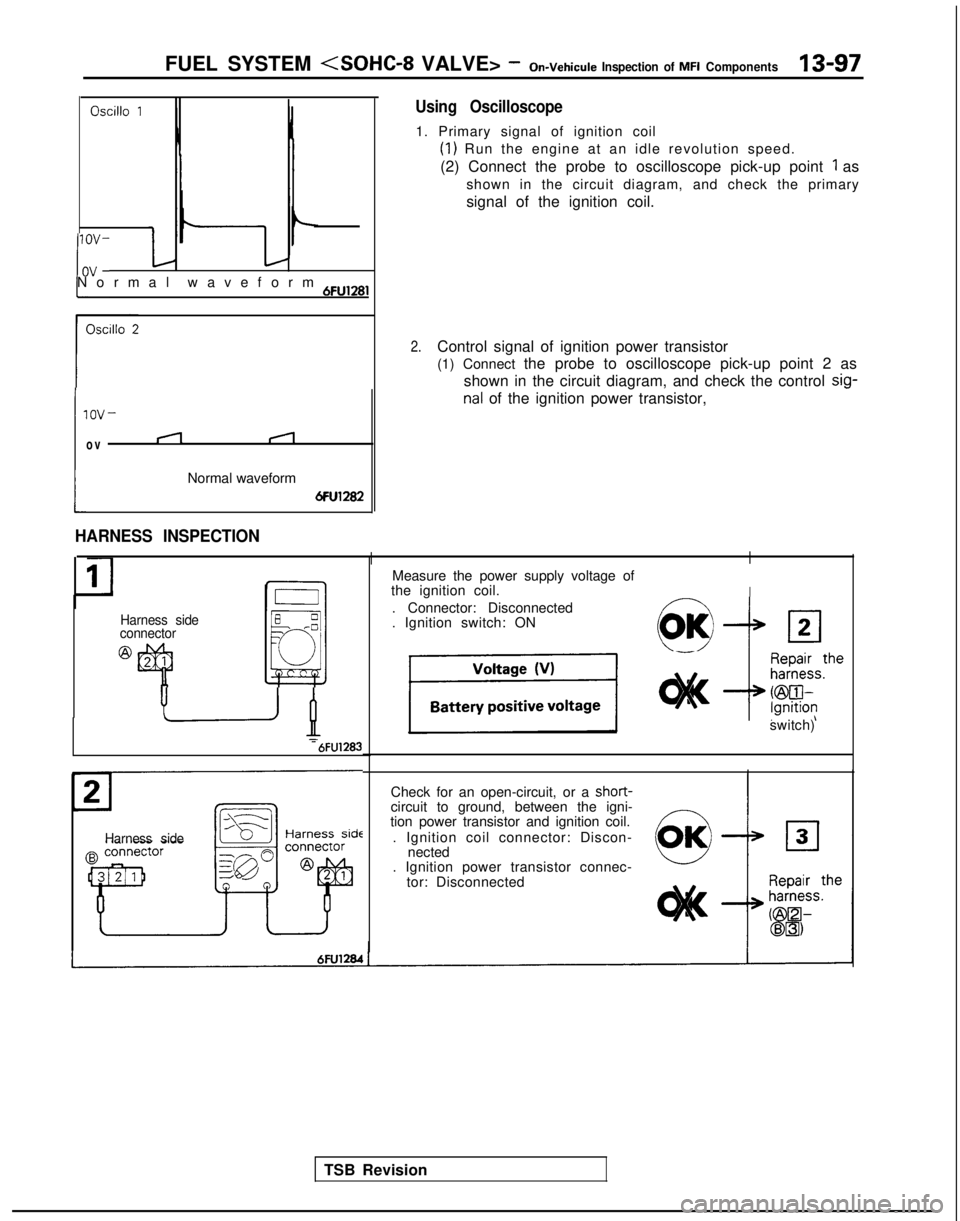
FUEL SYSTEM (SOHC-8 VALVE> -On-Vehicule Inspection of MFI Components13-97
Oscillo 1
If-Normal waveform 6Fu,28,
lOV-
ov
i
nal of the ignition power transistor,
(1
Normal waveform
6Fu1282
Using Oscilloscope
1. Primary signal of ignition coil
(1) Run the engine at an idle revolution speed.
(2) Connect the probe to oscilloscope pick-up point
1 as
shown in the circuit diagram, and check the primary
signal of the ignition coil.
2.Control signal of ignition power transistor
(1) Connect the probe to oscilloscope pick-up point 2 as shown in the circuit diagram, and check the control sig-
Harness side
connector
@
HARNESS INSPECTION
II
I I
I
Measure the power supply voltage of
the ignition coil.
. Connector: Disconnected
. Ignition switch: ON
c--vOK/III2
-‘B-6FU1283
TSB Revision
Harness side
switch)
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-
circuit to ground, between the igni-
tion power transistor and ignition coil.
. Ignition coil connector: Discon- nected
. Ignition power transistor connec-
tor: Disconnected
Page 241 of 1273
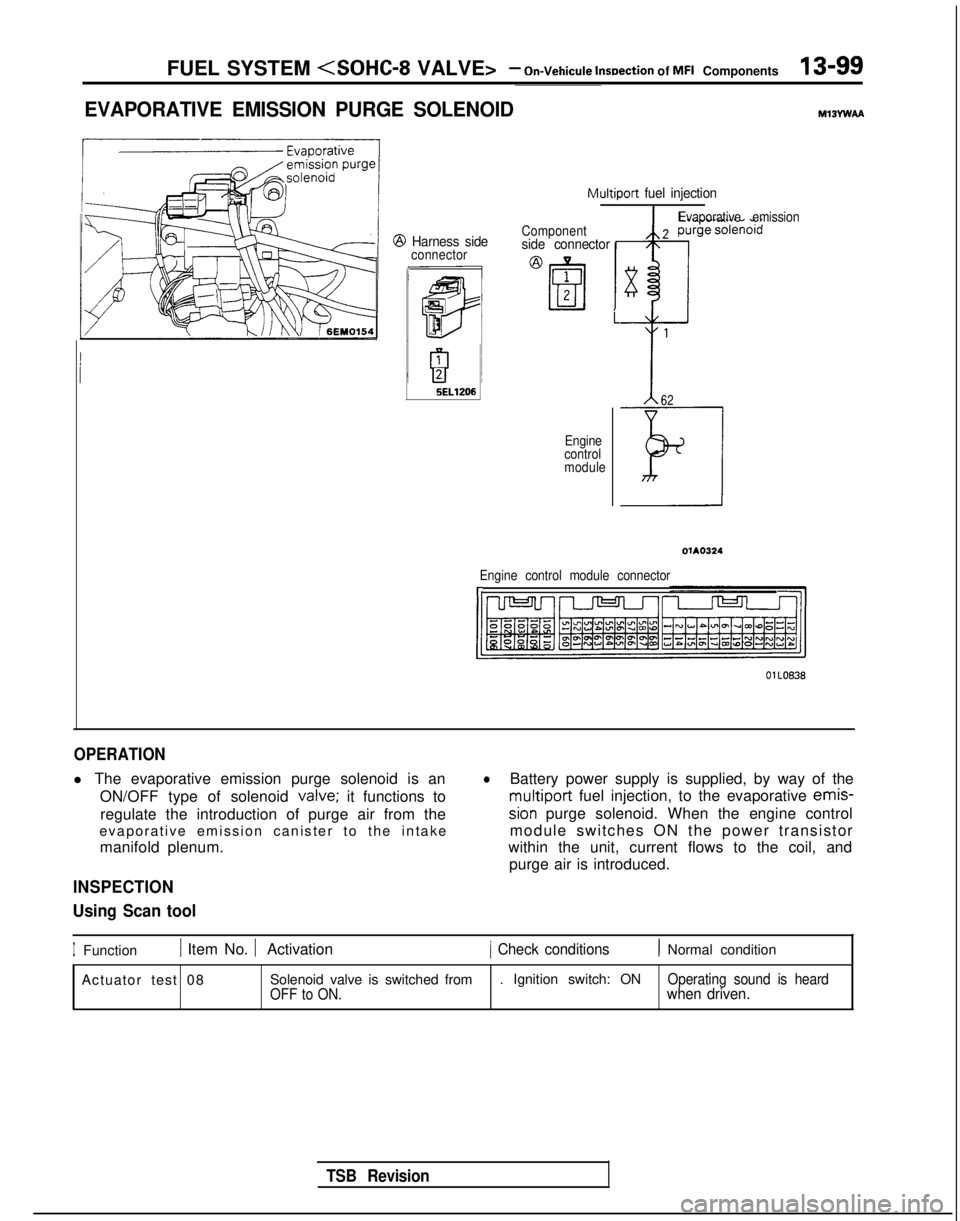
FUEL SYSTEM
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION PURGE SOLENOIDMlBYwAA
Multiport fuel injection
@ Harness sideconnector Componentside connector
i
5EL1206
Engine
control
module
TSB Revision
Evaporative emission
62
Engine control module connectorI,
OlLO838
OPERATION
l The evaporative emission purge solenoid is an
ON/OFF type of solenoid valve;
it functions to
regulate the introduction of purge air from the
evaporative emission canister to the intake
manifold plenum.
INSPECTION
Using Scan tool
lBattery power supply is supplied, by way of the multiport
fuel injection, to the evaporative emis-
sion purge solenoid. When the engine control
module switches ON the power transistor
within the unit, current flows to the coil, and
purge air is introduced.
IFunction1 Item No. 1 Activation1 Check conditions1 Normal condition
Actuator test 08 Solenoid valve is switched from . Ignition switch: ON
Operating sound is heard
OFF to ON.when driven.
Page 242 of 1273
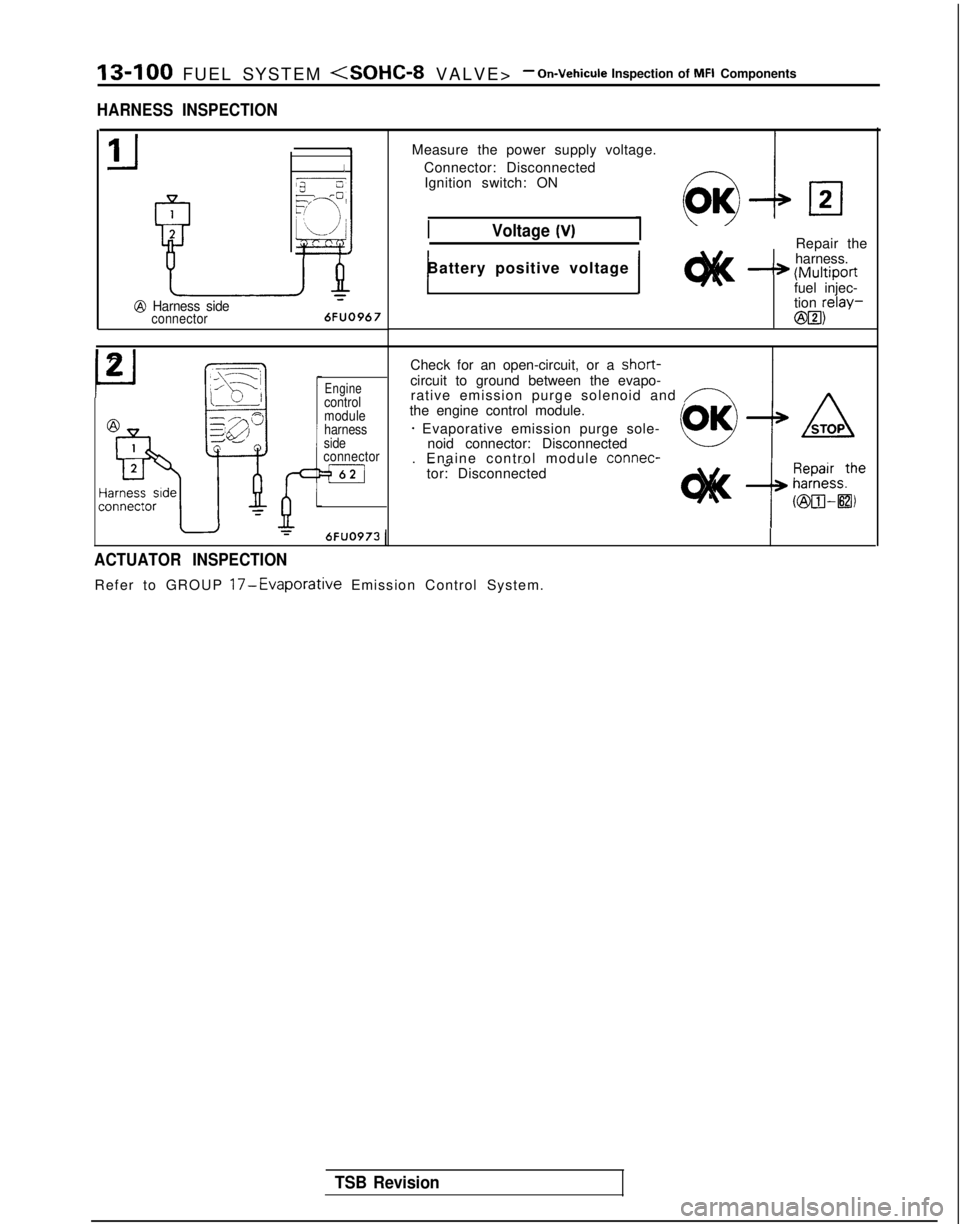
13-100 FUEL SYSTEM
- On-Vehicule Inspection of MFI Components
HARNESS INSPECTION
1
2
P
Izj----=2T !r/
‘3“L j
k&
-&@ Harness sideconnector
6FUO967
Measure
the power supply voltage.
Connector: Disconnected Ignition switch: ON
Voltage (V)Repair the
harness.
-* (Multiportfuel injec-
tion relay-
@B3)
1Battery positive voltage 1
P
2_Fq,/-\i-1- /-
F
&--
Y
Enginecontrol
module
harness
side
connector
=m
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground between the evapo-
rative emission purge solenoid and /-Athe engine control module.
* Evaporative emission purge sole- noid connector: Disconnected
. Enaine control module connec-
-a ~~tor: Disconnected
6FUO973
1
ACTUATOR INSPECTION
Refer to GROUP 17-Evaporative Emission Control System.
TSB Revision
Page 243 of 1273
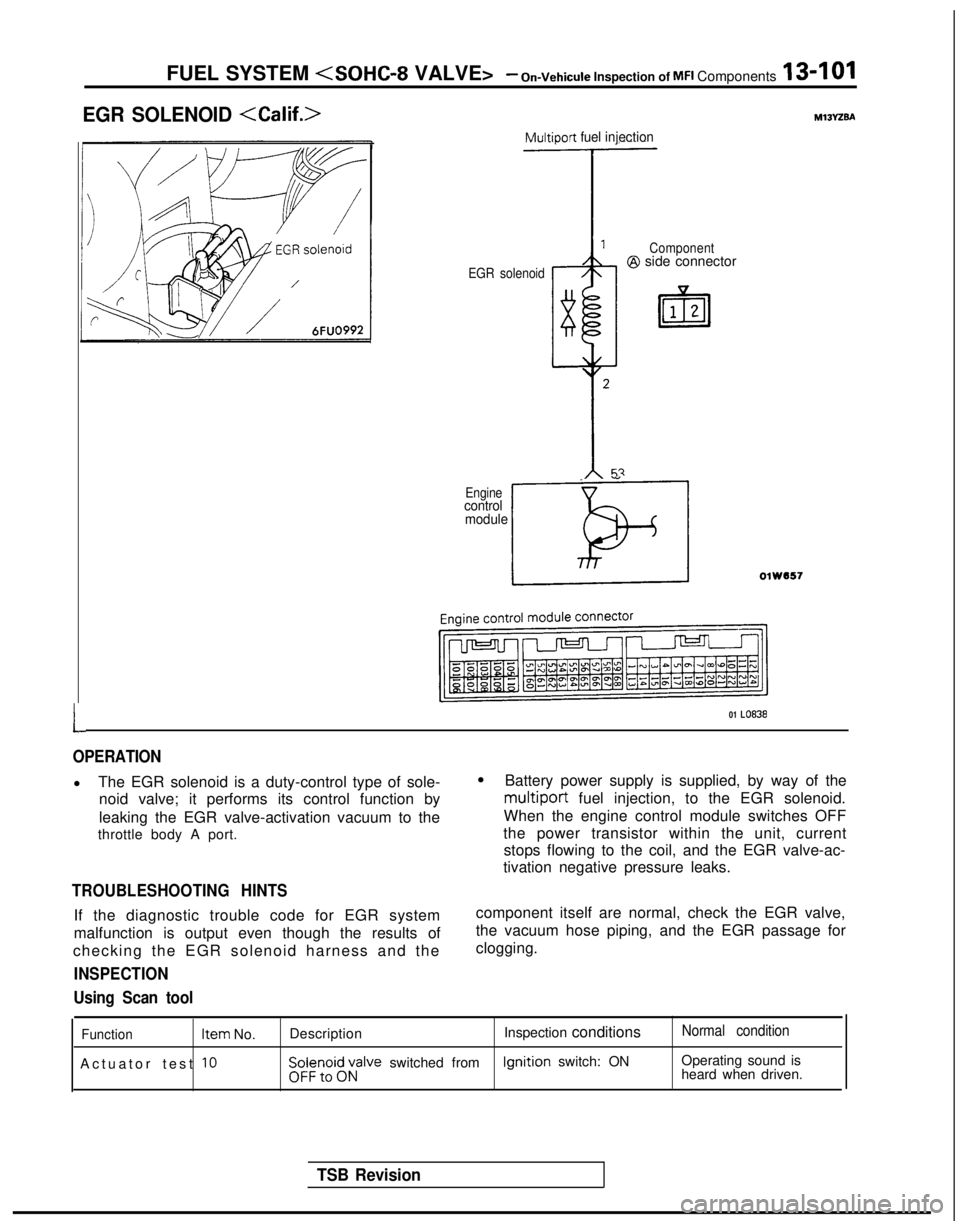
FUEL SYSTEM
EGR SOLENOID
L
Multiport fuel injection
EGR solenoid Component@I side connector
_ ”
Enginecontrol
module
LOlW557
01 LO838
OPERATION
l The EGR solenoid is a duty-control type of sole-
noid valve; it performs its control function by
leaking the EGR valve-activation vacuum to the
throttle body A port.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
If the diagnostic trouble code for EGR system
malfunction is output even though the results of
checking the EGR solenoid harness and the
INSPECTION
l Battery power supply is supplied, by way of the
multiport fuel injection, to the EGR solenoid.
When the engine control module switches OFF
the power transistor within the unit, current stops flowing to the coil, and the EGR valve-ac-
tivation negative pressure leaks.
component itself are normal, check the EGR valve,
the vacuum hose piping, and the EGR passage for
clogging.
Using Scan tool
Function Item
No.
Actuator test
10
Description Inspection conditionsNormal condition
$i;;,oi$;;alve switched from Ignition
switch: ON Operating sound is
heard when driven.
TSB Revision
Page 244 of 1273
13-102 FUEL SYSTEM
- On-Vehicule Inspection of MFI Components
HARNESS INSPECTION
Harness sideconnector
L
Harness side
connector
Engine
1
control module
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-
circuit to ground between the EGR
solenoid and the engine control mod-
harnessule.side. EGR solenoid connector: Discon-connectornected+ Engine control module connec- tor: Disconnected Repair the
-+ harness.
Kzix2l-a)
-I
Measure the power supply voltage.
. Connector: Disconnected
. Ignition switch: ON
-
ACTUATOR INSPECTION
Refer to GROUP 17-Exhaust Gas Recirculatin (EGR) System
.
FUEL PRESSURE
RELEASE OF RESIDUAL PRESSURE FROM HIGH PRESS-
URE FUEL HOSE
Make the following operations to release the pressure remain-
ing in fuel pipe line so that fuel will not flow out. @ Disconnect the fuel pump harness connector at the fuel
tank rear side.
@ Start the engine and after it stops by itself, turn the ignitionswitch to OFF.
@ Disconnect the battery (-) terminal.
@I Connect the fuel pump harness connector.
FUEL PUMP OPERATION CHECK
(1) Connect the (+)
battery terminal to the fuel pump drive
terminal and the
(-) terminal to the chassis. Confirm that
the fuel pump operates at this time.
( TSB Revision1
Page 245 of 1273
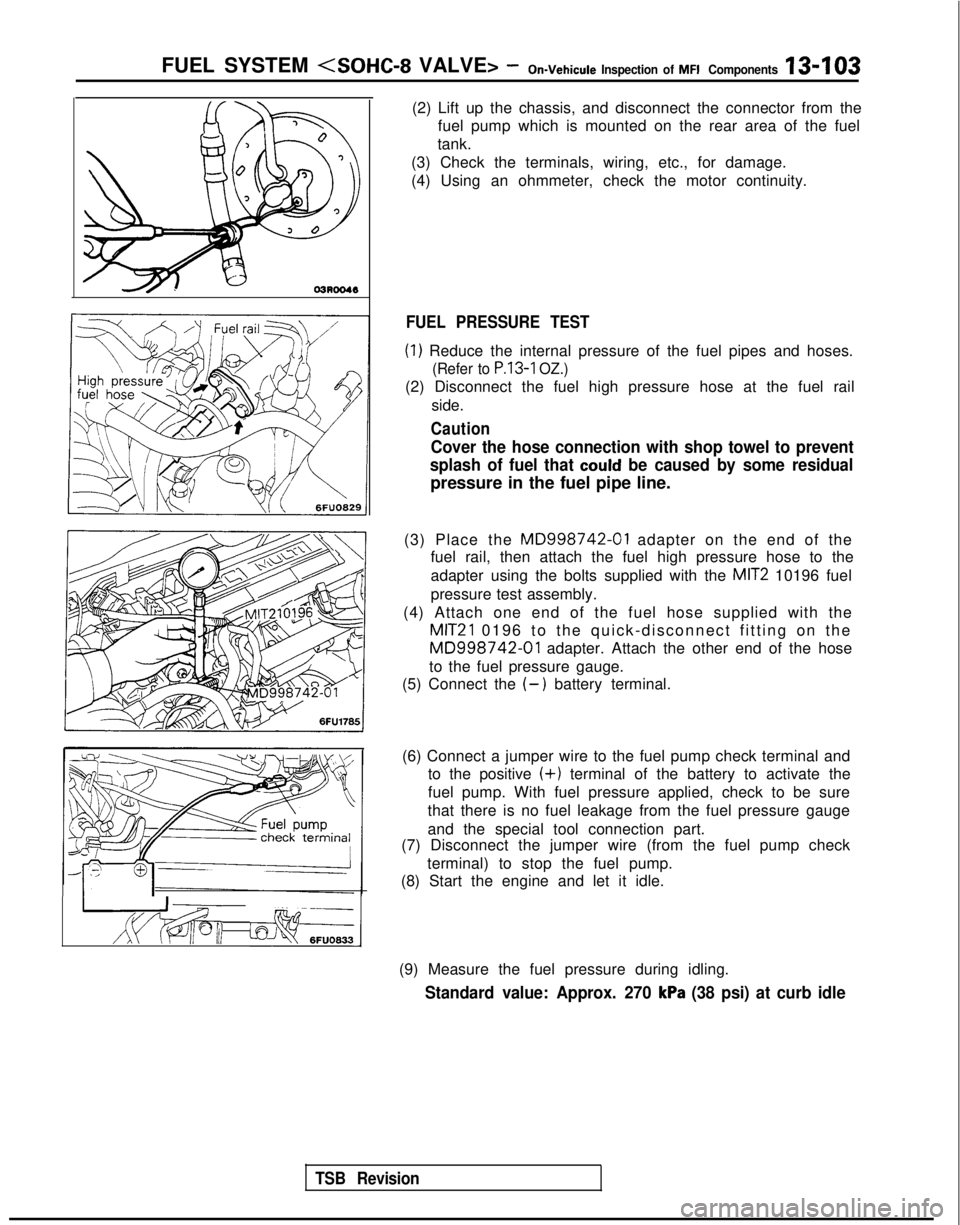
FUEL SYSTEM
TSB Revision
---
I g$qfq, tcJ-s6FUO633
(2) Lift up the chassis, and disconnect the connector from the
fuel pump which is mounted on the rear area of the fuel
tank.
(3) Check the terminals, wiring, etc., for damage.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, check the motor continuity.
FUEL PRESSURE TEST
(1) Reduce the internal pressure of the fuel pipes and hoses.
(Refer to P.13-1 OZ.)
(2) Disconnect the fuel high pressure hose at the fuel rail
side.
Caution
Cover the hose connection with shop towel to prevent
splash of fuel that
could be caused by some residual
pressure in the fuel pipe line.
(3) Place the
MD998742-01 adapter on the end of the
fuel rail, then attach the fuel high pressure hose to the
adapter using the bolts supplied with the
MIT2 10196 fuel
pressure test assembly.
(4) Attach one end of the fuel hose supplied with the
MIT21 0196 to the quick-disconnect fitting on the
MD998742-01 adapter. Attach the other end of the hose
to the fuel pressure gauge.
(5) Connect the
(-) battery terminal.
(6) Connect a jumper wire to the fuel pump check terminal and to the positive
(+) terminal of the battery to activate the
fuel pump. With fuel pressure applied, check to be sure
that there is no fuel leakage from the fuel pressure gauge
and the special tool connection part.
(7) Disconnect the jumper wire (from the fuel pump check
terminal) to stop the fuel pump.
(8) Start the engine and let it idle.
(9) Measure the fuel pressure during idling.
Standard value: Approx. 270 kPa (38 psi) at curb idle
Page 246 of 1273
13-I 04 FUEL SYSTEM
the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure
regulator, and then measure the fuel pressure while using a
finger to plug the end of the hose.
Standard value:
330-370 kPa (47-53 psi) at curb idle
speed
(11)Check to be sure that the fuel pressure during idling does
not decrease even after the engine is raced a few times.
(12)&e a finger to gently press the fuel return hose while
repeatedly racing the engine, and check to be sure that
there is fuel pressure in the return hose also.
NOTE
There will be no fuel pressure in the return hose if there is
insufficient fuel flow.
(13)lf the fuel pressure measured in steps (9) to (12) deviates
from the standard value range, check for the probable
cause by referring to the table below, and then make the
appropriate repair.
Condition Probable causeRemedy
. Fuel pressure IS too low. Fuel filter is clogged.Replace the fuel filter.
. Fuel pressure drops during racing.. No fuel pressure In fuel return hose. Malfunction of the valve seat with-Replace the fuel pressure regula-in the fuel pressure regulator, ortor.
fuel leakage to return side caused by spring deterioration.
Fuel pump low discharge pressure.Replace the fuel pump.
Fuel pressure is too
highThe valve within the fuel pressure Replace the fuel pressure regula-regulator is sticking.
tor.
Clogging of the fuel return hose Clean or replace the hose and/or
and/or the pipe.pipe.
No change of the fuel pressure when Damaged vacuum hose or nippleReplace the vacuum hose, or clean
vacuum hose IS connected and when not clogging.the nipple.connected.
(14)Stop the engine and check for a change of the value
indicated by the fuel pressure gauge. The condition is
normal if there is no decrease of the indicated value within
two minutes. If there is a decrease of the indicated value, monitor the
speed of the decrease, and, referring to the table below.
determine the cause of the problem and make the
appropriate repair.
Condition Probable cause
After the engine is stopped, the fuel Injector leakage
pressure drops graudally.
Remedy
Replace the injector.
Leakage at the fuel pressure reg-
Replace the fuel pressure regula-
ulator valve seat tor.
There IS a sudden sharp drop of the fuel The check valve
(within the fuel Replace the fuel pump.
pressure immediately after the engine is pump) is not closed.
stopped.
TSB Revision