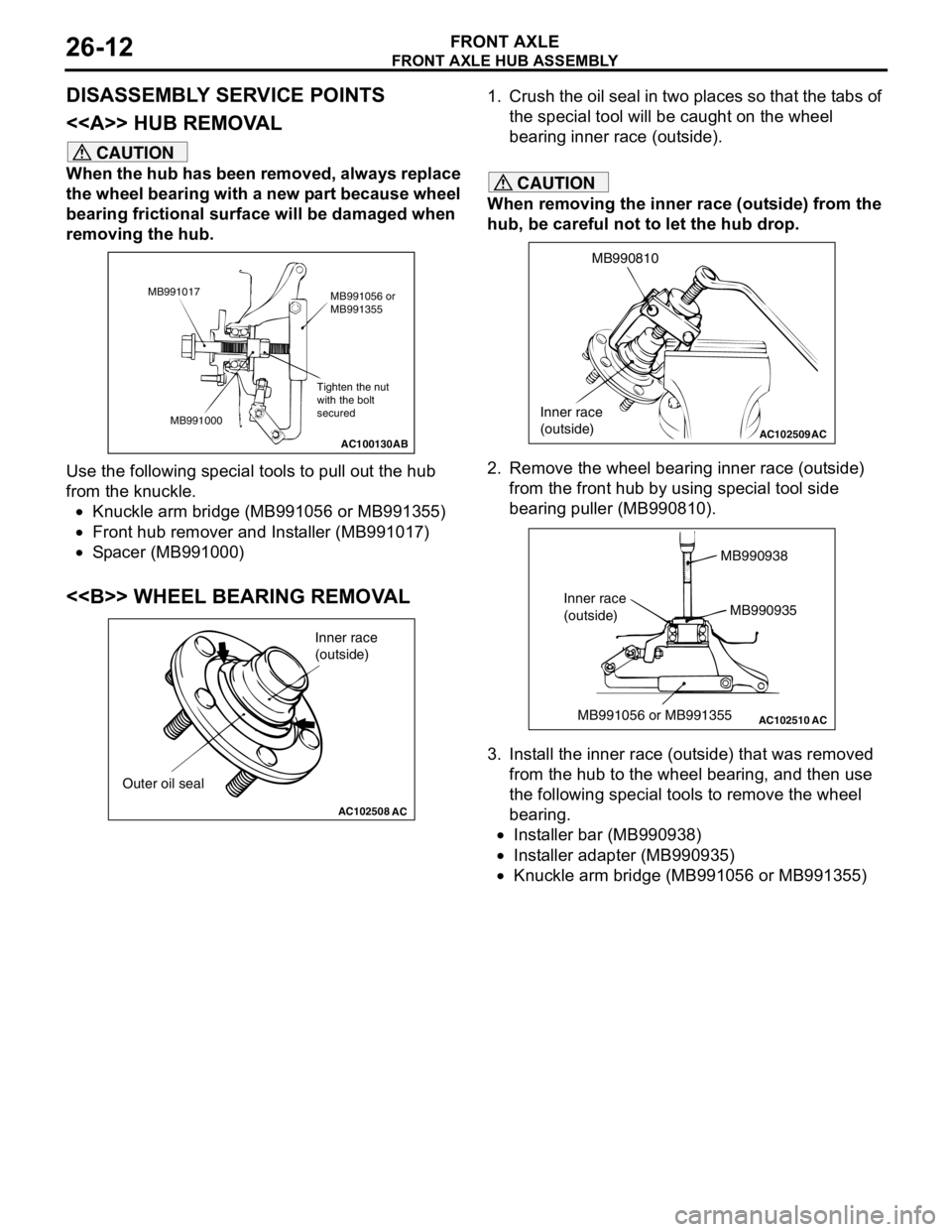
oil MITSUBISHI LANCER 2005 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: LANCER, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER 2005Pages: 788, PDF Size: 45.98 MB
Page 99 of 788
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-35
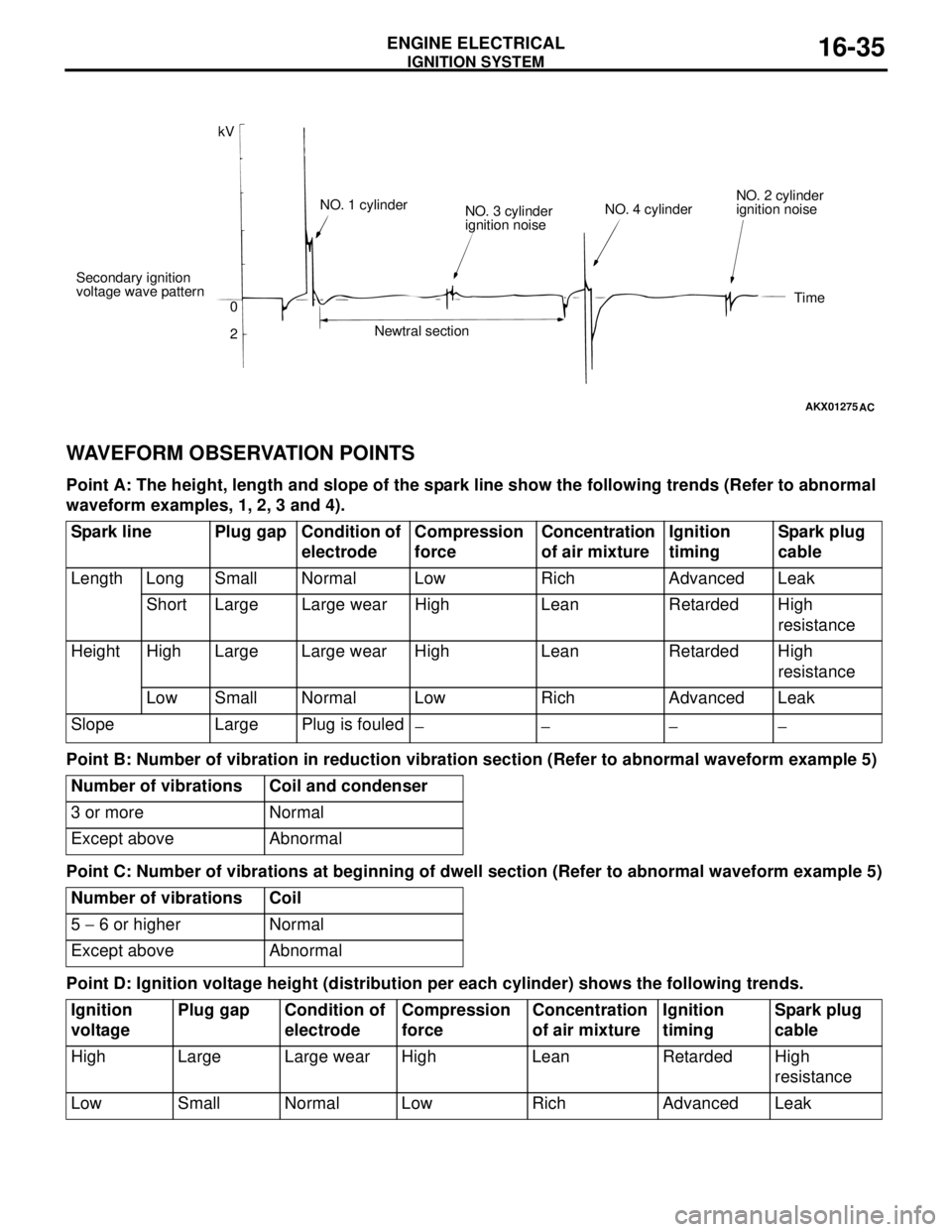
WAVEFORM OBSERVATION POINTS
Point A: The height, length and slope of the spark line show the following trends (Refer to abnormal
waveform examples, 1, 2, 3 and 4).
Point B: Number of vibration in reduction vibration section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Point C: Number of vibrations at beginning of dwell section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Point D: Ignition voltage height (distribution per each cylinder) shows the following trends.
AKX01275
kV
Secondary ignition
voltage wave pattern
0
2NO. 1 cylinder
NO. 3 cylinder
ignition noise
Newtral sectionNO. 4 cylinderNO. 2 cylinder
ignition noise
Time
AC
Spark line Plug gap Condition of
electrodeCompression
force Concentration
of air mixtureIgnition
timingSpark plug
cable
Length Long Small Normal Low Rich Advanced Leak
Short Large Large wear High Lean Retarded High
resistance
Height High Large Large wear High Lean Retarded High
resistance
Low Small Normal Low Rich Advanced Leak
Slope Large Plug is fouled
−− −−
Number of vibrations Coil and condenser
3 or more Normal
Except above Abnormal
Number of vibrations Coil
5 − 6 or higher Normal
Except above Abnormal
Ignition
voltagePlug gap Condition of
electrodeCompression
forceConcentration
of air mixtureIgnition
timingSpark plug
cable
High Large Large wear High Lean Retarded High
resistance
Low Small Normal Low Rich Advanced Leak
Page 100 of 788
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-36
EXAMPLES OF ABNORMAL
WAV E F O R M S
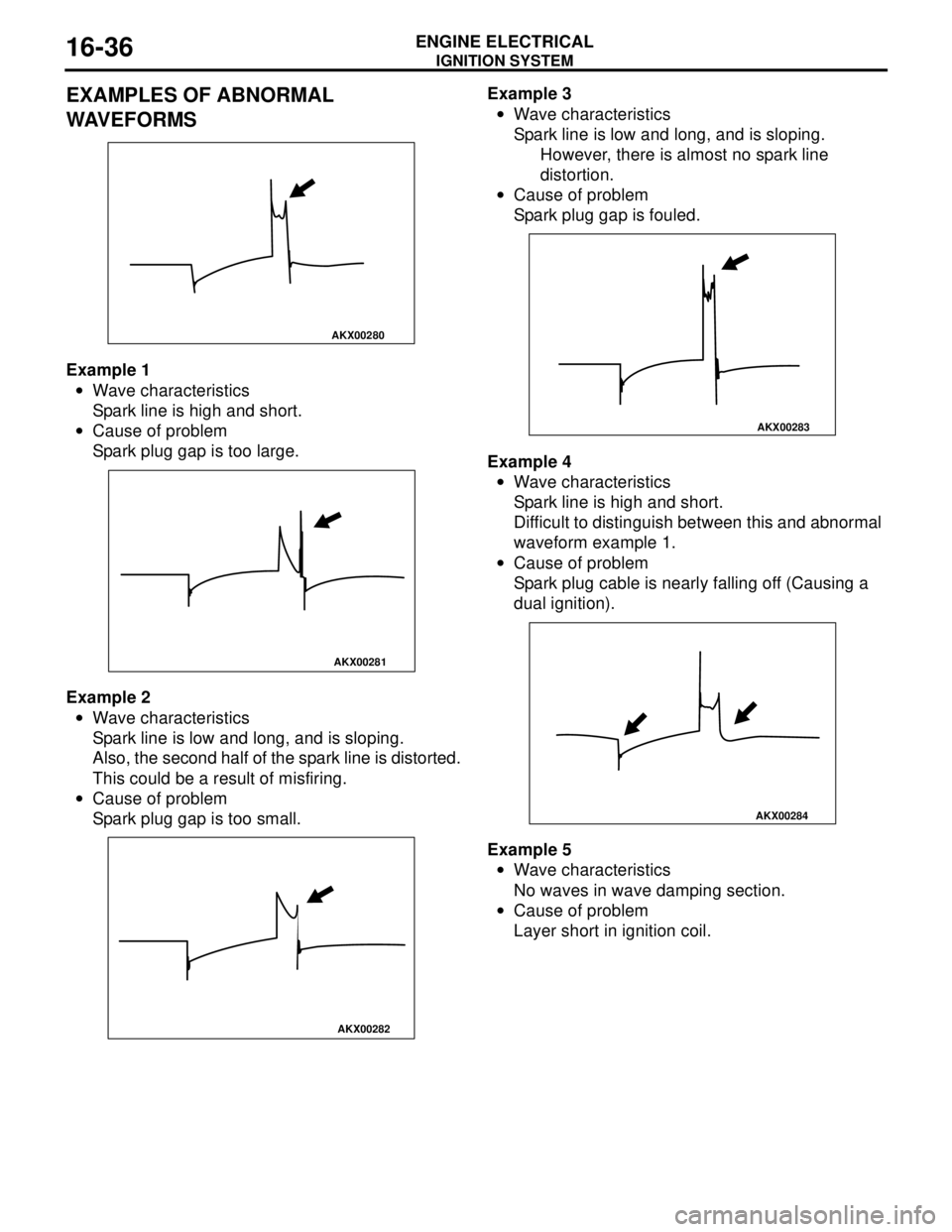
Example 1
•Wave characteristics
Spark line is high and short.
•Cause of problem
Spark plug gap is too large.
Example 2
•Wave characteristics
Spark line is low and long, and is sloping.
Also, the second half of the spark line is distorted.
This could be a result of misfiring.
•Cause of problem
Spark plug gap is too small.Example 3
•Wave characteristics
Spark line is low and long, and is sloping.
However, there is almost no spark line
distortion.
•Cause of problem
Spark plug gap is fouled.
Example 4
•Wave characteristics
Spark line is high and short.
Difficult to distinguish between this and abnormal
waveform example 1.
•Cause of problem
Spark plug cable is nearly falling off (Causing a
dual ignition).
Example 5
•Wave characteristics
No waves in wave damping section.
•Cause of problem
Layer short in ignition coil.
AKX00280
AKX00281
AKX00282
AKX00283
AKX00284
Page 101 of 788
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-37
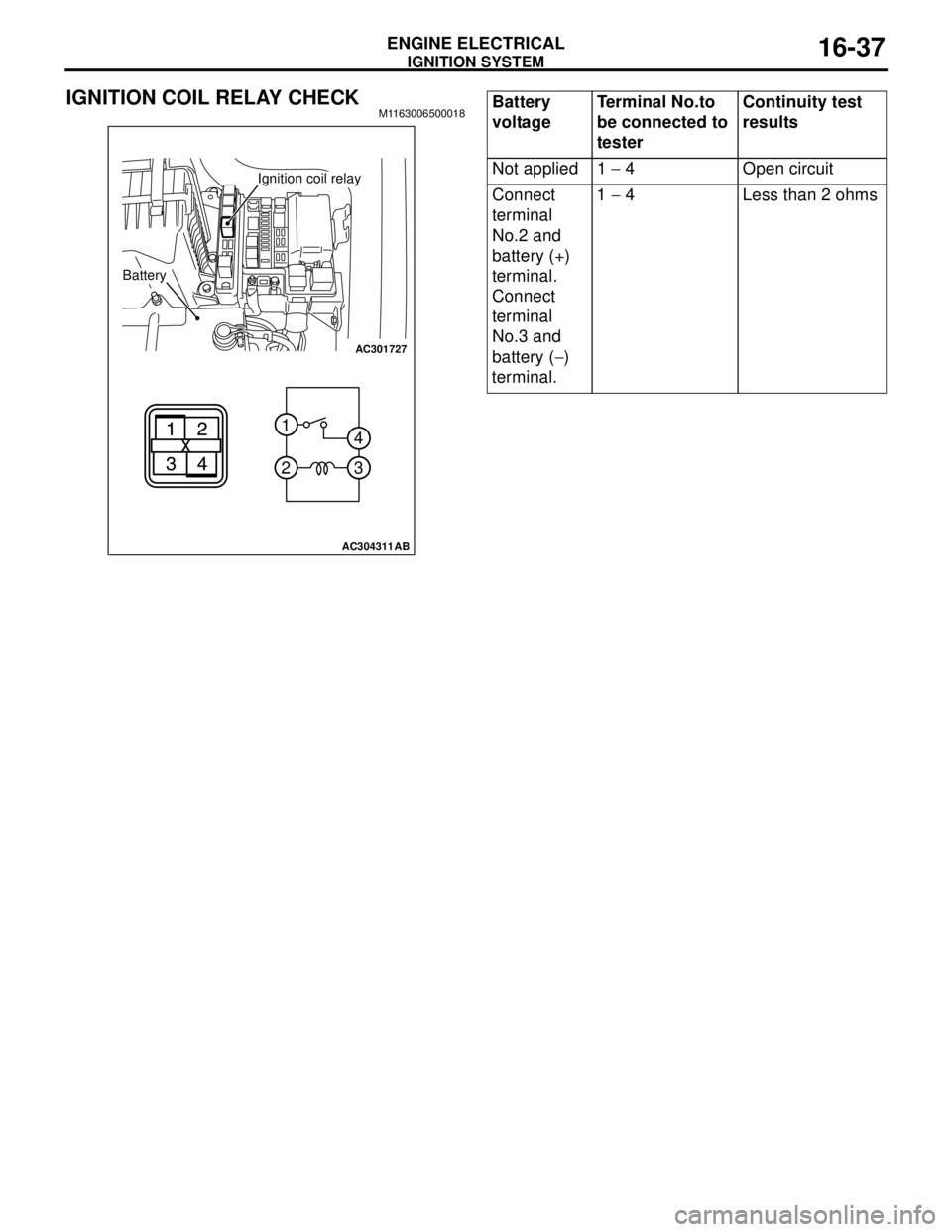
IGNITION COIL RELAY CHECKM1163006500018
AC301727
2 1
3 4
AC304311AB
Battery
Ignition coil relay
Battery
voltageTerminal No.to
be connected to
testerContinuity test
results
Not applied 1 − 4 Open circuit
Connect
terminal
No.2 and
battery (+)
terminal.
Connect
terminal
No.3 and
battery (−)
terminal.1 − 4 Less than 2 ohms
Page 102 of 788
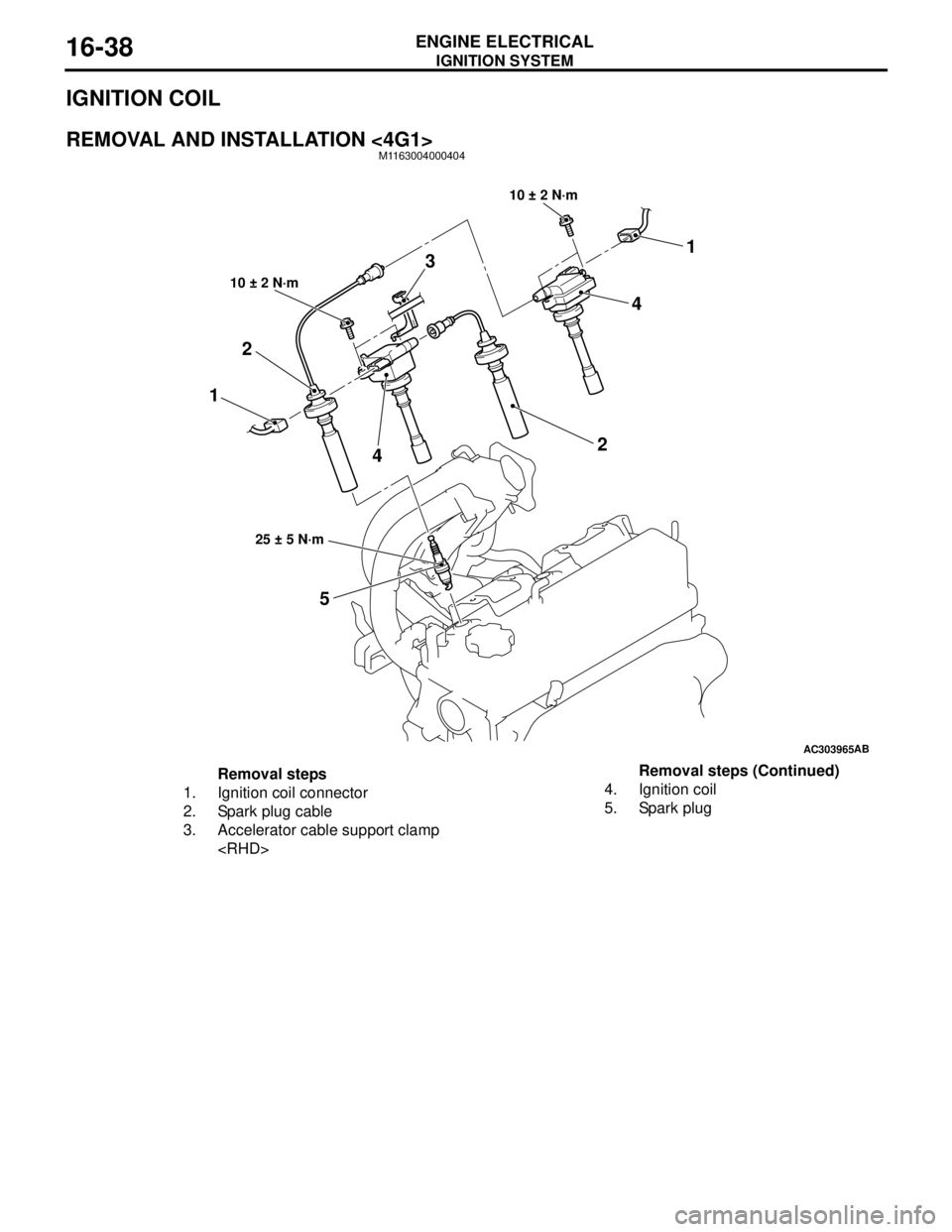
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-38
IGNITION COIL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G1>M1163004000404
AC303965AB
11
5 2
2
10 ± 2 N·m
10 ± 2 N·m
25 ± 5 N·m
3
4
4
Removal steps
1. Ignition coil connector
2. Spark plug cable
3. Accelerator cable support clamp
5. Spark plugRemoval steps (Continued)
Page 103 of 788
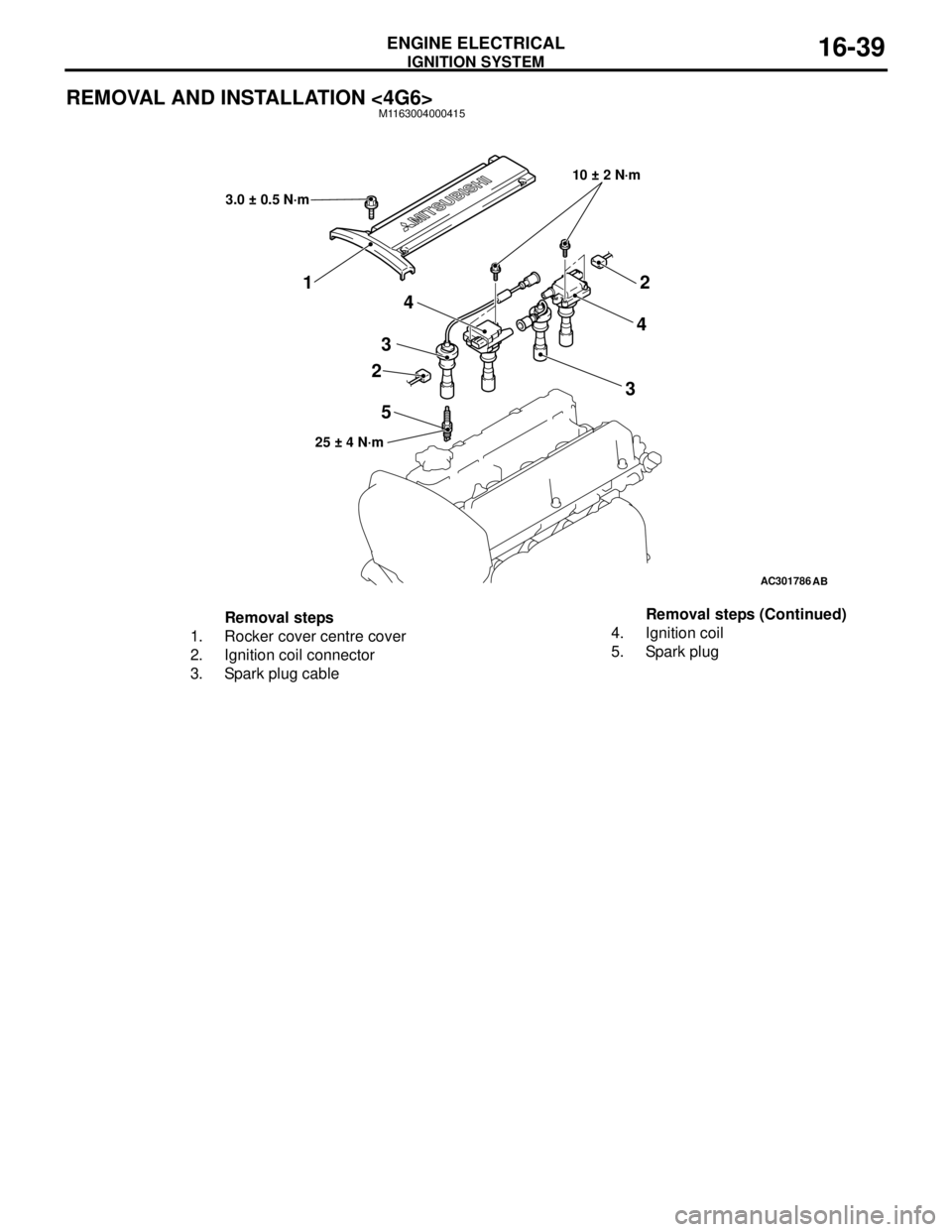
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-39
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G6>M1163004000415
AC301786
10 ± 2 N·m
25 ± 4 N·m
54
22
3 34
AB
1
3.0 ± 0.5 N·m
Removal steps
1. Rocker cover centre cover
2. Ignition coil connector
3. Spark plug cable4. Ignition coil
5. Spark plugRemoval steps (Continued)
Page 106 of 788
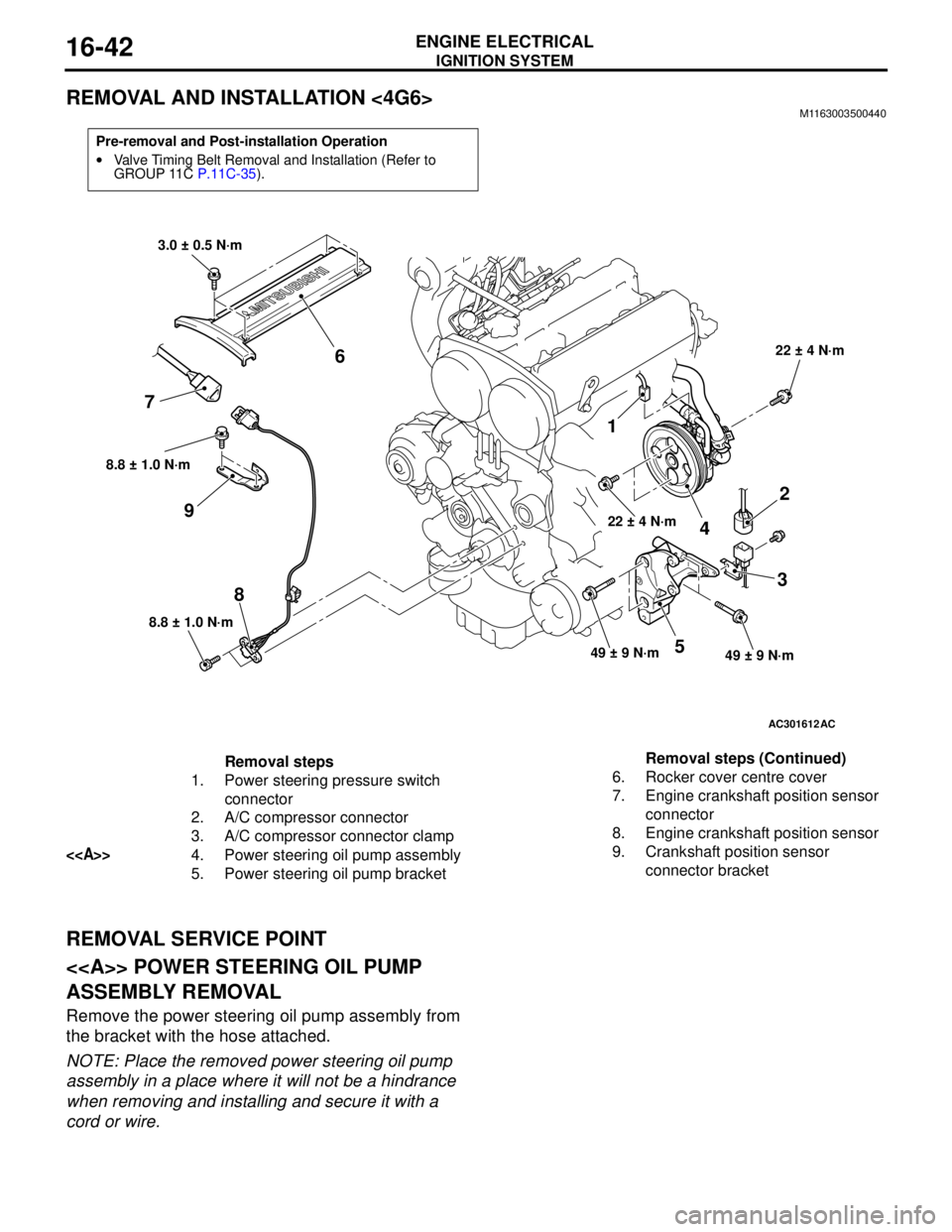
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-42
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G6>M1163003500440
REMOVAL SERVICE POINT
<> POWER STEERING OIL PUMP
ASSEMBLY REMOVAL
Remove the power steering oil pump assembly from
the bracket with the hose attached.
NOTE: Place the removed power steering oil pump
assembly in a place where it will not be a hindrance
when removing and installing and secure it with a
cord or wire.
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operation
•Valve Timing Belt Removal and Installation (Refer to
GROUP 11C P.11C-35).
AC301612
8.8 ± 1.0 N·m
8
8.8 ± 1.0 N·m
9
1
22 ± 4 N·m
4
2
3
49 ± 9 N·m49 ± 9 N·m5
22 ± 4 N·m
3.0 ± 0.5 N·m
6
7
AC
Removal steps
1. Power steering pressure switch
connector
2. A/C compressor connector
3. A/C compressor connector clamp
<>4. Power steering oil pump assembly
5. Power steering oil pump bracket6. Rocker cover centre cover
7. Engine crankshaft position sensor
connector
8. Engine crankshaft position sensor
9. Crankshaft position sensor
connector bracket Removal steps (Continued)
Page 113 of 788
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-5
EMISSION CONTROL
GENERAL INFORMATIONM1173000100370
The emission control system consists of the following
subsystems:•Crankcase emission control system
•Evaporative emission control system
•Exhaust emission control system
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE
REFERENCE TABLE
M1173006600135
SERVICE SPECIFICATION(S)M1173000300288
Items Name Specification
Crankcase emission control
systemPositive crankcase ventilation
(PCV) valveVariable flow type
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Evaporative emission control
systemCanister
Purge control solenoid valveEquipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Exhaust emission control system Air-fuel ratio control device - MPI
systemOxygen sensor feedback type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Exhaust gas recirculation system
•EGR valve
•EGR control solenoid valveEquipped
Single type
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
Catalytic converter Monolith type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Related parts Crankcase
emission
control
systemEvaporative
emission
control
systemAir/fuel ratio
control
systemCatalytic
converterExhaust gas
recirculation
system
PCV valve
×
Purge control solenoid valve
×
MPI system component
××
Catalytic converter
×
EGR valve
×
EGR control solenoid valve
×
Items Standard value
Purge control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20°C) Ω30 − 34
EGR control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20°C) Ω29 − 35
Page 134 of 788
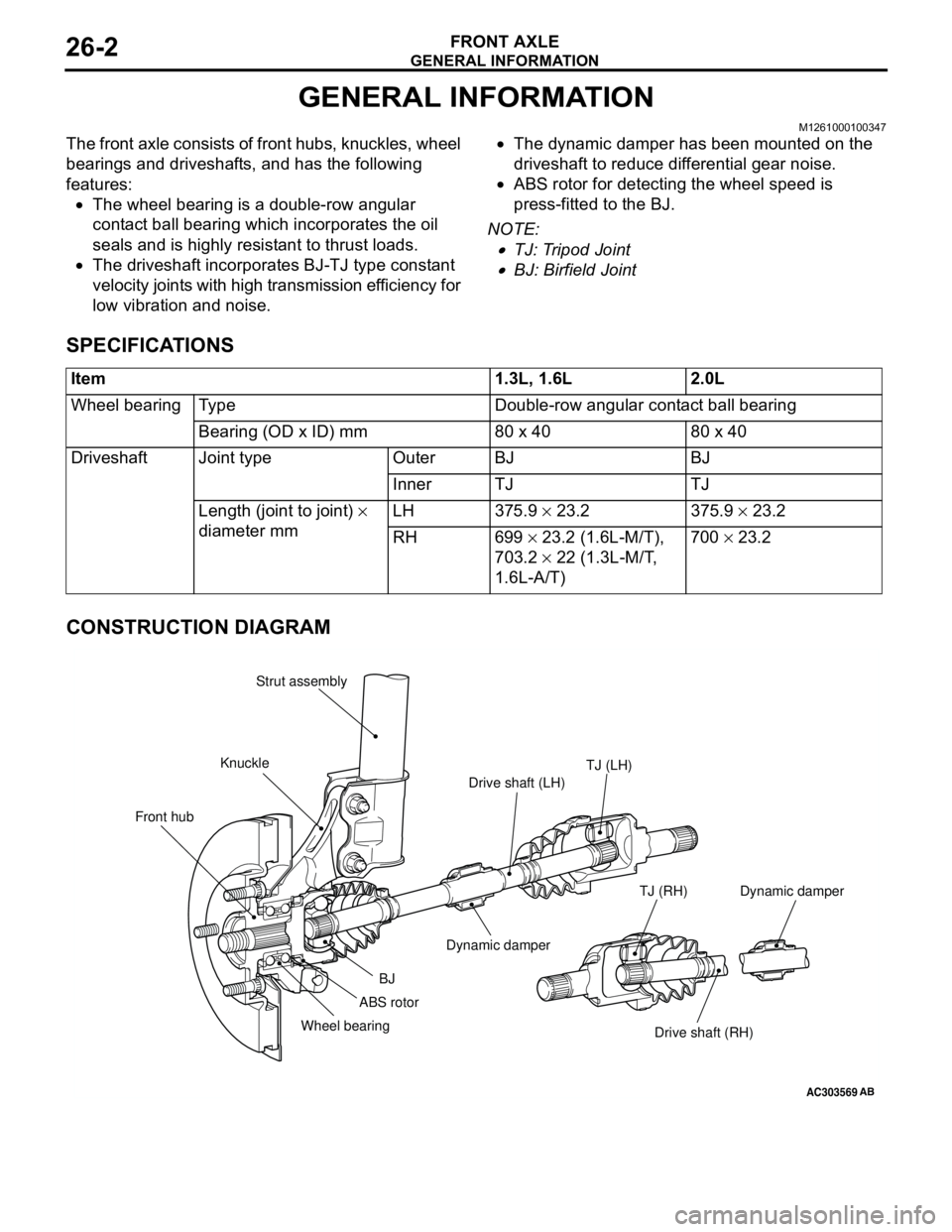
GENERAL INFORMATION
FRONT AXLE26-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
M1261000100347
The front axle consists of front hubs, knuckles, wheel
bearings and driveshafts, and has the following
features:
•The wheel bearing is a double-row angular
contact ball bearing which incorporates the oil
seals and is highly resistant to thrust loads.
•The driveshaft incorporates BJ-TJ type constant
velocity joints with high transmission efficiency for
low vibration and noise.•The dynamic damper has been mounted on the
driveshaft to reduce differential gear noise.
•ABS rotor for detecting the wheel speed is
press-fitted to the BJ.
NOTE: .
•TJ: Tripod Joint
•BJ: Birfield Joint
SPECIFICATIONS
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
Item 1.3L, 1.6L 2.0L
Wheel bearing Type Double-row angular contact ball bearing
Bearing (OD x ID) mm 80 x 40 80 x 40
Driveshaft Joint type Outer BJ BJ
Inner TJ TJ
Length (joint to joint) ×
diameter mm LH 375.9 × 23.2 375.9 × 23.2
RH 699 × 23.2 (1.6L-M/T),
703.2 × 22 (1.3L-M/T,
1.6L-A/T)700 × 23.2
AC303569
Front hubKnuckleStrut assembly
TJ (LH)
Drive shaft (LH)
Dynamic damper
BJ
Wheel bearing
Drive shaft (RH) TJ (RH)
AB
ABS rotorDynamic damper
Page 137 of 788
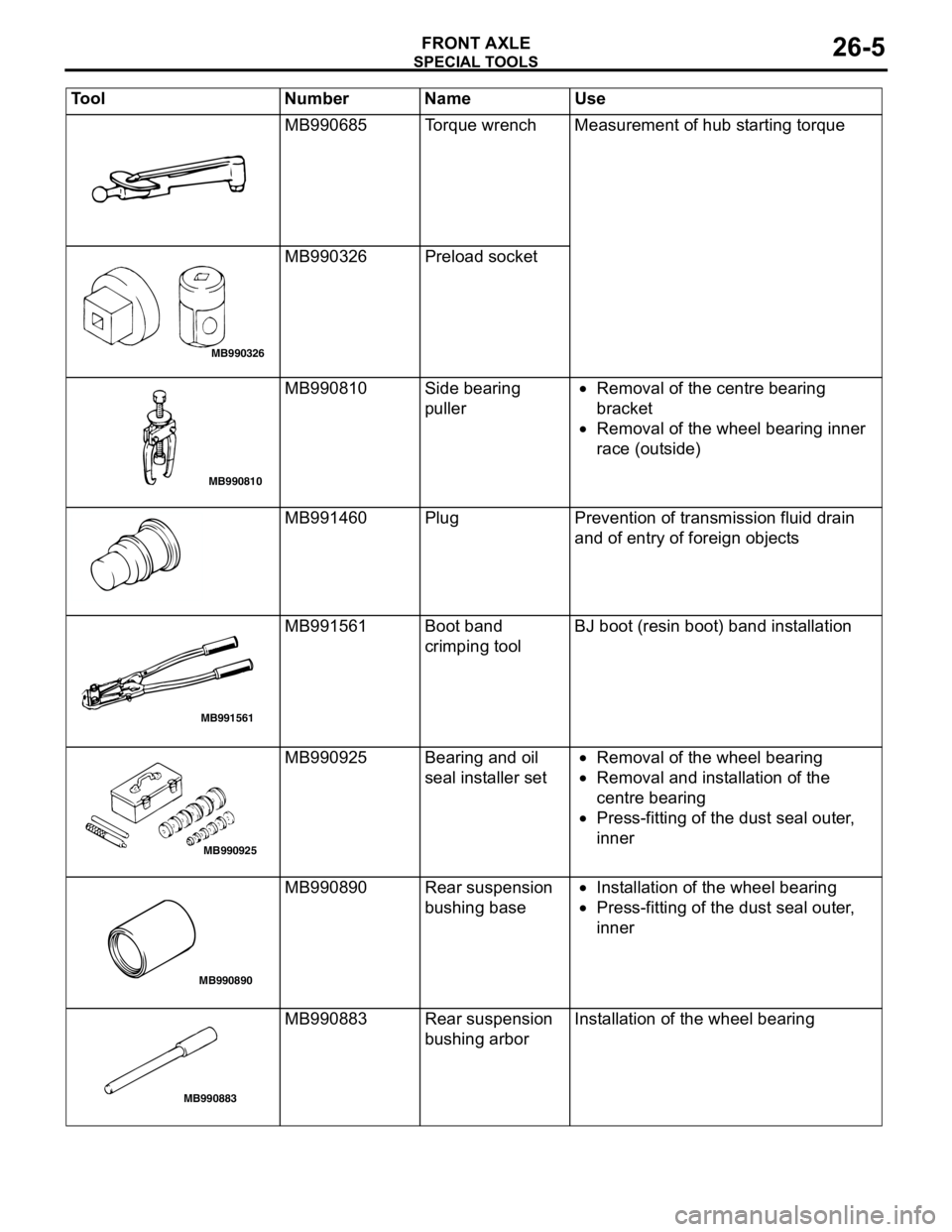
SPECIAL TOOLS
FRONT AXLE26-5
MB990685 Torque wrench Measurement of hub starting torque
MB990326 Preload socket
MB990810 Side bearing
puller•Removal of the centre bearing
bracket
•Removal of the wheel bearing inner
race (outside)
MB991460 Plug Prevention of transmission fluid drain
and of entry of foreign objects
MB991561 Boot band
crimping toolBJ boot (resin boot) band installation
MB990925 Bearing and oil
seal installer set•Removal of the wheel bearing
•Removal and installation of the
centre bearing
•Press-fitting of the dust seal outer,
inner
MB990890 Rear suspension
bushing base•Installation of the wheel bearing
•Press-fitting of the dust seal outer,
inner
MB990883 Rear suspension
bushing arborInstallation of the wheel bearing Tool Number Name Use
MB990326
MB990810
MB991561
MB990925
MB990890
MB990883
Page 144 of 788