NISSAN PATROL 1998 Y61 / 5.G Engine Mechanical Owner's Guide
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PATROL, Model: NISSAN PATROL 1998 Y61 / 5.GPages: 65, PDF Size: 2.4 MB
Page 31 of 65
CAUTION:
+When installing sliding parts such as camshaft and oil
seal, be sure to apply new engine oil on their sliding sur-
faces.
+When tightening cylinder head bolts, apply new engine oil
to thread portions and seat surfaces of bolts.
Removal
1. Remove charge air cooler assembly.
2. Set No. 1 cylinder at BDC on its expansion stroke.
3. Drain engine coolant from drain plugs on cylinder block and
radiator.
4. Remove air cleaner and/or air duct.
5. Remove timing belt.
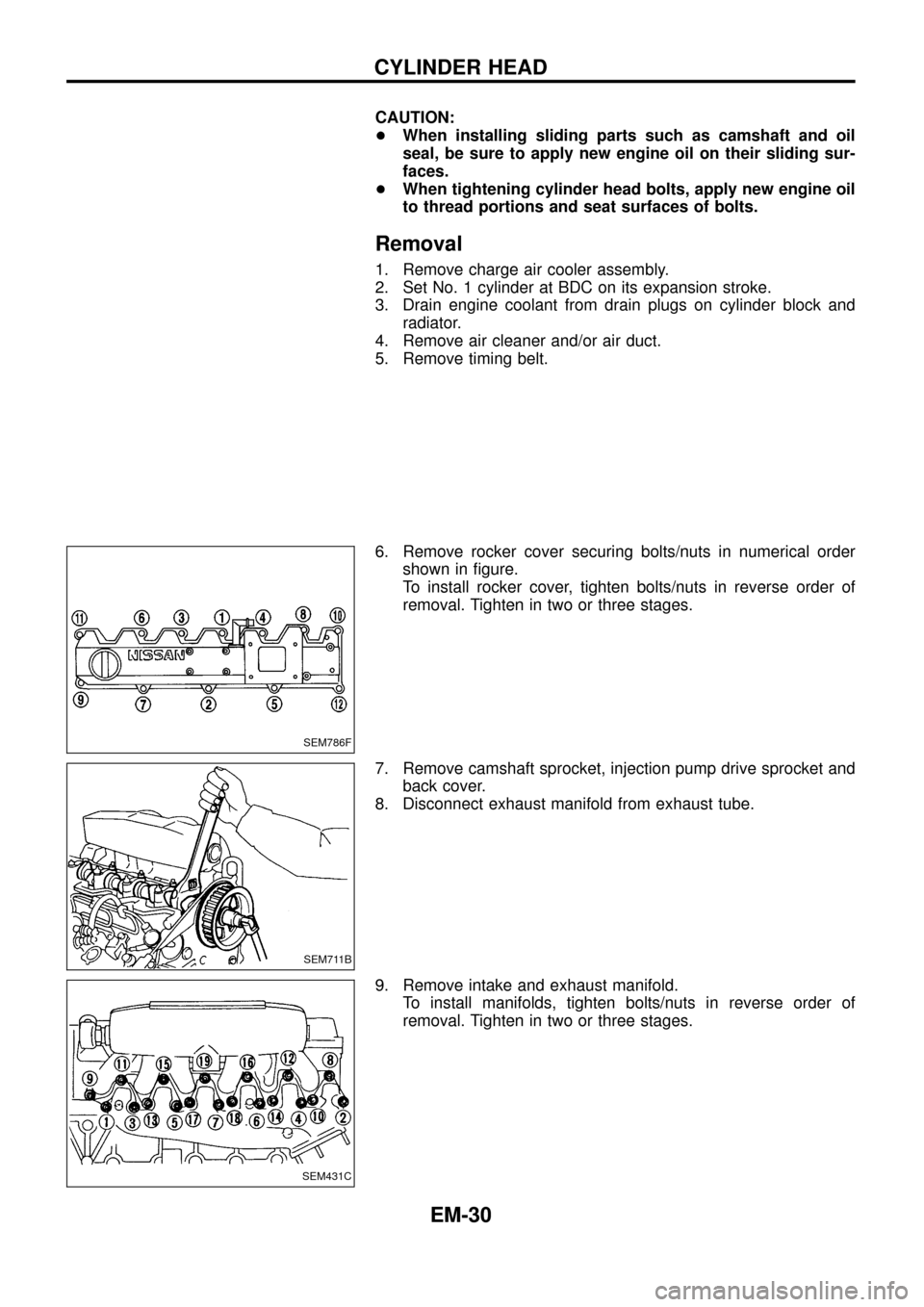
6. Remove rocker cover securing bolts/nuts in numerical order
shown in ®gure.
To install rocker cover, tighten bolts/nuts in reverse order of
removal. Tighten in two or three stages.
7. Remove camshaft sprocket, injection pump drive sprocket and
back cover.
8. Disconnect exhaust manifold from exhaust tube.
9. Remove intake and exhaust manifold.
To install manifolds, tighten bolts/nuts in reverse order of
removal. Tighten in two or three stages.
SEM786F
SEM711B
SEM431C
CYLINDER HEAD
EM-30
Page 32 of 65
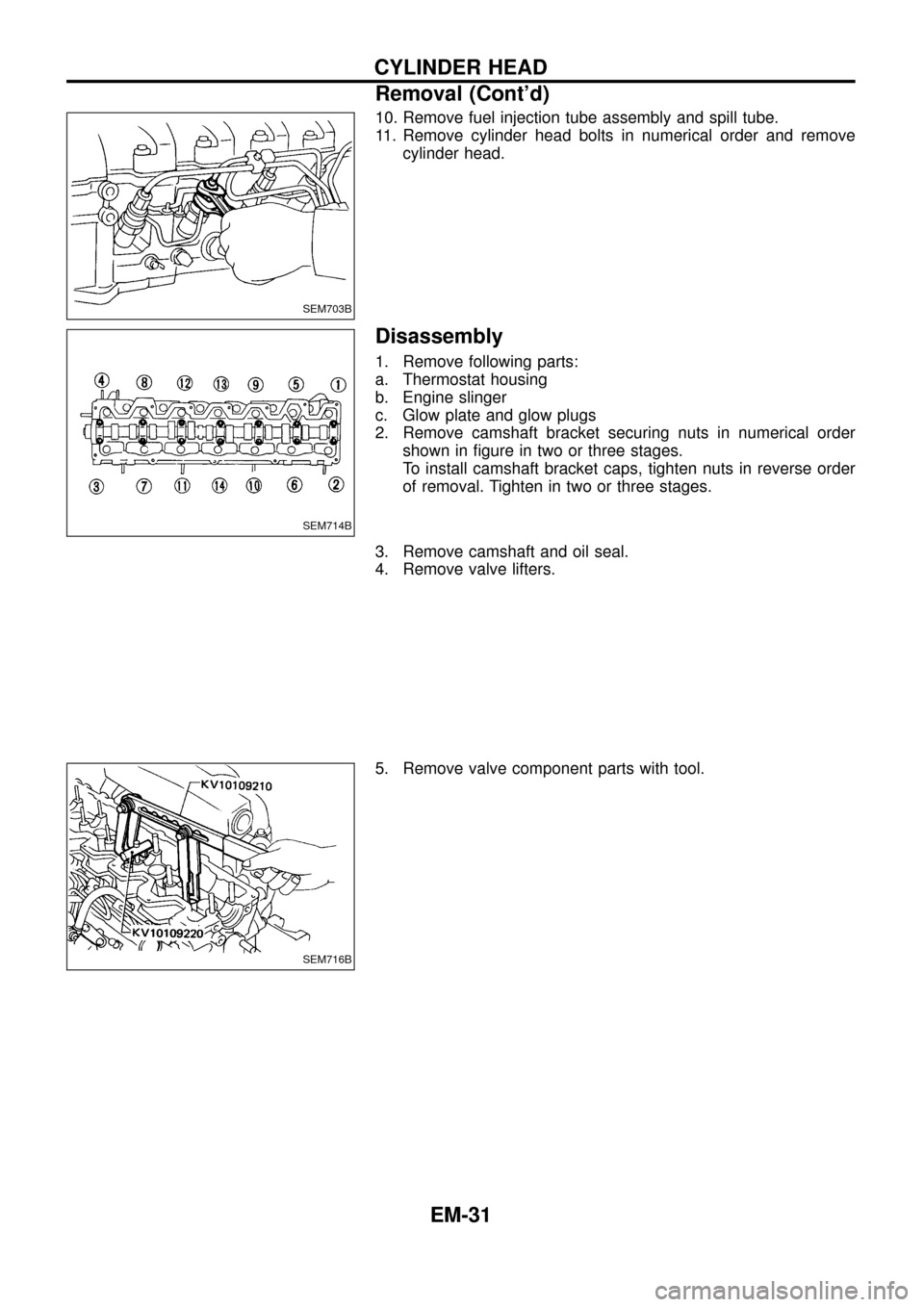
10. Remove fuel injection tube assembly and spill tube.
11. Remove cylinder head bolts in numerical order and remove
cylinder head.
Disassembly
1. Remove following parts:
a. Thermostat housing
b. Engine slinger
c. Glow plate and glow plugs
2. Remove camshaft bracket securing nuts in numerical order
shown in ®gure in two or three stages.
To install camshaft bracket caps, tighten nuts in reverse order
of removal. Tighten in two or three stages.
3. Remove camshaft and oil seal.
4. Remove valve lifters.
5. Remove valve component parts with tool.
SEM703B
SEM714B
SEM716B
CYLINDER HEAD
Removal (Cont'd)
EM-31
Page 33 of 65
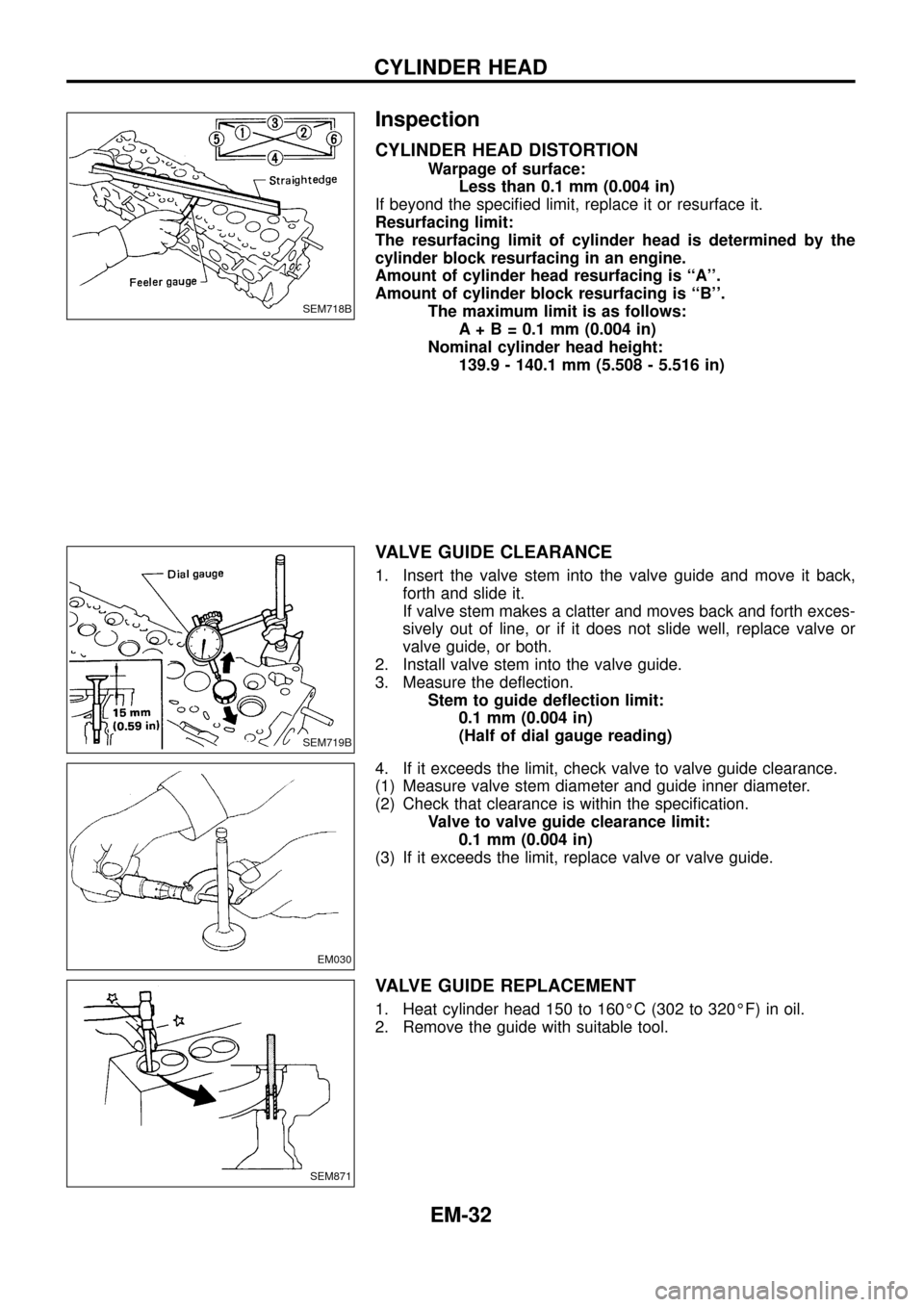
Inspection
CYLINDER HEAD DISTORTION
Warpage of surface:
Less than 0.1 mm (0.004 in)
If beyond the speci®ed limit, replace it or resurface it.
Resurfacing limit:
The resurfacing limit of cylinder head is determined by the
cylinder block resurfacing in an engine.
Amount of cylinder head resurfacing is ``A''.
Amount of cylinder block resurfacing is ``B''.
The maximum limit is as follows:
A + B = 0.1 mm (0.004 in)
Nominal cylinder head height:
139.9 - 140.1 mm (5.508 - 5.516 in)
VALVE GUIDE CLEARANCE
1. Insert the valve stem into the valve guide and move it back,
forth and slide it.
If valve stem makes a clatter and moves back and forth exces-
sively out of line, or if it does not slide well, replace valve or
valve guide, or both.
2. Install valve stem into the valve guide.
3. Measure the de¯ection.
Stem to guide de¯ection limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
(Half of dial gauge reading)
4. If it exceeds the limit, check valve to valve guide clearance.
(1) Measure valve stem diameter and guide inner diameter.
(2) Check that clearance is within the speci®cation.
Valve to valve guide clearance limit:
0.1 mm (0.004 in)
(3) If it exceeds the limit, replace valve or valve guide.
VALVE GUIDE REPLACEMENT
1. Heat cylinder head 150 to 160ÉC (302 to 320ÉF) in oil.
2. Remove the guide with suitable tool.
SEM718B
SEM719B
EM030
SEM871
CYLINDER HEAD
EM-32
Page 34 of 65

3. Drive in the new guide until it projects out 10.3 mm (0.406 in).
4. Ream the bore using suitable tool.
Reaming bore:
7.000 - 7.018 mm (0.2756 - 0.2763 in)
COMBUSTION CHAMBER REPLACEMENT
Usually combustion chamber should not be removed.
However, if there are cracks or extensive damage, it should be
replaced.
1. Remove glow plug connecting plate, glow plugs and injection
nozzle.
2. Remove combustion chamber so that cylinder head will not be
damaged.
Be careful not to scratch inside of nozzle hole.
3. Install combustion chamber.
(1) Heat cylinder head 150 to 160ÉC (302 to 320ÉF) in oil.
(2) Align combustion chamber knock pin with cylinder head notch,
and install it into cylinder head using a plastic-tip hammer.
VALVE SEATS
1. Check valve and valve seat for contact.
Coat the valve face with prussian red lead. If contact is wrong,
correct valve seat. If the valve red lead appears 360É around
face, the valve stem and face are concentric. If not, repair or
replace valve.
2. Check valve seats for any evidence of pitting on valve contact
surface, and reseat or replace if worn out excessively.
Correct valve seat surface.
+When repairing valve seat, check valve and valve guide for
wear beforehand. If worn, replace them. Then correct valve
seat.
+Cut with both hands to uniform the cutting surface.
SEM872
SEM720B
SEM721B
SEM722B
CYLINDER HEAD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-33
Page 35 of 65
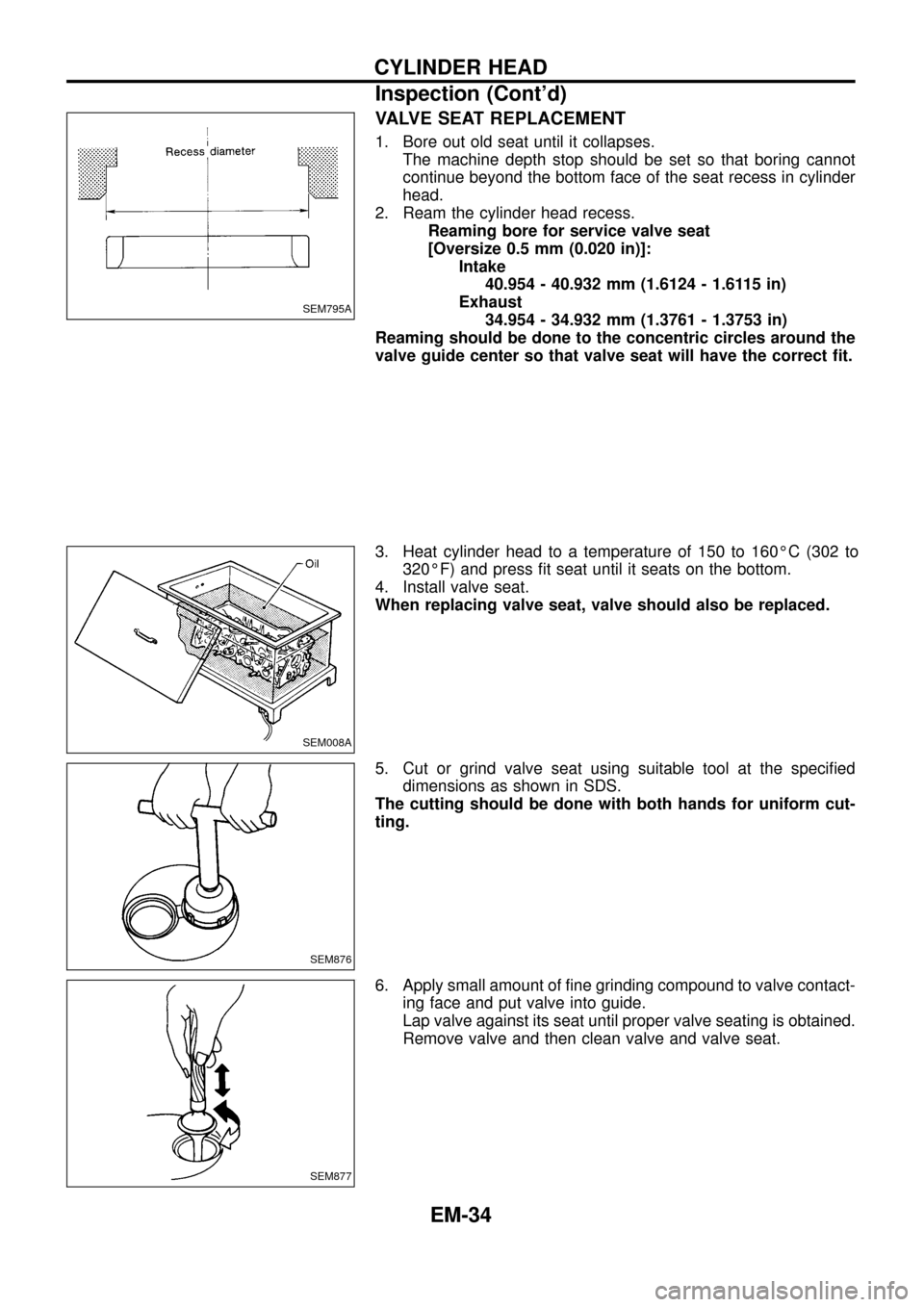
VALVE SEAT REPLACEMENT
1. Bore out old seat until it collapses.
The machine depth stop should be set so that boring cannot
continue beyond the bottom face of the seat recess in cylinder
head.
2. Ream the cylinder head recess.
Reaming bore for service valve seat
[Oversize 0.5 mm (0.020 in)]:
Intake
40.954 - 40.932 mm (1.6124 - 1.6115 in)
Exhaust
34.954 - 34.932 mm (1.3761 - 1.3753 in)
Reaming should be done to the concentric circles around the
valve guide center so that valve seat will have the correct ®t.
3. Heat cylinder head to a temperature of 150 to 160ÉC (302 to
320ÉF) and press ®t seat until it seats on the bottom.
4. Install valve seat.
When replacing valve seat, valve should also be replaced.
5. Cut or grind valve seat using suitable tool at the speci®ed
dimensions as shown in SDS.
The cutting should be done with both hands for uniform cut-
ting.
6. Apply small amount of ®ne grinding compound to valve contact-
ing face and put valve into guide.
Lap valve against its seat until proper valve seating is obtained.
Remove valve and then clean valve and valve seat.
SEM795A
SEM008A
SEM876
SEM877
CYLINDER HEAD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-34
Page 36 of 65

7. Measure distance from cylinder head surface to intake and
exhaust valves. If speci®ed distance is exceeded, replace
valve(s) or valve seat(s).
Speci®ed distance: mm (in)
Standard
þ0.069 to 0.269 (þ0.0027 to 0.0106)
VALVE DIMENSIONS
1. Check dimensions in each valve. For dimensions, refer to SDS.
2. Correct or replace any valve that is out of tolerance.
3. Valve face or valve stem end surface should be refaced by
using a valve grinder.
When valve head has been worn down to 0.5 mm (0.020 in) in
margin thickness, replace the valve.
Grinding allowance for valve stem tip is 0.2 mm (0.008 in) or
less.
VALVE SPRING SQUARENESS
Check valve spring for squareness using a steel square and sur-
face plate.
If spring is out-of-square ``S'' more than speci®ed limit, replace with
new one.
Out-of-square:
Outer
Less than 1.9 mm (0.075 in)
Inner
Less than 1.6 mm (0.063 in)
VALVE SPRING PRESSURE LOAD
Measure the free length and the tension of each spring. If the
measured value exceeds the speci®ed limit, replace spring. Refer
to SDS.
SEM787F
EM030
E M 111
SEM333
EM113
CYLINDER HEAD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-35
Page 37 of 65
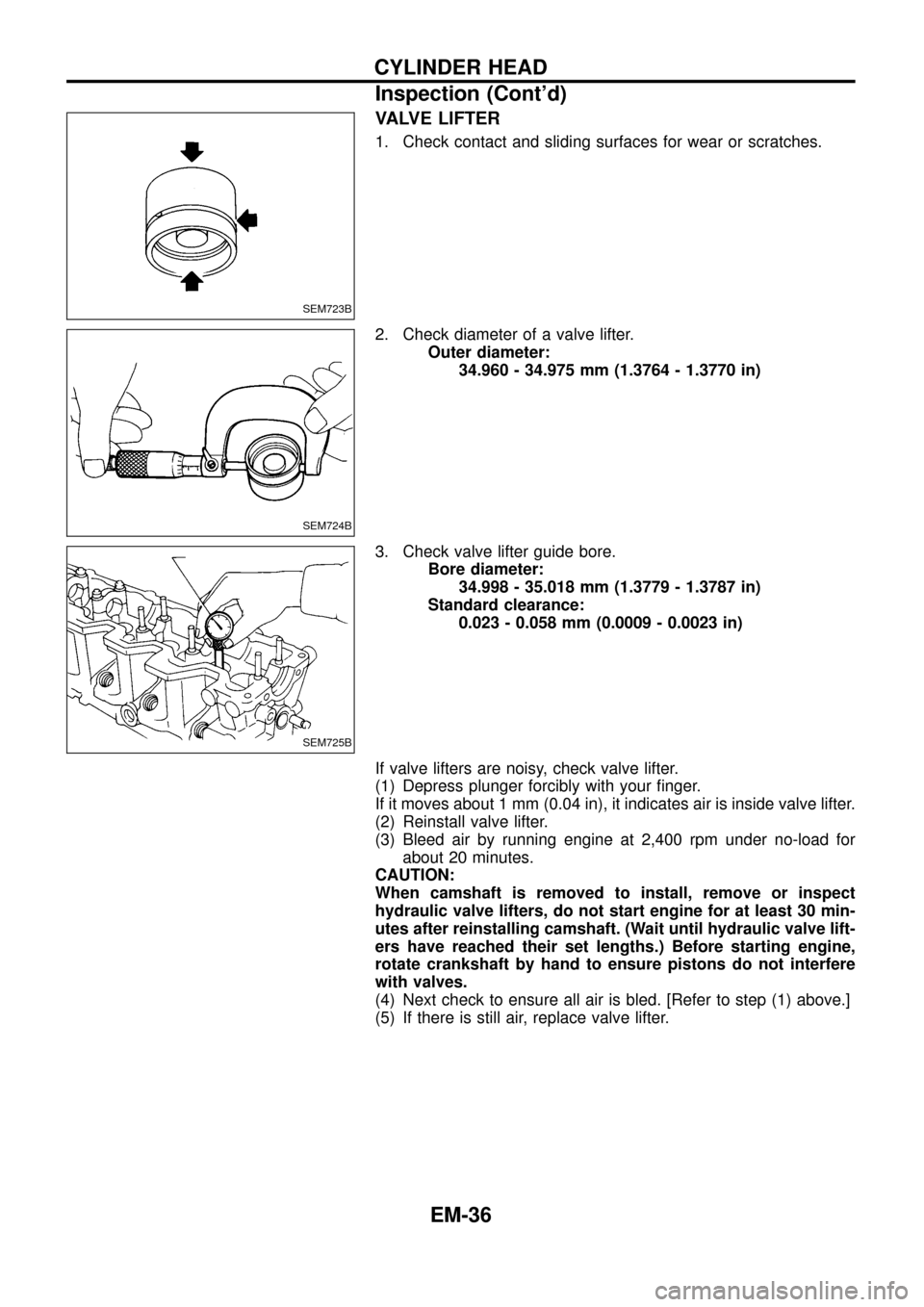
VALVE LIFTER
1. Check contact and sliding surfaces for wear or scratches.
2. Check diameter of a valve lifter.
Outer diameter:
34.960 - 34.975 mm (1.3764 - 1.3770 in)
3. Check valve lifter guide bore.
Bore diameter:
34.998 - 35.018 mm (1.3779 - 1.3787 in)
Standard clearance:
0.023 - 0.058 mm (0.0009 - 0.0023 in)
If valve lifters are noisy, check valve lifter.
(1) Depress plunger forcibly with your ®nger.
If it moves about 1 mm (0.04 in), it indicates air is inside valve lifter.
(2) Reinstall valve lifter.
(3) Bleed air by running engine at 2,400 rpm under no-load for
about 20 minutes.
CAUTION:
When camshaft is removed to install, remove or inspect
hydraulic valve lifters, do not start engine for at least 30 min-
utes after reinstalling camshaft. (Wait until hydraulic valve lift-
ers have reached their set lengths.) Before starting engine,
rotate crankshaft by hand to ensure pistons do not interfere
with valves.
(4) Next check to ensure all air is bled. [Refer to step (1) above.]
(5) If there is still air, replace valve lifter.
SEM723B
SEM724B
SEM725B
CYLINDER HEAD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-36
Page 38 of 65
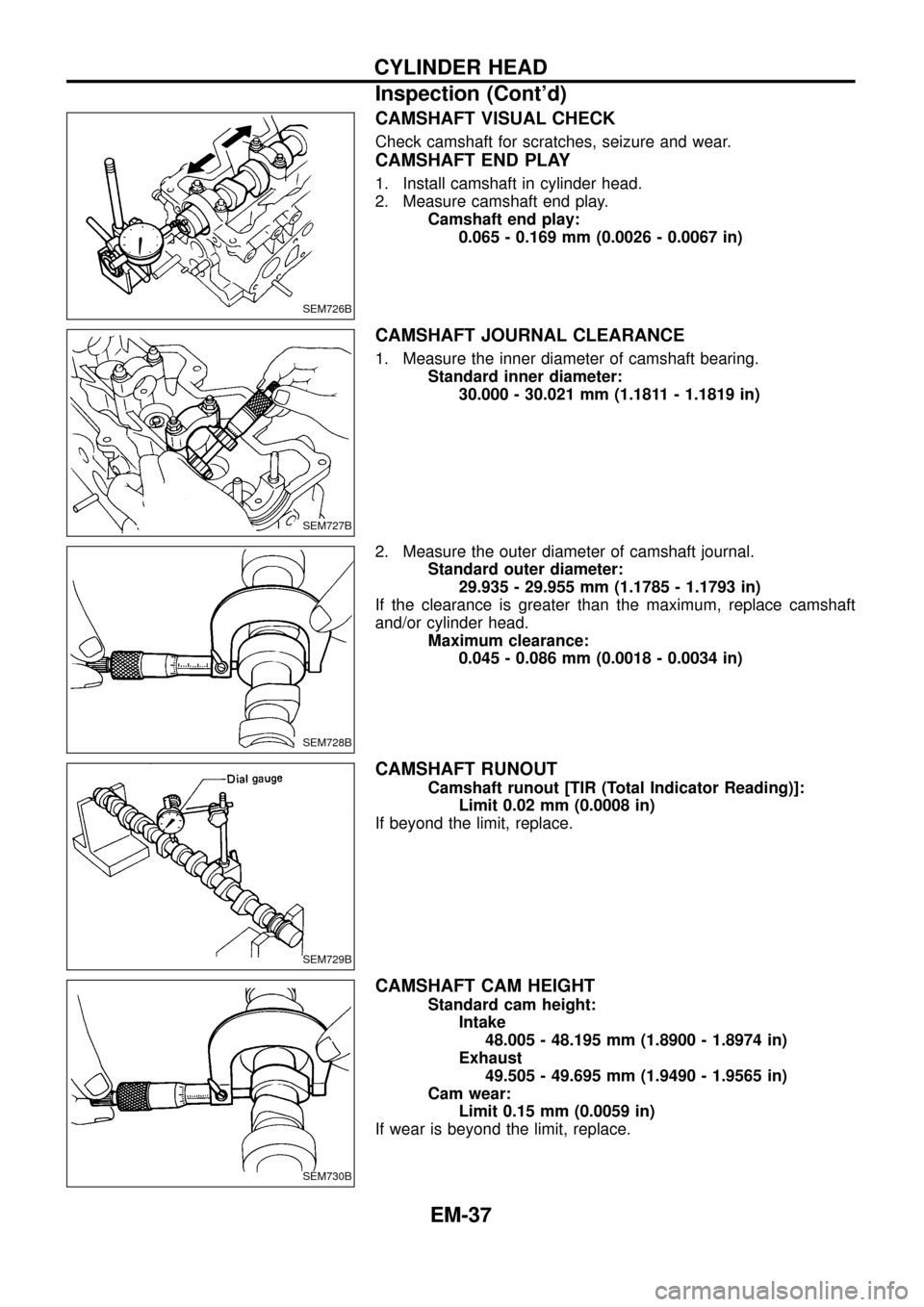

CAMSHAFT VISUAL CHECK
Check camshaft for scratches, seizure and wear.
CAMSHAFT END PLAY
1. Install camshaft in cylinder head.
2. Measure camshaft end play.
Camshaft end play:
0.065 - 0.169 mm (0.0026 - 0.0067 in)
CAMSHAFT JOURNAL CLEARANCE
1. Measure the inner diameter of camshaft bearing.
Standard inner diameter:
30.000 - 30.021 mm (1.1811 - 1.1819 in)
2. Measure the outer diameter of camshaft journal.
Standard outer diameter:
29.935 - 29.955 mm (1.1785 - 1.1793 in)
If the clearance is greater than the maximum, replace camshaft
and/or cylinder head.
Maximum clearance:
0.045 - 0.086 mm (0.0018 - 0.0034 in)
CAMSHAFT RUNOUT
Camshaft runout [TIR (Total Indicator Reading)]:
Limit 0.02 mm (0.0008 in)
If beyond the limit, replace.
CAMSHAFT CAM HEIGHT
Standard cam height:
Intake
48.005 - 48.195 mm (1.8900 - 1.8974 in)
Exhaust
49.505 - 49.695 mm (1.9490 - 1.9565 in)
Cam wear:
Limit 0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
If wear is beyond the limit, replace.
SEM726B
SEM727B
SEM728B
SEM729B
SEM730B
CYLINDER HEAD
Inspection (Cont'd)
EM-37
Page 39 of 65
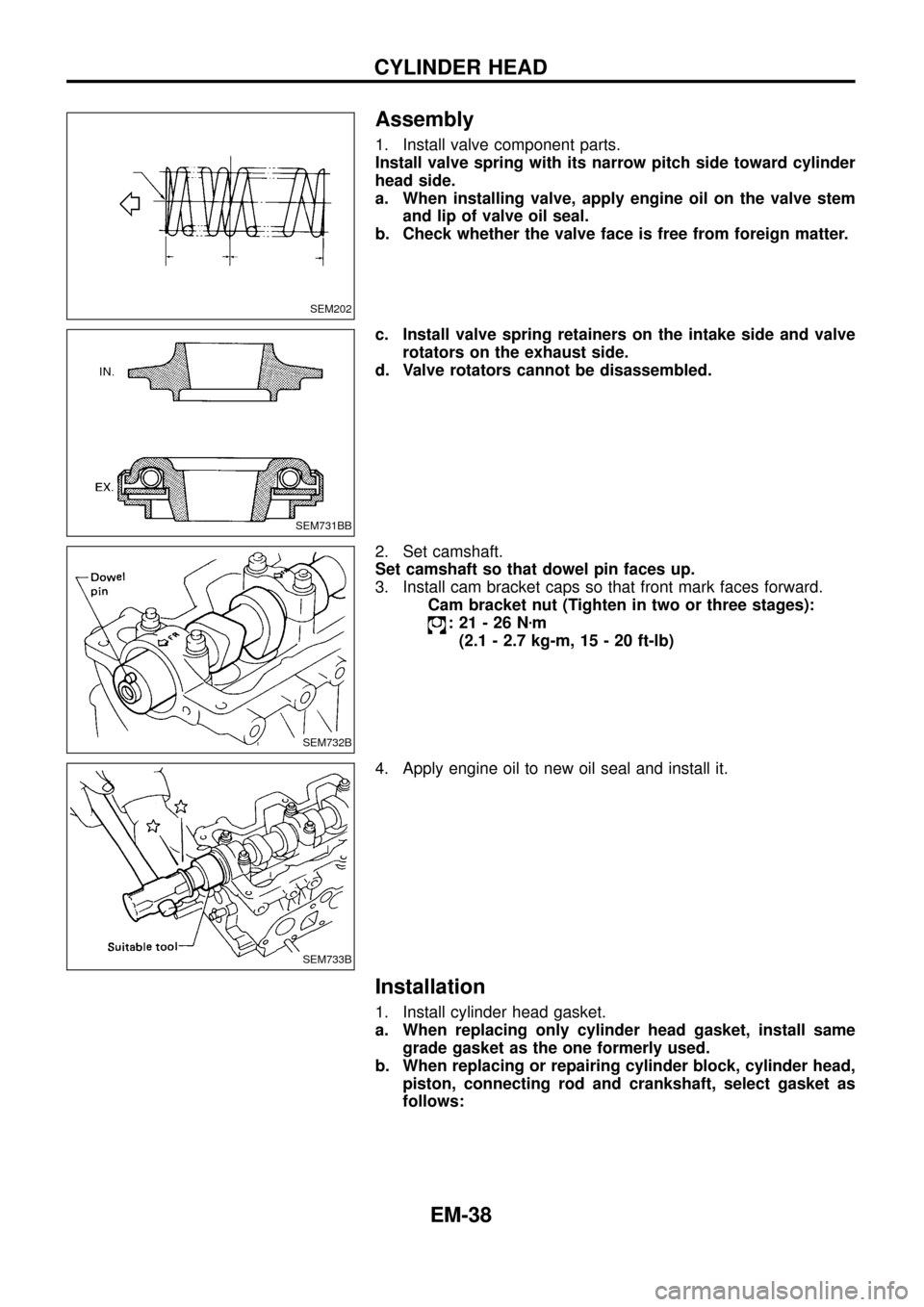

Assembly
1. Install valve component parts.
Install valve spring with its narrow pitch side toward cylinder
head side.
a. When installing valve, apply engine oil on the valve stem
and lip of valve oil seal.
b. Check whether the valve face is free from foreign matter.
c. Install valve spring retainers on the intake side and valve
rotators on the exhaust side.
d. Valve rotators cannot be disassembled.
2. Set camshaft.
Set camshaft so that dowel pin faces up.
3. Install cam bracket caps so that front mark faces forward.
Cam bracket nut (Tighten in two or three stages):
:21-26Nzm
(2.1 - 2.7 kg-m, 15 - 20 ft-lb)
4. Apply engine oil to new oil seal and install it.
Installation
1. Install cylinder head gasket.
a. When replacing only cylinder head gasket, install same
grade gasket as the one formerly used.
b. When replacing or repairing cylinder block, cylinder head,
piston, connecting rod and crankshaft, select gasket as
follows:
SEM202
SEM731BB
SEM732B
SEM733B
CYLINDER HEAD
EM-38
Page 40 of 65
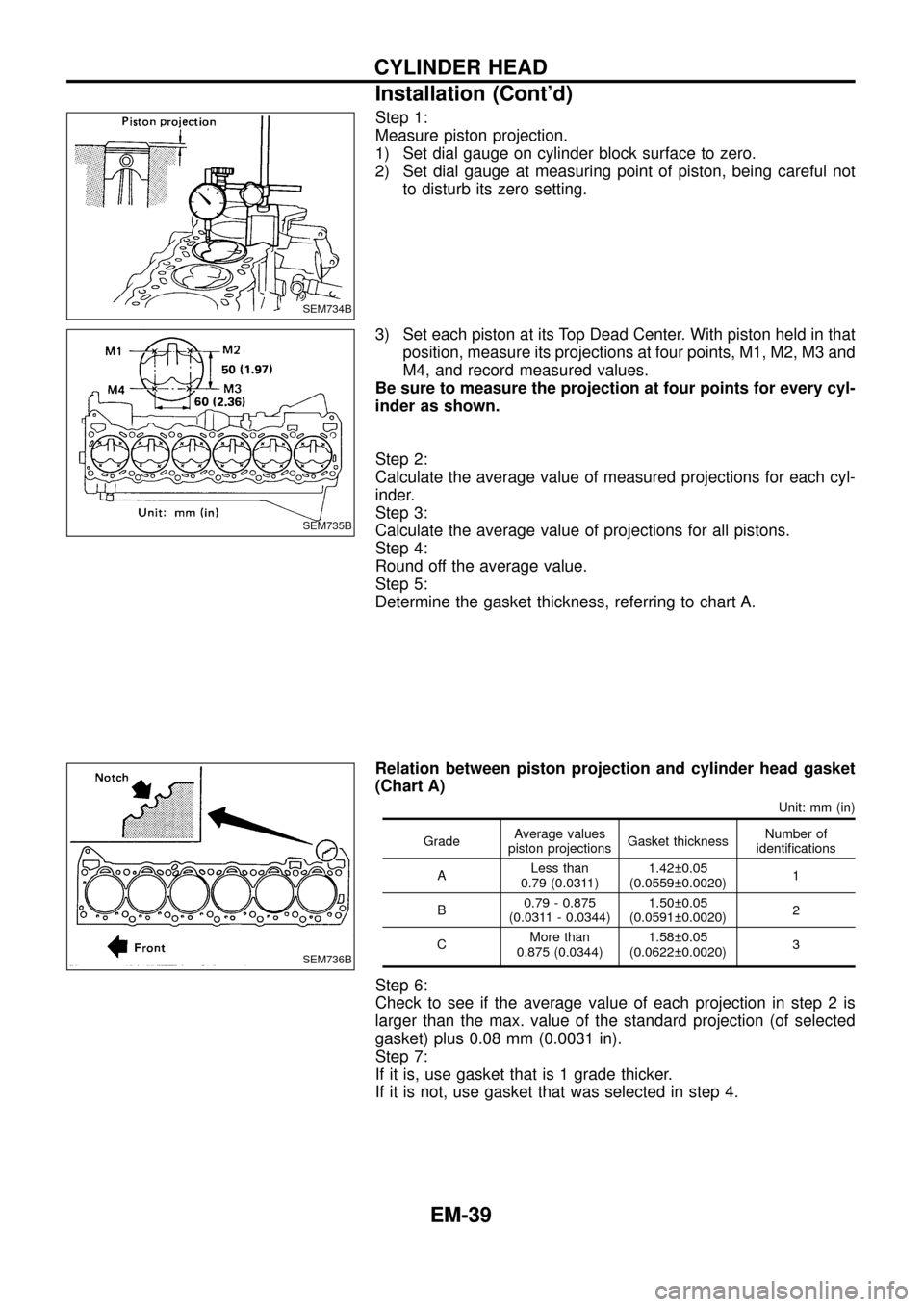
Step 1:
Measure piston projection.
1) Set dial gauge on cylinder block surface to zero.
2) Set dial gauge at measuring point of piston, being careful not
to disturb its zero setting.
3) Set each piston at its Top Dead Center. With piston held in that
position, measure its projections at four points, M1, M2, M3 and
M4, and record measured values.
Be sure to measure the projection at four points for every cyl-
inder as shown.
Step 2:
Calculate the average value of measured projections for each cyl-
inder.
Step 3:
Calculate the average value of projections for all pistons.
Step 4:
Round off the average value.
Step 5:
Determine the gasket thickness, referring to chart A.
Relation between piston projection and cylinder head gasket
(Chart A)
Unit: mm (in)
GradeAverage values
piston projectionsGasket thicknessNumber of
identi®cations
ALess than
0.79 (0.0311)1.42 0.05
(0.0559 0.0020)1
B0.79 - 0.875
(0.0311 - 0.0344)1.50 0.05
(0.0591 0.0020)2
CMore than
0.875 (0.0344)1.58 0.05
(0.0622 0.0020)3
Step 6:
Check to see if the average value of each projection in step 2 is
larger than the max. value of the standard projection (of selected
gasket) plus 0.08 mm (0.0031 in).
Step 7:
If it is, use gasket that is 1 grade thicker.
If it is not, use gasket that was selected in step 4.
SEM734B
SEM735B
SEM736B
CYLINDER HEAD
Installation (Cont'd)
EM-39