tow OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 279 of 6000
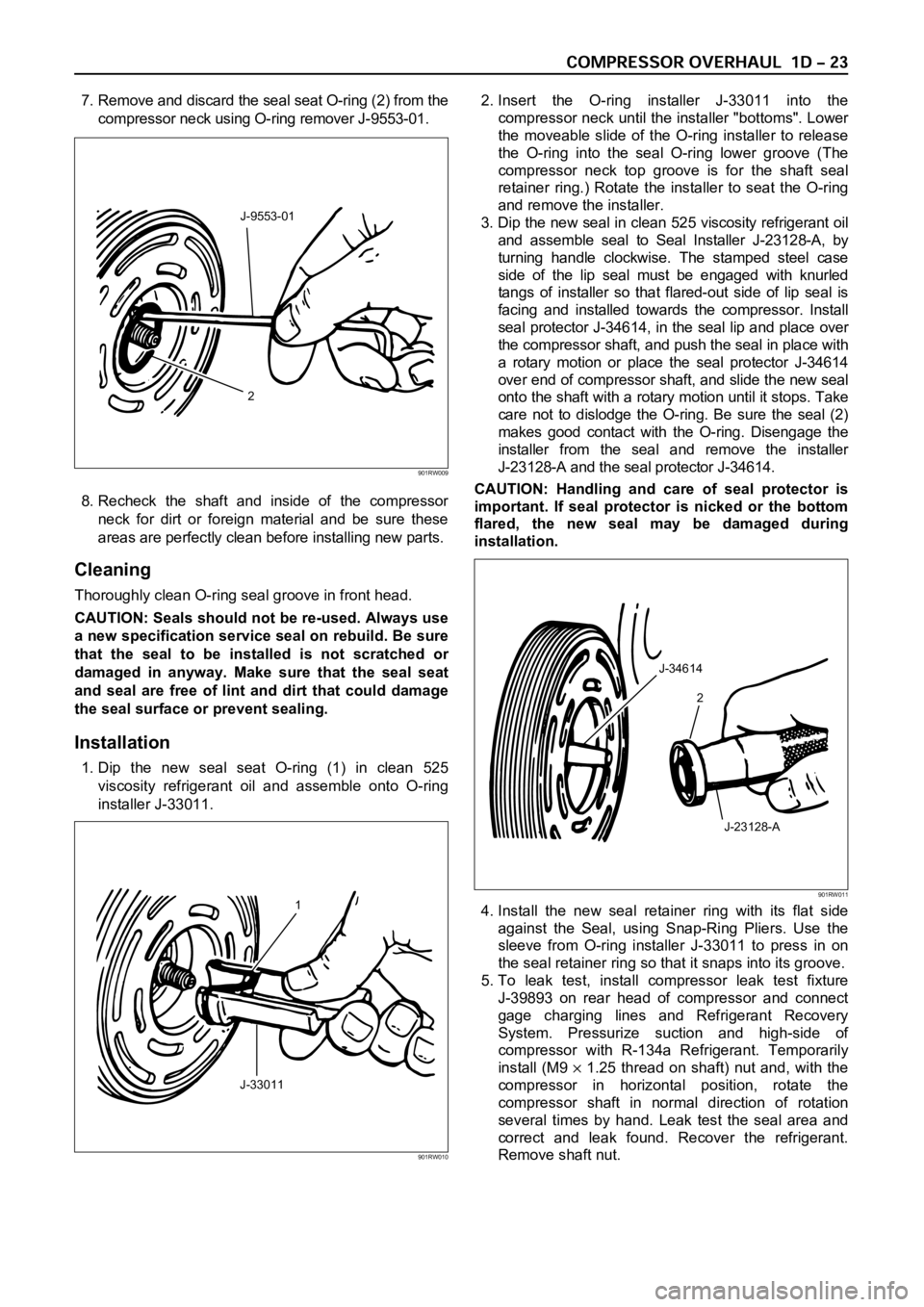
7. Remove and discard the seal seat O-ring (2) from the
compressor neck using O-ring remover J-9553-01.
8. Recheck the shaft and inside of the compressor
neck for dirt or foreign material and be sure these
areas are perfectly clean before installing new parts.
Cleaning
Thoroughly clean O-ring seal groove in front head.
CAUTION: Seals should not be re-used. Always use
a new specification service seal on rebuild. Be sure
that the seal to be installed is not scratched or
damaged in anyway. Make sure that the seal seat
and seal are free of lint and dirt that could damage
the seal surface or prevent sealing.
Installation
1. Dip the new seal seat O-ring (1) in clean 525
viscosity refrigerant oil and assemble onto O-ring
installer J-33011.2. Insert the O-ring installer J-33011 into the
compressor neck until the installer "bottoms". Lower
the moveable slide of the O-ring installer to release
the O-ring into the seal O-ring lower groove (The
compressor neck top groove is for the shaft seal
retainer ring.) Rotate the installer to seat the O-ring
and remove the installer.
3. Dip the new seal in clean 525 viscosity refrigerant oil
and assemble seal to Seal Installer J-23128-A, by
turning handle clockwise. The stamped steel case
side of the lip seal must be engaged with knurled
tangs of installer so that flared-out side of lip seal is
facing and installed towards the compressor. Install
seal protector J-34614, in the seal lip and place over
the compressor shaft, and push the seal in place with
a rotary motion or place the seal protector J-34614
over end of compressor shaft, and slide the new seal
onto the shaft with a rotary motion until it stops. Take
care not to dislodge the O-ring. Be sure the seal (2)
makes good contact with the O-ring. Disengage the
installer from the seal and remove the installer
J-23128-A and the seal protector J-34614.
CAUTION: Handling and care of seal protector is
important. If seal protector is nicked or the bottom
flared, the new seal may be damaged during
installation.
4. Install the new seal retainer ring with its flat side
against the Seal, using Snap-Ring Pliers. Use the
sleeve from O-ring installer J-33011 to press in on
the seal retainer ring so that it snaps into its groove.
5. To leak test, install compressor leak test fixture
J-39893 on rear head of compressor and connect
gage charging lines and Refrigerant Recovery
System. Pressurize suction and high-side of
compressor with R-134a Refrigerant. Temporarily
install (M9
1.25 thread on shaft) nut and, with the
compressor in horizontal position, rotate the
compressor shaft in normal direction of rotation
several times by hand. Leak test the seal area and
correct and leak found. Recover the refrigerant.
Remove shaft nut.
2 J-9553-01
901RW009
1
J-33011
901RW010
J-34614
2
J-23128-A
901RW011
Page 452 of 6000

4A1–15 DIFFERENTIAL (FRONT)
8. Select the shim using the chart;
Pinion marking+10+8+6+4+20–2–4–6–8–10
Dial indicator
reading
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)mm
(Inches)
0.0812.18
(0.0858)
0.0822.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)
0.0832.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.23
(0.0882)
0.0842.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)
0.0852.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)
0.0862.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)
0.0872.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)
0.0882.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)
0.0892.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)
0.0902.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)
0.0912.18
(0.0858)2.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)
0.0922.20
(0.0866)2.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)
0.0932.24
(0.0882)2.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)
0.0942.26
(0.0890)2.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)
0.0952.28
(0.0898)2.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)
0.0962.32
(0.0914)2.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0972.34
(0.0921)2.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0982.36
(0.0929)2.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0992.38
(0.0937)2.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
02.42
(0.0953)2.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0012.44
(0.0961)2.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0022.46
(0.0969)2.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0032.48
(0.0977)2.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0042.52
(0.0992)2.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0052.54
(0.1000)2.56
(0.1008)
0.0062.56
(0.1008)
NOTE: When ordering shims, find the part number in the
parts catalog by using the thickness of shims listed in the
above table.4. Place the shim on the drive pinion, with the chamfered
side turned towards the pinion head then install the
inner bearing onto the pinion using an installer
9–8522–1165–0 and a press.
Page 483 of 6000

4A2A–16
DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 220mm)
4. Place the shim on the drive pinion, with the chamfered
side turned towards the pinion head then install the
inner bearing onto the pinion using an installer
9–8522–1165–0 and a press.
NOTE: Do not apply pressure to the roller cage and apply
pressure only to the inner race.
425RW048
5. Discard the used collapsible spacer and install a new
one.
6. Install pinion gear.
7. Install outer bearing.
8. Use oil seal installer 5–8840–2165–0 to install a new
oil seal that has been soaked in rear axle lubricant.
NOTE: Take care to use a front differential oil seal, NOT
the rear differential oil seal.
415RW029
9. Install dust cover.
10. Install flange.
11. Install flange nut.
1. Apply lubricant to the pinion threads.2. Tighten the nut to the specified torque using the
pinion flange holder 5–8840–2157–0.
Torque: 245–294Nꞏm (25.0–28.0kgꞏm/181–217 lb f
t)
NOTE: Discard used flange nut and install new one and
do not over tighten the flange nut.
425RW057
3. Adjust pinion bearing preload.
a. Measure the bearing preload by using a torque
meter. Note the scale reading required to
rotate the flange.
b. Continue tightening flange nut until the
specified starting torque is obtained.
Starting torque:
New bear-
ing 0.7–1.3 Nꞏm(0.07-0.13kgꞏm/6.08–11.28 lb in)
Used bear-
ing 0.4–0.6Nꞏm(0.04–0.06kgꞏm/3.04-5.64 Ib in)
425RS027
4. Using punch 5–8840–2293–0, stake the flange
nut at two points.
Page 527 of 6000

4A2B–24DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 244mm)
4. Remove Differential shaft (2) using hammer and
punch.
Place shop towel behind case to prevent differential
shaft from dropping out of case.
425RW005
5. Assemble clutch pack unloading tool
5–8840–2586–0 .
a. Install cap (1) to the bottom differential side gear.
b. Install threaded screw cap (2) to top differential
side gear. Thread forcing screws (3) into threaded
screw cap until it becomes centered into the
bottom cap.
425RW064
c. Tighten forcing screw until tight enough to collapse
dished spacers and allow looseness between side
and pinion mate gears.6. Both pinion mate gear thrust washers using a shim
stock (1) of 0.51 mm (0.020 in.) or equivalent tool to
push out washers.
425RW007
7. Relieve tension of dished spacers by loosening
forcing screw.
NOTE:
You may have to adjust the forcing screw slightly to
allow the case to rotate.
8. Insert differential shaft into its hole of case. Pull on
shaft and rotate case until pinion mate gears can be
removed.
9. Remove pinion mate gears.
10. Hold side gear top clutch pack (1) with one hand and
remove positraction unloading tools.
425RW008
Page 683 of 6000

4C–17 DRIVE SHAFT SYSTEM
11. Install follower to clutch so that follower nails (large)
(1) will come closer to the bent portion of retaining
spring by aligning follower stopper nail with outer
teeth of clutch. Then, fit in with follower’s nails (small)
(2) caught in spring.
411RW016
12. Install compression ring.
Turn the smaller diameter side toward follower and fit
spring in clutch.
13. Align follower nail (1) to handle groove (2). and then
assemble clutch with knob by pushing and turning
clutch counterclockwise to knob.
411RW017
14. Install gasket.
Make sure that there is no breakage, etc.
15. Install outer bearing outer race by driving it into the
hub, by using installer 5–8522–2118–0 and grip
5–8840–0007–0.
411RW007
16. Install inner bearing outer race by driving it into the
hub, by using installer 5–8840–2119–0 and grip
5–8840–0007–0.
411RW006
Page 814 of 6000

5A–4
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in the
ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment front
right side. It consists of a Motor, Plunger Pump, Solenoid
Valves and Check Valve.
On the outside, the relay box containing a motor relay and
a valve relay is installed.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front disc brake or both rear disc brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Reservoir: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that returns
from the front and rear disc brake caliper so that pressure
of front disc brake caliper can be reduced smoothly.
Plunger Pump: Feeds the brake fluid held in the reservoir
to the master cylinder.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Check Valve: Controls the brake fluid flow.
ABS Warning Light
821RW033Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System have
an amber “ABS” warning light in the instrument panel.
The “ABS” warning light will illuminate if a malfunction in
the Anti-lock Brake System is detected by the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In case of an electronic
malfunction, the EHCU will turn “ON” the “ABS” warning
light and disable the Anti-lock braking function.
The “ABS” light will turn “ON” for approximately three
seconds after the ignition switch is to the “ON” position.
If the “ABS” light stays “ON” after the ignition switch is the
“ON” position, or comes “ON” and stays “ON” while
driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should be inspected
for a malfunction according to the diagnosis procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is attached
to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the axle shaft
bearing holder on the rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.The flux generated from electrodes magnetized by a
magnet in the sensor varies due to rotation of the rotor,
and the electromagnetic induction generates alternating
voltage in the coil. This voltage draws a “sine curve” with
the frequency proportional to rotor speed and it allows
detection of wheel speed.
G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the center console detects
the vehicle deceleration speed and sends a signal to the
EHCU. In 4WD operation, all four wheels may be
decelerated in almost the same phase, since all wheels
are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable particularly on roads with low
friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G-sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
road surface is low or high, and changes the EHCU’s
operating system to ensure ABS control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power assisted
brake system. However, with the detection of wheel
lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in the brake
pedal. This pedal “bump” will be followed by a series of
short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid succession.
The brake pedal pulsation will continue until there is no
longer a need for the anti-lock function or until the vehicle
is stopped. A slight ticking or popping noise may be heard
during brake applications when the Anti-lock features is
being used.
When the Anti-lock feature is being used, the brake pedal
may rise even as the brakes are being applied. This is
also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the pedal
will provide the shortest stopping distance.
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying more
force the pedal will continue to travel toward the floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left
Page 959 of 6000

6A–3
ENGINE MECHANICAL
General Description
Engine Cleanliness And Care
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the thousandths of a
millimeter (ten thousandths of an inch). Accordingly,
when any internal engine parts are serviced, care and
cleanliness are important. Throughout this section, it
should be understood that proper cleaning and protection
of machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the
repair procedure. This is considered standard shop
practice even if not specifically stated.
A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to all
friction areas during assembly to protect and lubricate
the surfaces on initial operation.
Whenever valve train components, pistons, piston
rings, connecting rods, rod bearings, and crankshaft
journal bearings are removed for service, they should
be retained in order.
At the time of installation, they should be installed in
the same locations and with the same mating
surfaces as when removed.
Battery cables should be disconnected before any
major work is performed on the engine. Failure to
disconnect cables may result in damage to wire
harness or other electrical parts.
The six cylinders of this engine are identified by
numbers; Right side cylinders 1, 3 and 5, Left side
cylinders 2, 4 and 6, as counted from crankshaft
pulley side to flywheel side.
General Information on Engine Service
The following information on engine service should be
noted carefully, as it is important in preventing damage
and contributing to reliable engine performance:
When raising or supporting the engine for any reason,
do not use a jack under the oil pan. Due to the small
clearance between the oil pan and the oil pump
strainer, jacking against the oil pan may cause
damage to the oil pick–up unit.
The 12–volt electrical system is capable of damaging
circuits. When performing any work where electrical
terminals could possibly be grounded, the ground
cable of the battery should be disconnected at the
battery.
Any time the intake air duct or air cleaner is removed,
the intake opening should be covered. This will
protect against accidental entrance of foreign
material into the cylinder which could cause extensive
damage when the engine is started.
Cylinder Block
The cylinder block is made of aluminum die–cast casting
for 75
V–type six cylinders. It has a rear plate integrated
structure and employs a deep skint. The cylinder liner is
cast and the liner inner diameter and crankshaft journal
diameter are classified into grades. The crankshaft is
supported by four bearings of which width of No.3 bearing
on the body side is different in order to support the thrust
bearing. The bearing cap is made of nodular cast iron and
each bearing cap uses four bolts and two side bolts.
Cylinder Head
The cylinder head, made of aluminum alloy casting
employs a pent–roof type combustion chamber with a
spark plug in the center. The intake and exhaust valves
are placed in V–type design. The ports are cross–flow
type.
Va l v e Tr a i n
Intake and exhaust camshaft on the both side of banks
are driven through an camshaft drive gear by timing belt.
The valves are operated by the camshaft and the valve
clearance is adjusted to select suitable thickness shim.
Intake Manifold
The intake manifold system is composed of the aluminum
cast common chamber and intake manifold attached with
six fuel injectors.
Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold is made of nodular cast iron.
Pistons and Connecting Rods
Aluminum pistons are used after selecting the grade that
meets the cylinder bore diameter. Each piston has two
compression rings and one oil ring. The piston pin is made
of chromium steel is offset 1mm toward the thrust side,
and the thrust pressure of piston to the cylinder wall varies
gradually as the piston travels. The connecting rods are
made of forged steel. The connecting rod bearings are
graded for correct seze selection.
Crankshaft and Bearings
The crankshaft is made of Ductile cast–iron. Pins and
journals are graded for correct size selection for their
bearing.
Engine Lubrication
The oil discharged by a trochoid–type oil pump driven by
the crankshaft is fed through full–flow oil filter and to the oil
gallery provided under the crankshaft bearing cap. The oil
is then led to the crankshaft journals and cylinder head.
The crank pins are lubricated with oil from crankshaft
journals through oil holes. Also, an oil jet is fed to each
cylinder from crankshaft juornals on the connecting rod
for piston cleaning. The oil pan flange is dealed with liquid
packing only; do not deform or damage the flange surface
during removal or installation.
Page 971 of 6000

6A–15
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Condition CorrectionPossible cause
Oil leaking into combustion
chambers due topoor seal in valve
Valve stem oil seal defectiveReplace
chambers due to oor seal in valve
systemValve stem or valve guide wornReplace valve and valve guide
Oil leaking into combustion
chambers due to poor seal in cylinder
t
Cylinders and pistons worn
excessivelyReplace cylinder body assembly and
pistons
partsPiston ring gaps incorrectly
positionedCorrect
Piston rings set with wrong side upCorrect
Piston ring stickingReplace cylinder body assembly and
pistons
Piston ring and ring groove wornReplace pistons and others
Return ports in oil rings cloggedClean piston and replace rings
Positive Crankcase Ventilation
System malfunctioningPositive Crankcase Ventilation Valve
cloggedClean
OthersImproper oil viscosityUse oil of recommended S.A.E.
viscosity
Continuous high speed driving
and/or severe usage such as trailer
towingContinuous high speed operation
and/or severe usage will normally
cause increased oil consumption
Fuel Consumption Excessive
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Trouble in fuel systemMixture too rich or too lean due to
trouble in fuel injection systemRefer to “Abnormal Combustion”
Fuel cut function does not workRefer to “Abnormal Combustion”
Trouble in ignition systemMisfiring or abnormal combustion
due to trouble in ignition systemRefer to “Hard Start” or “Abnormal
Combustion”
OthersEngine idle speed too highReset Idle Air Control Valve
Returning of accelerator control
sluggishCorrect
Fuel system leakageCorrect or replace
Clutch slippingCorrect
Brake dragCorrect
Selection of transmission gear
incorrectCaution operator of incorrect gear
selection
Excessive Exhaust Gas
Recirculation flow due to trouble in
Exhaust Gas Recirculation systemRefer to “Abnormal Combustion”
Page 1082 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL6D1–3
a. VOLTAGE DOES NOT DROP BELOW THE
MINIMUM LISTED IN THE TABLE – The battery is
good and should be returned to service.
b. VOLTAGE IS LESS THAN MINIMUM LISTED –
Replace battery.
ESTIMATED TEMPERATURE
MINIMUM
VOLTAGE
FCV
70219.6
60169.5
50109.4
4049.3
30–19.1
20–78.9
10–128.7
0–188.5
The battery temperature must be estimated by feel
and by the temperature the battery has been
exposed to for the preceding few hours.
Battery Charging
Observe the following safety precautions when charging
the battery:
1. Never attempt to charge the battery when the fluid
level is below the lower level line on the side of the
battery. In this case, the battery must be replaced.
2. Pay close attention to the battery during charging
procedure.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate of
charge reduced if the battery feels hot to the touch.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate of
charge reduced if the battery begins to gas or spew
electrolyte from the vent holes.
3. In order to more easily view the hydrometer blue dot
or ring, it may be necessary to jiggle or tilt the battery.
4. Battery temperature can have a great effect on
battery charging capacity.
5. The sealed battery used on this vehicle may be either
quick charged or slow charged in the same manner as
other batteries.
Whichever method you decide to use, be sure that
you completely charge the battery. Never partially
charge the battery.
Jump Starting
Jump Starting with an Auxiliary (Booster)
Battery
CAUTION: Never push or tow the vehicle in an
attempt to start it. Serious damage to the emission
system as well as other vehicle parts will result.Treat both the discharged battery and the booster
battery with great care when using jumper cables.
Carefully follow the jump starting procedure, being
careful at all times to avoid sparking.
WARNING: FAILURE TO CAREFULLY FOLLOW THE
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE COULD RESULT IN
THE FOLLOWING:
1. Serious personal injury, particularly to your eyes.
2. Property damage from a battery explosion, battery
acid, or an electrical fire.
3. Damage to the electronic components of one or both
vehicles particularly.
Never expose the battery to an open flame or electrical
spark. Gas generated by the battery may catch fire or
explode.
Remove any rings, watches, or other jewelry before
working around the battery. Protect your eyes by wearing
an approved set of goggles.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with your eyes
or skin.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with fabrics or
painted surfaces.
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.
Should battery fluid come in contact with your eyes, skin,
fabric, or a painted surface, immediately and thoroughly
rinse the affected area with clean tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come in
contact with the positive battery terminal, or any other
metal surface of the vehicle. This will protect against a
short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of reach of young children.
Jump Starting Procedure
1. Set the vehicle parking brake.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the selector level in the “PARK”
position.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission,
place the shift lever in the “NEUTRAL” position.
Turn “OFF” the ignition.
Turn “OFF” all lights and any other accessory
requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built–in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built–in hydrometer is
completely clear, do not try to jump start.
3. Attach the end of one jumper cable to the positive
terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive
terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other. This will
cause a ground connection, effectively neutralizing
the charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt rating.
Page 1096 of 6000
6D3–5 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Starter
Removal
1. Battery ground cable.
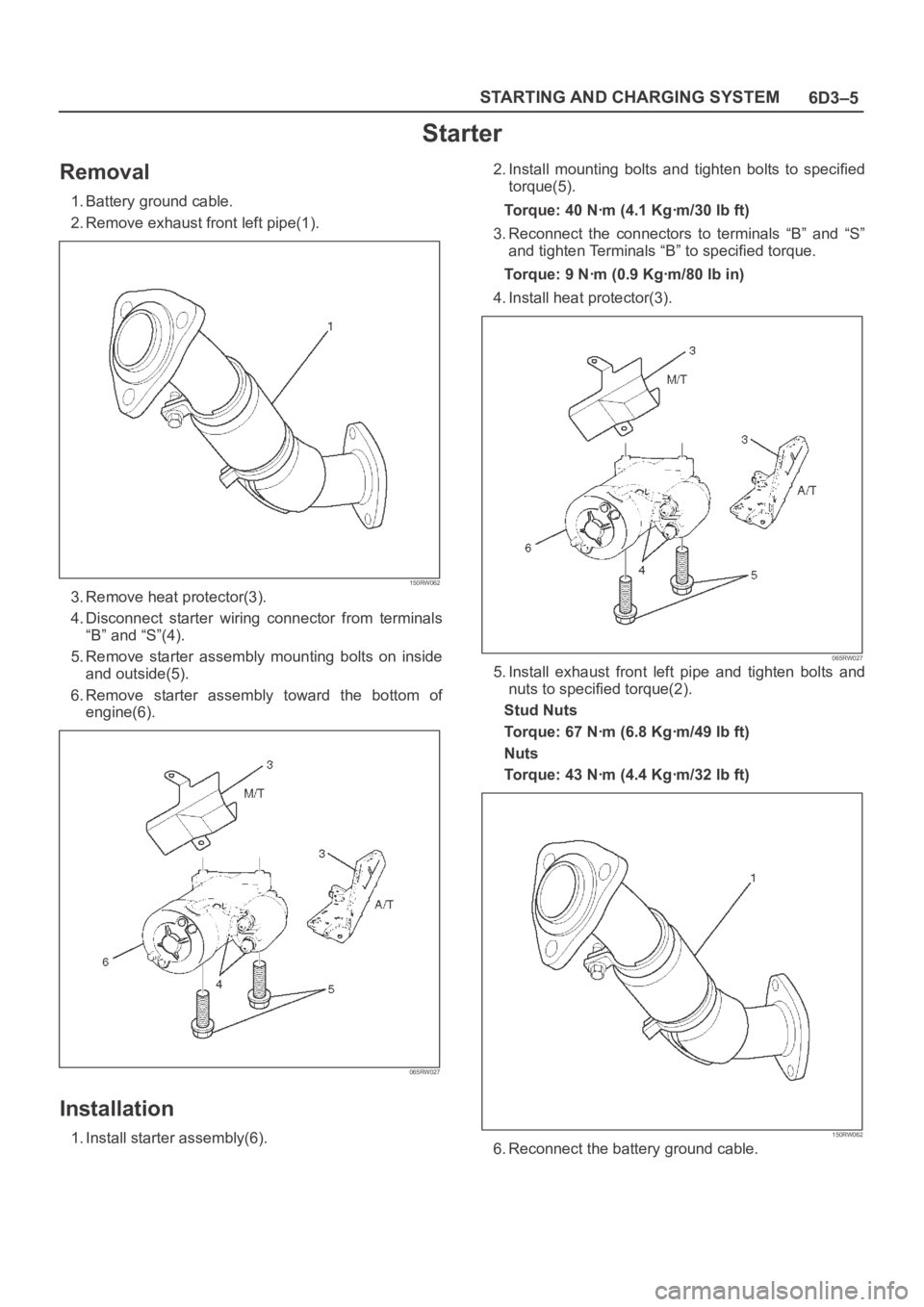
2. Remove exhaust front left pipe(1).
150RW062
3. Remove heat protector(3).
4. Disconnect starter wiring connector from terminals
“B” and “S”(4).
5. Remove starter assembly mounting bolts on inside
and outside(5).
6. Remove starter assembly toward the bottom of
engine(6).
065RW027
Installation
1. Install starter assembly(6).2. Install mounting bolts and tighten bolts to specified
torque(5).
Torque: 40 Nꞏm (4.1 Kgꞏm/30 lb ft)
3. Reconnect the connectors to terminals “B” and “S”
and tighten Terminals “B” to specified torque.
Torque: 9 Nꞏm (0.9 Kgꞏm/80 lb in)
4. Install heat protector(3).
065RW027
5. Install exhaust front left pipe and tighten bolts and
nuts to specified torque(2).
Stud Nuts
Torque: 67 Nꞏm (6.8 Kgꞏm/49 lb ft)
Nuts
Torque: 43 Nꞏm (4.4 Kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
150RW062
6. Reconnect the battery ground cable.