trouble code connector SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 507 of 2053
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 89
D AEW OO M Y_2000
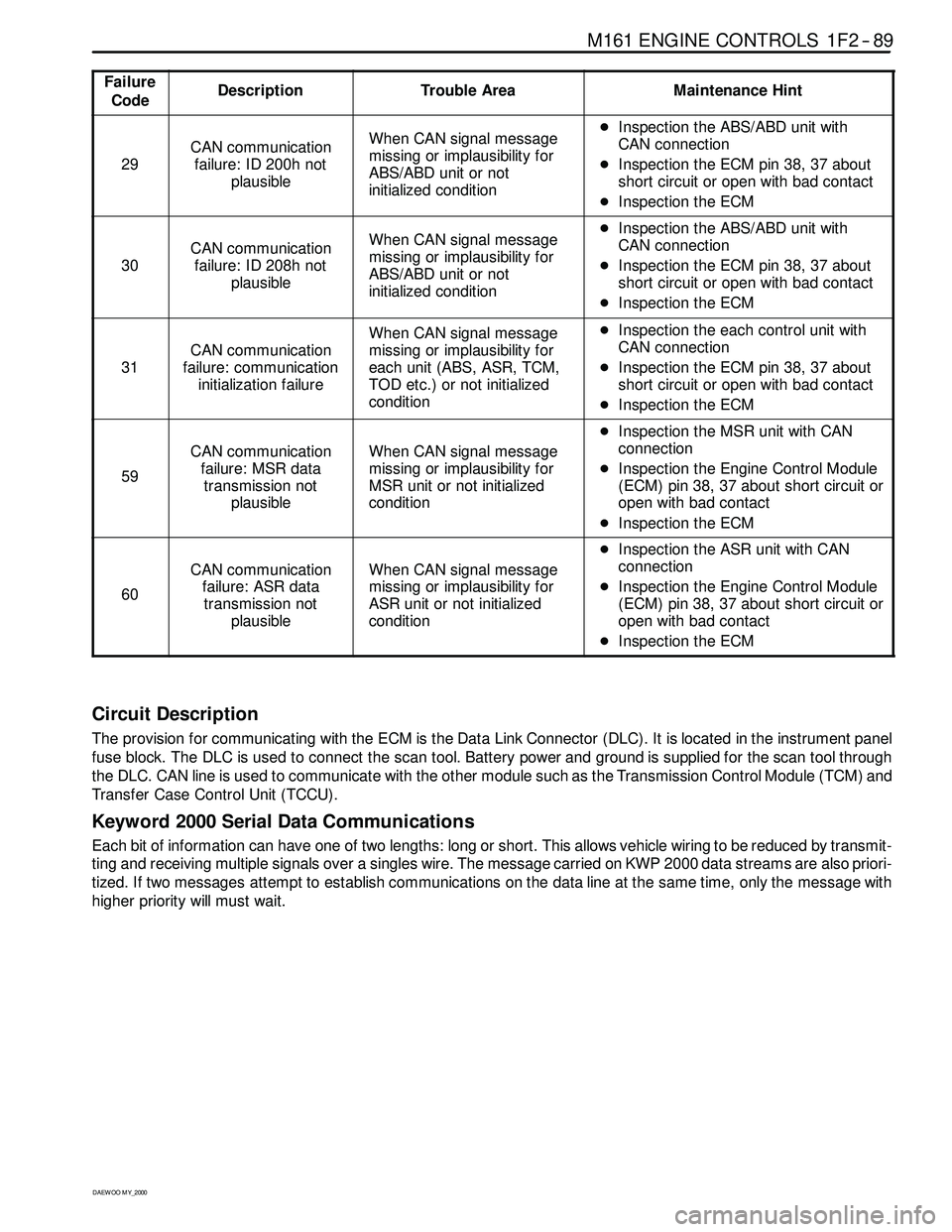
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
29
CAN communication
failure: ID 200h not
plausibleWhen CAN signal message
missing or implausibility for
ABS/ABD unit or not
initialized conditionDInspection the ABS/ABD unit with
CAN connection
DInspection the ECM pin 38, 37 about
short circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the ECM
30
CAN communication
failure: ID 208h not
plausibleWhen CAN signal message
missing or implausibility for
ABS/ABD unit or not
initialized conditionDInspection the ABS/ABD unit with
CAN connection
DInspection the ECM pin 38, 37 about
short circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the ECM
31
CAN communication
failure: communication
initialization failure
When CAN signal message
missing or implausibility for
each unit (ABS, ASR, TCM,
TOD etc.) or not initialized
conditionDInspection the each control unit with
CAN connection
DInspection the ECM pin 38, 37 about
short circuit or open with bad contact
DInspection the ECM
59
CAN communication
failure: MSR data
transmission not
plausibleWhen CAN signal message
missing or implausibility for
MSR unit or not initialized
condition
DInspection the MSR unit with CAN
connection
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 38, 37 about short circuit or
open with bad contact
DInspection the ECM
60
CAN communication
failure: ASR data
transmission not
plausibleWhen CAN signal message
missing or implausibility for
ASR unit or not initialized
condition
DInspection the ASR unit with CAN
connection
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 38, 37 about short circuit or
open with bad contact
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The provision for communicating with the ECM is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located in the instrument panel
fuse block. The DLC is used to connect the scan tool. Battery power and ground is supplied for the scan tool through
the DLC. CAN line is used to communicate with the other module such as the Transmission Control Module (TCM) and
Transfer Case Control Unit (TCCU).
Keyword 2000 Serial Data Communications
Each bit of information can have one of two lengths: long or short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by transmit-
ting and receiving multiple signals over a singles wire. The message carried on KWP 2000 data streams are also priori-
tized. If two messages attempt to establish communications on the data line at the same time, only the message with
higher prioritywill must wait.
Page 1021 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-38 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 03
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F140
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during a
road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings are unusual,
such as one sensor varying in speed from the other
three, a signal going intermittently high or low, etc. If
this does not identify the intermittent, wet the speed
sensor harness on the underside of the vehicle and
perform a road test, monitoring wheel speeds with the
scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 03 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1023 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-40 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 07
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F140
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1025 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-42 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 04
RIGHT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F150
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during a
road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings are unusual,
such as one sensor varying in speed from the other
three, a signal going intermittently high or low, etc. If
this does not identify the intermittent, wet the speed
sensor harness on the underside of the vehicle and
perform a road test, monitoring wheel speeds with the
scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 04 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1027 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-44 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 08
RIGHT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F150
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1029 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-46 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 05
LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F160
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel
speed sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the
wiring, or a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon
nected.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during a
road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings are unusual,
such as one sensor varying in speed from the other
three, a signal going intermittently high or low, etc. If
this does not identify the intermittent, wet the speed
sensor harness on the underside of the vehicle and
perform a road test, monitoring the wheel speeds with
the scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 05 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1031 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-48 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 09
LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F160
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1033 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-50 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 06
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F170
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective or disconnected.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds
during a road test. Watch the wheel speeds being
displayed on the scan tool to see if any of the readings
is unusual, such as one sensor varying in speed from
the other three, a signal going intermittently high or
low, etc. If this does not identify the intermittent, wet
the speed sensor harness on the underside of the
vehicle and perform a road test, monitoring the wheel
speeds with the scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 06 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1035 of 2053
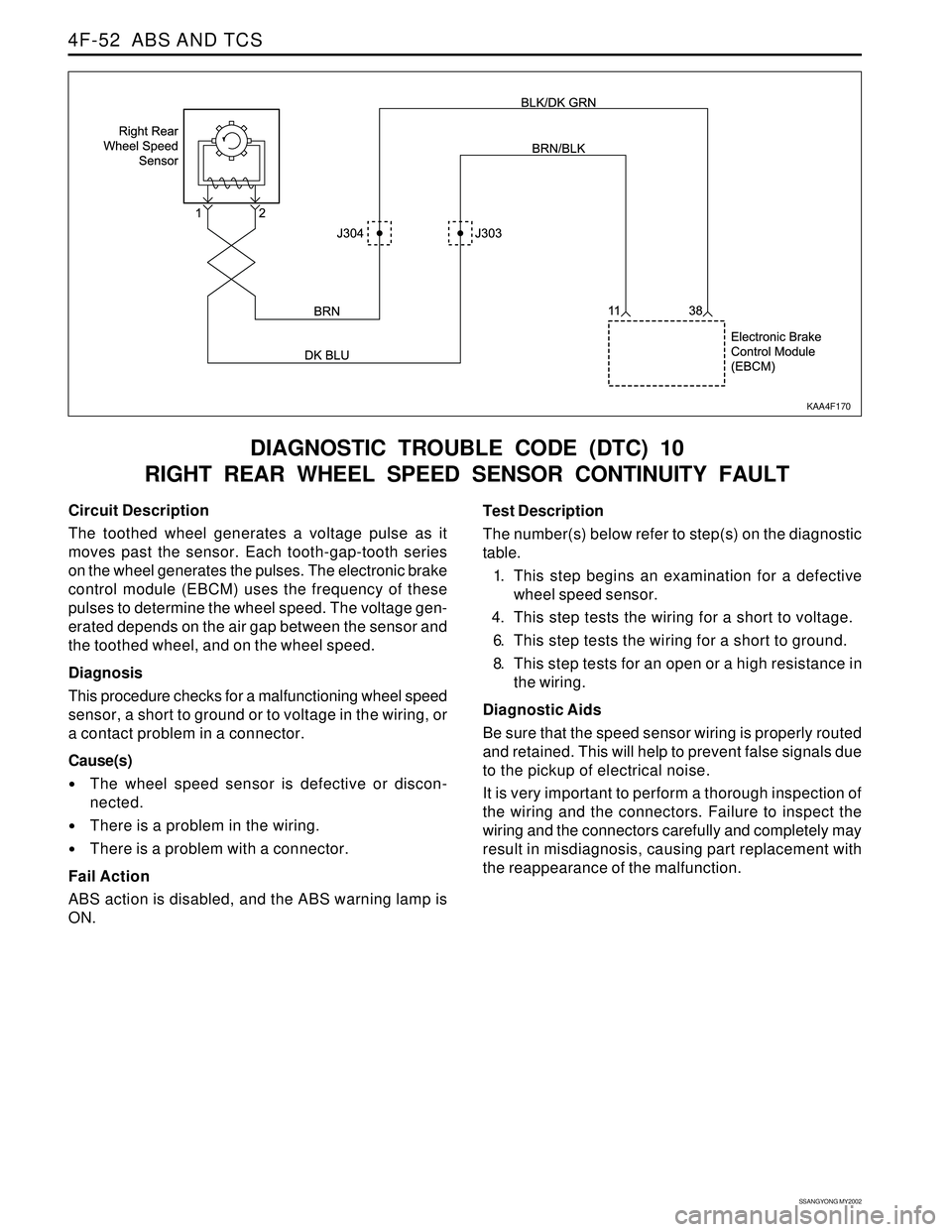
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-52 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 10
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F170
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
•The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon-
nected.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1041 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-58 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 42
ACCELERATION SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F190
Circuit Description
The acceleration sensor provides a voltage signal that
changes in relation to the acceleration of vehicle. The
signal voltage will vary from about 1.95 to 3.45 volt.
The electronic brake control module (EBCM) monitor a
signal voltage of deceleration in the vehicle.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning acceleration
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause
The vertical acceleration sensor is defective or dis
connected
There is a problem in the wiring
There is a problem with a connector
Wrong installed vertical acceleration sensor
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. This step checks for the voltage reference from
the EBCM.
5. This step checks for the voltage signal from the
acceleration sensor.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the acceleration sensor wiring is properly
routed and retained.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors carefully and completely
may result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement
with the reappearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor acceleration sensor
during a road test. Watch the acceleration sensor being
displayed on the scan tool to see if any of the reading
is unusual.