wiring CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 260 of 2438

(7) Using needle nose pliers, install the 3 brake fluid
reservoir to hydraulic assembly retaining pins (Fig.
14). Be sure retaining pins are fully installed with
barbs extending out past reservoir on opposite
side. (8) Install high pressure hose banjo fitting onto
hydraulic assembly and install banjo fitting attaching
bolt. Torque banjo fitting to hydraulic assembly banjo
bolt to 13 N Im (10 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install brake fluid spray shield onto hydraulic
assembly. Install bladder accumulator into hydraulic
assembly by hand (using care not to cross thread
accumulator) until O-ring seal is fully seated into
hydraulic assembly. (10) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent, (Fig. 12) torque bladder accumu-
lator to 48 N Im (35 ft. lbs.).
(11) Fill hydraulic assembly fluid reservoir to the top
of the screen on the filter rainer. Use only fresh clean
brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 requirements, such as
Mopar tor equivalent.
(12) Bleed the brake hydraulic system using proce-
dure shown in Bleeding Brake System in this section of
the service manual.
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH
REMOVE
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE THE
HYDRAULIC BLADDER ACCUMULATOR PRIOR TO
REMOVING DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH.
WILL RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAM-
AGE TO PAINTED SURFACES OF THE VEHICLE.
To remove the differential pressure switch (Fig. 18),
from the hydraulic assembly, removal of the hydraulic
assembly from the vehicle is notrequired. (1) De-pressurize hydraulic bladder accumulator on
hydraulic assembly by pumping the brake pedal a
minimum of 40 times. Refer to the procedure as de-
scribed in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
listed earlier in this section. (2) Disconnect the hydraulic assembly wiring har-
ness connector from the primary pressure transducer
(Fig. 19).
(3) Disconnect differential pressure switch wiring
harness connector from hydraulic assembly wiring
harness (Fig. 19). Do not attempt to remove wiring
harness from differential pressure switch. (4) Raise vehicle on a frame contact type hoist. See
Hoisting in the Lubrication And Maintenance section
of this manual, for the required lifting procedure to be
used for this vehicle. (5) Using a long extension and Socket, Special Tool
6684 loosen and remove differential pressure switch
from bottom of hydraulic assembly (Fig. 20)
Fig. 18 Differential Pressure Switch Location
Fig. 19 Primary Pressure Transducer And Differen- tial Pressure Switch Wiring Harness Connectors
Fig. 17 Primary Pressure Transducer Removal And Replacement
5 - 110 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 261 of 2438

INSTALL (1) Install differential pressure switch into hydrau-
lic assembly by hand, until fully threaded into hy-
draulic assembly. Then torque differential pressure
switch, into hydraulic assembly, using Socket, Spe-
cial Tool 6684, to 1.5 N Im (13 in. lbs.).
(2) Lower vehicle
(3) Connect differential pressure switch wiring
harness connector into hydraulic assembly wiring
harness (Fig. 19). (4) Connect the hydraulic assembly wiring harness
connector into the primary pressure transducer (Fig.
19). (5) Turn the ignition switch to the on position and
let the system pressurize. Check for any signs of
leakage at the differential pressure switch. (6) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic assembly a
second time to purge any air out that may have en-
tered hydraulic assembly when the differential pres-
sure switch was removed. Turn the ignition switch to
the on position and let the system pressurize again. (7) Fill hydraulic assembly fluid reservoir to the
top of the screen on the filter rainer. Use only fresh
clean brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 requirements,
such as Mopar tor equivalent.
(8) Road test vehicle to insure that the brake sys-
tem is performing correctly.
BOOST PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
REMOVE
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE
THE HYDRAULIC BLADDER ACCUMULATOR PRIOR
TO REMOVING BOOST PRESSURE TRANSDUCER.
MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAM-
AGE TO PAINTED SURFACES OF THE VEHICLE. To remove the boost pressure transducer (Fig. 21),
from the hydraulic assembly, removal of the hydrau-
lic assembly from the vehicle is notrequired.
(1) De-pressurize hydraulic bladder accumulator on
hydraulic assembly by pumping the brake pedal a
minimum of 40 times. Refer to the procedure as de-
scribed in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
listed earlier in this section. (2) Raise vehicle on a frame contact type hoist. See
Hoisting in the Lubrication And Maintenance section
of this manual, for the required lifting procedure to
be used for this vehicle. (3) Disconnect hydraulic assembly wiring harness
connectors from the dual function pressure switch
and boost pressure transducer (Fig. 21). (4) Using a long extension and Socket, Special Tool
6607, remove dual function pressure switch from bot-
tom of hydraulic assembly (Fig. 22)
(5) Remove boost pressure transducer from hydrau-
lic assembly, from under vehicle using a long exten-
sion and Socket, Special Tool 6684 (Fig. 23).
Fig. 20 Differential Pressure Switch Removal And Replacement
Fig. 21 Boost Pressure Transducer Location
Fig. 22 Remove And Install Dual Function Pressure Switch
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 111
Page 262 of 2438

INSTALL (1) Install boost pressure transducer (Fig. 23) into
hydraulic assembly by hand, until O-ring is fully
seated into hydraulic assembly. Then torque boost pressure transducer, into hydraulic assembly, using
Socket, Special Tool 6684, to 12 N Im (106 in. lbs.).
(2) Install Dual Function Pressure Switch (Fig. 22)
into hydraulic assembly by hand, until O-ring is
fully seated into hydraulic assembly. Then torque
dual function pressure switch, into hydraulic assem-
bly, using Socket, Special Tool 6607, to 12 N Im (106
in. lbs.). (3) Connect hydraulic assembly wiring harness
connectors, onto the dual function pressure switch
and boost pressure transducer (Fig. 21). (4) Turn the ignition switch to the on position and
let the system pressurize. Check for any signs of
leakage at the differential pressure switch. (5) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic assembly a
second time to purge any air out that may have en-
tered hydraulic assembly when the differential pres-
sure switch was removed. Turn the ignition switch to
the on position and let the system pressurize again. (6) Fill hydraulic assembly fluid reservoir to the
top of the screen on the filter rainer. Use only fresh
clean brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 requirements,
such as Mopar tor equivalent.
(7) Road test vehicle to insure that the brake sys-
tem is performing correctly.
Fig. 23 Remove And Install Boost Pressure Transducer
5 - 112 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 275 of 2438

MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of the DRB II diagnostics tester. The proper
application and procedures for the use of this tool are
described below.
DRB II DIAGNOSTIC TESTER Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB II
Diagnostics Tester to insure that proper diagnostics
are performed. Refer to those sections for proper test-
ing procedures and the DRB II operators manual for
its proper operational information.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent faults in the ABS system may be difficult to ac-
curately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of connector halves or terminals
not fully seated in the connector body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
carefully reformed to increase contact tension. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to in-
spect. (4) Pin presence in the connector assembly
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the Fault code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable Anti-
Lock function for the entire ignition cycle even if the
fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which a fail-
ure occurred. If the failure conditions are no longer
present. The following conditions may result in inter-
mittent illumination of the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp. All other failures will cause the lamp to
remain on until the ignition switch is turned off. Cir-
cuits involving these inputs to the (CAB) should be
investigated if a complaint of intermittent warning
system operation is encountered. (1) Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the (CAB), the (CAB) will turn on the
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp until normal sys-
tem voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen
at the (CAB), normal operation resumes. (2) Anti-Lock relay. If the relay fails to make the
ground circuit connection or is an intermittent
ground. The (CAB) will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Light. (3) Excess decay, an extended pressure decay pe-
riod, will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Light until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. Additionally, any condition which results in inter-
ruption of electrical current to the (CAB) or modula-
tor assembly. May cause the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Lamp to turn on intermittently.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self diagnostic
capability which may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the self diagnostics sys-
tem are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self diagnostic ABS start up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. An
electrical check is completed on the ABS components.
Such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity and System
and other Relay continuity. During this check the
Amber Anti-Lock Light is turned on for approxi-
mately 1- 2 seconds. Further Functional testing is accomplished once
the vehicle is set in motion.
² The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are acti-
vated briefly to verify function.
² The voltage output from the wheel speed sensors is
verified to be within the correct operating range. If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB II
or erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the (CAB) fault. A
(CAB) fault can only be erased by the technician us-
ing the DRB II diagnostic tester. More than one fault
can be stored at a time. The number of key cycles
since the most recent fault was stored is also dis-
played. Most functions of the (CAB) and ABS system
can be accessed by the technician for testing and di-
agnostic purposes by using the DRB II.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS
Some faults detected by the (CAB) are latching; the
fault is latched and (ABS) is disabled until the igni-
tion switch is reset. Thus ABS is disabled even if the
original fault has disappeared. Other faults are non-
latching; any warning lights that are turned on, are
only turned on as long as the fault condition exists.
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 125
Page 280 of 2438
junction block. Torque both lower mounting bracket
bolts to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.)
(4) Reinstall the 4 hydraulic brake tubes to the
Modulator Assembly and torque the fittings to 16
N Im (145 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect the 10 way Modulator assembly con-
nector, and the delta P switch connector. (6) Lower the vehicle and install the 2 master cyl-
inder supply tubes to the Modulator Assembly.
Torque the Modulator Assembly fittings and the
master cylinder fittings to 16 N Im (145 in.lbs.).
(7) Torque the Modulator to fender splash shield
attaching bolt to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.)
(8) Bleed the brake system. Refer to the Bleeding
Bendix Anti 6 Brake System in this section of the
manual for proper bleeding procedure. (9) Reinstall the acid shield and battery tray. Re-
install battery and connect battery cables.
MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BOOSTER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
If the Master Cylinder or the Power Booster need
to be serviced or replaced. Refer to Master Cylinder
or Power Brake Service section in this group of the
service manual. After servicing the Master Cylinder. Refer back to
this section of the service manual. For the appropri-
ate procedure and sequence, used to bleed the base
and ABS portion of the brake system
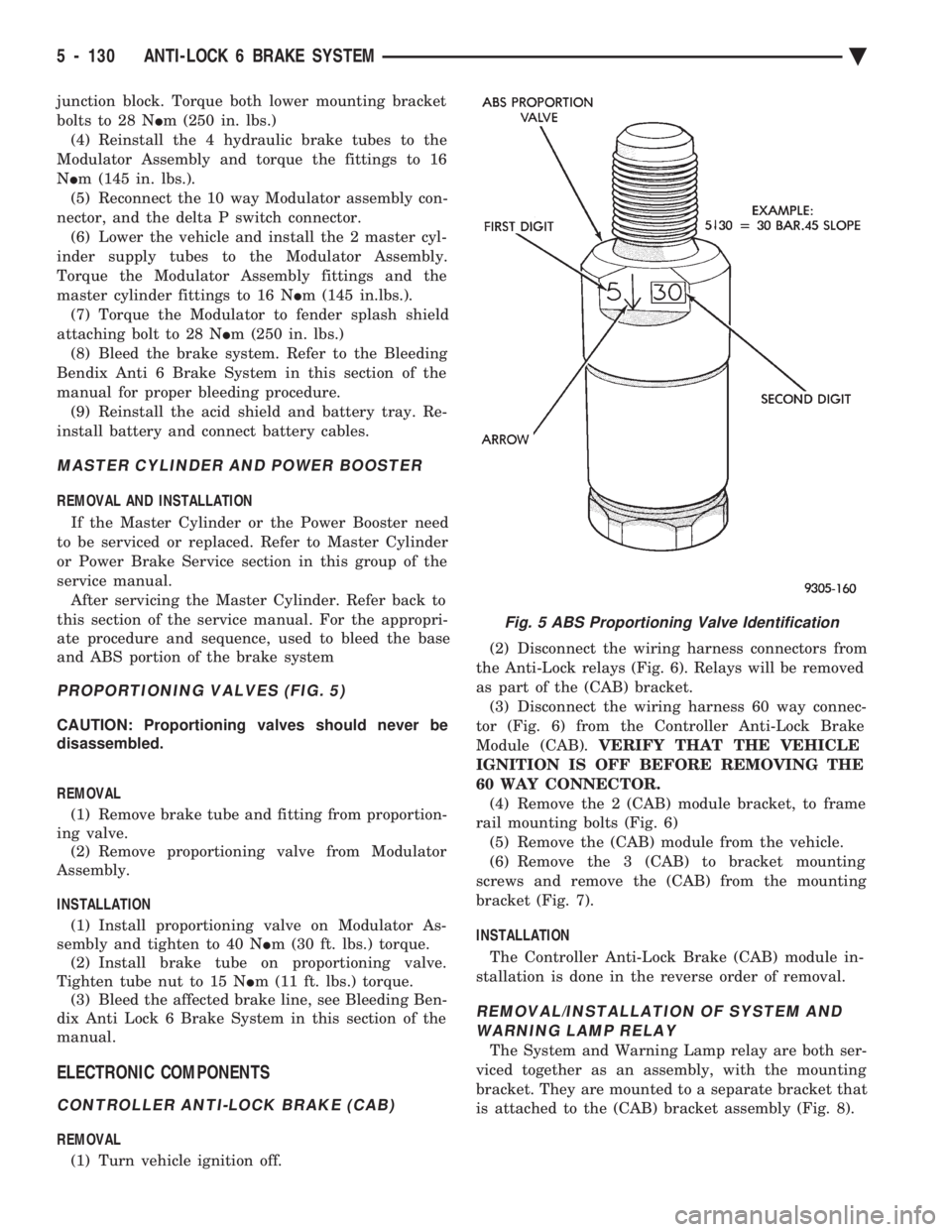
PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 5)
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be
disassembled.
REMOVAL (1) Remove brake tube and fitting from proportion-
ing valve. (2) Remove proportioning valve from Modulator
Assembly.
INSTALLATION (1) Install proportioning valve on Modulator As-
sembly and tighten to 40 N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install brake tube on proportioning valve.
Tighten tube nut to 15 N Im (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Bleed the affected brake line, see Bleeding Ben-
dix Anti Lock 6 Brake System in this section of the
manual.
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
REMOVAL
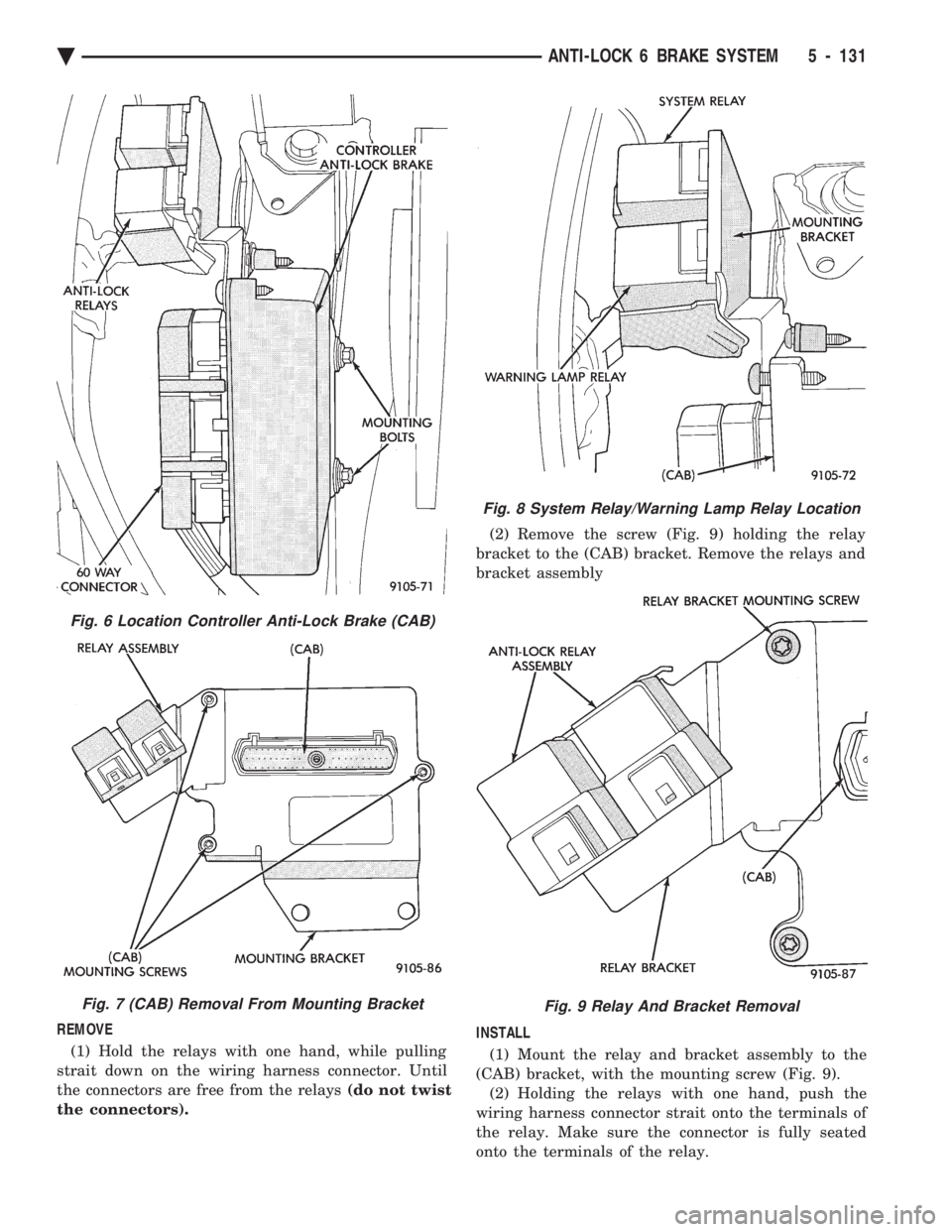
(1) Turn vehicle ignition off. (2) Disconnect the wiring harness connectors from
the Anti-Lock relays (Fig. 6). Relays will be removed
as part of the (CAB) bracket. (3) Disconnect the wiring harness 60 way connec-
tor (Fig. 6) from the Controller Anti-Lock Brake
Module (CAB). VERIFY THAT THE VEHICLE
IGNITION IS OFF BEFORE REMOVING THE
60 WAY CONNECTOR. (4) Remove the 2 (CAB) module bracket, to frame
rail mounting bolts (Fig. 6) (5) Remove the (CAB) module from the vehicle.
(6) Remove the 3 (CAB) to bracket mounting
screws and remove the (CAB) from the mounting
bracket (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
The Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) module in-
stallation is done in the reverse order of removal.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION OF SYSTEM AND WARNING LAMP RELAY
The System and Warning Lamp relay are both ser-
viced together as an assembly, with the mounting
bracket. They are mounted to a separate bracket that
is attached to the (CAB) bracket assembly (Fig. 8).
Fig. 5 ABS Proportioning Valve Identification
5 - 130 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 281 of 2438
REMOVE (1) Hold the relays with one hand, while pulling
strait down on the wiring harness connector. Until
the connectors are free from the relays (do not twist
the connectors). (2) Remove the screw (Fig. 9) holding the relay
bracket to the (CAB) bracket. Remove the relays and
bracket assembly
INSTALL
(1) Mount the relay and bracket assembly to the
(CAB) bracket, with the mounting screw (Fig. 9). (2) Holding the relays with one hand, push the
wiring harness connector strait onto the terminals of
the relay. Make sure the connector is fully seated
onto the terminals of the relay.
Fig. 6 Location Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB)
Fig. 7 (CAB) Removal From Mounting Bracket
Fig. 8 System Relay/Warning Lamp Relay Location
Fig. 9 Relay And Bracket Removal
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 131
Page 282 of 2438

REMOVE/INSTALL PUMP MOTOR RELAY
Find the location of the Pump Motor Relay (Fig. 10
& 11), depending on whether the vehicle has or does
not have a Power Distribution Center.
(1) Hold the relay with one hand. While pulling
the relay connector strait off the relay terminals. (2) Remove the relay from the vehicle.
(3) Installation is done in the reverse order off re-
moval. Be sure that the wiring harness connector is
fully seated onto the terminals of the Pump Motor
Relay.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
INSPECTION
Inspect tonewheel for missing or broken teeth, this
can cause erratic sensor signals. Tonewheel should show no evidence of contact with
the wheel speed sensor. If contact was made, deter-
mine cause and correct. Excessive runout of the tonewheel can cause er-
ratic wheel speed sensor. Replace assembly if runout
exceeds approximately 0.25 mm (0.010 inch).
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIG. 12)
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel and tire as-
sembly. (2) Remove screw from grommet retainer clip that
holds the grommet into fender shield (Fig. 12). (3) Remove the 2 screws that fasten the sensor
routing tube to the frame rail. (4) Carefully, pull sensor assembly grommet from
fender shield. (5) Unplug speed sensor connector from vehicle
wiring harness. (6) Remove the sensor assembly grommets from
the retainer brackets. (7) Remove sensor head screw.
(8) Carefully, remove sensor head from steering
knuckle. If the sensor has seized, due to corrosion,
DO NOT USE PLIERS ON SENSOR HEAD. Use
a hammer and a punch and tap edge of sensor ear,
rocking the sensor side to side until free.
Fig. 10 Pump Motor Relay Location With Power Distribution Center
Fig. 11 Pump Motor Relay Location W/O PowerDistribution Center
Fig. 12 Front Wheel Speed Sensor Routing
5 - 132 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 283 of 2438

INSTALLATION (1) Connect the wheel speed sensor connector to
the wiring harness. (2) Push sensor assembly grommet into hole in
fender shield. Install clip and screw. (3) Install the 2 screws that fasten the speed sen-
sor routing tube to the frame rail. (4) Install sensor grommets in brackets on fender
shield and strut damper. (5) Coat the speed sensor with High Temperature
Multi-purpose E.P. Grease before installing into the
steering knuckle. Install screw tighten to 7 N Im (60
in. lbs.)
CAUTION: Proper installation of wheel speed sen-
sor cables is critical to continued system operation.
Be sure that cables are installed in retainers. Fail-
ure to install cables in retainers, as shown in this
section, may result in contact with moving parts
and/or over extension of cables, resulting in an
open circuit.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIGS. 13 AND 14)
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel and tire as-
sembly. (2) Remove sensor assembly grommet from under-
body and pull harness through hole in underbody. (3) Unplug connector from harness.
(4) Remove sensor assembly grommets from
bracket which is screwed into the body hose bracket,
just forward of trailing arm bushing (batwing brack-
et.) (5) Remove sensor and brake tube assembly clip,
located on the inboard side of trailing arm. (6) Remove sensor wire fastener from rear brake
hose bracket. (7) Remove outboard sensor assembly retainer nut.
This nut also is used to capture the brake tube clip. (8) Remove sensor head screw.
(9) Carefully, remove sensor head from adapter as-
sembly. If the sensor has seized, due to corrosion, DO
NOT USE PLIERS ON SENSOR HEAD. Use a ham-
mer and a punch and tap edge of sensor ear, rocking
the sensor side to side until free.
INSTALLATION Installation is reverse order of removal. Be sure to
coat sensor with High Temperature Multi-purpose
E.P. Grease before installing into adapter assembly.
Tighten screw to 7 N Im (60 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 13 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Routing at Trailing Arm
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 133
Page 284 of 2438

Fig. 14 Body Routing of Rear Speed Sensor Wiring
5 - 134 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 306 of 2438

ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP DIODE
The Warning Lamp Relay on the Bendix Antilock
4 Brake System has been replaced with a diode. The
diode is used to control the function of the warning
lamp and is located inside the CAB module wiring
harness. The diode is a replaceable component of the
wiring harness, and will not require replacement of
the entire wiring harness if only the diode is diag-
nosed to have failed. When the system relay is de-energized, the Anti-
lock warning lamp will be lit. This will occur because
a ground path exists for the Antilock warning lamp
through the Antilock warning lamp diode and the
system relay armature. When the system relay is en-
ergized by the CAB, the system relay armature will
no longer provide a ground and the lamp will turn
off. Thus, the lamp will be lit if either the CAB is
disconnected or a system fault causes the Antilock to
be turned off.
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor Relay is either mounted on
the left front inner fender shield, or the front of the
left shock tower. The mounting location is dependent
on whether the vehicle is or is not equipped with a
power distribution center. See (Fig. 11 and 12) for
specific mounting locations.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay Energized
From pin 57, the CAB energizes the Antilock sys-
tem relay coil, thus the electrical current flow in the
coil closes the system relay. Then electrical current
is provided to pins 47 and 41 of the CAB to provide
power to the modulator valves. The CAB turns off the Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp by breaking the ground path through pin 15 of
the CAB.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP ON
System Relay De-Energized.
When the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is on,
there is no electrical current flow from the CAB at
pin 57 and the System Relay coil is NOT energized.
No electrical current flows to pin 47 and 41 (modula-
tor valve power), or to the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode. Thus, the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
not energized. The Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
now grounded through the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode and pin 15 of the CAB turning on the Amber
Antilock Warning Lamp.
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
Through the following operation descriptions and
diagrams. The function of the various hydraulic con-
trol valves in the ABS system will be described. The
fluid control valves mentioned below, control the flow
of pressurized brake fluid to the wheel brakes during
the different modes of Antilock braking. For explanation purposes we will assume all speed
sensors are sending the same wheel speed informa-
tion, requiring the same hydraulic fluid modulation
at the same rate.
NORMAL BRAKING
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Closed (Fig. 1)
The brake pedal is applied. The travel of the brake
pedal closes primary and secondary circuits from the
master cylinder fluid supply. Brake fluid from the
master cylinder primary and secondary circuits flows
through the build/decay valves to the wheel brakes.
ABS BRAKING-BUILD PRESSURE
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Open (Fig. 2)
Fig. 11 Pump Motor Relay Location On AA Body W/O Power Distribution Center
Fig. 12 Pump Motor Relay Location On AJ BodyWith Power Distribution Center
5 - 20 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä