check engine CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 30 of 1938

²Check glow plug operation.
²Replace drive belt.
²Check engine smoke.
²Replace engine coolant.
35 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Change MTX Fluid
40 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Diesel engines onlyÐReplace fuel filter/water
separator element.
45 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
50 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
55 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
60 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Diesel engines onlyÐReplace fuel filter/water
separator element.
65 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
70 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Change MTX fluid
75 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
80 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Replace drive belt.
²Check engine smoke.
²Replace engine coolant.
85 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
90 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
95 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
100 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Diesel engines onlyÐReplace fuel filter/water
separator element.
²Change MTX fluid
EVERY 5 000 KM AFTER 100 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
EVERY 10 000 KM AFTER 100 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
EVERY 20 000 KM AFTER 100 000 KM
²Diesel engines onlyÐReplace fuel filter/water
separator element.
EVERY 35 000 KM AFTER 100 000 KM
²Change MTX fluid
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 35 of 1938
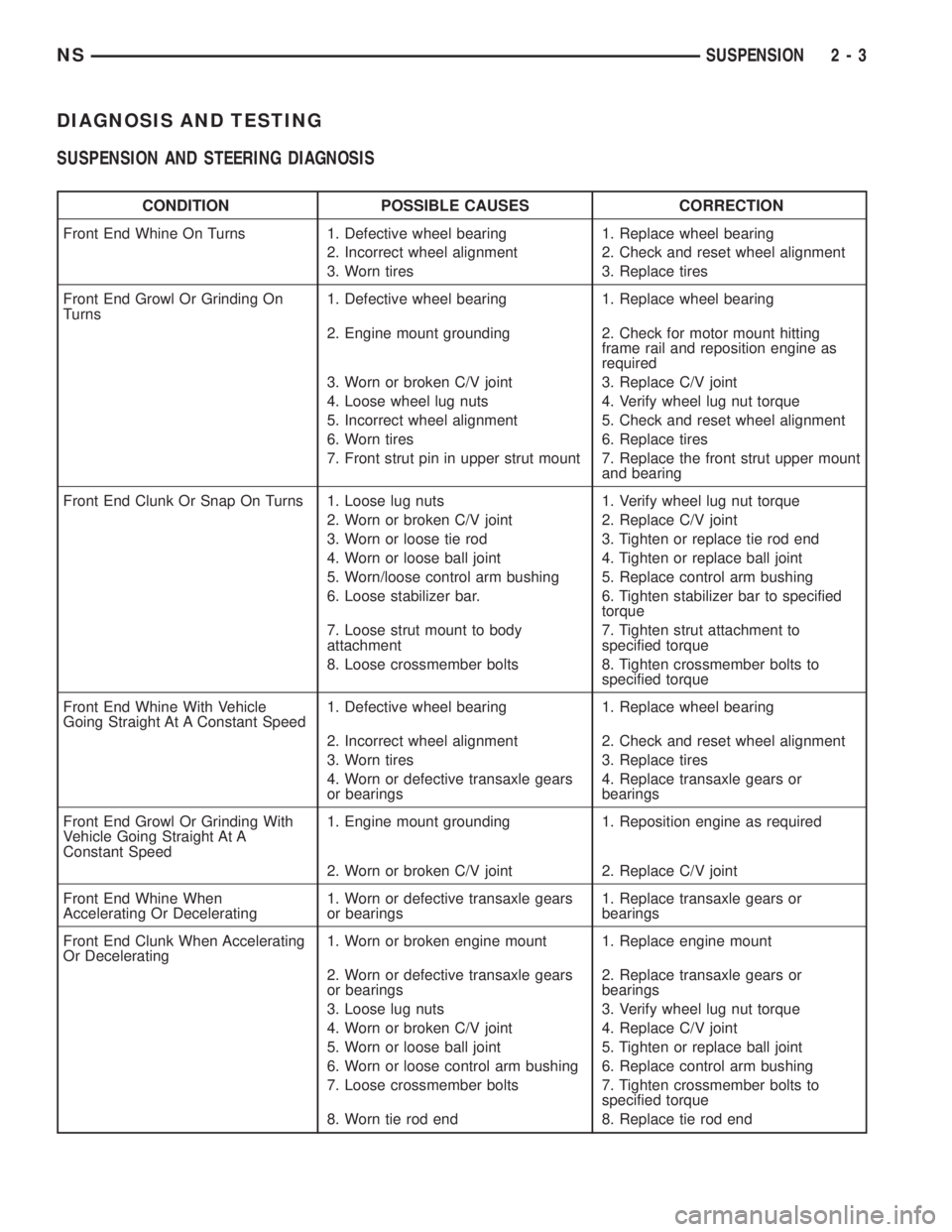
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SUSPENSION AND STEERING DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Front End Whine On Turns 1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
Front End Growl Or Grinding On
Turns1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Engine mount grounding 2. Check for motor mount hitting
frame rail and reposition engine as
required
3. Worn or broken C/V joint 3. Replace C/V joint
4. Loose wheel lug nuts 4. Verify wheel lug nut torque
5. Incorrect wheel alignment 5. Check and reset wheel alignment
6. Worn tires 6. Replace tires
7. Front strut pin in upper strut mount 7. Replace the front strut upper mount
and bearing
Front End Clunk Or Snap On Turns 1. Loose lug nuts 1. Verify wheel lug nut torque
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
3. Worn or loose tie rod 3. Tighten or replace tie rod end
4. Worn or loose ball joint 4. Tighten or replace ball joint
5. Worn/loose control arm bushing 5. Replace control arm bushing
6. Loose stabilizer bar. 6. Tighten stabilizer bar to specified
torque
7. Loose strut mount to body
attachment7. Tighten strut attachment to
specified torque
8. Loose crossmember bolts 8. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
Front End Whine With Vehicle
Going Straight At A Constant Speed1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
4. Worn or defective transaxle gears
or bearings4. Replace transaxle gears or
bearings
Front End Growl Or Grinding With
Vehicle Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Engine mount grounding 1. Reposition engine as required
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
Front End Whine When
Accelerating Or Decelerating1. Worn or defective transaxle gears
or bearings1. Replace transaxle gears or
bearings
Front End Clunk When Accelerating
Or Decelerating1. Worn or broken engine mount 1. Replace engine mount
2. Worn or defective transaxle gears
or bearings2. Replace transaxle gears or
bearings
3. Loose lug nuts 3. Verify wheel lug nut torque
4. Worn or broken C/V joint 4. Replace C/V joint
5. Worn or loose ball joint 5. Tighten or replace ball joint
6. Worn or loose control arm bushing 6. Replace control arm bushing
7. Loose crossmember bolts 7. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
8. Worn tie rod end 8. Replace tie rod end
NSSUSPENSION 2 - 3
Page 85 of 1938

BASE BRAKE SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CHASSIS TUBES AND HOSES.............. 7
FRONT DISC BRAKE SYSTEM.............. 4
HUB/BEARING REAR WHEEL............... 9
MASTER CYLINDER...................... 7
PARKING BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION....... 5
POWER BRAKE VACUUM BOOSTER
OPERATION........................... 8
PROPORTIONING VALVES................. 5
REAR DISC BRAKES...................... 5
REAR DRUM BRAKES..................... 5
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP OPERATION..... 8
STOP LAMP SWITCH...................... 9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ADJUSTER REAR DRUM BRAKE
(AUTOMATIC)......................... 14
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION............ 19
BRAKE ROTOR......................... 14
BRAKE SYSTEM BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE.... 9
BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS....... 10
PROPORTIONING VALVES................ 16
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP TEST......... 19
STOP LAMP SWITCH TEST PROCEDURE..... 19
TRACTION CONTROL LAMP TEST.......... 19
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BLEEDING BASE BRAKE
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM................... 20
BRAKE DRUM MACHINING................ 24
BRAKE TUBE REPAIR PROCEDURE......... 24
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING
PROCEDURE......................... 22
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL CHECK.... 20
PARK BRAKE AUTO ADJUSTER
MECHANISM RELEASE................. 26
ROTOR MACHINING (FRONT/REAR)......... 22
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BRAKE SUPPORT PLATE (REAR DRUM
BRAKES)............................ 37
FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER............. 27
FRONT DISC BRAKE PADS................ 30
FRONT PARK BRAKE CABLE.............. 65
HUB/BEARING.......................... 40
HYDRAULIC BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES..... 58
INTERMEDIATE PARK BRAKE CABLE....... 66
JUNCTION BLOCK....................... 55
LEFT REAR PARK BRAKE CABLE........... 67
MASTER CYLINDER..................... 44
PARK BRAKE PEDAL MECHANISM.......... 58PARK BRAKE SHOES (WITH REAR DISC
BRAKES)............................ 60
PROPORTIONING VALVE (W/ABS BRAKES) . . . 56
PROPORTIONING VALVE
(W/O ABS BRAKES).................... 57
REAR BRAKE DRUM..................... 33
REAR BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER........... 39
REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER.............. 28
REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES................ 31
REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOES............... 34
RIGHT REAR PARK BRAKE CABLE......... 66
STOP LAMP SWITCH..................... 69
VACUUM BOOSTER 2.4 LITER ENGINE...... 47
VACUUM BOOSTER 3.0 LITER ENGINE...... 49
VACUUM BOOSTER 3.3/3.8 LITER ENGINE.... 52
WHEEL AND TIRE INSTALLATION........... 27
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER............. 71
MASTER CYLINDER BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
SWITCH............................. 71
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID RESERVOIR
FILL TUBE............................ 71
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID RESERVOIR...... 70
MASTER CYLINDER TO POWER BRAKE
BOOSTER VACUUM SEAL............... 69
WHEEL CYLINDER REAR DRUM BRAKE...... 76
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
BRAKE HOSE AND BRAKE LINES
INSPECTION.......................... 78
FRONT DISC BRAKE PAD LINING
INSPECTION.......................... 76
REAR DISC BRAKES..................... 76
REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOE LINING
INSPECTION.......................... 77
REAR DRUM BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER...... 78
REAR WHEEL HUB AND BEARING
ASSEMBLY........................... 78
ADJUSTMENTS
PARK BRAKE CABLE ADJUSTMENT......... 81
PARK BRAKE SHOES (WITH REAR DISC
BRAKES)............................ 79
PROPORTIONING VALVE
(HEIGHT SENSING).................... 81
REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOE ADJUSTMENT.... 79
STOP LAMP SWITCH..................... 78
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE ACTUATION SYSTEM.............. 83
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS...................... 83
NSBRAKES 5 - 3
Page 90 of 1938

brakes. The secondary outlet port supplies hydraulic
pressure to the left front and right rear brakes.
POWER BRAKE VACUUM BOOSTER OPERATION
All vehicles use a 270 mm single diaphragm power
brake vacuum booster.
The power brake booster can be identified if
required, by the tag attached to the body of the
booster assembly (Fig. 10). This tag contains the fol-
lowing information: The production part number of
the power booster assembly, the date it was built,
and who was the manufacturer of the power brake
vacuum booster.
NOTE: The power brake booster assembly is not a
repairable component and must be replaced as a
complete assembly if it is found to be faulty in any
way. The check valve located in the power brake
booster (Fig. 10) is not repairable but it can be
replaced as an assembly separate from the power
brake booster.
The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through the power brake booster check valve
(Fig. 10) and (Fig. 11).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power brake
boosters input rod moves forward (Fig. 11). This
opens and closes valves in the power booster, allow-
ing atmospheric pressure to enter on one side of a
diaphragm. Engine vacuum is always present on the
other side. This difference in pressure forces the out-
put rod of the power booster (Fig. 11) out against the
primary piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons
in the master cylinder move forward this creates the
hydraulic pressure in the brake system.The different engine combinations used on this
vehicle require that different vacuum hose routings
to the power brake vacuum booster be used.
All vacuum hoses must be routed from the engine
to the power brake vacuum booster without kinks,
excessively tight bends or potential for damage to the
vacuum hose.
The power brake vacuum booster assembly mounts
on the engine side of the dash panel, and is con-
nected to the brake pedal by the input push rod (Fig.
11). A vacuum line connects the power booster to the
intake manifold. The master cylinder is bolted to the
front of the power brake vacuum booster assembly.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP OPERATION
The red Brake warning lamp is located in the
instrument panel cluster and is used to indicate a
low brake fluid condition or that the parking brake is
applied. In addition, the brake warning lamp is
turned on as a bulb check by the ignition switch
every time the ignition switch is turned to the crank
position.
The warning lamp bulb is supplied a 12 volt igni-
tion feed anytime the ignition switch is on. The bulb
is then illuminated by completing the ground circuit
either through the park brake switch, the fluid level
sensor in the master cylinder reservoir, or the igni-
tion switch when it is turned to the crank position.
The Brake Fluid Level sensor is located in the
brake fluid reservoir of the master cylinder assembly.
The purpose of the sensor is to provide the driver
with an early warning that brake fluid level in the
master cylinder fluid reservoir has dropped to below
Fig. 10 Power Brake Booster Identification
Fig. 11 Power Brake Booster Assembly
5 - 8 BRAKESNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 91 of 1938

normal. This may indicate:(1)Abnormal loss of
brake fluid in the master cylinder fluid reservoir
resulting from a leak in the hydraulic system.(2)
Brake shoe linings which have worn to a point
requiring replacement.
As the brake fluid drops below the minimum level,
the brake fluid level sensor closes to ground the
brake warning light circuit. This will turn on the red
brake warning light. At this time, master cylinder
fluid reservoir should be checked and filled to the full
mark with DOT 3 brake fluid.If brake fluid level
has dropped below the add line in the master
cylinder fluid reservoir, the entire brake
hydraulic system should be checked for evi-
dence of a leak.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
The stop lamp switch controls operation of the
vehicles stop lamps. Also, if the vehicle is equippedwith speed control, the stop lamp switch will deacti-
vate speed control when the brake pedal is
depressed.
The stop lamp switch controls operation of the
right and left tail, stop and turn signal lamp and
CHMSL lamp, by supplying battery current to these
lamps.
The stop lamp switch controls the lamp operation
by opening and closing the electrical circuit to the
stop lamps.
HUB/BEARING REAR WHEEL
The rear hub and bearing assembly used on this
vehicle is serviceable only as a complete assembly. No
attempt should be made to disassemble a rear hub
and bearing assembly in an effort to repair it.
The rear hub and bearing assembly is attached to
the rear axle using 4 mounting bolts that are remov-
able from the back of the rear hub/bearing.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BRAKE SYSTEM BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
SYMPTOMCHART 1
MISC.
COND.CHART 2
WARNING
LIGHTCHART 3
POWER
BRAKESCHART 4
BRAKE
NOISECHART 5
WHEEL
BRAKES
Brake Warning Light On X NO NO
Excessive Pedal Travel 6 X NO O
Pedal Goes To The Floor 6 X
Stop Light On Without Brakes 3
All Brakes Drag 5
Rear Brakes Drag 2 NO NO
Grabby Brakes O X
Spongy Brake Pedal X NO
Premature Rear Brake Lockup 4 NO NO O
Excessive Pedal Effort 1 O
Rough Engine Idle NO O
Brake Chatter (Rough) NO NO X
Surge During Braking NO NO X
Noise During Braking NO NO X
Rattle Or Clunking Noise NO NO X
Pedal Pulsates During Braking NO NO X
Pull To Right Or Left NO NO X
No: Not A Possible Cause X: Most Likely Cause O: Possible Cause
NSBRAKES 5 - 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 102 of 1938

SERVICE PROCEDURES
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Master cylinder reservoirs are marked with the
words FULL and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid
fill level of the master cylinder (Fig. 26).
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.When filling master
cylinder fluid reservoir do not fill the filler
neck of the fluid reservoir (Fig. 26) with brake
fluid.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or an equivalent from
a sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT
3, specifications.
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid ect.
BLEEDING BASE BRAKE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
NOTE: This bleeding procedure is only for the vehi-
cle's base brakes hydraulic system. For bleeding
the antilock brakes hydraulic system, refer to the
ITT Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake System bleeding
procedure in the antilock brakes section of this ser-
vice manual.
PRESSURE BLEEDING PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
cover, throughly clean the cover and master cylin-
der fluid reservoir to prevent dirt and other foreign
matter from dropping into the master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
CAUTION: Use bleeder tank Special Tool C-3496-B
with adapter Special Tool 6921 to pressurize the
hydraulic system for bleeding.
CAUTION: When pressure bleeding the brakes
hydraulic system the fluid reservoir filler neck must
be removed from the master cylinder fluid reservoir.
Failure to remove the filler neck from the fluid res-
ervoir, may result in the filler neck separating from
the fluid reservoir when the hydraulic system is
pressurized.
Follow pressure bleeder manufacturer's instruc-
tions, for use of pressure bleeding equipment.
When bleeding the brake system, some air may be
trapped in the brake lines or valves far upstream, as
much as ten feet from the bleeder screw (Fig. 27).
Therefore, it is essential to have a fast flow of a large
volume of brake fluid when bleeding the brakes to
ensure all the air gets out.
(1) Remove the filler neck from the master cylin-
der fluid reservoir.
(2) Install the Adapter Master Cylinder Pressure
Bleed Cap, Special Tool 6921 on the fluid reservoir of
the master cylinder (Fig. 28). Attach the fluid hose
from the pressure bleeder to the fitting on Special
Tool 6921.
(3) Attach a clear plastic hose to the bleeder screw
at one wheel and feed the hose into a clear jar con-
taining fresh brake fluid.
Fig. 26 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Marks
Fig. 27 Trapped Air In Brake Fluid Line
5 - 20 BRAKESNS
Page 131 of 1938

(7) Install aNEWvacuum seal on mounting flange
of master cylinder (Fig. 110).
(8) Position master cylinder on studs of vacuum
booster aligning push rod on vacuum booster with
master cylinder piston.
(9) Install the 2 nuts (Fig. 107) mounting the mas-
ter cylinder to the vacuum booster. Tighten the
mounting nuts to a torque of 25 N´m (225 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the wiper module drain hose (Fig. 107)
on the wiper module. Install the tie strap attaching
the wiper module drain hose to the brake tube at the
master cylinder.Tie strap should be loosely tight-
ened so as not to collapse the wiper module
drain hose.
(11) Install the wiring harness connector on the
brake fluid level sensor in the master cylinder fluid
reservoir (Fig. 106).
(12) Install the battery tray in the vehicle. Install
the 2 bolts and the nut (Fig. 105) attaching the bat-
tery tray. Tighten the 2 bolts and the nut to a torque
of 14 N´m (125 in lbs.).(13) If vehicle is equipped with speed control,
install the speed control servo and bracket on the
battery tray. Install and securely tighten bolt attach-
ing bracket to battery tray.
(14) If vehicle is equipped with speed control,
install the wiring harness connector on the speed
control servo. Then connect the vacuum lines onto
the speed control servo and vacuum reservoir on bat-
tery tray.
(15) Install the air inlet resonator and hoses as an
assembly on the throttle body and air cleaner hous-
ing (Fig. 104). Securely tighten the hose clamp at the
air cleaner housing and throttle body.
(16) Install the battery and the battery thermal
guard.
(17) Install the battery cables on the battery.
(18) Check the operation of the stop lamp switch
and adjust if necessary.
VACUUM BOOSTER 3.0 LITER ENGINE
REMOVE
CAUTION: Stored vacuum in the vacuum booster
must be pumped down (removed) before removing
master cylinder from power brake booster. This is
necessary to prevent the power brake booster from
sucking in any contamination as the master cylin-
der is removed. This can be done simply by pump-
ing the brake pedal, with the vehicle's engine not
running, until a firm feeling brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With engine not running, pump the brake
pedal until a firm pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Remove both battery cables from battery.
(3) Remove the battery thermal guard and the bat-
tery from the battery tray.
(4) Remove the air inlet resonator and hoses as an
assembly from the throttle body and air cleaner
housing (Fig. 111)
(5) If vehicle is equipped with speed control,
unplug wiring harness connector from the speed con-
trol servo. Then disconnect vacuum lines from the
speed control servo and vacuum reservoir on battery
tray.
(6) Remove bolt attaching the speed control servo
bracket to the battery tray. Slide the bracket forward
to unhook it from the battery tray and remove.
(7) Remove the 2 bolts and the nut (Fig. 112)
attaching the battery tray to the body of the vehicle.
(8) Remove wiring harness connector from brake
fluid level sensor in master cylinder fluid reservoir
(Fig. 113).
(9) Clean the area where the master cylinder
assembly attaches to the power brake booster. Use
only a solvent such as Mopar Brake Parts Cleaner or
an equivalent.
Fig. 109 Retaining Clip Installed On Brake Pedal Pin
Fig. 110 Vacuum Seal Installed On Master Cylinder
NSBRAKES 5 - 49
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 134 of 1938

(11) Install the wiring harness connector on the
brake fluid level sensor in the master cylinder fluid
reservoir (Fig. 113).
(12) Install the battery tray in the vehicle. Install
the 2 bolts and the nut (Fig. 112) attaching the bat-
tery tray to the vehicle. Tighten the 2 bolts and the
nut to a torque of 14 N´m (125 in lbs.).
(13) If vehicle is equipped with speed control,
install the speed control servo and bracket on the
battery tray. Install and securely tighten bolt attach-
ing bracket to battery tray.
(14) If vehicle is equipped with speed control,
install the wiring harness connector on the speed
control servo. Then connect the vacuum lines onto
the speed control servo and vacuum reservoir on bat-
tery tray.
(15) Install the air inlet resonator and hoses as an
assembly on the throttle body and air cleaner hous-
ing (Fig. 111). Securely tighten the hose clamp at the
air cleaner housing and throttle body.
(16) Install the battery and the battery thermal
guard.
(17) Install the battery cables on the battery.
(18) Check the operation of the stop lamp switch
and adjust if necessary.
VACUUM BOOSTER 3.3/3.8 LITER ENGINE
REMOVE
CAUTION: Reserve vacuum in the vacuum booster
must be pumped down (removed) before removing
master cylinder from vacuum booster. This is nec-
essary to prevent the vacuum booster from sucking
in any contamination as the master cylinder is
removed. This can be done simply by pumping the
brake pedal, with the vehicle's engine not running,
until a firm feeling brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With engine not running, pump the brake
pedal until a firm pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Remove both battery cables from battery.
(3) Remove the battery thermal guard and the bat-
tery from the battery tray.
(4) Remove the air inlet resonator and hoses as an
assembly from the throttle body and air cleaner
housing (Fig. 118)
(5) If vehicle is equipped with speed control,
unplug wiring harness connector from the speed con-
trol servo. Then disconnect vacuum lines from the
speed control servo and vacuum reservoir on battery
tray.
(6) Remove bolt attaching the speed control servo
bracket to the battery tray. Slide the bracket forward
to unhook it from the battery tray and remove.
(7) Remove the 2 bolts and the nut (Fig. 119)
attaching the battery tray to the body of the vehicle.(8) Remove the wiring harness connector (Fig. 120)
from the EGR valve transducer.
(9) Remove wiring harness connectors from throt-
tle position sensor and AIS motor on throttle body
(Fig. 121).
(10) Remove the 2 bolts (Fig. 122) attaching the
throttle body to the intake manifold and the clip (Fig.
122) attaching the wiring harness to the throttle
cable bracket. Then remove the throttle body and
throttle cable bracket as an assembly from the intake
manifold.
(11) Remove wiring harness connector from brake
fluid level sensor in master cylinder fluid reservoir
(Fig. 123).
(12) Clean the area where the master cylinder
assembly attaches to the power brake booster. Use
Fig. 118 Air Inlet Resonator
Fig. 119 Battery Tray Mounting Locations
5 - 52 BRAKESNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 160 of 1938

REAR DRUM BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER
With brake drums removed, inspect the wheel cyl-
inder boots for evidence of a brake fluid leak. Visu-
ally check the boots for cuts, tears, or heat cracks. If
any of these conditions exist, the wheel cylinders
should be completely cleaned, inspected and new
parts installed.
If a wheel cylinder is leaking and the brake lining
material is saturated with brake fluid, the brake
shoes must be replaced.
BRAKE HOSE AND BRAKE LINES INSPECTION
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses
should be performed whenever the brake system is
serviced and every 7,500 miles or 12 months, which-
ever comes first (every engine oil change). Inspect
hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing,
or worn spots. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose
becomes exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the
rubber hose cover, the hose should be replaced imme-
diately. Eventual deterioration of the hose can take
place with possible burst failure. Faulty installation
can cause twisting, resulting in wheel, tire, or chassis
interference.
The steel brake tubing should be inspected period-
ically for evidence of physical damage or contact with
moving or hot components.
The flexible brake tube sections used on this vehi-
cle in the primary and secondary tubes from the
master cylinder to the ABS hydraulic control unit
connections and the chassis brake tubes between the
hydraulic control unit and the proportioning valve
must also be inspected. This flexible tubing must be
inspected for kinks, fraying and its contact with
other components of the vehicle or contact with the
body of the vehicle.
REAR WHEEL HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
The rear hub and bearing assembly is designed for
the life of the vehicle and should require no mainte-
nance. The following procedure may be used for eval-
uation of bearing condition.
With wheel and brake drum removed, rotate
flanged outer ring of hub. Excessive roughness, lat-
eral play or resistance to rotation may indicate dirt
intrusion or bearing failure. If the rear wheel bear-
ings exhibit these conditions during inspection, the
hub and bearing assembly should be replaced.
Damaged bearing seals and resulting excessive
grease loss may also require bearing replacement.
Moderate grease loss from bearing is considered nor-
mal and should not require replacement of the hub
and bearing assembly.
ADJUSTMENTS
STOP LAMP SWITCH
(1) Remove stop lamp switch from its bracket by
rotating it approximately 30É in a counter-clockwise
direction.
(2) Disconnect wiring harness connector from stop
lamp switch.
(3) Hold stop lamp switch firmly in one hand.
Then using other hand, pull outward on the plunger
of the stop lamp switch until it has ratcheted out to
its fully extended position.
(4) Install the stop lamp switch into the bracket
using the following procedure. Depress the brake
pedal as far down as possible. Then while keeping
the brake pedal depressed, install the stop lamp
switch into the bracket by aligning index key on
switch with slot at top of square hole in mounting
bracket. When switch is fully installed in the square
hole of the bracket, rotate switch clockwise approxi-
mately 30É to lock the switch into the bracket.
CAUTION: Do not use excessive force when pulling
back on brake pedal to adjust the stop lamp switch.
If too much force is used, damage to the vacuum
booster, stop lamp switch or striker (Fig. 195) can
result.
(5) Connect the wiring harness connector to the
stop lamp switch.
(6) Gently pull back on brake pedal until the pedal
stops moving. This will cause the switch plunger
(Fig. 195) to ratchet backward to the correct position.
Fig. 195 Stop Light Switch Location In Vehicle
5 - 78 BRAKESNS
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 171 of 1938
fluid accumulators temporarily store brake fluid that
is decayed from the wheel brakes during an ABS
cycle. This stored brake fluid is then used by the
pump in the HCU to provide build pressure for the
brake hydraulic system.
Additionally on vehicles that are equipped with
only ABS (non-traction control vehicles) there is a
mini brake fluid accumulator on the secondary
hydraulic circuit which protects the master cylinder's
seals during an ABS stop. There is also a noise
damping chamber on the primary hydraulic circuit.
On ABS equipped vehicles with traction control, in
addition to the brake fluid accumulators there are
also two noise damping chambers in the HCU.
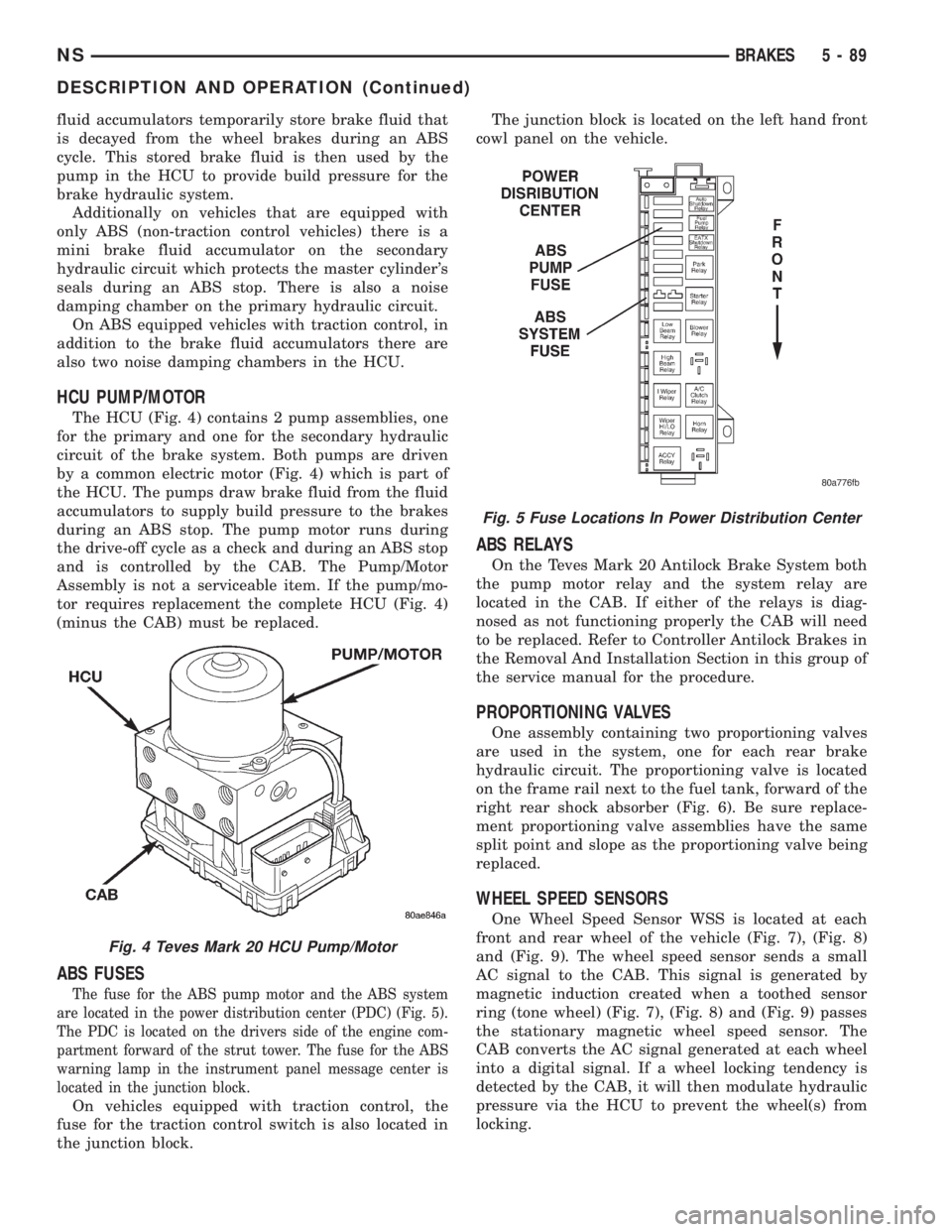
HCU PUMP/MOTOR
The HCU (Fig. 4) contains 2 pump assemblies, one
for the primary and one for the secondary hydraulic
circuit of the brake system. Both pumps are driven
by a common electric motor (Fig. 4) which is part of
the HCU. The pumps draw brake fluid from the fluid
accumulators to supply build pressure to the brakes
during an ABS stop. The pump motor runs during
the drive-off cycle as a check and during an ABS stop
and is controlled by the CAB. The Pump/Motor
Assembly is not a serviceable item. If the pump/mo-
tor requires replacement the complete HCU (Fig. 4)
(minus the CAB) must be replaced.
ABS FUSES
The fuse for the ABS pump motor and the ABS system
are located in the power distribution center (PDC) (Fig. 5).
The PDC is located on the drivers side of the engine com-
partment forward of the strut tower. The fuse for the ABS
warning lamp in the instrument panel message center is
located in the junction block.
On vehicles equipped with traction control, the
fuse for the traction control switch is also located in
the junction block.The junction block is located on the left hand front
cowl panel on the vehicle.
ABS RELAYS
On the Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake System both
the pump motor relay and the system relay are
located in the CAB. If either of the relays is diag-
nosed as not functioning properly the CAB will need
to be replaced. Refer to Controller Antilock Brakes in
the Removal And Installation Section in this group of
the service manual for the procedure.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
One assembly containing two proportioning valves
are used in the system, one for each rear brake
hydraulic circuit. The proportioning valve is located
on the frame rail next to the fuel tank, forward of the
right rear shock absorber (Fig. 6). Be sure replace-
ment proportioning valve assemblies have the same
split point and slope as the proportioning valve being
replaced.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
One Wheel Speed Sensor WSS is located at each
front and rear wheel of the vehicle (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8)
and (Fig. 9). The wheel speed sensor sends a small
AC signal to the CAB. This signal is generated by
magnetic induction created when a toothed sensor
ring (tone wheel) (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8) and (Fig. 9) passes
the stationary magnetic wheel speed sensor. The
CAB converts the AC signal generated at each wheel
into a digital signal. If a wheel locking tendency is
detected by the CAB, it will then modulate hydraulic
pressure via the HCU to prevent the wheel(s) from
locking.
Fig. 4 Teves Mark 20 HCU Pump/Motor
Fig. 5 Fuse Locations In Power Distribution Center
NSBRAKES 5 - 89
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)