torque DATSUN B110 1973 Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 367 of 513

ENGINE
MECHANICAL
3
Apply
engine
oil
to
the
main
bearing
surfaces
on
both
sides
of
the
cylinder
block
and
cap
Install
the
crankshaft
4
Install
the
main
bearing
cap
and
tighten
the
bolts
with
specified
torque
Tightening
torque
5
0
to
6
0
kg
m
36
to
43
ft
lb
Notes
a
Arrange
the
parts
so
that
the
arrow
mark
on
the
bearing
cap
is
faced
toward
the
front
of
the
engine
b
Prior
to
tightening
the
bearing
cap
bolts
place
the
bearing
cap
at
a
proper
position
by
shifting
the
crankshaft
in
the
axial
direction
c
Tighten
the
bearing
cap
bolts
gradually
in
separating
two
to
three
stages
and
outwardly
from
the
center
beari
ng
d
After
securing
the
bearing
cap
bolts
ascertain
that
the
crankshaft
can
be
easily
rotated
5
Make
sure
that
the
crankshaft
end
play
is
correct
Crankshaft
end
play
0
05
to
0
15
rom
0
0020
to
0
0059
in
Fig
EM
73
Crankshaft
end
play
check
EM
27
Fig
EM
73
t
Applying
adhesive
6
Install
the
rear
oil
seal
7
Install
the
flywheel
securely
using
the
lock
washers
and
tighten
the
bolts
with
specified
torque
Tightening
torque
6
5
to
7
5
kg
m
47
to
54
ft
lb
Iii
Fig
EM
74
Flywheel
installation
8
Rotate
the
engine
a
quarter
turn
and
install
the
piston
rod
assembly
Page 368 of 513
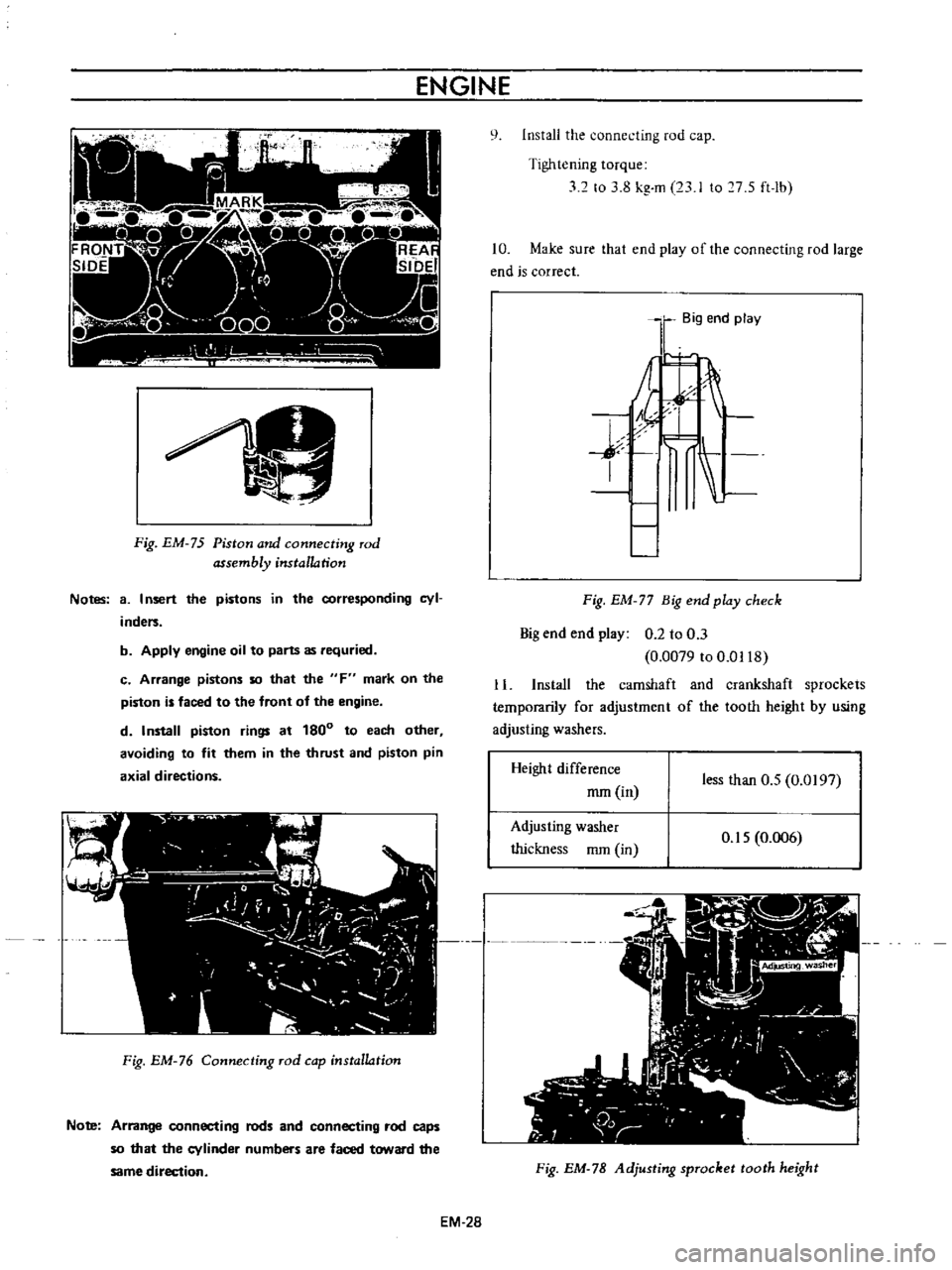
ENGINE
Fig
EM
75
Piston
and
connecting
rod
assembly
installation
Notes
8
I
nsert
the
pistons
in
the
corresponding
cyl
inders
b
Apply
engine
oil
to
parts
as
requried
c
Arrange
pistons
so
that
the
F
mark
on
the
piston
is
faced
to
the
front
of
the
engine
d
Install
piston
rings
at
180
to
each
other
avoiding
to
fit
them
in
the
thrust
and
piston
pin
axial
directions
Fig
EM
76
Connecting
rod
cap
installation
Note
Arrange
connecting
rods
and
connecting
rod
caps
so
that
the
cylinder
numbers
are
faced
toward
the
same
direction
EM
28
q
Install
the
connecting
rod
cap
Tightening
torque
32
to
3
8
kg
m
23
I
to
7
S
ft
lb
10
Make
sure
that
end
play
of
the
connecting
rod
large
end
is
correct
Big
end
play
j
I
Fig
EM
77
Big
end
play
check
Big
end
end
play
0
2
to
0
3
0
0079
to
0
0118
11
Install
the
camshaft
and
crankshaft
sprockets
temporarily
for
adjustment
of
the
tooth
height
by
using
adjusting
washers
Height
difference
mm
in
less
than
O
S
0
0197
Adjusting
washer
thickness
mm
in
O
IS
0
006
Fig
EM
78
Adjusting
sprocket
tooth
height
Page 369 of 513
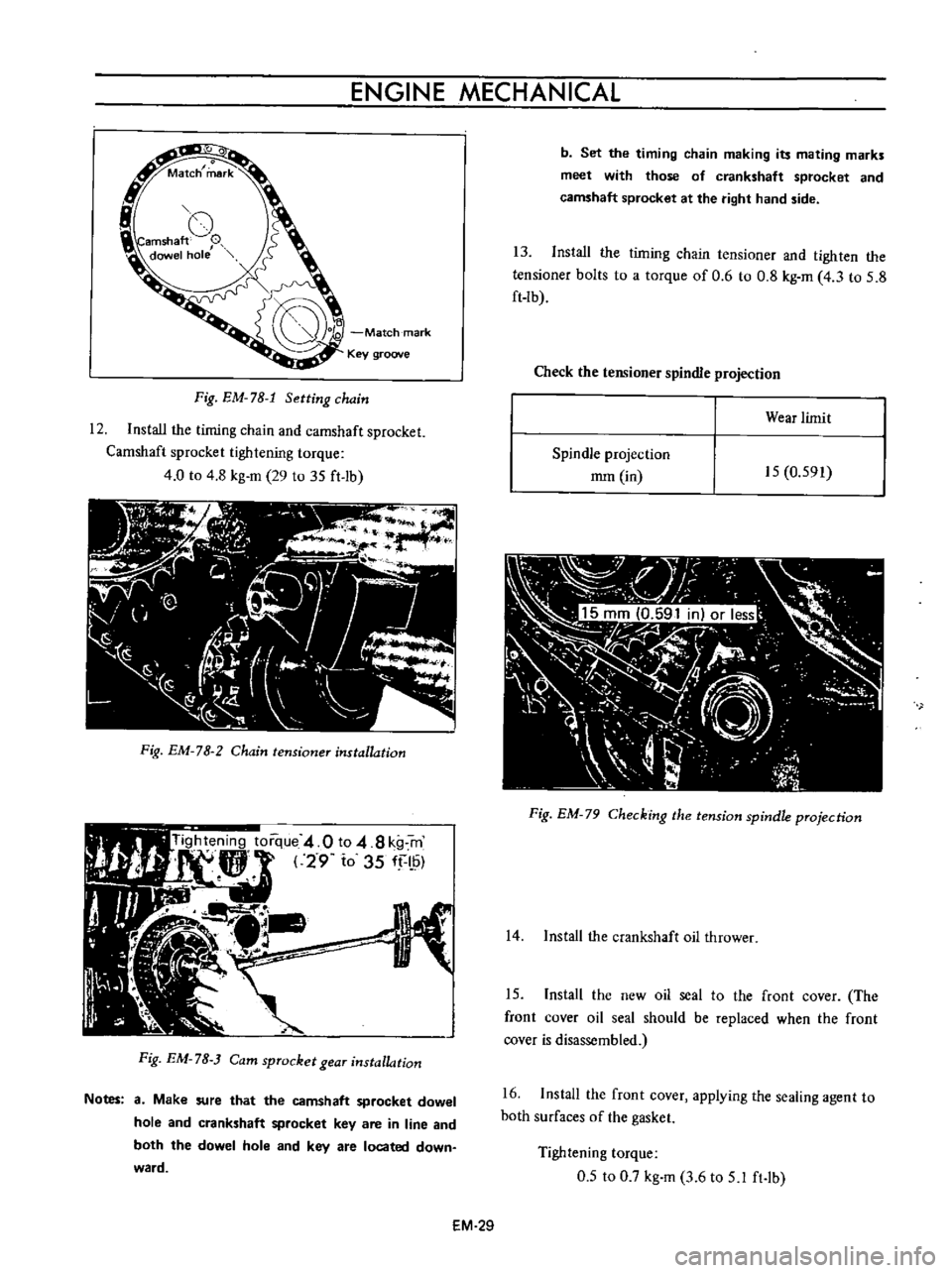
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
o
Match
mark
Key
groove
Fig
EM
78
1
Setting
chain
12
Install
the
timing
chain
and
camshaft
sprocket
Camshaft
sprocket
tightening
torque
4
0
to
4
8
kg
m
29
to
35
ft
lb
Fig
EM
78
2
Chain
tensioner
installation
Fig
EM
7B
Cam
sprocket
gear
installation
Notes
a
Make
sure
that
the
camshaft
sprocket
dowel
hole
and
crankshaft
sprocket
key
are
in
line
and
both
the
dowel
hole
and
key
are
located
down
ward
b
Set
the
timing
chain
making
its
mating
marks
meet
with
those
of
crankshaft
sprocket
and
camshaft
sprocket
at
the
right
hand
side
13
Install
the
timing
chain
tensioner
and
tighten
the
tensioner
bolts
to
a
torque
of
0
6
to
0
8
kg
m
4
3
to
5
8
ft
lb
Check
the
tensioner
spindle
projection
Wear
limit
Spindle
projection
mm
in
15
0
591
Fig
EM
79
Checking
the
tension
spindle
projection
14
Install
the
crankshaft
oil
thrower
15
Install
the
new
oil
seal
to
the
front
cover
The
front
cover
oil
seal
should
be
replaced
when
the
front
cover
is
disassembled
16
Install
the
front
cover
applying
the
sealing
agent
to
both
surfaces
of
the
gasket
Tightening
torque
0
5
to
0
7
kg
m
3
6
to
5
1
ft
lb
EM
29
Page 370 of 513
ENGINE
17
Install
the
oil
strainer
and
the
oil
pan
using
the
gasket
Apply
sealing
agent
on
hath
surfaces
of
the
gasket
especially
on
the
front
and
rear
portions
of
the
oil
pan
Oil
pan
tightening
torque
0
4
to
0
6
kg
m
I
9
to
4
3
ft
lbJ
I
R
I
nvcrt
the
engine
and
install
the
cylinder
head
assembly
and
gasket
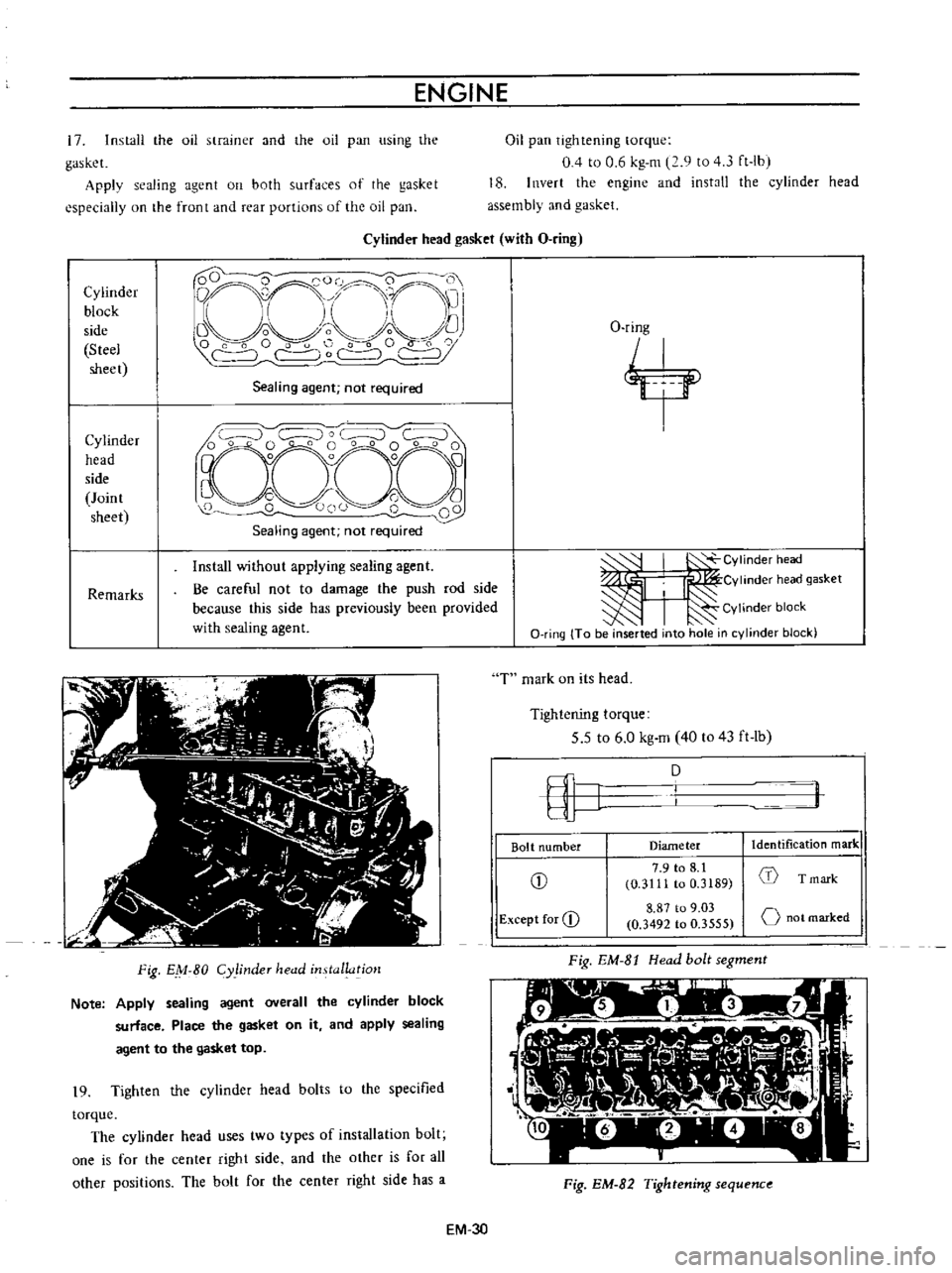
Cylinder
head
gasket
with
O
ring
Cylinder
block
side
Steel
sheet
D
QCO
0
0
i
O
1
nrr
11
I
Li
I
I
Vo
o
f
C
C
r
c
Sealing
agent
not
required
Cylinder
head
side
Joint
sheet
Remarks
Install
without
applying
sealing
agent
Be
careful
not
to
damage
the
push
rod
side
because
this
side
has
previously
been
provided
with
sealing
agent
Fig
EM
80
Cy
linder
head
installatjo
1
Note
Apply
sealing
agent
overall
the
cylinder
block
surface
Place
the
gasket
on
it
and
apply
sealing
agent
to
the
gasket
top
19
Tighten
the
cylinder
head
bolts
to
the
specified
torque
The
cylinder
head
uses
two
types
of
installation
bolt
one
is
for
the
center
right
side
and
the
other
is
for
all
other
positions
The
bolt
for
the
center
right
side
has
a
O
ring
j
I
Y
J
CYlinder
head
I
I
Cvlinderheadgasket
I
Cylinder
block
O
ring
To
be
inserted
into
hole
in
cylinder
block
T
mark
on
its
head
Tightening
torque
5
5
to
6
0
kg
m
40
to
43
ft
lb
fI
J
D
Bolt
number
Diameter
Identification
mark
CD
7
9
to
8
1
1
0
3111
to
0
3189
T
mark
Except
for
CD
8
87
to
9
03
o
not
marked
0
3492
to
0
3555
Fig
EM
8t
Head
bolt
segment
l
Fig
EM
82
Tightening
sequenc
EM
3D
Page 371 of 513
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
20
Install
the
push
rods
21
Install
the
rocker
shaft
assembly
and
tighten
the
rocker
shaft
bracket
bolts
to
the
specified
torque
Tightening
torque
2
0
to
2
5
kg
m
15
to
18
ft
Ib
Note
Tightening
operation
should
be
made
gradually
in
separating
two
or
three
stages
and
outwardly
from
the
center
bracket
Fig
EM
B
RockeT
shaft
installation
22
Install
the
intake
and
exhaust
manifolds
Tightening
torque
0
9
to
I
4
kg
m
6
5
to
10
ft
lb
Fig
EM
B4
Installation
of
intake
and
exhaust
manifolds
23
Adjust
valve
clearance
with
the
specified
di
mensions
Fig
EM
85
Valve
clearance
adjustment
Intake
at
cold
rom
in
0
35
0
0138
Exhaust
at
cold
rom
in
0
35
0
0138
24
Install
the
rocker
cover
and
carburetor
assembly
25
Install
the
water
pump
and
thermostat
Tightening
torque
0
9
to
I
4
kg
m
6
5
to
10
ft
lb
26
Install
the
crankshaft
pulley
Tighten
the
crank
pulley
bolt
to
the
specified
torque
Tightening
torque
15
to
16
kg
m
109
to
116
ft
lb
Tightening
tOI
q
e
15
JP
16
g
m
10l
to
11
ft
Ib
Fig
EM
B6
CTankshaft
pulky
installation
EM
31
Page 373 of 513
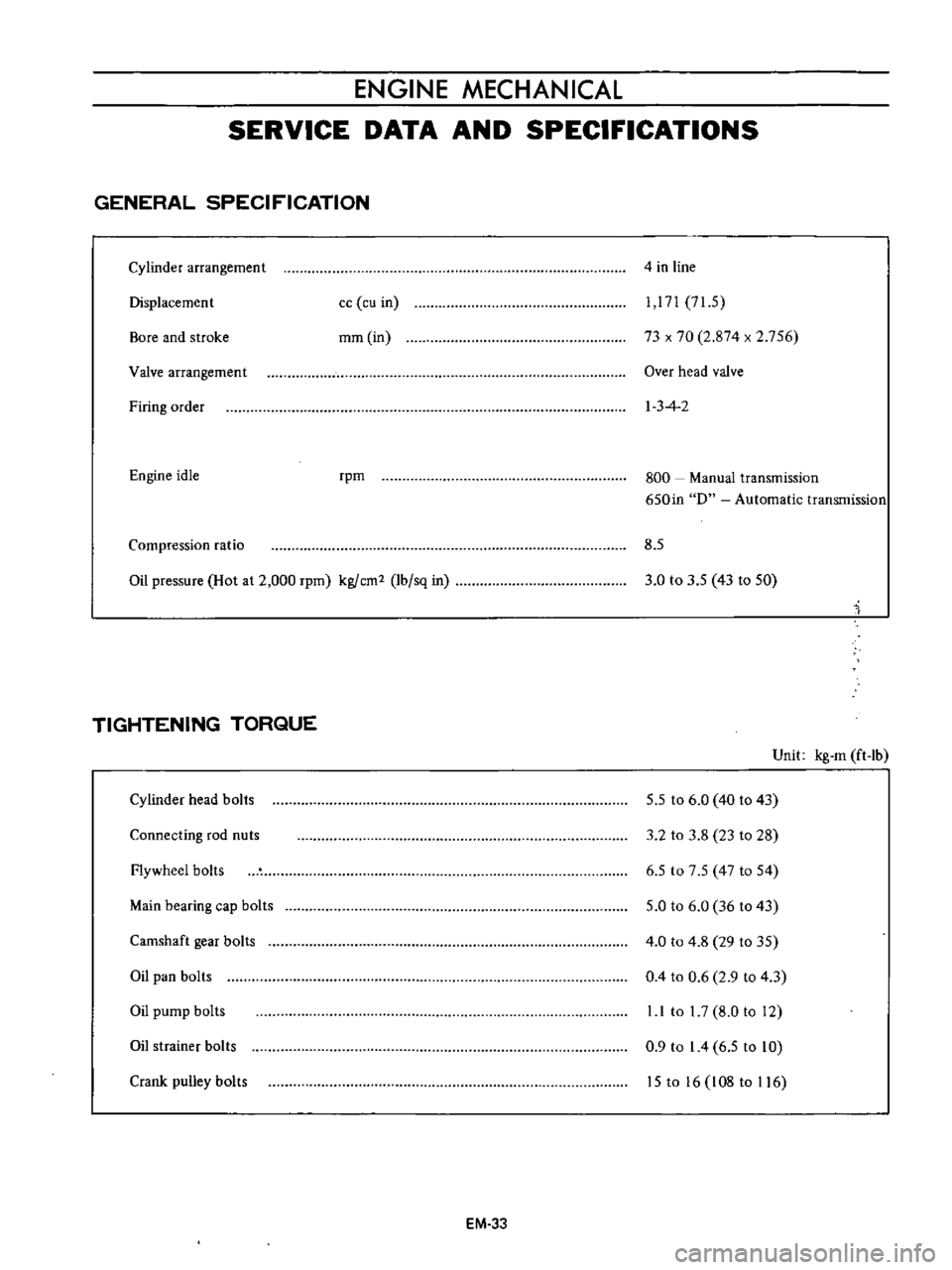
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
SPECIFICATION
Cylinder
arrangement
4
in
line
Displacement
cc
cu
in
mm
in
1
171
71
5
73
x
70
2
874
x
2
756
Bore
and
stroke
Valve
arrangemen
t
Over
head
valve
Firing
order
I
3
4
2
Engine
idle
rpm
800
Manual
transmission
650in
D
Automatic
transmission
Compression
ratio
8
5
Oil
pressure
Hot
at
2
000
rpm
kgfcm2
Ibfsq
in
3
0
to
3
5
43
to
50
TIGHTENING
TORQUE
Unit
kg
m
ft
lb
Cylinder
head
bolts
Flywheel
bolts
5
5
to
6
0
40
to
43
3
2
to
3
8
23
to
28
6
5
to
7
5
47
to
54
5
0
to
6
0
36
to
43
4
0
to
4
8
29
to
35
0
4
to
0
6
2
9
to
4
3
l
l
to
I
7
8
0
to
12
0
9
to
I
4
6
5
to
10
15
to
16
108
to
116
Connecting
rod
nuts
Main
bearing
cap
bolts
Camshaft
gear
bolts
Oil
pan
bolts
Oil
pump
bolts
Oil
strainer
bolts
Crank
pulley
bolts
EM
33
Page 384 of 513
ENGINE
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
Inspection
and
repair
Clean
the
disassembled
parts
with
cleaning
solvent
and
inspect
for
defects
Inspect
the
drive
rotor
shaft
for
excessive
wear
and
scores
and
check
the
following
clearances
Side
clearance
between
Quter
and
inner
rotors
0
12
mm
0
0047
in
or
below
Tip
clearance
0
04
to
0
I2mm
0
0016
to
0
0047
in
Clearance
between
outer
rotor
and
body
0
15
to
0
21
rom
0
0059
to
0
0083
in
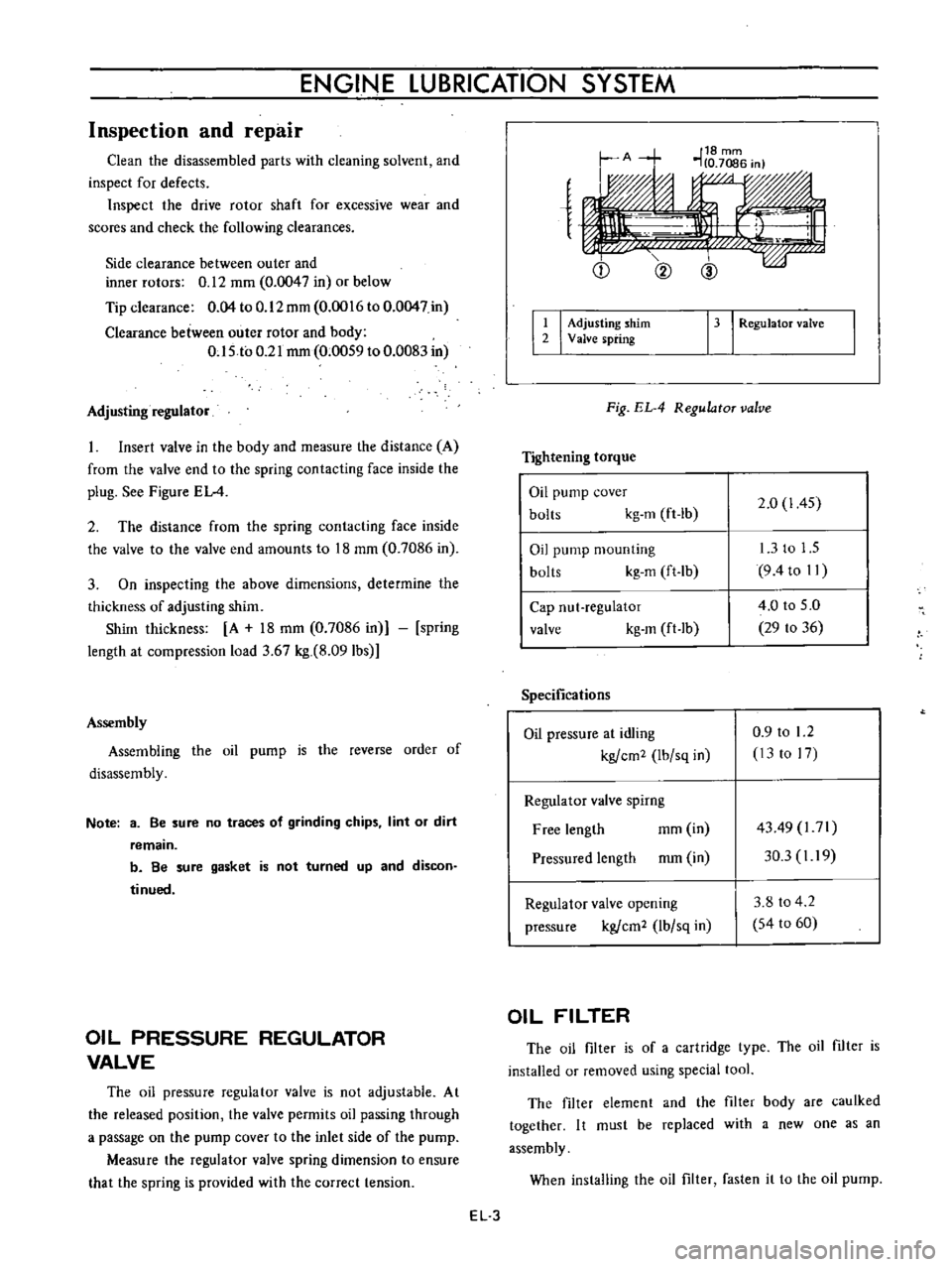
Adjusting
regulator
Insert
valve
in
the
body
and
measure
the
distance
A
from
the
valve
end
to
the
spring
contacting
face
inside
the
plug
See
Figure
EL
4
2
The
distance
from
the
spring
contacting
face
inside
the
valve
to
the
valve
end
amounts
to
18
mm
0
7086
in
3
On
inspecting
the
above
dimensions
determine
the
thickness
of
adjusting
shim
Shim
thickness
A
18
mm
0
7086
in
spring
length
at
compression
load
3
67
kg
8
091bs
Assembly
Assembling
the
oil
pump
is
the
reverse
order
of
disassembly
Note
3
Be
sure
no
traces
of
grinding
chips
lint
or
dirt
remain
b
Be
sure
gasket
is
not
turned
up
and
discon
tinued
OIL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
VALVE
The
oil
pressure
regulator
valve
is
not
adjustable
At
the
released
position
the
valve
permits
oil
passing
through
a
passage
on
the
pump
cover
to
the
inlet
side
of
the
pump
Measure
the
regulator
valve
spring
dimension
to
ensure
that
the
spring
is
provided
with
the
correct
tension
e
Q
@
I
I
Adjusting
shim
2
Valve
spring
13
I
RegulatoT
valve
Fig
EL
4
RegulatoT
valve
Tightening
torque
Oil
pump
cover
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
2
0
1
45
Oil
pump
mounting
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
13
to
1
5
9
4to
II
Cap
nut
regulator
valve
kg
m
ft
lb
4
0
to
5
0
29
to
36
Specifications
Oil
pressure
at
idling
kgfcm2
Ibfsq
in
0
9
to
1
2
13
to
17
Regulator
valve
spirng
Free
length
mm
in
Pressured
length
mm
in
4349
l71
30
3
I
19
Regulator
valve
opening
pressure
kgfcm2
lbfsq
in
3
8
to
4
2
54
to
60
OIL
FILTER
The
oil
filter
is
of
a
cartridge
type
The
oil
filter
is
installed
or
removed
using
special
tool
The
filter
element
and
the
filter
body
are
caulked
together
I
t
must
be
replaced
with
a
new
one
as
an
assembly
When
installing
the
oil
filter
fasten
it
to
the
oil
pump
EL
3
Page 403 of 513
ENGINE
Step
system
The
construction
of
this
system
corresponds
to
the
idling
and
slow
system
of
the
primary
system
This
system
aims
at
the
power
filling
up
of
the
gap
when
fuel
supply
is
transferred
from
the
primary
system
to
the
secondary
system
The
step
port
is
located
near
the
auxiliary
valve
in
its
fully
closed
state
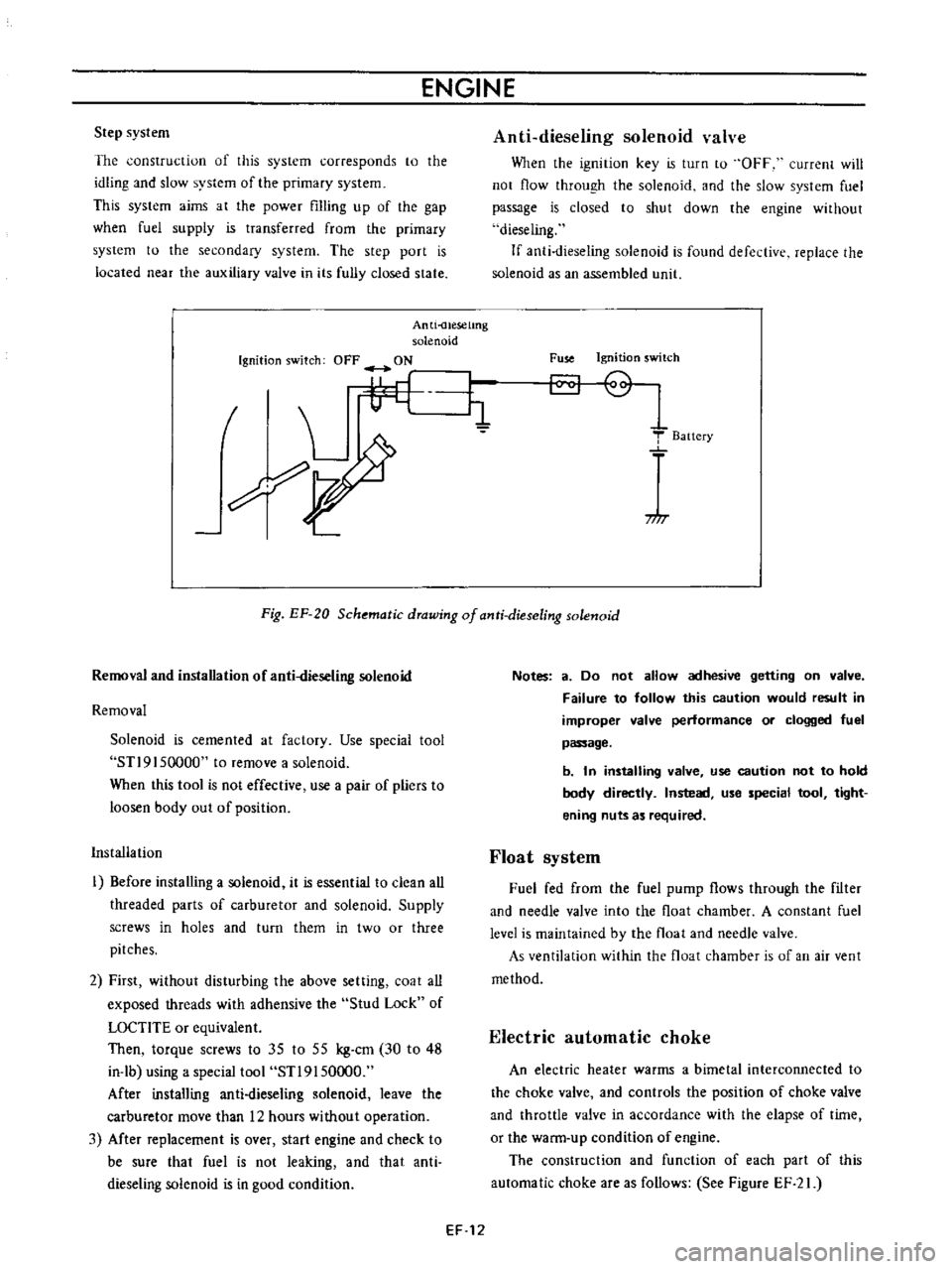
Anti
uesetmg
solenoid
Ignition
switch
OFF
ON
I
L
i1
7
I
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
When
the
ignition
key
is
turn
to
OFF
current
will
not
flow
through
the
solenoid
and
the
slow
system
fuel
passage
is
closed
to
shut
down
the
engine
without
dieseling
If
anti
dieseling
solenoid
is
found
defective
replace
the
solenoid
as
an
assembled
llnit
Fuse
Ignition
switch
T
Baitery
717
Fig
EF
20
Schematic
drawing
of
anti
dieseling
solenoid
Removal
and
installation
of
anti
dieseling
solenoid
Removal
Solenoid
is
cemented
at
factory
Use
special
tool
STl9
I
50000
to
remove
a
solenoid
When
this
tool
is
not
effective
use
a
pair
of
pliers
to
loosen
body
out
of
position
Installation
I
Before
installing
a
solenoid
it
is
essential
to
clean
all
threaded
parts
of
carburetor
and
solenoid
Supply
screws
in
holes
and
turn
them
in
two
or
three
pitches
2
First
without
disturbing
the
above
setting
coat
all
exposed
threads
with
adhensive
the
Stud
Lock
of
LOCTlTE
or
equivalent
Then
torque
screws
to
35
to
55
kg
cm
30
to
48
in
lb
using
a
special
tool
STl9150000
After
installing
anti
dieseling
solenoid
leave
the
carburetor
move
than
12
hours
without
operation
3
Mter
replacement
is
over
start
engine
and
check
to
be
sure
that
fuel
is
not
leaking
and
that
anti
dieseling
solenoid
is
in
good
condition
Notes
a
Do
not
allow
adhesive
getting
on
valve
Failure
to
follow
this
caution
would
result
in
improper
valve
performance
or
clogged
fuel
passage
b
In
installing
valve
use
caution
not
to
hold
body
directly
Instead
use
special
tool
tight
ening
nuts
as
required
Float
system
Fuel
fed
from
the
fuel
pump
flows
through
the
filter
and
needle
valve
into
the
float
chamber
A
constant
fuel
level
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
needle
valve
As
ventilation
within
the
float
chamber
is
of
an
air
vent
method
Electric
automatic
choke
An
electric
heater
warms
a
bimetal
interconnected
to
the
choke
valve
and
controls
the
position
of
choke
valve
and
throttle
valve
in
accordance
with
the
elapse
of
time
or
the
warm
up
condition
of
engine
The
construction
and
function
of
each
part
of
this
automatic
choke
are
as
follows
See
Figure
EF
21
EF
12
Page 424 of 513
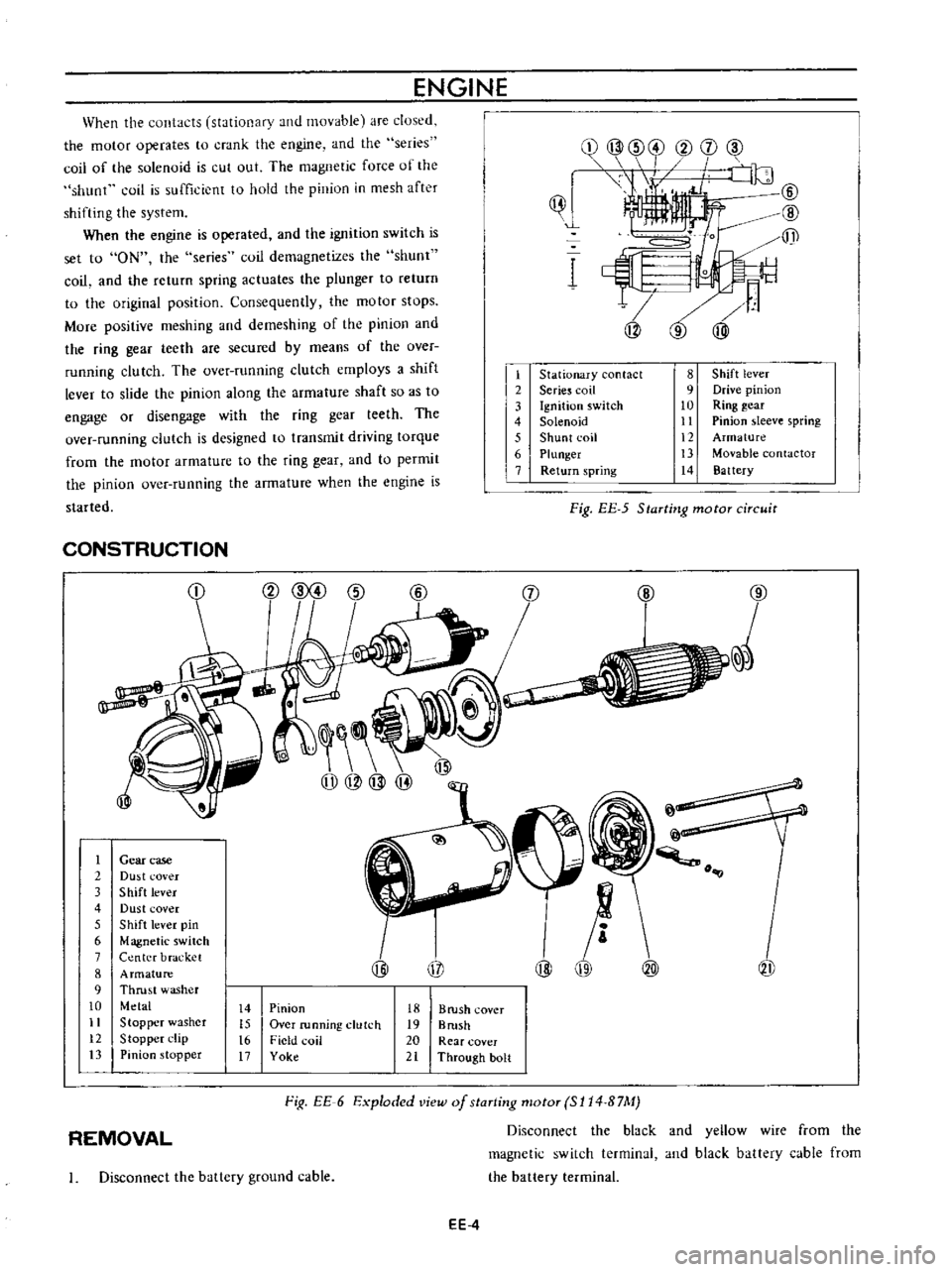
When
the
contacts
stationary
and
movable
are
dused
the
motor
operates
to
crank
the
engine
and
the
series
coil
of
the
solenoid
is
cut
out
The
magnetic
force
of
the
shunt
coil
is
sufficient
to
hold
the
pinion
in
mesh
after
shifting
the
system
When
the
engine
is
operated
and
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
the
series
coil
demagnetizes
the
shunt
coil
and
the
return
spring
actuates
the
plunger
to
return
to
the
original
position
Consequently
the
motor
stops
More
positive
meshing
and
demeshing
of
the
pinion
and
the
ring
gear
teeth
are
secured
by
means
of
the
over
running
clutch
The
over
running
clutch
employs
a
shift
lever
to
slide
the
pinion
along
the
armature
shaft
so
as
to
engage
or
disengage
with
the
ring
gear
teeth
The
over
running
clutch
is
designed
to
transmit
driving
torque
from
the
motor
armature
to
the
ring
gear
and
to
permit
the
pinion
over
running
the
armature
when
the
engine
is
started
ENGINE
ijJ
1
t
2
3
4
5
6
7
Stationary
contact
Serie
coil
Ignition
switch
Solenoid
Shunt
coil
Plunger
Return
spring
8
Shift
lever
9
Drive
pinion
10
Ring
gear
11
Pinion
sleeve
spring
12
Armature
13
Movable
contactor
14
Battery
Fig
EE
5
Starting
motor
circuit
CONSTRUCTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
j
@
Gear
case
Du
t
cover
Shift
lever
Dust
cover
Shift
lever
pin
Magnetic
switch
Center
bracket
Armature
Thrust
washer
Metal
Stopper
washer
Stopper
l
lip
Pinion
stopper
@
@
o
@
i
1I
@
@
@
14
15
t6
17
Pinion
Over
running
clutch
Field
coil
Yoke
18
B
rush
cover
19
Brush
20
Rear
cover
21
Through
bolt
Fig
EE
6
Exploded
view
of
staTting
motoT
SI14
B7M
Disconnect
the
black
and
yellow
wire
from
the
magnetic
switch
terminal
and
black
battery
cable
from
the
battery
terminal
REMOVAL
I
Disconnect
the
ballery
ground
cable
EE
4
Page 429 of 513
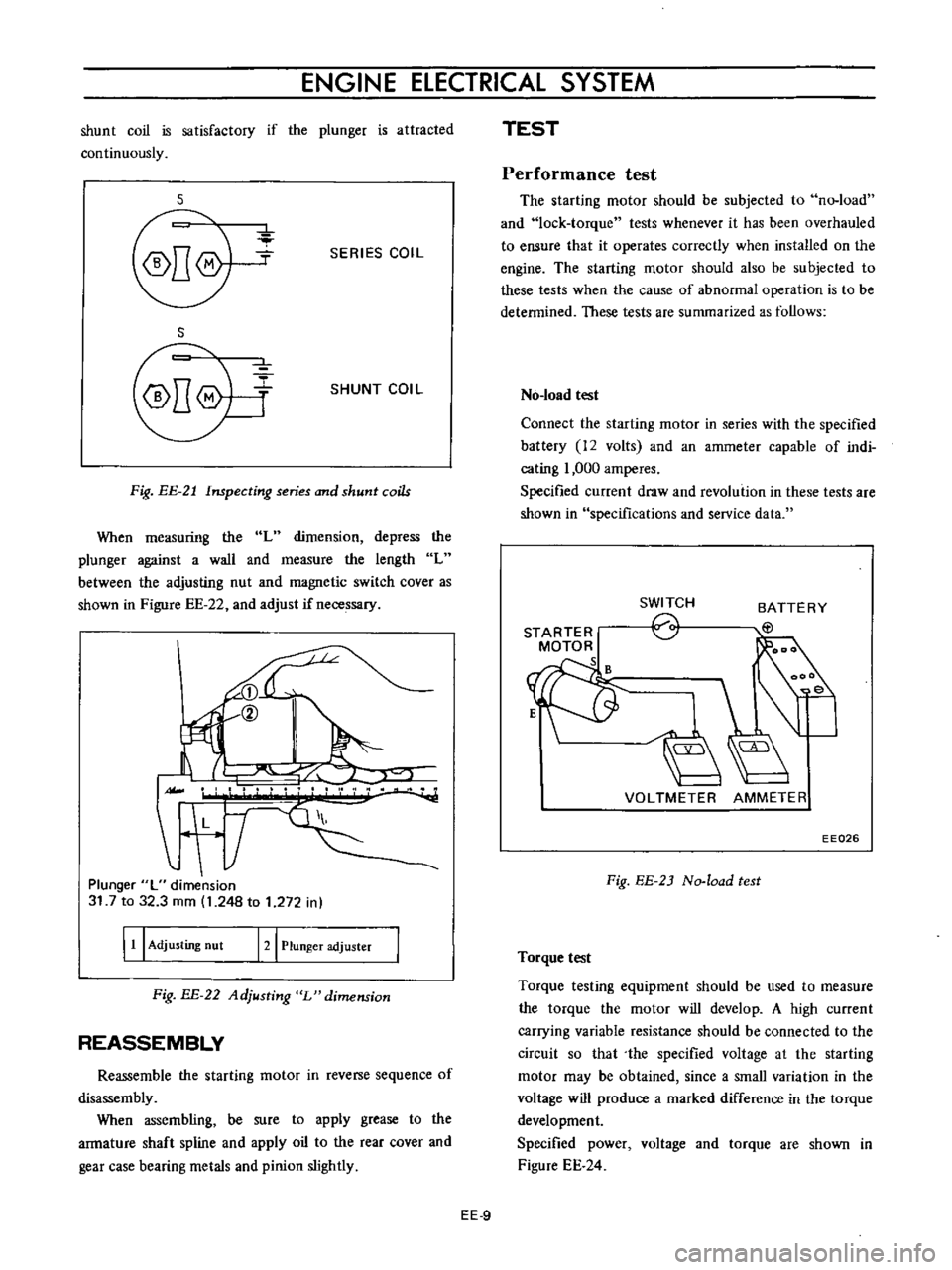
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
shunt
coil
is
satisfactory
if
the
plunger
is
attracted
continuously
s
SERIES
COIL
S
SHUNT
COIL
Fig
EE
21
Inspecting
series
and
shunt
coils
When
measuring
the
L
dimension
depress
the
plunger
against
a
wall
and
measure
the
length
L
between
the
adjusting
nut
and
magnetic
switch
cover
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
22
and
adjust
if
necessary
II
L
T
Plunger
L
dimension
31
7
to
32
3
mm
1
248
to
1
272
in
I
11
I
Adjusting
nut
121
Plunger
adjuster
Fig
BE
22
Adjusting
L
dimension
REASSEMBLY
Reassemble
the
starting
motor
in
reverse
sequence
of
disassembly
When
assembling
be
sure
to
apply
grease
to
the
armature
shaft
spline
and
apply
oil
to
the
rear
cover
and
gear
case
bearing
metals
and
pinion
slightly
TEST
Performance
test
The
starting
motor
should
be
subjected
to
no
load
and
lock
torque
tests
whenever
it
has
been
overhauled
to
ensure
that
it
operates
correctly
when
installed
on
the
engine
The
starting
motor
should
also
be
subjected
to
these
tests
when
the
cause
of
abnormal
operation
is
to
be
determined
These
tests
are
summarized
as
follows
No
load
test
Connect
the
starting
motor
in
series
with
the
specified
battery
12
volts
and
an
ammeter
capable
of
indi
cating
1
000
amperes
Specified
current
draw
and
revolution
in
these
tests
are
shown
in
specifications
and
service
data
STARTER
MOTOR
s
SWITCH
o
BATTERY
EtJ
VOLTMETER
AMMETER
EE026
Fig
EE
2J
No
load
test
Torque
test
Torque
testing
equipment
should
be
used
to
measure
the
torque
the
motor
will
develop
A
high
current
carrying
variable
resistance
should
be
connected
to
the
circuit
so
that
the
specified
voltage
at
the
starting
motor
may
be
obtained
since
a
small
variation
in
the
voltage
will
produce
a
marked
difference
in
the
torque
development
Specified
power
voltage
and
torque
are
shown
in
Figure
EE
24
EE
9