lock DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 1151 of 1200

If a thorough leak check has been completed with-
out indication of a leak, proceed to System Charge
Level.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C SERVICE PORT VALVE CORES
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the valve caps (Fig. 5) and (Fig. 6)
(2) Using a R-134a refrigerant recovery machine,
Remove the refrigerant from A/C system.
(3) Using a standard valve core tool, remove the
valve core.Be careful to prevent any dirt/debris
from entering the valve core opening or getting
on the replacement valve core.
INSTALLATION
(1) When assembling the new valve core into the
port, the core should be oiled with clean ND8 PAG
compressor oil.
CAUTION: A valve that is not fully seated can lead
to damage to the valve during evacuation and
charge. This can result in system refrigerant dis-
charge while uncoupling the charge adapters.
(2) Install valve core into port.
(3) Evacuate and charge the A/C system.
(4) Install the valve caps.
BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
The blower motor is located on the bottom right
side of the unit housing. The blower motor can be
removed from the vehicle without having to remove
the unit housing assembly.
WITH AIR CONDITIONING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove right side scuff plate.
(2) Pull back carpet.
(3) Cut wheel housing silencer in line with blower
motor wiring.
(4) Disconnect blower motor wiring connector.
(5) RHD vehicle remove the motor cover.
(6) Remove three blower motor retaining screws
(Fig. 18).
(7) Lower blower motor assembly from unit hous-
ing.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Then tape silencer into position.
WITHOUT AIR CONDITIONING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect blower motor wiring connector.
(2) Grasp the blower motor while pulling down
tab. Turn approximately 1/8 turn counterclockwise
and remove blower motor assembly from unit hous-
ing (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
CAUTION: Stay clear of the blower motor and resis-
tor block (Hot). Do not operate the blower motor
with the resistor block removed.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove windshield wipers.
(2) Remove cowl top screen.
(3) Disconnect the resistor block wiring connector.
Fig. 18 Blower Motor Retaining Screws
Fig. 19 Blower Motor Removal
24 - 18 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1152 of 1200

(4) Remove two resistor block retaining screws.
The screw threads attaching the resistor block are
not full length. It is necessary to gently pry out the
resistor block while turning the screws counterclock-
wise enabling the threads to engages.
(5) Remove resistor block from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
BLOWER MOTOR WHEEL
The blower motor wheel is only serviced with the
blower motor. The wheel and the motor are balanced
as an assembly. If the blower motor wheel requires
replacement, the blower motor must also be replaced.
Refer to blower motor for replacement procedure.
COMPRESSOR
CAUTION: Add only new lubricant when system
requires additional lubricant. Do not use old
reclaimed lubricant.
REMOVAL
The A/C compressor may be unbolted and reposi-
tioned without discharging the refrigerant system.
Discharging is not necessary if removing the com-
pressor clutch/coil assembly, engine, cylinder head, or
alternator.
WARNING: REFRIGERANT PRESSURES REMAIN
HIGH EVEN THOUGH THE ENGINE MAY BE
TURNED OFF. DO NOT TWIST OR KINK THE
REFRIGERANT LINES WHEN REMOVING A FULLY
CHARGED COMPRESSOR. SAFETY GLASSES
MUST BE WORN.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Loosen and remove drive belts, refer to Group
7, Engine Cooling.
(3) Using a R-134a refrigerant recovery machine,
remove the refrigerant from A/C system. If the com-
pressor is being replaced.
(4) Disconnect compressor clutch wire lead.
(5) Remove refrigerant lines from compressor, if
necessary.
(6) If system is left open place plug/cap over open
lines.
(7) Remove compressor attaching bolt.
(8) Remove compressor. If refrigerant lines were
not removed, lift compressor/clutch assembly and tie
it to a suitable component.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL ASSEMBLY
Compressor assembly must be removed from mount-
ing. Although, refrigerant discharge is not necessary.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the compressor shaft bolt (Fig. 20). A
band type oil filter removal tool can be placed around
the clutch plate to aid in bolt removal.
(2) Tap the clutch plate with a plastic hammer and
remove clutch plate and shim(s) (Fig. 21).
NOTE: Use care not to lose any of the shim(s).
CAUTION: Do not use screwdrivers between the
clutch plate assembly and pulley to remove front
plate as this may damage the front plate assembly.
Fig. 20 Compressor Shaft Bolt and Clutch Plate
Fig. 21 Clutch Plate and Shim(s)
PLHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1153 of 1200

(3) Remove pulley retaining snap ring with Snap
Ring Pliers, and slide pulley assembly off of compres-
sor (Fig. 22).
(4) Remove coil wire bracket/ground clip screw and
wire harness.
(5) Remove snap ring retaining field coil onto com-
pressor housing (Fig. 23). Slide field coil off of com-
pressor housing.(6) Examine frictional faces of the clutch pulley
and front plate for wear. The pulley and front plate
should be replaced if there is excessive wear or scor-
ing. If the friction surfaces are oily, inspect the shaft
nose area of the compressor for oil and remove the
felt from the front cover. If the compressor felt is sat-
urated with oil, the shaft seal is leaking and will
have to be replaced.
(7) Check bearing for roughness or excessive leak-
age of grease. Replace bearing as required.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align pin in back of field coil with hole in com-
pressor end housing, and position field coil into place.
Make sure that lead wires are properly routed, and
fasten the coil wire bracket/ground retaining screw.
NOTE: A new snap ring must be used. The bevel
side of the snap ring must be outward.
(2) Install field coil retaining snap ring with Snap
Ring Pliers. Press snap ring to make sure it is prop-
erly seated in the groove.
CAUTION: If snap ring is not fully seated it will
vibrate out, resulting in a clutch failure and severe
damage to the front face of the compressor.
Do not mar the pulley frictional surface.
(3) Install pulley assembly to compressor. If neces-
sary, tap gently with a block of wood on the friction
surface (Fig. 24).
Fig. 22 Removing Pulley Snap Ring
Fig. 23 Clutch Coil Snap RingFig. 24 Installing Pulley Assembly
24 - 20 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1157 of 1200
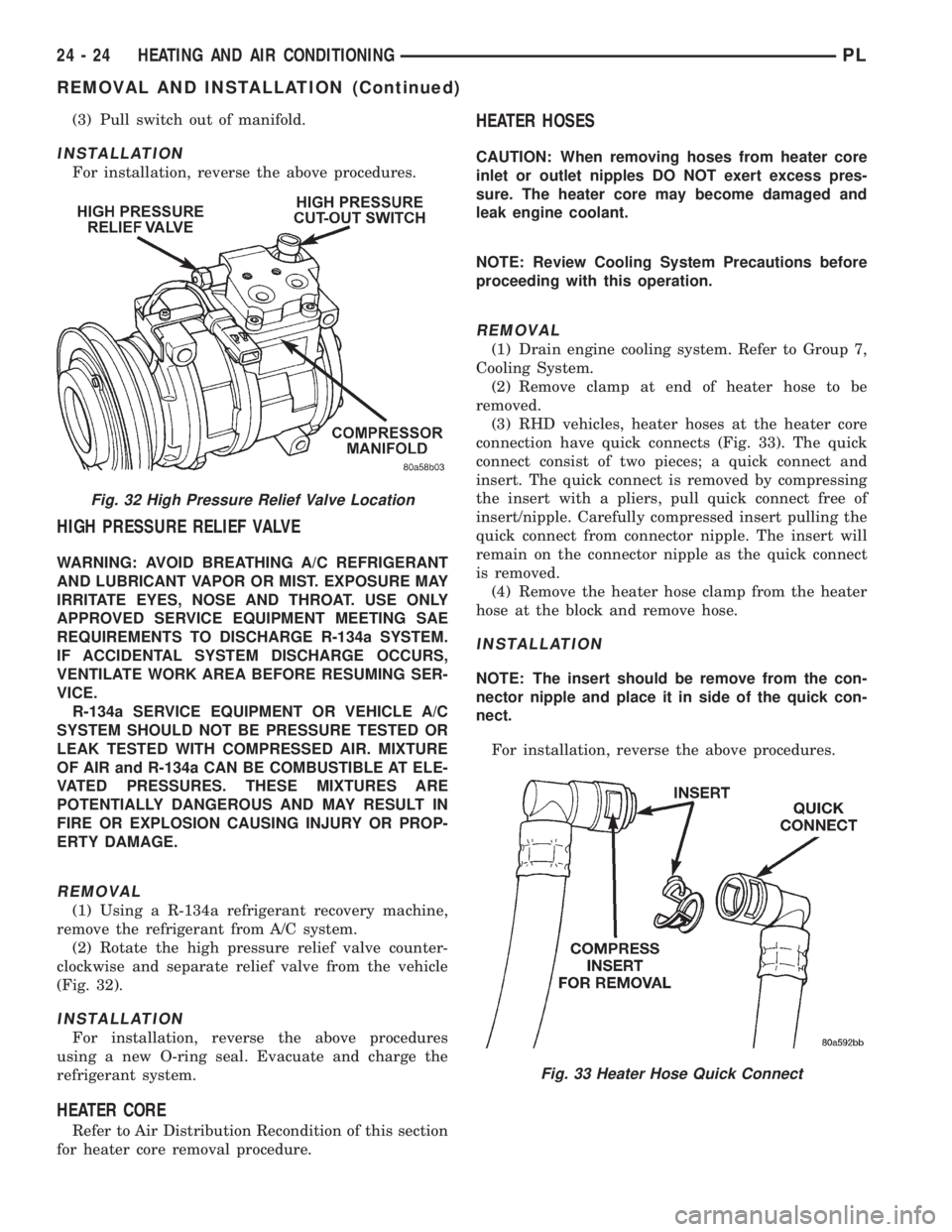
(3) Pull switch out of manifold.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
WARNING: AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT
AND LUBRICANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY
IRRITATE EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY
APPROVED SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE
REQUIREMENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM.
IF ACCIDENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHICLE A/C
SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE TESTED OR
LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED AIR. MIXTURE
OF AIR and R-134a CAN BE COMBUSTIBLE AT ELE-
VATED PRESSURES. THESE MIXTURES ARE
POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS AND MAY RESULT IN
FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY OR PROP-
ERTY DAMAGE.
REMOVAL
(1) Using a R-134a refrigerant recovery machine,
remove the refrigerant from A/C system.
(2) Rotate the high pressure relief valve counter-
clockwise and separate relief valve from the vehicle
(Fig. 32).
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures
using a new O-ring seal. Evacuate and charge the
refrigerant system.
HEATER CORE
Refer to Air Distribution Recondition of this section
for heater core removal procedure.
HEATER HOSES
CAUTION: When removing hoses from heater core
inlet or outlet nipples DO NOT exert excess pres-
sure. The heater core may become damaged and
leak engine coolant.
NOTE: Review Cooling System Precautions before
proceeding with this operation.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain engine cooling system. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System.
(2) Remove clamp at end of heater hose to be
removed.
(3) RHD vehicles, heater hoses at the heater core
connection have quick connects (Fig. 33). The quick
connect consist of two pieces; a quick connect and
insert. The quick connect is removed by compressing
the insert with a pliers, pull quick connect free of
insert/nipple. Carefully compressed insert pulling the
quick connect from connector nipple. The insert will
remain on the connector nipple as the quick connect
is removed.
(4) Remove the heater hose clamp from the heater
hose at the block and remove hose.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The insert should be remove from the con-
nector nipple and place it in side of the quick con-
nect.
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Fig. 33 Heater Hose Quick Connect
Fig. 32 High Pressure Relief Valve Location
24 - 24 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1163 of 1200

ASSEMBLE
To reassemble, reverse the above procedures.
ADJUSTMENTS
MODE CONTROL CABLE
(1) Attach cable to actuator arm on mode door and
clip black casing against the stop.
(2) Attach other end of cable to instrument panel
control.
(3) Turn the mode knob completely counterclock-
wise.
(4) While holding the knob in the counterclockwise
position, pull on the black casing of the mode cable.
This will take up any free play in the cable and index
the mode door to the mode knob.
(5) Then snap the cable hold down clip into posi-
tion.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL CABLE
(1) Attach cable to actuator arm on temperature
door and clip black casing against the stop.
(2) Attach other end of cable to instrument panel
control.
(3) Turn the temperature knob completely counter-
clockwise.
(4) While holding the knob in the counterclockwise
position, pull on the black casing of the temperature
cable. This will take up any free play in the cable
and index the temperature door to the temperature
knob.
(5) Then snap the cable hold down clip into posi-
tion.
(6) Remount control.
Fig. 50 Cam and Lever Removal
Fig. 51 Pivot Screw Removal
24 - 30 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1166 of 1200
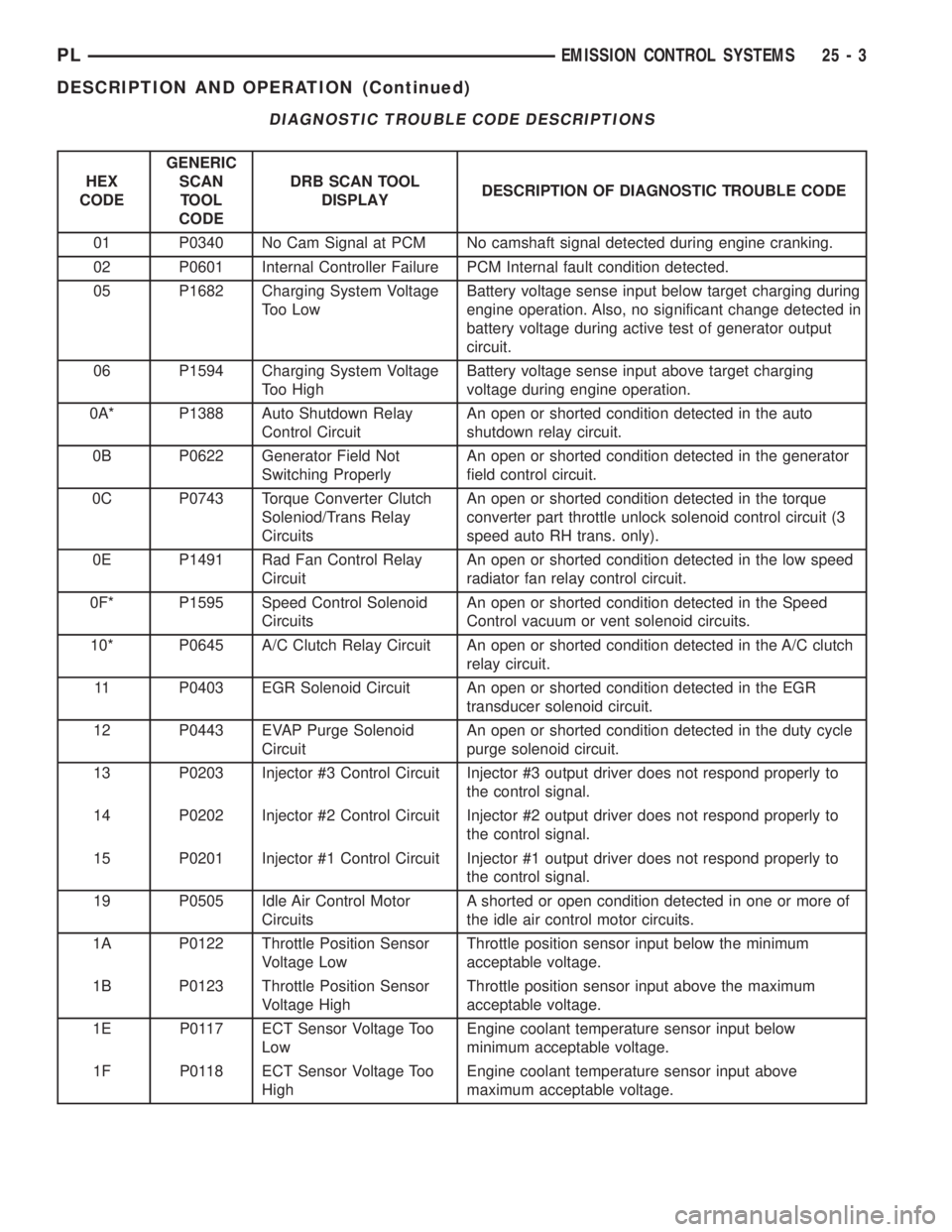
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONS
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
01 P0340 No Cam Signal at PCM No camshaft signal detected during engine cranking.
02 P0601 Internal Controller Failure PCM Internal fault condition detected.
05 P1682 Charging System Voltage
Too LowBattery voltage sense input below target charging during
engine operation. Also, no significant change detected in
battery voltage during active test of generator output
circuit.
06 P1594 Charging System Voltage
Too HighBattery voltage sense input above target charging
voltage during engine operation.
0A* P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay
Control CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
0B P0622 Generator Field Not
Switching ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator
field control circuit.
0C P0743 Torque Converter Clutch
Soleniod/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter part throttle unlock solenoid control circuit (3
speed auto RH trans. only).
0E P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the low speed
radiator fan relay control circuit.
0F* P1595 Speed Control Solenoid
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Speed
Control vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
10* P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch
relay circuit.
11 P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR
transducer solenoid circuit.
12 P0443 EVAP Purge Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the duty cycle
purge solenoid circuit.
13 P0203 Injector #3 Control Circuit Injector #3 output driver does not respond properly to
the control signal.
14 P0202 Injector #2 Control Circuit Injector #2 output driver does not respond properly to
the control signal.
15 P0201 Injector #1 Control Circuit Injector #1 output driver does not respond properly to
the control signal.
19 P0505 Idle Air Control Motor
CircuitsA shorted or open condition detected in one or more of
the idle air control motor circuits.
1A P0122 Throttle Position Sensor
Voltage LowThrottle position sensor input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
1B P0123 Throttle Position Sensor
Voltage HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
1E P0117 ECT Sensor Voltage Too
LowEngine coolant temperature sensor input below
minimum acceptable voltage.
1F P0118 ECT Sensor Voltage Too
HighEngine coolant temperature sensor input above
maximum acceptable voltage.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1168 of 1200
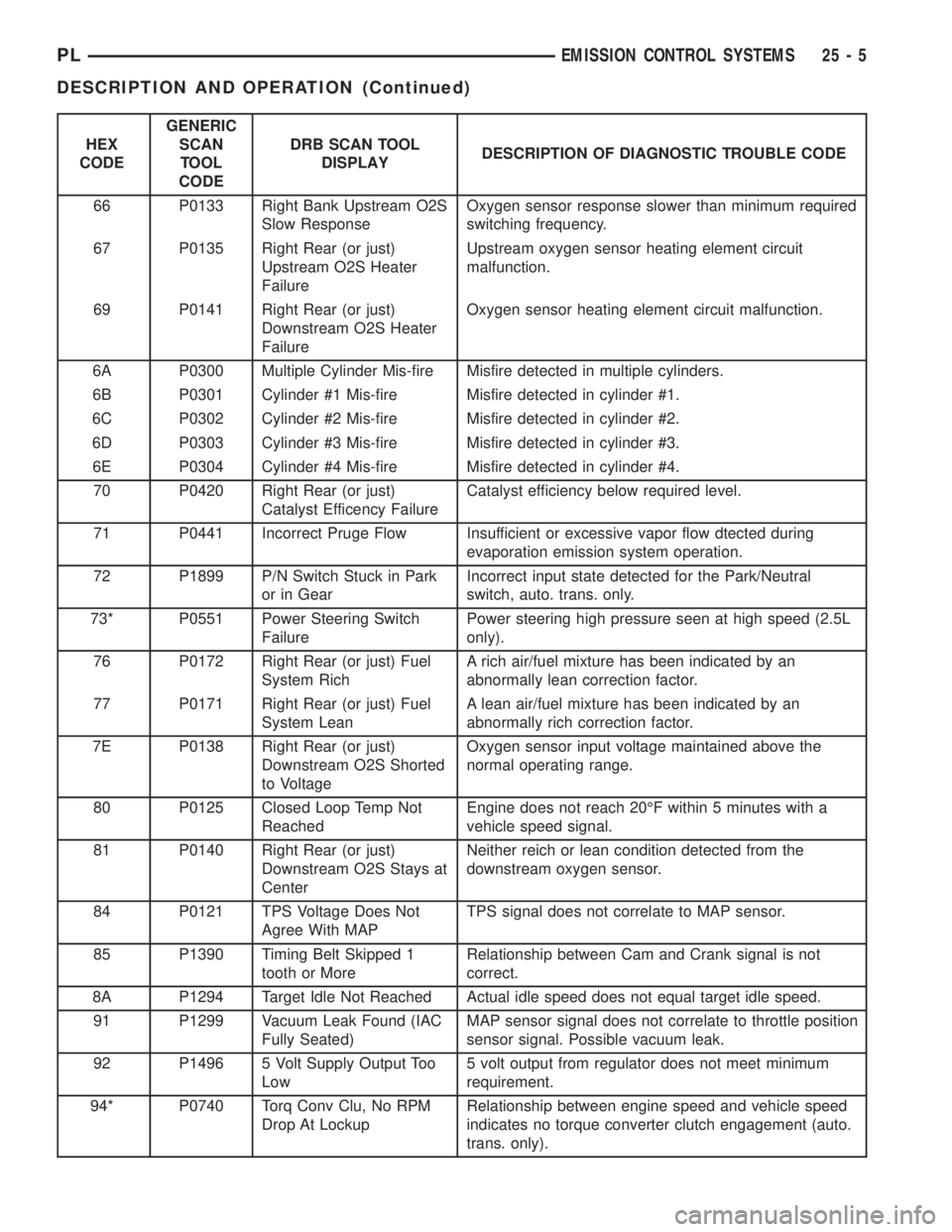
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
66 P0133 Right Bank Upstream O2S
Slow ResponseOxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
67 P0135 Right Rear (or just)
Upstream O2S Heater
FailureUpstream oxygen sensor heating element circuit
malfunction.
69 P0141 Right Rear (or just)
Downstream O2S Heater
FailureOxygen sensor heating element circuit malfunction.
6A P0300 Multiple Cylinder Mis-fire Misfire detected in multiple cylinders.
6B P0301 Cylinder #1 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #1.
6C P0302 Cylinder #2 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #2.
6D P0303 Cylinder #3 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #3.
6E P0304 Cylinder #4 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #4.
70 P0420 Right Rear (or just)
Catalyst Efficency FailureCatalyst efficiency below required level.
71 P0441 Incorrect Pruge Flow Insufficient or excessive vapor flow dtected during
evaporation emission system operation.
72 P1899 P/N Switch Stuck in Park
or in GearIncorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral
switch, auto. trans. only.
73* P0551 Power Steering Switch
FailurePower steering high pressure seen at high speed (2.5L
only).
76 P0172 Right Rear (or just) Fuel
System RichA rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally lean correction factor.
77 P0171 Right Rear (or just) Fuel
System LeanA lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally rich correction factor.
7E P0138 Right Rear (or just)
Downstream O2S Shorted
to VoltageOxygen sensor input voltage maintained above the
normal operating range.
80 P0125 Closed Loop Temp Not
ReachedEngine does not reach 20ÉF within 5 minutes with a
vehicle speed signal.
81 P0140 Right Rear (or just)
Downstream O2S Stays at
CenterNeither reich or lean condition detected from the
downstream oxygen sensor.
84 P0121 TPS Voltage Does Not
Agree With MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor.
85 P1390 Timing Belt Skipped 1
tooth or MoreRelationship between Cam and Crank signal is not
correct.
8A P1294 Target Idle Not Reached Actual idle speed does not equal target idle speed.
91 P1299 Vacuum Leak Found (IAC
Fully Seated)MAP sensor signal does not correlate to throttle position
sensor signal. Possible vacuum leak.
92 P1496 5 Volt Supply Output Too
Low5 volt output from regulator does not meet minimum
requirement.
94* P0740 Torq Conv Clu, No RPM
Drop At LockupRelationship between engine speed and vehicle speed
indicates no torque converter clutch engagement (auto.
trans. only).
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1172 of 1200

system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .020º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
TRIP DEFINITION
A ªTripº means vehicle operation (following an
engine-off period) of duration and driving mode such
that all components and systems are monitored at
least once by the diagnostic system. The monitors
must successfully pass before the PCM can verify
that a previously malfunctioning component is meet-
ing the normal operating conditions of that compo-
nent. For misfire or fuel system malfunction, the
MIL may be extinguished if the fault does not recur
when monitored during three subsequent sequential
driving cycles in which conditions are similar to
those under which the malfunction was first deter-
mined.
Anytime the MIL is illuminated, a DTC is stored.
The DTC can self erase only when the MIL has been
extinguished. Once the MIL is extinguished, the
PCM must pass the diagnostic test for the most
recent DTC for 40 warm-up cycles (80 warm-up
cycles for the Fuel System Monitor and the Misfire
Monitor). A warm-up cycle can best be described by
the following:
²The engine must be running²A rise of 40ÉF in engine temperature must occur
from the time when the engine was started
²Engine coolant temperature must reach at least
160ÉF
²A ªdriving cycleº that consists of engine start up
and engine shut off.
Once the above conditions occur, the PCM is con-
sidered to have passed a warm-up cycle. Due to the
conditions required to extinguish the MIL and erase
the DTC, it is most important that after a repair has
been made, all DTC's be erased and the repair veri-
fied.
COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.
Any component that has an associated limp in will
set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunction present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1177 of 1200

The label contains the vehicle's emission specifica-
tions and vacuum hose routings. All hoses must be
connected and routed according to the label.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Manual for testing procedures.
PCV VALVE TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST
OR ADJUSTMENT WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
With the engine idling, remove the PCV valve from
its attaching point. If the valve is operating properly,
a hissing noise will be heard and a strong vacuum
felt when placing a finger over the valve inlet (Fig.
9). With the engine off, shake the valve. The valve
should rattle when shaken. Replace the valve if it
does not operate properly.Do not attempt to clean
the PCV valve.
VACUUM SCHEMATIC
If any difference exists between the diagram on the
Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) label
and this illustration, refer to the label on the vehicle.
Fig. 9 PCV Test ÐTypical
25 - 14 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1180 of 1200

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
LEAK DETECTION PUMP REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Remove right front wheel.
(3) Remove splash shield.
(4) Disconnect vacuum lines from EVAP canister.
(5) Push locking tab on electrical connector to
unlock and remove connector.
(6) Remove 3 nuts from EVAP canister and remove
canister.
(7) Remove pump and bracket as an assembly.
(8) Remove pump from bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install pump to bracket and tighten bolts to 1.2
N´m (10.6 in. lbs.).(2) Install pump and bracket assembly to body and
tighten bolts to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(3) Install EVAP canister to bracket and tighten
nutts to 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(4) Install electrical connetor to pump and push
locking tab to lock.
(5)Before installing hoses to LDP, make sure
they are not cracked or split. If a hose leaks, it
will cause the Check Engine Lamp to illumu-
nate.Connect lines to EVAP canister and LDP.
(6) Use the DRB scan tool, verify proper operation
of LDP.
(7) Install splash shield.
(8) Install wheel.
(9) Lower vehicle
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17