DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 641 of 1502
9
- 36 3.9L
ENGINE
• Install inner rotor and shaft into pump body. If
clearance between inner and outer rotors is 0.203
mm (0.008 inch) or more, replace shaft and both ro
tors (Fig. 9).
OUTER
ROTOR
INNER
ROTOR
RH179
Fig. 9 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
Place a straightedge across the face of the pump,
between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge of 0,102 mm (0.004 inch) or more can be inserted between rotors
and the straightedge, replace pump assembly (Fig.
10).
Fig. 10 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
Inspect oil pressure relief valve plunger for scoring
and free operation in its bore. Small marks may be
removed with 400-grit wet or dry sandpaper.
The relief valve spring has a free length of approx
imately 49.5 mm (1.95 inches). The spring should
test between 19.5 and 20.5 pounds when compressed to 34 mm (1-11/32 inches). Replace spring that fails
to meet these specifications (Fig. 11).
If oil pressure was low and pump is within specifi
cations, inspect for worn engine bearings or other
reasons for oil pressure loss.
ASSEMBLE
(1) Install pump rotors and shaft, using new parts
as required. RN98
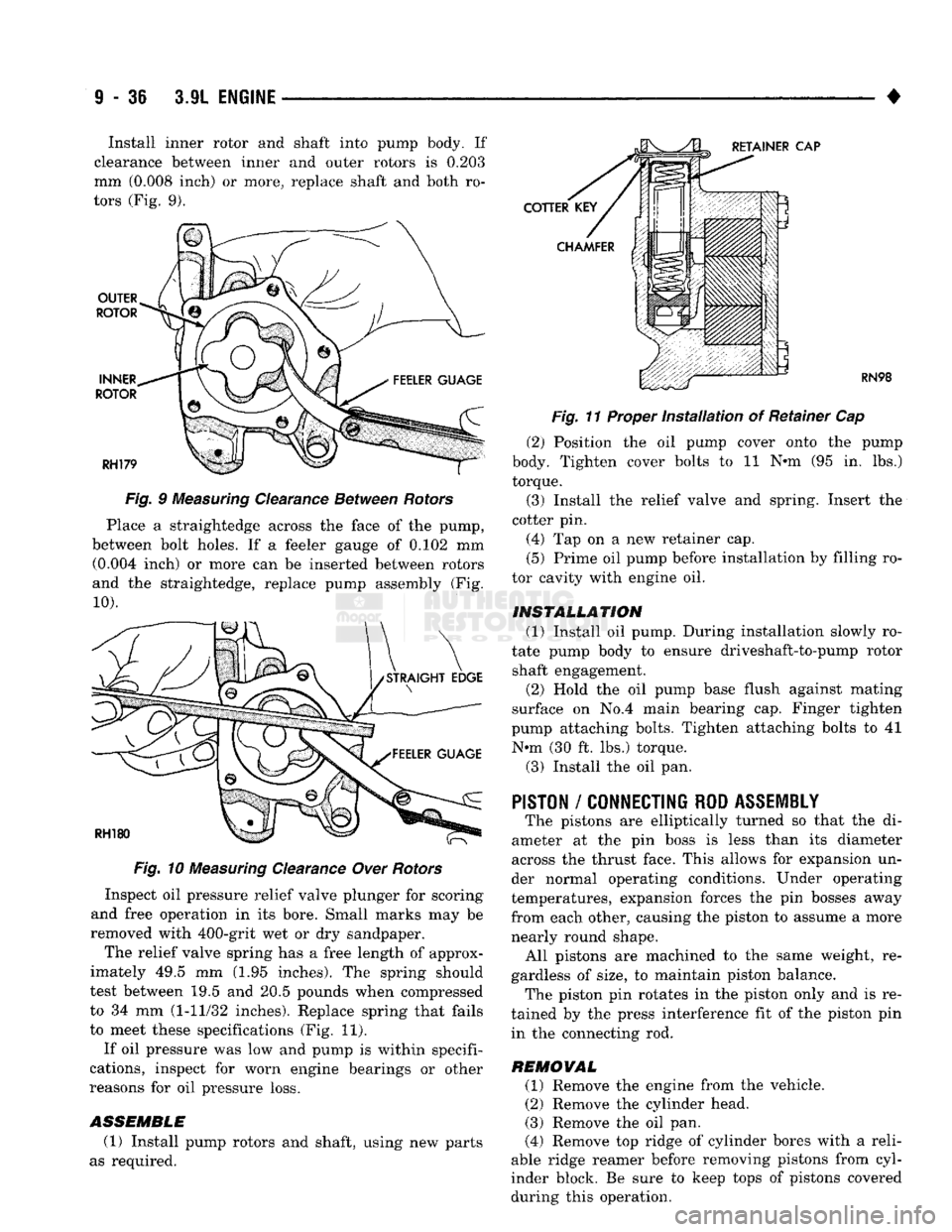
Fig.
11 Proper
Installation
of Retainer Cap
(2) Position the oil pump cover onto the pump
body. Tighten cover bolts to 11 N-m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the relief valve and spring. Insert the
cotter pin.
(4) Tap on a new retainer cap.
(5) Prime oil pump before installation by filling ro
tor cavity with engine oil.
INSTALLATION (1) Install oil pump. During installation slowly ro
tate pump body to ensure driveshaft-to-pump rotor shaft engagement.
(2) Hold the oil pump base flush against mating
surface on No.4 main bearing cap. Finger tighten
pump attaching bolts. Tighten attaching bolts to 41 N-m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the oil pan.
PISTON
/
CONNECTING ROD
ASSEMBLY
The pistons are elliptically turned so that the di
ameter at the pin boss is less than its diameter
across the thrust face. This allows for expansion un
der normal operating conditions. Under operating
temperatures, expansion forces the pin bosses away from each other, causing the piston to assume a more nearly round shape. All pistons are machined to the same weight, re
gardless of size, to maintain piston balance. The piston pin rotates in the piston only and is re
tained by the press interference fit of the piston pin
in the connecting rod.
REMOVAL (1) Remove the engine from the vehicle.
(2) Remove the cylinder head.
(3) Remove the oil pan.
(4) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl
inder block. Be sure to keep tops of pistons covered
during this operation.
Page 642 of 1502
(5) Be sure the connecting rod and connecting rod
cap are identified with the cylinder number. Remove
connecting rod cap. Install connecting rod bolt guide
set on connecting rod bolts.
(6) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. When removing piston and connecting rod assemblies from the engine, ro
tate crankshaft so that the connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore and at BDC. Be careful not to nick
crankshaft journals.
(7) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat
ing rod.
INSPECTION
Check the crankshaft connecting rod journal for ex
cessive wear, taper and scoring. Check the cylinder block bore for out-of-round,
taper, scoring and scuffing.
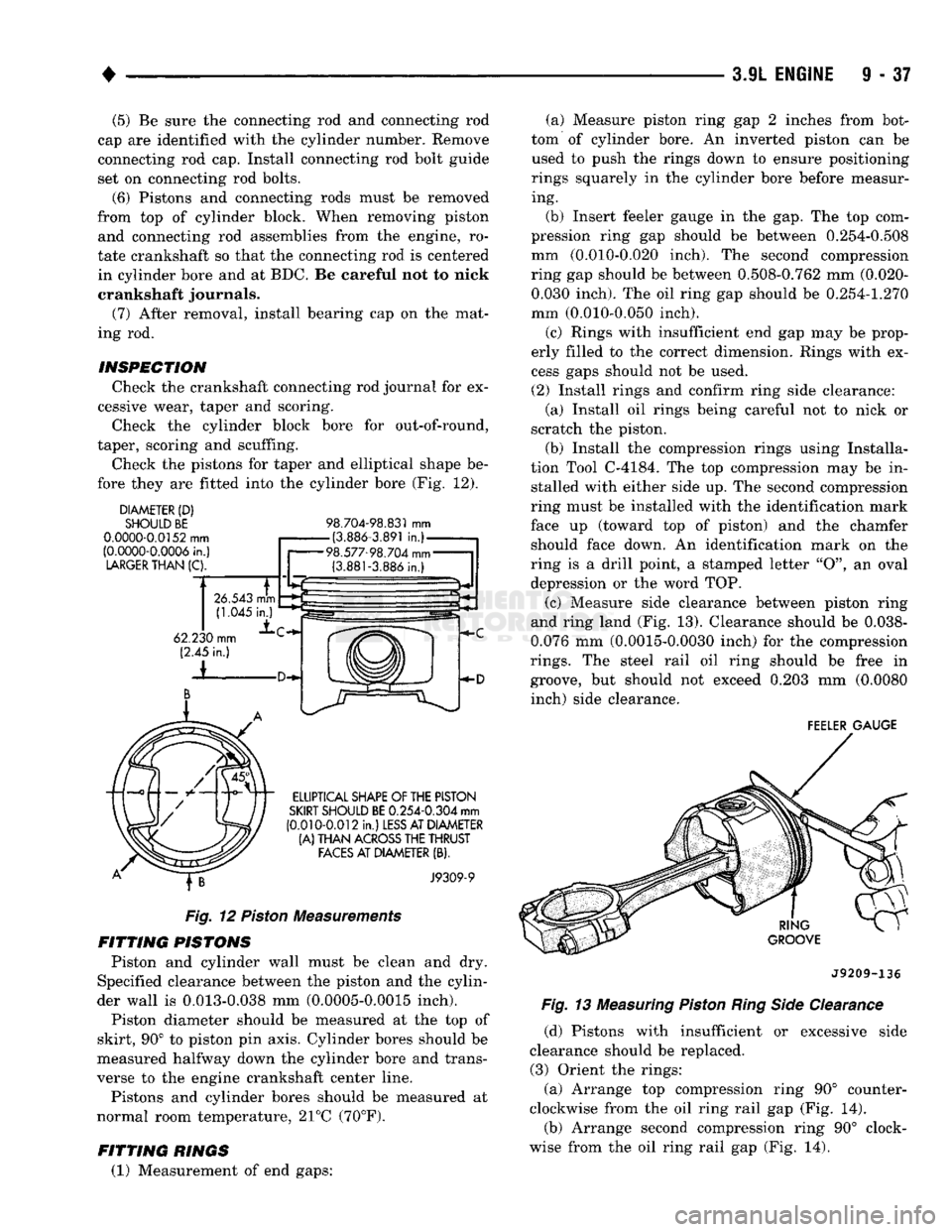
Check the pistons for taper and elliptical shape be
fore they are fitted into the cylinder bore (Fig. 12).
DIAMETER
(D)
SHOULD BE
0.0000-0.0152
mm
(0.0000-0.0006
in.)
LARGER
THAN
(C).
98.704-98.831
mm
-(3.886-3.891
in.)-
98.577-98.704
mm-
(3.881-3.886
in.) (a) Measure piston ring gap 2 inches from bot
tom of cylinder bore. An inverted piston can be used to push the rings down to ensure positioning
rings squarely in the cylinder bore before measur ing.
(b) Insert feeler gauge in the gap. The top com
pression ring gap should be between 0.254-0.508
mm (0.010-0.020 inch). The second compression
ring gap should be between 0.508-0.762 mm (0.020- 0.030 inch). The oil ring gap should be 0.254-1.270
mm (0.010-0.050 inch).
(c) Rings with insufficient end gap may be prop
erly filled to the correct dimension. Rings with ex
cess gaps should not be used.
(2) Install rings and confirm ring side clearance: (a) Install oil rings being careful not to nick or
scratch the piston.
(b) Install the compression rings using Installa
tion Tool C-4184. The top compression may be in stalled with either side up. The second compression
ring must be installed with the identification mark
face up (toward top of piston) and the chamfer should face down. An identification mark on the
ring is a drill point, a stamped letter "O", an oval
depression or the word TOP.
(c) Measure side clearance between piston ring
and ring land (Fig. 13). Clearance should be 0.038-
0.076 mm (0.0015-0.0030 inch) for the compression
rings.
The steel rail oil ring should be free in groove, but should not exceed 0.203 mm (0.0080 inch) side clearance.
FEELER
GAUGE
ELLIPTICAL SHAPE
OF
THE PISTON
SKIRT
SHOULD
BE
0.254-0.304
mm
(0.010-0.012
in.)
LESS
AT DIAMETER
(A)
THAN
ACROSS
THE THRUST
FACES
AT DIAMETER
(B).
J9309-9
Fig.
12
Piston
Measurements
FITTING
PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Specified clearance between the piston and the cylin
der wall is 0.013-0.038 mm (0.0005-0.0015 inch). Piston diameter should be measured at the top of
skirt, 90° to piston pin axis. Cylinder bores should be
measured halfway down the cylinder bore and trans
verse to the engine crankshaft center line.
Pistons and cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21°C (70°F).
FITTING
RINGS
(1) Measurement of end gaps: J9209-136
Fig.
13
Measuring
Piston
Ring Side
Clearance (d) Pistons with insufficient or excessive side
clearance should be replaced. (3) Orient the rings:
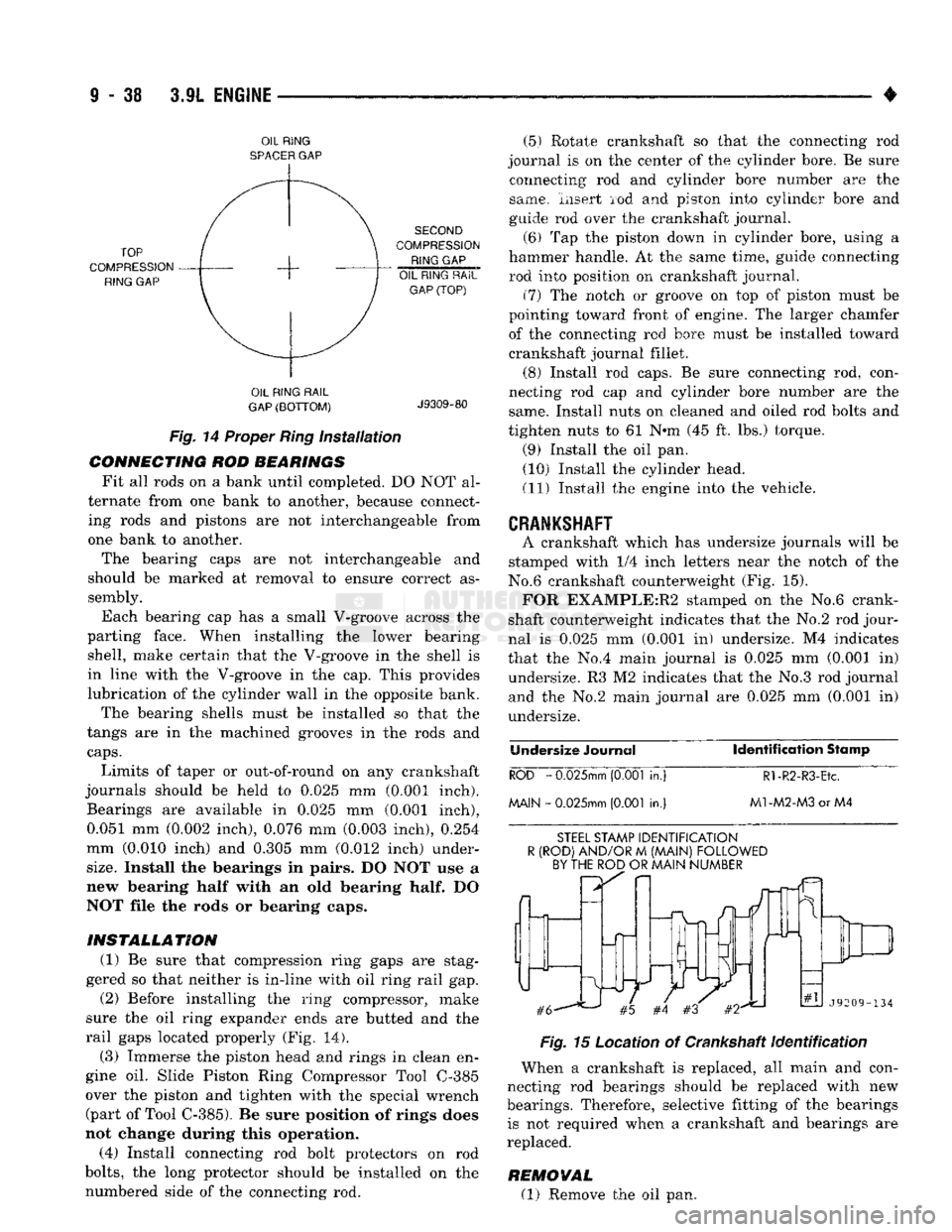
(a) Arrange top compression ring 90° counter
clockwise from the oil ring rail gap (Fig. 14). (b) Arrange second compression ring 90° clock
wise from the oil ring rail gap (Fig. 14).
Page 643 of 1502
9
- 38 3.9L
ENGINE
•
OIL
RING
SPACER
GAP
TOP
COMPRESSION
RING
GAP
SECOND
COMPRESSION
RING
GAP
OIL
RING
RAiL
GAP (TOP) OIL
RING
RAIL
GAP
(BOTTOM)
J9309-80
Fig.
14 Proper
Ring
Installation
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS Fit all rods on a bank until completed. DO NOT al
ternate from one bank to another, because connect ing rods and pistons are not interchangeable from
one bank to another.
The bearing caps are not interchangeable and
should be marked at removal to ensure correct as sembly.
Each bearing cap has a small V-groove across the
parting face. When installing the lower bearing shell, make certain that the V-groove in the shell is
in line with the V-groove in the cap. This provides
lubrication of the cylinder wall in the opposite bank.
The bearing shells must be installed so that the
tangs are in the machined grooves in the rods and
caps.
Limits of taper or out-of-round on any crankshaft
journals should be held to 0.025 mm (0.001 inch). Bearings are available in 0.025 mm (0.001 inch), 0.051 mm (0.002 inch), 0.076 mm (0.003 inch), 0.254
mm (0.010 inch) and 0.305 mm (0.012 inch) under-
size.
Install the bearings in pairs. DO NOT use a
new bearing half with an old bearing
half.
DO
NOT file the rods or bearing caps.
INSTALLATION (1) Be sure that compression ring gaps are stag
gered so that neither is in-line with oil ring rail gap. (2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located properly (Fig. 14).
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean en
gine oil. Slide Piston Ring Compressor Tool C-385
over the piston and tighten with the special wrench (part of Tool C-385). Be sure position of rings does
not change during this operation.
(4) Install connecting rod bolt protectors on rod
bolts,
the long protector should be installed on the numbered side of the connecting rod. (5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Be sure connecting rod and cylinder bore number are the
same. Insert rod and piston into cylinder bore and
guide rod over the crankshaft journal.
(6) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on crankshaft journal.
(7) The notch or groove on top of piston must be
pointing toward front of engine. The larger chamfer
of the connecting rod bore must be installed toward
crankshaft journal fillet.
(8) Install rod caps. Be sure connecting rod, con
necting rod cap and cylinder bore number are the same. Install nuts on cleaned and oiled rod bolts and
tighten nuts to 61 N»m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the oil pan. (10) Install the cylinder head.
(11) Install the engine into the vehicle.
CRANKSHAFT
A crankshaft which has undersize journals will be
stamped with 1/4 inch letters near the notch of the
No.6 crankshaft counterweight (Fig. 15). FOR EXAMPLE:R2 stamped on the No.6 crank
shaft counterweight indicates that the No.2 rod jour
nal is 0.025 mm (0.001 in) undersize. M4 indicates
that the No.4 main journal is 0.025 mm (0.001 in) undersize. R3 M2 indicates that the No.3 rod journal
and the No.2 main journal are 0.025 mm (0.001 in) undersize.
Undersize
Journal Identification
Stamp
ROD
-
0.025mm
(0.001
in.)
Rl-R2-R3-Etc.
MAIN -
0.025mm
(0.001
in.)
M1-M2-M3
or M4
STEEL
STAMP
IDENTIFICATION
R
(ROD)
AND/OR
M
(MAIN)
FOLLOWED
BY THE ROD
OR
MAIN
NUMBER
Fig.
15 Location of Crankshaft
Identification
When a crankshaft is replaced, all main and con
necting rod bearings should be replaced with new
bearings. Therefore, selective fitting of the bearings is not required when a crankshaft and bearings are
replaced.
REMOVAL (1) Remove the oil pan.
Page 644 of 1502
•
3.9L
ENGINE
9 - 39 (2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear
ing cap.
(8)
Identify bearing caps before removal. Remove
bearing caps and bearings one at a time.
(4) Lift the crankshaft out of the block.
(5) Remove and discard the crankshaft rear oil
seals.
(6)
Remove and discard the front crankshaft oil
seal.
INSPECTION OF JOURNALS The crankshaft connecting rod and main journals
should be checked for excessive wear, taper and scor
ing. The maximum taper or out-of-round on any
crankshaft journal is 0.025 mm (0.001 inch).
Journal grinding should not exceed 0.305 mm
(0.012 inch) under the standard journal diameter. DO
NOT grind thrust faces of No.3 main bearing. DO
NOT nick crank pin or bearing fillets. After grind
ing, remove rough edges from crankshaft oil holes and clean out all oil passages.
CAUTION:
After any journal
grind,
it is important
that
the
final
paper or cloth
polish
be in the
same
direction as the engine rotates.
INSTALLATION (1) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil.
(2) Install the new upper rear bearing oil seal with
the yellow paint facing towards the rear of the en
gine.
(3) Position the crankshaft into the cylinder block.
(4) Lightly oil the new lower seal lips with engine
oil.
(5) Install the new lower rear bearing oil seal into
the bearing cap with the yellow paint facing towards the rear of the engine.
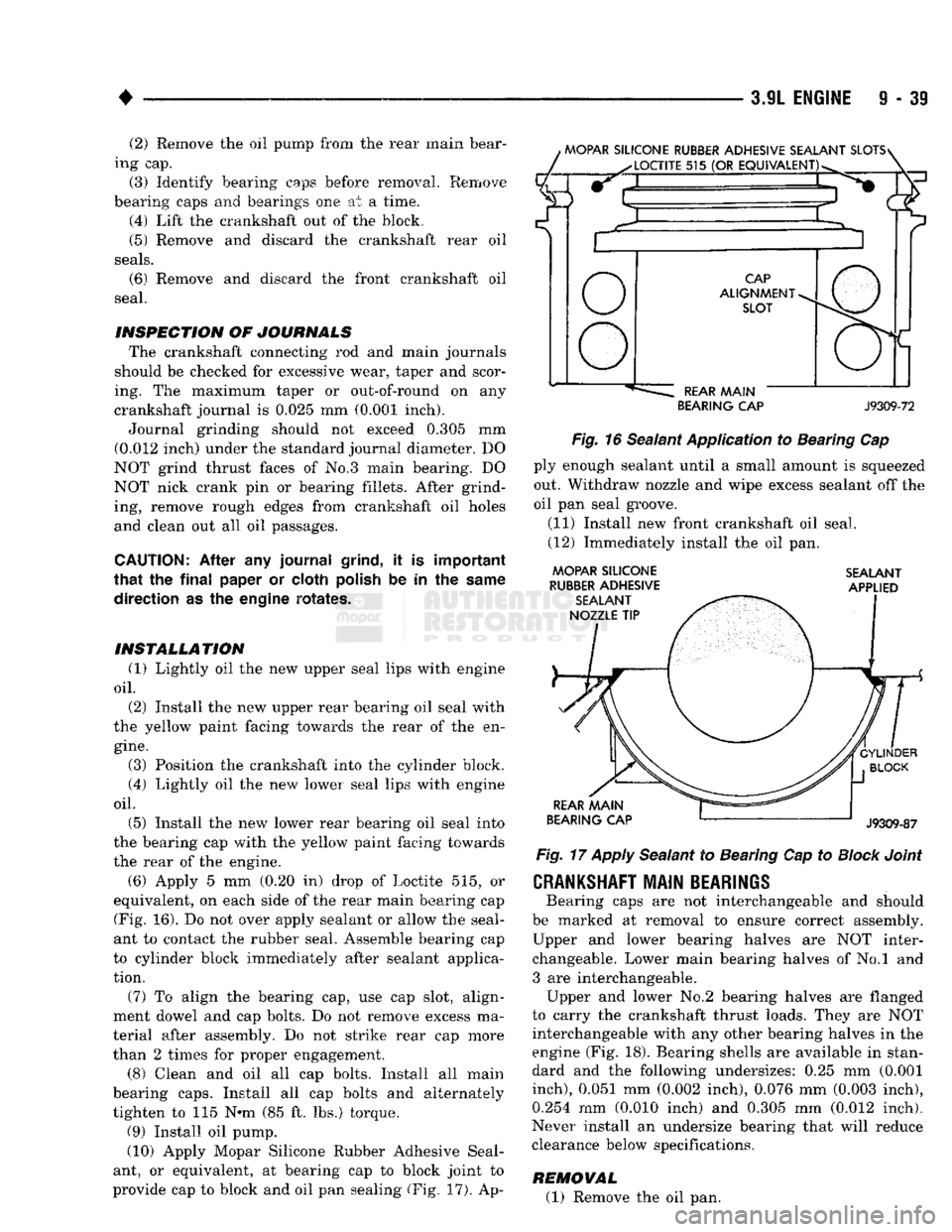
(6) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in) drop of Loctite 515, or
equivalent, on each side of the rear main bearing cap (Fig. 16). Do not over apply sealant or allow the seal
ant to contact the rubber seal. Assemble bearing cap
to cylinder block immediately after sealant applica tion.
(7) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align
ment dowel and cap bolts. Do not remove excess ma
terial after assembly. Do not strike rear cap more
than 2 times for proper engagement.
(8) Clean and oil all cap bolts. Install all main
bearing caps. Install all cap bolts and alternately
tighten to 115 N»m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9)
Install oil pump.
(10) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal
ant, or equivalent, at bearing cap to block joint to
provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig. 17). Ap-
BEARING CAP
J9309-72
Fig.
16 Sealant Application to Bearing Cap ply enough sealant until a small amount is squeezed
out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess sealant off the
oil pan seal groove.
(11) Install new front crankshaft oil seal. (12) Immediately install the oil pan.
MOPAR SILICONE SEALANT
RUBBER
ADHESIVE APPLIED
Fig.
17
Apply
Sealant to Bearing Cap to
Block
Joint
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
Bearing caps are not interchangeable and should
be marked at removal to ensure correct assembly.
Upper and lower bearing halves are NOT inter changeable. Lower main bearing halves of No.l and
3 are interchangeable. Upper and lower No.2 bearing halves are flanged
to carry the crankshaft thrust loads. They are NOT interchangeable with any other bearing halves in the
engine (Fig. 18). Bearing shells are available in stan
dard and the following undersizes: 0.25 mm (0.001
inch),
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), 0.076 mm (0.003 inch),
0.254 mm (0.010 inch) and 0.305 mm (0.012 inch).
Never install an undersize bearing that will reduce
clearance below specifications.
REMOVAL (1) Remove the oil pan.
Page 645 of 1502
S
- 40 3.9L
ENGINE
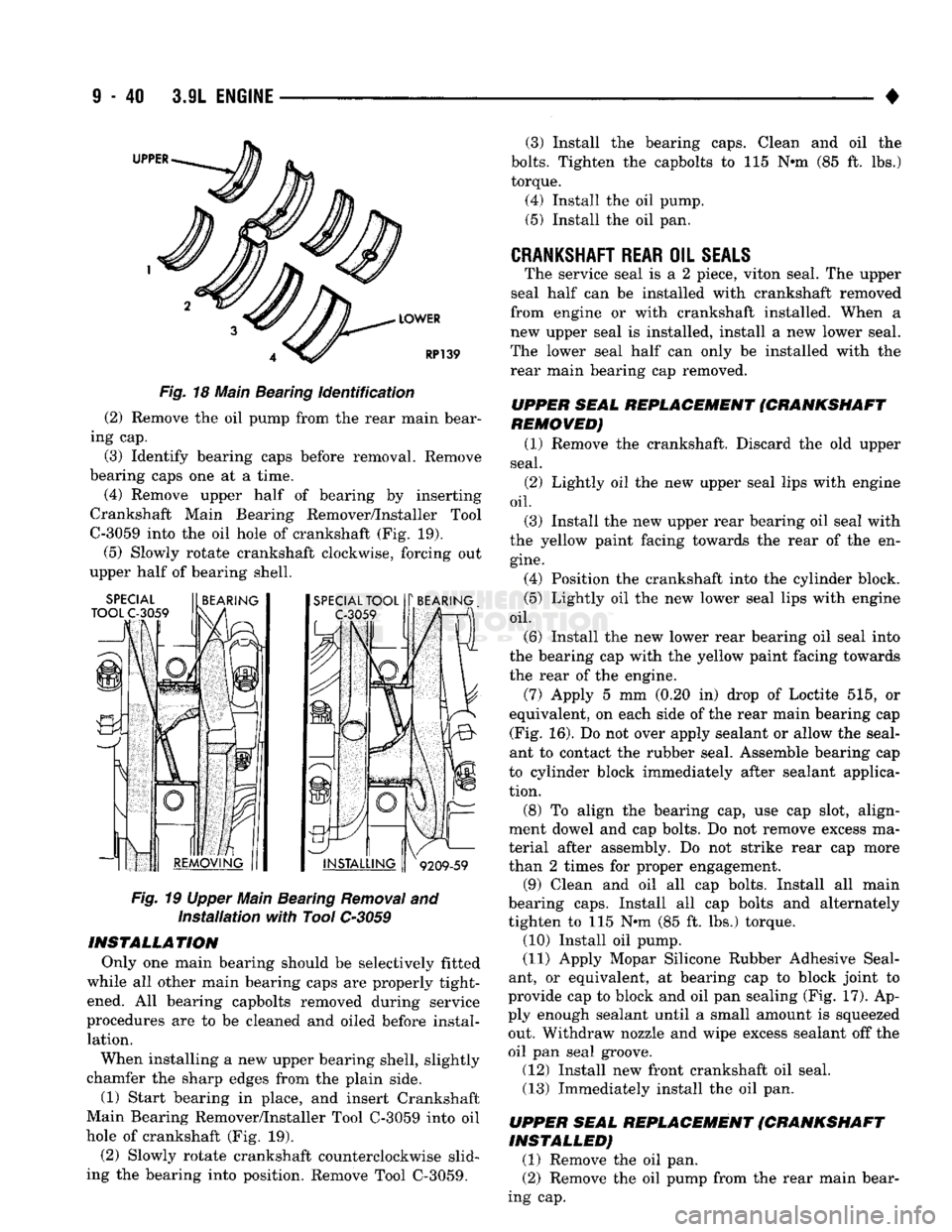
39 Fig.
18 Main Bearing identification
(2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear
ing cap.
(3) Identify bearing caps before removal. Remove
bearing caps one at a time.
(4) Remove upper half of bearing by inserting
Crankshaft Main Bearing Remover/Installer Tool
C-3059 into the oil hole of crankshaft (Fig. 19).
(5)
Slowly rotate crankshaft clockwise, forcing out
upper half of bearing shell.
Fig.
19 Upper Main Bearing Removal and installation with Tool
C-3059
INSTALLATION Only one main bearing should be selectively fitted
while all other main bearing caps are properly tight ened. All bearing capbolts removed during service
procedures are to be cleaned and oiled before instal lation.
When installing a new upper bearing shell, slightly
chamfer the sharp edges from the plain side.
(1) Start bearing in place, and insert Crankshaft
Main Bearing Remover/Installer Tool C-3059 into oil
hole of crankshaft (Fig. 19).
(2) Slowly rotate crankshaft counterclockwise slid
ing the bearing into position. Remove Tool C-3059. (3) Install the bearing caps. Clean and oil the
bolts.
Tighten the capbolts to 115 N*m (85 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install the oil pump. (5) Install the oil pan.
CRANKSHAFT REAR
OIL
SEALS
The service seal is a 2 piece, viton seal. The upper
seal half can be installed with crankshaft removed
from engine or with crankshaft installed. When a
new upper seal is installed, install a new lower seal.
The lower seal half can only be installed with the
rear main bearing cap removed.
UPPER SEAL REPLACEMENT (CRANKSHAFT
REMOVED)
(1) Remove the crankshaft. Discard the old upper
seal.
(2) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil.
(3) Install the new upper rear bearing oil seal with
the yellow paint facing towards the rear of the en
gine.
(4) Position the crankshaft into the cylinder block.
(5) Lightly oil the new lower seal lips with engine
oil.
(6) Install the new lower rear bearing oil seal into
the bearing cap with the yellow paint facing towards the rear of the engine.
(7) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in) drop of Loctite 515, or
equivalent, on each side of the rear main bearing cap (Fig. 16). Do not over apply sealant or allow the seal
ant to contact the rubber seal. Assemble bearing cap
to cylinder block immediately after sealant applica
tion.
(8) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align
ment dowel and cap bolts. Do not remove excess ma
terial after assembly. Do not strike rear cap more
than 2 times for proper engagement. (9) Clean and oil all cap bolts. Install all main
bearing caps. Install all cap bolts and alternately
tighten to 115 N*m (85 ft. lbs.) torque. (10) Install oil pump.
(11) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal
ant, or equivalent, at bearing cap to block joint to
provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig. 17). Ap
ply enough sealant until a small amount is squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess sealant off the
oil pan seal groove. (12) Install new front crankshaft oil seal.
(13) Immediately install the oil pan.
UPPER SEAL REPLACEMENT (CRANKSHAFT
INSTALLED)
(1) Remove the oil pan. (2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear
ing cap.
Page 646 of 1502

•
3.9L ENGINE
9 - 41 (3) Remove the rear main bearing cap. Remove
and discard the old lower oil seal.
(4) Carefully remove and discard the old upper oil
seal.
(5) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil.
To allow ease of installation of the seal, loosen at
least the 2 main bearing caps forward of the rear
bearing cap.
(6) Rotate the new upper seal into the cylinder
block being careful not to shave or cut the outer sur face of the seal. To assure proper installation, use the installation tool provided with the kit. Install the
new seal with the yellow paint facing towards the
rear of the engine.
(7) Install the new lower rear bearing oil seal into
the bearing cap with the yellow paint facing towards
the rear of the engine.
(8) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in) drop of Loctite 515, or
equivalent, on each side of the rear main bearing cap (Fig. 16). Do not over apply sealant or allow the seal
ant to contact the rubber seal. Assemble bearing cap
to cylinder block immediately after sealant applica
tion. Be sure the yellow paint faces toward the rear of the engine.
(9) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align
ment dowel and cap bolts. Do not remove excess ma
terial after assembly. Do not strike rear cap more
than 2 times for proper engagement.
(10) Install the rear main bearing cap with cleaned
and oiled cap bolts. Alternately tighten ALL cap
bolts to 115 N-m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Install oil pump.
(12) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal
ant, or equivalent, at bearing cap to block joint to
provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig. 17). Ap
ply enough sealant until a small amount is squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess sealant off the
oil pan seal groove.
(13) Immediately install the oil pan.
LOWER SEAL REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the oil pan.
(2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear
ing cap.
(3) Remove the rear main bearing cap and discard
the old lower seal.
(4) Carefully install a new upper seal (refer to Up
per Seal Replacement - Crankshaft Installed proce dure above).
(5) Lightly oil the new lower seal lips with engine
oil.
(6) Install a new lower seal in bearing cap with
yellow paint facing the rear of engine. (7) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in) drop of Loctite 515, or
equivalent, on each side of the rear main bearing cap (Fig. 16). Do not over apply sealant or allow the seal ant to contact the rubber seal. Assemble bearing cap
to cylinder block immediately after sealant applica tion.
(8) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align
ment dowel and cap bolts. Do not remove excess ma
terial after assembly. Do not strike rear cap more
than 2 times for proper engagement.
(9) Install the rear main bearing cap with cleaned
and oiled cap bolts. Alternately tighten the cap bolts
to 115 Nnn (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Install oil pump.
(11) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal
ant, or equivalent, at bearing cap to block joint to
provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig. 17). Ap
ply enough sealant until a small amount is squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess sealant off the
oil pan seal groove.
(12) Immediately install the oil pan.
CYLINDER
BLOCK
Remove the engine assembly from the vehicle.
DISASSEMBLE
(1) Remove the cylinder head. (2) Remove the oil pan.
(3) Remove the piston/connecting rod assembly.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all core
hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
INSPECTION
Examine block for cracks or fractures.
The cylinder walls should be checked for
out-of-
round and taper with Cylinder Bore Indicator Tool C-119. The cylinder block should be bored and honed
with new pistons and rings fitted if:
• The cylinder bores show more than 0.127 mm (0.005 inch) out-of-round.
• The cylinder bores show a taper of more than 0.254 mm (0.010 inch).
• The cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored. Boring and honing operation should be closely co
ordinated with the fitting of pistons and rings so specified clearances may be maintained.
Refer to Standard Service Procedures in the begin
ning of this Group for the proper honing of cylinder
bores.
OIL LINE PLUG
The oil line plug is located in the vertical passage
at the rear of the block between the Oil-To-Filter and
Oil-From-Filter passages (Fig. 20). Improper installa
tion or plug missing could cause erratic, low or no oil pressure.
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit from back of
block.
Page 647 of 1502
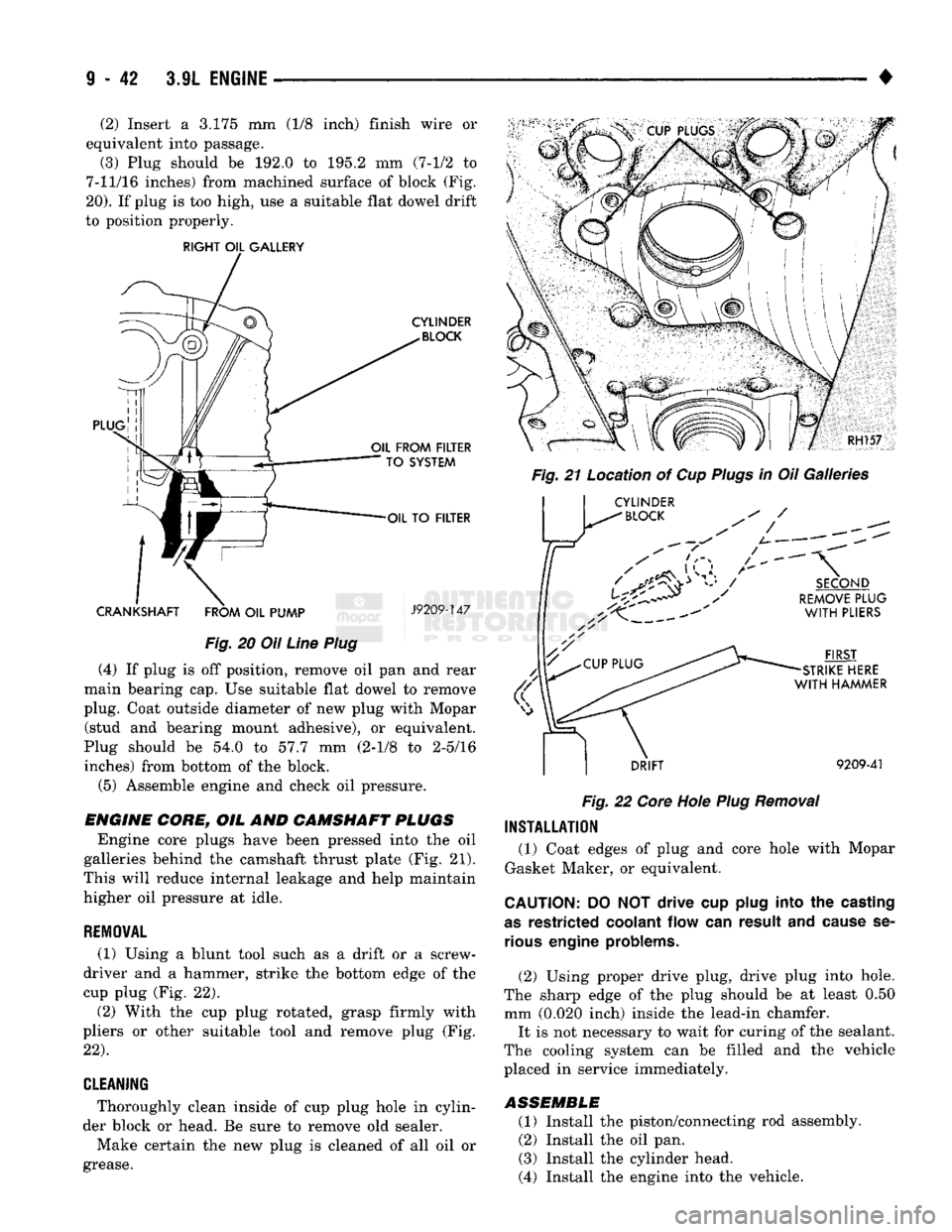
(2) Insert a 3.175 mm (1/8 inch) finish wire or
equivalent into passage.
(3) Plug should be 192.0 to 195.2 mm (7-1/2 to
7-11/16 inches) from machined surface of block (Fig.
20).
If plug is too high, use a suitable flat dowel drift
to position properly.
RIGHT
OIL
GALLERY
CYLINDER
BLOCK
PLUG
OIL
FROM
FILTER
TO
SYSTEM
OIL
TO
FILTER
CRANKSHAFT
FROM
OIL
PUMP
J9209-147
Fig.
20 Oil
Line
Plug
(4) If plug is off position, remove oil pan and rear
main bearing cap. Use suitable flat dowel to remove
plug. Coat outside diameter of new plug with Mopar (stud and bearing mount adhesive), or equivalent.
Plug should be 54.0 to 57.7 mm (2-1/8 to 2-5/16 inches) from bottom of the block.
(5) Assemble engine and check oil pressure.
ENGINE
CORE,
OIL AND
CAMSHAFT
PLUGS
Engine core plugs have been pressed into the oil
galleries behind the camshaft thrust plate (Fig. 21).
This will reduce internal leakage and help maintain
higher oil pressure at idle.
REMOWAL
(1) Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screw
driver and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the
cup plug (Fig. 22).
(2) With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly with
pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug (Fig.
22).
CLEANING
* Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Make certain the new plug is cleaned of all oil or
grease. RH157
Fig.
21 Location of Cup
Plugs
in Oil Galleries Jr
CYLINDER
^
BLOCK
/
SECOND
REMOVE
PLUG
WITH
PLIERS
FIRST
STRIKE
HERE
WITH
HAMMER
DRIFT
9209-41
Fig.
22
Core
Hole
Plug
Removal
INSTALLATION
(1) Coat edges of plug and core hole with Mopar
Gasket Maker, or equivalent.
CAUTION:
DO NOT drive cup
plug
into the
casting
as
restricted
coolant
flow can result and
cause
se
rious
engine
problems.
(2) Using proper drive plug, drive plug into hole.
The sharp edge of the plug should be at least 0.50 mm (0.020 inch) inside the lead-in chamfer. It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be filled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
ASSEMBLE
(1) Install the piston/connecting rod assembly.
(2) Install the oil pan.
(3) Install the cylinder head.
(4) Install the engine into the vehicle.
Page 648 of 1502

SPECIFICATIONS—3.9L
ENGINE
ENGINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Camshaft Bearing
Diameter
No.
1 50.800-50.825 mm
(2.000-2.001
in)
No.
2... 50.394-50.419 mm (1.984-1.985 in)
No.
3 49.606-49.632 mm (1.953-1.954 in)
No.
4 39.688-39.713 mm (1.5625-1.5635 in)
Diametrical
Clearance 0.0254-0.0762 mm (0.001-0.003 in)
Max. Allowable 0.127 mm (0.005 in)
End
Play 0.051-0.254 mm (0.002-0.010 in)
Bearing Journal
Diameter
No.
1.... 50.749-50.775 mm (1.998-1.999 in)
No.
2 50.343-50.368 mm
(1.982-1.983
in)
No.
3 49.555-49.581 mm
(1.951-1.952
in)
No.
4 .... 39.637-39.662 mm (1.5605-1.5615 in)
Connecting
Rods
Bearing Clearance 0.0127-0.0559 mm (0.0005-0.0022 in)
Piston Pin Bore
Diameter
24.940-24.978 mm (0.9819-0.9834 in)
Side
Clearance (Two
Rods)
0.152-0.356 mm (0.006-0.014 in)
Total
Weight
(Less
Bearing) 726 grams
(25.61 oz)
Crankshaft
Connect Rod Journal
Diameter
53.950-53.975 mm
(2.124-2.125 in)
Out-of-Round (Max.) . 0.0254 mm (0.001 in)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in)
Diametrical
Clearance
No.
1 0.0127-0.0381 mm (0.0005-0.0015 in)
Nos.
2, 3, and 4 0.0127-0.0508 mm (0.0005-0.0020 in)
Max. Allowable (Nos. 2, 3, & 4) . . . 0.0635 mm
(0.0025 in)
End
Play 0.051-0.178 mm
(0.002-0.007 in)
Max. Allowable . 0.254 mm (0.010 in)
Main Bearing Journals
Diameter
63.487-63.513 mm (2.4995-2.5005 in)
Out-of-Round (Max.) . 0.0254 mm (0.001 in)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in)
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore
Diameter
. 99.314-99.365 mm (3.910-3.912 in)
Out-of-Round (Max.) 0.127 mm (0.005 in)
Taper (Max.) . 0.254 mm (0.010 in)
Oversize (Max.) . 1.016 mm (0.040 in)
Distributor Lower Drive Shaft
Bushing
(Press Fit in Block) .... 0.0127-0.3556 mm (0.0005-0.0140 in)
Shaft-to-Bushing Clearance 0.0178-0.0686 mm (0.0007-0.0027 in)
Tappet Bore
Diameter
22.99-23.01 mm (0.9051-0.9059 in)
Cylinder Head
Compression
Pressure 689 kPa (100 psi)
Gasket Thickness (Compressed) 1.2065 mm (0.0475 in)
Valve Seat
Angle
44.25° - 44.75° Runout (Max.) 0.0762 mm (0.003 in)
Width (Finish) -
Intake
1.016-1.542mm (0.040-0.060 in)
Width (Finish) - Exhaust. 1.524-2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 in)
Hydraulic Tappets
Body
Diameter
. . 22.949-22.962 mm
(0.9035-0.9040 in)
Clearance in Block. . 0.0279-0.0610 mm (0.0011-0.0024 in)
Dry
Lash
1.524-5.334 mm (0.060-0.210 in)
Push
Rod Length 172.57-173.08 mm (6.794-6.814 in)
J9309-96
Page 649 of 1502

ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS (CONT.f
Oil
Pump
Clearance
Over
Rotors
(Max.).....
0.1016
mm (0.004 in)
Cover
Out-of-Flat
(Max.)
0.0381 mm (0.0015 in)
Inner
Rotor
Thickness
(Min.) ...... 20.955 mm (0.825 in)
Outer
Rotor
Clearance
(Max.)
0.3556 mm (0.014 in)
Diameter
(Min.) 62.7126 mm (2.469 in)
Thickness
(Min.) . . ........ 20.955 mm
(0.825 in)
Tip
Clearance
Between
Rotors
(Max).
. 0.2032 mm
(0.008 in)
Oil
Pressure
At
Curb
Idle
Speed*
41.4 kPa
(6 psi)
At
3000 rpm 207-552 kPa
(30-80 psi)
Oil
Pressure
Switch
Actuating
Pressure
(Min.) ... 34.5-48.3 kPa (5-7 psi)
*CAUTION:
If
pressure
is
ZERO
at
curb
idle,
DO
NOT run
engine
at
3,000
rpm.
Oil
Filter
Bypass
Valve
Setting
. 62-103 kPa (9-15 psi)
Pistons
Clearance
at
Top
of
Skirt
0.0127-0.0381 mm
(0.0005-0.0015 in)
Land
Clearance
(Diametrical) 0.635-1.016 mm (0.025-0.040 in)
Piston
Length
86.360 mm (3.40 in)
Piston
Ring
Groove
Depth
Nos.
1 and 2 4.572-4.826 mm (0.180-0.190 in)
No.
3 3.810-4.064 mm (0.150-0.160 in)
Weight
592.6-596.6
grams
(20.90-21.04
oz)
Piston
Pins
Clearance
In
Piston
0.00635-0.01905 mm (0.00025-0.00075 in)
In
Rod
(Interference) 0.0178-0.0356 mm (0.0007-0.0014 in)
Diameter.
24.996-25.001 mm (0.9841-0.9843 in)
End
Play..
NONE
Length
75.946-76.454 mm (2.990-3.010 in)
Piston
Rings
Ring
Gap
Compression
Rings
0.254-0.508 mm (0.010-0.020 in)
Oil
Control
(Steel
Rails)
0.254-1.270 mm (0.010-0.050 in)
Ring
Side
Clearance
Compression
Rings
0.038-0.076 mm
(0.0015-0.0030 in)
Oil
Ring
(Steel
Rails)
0.06-0.21
mm
(0.002-0.008 in)
Ring
Width
Compression
Rings
1.971-1.989 mm
(0.0776-0.0783 in)
Oil
Ring
(Steel
Rails)
3.848-3.975 mm (0.1515-0.1565 in)
Valves
Face
Angle
43.25° - 43.75°
Head
Diameter
Intake
48.666 mm (1.916 in)
Exhaust
41.250 mm (1.624 in)
Length
(Overall)
Intake
124.28-125.92 mm (4.893-4.918 in)
Exhaust
124.64-125.27 mm (4.907-4.932 in)
Lift
(Zero
Lash)
10.973 mm (0.432 in)
Stem
Diameter 7.899-7.925 mm (0.311-0.312 in)
Stem-to-Guide
Clearance
0.0254-0.0762 mm
(0.001-0.003 in)
Max.
Allowable
(Rocking
Method).
. 0.4318 mm (0.017 in)
Guide
Bore
Diameter (Std) 7.950-7.976 mm (0.313-0.314 in)
J9309-32
Page 650 of 1502
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
(CONT.)
Valve
Springs
Free
Length (Approx.)
49.962
mm
(1.967
in)
Spring
Tension @ 41.66 mm = 378 N (Valve Closed) (@ 1.64 in = 85 lbs)
Spring
Tension @ 30.89 mm = 890 N (Valve Open) (@ 1.212 in = 200 lbs)
Number of
Coils
6.8
Installed Height. 41.66 mm
(Spring
Seat to Retainer) (1.64 in)
Wire Diameter 4.50 mm (0.177 in) Valve Timing
Exhaust
Valve
Closes
(ATC) 16°
Opens
(BBC) 52°
Duration
248°
Intake
Valve
Closes
(ABC) 50°
Opens
(BTC) . . 10°
Duration
240°
Valve Overlap 26°
J9309-33
OVERSIZE AND UNDERSIZE ENGINE COMPONENT MARKINGS
CONDITION
IDENTIFICATION
LOCATION
OF IDENTIFICATION
CRANKSHAFT
JOURNALS
(UNDERSIZE)
0.0254
mm
(0.001
in.)
RorM
M-2-3 etc. (indicating no. 2 and 3 main bearing
journal)
and/or R-l-4 etc. (indicating no. 1 and 4 connecting rod
journal)
Steel stamped (near notch) on no. 6 crankshaft
counterweight.
HYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
(OVERSIZE)
0.2032
mm
(0.008
in.)
Diamond-shaped
stamp
Top
pad -
front
of engine and
flat
ground on outside surface of each O/S
tappet
bore.
VALVE
STEMS
(OVERSIZE)
0.127 mm
(0.005
in.)
X
Milled pad adjacent to two tapped holes
(3/8 in.) on each end of cylinder head.
J9309-81