torque ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3612 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–4
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with greater
ease.
1.2 Components
Starting System Components
The main components of the starting system are:
• battery,
• wiring,
• ignition switch,
• theft deterrent engine crank inhibitor (a function of the theft deterrent system),
• park / neutral and back-up switch (on vehicles with 4 speed automatic transmission),
• engine control module (ECM),
• start relay,
• solenoid switch, and
• starter motor.
Starter Motor and Solenoid Switch Components
Solenoid Switch
The solenoid switch is used to activate the DC motor and has two windings; the pull-in winding and the hold-in winding.
The pull-in winding has heavier wire and is grounded through the DC motor winding and brushes. The hold-in winding is
grounded through the solenoid casing.
Planetary Drive Train
The planetary drive train consists of an internally toothed ring gear and three planetary gear wheels, which rotate on
sleeve bearings on the planetary drive shaft. The ring gear is keyed into the drive-end housing and is made from
high-grade polyamide with mineral additives.
W hen the starter motor operates, the armature turns the planetary gears inside the fixed planetary ring gear. This drives
the planetary shaft at a reduced speed ratio which turns the drive assembly. A fork lever in the drive-end housing forces
the drive assembly forward to engage with the flexplate / flywheel ring gear on the engine and transmit cranking torque.
An internal clutch allows the drive assembly pinion gear to rotate freely when the engine starts. This prevents the
armature from being driven at excessive speed by the engine.
Armature
The armature shaft is supported at each end by oil absorbent, sintered metal bushes; one in the commutator end shield
and one in the planetary drive shaft. The front end of the armature has a gear profile. This meshes with the three
planetary gear wheels. These in turn, mesh with the internal teeth of the ring gear.
Brushes
A brush plate supports four commutator brushes. This plate is fixed to the commutator end shield with two retaining
screws. Two negative brushes are grounded to the pole housing. The two positive brushes are insulated from the pole
housing and connected to the solenoid switch M terminal, refer to Figure 6D1-2 – 1.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3614 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–6
Sequence of Operation
1 W hen the ignition switch is turned to the START position, a signal is also sent to the ECM to request the engine to
crank.
• For automatic vehicles the transmission must be in either park (P) or neutral (N) for the ECM to allow
cranking to commence.
• The ECM will only allow cranking if the battery voltage is above the minimum battery voltage threshold value,
refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for further information.
2 The ECM operates the start relay which provides power to the pull-in winding of the start solenoid.
3 Current flow to the pull-in winding develops powerful magnetism which pulls in the solenoid switch plunger.
4 The plunger closes the switch contacts connecting battery voltage to the DC motor and pivots the fork lever to engage the drive assembly to the flexplate / flywheel ring gear. Closing the solenoid switch contacts deactivates the
pull-in winding, the hold-in winding remains active.
5 W ith the solenoid switch contacts closed, current flows from the battery through the DC motor, which rotates the armature at high speed and provides cranking torque.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3629 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–21
10 Unclip the oil level sensor harness from the heat shield
(1).
11 Remove the heat shield attaching screw (2).
12 Remove the lower starter motor attaching bolt (3).
13 Remove the heat shield.
14 Remove the upper starter motor retaining bolt (3).
15 Remove the starter motor from the engine block and lower the starter motor as far as possible to gain
access to the wiring harness connections.
Figure 6D1-2 – 12
16 Remove the wiring harness connector P – 3 (1) from the solenoid switch (2).
17 Remove the flange nut (3) and battery connector P – 4 (4) from the solenoid switch.
18 Remove the starter motor from the vehicle.
Figure 6D1-2 – 13
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the starter motor is the reverse of the removal procedure noting the following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
Solenoid switch connector P – 4 nut (B+)
torque specification ............................................10.0 Nm
Starter motor heat shield lower bolts
torque specification ............................................23.0 Nm
Starter motor heat shield upper screw
torque specification .....................................3.0 – 5.0 Nm
Starter motor mounting bolt
torque specification ............................................45.0 Nm
Knock sensor bolt
torque specification ............................................23.0 Nm
2 Check the starter motor operates correctly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3634 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–26
Reassemble
1 Reassemble the solenoid in the reverse order of the disassembly procedure noting the following points.
Dry all parts thoroughly before assembly,
taking care not to breathe in any vapours.
2 Lightly coat the solenoid switch plunger with 10% molybdenum disulphide grease.
Excess grease can enter the contact chamber
of the solenoid switch and cause contact
problems. Do not use too much grease.
3 Hook the plunger over the fork lever.
4 Insert the return spring into the plunger.
5 Slide solenoid switch over the plunger.
6 Align the solenoid switch with drive-end housing ensuring the solenoid switch terminal P – 4 faces away from the pole housing.
7 Install and tighten the solenoid switch mounting screws.
Solenoid switch mounting screw
torque specification .....................................4.1 – 7.6 Nm
8 W ith the starter motor reassembled, perform a No Load Test, refer to 4.3 Starter Motor Bench Tests.
9 If the starter motor fails the No Load Test specification, replace the starter motor.
4.5 Solenoid Switch Tests
Test the Solenoid Switch
1 Inspect the solenoid switch for any external damage.
2 Replace the solenoid switch if it displays significant damage.
3 Install the return spring and plunger into the solenoid switch.
4 Check the movement of the plunger, as follows: a Depress the plunger fully.
b Release the plunger.
c If the plunger sticks or binds in the switch bore, clean or replace the solenoid switch
assembly as required.
Figure 6D1-2 – 22
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3638 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–30
5 Specifications
Type............................................... Six Pole Permanent Magnet, Four Brush, Planetary Drive
Rotation (Drive-End View) ....................................................................................... Clockwise
Number of Pinion Teeth ........................................................................................................ 1 0
No load:
Minimum RPM .................................................................................................................. 23 70
Maximum Current Draw ............................................................................ 65 A at 12.0 ± 0.1 V
M Terminal Voltage..................................................................................................... 12 ± 1 V
Locked:
Maximum Current (Including Solenoid Switch) ............................................................... 780 A
M Terminal Voltage............................................................................................................. 4 V
Minimum Torque ............................................................................................................ 20 Nm
Solenoid detached:
Pull-in Winding Resistance @ 20°C ................................................................... 0.33 – 0.37 Ω
Hold-in Winding Resistance @ 20°C .................................................................. 0.75 – 0.87 Ω
Pull-in Voltage @ 20°C .......................................................................................... 8 V @ 20 °C
Hold-in Voltage @ 20°C.......................................................................................... 1.7 – 3.0 V
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3639 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–31
6 Torque Wrench Specifications
..................................................................................................................... Nm
Solenoid Switch Mounting Screw ........................................................ 4.1 – 7.6
Solenoid Switch Terminal M Nut ................................................................ 10.0
Solenoid Switch Terminal P – 3 Nut ........................................................... 10.0
Starter Motor Mounting Bolt........................................................................ 45.0
Knock Sensor Bolt ................................................................................ 23.0 Nm
Starter Motor Heat Shield Lower Bolt ................................................... 23.0 Nm
Starter Motor Heat Shield Upper Screw ........................................ 3.0 – 5.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3642 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–2
6 Torque Wrench Specifications............................................................................................................20
7 Special Tools ........................................................................................................................................21
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3649 of 6020
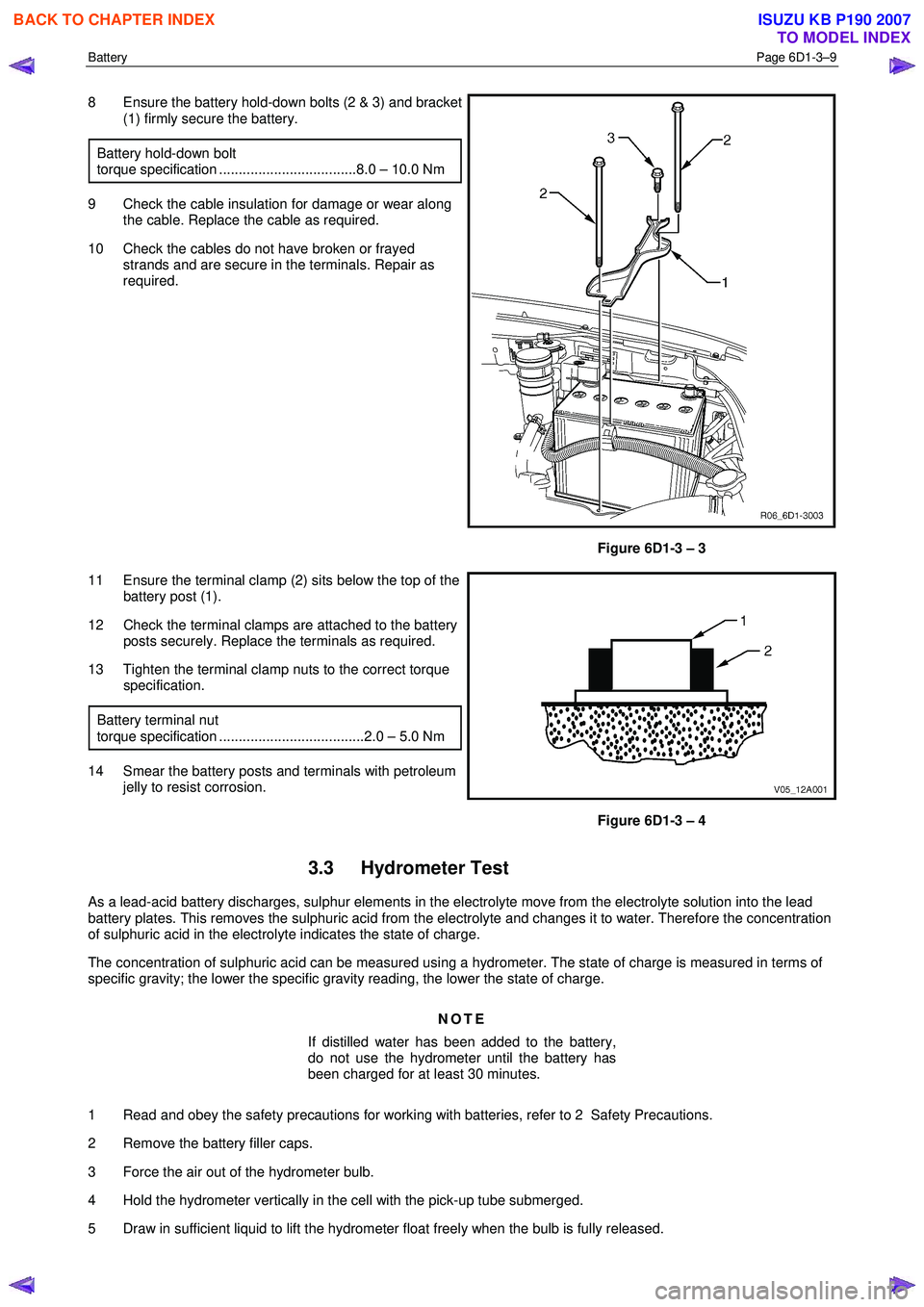
Battery Page 6D1-3–9
8 Ensure the battery hold-down bolts (2 & 3) and bracket
(1) firmly secure the battery.
Battery hold-down bolt
torque specification ...................................8.0 – 10.0 Nm
9 Check the cable insulation for damage or wear along the cable. Replace the cable as required.
10 Check the cables do not have broken or frayed strands and are secure in the terminals. Repair as
required.
Figure 6D1-3 – 3
11 Ensure the terminal clamp (2) sits below the top of the battery post (1).
12 Check the terminal clamps are attached to the battery posts securely. Replace the terminals as required.
13 Tighten the terminal clamp nuts to the correct torque specification.
Battery terminal nut
torque specification .....................................2.0 – 5.0 Nm
14 Smear the battery posts and terminals with petroleum jelly to resist corrosion.
Figure 6D1-3 – 4
3.3 Hydrometer Test
As a lead-acid battery discharges, sulphur elements in the electrolyte move from the electrolyte solution into the lead
battery plates. This removes the sulphuric acid from the electrolyte and changes it to water. Therefore the concentration
of sulphuric acid in the electrolyte indicates the state of charge.
The concentration of sulphuric acid can be measured using a hydrometer. The state of charge is measured in terms of
specific gravity; the lower the specific gravity reading, the lower the state of charge.
NOTE
If distilled water has been added to the battery,
do not use the hydrometer until the battery has
been charged for at least 30 minutes.
1 Read and obey the safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
2 Remove the battery filler caps.
3 Force the air out of the hydrometer bulb.
4 Hold the hydrometer vertically in the cell with the pick-up tube submerged.
5 Draw in sufficient liquid to lift the hydrometer float freely when the bulb is fully released.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3653 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–13
3 W hen the circuit group is determined, install the fuse / circuit breaker and identify the specific circuit within this
group that is drawing the excess current. Disconnect the wiring harness connectors in this circuit group one at a
time. Refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
4 W hen the cause is disconnected, the multimeter reading should drop to the correct reading as outlined in Step 9 of the Test Procedure in this Section.
5 If required, remove the components in this circuit one at a time to determine the cause of the excessive standing current. Refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
6 Repair the fault, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
7 Ensure any fuses, circuit breakers and connectors that have been removed are secure.
Restore
1 Reconnect the electrical earth cable to the battery terminal and tighten the nut to the correct torque specification.
Battery terminal nut
torque specification .....................................2.0 – 5.0 Nm
2 Disconnect the multimeter connections.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3654 of 6020
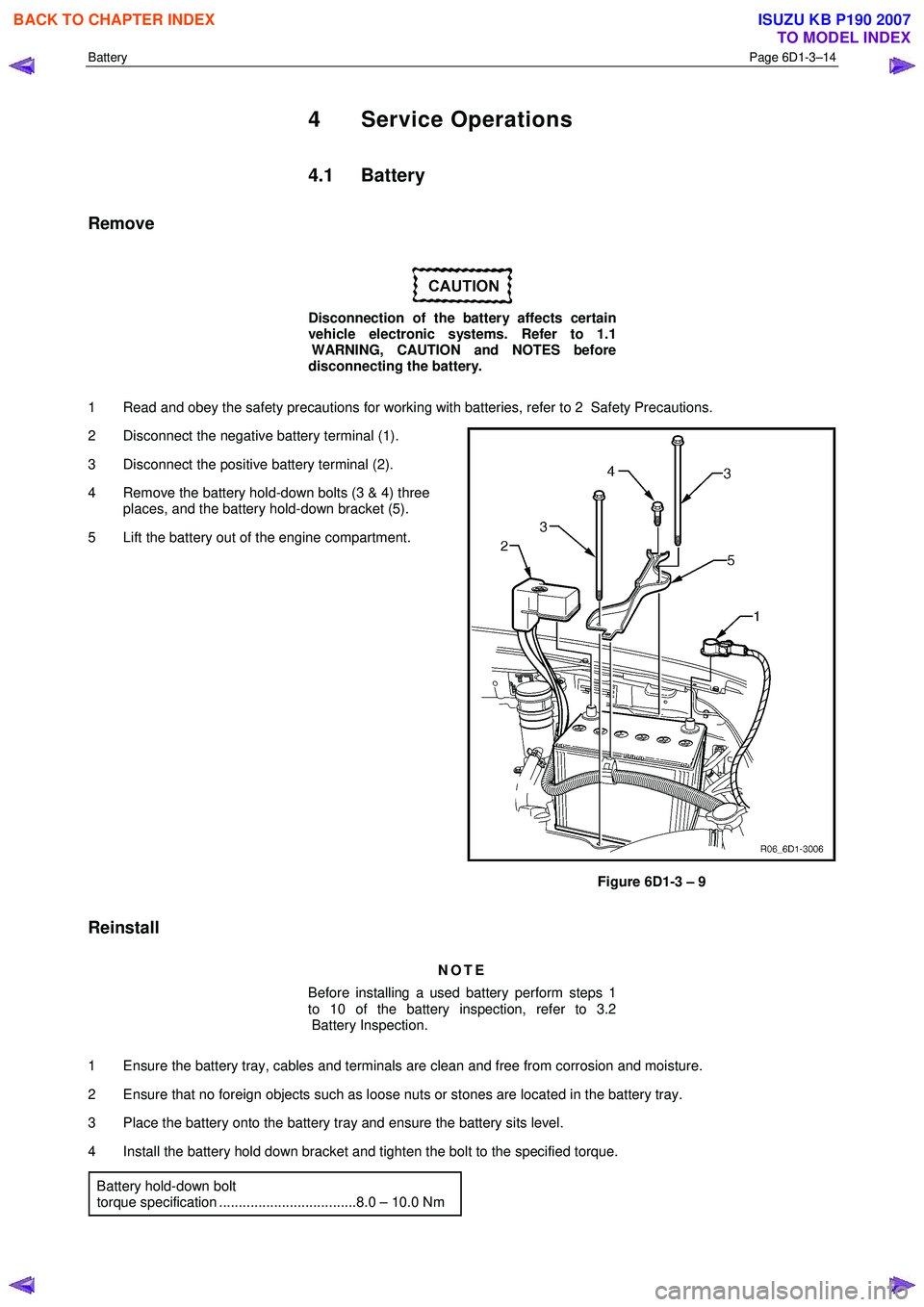
Battery Page 6D1-3–14
4 Service Operations
4.1 Battery
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems. Refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Read and obey the safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
2 Disconnect the negative battery terminal (1).
3 Disconnect the positive battery terminal (2).
4 Remove the battery hold-down bolts (3 & 4) three places, and the battery hold-down bracket (5).
5 Lift the battery out of the engine compartment.
Figure 6D1-3 – 9
Reinstall
NOTE
Before installing a used battery perform steps 1
to 10 of the battery inspection, refer to 3.2
Battery Inspection.
1 Ensure the battery tray, cables and terminals are clean and free from corrosion and moisture.
2 Ensure that no foreign objects such as loose nuts or stones are located in the battery tray.
3 Place the battery onto the battery tray and ensure the battery sits level.
4 Install the battery hold down bracket and tighten the bolt to the specified torque. Battery hold-down bolt
torque specification ...................................8.0 – 10.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007