torque ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3576 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–52
Oil Fouled (3)
W et, oily deposits with minor electrode wear possibly due to oil leaking past worn piston rings.
Breaking in a new or recently overhauled engine before the rings are fully seated may also result in this condition.
Deposit Fouling A (4)
Red brown, yellow and white coloured coatings on the insulator tip which are by-products of combustion. They come
from fuel and lubricating oil which generally contain additives. Most powdery deposits have no adverse effect on spark
plug operation, however, they may cause intermittent missing under severe operating conditions.
Deposit Fouling B (5)
Deposits similar to those identified in deposit fouling A (4). These are also by-products of combustion from fuel and
lubricating oil. Excessive valve stem clearances and / or defective intake valve seals allow too much oil to enter the
combustion chamber. The deposits will accumulate on the portion of the spark plug that projects into the chamber and
will be heaviest on the side facing the intake valve. If this condition is only detected in one or two cylinders, check the
valve stem seals.
Deposit Fouling C (6)
Most powdery deposits identified in deposit fouling A (4) have no adverse effect on the operation of the spark plug as
long as they remain powdery.
Under certain conditions of operation however, these deposits melt and form a shiny glaze coating on the insulator.
W hen hot, this acts as a good electrical conductor allowing the current to flow along the deposit instead of sparking
across the gap.
Detonation (7)
Commonly referred to as engine knock or pinging, detonation causes severe shocks inside the combustion chamber
causing damage to parts.
Pre-ignition (8)
Burnt or blistered insulator tip and badly eroded electrodes probably due to the excessive heat.
This is often caused by a cooling system blockage, sticking valves, improperly installed spark plugs or plugs that are the
wrong heat rating (too hot).
Sustained high speed with a heavy load can produce temperatures high enough to cause pre-ignition.
Heat Shock Failure (9)
A rapid increase in spark plug tip temperature under severe operating conditions can cause heat shock and result in
fractured insulators. This is a common cause of broken and cracked insulator tips.
Insufficient Installation Torque (10)
Poor contact between the spark plug and the cylinder head seat.
The lack of proper heat transfer that results from poor seat contact causes overheating of the spark plug. In many cases,
severe damage occurs. Dirty threads in the cylinder head can cause the plug to seize before it is seated.
Ensure the cylinder head and spark plug threads are free of deposits, burrs and scale before installation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3577 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–53
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the spark plug is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
• Discard the spark plug if it has been
dropped.
• Do not use anti-seize compound or similar
lubricant on the spark plug threads.
1 Using a suitably sized rubber tube attached to the spark plug terminal post, hand start each spark plug into the cylinder head thread.
Failure to tighten a spark plug to the correct
torque specification may result in premature
spark plug failure, and / or engine damage.
2 Tighten the spark plug/s to the correct torque specification. Spark plug torque specification ...............16.0 – 20.0 Nm
3 Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation.
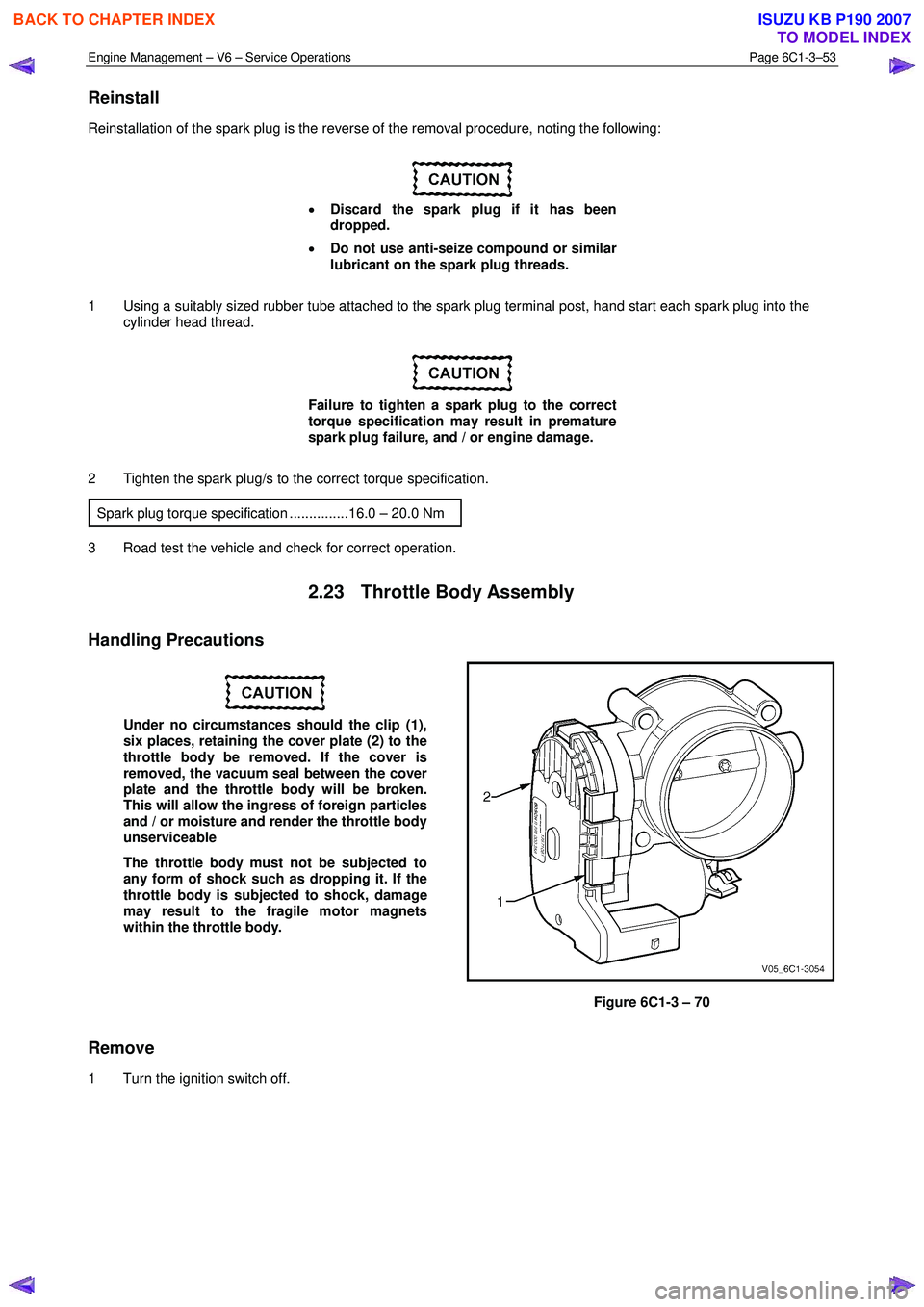
2.23 Throttle Body Assembly
Handling Precautions
Under no circumstances should the clip (1),
six places, retaining the cover plate (2) to the
throttle body be removed. If the cover is
removed, the vacuum seal between the cover
plate and the throttle body will be broken.
This will allow the ingress of foreign particles
and / or moisture and render the throttle body
unserviceable
The throttle body must not be subjected to
any form of shock such as dropping it. If the
throttle body is subjected to shock, damage
may result to the fragile motor magnets
within the throttle body.
Figure 6C1-3 – 70
Remove
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3580 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–56
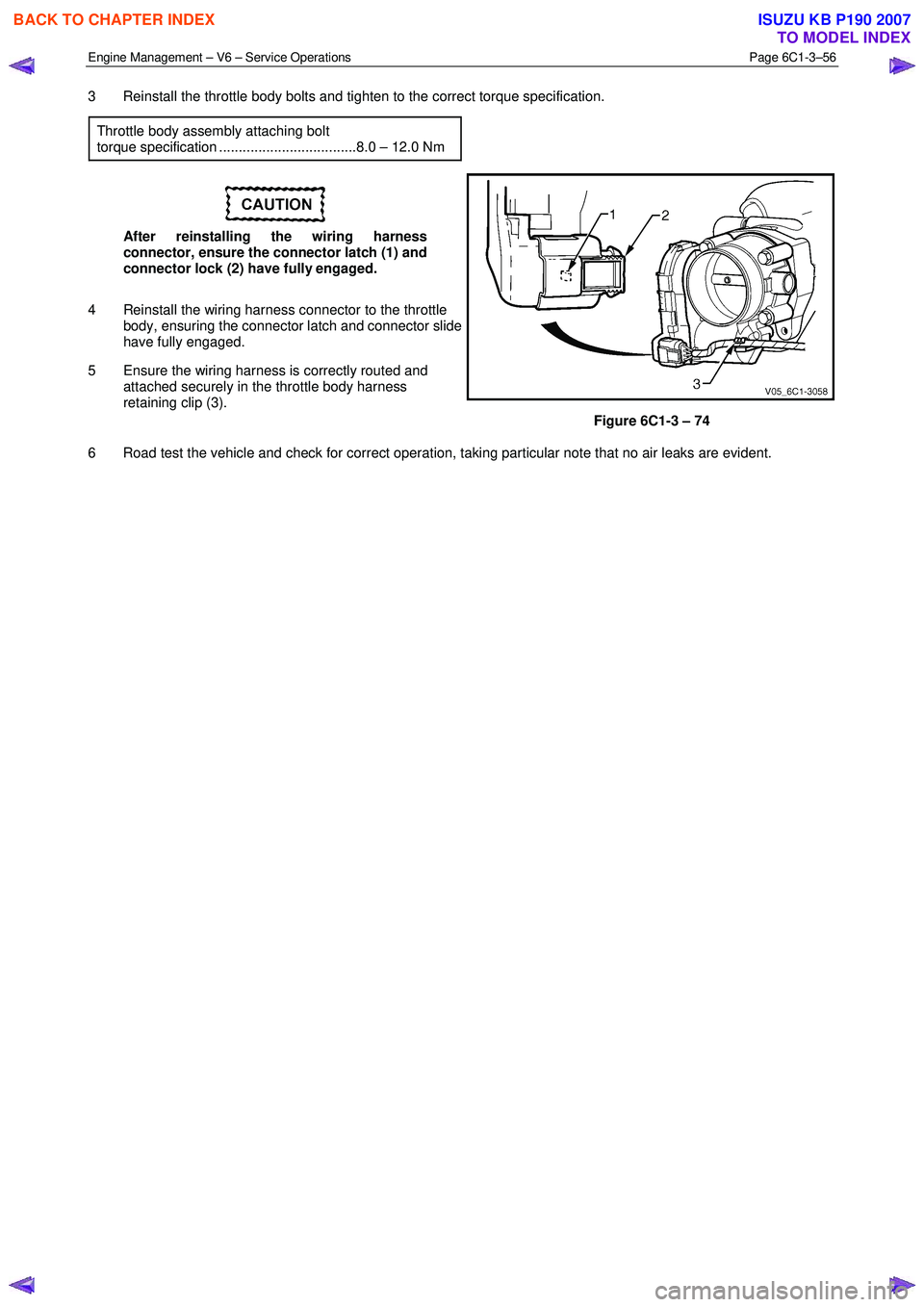
3 Reinstall the throttle body bolts and tighten to the correct torque specification.
Throttle body assembly attaching bolt
torque specification ...................................8.0 – 12.0 Nm
After reinstalling the wiring harness
connector, ensure the connector latch (1) and
connector lock (2) have fully engaged.
4 Reinstall the wiring harness connector to the throttle body, ensuring the connector latch and connector slide
have fully engaged.
5 Ensure the wiring harness is correctly routed and attached securely in the throttle body harness
retaining clip (3).
Figure 6C1-3 – 74
6 Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation, taking particular note that no air leaks are evident.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3585 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–61
5 Torque Specifications
Fuel Rail Attaching Bolt ............................................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Support Bracket
Attaching Nut ............................................................................... 8.5 – 11.5 Nm
Air Cleaner Lower Housing Attaching Bolt................................. 18.0 – 22.0 Nm
Barometric Pressure Sensor Attaching Bolt ................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Camshaft Position Sensor Attaching Bolt .................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Crankshaft Position Sensor Attaching Bolt .................................. 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor ................................................... 22.0 Nm
Engine Control Module Attaching Bolt ......................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Ground Terminal Attaching Screw.......................................................... 4.5 Nm
Engine Control Module Bracket Assembly
Attaching bolt (6mm Bolt) ............................................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Engine Control Module Bracket Assembly
Attaching bolt (8mm Bolt) .......................................................... 20.0 – 25.0 Nm
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor ...................................................... 12.0 – 14.0 Nm
Heated Oxygen Sensor ............................................................. 40.0 – 50.0 Nm
Ignition Coil Attaching Bolt........................................................... 7.0 – 11.0 Nm
Air Intake Duct Retaining Clamp ................................................... 1.5 – 2.5 Nm
Knock Sensor Attaching Bolt ..................................................... 21.0 – 25.0 Nm
Mass Air Flow Sensor Attaching Nut ............................................. 1.8 – 2.2 Nm
Spark Plug ................................................................................. 16.0 – 20.0 Nm
Throttle Body Assembly Attaching Bolt........................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3589 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-2
4.3 Drive Belt Routing................................................................................................................................................ 18
Without Air Conditioning ....................................................................................................... ............................. 18
6 Specifications .......................................................................................................................................19
7 Torque Wrench Specifications................................................................................................... .........20
8 Special Tools ........................................................................................................................................21
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3603 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-16
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the generator is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
2 Reconnect the battery ground lead.
3 Start the engine.
4 Check the generator warning indicator operation.
5 Check the drive belt is correctly routed and aligned.
6 Check the generator output. Refer to 3.3 On-vehicle Testing.
7 Check the voltage regulator operation. Refer to 3.3 On-vehicle Testing.
8 Turn the ignition switch off.
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (1) 58.0 Nm
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (2) 58.0 Nm
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (4) 58.0 Nm
Battery harness to P-9 pin B nut
torque specification ...................................7.1 – 13.3 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3604 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-17
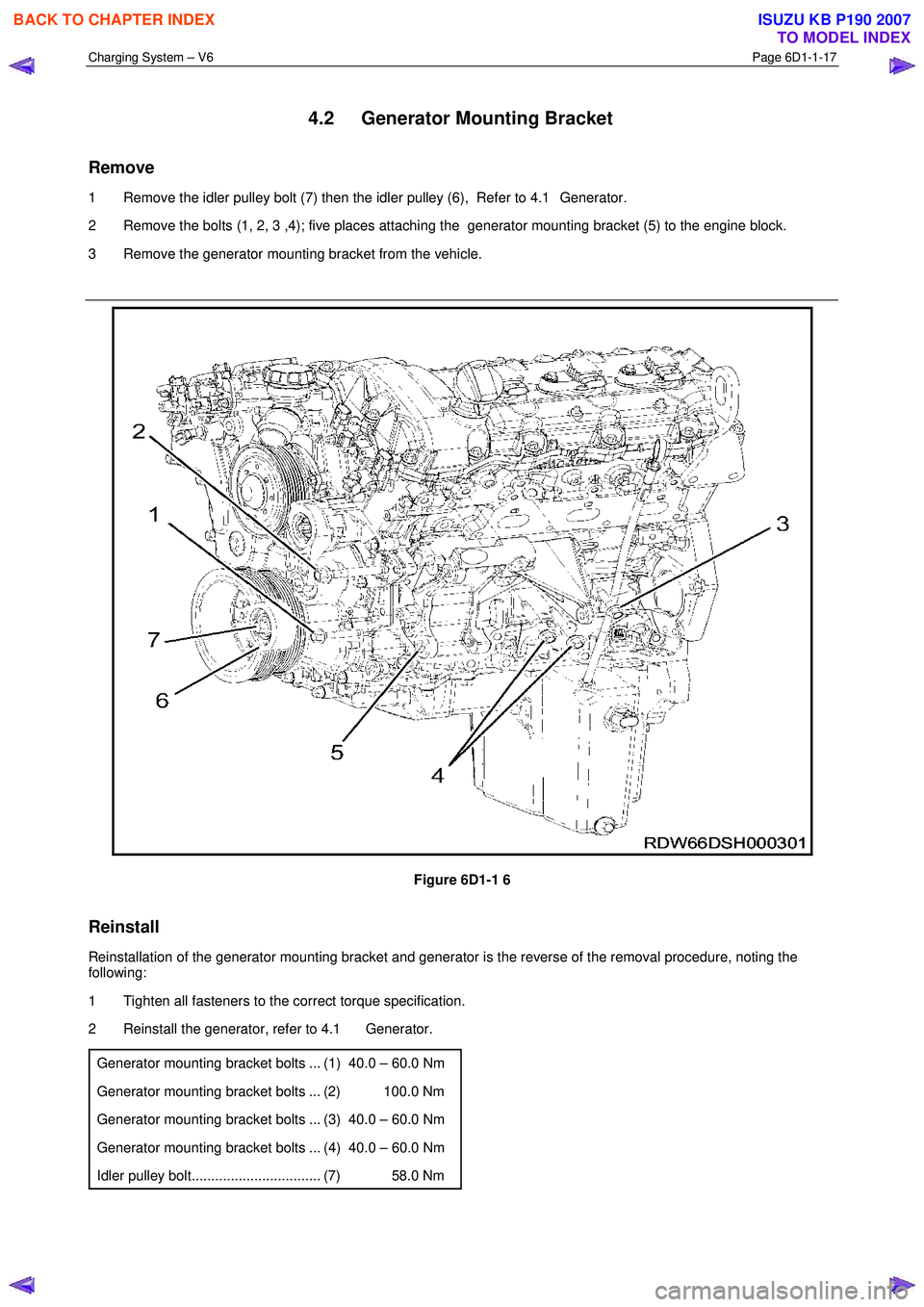
4.2 Generator Mounting Bracket
Remove
1 Remove the idler pulley bolt (7) then the idler pulley (6), Refer to 4.1 Generator.
2 Remove the bolts (1, 2, 3 ,4); five places attaching the generator mounting bracket (5) to the engine block.
3 Remove the generator mounting bracket from the vehicle.
Figure 6D1-1 6
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the generator mounting bracket and generator is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
2 Reinstall the generator, refer to 4.1 Generator.
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (1) 40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (2) 100.0 Nm
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (3) 40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (4) 40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Idler pulley bolt................................. (7) 58.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3607 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-20
7 Torque Wrench Specifications
..................................................................................................................... Nm
Generator Mounting Bolts (1, 2, 4) ..............................................................58.0
Generator Mounting Bracket Bolts (1, 3, 4) ......................................40.0 – 60.0
Generator Mounting Bracket Bolts (2) ...........................................................0.0
Battery Harness to G8 – X1 pin A Nut................................................5.0 – 12.0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3610 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–2
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 21
4.3 Starter Motor Bench Tests ...................................................................................................... ............................ 22
Preliminary Checks.............................................................................................................................................. 22
Pull-in Test............................................................................................................................................................ 22
Hold-in Test ................................................................................................................... ....................................... 23
Drive Assembly Return Test ..................................................................................................... .......................... 23
No Load Test ........................................................................................................................................................ 24
4.4 Starter Motor Disassemble and Reassemble ....................................................................................... ............. 25
Disassemble ......................................................................................................................................................... 25
Reassemble .......................................................................................................................................................... 26
4.5 Solenoid Switch Tests ......................................................................................................................................... 26
Test the Solenoid Switch .................................................................................................................................. 26
5 Specifications .......................................................................................................................................30
6 Torque Wrench Specifications................................................................................................... .........31
7 Special Tools ........................................................................................................................................32
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3611 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–3
1 General Information
All HFV6 engines are fitted with a Mitsubishi starter motor. This consists of a solenoid switch on a DC motor. The motor
has permanent magnet excitation, which has the advantage of low weight a with high output torque and is visually
identifiable by the absence of pole-shoe retaining screws.
The starter motor does not have field coil windings or pole shoes. These parts have been replaced by six permanent
magnets that are held in the pole housing by clips. The positive brushes are now part of the brush plate assembly.
The solenoid switch is the only component of the starter motor assembly that is serviced separately. If any other parts
require replacement, the starter motor must be replaced.
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007