body JAGUAR X308 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1998, Model line: X308, Model: JAGUAR X308 1998 2.GPages: 2490, PDF Size: 69.81 MB
Page 1064 of 2490
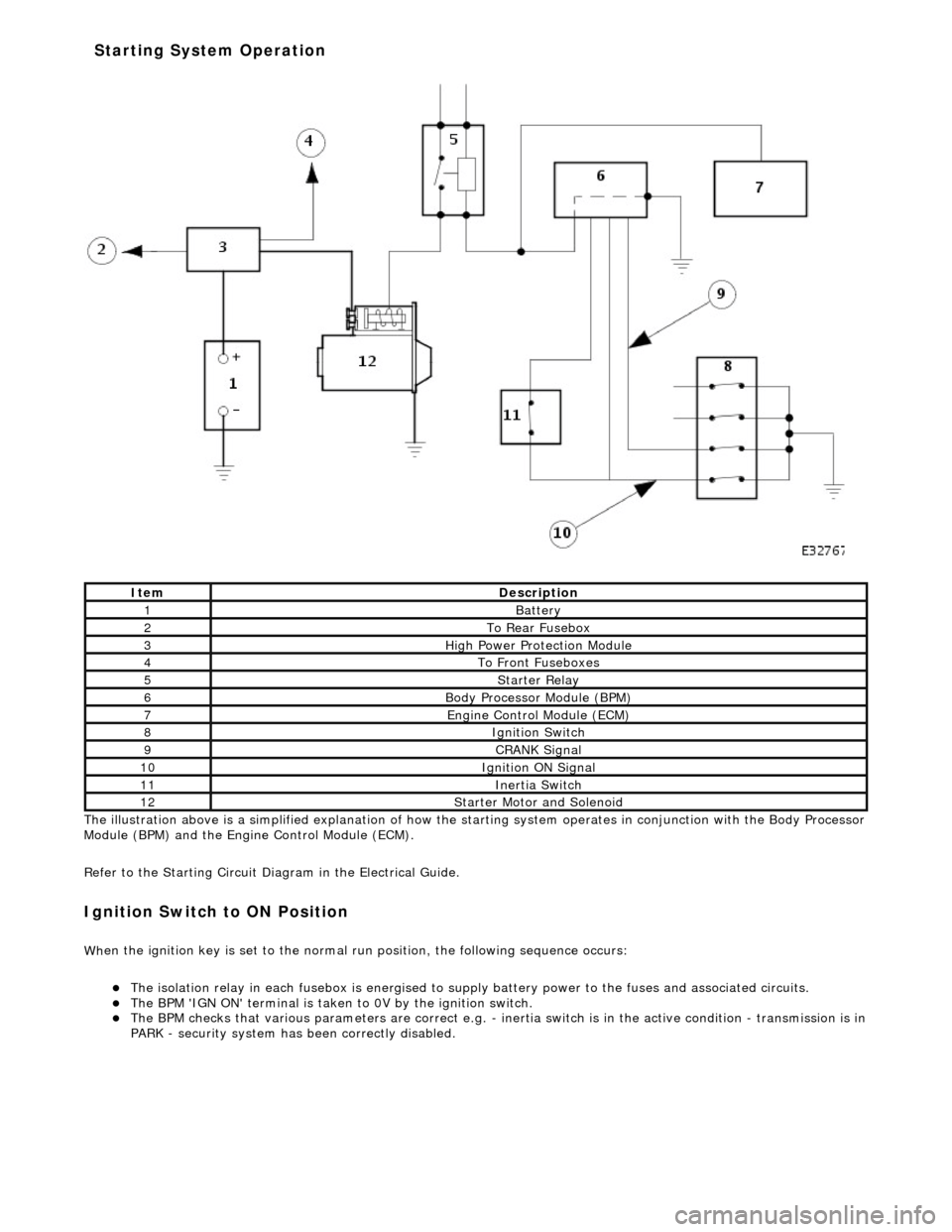
The il
lustration above is a simplified expl
anation of how the starting system operates in conjunction with the Body Processor
Module (BPM) and the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Refer to the Starting Circuit Diagram in the Electrical Guide.
I g
nition Switch to ON Position
W
h
en the ignition key is set to the normal run position, the following sequence occurs:
The
is
olation relay in each fusebox is
energised to supply battery power to the fuses and associated circuits.
The BPM 'IGN
ON' terminal
is taken to 0V by the ignition switch.
The BPM
checks that various parameters are correct e.g. -
inertia switch is in the active condition - transmission is in
PARK - security system has been correctly disabled.
It e
m
De
scr
iption
1Batt
ery
2To Re ar
Fusebox
3Hi
gh Power Pr
otection Module
4To Front
Fu
seboxes
5Starter Re
lay
6Body Processor M
odule (BPM)
7Engine
C
ontrol Module (ECM)
8Ignition Switch
9CRANK Signal
10Ignition ON Signal
11Inertia Switch
12St
arte
r Motor and Solenoid
Starting System Operation
Page 1065 of 2490
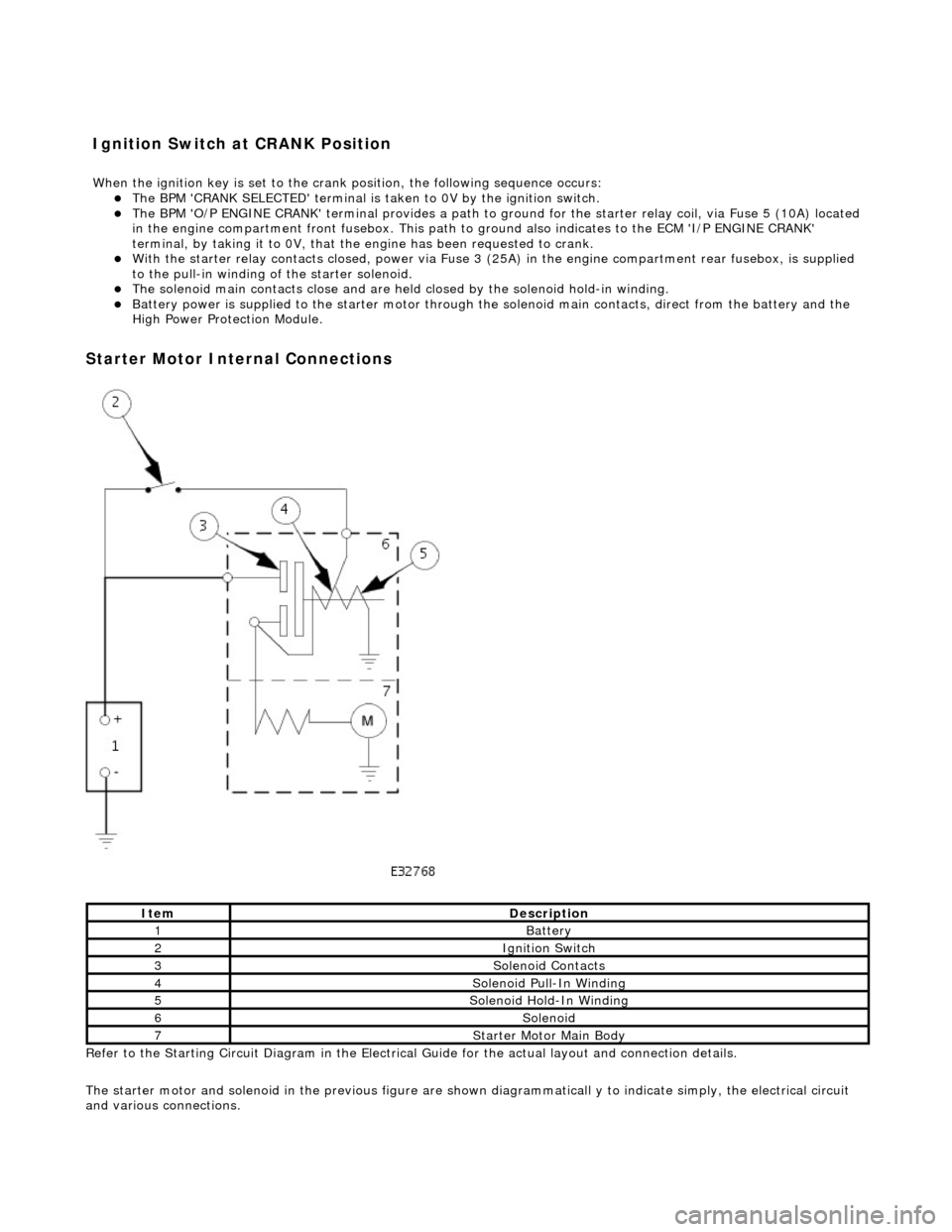
The BPM
'CRANK SELECTED' terminal is ta
ken to 0V by the ignition switch.
The BPM
'O/P ENGINE CRANK' terminal pr
ovides a path to ground for the starte r relay coil, via Fuse 5 (10A) located
in the engine compartment front fusebo x. This path to ground also indicates to the ECM 'I/P ENGINE CRANK'
terminal, by taking it to 0V, that the engine has been requested to crank.
Wi
th the starter relay contacts closed,
power via Fuse 3 (25A) in the engine compartment rear fusebox, is supplied
to the pull-in winding of the starter solenoid.
The s
olenoid main contacts close and are held
closed by the solenoid hold-in winding.
Battery power is supplied
to
the starter motor through the solenoid main contacts, direct from the battery and the
High Power Protection Module.
Starter
Motor Internal Connections
Re
fer to the Starting Circuit Diagram in the Electrical
Guide for the actual layout and connection details.
The starter motor and solenoid in the previous figure are shown diagrammaticall y to indicate simply, the electrical circuit
and various connections.
It
em
De
scription
1Batt
ery
2Ignition Switch
3So
lenoid Contacts
4So
lenoid Pull-In Winding
5So
lenoid Hold-In Winding
6So
lenoid
7St
arter Motor Main Body
I
gnition Switch at CRANK Position
W
hen the ignition key is set to the crank position, the following sequence occurs:
Page 1066 of 2490
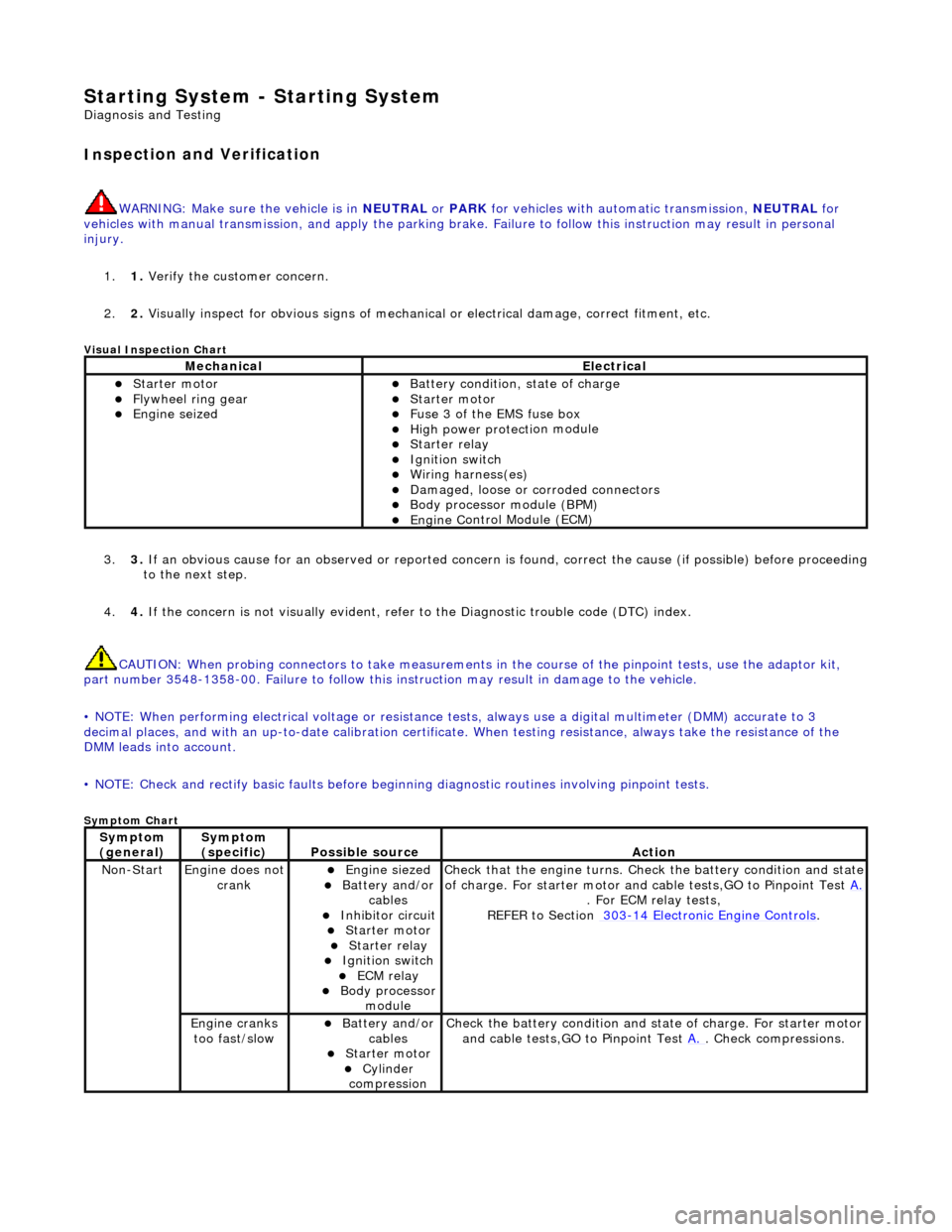
Starting System - Starting System
Diagn
osis and Testing
I
n
spection and Verification
W
A
RNING: Make sure
the vehicle is in NEUTRAL or PARK for vehicles with au tomatic transmission, NEUTRAL for
vehicles with manual transmissi on, and apply the parking brake. Failure to foll ow this instruction may result in personal
injury.
1. 1. Verify the customer concern.
2. 2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage, correct fitment, etc.
Vi
sual Inspection Chart
3.
3. If an obvi
ous cause for an observed or
reported concern is found, correct th e cause (if possible) before proceeding
to the next step.
4. 4. If the concern is not visually evident, refer to the Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) index.
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit,
part number 3548-1358-00. Failure to follow this in struction may result in damage to the vehicle.
• NOTE: When performing electrical voltag e or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to 3
decimal places, and with an up-t o-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the
DMM leads into account.
• NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic ro utines involving pinpoint tests.
Sym
ptom Chart
MechanicalElectrical
Starte
r motor
Flywheel
ring gear
Engine
s
eized
Batter
y condition, state of charge
Starte
r motor
F
u
se 3 of the EMS fuse box
High
power protec ti
on module
Starter relay Ignition switc
h
W
i
ring harness(es)
Damaged, loose or corroded connector
s
Body processor module (B
PM)
Engine
C
ontrol Module (ECM)
Sy
m
ptom
(
gene r
al)
Sy
m
ptom
(specific)
Possib l
e source
Acti
o
n
No
n
-Start
Engine does
not
crankEngine s
iezed
Batt
ery and
/or
cables
Inhibitor circuit St arte
r motor
Starter relay Ignition switc
h
ECM relay Body processor
modu le
Check that
the engine turns. Check the battery condition and state
of charge. For starter motor and ca ble tests,GO to Pinpoint Test A.
. For ECM relay
tests,
REFER to Section 303
-14
Electronic Engine Controls
.
Engine
c
ranks
too fast/slow
Batt ery and
/or
cables
St arte
r motor
Cy
linder
com
pression
Check the battery con
dition
and st
ate of charge. For starter motor
and cable tests,GO to Pinpoint Test A.
. Chec
k compressions.
Page 1067 of 2490
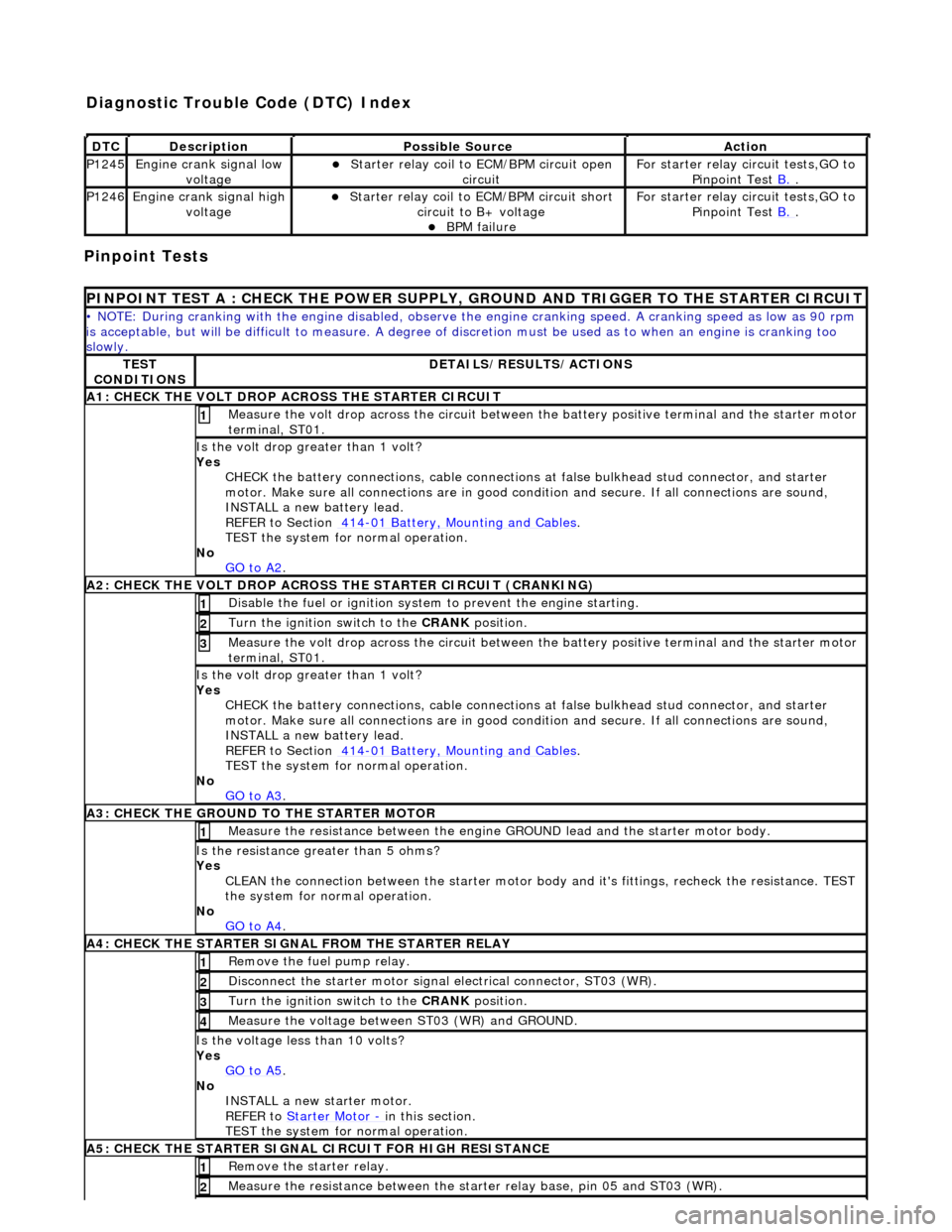
Pinpoint Tests
DT
C
De
scription
Possib
le Source
Acti
on
P1245Engine
crank signal low
voltage
Starter relay
coil to
ECM/BPM circuit open
circuit
F
or starter relay circuit tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test B.
.
P1246Engine
crank signal high
voltage
Starter relay
coil to ECM/BPM circuit short
circuit to B+ voltage
B
PM failure
F
or starter relay circuit tests,GO to
Pinpoint Test B.
.
P
INPOINT TEST A : CHECK THE
POWER SUPPLY, GROUND AND TRI GGER TO THE STARTER CIRCUIT
•
NOTE: During cranking with the engine disabled, observe the engine cranking speed. A cranking speed as low as 90 rpm
is acceptable, but will be difficult to measure. A degree of discretion must be used as to when an engine is cranking too
slowly.
TE
ST
CONDITIONS
D
ETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
A1: CHECK
THE VOLT DROP AC
ROSS THE STARTER CIRCUIT
M
easure the volt drop across the circuit between the battery positive terminal and the starter motor
terminal, ST01.
1
Is the vol
t drop greater than 1 volt?
Yes CHECK the battery connections, cable connections at false bulkhead stud connector, and starter
motor. Make sure all connections are in good co ndition and secure. If all connections are sound,
INSTALL a new battery lead.
REFER to Section 414
-0
1 Battery, Mounting and Cables
.
TEST the system
for normal operation.
No GO to A2
.
A2: CHECK
THE VOLT DROP ACROSS
THE STARTER CIRCUIT (CRANKING)
Di
sable the fuel or ignition system to prevent the engine starting.
1
Turn the ignition swi
tch to the CRANK
position.
2
M
easure the volt drop across the circuit between the battery positive terminal and the starter motor
terminal, ST01.
3
Is the vol
t drop greater than 1 volt?
Yes CHECK the battery connections, cable connections at false bulkhead stud connector, and starter
motor. Make sure all connections are in good co ndition and secure. If all connections are sound,
INSTALL a new battery lead.
REFER to Section 414
-0
1 Battery, Mounting and Cables
.
TEST the system
for normal operation.
No GO to A3
.
A3:
CHECK THE GROUND TO THE STARTER MOTOR
Meas
ure the resistance between the engine GROUND lead and the starter motor body.
1
Is th
e resistance greater than 5 ohms?
Yes CLEAN the connection between the starter motor body and it's fittings, recheck the resistance. TEST
the system for normal operation.
No GO to A4
.
A4
: CHECK THE STARTER SIGNAL FROM THE STARTER RELAY
R
emove the fuel pump relay.
1
Di
sconnect the starter motor signal
electrical connector, ST03 (WR).
2
Turn the ignition swi
tch to the CRANK
position.
3
M
easure the voltage between ST03 (WR) and GROUND.
4
Is th
e voltage less than 10 volts?
Yes GO to A5
.
No
INSTALL a new starter motor.
REFER to Starter Motor
-
in t
his section.
TEST the system for normal operation.
A5
: CHECK THE STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR HIGH RESISTANCE
R
emove the starter relay.
1
Meas
ure the resistance between the st
arter relay base, pin 05 and ST03 (WR).
2
Diagnostic Trouble Code (D
TC) Index
Page 1077 of 2490

Engine Igni
tion -
Engine Ignition
D
iagnosis and Testing
I
nspection and Verification
1.
1. Veri
fy the customer concern.
2. 2. Confirm which, if any, warning li ghts and/or messages were displayed on the instrument cluster.
• NOTE: If any warning lights and/or me ssages were displayed when the fault occurred, refer to the Driver Information
table for DTCs associated with the display, then to the DTC index table for possible sources and actions. Some warnings will
appear to clear when the ignition is cycl ed. This is often because the warning has flagged as a resu lt of one of the vehicle's
on-board diagnostic routines having run to detect the fault. If the same routine is not run when the ignition is switched ON,
the warning will not reflag until the routine does run. See the DTC summaries for drive cycle routines.
3. 3. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
V
isual Inspection Chart
4.
4. Veri
fy the following syst
ems are working correctly:
Air in
take system
Coo
ling system
Charging system
F
uel charging system
5. 5. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding
to the next step.
6. 6. Where the Jaguar approved diagnostic sy stem is available, complete the S93 report before clearing any or all fault
codes from the vehicle.
• NOTE: If a DTC cannot be cleared, then there is a permanent fault present that flag s again as soon as it is cleared (the
exception to this is P1260, which will only clear following an ignition OFF/ON cycle after rectification).
7. 7. If the cause is not visually evident and the Jaguar approv ed diagnostic system is not available, use a fault code
reader to retrieve the fault codes be fore proceeding to the Diagnostic Trou ble Code (DTC) Index Chart, or the
Symptom Chart if no DTCs are set.
• NOTE: If the DTC flagged was not present for two or more co nsecutive cycles, it is classed as temporary, and will be
deleted following three cycl es during which no fault was present. This could result in a reported wa rning light/message with
no stored DTCs. If a fault is present for three consecutive cycles, the DTC becomes permanent, and will remain in the
module's memory for 40 drive cycles (a cy cle is an ignition ON/OFF, which will occur during the owner's normal use of the
vehicle. No action on the part of the technician is necessary to perform this cycle. A drive cycle is a series of conditions
needed to make the on-board diagnostic ro utine run, and may need a specific action on the part of the technician. See the
DTC summaries for driv e cycle routines).
8. 8. Using the Jaguar approved diagnostic system where available, and a scan tool where not, check the freeze frame
data for information on the conditions applicable when the fault was flagged. The format of this will vary,
depending on the tool used, but can pr ovide information useful to the technician in diagnosing the fault.
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit,
part number 3548-1358-00.
MechanicalElectrical
Engi
ne oil level
Coo
ling system coolant
level
Fuel contamination
Throttle body Poly
-vee belt
F
uses
W
iring harness
E
lectrical connector(s)
Sens
or(s)
Engine
control module (ECM)
Relay date codes.
If the date on the relay is between R6 k1 and R6 k8, replace
the relay
Page 1093 of 2490

En
gine Emission Control -
Torque Specific
ations
De
scription
Nmlb
-ft
lb
-in
EGR valve tube to EGR valv
e retaining bolts
2115-
Exhaus
t manifold to EGR valve tube retaining bolts
2115-
Exhaus
t manifold to EGR valve tube retaining nuts
2115-
Evaporati
ve emission canister purge valve retaining bolts
6-53
EGR valve to th
rottle body elbow retaining bolts
129-
Page 1094 of 2490

Engine Emission
Control - Engine Emission Control
D
iagn
osis and Testing
I
n
spection and Verification
1.
1. Veri fy the customer concern.
2. 2. Vis
ually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical
or electrical damage, correct fitment, etc.
Vi
sual Inspection Chart
3.
3. Veri fy the foll
owing syst
ems are working correctly:
Air intake
system
Coo
ling system
Charging system
Fu
el charging system
Ignition sys
t
em
4. 4. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding
to the next step
5. 5. Where the Jaguar approved diagnostic sy stem is available, complete the S93 report before clearing any or all fault
codes from the vehicle.
• NOTE: If a DTC cannot be cleared, then there is a permanent fault present that flag s again as soon as it is cleared (the
exception to this is P1260, which will only clear following an ignition OFF/ON cycle after rectification).
6. 6. If the cause is not visually evident and the Jaguar approv ed diagnostic system is not available, use a fault code
reader to retrieve the fault codes be fore proceeding to the Diagnostic Trou ble Code (DTC) Index Chart, or the
Symptom Chart if no DTCs are set.
7. 7. Using the Jaguar approved diagnostic system where available, and a scan tool where not, check the freeze frame
data for information on the conditions applicable when the fault was flagged. The format of this will vary,
depending on the tool used, but can pr ovide information useful to the technician in diagnosing the fault.
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit,
part number 3548-1358-00.
• NOTE: When performing electrical voltag e or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to 3
decimal places, and with an up-t o-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the
DMM leads into account.
• NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic ro utines involving pinpoint tests.
Sym
ptom Chart
MechanicalElectrical
Engi
ne
oil level
Coo
ling system coolant level
Fue
l
level
Fuel contaminatio
n
/
grade/quality
Throttle body Poly
-ve
e belt
Engine breath
er
system
pipework/connections
EGR pipework
condition (cracking, etc)
F
u
ses
W
i
ring harness
E
l
ectrical connector(s)
Sens
o
r(s)
Engine
control module (E
CM)
Sy
m
ptom
(general)
S y
mptom (specific)
Possib
l
e source
Acti
o
n
Poor
dr iveabilityEngine h e
sitates/poor
acceleration
Fue l
pump
Air leakage F
u
el pressure regulator
Chec
k fu
el pressure,
REFER to Section 310
-00 Fu
el
Sy
ste
m
- General Informati
on.
Page 1099 of 2490
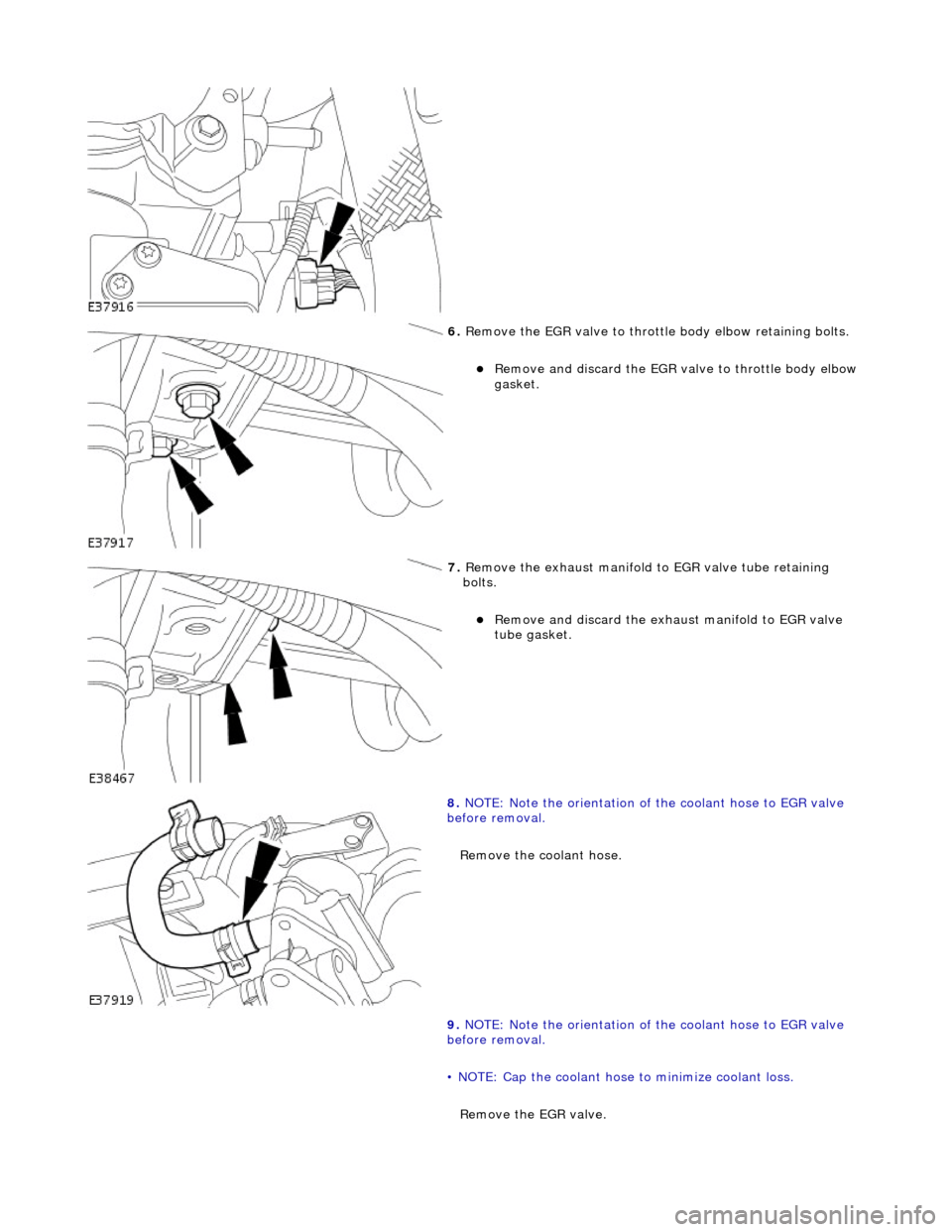
6. R
emove the EGR valve to throttle
body elbow retaining bolts.
Remove an
d discard the EGR valve to throttle body elbow
gasket.
7. R
emove the exhaust manifold to EGR valve tube retaining
bolts.
Remove an
d discard the exhaust manifold to EGR valve
tube gasket.
8. N
OTE: Note the orientation of the coolant hose to EGR valve
before removal.
Remove the coolant hose.
9. NOTE: Note the orientation of the coolant hose to EGR valve
before removal.
• NOTE: Cap the coolant hose to minimize coolant loss.
Remove the EGR valve.
Page 1100 of 2490
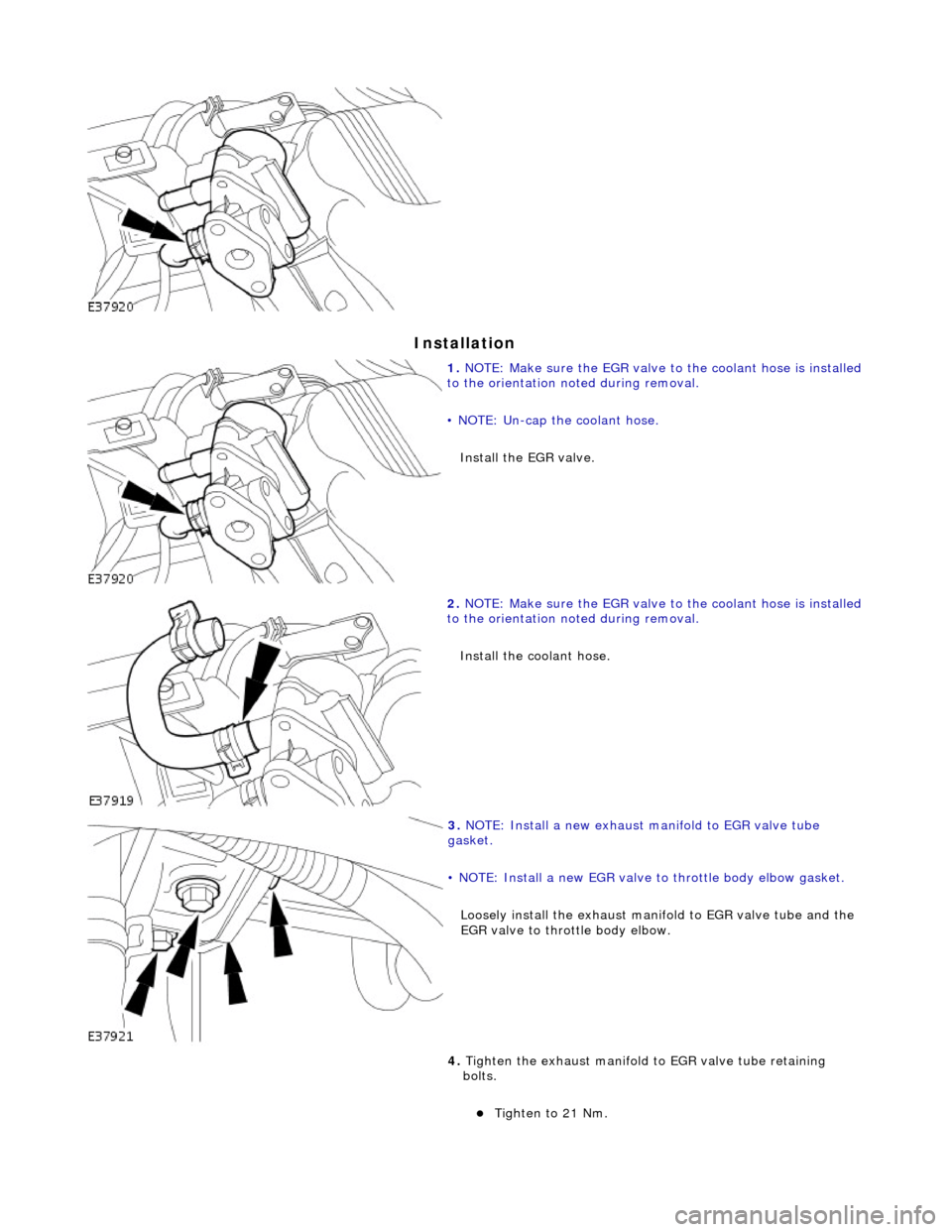
In
stallation
1.
NO TE
: Make sure the EGR valve to the coolant hose is installed
to the orientation noted during removal.
• NOTE: Un-cap the coolant hose.
Install the EGR valve.
2. NO TE
: Make sure the EGR valve to the coolant hose is installed
to the orientation noted during removal.
Install the coolant hose.
3. NOTE:
Install a new exhaust manifold to EGR valve tube
gasket.
• NOTE: Install a new EGR valve to throttle body elbow gasket.
Loosely install the exhaust manifold to EGR valve tube and the
EGR valve to throttle body elbow.
4. Tighten the exhaust manifold to EGR valve tube retaining
bolts.
Tigh te
n to 21 Nm.
Page 1101 of 2490

5. Tigh
ten the EGR valve to throttle body retaining bolts.
Tigh
ten to 12 Nm.
6. Con
nect the EGR valve electrical connector.
7. NO
TE: Un-cap the coolant hose.
Connect the coolant hose.
8. Attach the evaporative emission canister purge valve.
Tigh
ten to 6 Nm.