JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1281 of 3039
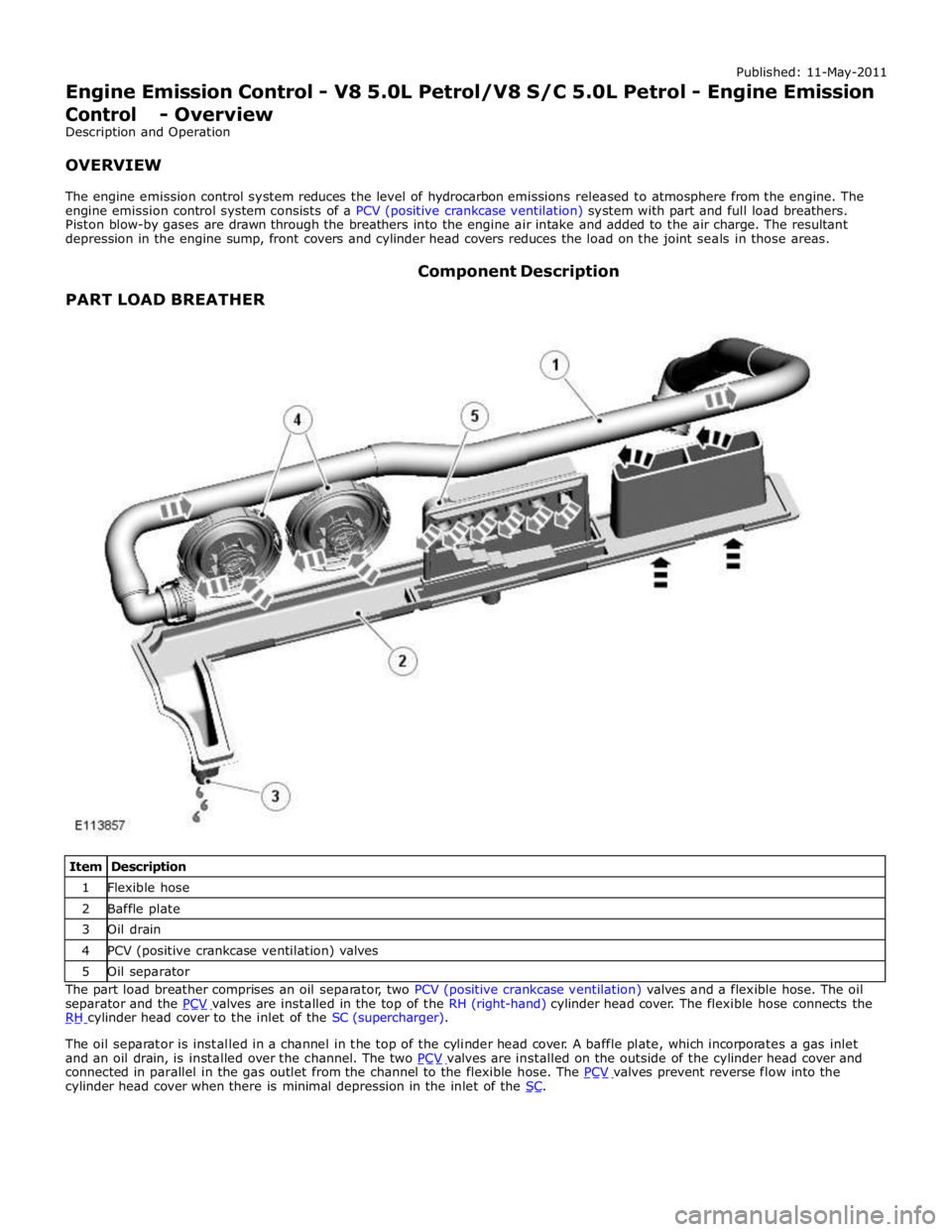
PARTLOADBREATHERComponentDescription
ItemDescription1Flexiblehose2Baffleplate3Oildrain4PCV(positivecrankcaseventilation)valves5OilseparatorThepartloadbreathercomprisesan oilseparator,twoPCV(positivecrankcaseventilation) valvesand aflexiblehose.Theoil
separatorandthePCVvalvesareinstalledinthetopoftheRH(right-hand)cylinderhead cover.TheflexiblehoseconnectstheRHcylinderheadcovertotheinletoftheSC(supercharger).Theoilseparatorisinstalledinachannelin thetopofthecylinderheadcover.Abaffleplate,whichincorporatesagasinlet
andanoildrain,isinstalledoverthechannel.ThetwoPCVvalvesareinstalledontheoutsideofthecylinderheadcoverandconnectedinparallelinthegasoutletfromthechannelto theflexiblehose.ThePCVvalvespreventreverseflowintothecylinderheadcoverwhen thereisminimaldepressionintheinletoftheSC.
Page 1282 of 3039
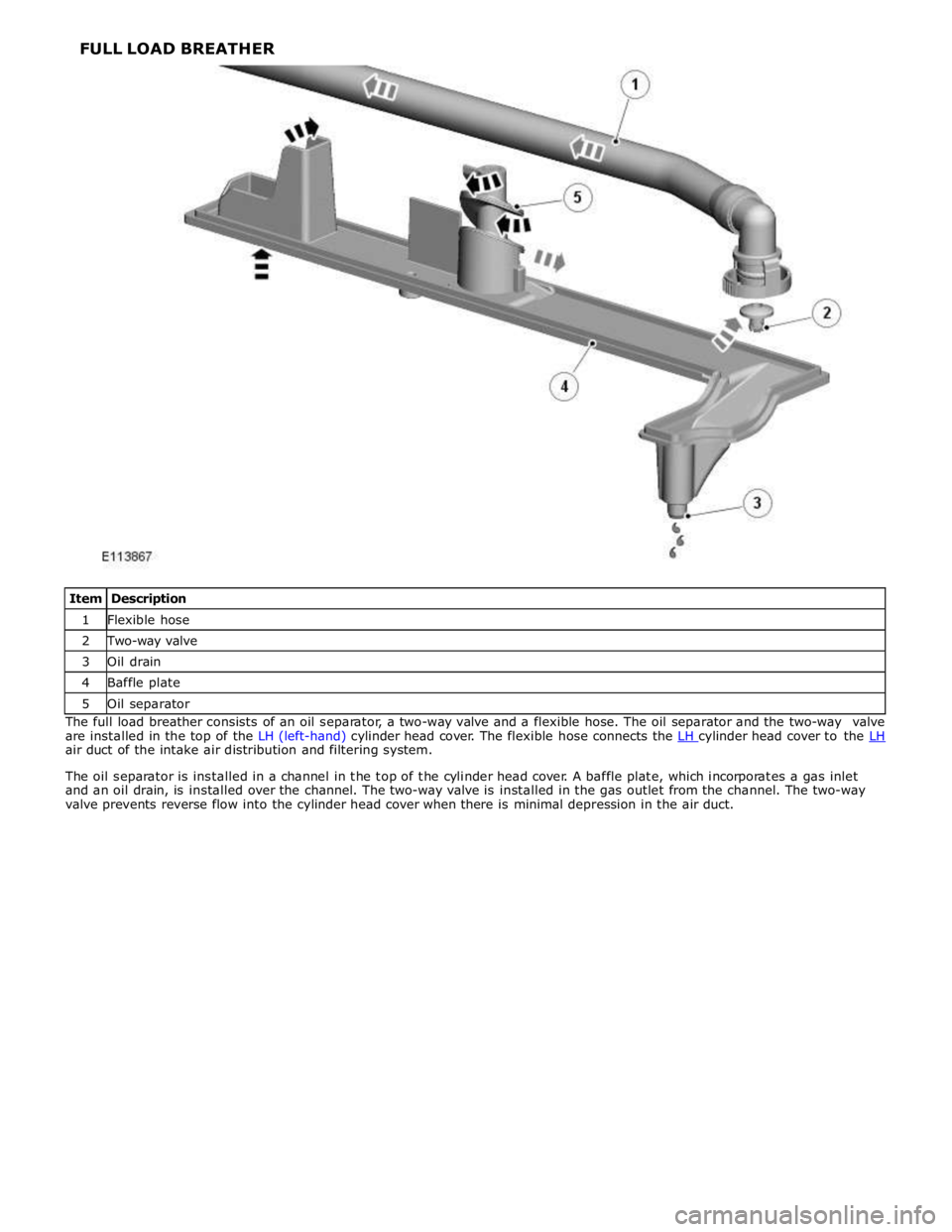
1 Flexible hose 2 Two-way valve 3 Oil drain 4 Baffle plate 5 Oil separator The full load breather consists of an oil separator, a two-way valve and a flexible hose. The oil separator and the two-way valve
are installed in the top of the LH (left-hand) cylinder head cover. The flexible hose connects the LH cylinder head cover to the LH air duct of the intake air distribution and filtering system.
The oil separator is installed in a channel in the top of the cylinder head cover. A baffle plate, which incorporates a gas inlet
and an oil drain, is installed over the channel. The two-way valve is installed in the gas outlet from the channel. The two-way
valve prevents reverse flow into the cylinder head cover when there is minimal depression in the air duct. FULL LOAD BREATHER
Page 1283 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Emission Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Emission
Control
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the engine emission control system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (303-08C Engine Emission Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Engine Emission Control (Description and Operation), Engine Emission Control (Description and Operation), Engine Emission Control (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Exhaust gas recirculation system
Breather hoses
Positive crankcase ventilation valve
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Throttle body
Fuses
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve
Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Difficult to
start cold
Battery
Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel system
Evaporative emissions purge
valve For battery information, CKP sensor, fuel system and purge valve tests,
refer to relevant workshop manual section. Check the EGR valve. Engine stalls
soon after
start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Engine Control Module (ECM)
relay
MAF sensor
Ignition system
Air filter restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines Check the engine breather hoses, PCV, etc. Check the Engine Control
Module (ECM) relay operation. For MAF sensor, ignition system tests, air
intake and fuel line information, refer to relevant workshop manual
section. Poor throttle
response
APP sensor malfunction
TP sensors
ECT sensor
MAF sensor
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event Air
leakage For APP, TP, ECT, MAF sensor tests, intake system checks and
transmission information, refer to relevant workshop manual section.
Check the breather system hoses, PCV, etc.
Page 1284 of 3039

Symptom Possible Causes Action Breather system
disconnected/restricted DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Engine Control Module (ECM), please refer to Section
303-14. REFER to:
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing), Electronic Engine Controls (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing).
Page 1285 of 3039

Air cleaner retaining bolts 8 - 71 Supercharger retaining bolts 25 18 - Charge air cooler lower assembly retaining bolts 20 15 - Throttle body retaining studs 10 7 - Charge air cooler top assembly retaining bolts 25 18 - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor 5 - 44 Coolant outlet pipe 11 8 -
Page 1286 of 3039
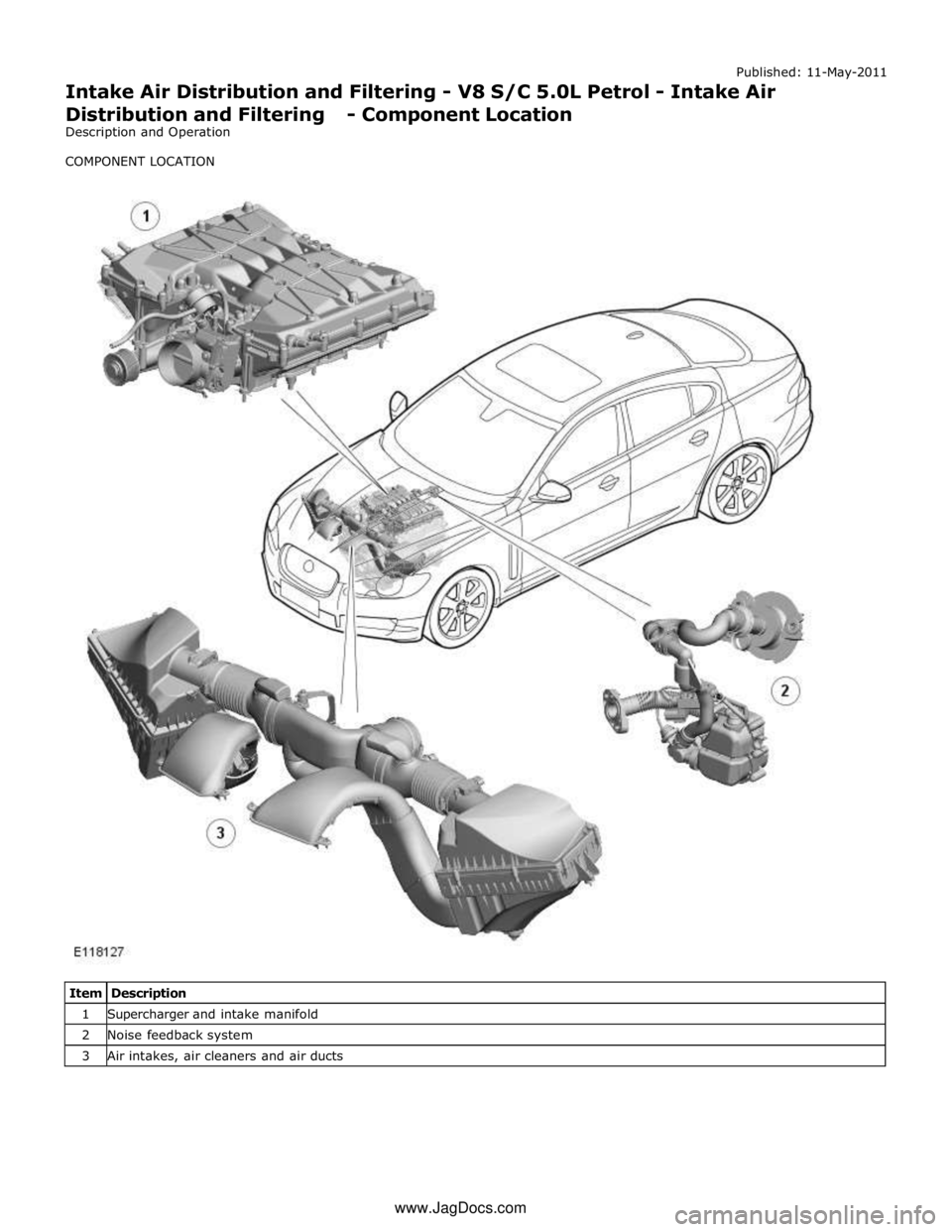
1 Supercharger and intake manifold 2 Noise feedback system 3 Air intakes, air cleaners and air ducts www.JagDocs.com
Page 1287 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
The intake air distribution and filtering system comprises:
Dual air intakes, air cleaners and air ducts.
A SC (supercharger) and intake manifolds.
A noise feedback system.
Page 1288 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB (battery junction box) (250 A megafuse) 3 EJB (engine junction box) (EMS high current relay) 4 Tuning valve 5 ECM (engine control module)
Page 1289 of 3039

SUPERCHARGER System Operation
At closed or partially open throttle positions, the bypass valve is fully open, allowing a flow of air from the SC (supercharger)
outlet back to the inlet side. This results in little or no pressure increase across the SC. Progressive opening of the throttle reduces the depression downstream of the electric throttle. This is sensed by the pneumatic actuator, which moves to close
the bypass valve. As the bypass valve closes there is a corresponding increase in the outlet pressure from the SC, which increases engine power output.
NOISE FEEDBACK SYSTEM
Sound waves from the RH (right-hand) intake manifold are filtered by the calibrated orifice in the inlet pipe connection on the
symposer. The sound waves make the paddle oscillate and generate pulsations in the outlet chambers. When the pneumatic
valve is open, the pulsations are transmitted through the outlet pipe and feedback tube to the resonator in the passenger
compartment.
The tuning valve of the noise feedback system receives a power feed from the power distribution box and is connected to
ground through the ECM (engine control module). At lower engine loads and speeds the ECM keeps the ground open circuit and the tuning valve is de-energized closed. Atmospheric pressure is sensed at the pneumatic valve through the vent cap on the
tuning valve, which keeps the pneumatic valve closed and prevents sound from the symposer entering the feedback system.
At higher engine loads and speeds the ECM connects the tuning valve to ground. The tuning valve energizes, blanks off the atmospheric vent and opens the vacuum line between the brake vacuum system and the pneumatic valve. The depression in
the brake vacuum system is sensed at the pneumatic valve, which opens and allows sound from the symposer into the
feedback system.
The status of the pneumatic valve at various engine loads and speeds is given below:
Pneumatic Valve Status
NOTE: Values are for valve opening with increasing engine load and speed. Deduct 0.05 g/rev and 50 rev/min for valve
closing with decreasing engine load and speed.
Engine Load: g/rev Engine Speed: rev/min 0 500 1000 2500 3000 4000 5800 6500 1.30 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed 1.35 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed 1.40 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open 1.60 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open 1.80 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open 2.50 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open Open Open 3.00 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open Open Open 3.50 Closed Closed Closed Open Open Open Open Open
Page 1290 of 3039
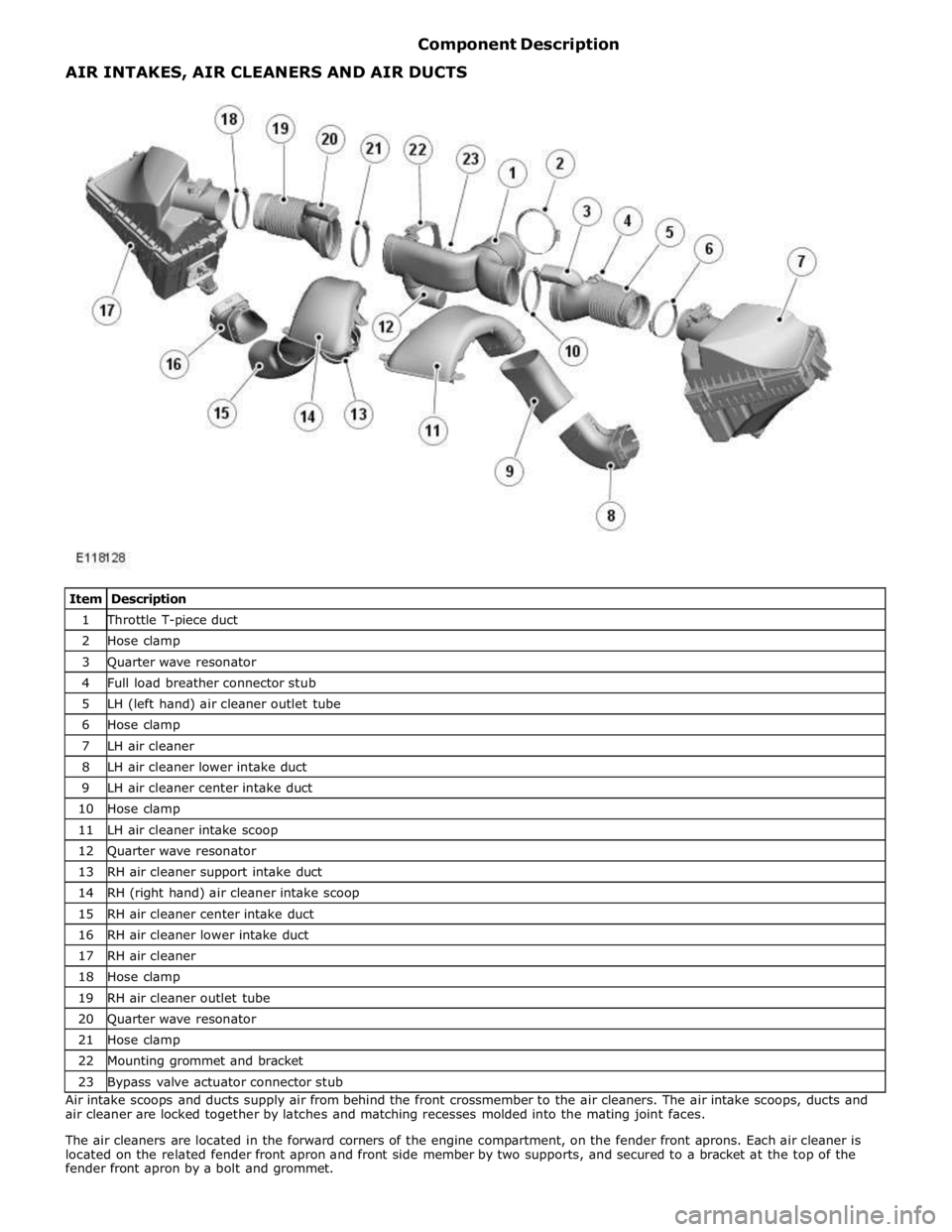
1 Throttle T-piece duct 2 Hose clamp 3 Quarter wave resonator 4 Full load breather connector stub 5 LH (left hand) air cleaner outlet tube 6 Hose clamp 7 LH air cleaner 8 LH air cleaner lower intake duct 9 LH air cleaner center intake duct 10 Hose clamp 11 LH air cleaner intake scoop 12 Quarter wave resonator 13 RH air cleaner support intake duct 14 RH (right hand) air cleaner intake scoop 15 RH air cleaner center intake duct 16 RH air cleaner lower intake duct 17 RH air cleaner 18 Hose clamp 19 RH air cleaner outlet tube 20 Quarter wave resonator 21 Hose clamp 22 Mounting grommet and bracket 23 Bypass valve actuator connector stub Air intake scoops and ducts supply air from behind the front crossmember to the air cleaners. The air intake scoops, ducts and
air cleaner are locked together by latches and matching recesses molded into the mating joint faces.
The air cleaners are located in the forward corners of the engine compartment, on the fender front aprons. Each air cleaner is
located on the related fender front apron and front side member by two supports, and secured to a bracket at the top of the
fender front apron by a bolt and grommet. AIR INTAKES, AIR CLEANERS AND AIR DUCTS