Bolt JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 351 of 3039
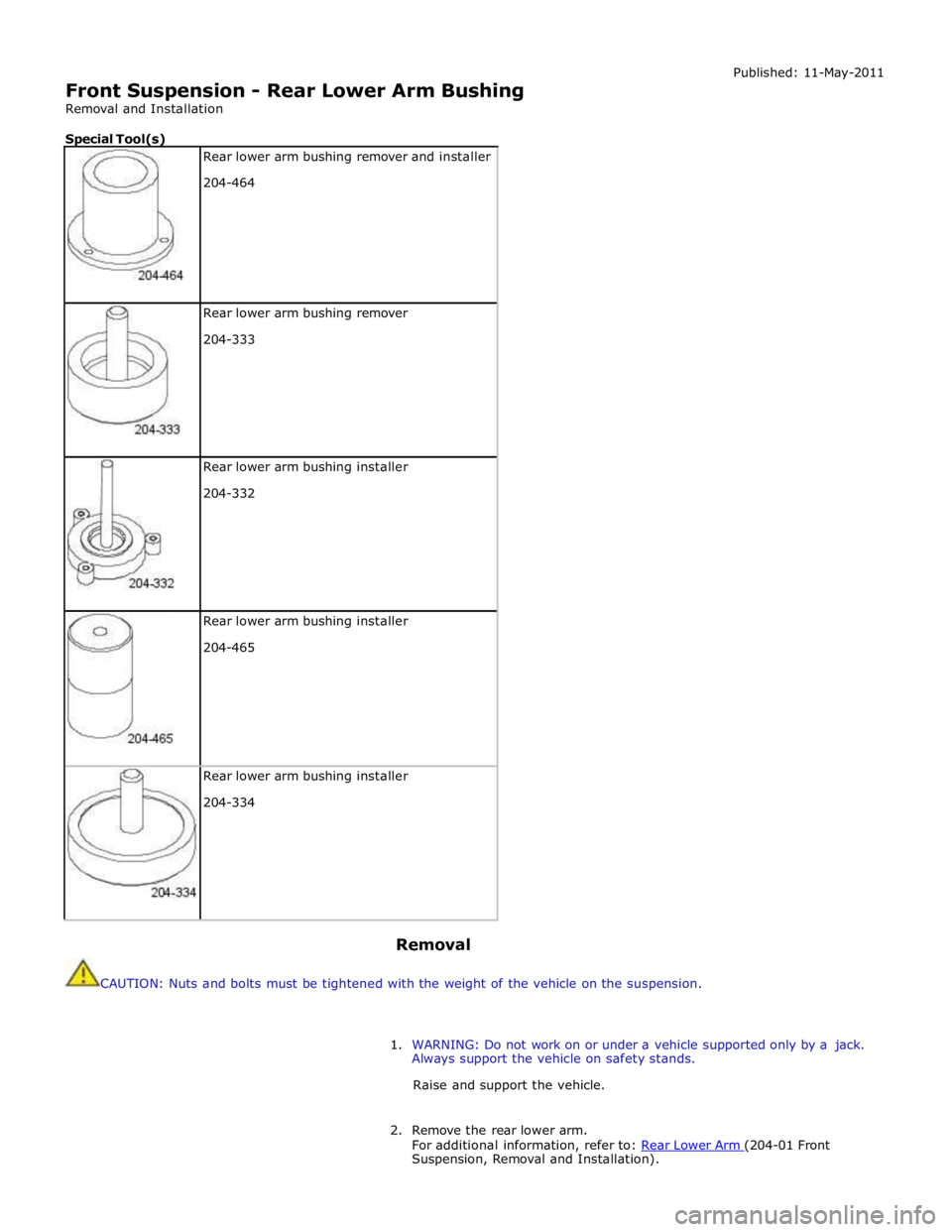
Front Suspension - Rear Lower Arm Bushing
Removal and Installation
Special Tool(s)
Rear lower arm bushing remover and installer
204-464
Rear lower arm bushing remover
204-333
Rear lower arm bushing installer
204-332
Rear lower arm bushing installer
204-465
Rear lower arm bushing installer
204-334
Removal
CAUTION: Nuts and bolts must be tightened with the weight of the vehicle on the suspension. Published: 11-May-2011
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Remove the rear lower arm.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Lower Arm (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation).
Page 352 of 3039
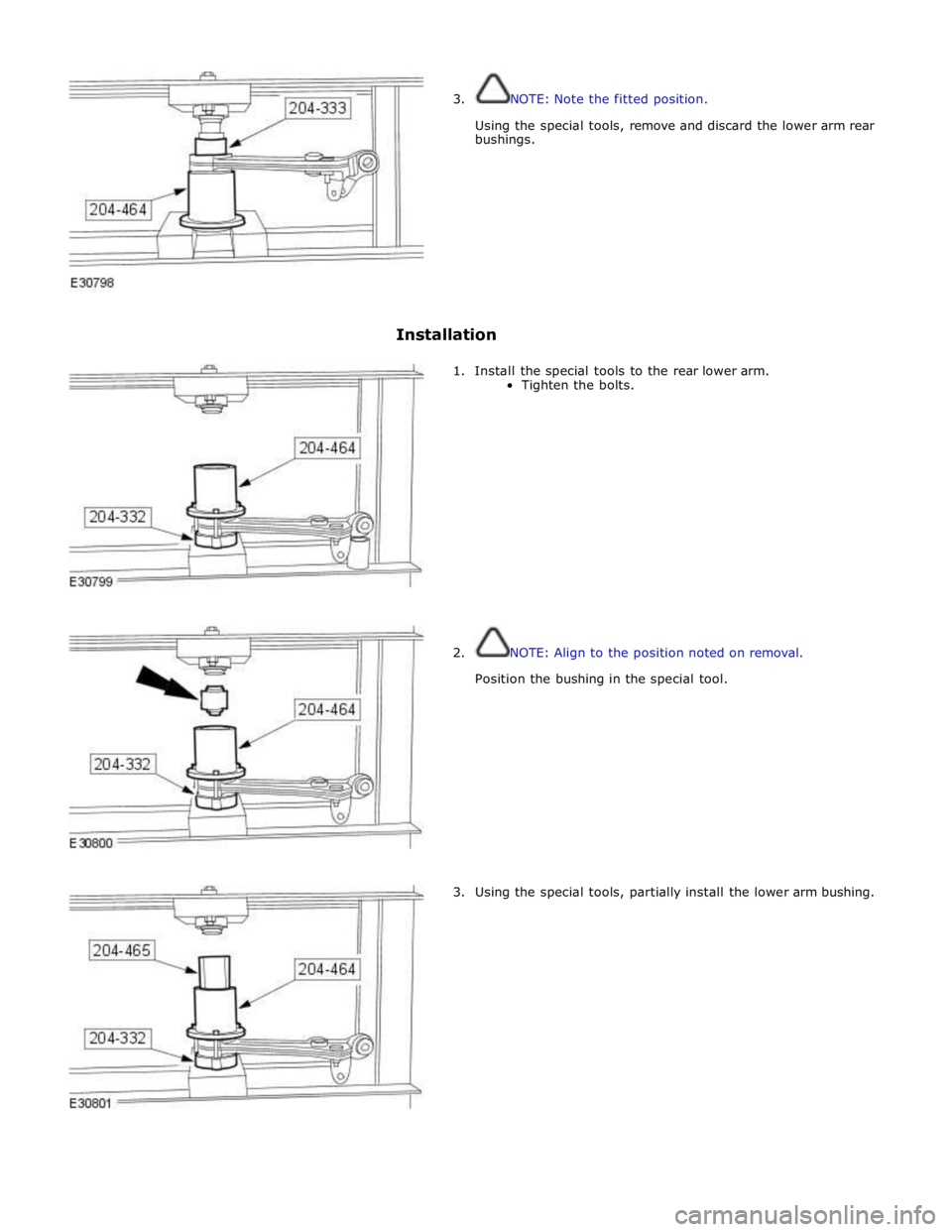
3. NOTE: Note the fitted position.
Using the special tools, remove and discard the lower arm rear
bushings.
Installation
1. Install the special tools to the rear lower arm.
Tighten the bolts.
2. NOTE: Align to the position noted on removal.
Position the bushing in the special tool.
3. Using the special tools, partially install the lower arm bushing.
Page 354 of 3039
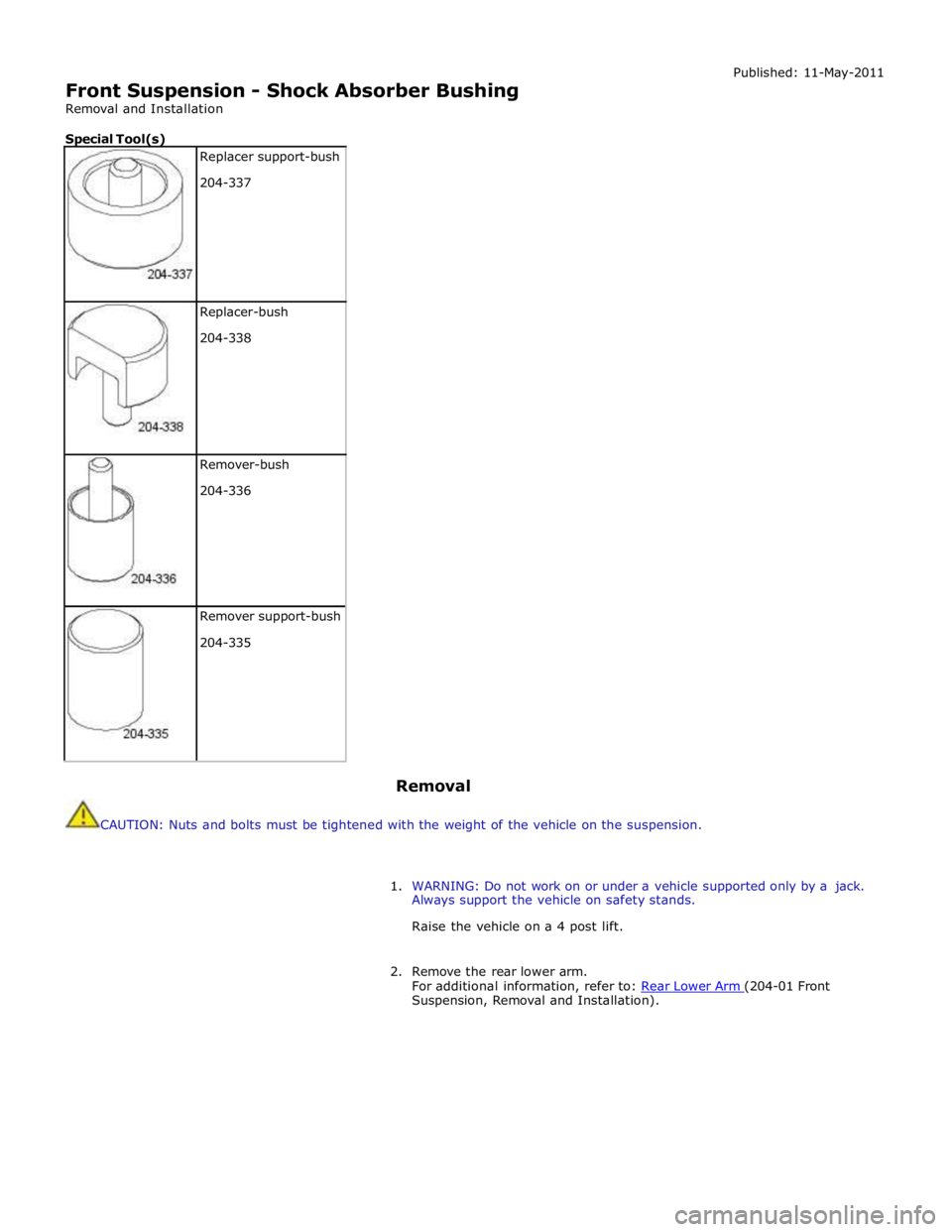
Front Suspension - Shock Absorber Bushing
Removal and Installation
Special Tool(s)
Replacer support-bush
204-337
Replacer-bush
204-338
Remover-bush
204-336
Remover support-bush
204-335
Removal
CAUTION: Nuts and bolts must be tightened with the weight of the vehicle on the suspension. Published: 11-May-2011
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise the vehicle on a 4 post lift.
2. Remove the rear lower arm.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Lower Arm (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation).
Page 362 of 3039
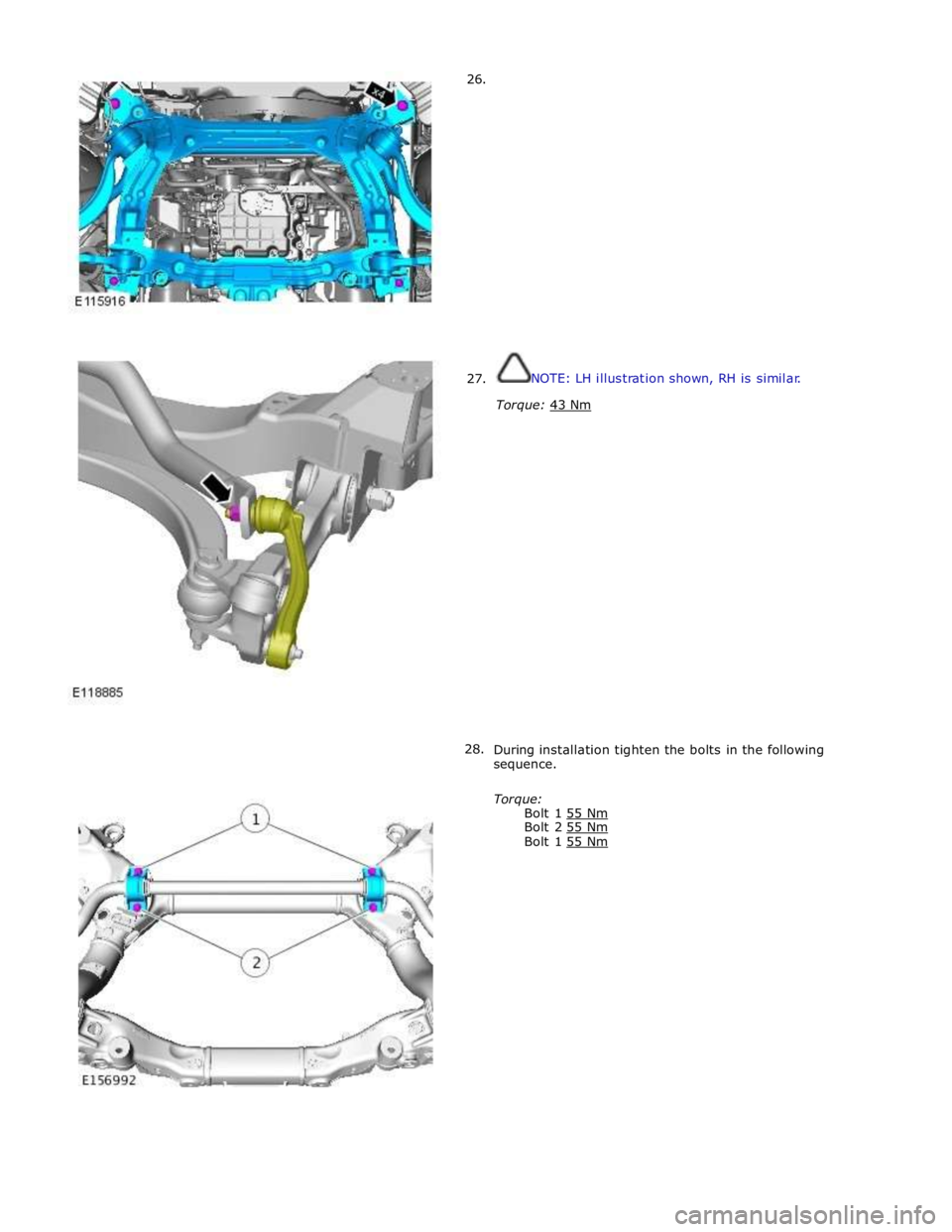
26.
27.
28.
NOTE: LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
Torque: 43 Nm
During installation tighten the bolts in the following
sequence.
Torque:
Bolt 1 55 Nm Bolt 2 55 Nm Bolt 1 55 Nm
Page 374 of 3039
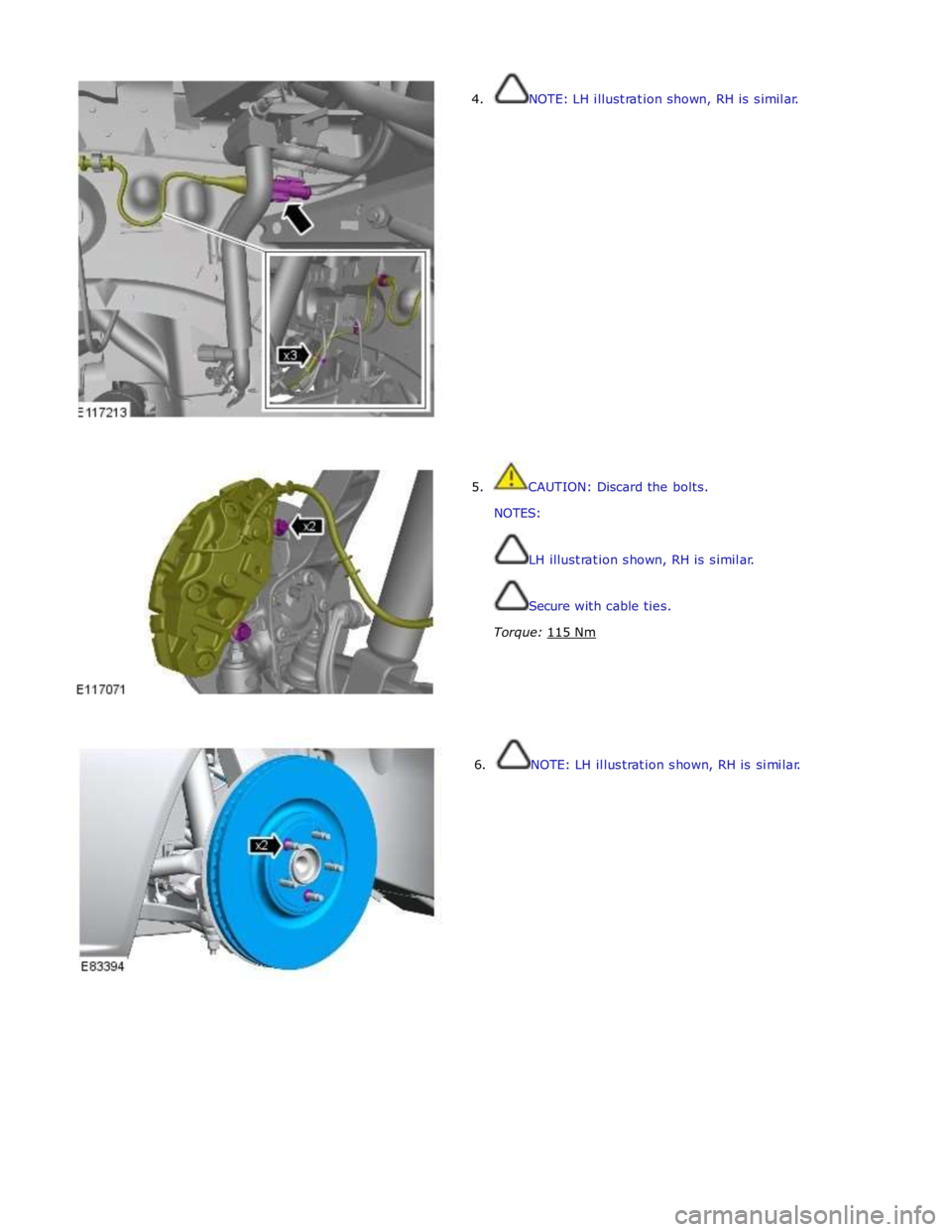
4. NOTE: LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
5. CAUTION: Discard the bolts.
NOTES:
LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
Secure with cable ties.
Torque: 115 Nm
6. NOTE: LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
Page 375 of 3039

7. CAUTIONS:
Discard the bolts.
Make sure that the area around the component is
clean and free of foreign material.
Do not attempt to release the wheel hub by hitting it
with a hammer directly, loosen the wheel hub retaining
bolts partially before applying an even amount of force to
the head of each bolts to release the wheel hub from the
wheel knuckle. Failure to follow this instruction may cause
damage to the component.
NOTES:
Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but the
essential information is always correct.
LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
Install the components to their original fitted
positions.
Torque: 90 Nm
Installation
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure. www.JagDocs.com
Page 390 of 3039
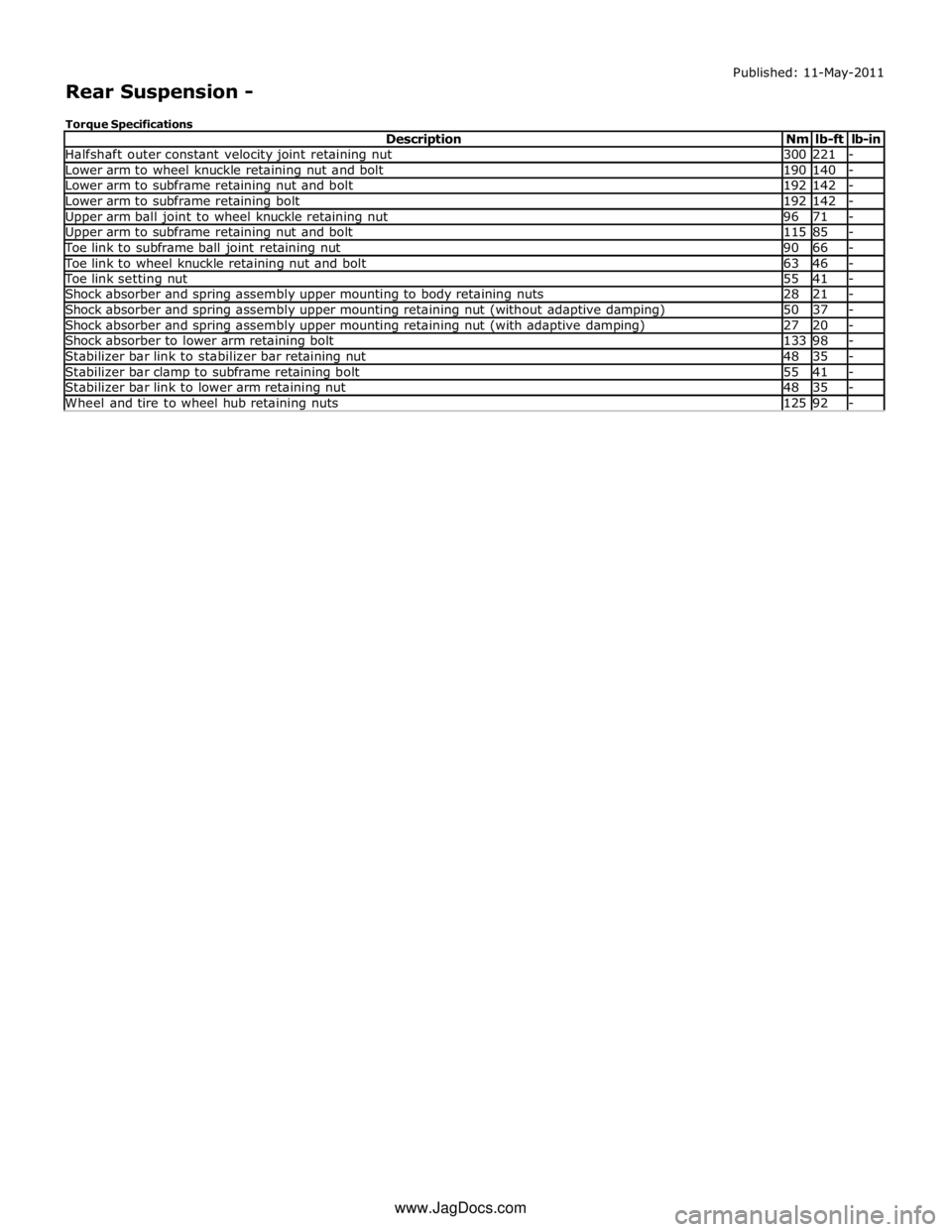

Halfshaft outer constant velocity joint retaining nut 300 221 - Lower arm to wheel knuckle retaining nut and bolt 190 140 - Lower arm to subframe retaining nut and bolt 192 142 - Lower arm to subframe retaining bolt 192 142 - Upper arm ball joint to wheel knuckle retaining nut 96 71 - Upper arm to subframe retaining nut and bolt 115 85 - Toe link to subframe ball joint retaining nut 90 66 - Toe link to wheel knuckle retaining nut and bolt 63 46 - Toe link setting nut 55 41 - Shock absorber and spring assembly upper mounting to body retaining nuts 28 21 - Shock absorber and spring assembly upper mounting retaining nut (without adaptive damping) 50 37 - Shock absorber and spring assembly upper mounting retaining nut (with adaptive damping) 27 20 - Shock absorber to lower arm retaining bolt 133 98 - Stabilizer bar link to stabilizer bar retaining nut 48 35 - Stabilizer bar clamp to subframe retaining bolt 55 41 - Stabilizer bar link to lower arm retaining nut 48 35 - Wheel and tire to wheel hub retaining nuts 125 92 - www.JagDocs.com
Page 395 of 3039

the aluminum wheel knuckle via an integral ball-joint.
Lower Control Arm
The aluminum lower arm locates to the subframe via one cross-axis joint and one plain rubber bush, and to the wheel knuckle
via a second plain rubber bush.
The rear of the control arm has mounting points for the damper and the stabilizer link.
Toe-Link
The toe-link is located between the wheel knuckle and brackets on the subframe.
The toe-link comprises an inner rod with integral axial ball joint. The inner ball joint has a threaded spigot which locates in a
bracket on the subframe and is secured with a locknut. The rod has an internal thread which accepts the outer rod.
The outer rod has a cross-axis joint at its outer end which is located in a clevis on the wheel knuckle, and is secured with a
bolt and locknut.
The length of the toe-link can be adjusted by rotating the inner rod. This allows for adjustment of the toe angle for the rear
wheel. Once set the inner rod can be locked in position by tightening a locknut on the outer rod against the inner rod.
Wheel Knuckle
The cast aluminum wheel knuckle attaches to:
the upper control arm via a ball-joint located in the arm,
the lower control arm via a plain rubber bush located in the arm,
the toe-link via a cross-axis joint located in the toe link.
The wheel knuckle also provides the mounting locations for the:
wheel hub assembly,
wheel bearing,
wheel speed sensor,
brake caliper,
and disc shield.
Stabilizer Bar
The solid construction stabilizer bar and bushes have been designed to provide particular characteristics in maintaining roll
rates, specifically in primary ride comfort. There are six derivatives of rear stabilizer bar, with different diameters, to support
the various powertrains:
V6 gasoline - 12.7 mm solid bar
V8 4.2L and 5.0L gasoline - 13.6 mm solid bar
V6 2.7L diesel -14.5 mm solid bar
V6 3.0L diesel - 14.5 mm solid bar
V6 3.0L diesel with Adaptive Damping – 16mm tubular
V8 4.2L gasoline supercharged – 16mm tubular
V8 5.0L gasoline supercharged
- SV8 - 17mm tubular
- XFR - 18mm tubular
The stabilizer bar is attached to the top of the subframe with two bushes and mounting brackets. The stabilizer bar has
crimped, 'anti-shuffle' collars pressed in position on the inside edges of the bushes. The collars prevent sideways movement of
the stabilizer bar.
Each end of the stabilizer bar curves rearward to attach to a ball joint on each stabilizer link. Each link is attached via a
second ball joint to a cast bracket on the lower control arm. The links allow the stabilizer bar to move with the wheel travel
providing maximum effectiveness.
Spring and Damper Assembly
The spring and damper assembly are attached to cast brackets on the lower control arms and to the vehicle body by four studs
secured by locking nuts. Dependant on vehicle model there are three types of coil spring and damper available:
a standard oil passive damper (All models except supercharged),
an adaptive damper, also known as Computer Active Technology Suspension (CATS) on 4.2L supercharged vehicles up to
2010MY, For additional information refer to Vehicle Dynamic Suspension 4.2L.
a continuously variable adaptive damper, also known as Adaptive Dynamics System on 5.0L supercharged vehicles from
2010MY. For additional information refer to Vehicle Dynamic Suspension 5.0L.
The dampers are a monotube design with a spring located by a circlip onto the damper tube. The lower end of the damper has
a spherical joint which locates in the lower control arm and is secured with a bolt.
The damper piston is connected to a damper rod which is sealed at its exit point from the damper body. The threaded outer
end of the damper rod locates through a hole in the top mount. A self locking nut secures the top mount to the damper rod.
The damper rod on the adaptive damper has an electrical connector on the outer end of the damper rod. www.JagDocs.com
Page 400 of 3039
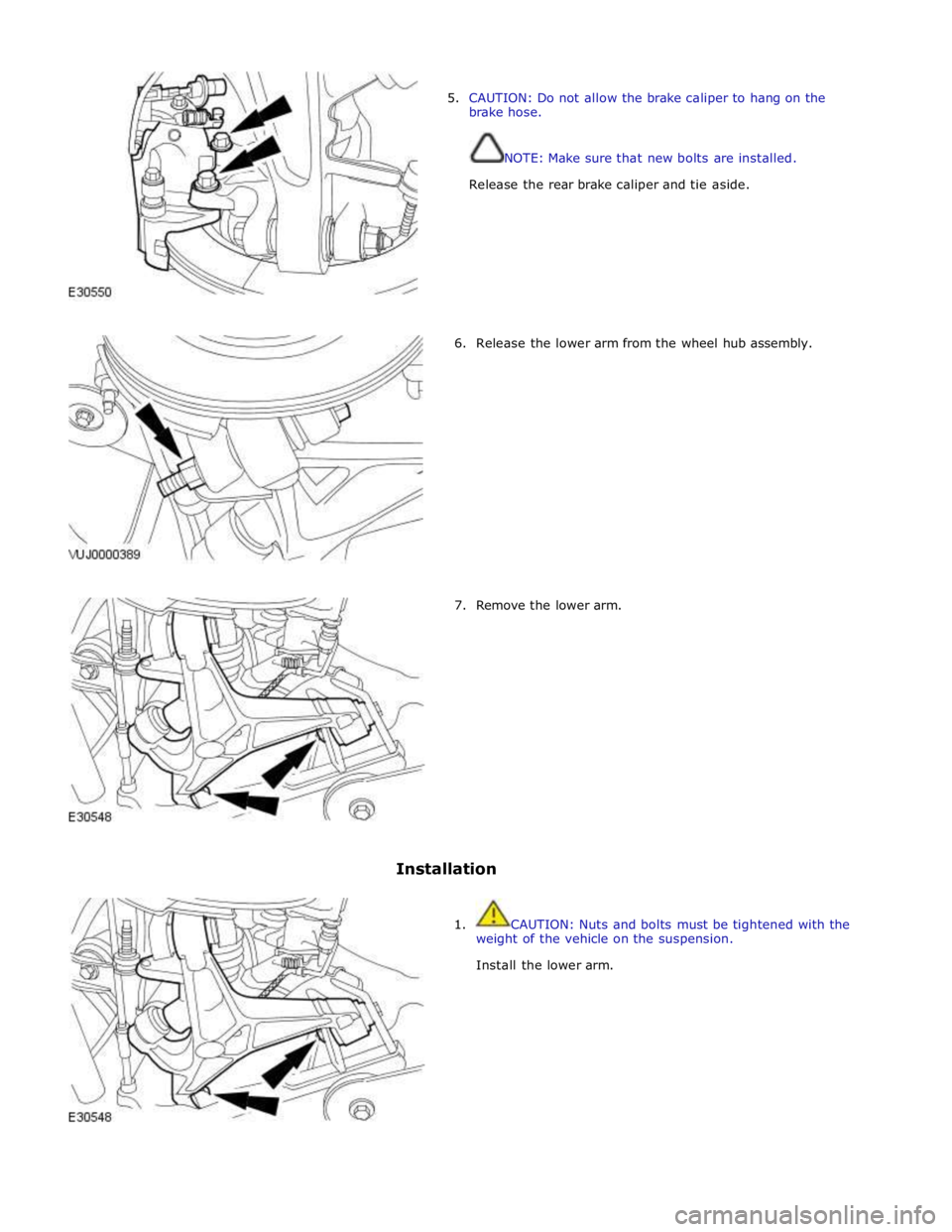
5. CAUTION: Do not allow the brake caliper to hang on the
brake hose.
NOTE: Make sure that new bolts are installed.
Release the rear brake caliper and tie aside.
6. Release the lower arm from the wheel hub assembly.
7. Remove the lower arm.
Installation
1. CAUTION: Nuts and bolts must be tightened with the
weight of the vehicle on the suspension.
Install the lower arm.
Page 401 of 3039
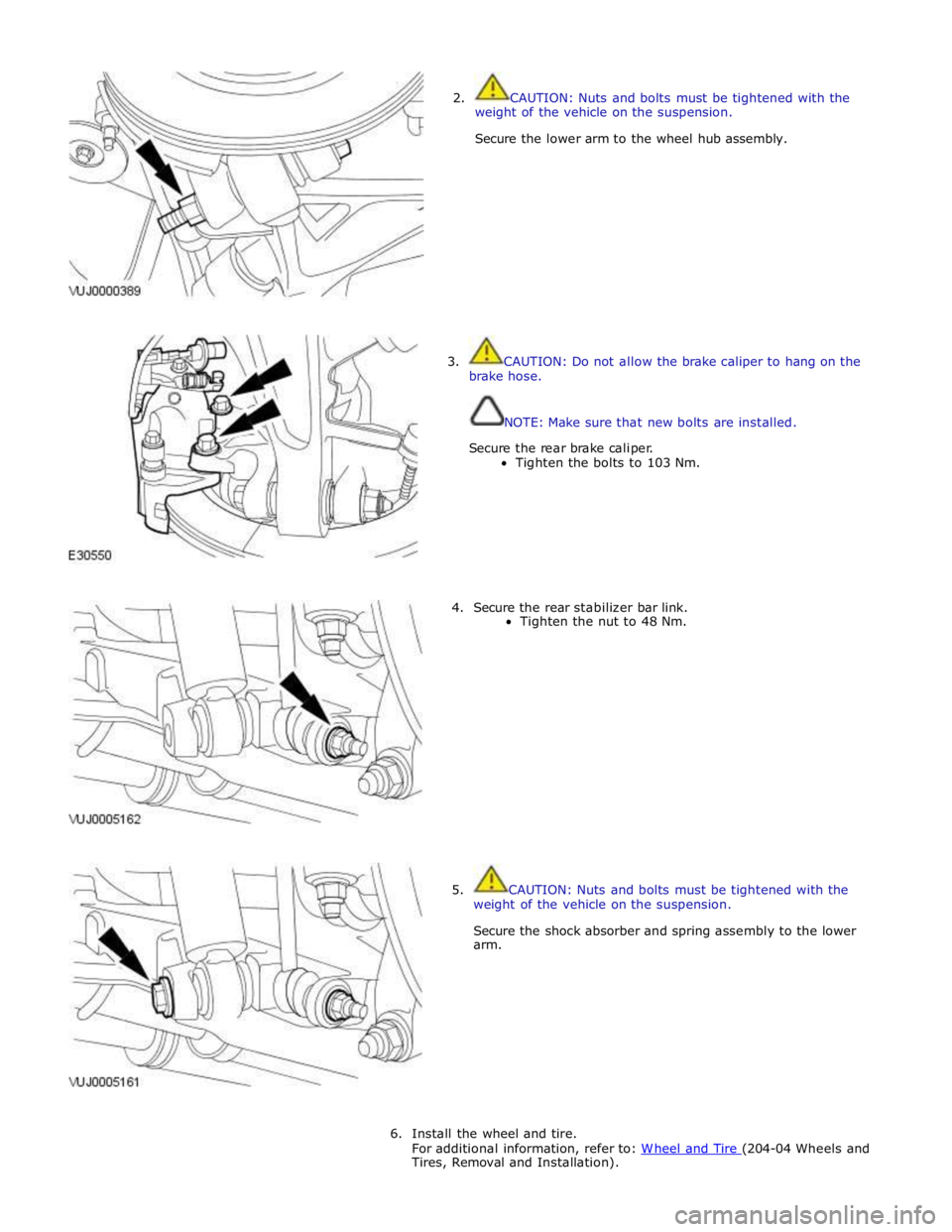
2. CAUTION: Nuts and bolts must be tightened with the
weight of the vehicle on the suspension.
Secure the lower arm to the wheel hub assembly.
3. CAUTION: Do not allow the brake caliper to hang on the
brake hose.
NOTE: Make sure that new bolts are installed.
Secure the rear brake caliper.
Tighten the bolts to 103 Nm.
4. Secure the rear stabilizer bar link.
Tighten the nut to 48 Nm.
5. CAUTION: Nuts and bolts must be tightened with the
weight of the vehicle on the suspension.
Secure the shock absorber and spring assembly to the lower
arm.
6. Install the wheel and tire.
For additional information, refer to: W heel and Tire (204-04 Wheels and Tires, Removal and Installation).