suspension JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.GPages: 521, PDF Size: 17.35 MB
Page 216 of 521

may include:
0
0
Loose or worn wheel bearings.
Loose or worn suspensions or steering components.
0 Worn or damaged drive shaft slip yoke joint.
0 Front disc rotor runout.
o Loose engine or transmission supports.
0 Driveline alignment.
0 Engine driven accessories.
Suspension Systems
11.4 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
' 11.4.1 Tire Wear
Tires should be inspected as abnormal or excessive wear may becaused by incorrect wheel alignment, wheelbire im- balance, or incorrect tire pressure.
1 1.4.2 vibration and Roughness
Vibration, roughness, and shimmy conditions may be caused by excessive tire or wheel runout, worn or cupped tires,
or wheel and tire unbalance.
Most of these conditions are due to irregularities in the road surface, hence driving the vehicle on different types of
road surface will often indicate the cause of the condition.
Do not automatically suspect the tires when attempting to diagnose a vibration concern as other sources of vibration
Before investigating any other vibration concerns,
a roaG &est and a customer inter\,.dw (if possible) should be carried
out. This can provide much of the information needed to find the source of vibration.
Drive the vehicle on a road that is preferably smooth and free of undulation and
if vibration is apparent note, the speed at which thevibration occurs, whattype of vibration occurs in each speed range (mechanical or audible), howthevibra- tion is affected by changes in vehicle speed , engine speed and engine torque, and the type of vibration sensitivity
(torque sensitive, vehicle speed sensitive, or speed sensitive).
Some of the condition terms used when describing sources of vibration are explained as follows:
0 Torque Sensitive
This condition can be improved or worsened by accelerating, decelerating, coasting, maintaining
a steady
vehicle speed and application of engine torque.
0 Vehicle Speed Sensitive
This means that the vibration always occurs at the same vehicle speed and is not affected by engine torque,
engine rpm, or transmission gear selection.
B
0 Engine Speed Sensitive
This means that the vibration occurs
at varying vehicle speeds when a different transmission gear is selected.
It can sometimes be isolated by increasing or decreasing engine speed with the transmission in 'NEUTRAL', or
by stall testing with the engine in gear. If the condition is enginesensitive, the condition is not related to tires.
If the road tests indicates that the vibration is related to the tires or wheels,use a 'lire Wear Diagnosis Chart' to
investigate the cause of concern. Should the road test indicate that there is tire whine, but noshake or vibration,
the noise originates from the contact between the tire and the road surface.
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 217 of 521

Suspension Systems
11.4.3 Front End Inspection
Do not check and adjust front wheel alignment without carrying out the following inspection for front end damage and
wear:
. Check for specified air pressure in all four tires.
Raise front of vehicle off the floor; grasping upper and lower surface of the tire, shake each front wheel to check for
. Check front suspension lower arm ball joint and mounts for looseness, wear and damage.
Check steering gear mountings and all steering linkages for looseness.
. Renew parts if necessary.
. Grasp upper and lower surface of tire and shake each wheel to check wheel bearing end play.
. Check the action of the front dampers and the condition of their attachments, as sticking or binding front dampers
worn
bearings.
Check brake caliper mountings.
may not allow the vehicle to settle in to a normal level position, possibly affecting the front-wheel alignment.
m: Front wheel bearings are adjustable (0.001 to 0.003 in. endfloat).
11.4.4
. Check the wheel bearings.
. Inspect the front suspension upper joint and renew front suspension lower wishbone if needed.
Raise vehicle and position floor jacks beneath the front suspension lower wishbone.
Grasp the lower edge of the tire and move the wheel in and out.
While moving the wheel, observe the upper and lower wishbone.
. Movement between the vertical links and the wishbones indicates abnormal ball joint wear.
. Renew ball joints.
. Check the front wheel bearings.
. Check for excessive play and wear.
Upper / Lower Ball Joint Inspection
11.4.5 Damper Inspection
m: The gas-pressurized hydraulic front dampers are not serviceable, adjustable or refillable.
Verify that all attachments of the suspension components and the front dampers are tight. Renew any front damper
. Check front dampers for external damage.
. Check for oil leakage and vehicle sag.
that
has a damaged integral lower mounting bushing.
0 Oil Leak
Leakage is the condition in which the entire damper body is covered with oil and from where
it will drip on to
the pavement. Due to correct damper lubrication a light film of oil (weepage) can usually be seen on the upper
portion of the damper.
Should there be any leakage, ensure that the fluid does not originate from sources other than the front damper.
Renew worn or damaged dampers.
0 Vehicle Sag
Renewing front dampers will not correct the problem of vehicle sag, as basically this is controlled by the spring
units.
issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 218 of 521

Suspension Systems
1 1.4.6 Rear Suspension lnspe&on
Check damper operation.
Check condition of rear wishbone bushings and rear suspension strut bushings.
Renew damaged or worn components.
0 Check for evidence of fluid leaks on rear dampers.
11.4.7 Vehicle Inspection
Check all tires for correct inflation pressure.
Checktire condition to confirm correct front end alignment, tire balance and overall tire conditions such as separation
Check the vehicle attitude for evidence of possible overload or sagging.
Check luggage compartment area.
. Road test vehicle to confirm customer's concern.
or
bulges.
X300 VSM 5 Issue 1 August 1994 ~ ~~
Page 219 of 521
Suspension Systems
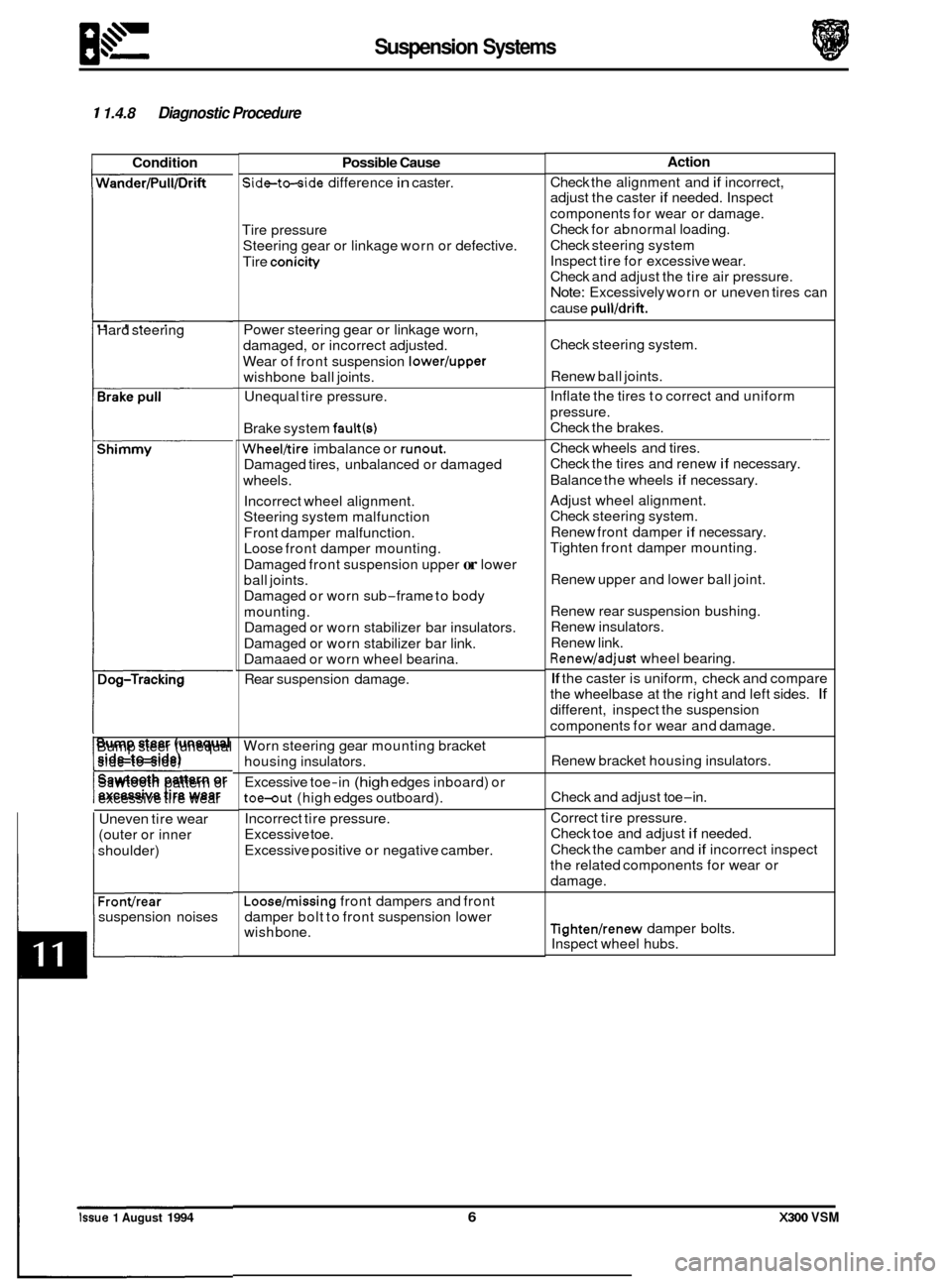
1 1.4.8 Diagnostic Procedure
Condition
Hard steering
Shimmy
I----
Bump steer (unequal
side-to-side)
Sawtooth pattern or
t excessive tire wear
Uneven tire wear
(outer or inner
shoulder)
Fronvrear
suspension noises
Possible Cause
Side-to-side difference in caster.
Tire pressure Steering gear or linkage worn or defective.
Tire
conicity
Power steering gear or linkage worn,
damaged, or incorrect adjusted.
Wear of front suspension
lower/upper
wishbone ball joints.
Unequal tire pressure.
Brake system
fault(s)
Wheel/tire imbalance or runout.
Damaged tires, unbalanced or damaged
wheels.
Incorrect wheel alignment.
Steering system malfunction
Front damper malfunction.
Loose front damper mounting.
Damaged front suspension upper
or lower
ball joints.
Damaged or worn sub
-frame to body
mounting. Damaged or worn stabilizer bar insulators.
Damaged or worn stabilizer bar link.
Damaaed or worn wheel bearina.
Rear suspension damage.
Worn steering gear mounting bracket
housing insulators.
Excessive toe
-in (high edges inboard) or
toe-out (high edges outboard).
Incorrect tire pressure.
Excessive toe.
Excessive positive or negative camber.
Loose/missing front dampers and front
damper bolt to front suspension lower
wish bone.
Action
Check the alignment and if incorrect,
adjust the caster
if needed. Inspect
components for wear or damage.
Check for abnormal loading.
Check steering system
Inspect tire for excessive wear.
Check and adjust the tire air pressure.
Note: Excessively worn or uneven tires can
cause
pull/drift.
Check steering system.
Renew ball joints.
Inflate the tires to correct and uniform
pressure.
Check the brakes.
Check wheels and tires.
Check the tires and renew
if necessary.
Balance the wheels
if necessary.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Check steering system.
Renew front damper
if necessary.
Tighten front damper mounting.
-
Renew upper and lower ball joint.
Renew rear suspension bushing.
Renew insulators.
Renew link.
Renew/adjust wheel bearing.
If the caster is uniform, check and compare
the wheelbase at the right and left sides.
If
different, inspect the suspension
components for wear and damage.
Renew bracket housing insulators.
Check and adjust toe
-in.
Correct tire pressure.
Check toe and adjust
if needed.
Check the camber and
if incorrect inspect
the related components for wear or
damage.
Tighten/renew damper bolts.
Inspect wheel hubs.
0
0
0
lssue 1 August 1994 6 X300 VSM
Page 220 of 521
Suspension Systems I.\" b-
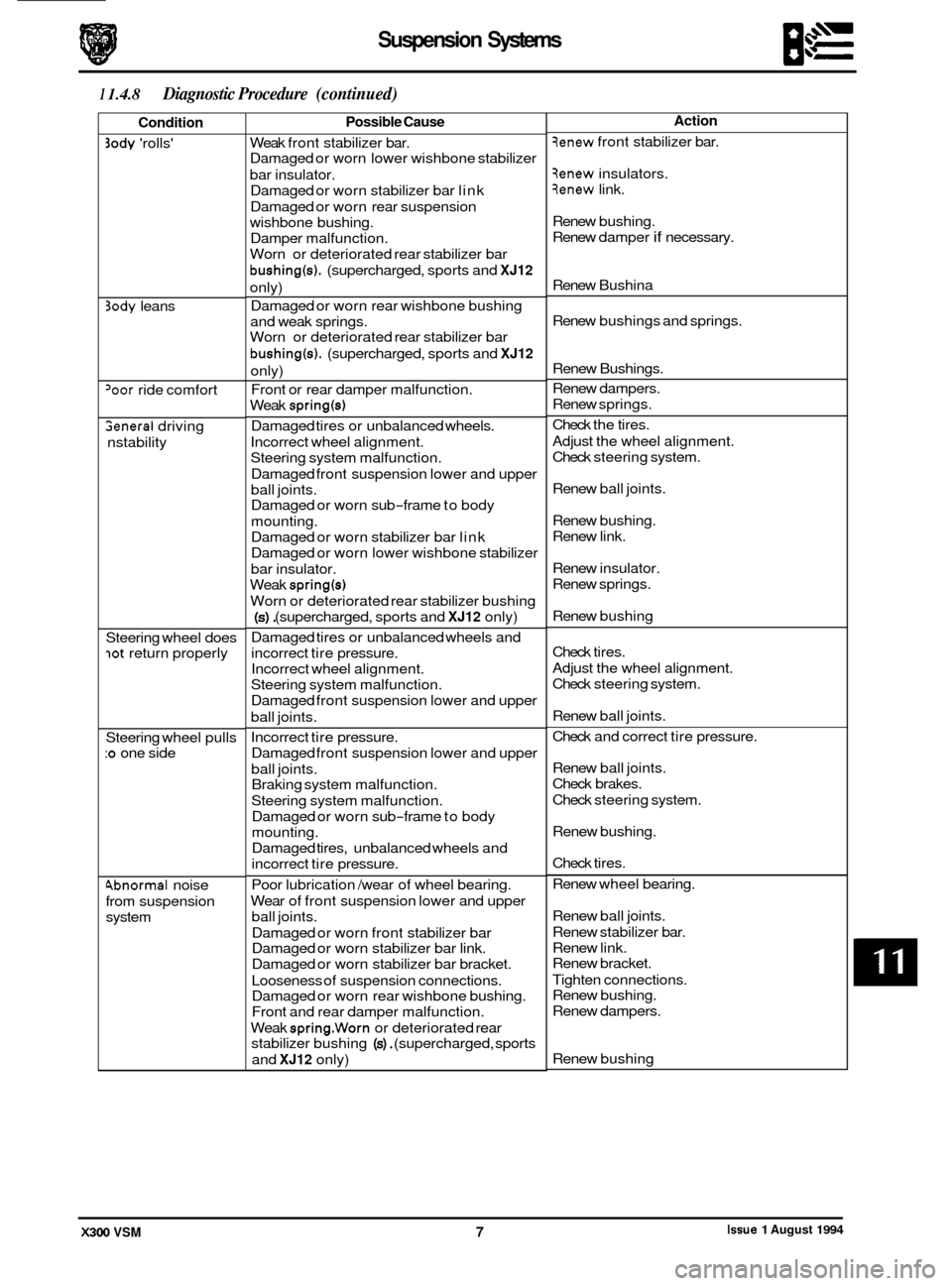
1 1.4.8 Diagnostic Procedure (continued)
Condition
30dy 'rolls'
3ody leans
'oor ride comfort
Seneral driving
nstability
Steering wheel does
lot return properly
Steering wheel pulls
:o one side
4bnormal noise
from suspension
system
Possible Cause
Weak front stabilizer bar.
Damaged or worn lower wishbone stabilizer
bar insulator. Damaged or worn stabilizer bar link
Damaged or worn rear suspension
wishbone bushing.
Damper malfunction.
Worn or deteriorated rear stabilizer bar
bushing(s). (supercharged, sports and XJ12
only)
Damaged or worn rear wishbone bushing
and weak springs.
Worn or deteriorated rear stabilizer bar
bushing(s). (supercharged, sports and XJ12
only)
Front or rear damper malfunction.
Weak
spring(s1
Damaged tires or unbalanced wheels.
Incorrect wheel alignment.
Steering system malfunction.
Damaged front suspension lower and upper
ball joints.
Damaged or worn sub
-frame to body
mounting.
Damaged or worn stabilizer bar link
Damaged or worn lower wishbone stabilizer
bar insulator.
Weak
spring(s)
Worn or deteriorated rear stabilizer bushing
(s). (supercharged, sports and XJ12 only)
Damaged tires or unbalanced wheels and
incorrect tire pressure.
Incorrect wheel alignment.
Steering system malfunction.
Damaged front suspension lower and upper
ball joints.
Incorrect tire pressure.
Damaged front suspension lower and upper
ball joints. Braking system malfunction.
Steering system malfunction.
Damaged or worn sub
-frame to body
mounting.
Damaged tires, unbalanced wheels and
incorrect tire pressure.
Poor lubrication /wear of wheel bearing.
Wear of front suspension lower and upper
ball joints.
Damaged or worn front stabilizer bar
Damaged or worn stabilizer bar link.
Damaged or worn stabilizer bar bracket.
Looseness of suspension connections.
Damaged or worn rear wishbone bushing.
Front and rear damper malfunction.
Weak
spring.Worn or deteriorated rear
stabilizer bushing
(s). (supercharged, sports
and
XJ12 only)
Action
3enew front stabilizer bar.
3enew insulators.
3enew link.
Renew bushing.
Renew damper
if necessary.
Renew Bushina
Renew bushings and springs.
Renew Bushings.
Renew dampers.
Renew springs.
Check the tires.
Adjust the wheel alignment.
Check steering system.
Renew ball joints.
Renew bushing.
Renew link.
Renew insulator.
Renew springs.
Renew bushing
Check tires.
Adjust the wheel alignment.
Check steering system.
Renew ball joints.
Check and correct tire pressure.
Renew ball joints.
Check brakes.
Check steering system.
Renew bushing.
Check tires.
Renew wheel bearing.
Renew ball joints.
Renew stabilizer bar.
Renew link.
Renew bracket.
Tighten connections.
Renew bushing.
Renew dampers.
Renew bushing
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM 7
Page 230 of 521
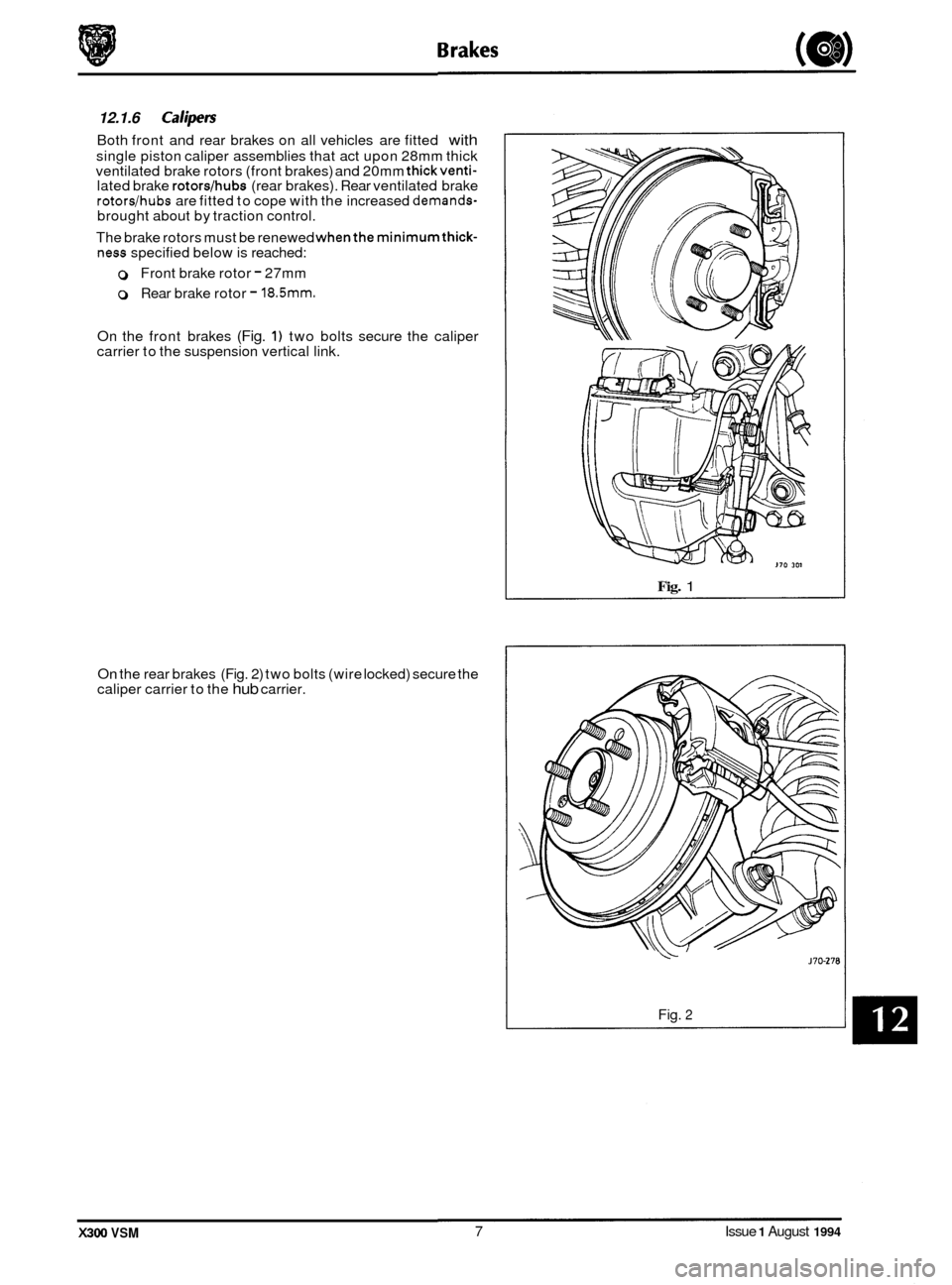
0 12.1.6 Calipers
Both front and rear brakes on all vehicles are fitted with
single piston caliper assemblies that act upon 28mm thick
ventilated brake rotors (front brakes) and 20mm thickventi- lated brake rotors/hubs (rear brakes). Rear ventilated brake rotordhubs are fitted to cope with the increased demands- brought about by traction control.
The brake rotors must be renewed
whenthe minimumthick- ness specified below is reached:
0 Front brake rotor - 27mm
0 Rear brake rotor - 18.5mm.
On the front brakes (Fig. 1) two bolts secure the caliper
carrier to the suspension vertical link.
On the rear brakes (Fig. 2) two bolts (wire locked) secure the
caliper carrier to the hub carrier.
Fig. 1
\
Fig. 2
J70-278
X300 VSM 7 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 382 of 521

Snecif icat ion W -I- ..........
e
0
CON TENTS
Title Page
Specification. 1995 Model Year Vehicles ................................................................... 1
EngineManagementSystem ........................................................................\
. 1
Cooling System ........................................................................\
............ 7
Fuelsystem Pump ........................................................................\
......... 7
Clutch ........................................................................\
................... 7
Manual Transmission Ratios ........................................................................\
. 1
Automatic Transmission Ratios ....................................................................... \
2
Final Drive Unit Ratios ........................................................................\
..... 2
Climate Control System ........................................................................\
..... 2
Braking System ........................................................................\
............ 3
Steering&Suspension ........................................................................\
...... 4
Electrical Equipment ........................................................................\
....... 5
Lubricants & Fluids ........................................................................\
......... 7
Vehicle Weights ........................................................................\
........... 9
Tires ........................................................................\
.................... 10
Snowchains ........................................................................\
............. 17
Bulbs ........................................................................\
................... 12
Fuses ........................................................................\
................... 14
Issue 1 August 1994 AI-95MY i X300 VSM
Page 387 of 521

Steering and Suspension
W: When checking the steering geometry, use the pull-down tools front and rear to set the ride height front and
rear to the following dimensions:
Front ride height
................................................... 153 f 5mm to underside of front
crossbeam
Rear ride height
.................................................... 160 f 5mm to underside of rear
edge of A frame
Front ride height
................................................... 143 f 5mm to underside of front
crossbeam
Rear ride height
.................................................... 160 f 5mm to underside of rear
edge of A frame
U: Sportspack derivatives whose kerb height is below the above figures can have their geometry checked at that
height.
Front Suspension
..............................................................
0
Type Independent front suspension
consisting of double wishbones
with coil springs and separate
dampers and anti
-roll bar.
Dampers
.......................................................... Telescopic, gas pressurised
Caster angle
....................................................... 3,0° to 6,0° and with opposing
wheels within Io of each other
Camberangle
...................................................... 0,3°to-0,80
Front wheel alignment .............................................. Total toe: 5 minutes in f 10 minutes
Rear Suspension
Type .............................................................. Fully independent rear suspension of double wishbone principle with
axle shaft operating as upper
wishbone incorporating coaxial
springs and dampers with optional
rear anti
-roll bar.
Camber angle
(at design ride height):
all vehicles except supercharged ................................. -0,75O f 0,4O
supercharged only -1,6O f 0,4O ..............................................
0 Rear wheel alignment .............................................. Total toe: 15 minutes in f20
Dampers .......................................................... Telescopic, gas pressurised
minutes
Power Assisted Steering
Type .............................................................. ZF
Servotronic speed-sensitive rack
and pinion
Number
of turns lock to lock ........................................ 2,768
Turning circle: (wall to wall)
....................................................... 12,9m (42ft 4in)
(curb to curb) ...................................................... 12,4m (40ft 8in)
0
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 AI-95MY 4 ~~~~
Page 408 of 521
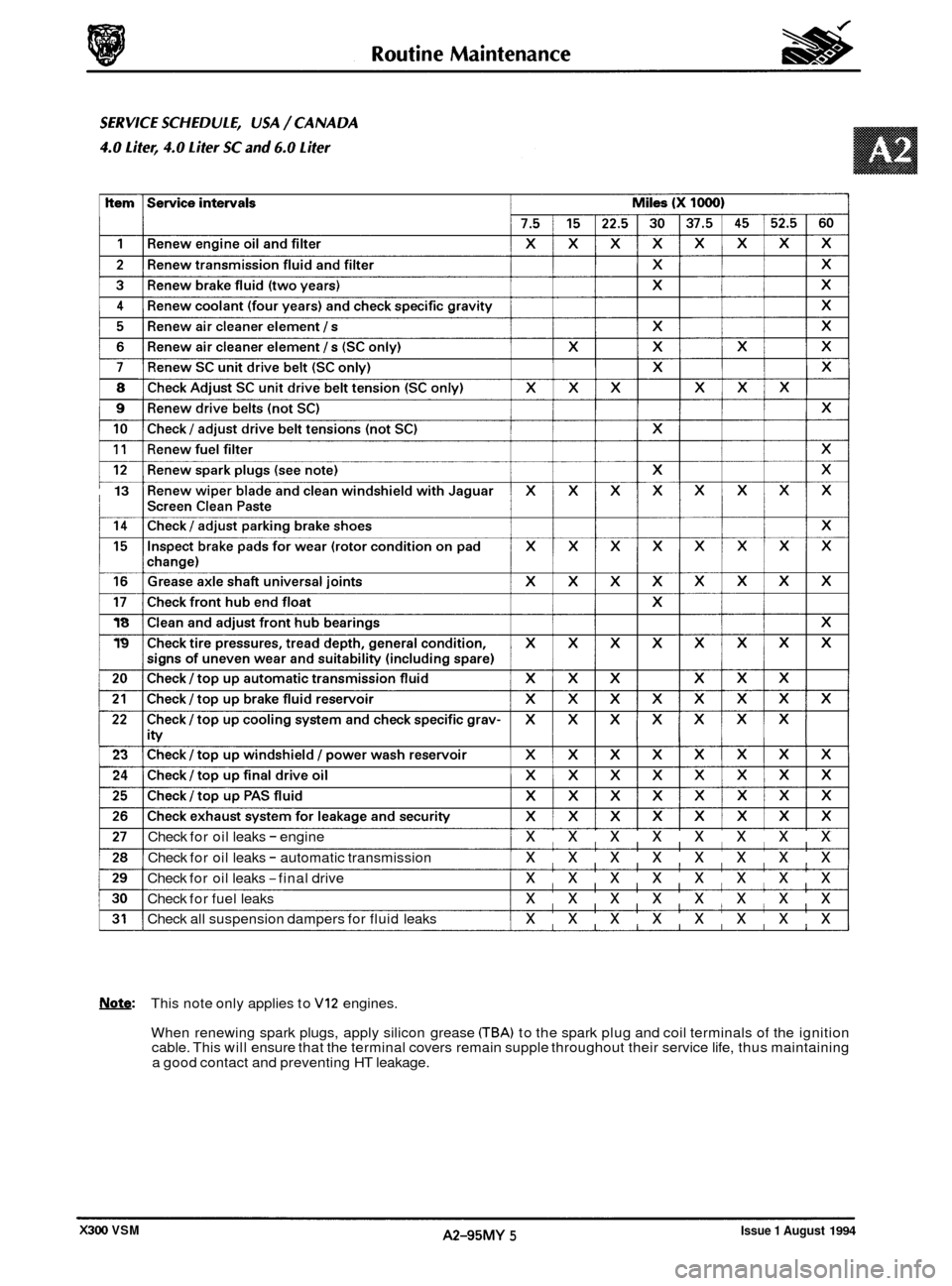
j
8
9
10
13 I
18
19
23
24
Check for oil leaks - engine xxxxxxxx
Check for oil leaks - automatic transmission xxxxxxxx
Check for oil leaks -final drive xxxxxxxx
Check for fuel leaks xxxxxxxx
Check all suspension dampers for fluid leaks xxxxxxxx
Note: This note only applies to VI2 engines.
When renewing spark plugs, apply silicon grease
CTBA) to the spark plug and coil terminals of the ignition
cable. This will ensure that the terminal covers remain supple throughout their service life, thus maintaining
a good contact and preventing HT leakage.
Issue 1 August 1994 A2-95MY 5 X300 VSM
Page 428 of 521

0
0
0
Body Systems Body Repair
A4.1 BODY REPAIR
Introduction
This section contains information, specifications and procedures for body repair and rectification of the Jaguar sedan
range (with standard wheelbase).
All repairs, whether structural or cosmetic, must ensure the continuance of the Paint Surface and Corrosion warranty,
where applicable.
Following repair or rectification, the vehicle must be returned to the original manufactured condition with regard to
occupant safety, dimensional accuracy, finish and corrosion protection.
Similarly, repaired vehicles must be fully checked, and where appropriate reset, with regard to steering, suspension,
restraint and
braking systems.
A4.1.1 Health and Safety
(Please Read The
Fol/owing Notes Carethlly)
Where legislation governing working conditions and practises is applicable, you should observe it. Do not forget that
you have a duty, to yourself and those around you, to act in a responsible manner in the workplace.
In the United Kingdom the Health and Safety
at Work Act (1974) places a duty on employers and employees to ensure,
whenever possible, safe working conditions and practices. Wherever a potential hazard is notified to, or identified by
the operator, he must employ the correct safety procedures and equipment.
Should
a personal injury occur as a result of any workshop activity, seek medical help as soon as possible and do not
attempt self-treatment other than by the application of first aid.
With the constant introduction of new materials in the manufacture of vehicles,
it is important that potential risks are
identified and precautions made known.
WARNING: READ AND UNDERSTAND WORKING PRACTICES CLIMATE CONTROL SYSTEMS, SECTION 14, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO
ERY
/ RECYCLE / RECHARGE EQUIPMENT.
WEAR SUITABLE EYE AND SKIN PROTECTION.
OBSERVE ALL APPLICABLE SAFETY REQUIREMENTS.
DO
NOT VENT REFRIGERANT DIRECTLY TO ATMOSPHERE, ALWAYS USE JAGUAR APPROVED RECOV
-
Issue 1 August 1994 1 X300 VSM