electrical JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.GPages: 521, PDF Size: 17.35 MB
Page 328 of 521

Climate Control Systems
14.10 FAULT DIAGNOSIS
14.10.1 Introduction
It is very important to positively identifythe area of concern before starting a rectification procedure. A little time spent
with your customer to identify the conditions under which a problem occurs will be beneficial. Relevant criteria are:
Weather conditions, ambient temperature, intermittent or continuous fault, airflow fault, temperature control fault, dis
- tribution fault and air inlet problem.
14.10.2 Functional Check
This simple 'first line check' will allow you to ascertain whether the system is operating within its design parameters,
without recourse to (JDE). Please carry out the following, in order.
0 Start engine and attain normal running temperature.
0 Presss AUTO to display selected temperature and illuminate AUTO & AJC state lamps.
0 Rotate FAN to increase or decrease lower speed, verify bar graph representation.
0 Operate AJC to toggle on or off. Because the compressor can be inhibited by the engine management system,
ensure that the engine temperature is normal and that the ambient is above 5O C.
0 Operate RECIRC, state lamp should be lit and the flap behind the blower grille open.
0 Operate distribution buttons in turn, verify correct air distribution and relevant state lamp.
0 Operate DEFROST, check max fans and air to front screen.
0 Cycle TEMPERATURE to 'Hi' and 'Lo' to verify demanded variations and display operation. Note that extremes
will provide max heat or cold independent of in-car temperature.
0 Operate EX to toggle between ambient and control temperatures.
0 Operate HFS and HRW to note timer and mirror operation.
0 Initiate System Self Test to check for, and extract, stored faults should any of the above not perform as stated.
14.10.3 System symptoms
There are five basic symptoms associated with air conditioning fault diagnosis. The following conditions are not in order of priority.
No Cooling
0 Is the electrical circuit to the compressor clutch functional?
0 Is the electrical circuit to the blower motor(s) functional?
0 Slack or broken compressor drive belt.
0 Compressor partially or completely seized.
0 Compressor shaft seal leak.
0 Compressor valve or piston damage (may be indicated by small variation between HIGH &LOW side pressures
relative to engine speed).
0 Broken refrigerant pipe (causing total loss of refrigerant).
0 Leak in system (causing total loss of refrigerant) - possible code 23.
0 Blocked filter in the receiver drier.
0 Evaporator sensor disconnected - possible code 13.
0 Pressure switch faulty - possible code 23.
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994
Page 329 of 521

Climate Control Systems
lnsufficent Cooling
0 Sluggish blower motor(s).
0 Restricted blower inlet or outlet passage
0 Blocked or partially restricted condenser matrix or fins.
0 Blocked or partially restricted evaporator matrix.
0 Blocked or partially restricted filter in the receiver drier.
0 Blocked or partially restricted expansion valve.
0 Partially collapsed flexible pipe.
0 Expansion valve temperature sensor faulty (this sensor is integral with valve and is not serviceable).
0 Excessive moisture in the system.
0 Air in the system.
0 Low refrigerant charge - possible code 23.
0 Compressor clutch slipping.
0 Blower flaps or distribution vents closed or partially seized - possible codes 41 or 46.
0 Coolant flow valve not closed.
0 Evaporator sensor incorrectly positioned
m: Should a leakor low refrigerant be established as the cause of /NSUff/C/€NTCOOL/NG,followthe procedures
Recovery / Recycle / Recharge, this section, and observe all refrigerant and oil handling instructions.
lntermiffent Cooling
0 Is the electrical circuit to the compressor clutch consistent?
0 Is the electrical circuit to the blower motor(s) consistent?
0 Compressor clutch slipping?
0 Motorized in-car aspirator or evaporator temperature sensor faulty, causing temperature variations - possible
codes 11 or 13.
0 Blocked or partially restricted evaporator or condenser.
Noisy System
0 Loose or damaged compressor drive belt.
0 Loose or damaged compressor mountings.
0 Compressor oil level low, look for evidence of leakage.
0 Compressor damage caused by low oil level or internal debris.
0 Blower motor(s) noisy.
0 Excessive refrigerant charge, witnessed by vibration and 'thumping' in the high pressure line (may be indicated
by high HIGH & high LOW side pressures).
0 Low refrigerant charge causing 'hissing' at the expansion valve (may be indicated by low HIGH side pressure).
0 Excessive moisture in the system causing expansion valve noise.
0 Air-lock in water pump*.
lnsufficent Heating
0 Coolant flow valve stuck in the closed position.
0 Motorized in-car aspirator seized.
0 Cool air by-pass damper stuck or seized - possible code 43.
0 Blocked or restricted blower inlet or outlet.
0 Low coolant level.
0 Blower fan speed low.
0 Coolant thermostat faulty or seized open.
0 Water pump inoperative or blocked
0 Air-lock in matrix*.
m: * Please see Sections 4.1 and 4.2 for specific coolant fill / bleed procedures.
Electrical faults may be more rapidly traced using
(JDE), please refer to the (EDM).
Issue 1 August 1994 16 X300 VSM
Page 338 of 521

Electrical cl
.
SECTION CONTENTS
Subsection Title SRO Page
i ................ PreliminaryPages .................................................................... i
15.1 ............. Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) .................................................... 1
15.1.1 ............ SRS. General Description .............................................................. 1
15.1.2 ............ SRS. Handling Undeployed Modules .................................................... 2
15.1.3 ............ SRS. Emergency First Aid Procedures .................................................... 3
15.1.4
............ SRS. Safety Procedures. Handling Deployed Modules ...................................... 3
15.1.5 ............ SRS. Safety Procedures. Handling Undeployed Damaged Modules ........................... 3
15.1.6. ........... SRS. Fire Hazard Information .......................................................... 4
15.1.7.
........... SRS. Ventilation ...................................................................... 4
15.1.8 ............ SRS. RespiratoryPrecautions ........................................................... 4
15.1.9.
........... SRS. Eye Protection ................................................................... 4
15.1.10
.......... SRS. Protective Clothing ............................................................... 4
15.1.11 ........... SRS. Handling & Storage Precautions .................................................... 4
15.1.12 .......... SRS. Modules. Assembly/ Removal/Setvice Instructions ................................... 4
15.1.13 .......... SRS. Spillage & Leakage ............................................................... 5
15.1.14 .......... SRS. Scrapping Vehicles With Live Airbags ............................................... 5
15.1.15 .......... SRS. Scrapping Vehicles With Deployed Airbags .......................................... 6
15.1.16 .......... SRS. Disposal of Live Airbag Modules ................................................... 6
15.1.17 .......... SRS. Disposal of Deployed Airbag Modules .............................................. 7
15.2 ............. Instruments ........................................................................\
. 8
15.2.1
............ Instruments. General Description ....................................................... 8
15.2.2 ............ Instruments. Analog Display ........................................................... 8
15.2.3
............ Instruments. Indicator Lamps ........................................................... 8
15.2.4.
........... Instruments. Liquid Crystal Display ..................................................... 8
15.2.5.
........... Instruments. Transducers .............................................................. 8
15.2.6. ........... Instruments. Panel. General ........................................................... 8
15.2.7.
........... Instruments. Gauges .................................................................. 9
15.2.8. ........... Instruments. Odometer ............................................................... 10
15.2.9
............ Instruments. Trip Computer ........................................................... 10
15.2.10 .......... Instruments. Driver Information Messages ............................................... 10
15.2.11 ........... Instruments. Illumination ............................................................. 10
15.2.12 .......... Instruments. General Repair Notes ..................................................... 10
15.3 ............. Speed Control ...................................................................... 11
15.4 ............. Driver Ergonomics .................................................................. 12
15.5
............. Battery& ChargingSystem ........................................................... 13
15.5.1 ............ Battery, General .................................................................... 13
15.5.2 ............ Battery, ReserveCapaci ty ............................................................. 13
15.5.3.
........... Battery. Cranking Performance ........................................................ 13
15.5.4 ............ Battery. Electrical Data ............................................................... 13
15.5.5
............ Battery. State of Charge .............................................................. 13
15.5.6 ............ Battery, Rate of Charge ............................................................... 13
15.5.7 ............ Battery. LoadTest ................................................................... 13
15.5.8 ............ Battey. Specific Gravity Test .......................................................... 14
15.5.9 ............ Battery. Electrolyte Temperature Correction .............................................. 14
15.5.10 .......... Battery. Health & Safety Precautions ................................................... 14
15.5.11. .......... Battery. Remove & Refit ......................................... 86.15.01 ............ 15
e
e
X300 VSM i Issue 1 August 1994
Page 339 of 521
rl Electrical
SECTION CONTENTS
Sub-section Title SRO Page
15.6 .............
15.6.1 ............
15.6.2 ............
15.6.2.1 ..........
15.6.2.2 ..........
15.6.2.3 ..........
15.7 .............
15.8 .............
15.9 .............
15.9.1 ............
15.9.2 ............
15.10 ............
15.10.1 ..........
15.10.2 ..........
15.10.3 ..........
15.10.4 ..........
15.11 ............
15.11.1 ...........
15.12 ............
15.12.1 ..........
15.12.2 ..........
15.12.3 ..........
15.13 ............
15.13.1 ..........
Power Wash & Screen Wash / Wipe .................................................... 16
Windscreen Wipers and Washers. General Description .................................... 16
Windscreen Wipers and Washers. Switch ............................................... 16
Windscreen Wipers and Washers. Single Wipe Operation ................................. 16
Windscreen Wipers and Washers. Programmed Wash / Wipe Operation ..................... 77
Windscreen Wipers and Washers. Headlamp Power Wash Operation ....................... 17
Closures Switching .................................................................. 18
In-Car Entertainment ................................................................ 19
Lamps & Lighting Logic .............................................................. 20
Lamps & Lighting Logic. Exterior Lighting. General Description ............................ 20
Lamps & Lighting Logic. Interior Lighting. General Description ............................ 21
Harnesses &Cables ................................................................. 22
Harnesses
& Cables. Battery Power Distribution Cables. General ........................... 22
Harnesses & Cables. Main Harnesses. General Description ................................ 24
Harnesses & Cables. Link Harnesses. General Description ................................. 26
Harnesses & Cables. Harness Connectors. General Description ............................. 28
Motors and Solenoids ................................................................ 30
Motors and Solenoids. General Description ............................................. 30
Relays ........................................................................\
..... 32
Relays. Engine Compartment. General Description ....................................... 32
Relays. Passenger Compartment. General Description .................................... 34
Relays. Trunk. General Description .................................................... 36
Control Modules .................................................................... 38
Control Modules. General Description ................................................. 38
Page 343 of 521

15.1.2 Handling Undeployed Modules
The electrically-activated airbag module contains sodium azide and sodium nitrate which are poisonous and
extremely flammable substances.
Their contact with acid, water or heavy metals may produce harmful and irritating gases or combustible compounds.
The airbag module is
non-serviceable and must not be dismantled, punctured, incinerated or welded.
WARNING: DO NOT ATTEMPT ANY REPAIRS TO THE AIRBAG MODULE.
Never measure the resistance of the airbag module, as this may cause the airbag to deploy. Suspect modules must be returned to Jaguar Cars Ltd. or their importer for replacement.
Tampering or mishandling can result in personal injury.
Keep away from heat, sparks and open flames. Do not store
at temperatures exceeding 93O Celsius (200OF).
Keep away from electrical equipment as electrical contact may cause ignition.
Do not drop or impact airbag module.
Always position module 'cover
-up'.
Ensure that the connector is protected to prevent damage.
J76-1058
Fig. 1 The Driver-side Airbag
Store modules in a secure lockable cabinet.
Never position projectile material over the undeployed airbag as this can cause injury in the event of inadvertent
deployment.
Page 344 of 521

Do not wrap arms around module when carrying and always carry module with cover and ventsfacing awayfrom body
to avoid personal injury in the event of inadvertent deployment.
Never carry airbag module by wires or the connector.
The chemical propellant mixture deploying the airbag is
a solid and therefore inhalation exposure is unlikely even if module is ruptured without deployment.
As far as practicable, avoid skin contact with, or ingestion of, the materials present after combustion. Exposure to high
concentrations of propellant mixture may cause headache, nausea, blurred vision, faintness, cyanosis, lowering of
blood pressure, tachycardia and shortness of breath.
WARNING:SODlUM AZlDE HAS BEEN LISTED AS AN 'EXTRAORDINARY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE OR
CARCINOGEN BY THE STATE OF MASSACHUSETTS, USA. SODIUM AZlDE HAS BEEN LISTED ON THE 'RIGHT TO KNOW HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE LIST' BY THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY AND IS ALSO
REGARDED AS A 'SPECIAL HEALTH HAZARD SUBSTANCE BY THE STATE. THE PROPELLANT MIXTURE IS SENSITIVE TO PREMATURE IGNITION BY ELECTRICAL SOURCES IF NOT PROPERLY PROTECTED AND
ISOLATED.
15.1.3 Emergency First Aid Procedures
If the airbag is ruptured without deployment and exposure to the propellant mixture occurs, observe the following
first-aid treatments:
0 Ingestion - Do not induce vomiting and seek prompt medical attention.
0 Skin contact- Immediately wash skin with soap and water and seek medical attention.
0 Eyes - Immediately flush eyes with water for at least 20 minutes and seek prompt medical attention.
0 Inhalation - Immediately move victim to fresh air and seek medical attention.
0 Physical trauma, eg burns, abrasions, or impact due to premature ignition or deployment of the inflator
assembly - Treat symptomatically and seek prompt medical attention.
0
15.1.4
See 'Emergency First Aid Procedures' above.
Prevent contact of the inflator with liquids, combustibles and flammable materials. Failure to followthese instructions
could result in chemical burns and personal injury.
Ensure modules are cool before handling.
After deployment the airbag surface contains small deposits of sodium hydroxide which can cause irritation to the skin
and eyes.
When handling deployed airbags, always wear rubber gloves to
BS 1651 grade 2 or equivalent, and chemical resistant
goggles to BS 2092 grade 2 or equivalent.
After handling deployed airbags, immediately wash hands and exposed skin surface areas with mild soap and water.
Sakty Procedures For Handling Depbyed (Fid) Modules
15.1.5 Safety Procedures For Handling Undeployed Damaged Modules
The material inside the module is hermetically sealed and is completely consumed during deployment.
No attempt should be made to open the module
as this leads to a risk of exposure to sodium azide.
In the unlikely event of
a gas generator being damaged, it must be examined by trained personnel before any attempt
is made to remove and/or deploy.
Full protective clothing must be worn when dealing with any spillage.
Ruptured units must be stored away from acids, halogens, heavy metals and metal salts. Damaged units may produce
hydrazoic acid if exposed to liquids.
Failure to comply with these instructions may result in fire, noxious fumes and severe personal injury or death.
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 345 of 521

rl Electrical
15.1.6 Fire Hazard Infonnath
Thermal decomposition or combustion may produce dense smoke and other dangerous fumes which in fire situations
form
a highly toxic explosive.
In the event of fire the surrounding area must be evacuated and
all personnel kept well upwind of the area.
Full fire fighting protective gear and
a self contained breathing apparatus operating in the positive pressure mode must
be worn for combating fire. Material near fires must be cooled with water spray to prevent ignition.
Fires should be allowed to burn themselves
out if not threatening to life or property. If fire is threatening to life or prop- erty use copious quantities of water to extinguish.
15.1.7 Ventilath
Local exhaust ventilation designed by a professional engineer should be provided if vapours, fumes, or dusts are gen- erated whilst working with airbag module.
The latest issue of the manual for recommended practices on 'Industrial Ventilation' is available from the
ACGIH Com- mittee on Industrial Ventilation, PO Box 16153, Lansing, MI 48910, USA.
The need for local exhaust ventilation should be evaluated by a professional industrial hygienist.
15.1.8 Respiratory Precauth
To prevent the inhalation of dangerous fumes and dusts, an approved mask should be worn.
15.1.9 Eye Protection
Chemical protective goggles are recommended where there is a possibility of eye contact with the propellant.
Safety glasses with side shields are recommended for
all other operations.
15.1. I0 Protective Clothing
Approved protective gloves, overalls and shoes / boots should be worn.
15.1.1 1 Handling and Storage Precautions
Do not store airbag module near live electrical equipment or circuitry. Store in a dry environment at ambient tempera-
tures.
Good housekeeping and engineering practices should be employed to prevent the generation and accumulation of
dusts. Store in compliance with
all local state and federal regulations.
15.1.12 Driver And Passenger Airbag Modules Assembly / Removal / Service Instructions
Before starting work, ensure ignition switch is in 'IocK position, key is removed and negative terminal cable
is disconnected from the battery.
As the airbag is equipped with a back up power source and due to the risk of airbag being inadvertently
deployed, wait one minute or longer before starting work.
0 Disconnecting the battery cancels the memory for clock, radio, seats, mirrors, steering column and any other
components using battery power. Reset memory after work is completed.
0 Never use airbags from other vehicles, always use new parts.
0 After work is completed, reconnect battery and perform warning light check see diagnostic manual.
0 Never use electrical probes to check voltage or electrical resistance.
0 Disconnect the airbag before carrying out any work on, or in the vicinity of module, or when using electric weld- ing equipment.
0 Always ensure that battery negative has been disconnected for one minute or longer before commencing any
removal procedure.
EB
Issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 347 of 521

Electrical
(continued from previous page)
. The vehicle is now to be scrapped in normal manner with module installed.
Fig.
1
. In the event of any problems or queries, contact Jaguar Cars Ltd. or the importer.
15.1.15 Scrapping Vehicles With Deployed Airbag@
0 Verify that all installed airbags have been deployed or removed.
0 In the event of one airbag being deployed and one not deployed, it must be assumed that the undeployed airbag
is still live, therefore it must first be deployed.
0 The vehicle is now to be scrapped in a normal manner.
15.1.16 Disposal of live Airbag Modules
W
€AUTIQN: Never use a customer's vehicle to deploy airbags.
Equipment required: Deployment Cage,
IDC link harness (see 15.1.14 for details of components required), Battery,
Safety Goggles to BS 2092 grade 2 or equivalent, Rubber Gloves to PREN 374 class 2 or equivalent, Ear Protectors to BS EN 24869 or equivalent, Particulate Respirator to EN 149 grade FFP 25 or equivalent.
The deployment procedure should be performed outdoors away from other personnel.
Remove any loose debris from around airbag and ensure no flammable liquids are present.
Assemble the disposal cabinet
as shown in Fig.1 in line with the following procedures:
. Remove mesh guard from rig frame.
Attach guard to frame by bolting hinges to the frame.
(continued next page)
Modules
removedlrenewed by
Jaguar Service are to be returned to the importer for deployment and disposal.
X#w) VSM Issue 1 August 1994 6
Page 349 of 521
Electrical rl
15.2 INSTRUMENTS
15.2.1 General Description
The instruments measure, monitor and display data relevant to the vehicle’s performance. Data is received from
sensors positioned at various locations around the vehicle via two multi-pin sockets located at the rear of the
instrument panel and is than presented using three different visual display methods described as follows:
15.2.2 Analog Display
This is used to display road speed, engine speed, oil pressure, battery condition, fuel level and coolant temperature.
15.2.3 Indicator Lamps
These indicate the presence of any hazard /fault conditions or operational actions.
15.2.4 LCD (Liquid Crystal Disp/ay)
This single line, six digit seven segment display is normally used to display the odometer reading but can also be used
to display vehicle condition messages associated with particular warning lamps and trip computer information.
15.2.5 Transducers
These devices listed as follows transmit vehicle condition to the instruments:
0 Engine Coolant Temperature Transmitter
0 Low Coolant Level Probe
0 Oil Pressure Transmitter - AJ16N12
0 Fuel Gauge Tank Unit - AJlW12
Fault conditions and their causes displayed by the instruments and warning lamps are covered in more detail
by further information contained within the
Electrical Diagnostic Manual.
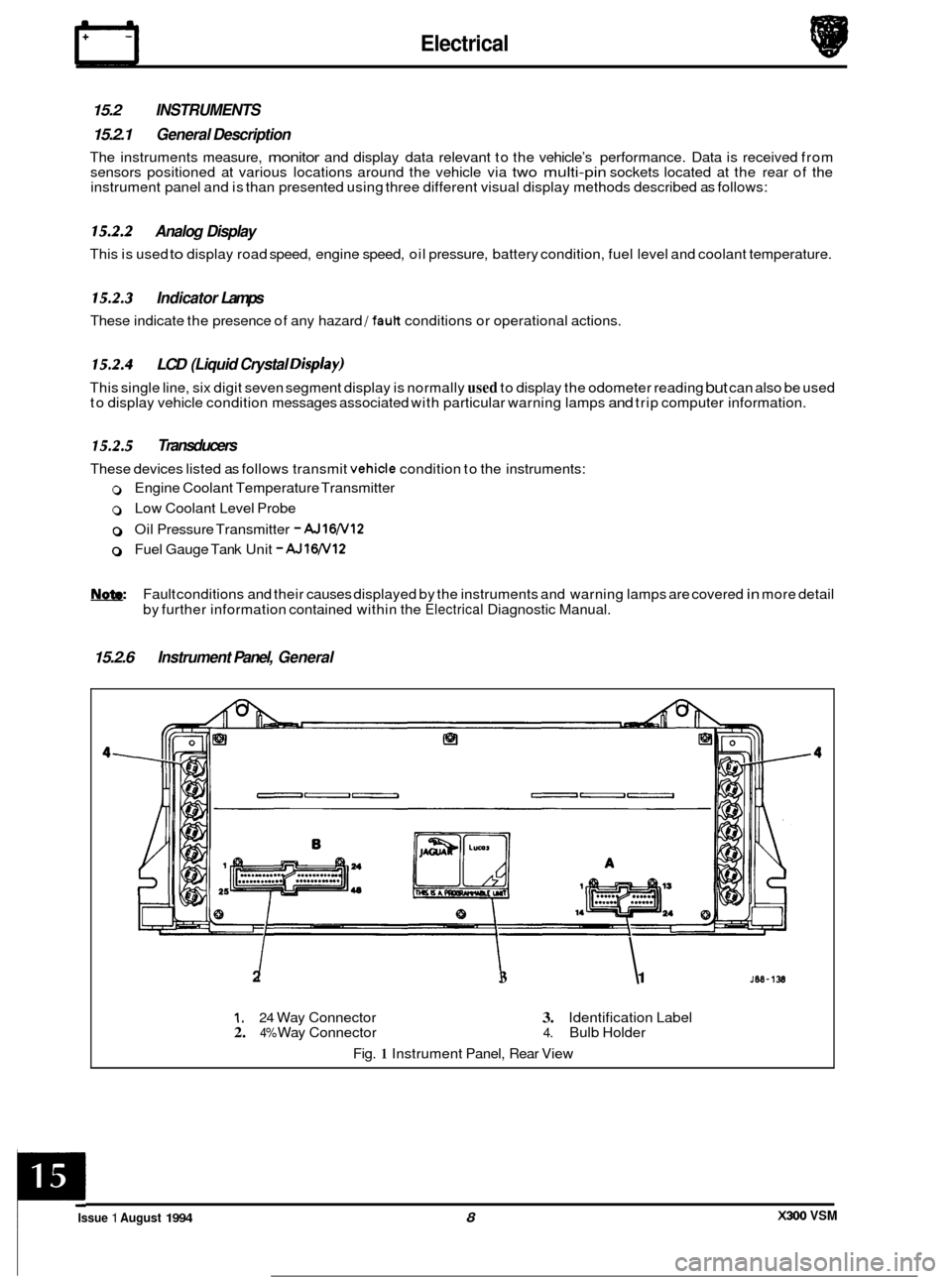
15.2.6 Instrument Panel, General
2 I I 3 1
1. 24 Way Connector 3. Identification Label 2. 4% Way Connector 4. Bulb Holder
Fig.
1 Instrument Panel, Rear View
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 8
c
Page 351 of 521

IT Electrical
15.2.8 Odometer
With the ignition 'OFF' the odometer is permanently dis-
played but not illuminated. With the ignition 'ON' the odo- meter is displayed and also illuminated.
Trip information or driver information messages may be dis
-
played instead of the 'ODO'. By pressing the 'ODO' button
once or twice the trip and driver information messages can
be deleted and the
'ODO rdisplayed.
W. The odometer value is not stored within the LCD
module.
15.2.9 Trip Computev
This provides information on the vehicle's speed, fuel usage
and distance traveled
all of which are calculated by a micro
processor.
The controls, part of the fascia switch assembly, are located
on the right
-hand side pod positioned to the right-hand side
of the steering column.
I
/
J86-192L
Fig. 1
15.2.10 Driver Information Messages
Two fault messages, FLUID - AIRBAG are displayed via the LCD in conjunction with relevant warning lamps.
If an
airbag fault exists or the brake fluid is low, a message will automatically be displayed on the LCD and the relevant
warning lights illuminated. Should both faults exist at the same time, each message is displayed alternatively for ap
- proximately 2 seconds.
Messages may becancelled
by pressing the 'ODO button which allowsthe LCD to return to its last displayed message.
The warning lamps will not be extinguished. If the fault is not repaired the message(s) and the warning lamp(s) will
be redisplayed when the ignition is switched on.
15.2.11 /llumination
Warning indicator lamp illumination is controlled by a microprocessor located inside the instrument panel.
The seven right
-hand warning indicators are primary warning lamps illuminating 'RED and the seven left-hand warn-
ing indicators are secondary warning lamps illuminating 'AMBER'
The eight lower lamps are
a mixture of status and warning lamps.
With the ignition
'OFF' the LCD is not illuminated.
With ignition
'ON' and side lights 'OFF' the LCD is illuminated at maximum brightness.
With the ignition on and side lights
'OFF' the LCD is dimmed as are the gauges.
The long
life type bulbs are enclosed by orange and brown coloured bulb holders which must never be interchanged.
Replacement bulbs must always be of the same colour.
CAUTIQN: Always dwonnect the battery ground lead before commencing with any instrument rsimwal procedure.
15.2.12 General Repair Notes
0 After lens removal do not rest instrument panel face down as this causes damage to the delicate gauge needles.
Avoid scratching the gauge faces and ensure cleanliness when handling the panel.
0 To minimize the risk of damage and contamination to the instrument panel, all repairs must be carried out in a non - static and dust -free environment. Avoid touching connector pins and pcb components to minimize
risk of static damage.
0 The instrument panel has two different types of bulb holders each of which must be located correctly when
changing the bulbs.
Issue 1 August 1994 10 X300 VSM