check oil KIA CARNIVAL 2007 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: KIA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: CARNIVAL, Model: KIA CARNIVAL 2007Pages: 1575, PDF Size: 44.86 MB
Page 149 of 1575
2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
TROUBLE SHOOTING
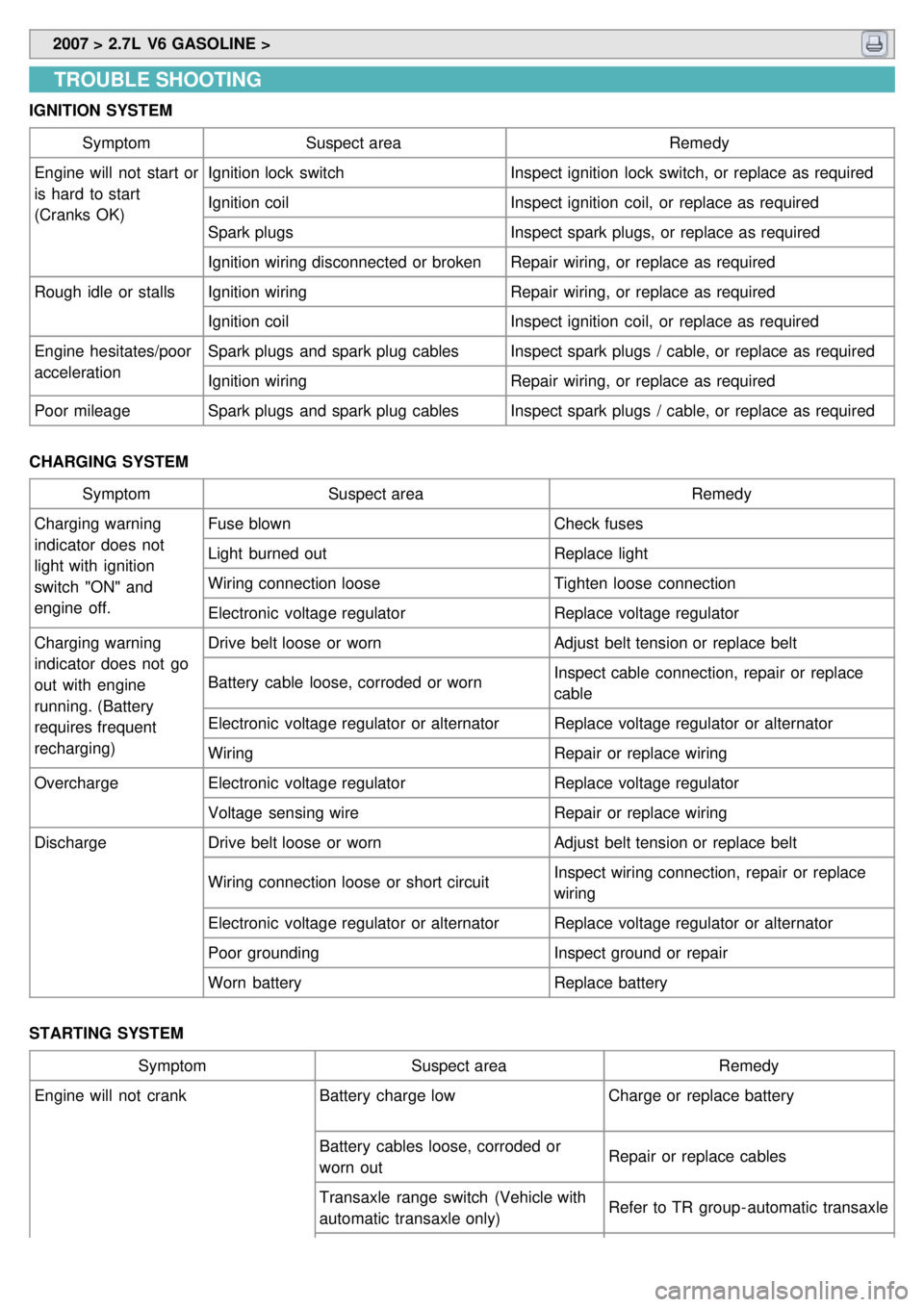
IGNITION SYSTEM
Symptom Suspect area Remedy
Engine will not start or
is hard to start
(Cranks OK) Ignition lock switch
Inspect ignition lock switch, or replace as required
Ignition coil Inspect ignition coil, or replace as required
Spark plugs Inspect spark plugs, or replace as required
Ignition wiring disconnected or broken Repair wiring, or replace as required
Rough idle or stalls Ignition wiring Repair wiring, or replace as required
Ignition coil Inspect ignition coil, or replace as required
Engine hesitates/poor
acceleration Spark plugs and spark plug cables
Inspect spark plugs / cable, or replace as required
Ignition wiring Repair wiring, or replace as required
Poor mileage Spark plugs and spark plug cables Inspect spark plugs / cable, or replace as required
CHARGING SYSTEM Symptom Suspect area Remedy
Charging warning
indicator does not
light with ignition
switch "ON" and
engine off. Fuse blown
Check fuses
Light burned out Replace light
Wiring connection loose Tighten loose connection
Electronic voltage regulator Replace voltage regulator
Charging warning
indicator does not go
out with engine
running. (Battery
requires frequent
recharging) Drive belt loose or worn
Adjust belt tension or replace belt
Battery cable loose, corroded or worn Inspect cable connection, repair or replace
cable
Electronic voltage regulator or alternator Replace voltage regulator or alternator
Wiring Repair or replace wiring
Overcharge Electronic voltage regulator Replace voltage regulator
Voltage sensing wire Repair or replace wiring
Discharge Drive belt loose or worn Adjust belt tension or replace belt
Wiring connection loose or short circuit Inspect wiring connection, repair or replace
wiring
Electronic voltage regulator or alternator Replace voltage regulator or alternator
Poor grounding Inspect ground or repair
Worn battery Replace battery
STARTING SYSTEM Symptom Suspect area Remedy
Engine will not crank Battery charge low Charge or replace battery
Battery cables loose, corroded or
worn out Repair or replace cables
Transaxle range switch (Vehicle with
automatic transaxle only) Refer to TR group - automatic transaxle
Page 155 of 1575
![KIA CARNIVAL 2007 Owners Manual a.[U2.7]
L nleaded : ILFR5B11
Leaded : LFR5A
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
SPARK TEST
1. Remove the ignition coil connector(A).
Disconnect the iguition coil connector while pulling up tre connector KIA CARNIVAL 2007 Owners Manual a.[U2.7]
L nleaded : ILFR5B11
Leaded : LFR5A
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
SPARK TEST
1. Remove the ignition coil connector(A).
Disconnect the iguition coil connector while pulling up tre connector](/img/2/57045/w960_57045-154.png)
a.[U2.7]
L nleaded : ILFR5B11
Leaded : LFR5A
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
SPARK TEST
1. Remove the ignition coil connector(A).
Disconnect the iguition coil connector while pulling up tre connector lock.
2. Remove the ignition coil.
3. Using a spark plug socket, remove the spark plug.
4. Install the spark plug to the ignition coil.
5. Ground the spark plug to the engine.
6.Check is spark occurs while engine is being cranked.
To prevent fuel being injected from injectors while the engine is being cranked, remove the fuel pump(A) relay
from the fuse box.
Crank the engine for no more than 5 ~ 10 seconds.
7. Inspect all the spark plugs.
8. Using a spark plug socket, install the spark plug.
9. Install the ignition coil.
10. Reconnect the ignition coil connector.
Page 168 of 1575

2.Check that there is no continuity between the slip rings and the rotor (B) or rotor shaft (C).
3. If the rotor fails either continuity check, replace the alternator.
INSPECT STATOR
1.Check that there is continuity between each pair of leads (A).
2.Check that there is no continuity between each lead and the coil core.
3. If the coil fails either continuity check, replace the alternator.
Page 176 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
STARTER CIRCUIT TROUBLESHOOTING
The battery must be in good condition and fully charged.
1. Remove the fuel pump relay(A) from the fuse box.
2. With the shift lever in N or P (A/T) or clutch pedal pressed (M/T), turn the ignition switch to "START"
If the starter normally cranks the engine, starting system is OK. If the starter will not crank the engine at all, go to
next step.
If it won't disengage from the ring gear when you release key, check for the following until you find the cause.
a. Solenoid plunger and switch malfunction.
b. Dirty pinion gear or damaged overrunning clutch.
3. Check the battery condition. Check electrical connections at the battery, battery negative cable connected to the
body, engine ground cables, and the starter for looseness and corrosion. Then try starting the engine again.
If the starter cranks normally the engine, repairing the loose connection repaired the problem. The starting system
is now OK.
If the starter still does not crank the engine, go to next step.
4. Disconnect the connector from the S- terminal of solenoid. Connect a jumper wire from the B- terminal of solenoid to
the S- terminal of solenoid.
If the starter cranks the engine, go to next step.
If the starter still does not crank the engine, remove the starter, and repair or replace as necessary.
5. Check the following items in the order listed until you find the open circuit.
a. Check the wire and connectors between the driver's under - dash fuse/relay box and the ignition switch, and
between the driver's under - dash fuse/relay box and the starter.
b. Check the ignition switch (Refer to BE group - ignition system)
c. Check the transaxle range switch connector or ignition lock switch connector.
d. Inspect the starter relay.
STATER SOLENOID TEST
1.Disconnect the field coil wire from the M- terminal of solenoid switch.
2. Connect the battery as shown. If the starter pinion pops out, it is working properly. To avoid damaging the starter,
do not leave the battery connected for more than 10 seconds.
3.Disconnect the battery from the M terminal.
If the pinion does not retract, the hold- in coil is working properly. To avoid damaging the starter, do not leave the
battery connected for more than 10 seconds.
Page 184 of 1575

6.Check the mica depth (A). If the mica is too high (B), undercut the mica with a hacksaw blade to the proper depth.
Cut away all the mica (C) between the commutator segments. The undercut should not be too shallow, too narrow,
or v- shaped (D).
Commutator mica depth
Standard (New) : 0.5 mm (0.0197 in.)
Limit : 0.2mm (0.0079 in.)
7.Check for continuity between the segments of the commutator. If an open circuit exists between any segments,
replace the armature.
8.Check with an ohmmeter that no continuity exists between the commutator (A) and armature coil core (B), and
between the commutator and armature shaft (C). If continuity exists, replace the armature.
INSPECT STARTER BRUSH
Brushes that are worm out, or oil - soaked, should be replaced.
Page 195 of 1575
2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
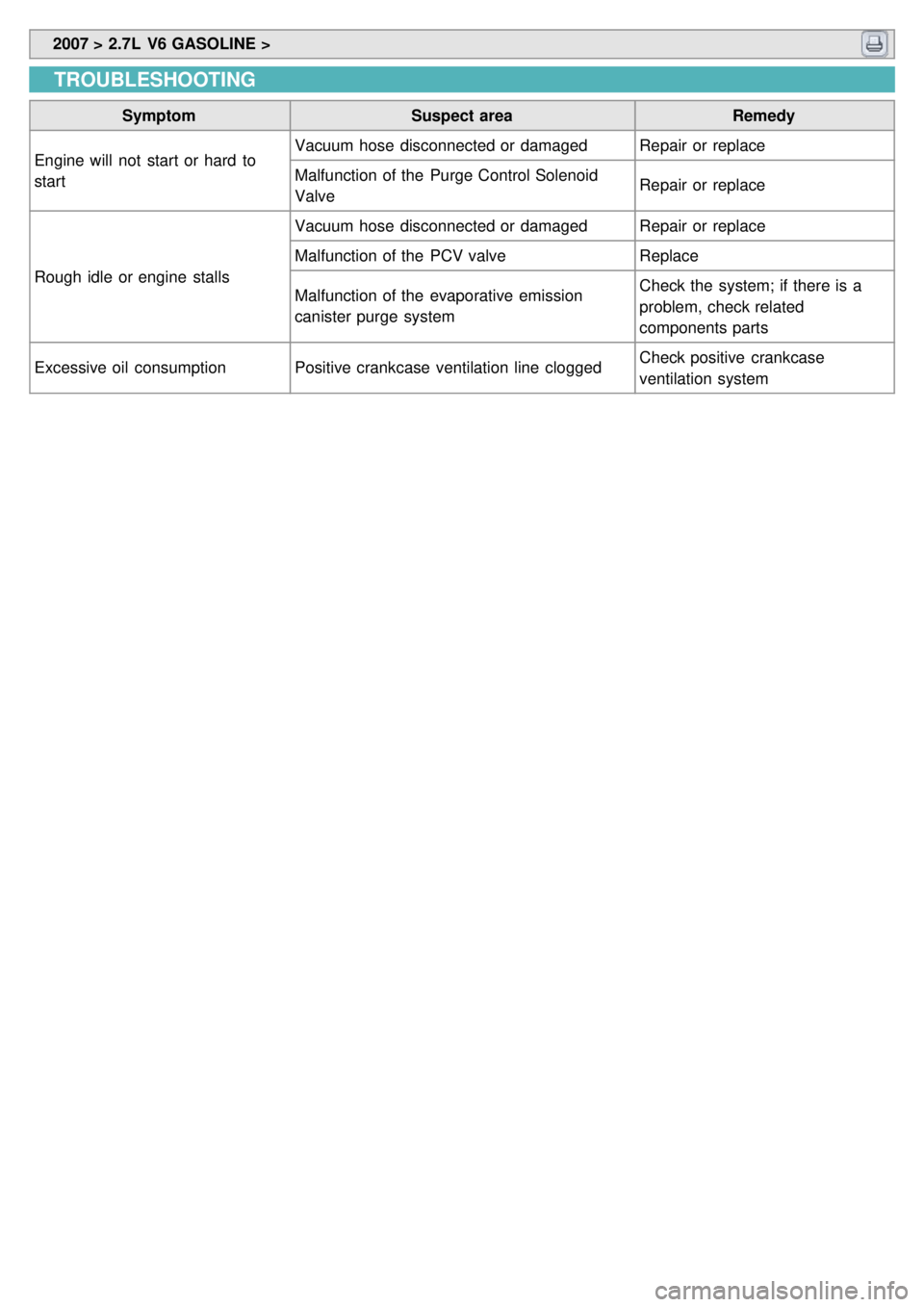
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Suspect area Remedy
Engine will not start or hard to
start Vacuum hose disconnected or damaged
Repair or replace
Malfunction of the Purge Control Solenoid
Valve Repair or replace
Rough idle or engine stalls Vacuum hose disconnected or damaged
Repair or replace
Malfunction of the PCV valve Replace
Malfunction of the evaporative emission
canister purge system Check the system; if there is a
problem, check related
components parts
Excessive oil consumption Positive crankcase ventilation line clogged Check positive crankcase
ventilation system
Page 210 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
INSPECTION
When disconnecting the vacuum hose, make an identification mark on it so that it can be reconnected to its
original position.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the solenoid valve.
2. Detach the harness connector.
3. Connect a vacuum pump to the nipple which is connected to intake manifold.
4. Apply vacuum and check when voltage is applied to the PCSV and when the voltage is discontinued.
Battery voltage Normal condition
When applied Vacuum is released
When discontinued Vacuum is maintained
5. Measure the resistance between the terminals of the solenoid valve.
PCSV coil resistance(Ω) :
14.0 ~ 18.0Ω at 20°C (68°F)
INSPECTION
FUNCTION AND OPERATION PRICIPLE
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV) is installed on the surge tank and controls the passage between the canister
and the intake manifold. It is a solenoid valve and is open when the PCM grounds the valve control line. When the
passage is open (PCSV ON), fuel vapors stored in the canister is transferred to the intake manifold.
SPECIFICATION
Item Specification
Coil Resistance (Ω) 14.0 ~ 18.0Ω at 20°C (68°F)
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Page 328 of 1575
2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
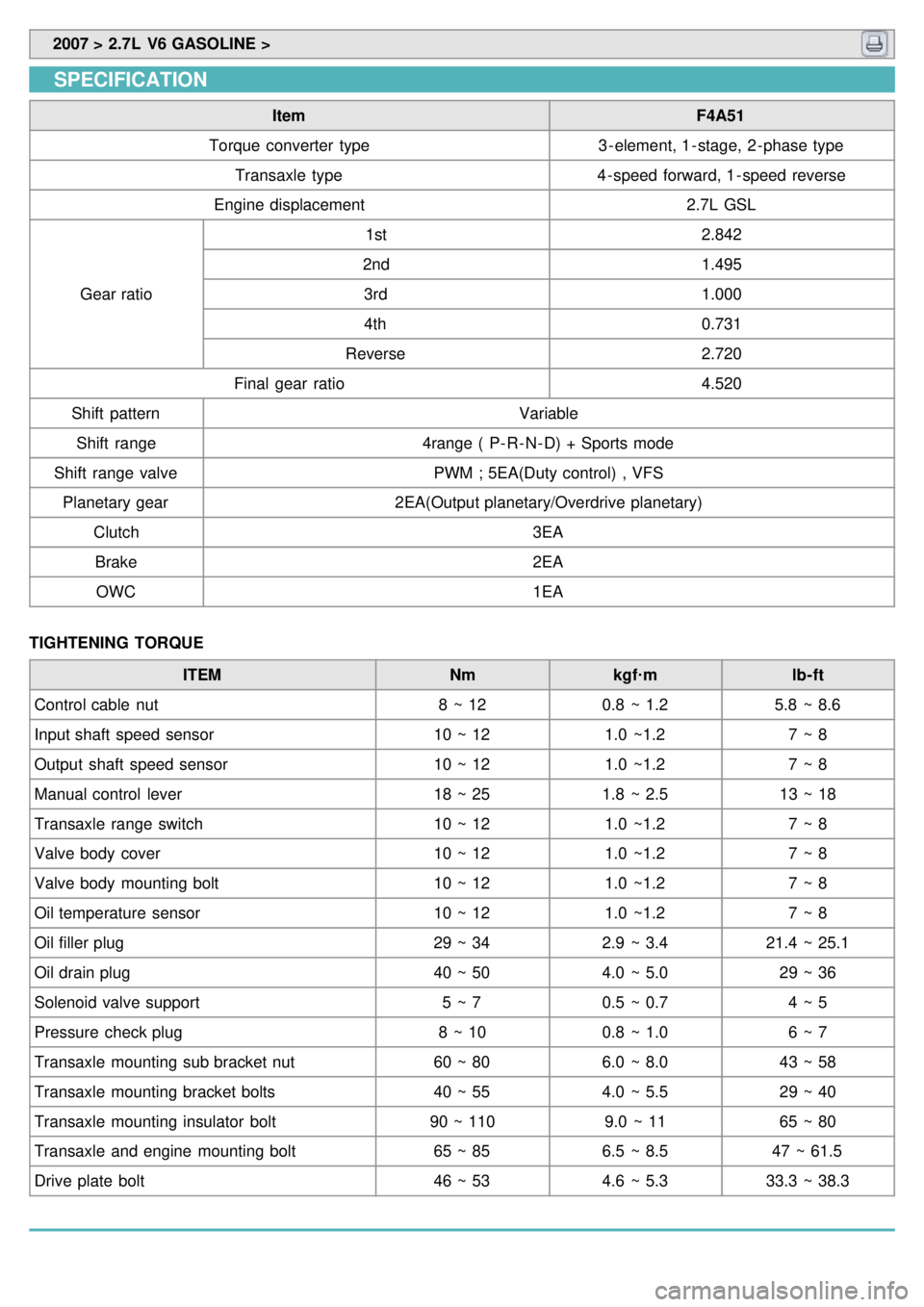
SPECIFICATION
Item F4A51
Torque converter type 3 - element, 1 - stage, 2 - phase type
Transaxle type 4 - speed forward, 1 - speed reverse
Engine displacement 2.7L GSL
Gear ratio 1st
2.842
2nd 1.495
3rd 1.000
4th 0.731
Reverse 2.720
Final gear ratio 4.520
Shift pattern Variable
Shift range 4range ( P- R- N- D) + Sports mode
Shift range valve PWM ; 5EA(Duty control) , VFS
Planetary gear 2EA(Output planetary/Overdrive planetary)
Clutch 3EA
Brake 2EA
OWC 1EA
TIGHTENING TORQUE ITEM Nmkgf·m lb- ft
Control cable nut 8 ~ 120.8 ~ 1.2 5.8 ~ 8.6
Input shaft speed sensor 10 ~ 121.0 ~1.2 7 ~ 8
Output shaft speed sensor 10 ~ 121.0 ~1.2 7 ~ 8
Manual control lever 18 ~ 251.8 ~ 2.5 13 ~ 18
Transaxle range switch 10 ~ 121.0 ~1.2 7 ~ 8
Valve body cover 10 ~ 121.0 ~1.2 7 ~ 8
Valve body mounting bolt 10 ~ 121.0 ~1.2 7 ~ 8
Oil temperature sensor 10 ~ 121.0 ~1.2 7 ~ 8
Oil filler plug 29 ~ 342.9 ~ 3.421.4 ~ 25.1
Oil drain plug 40 ~ 504.0 ~ 5.0 29 ~ 36
Solenoid valve support 5 ~ 70.5 ~ 0.7 4 ~ 5
Pressure check plug 8 ~ 100.8 ~ 1.0 6 ~ 7
Transaxle mounting sub bracket nut 60 ~ 806.0 ~ 8.0 43 ~ 58
Transaxle mounting bracket bolts 40 ~ 554.0 ~ 5.5 29 ~ 40
Transaxle mounting insulator bolt 90 ~ 1109.0 ~ 1165 ~ 80
Transaxle and engine mounting bolt 65 ~ 856.5 ~ 8.5 47 ~ 61.5
Drive plate bolt 46 ~ 534.6 ~ 5.333.3 ~ 38.3
Page 337 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
Hydraulic Control System
DESCRIPTION
a.Better and smoother shift quality.
b. In order to prevent ATF leakage from the valve body or each elements, the exhaust ports have been grouped into
only one with an addition of a check ball.
c. If a failure occurs in its electric control, the switch valve and fail safe valve is able to move to enable 3rd speed
drive or reverse.
d. The hydraulic system consists of oil pump, regulator valve, solenoid valves, pressure control valve and valve body.
e. In order to control the optimal line pressure and inprove the efficiency of power transmission according to maximize
the efficiency of the oil pump, VFS(Variable Force Solenoid) valve has been added in the valve body hydralic
circuit.
Page 351 of 1575
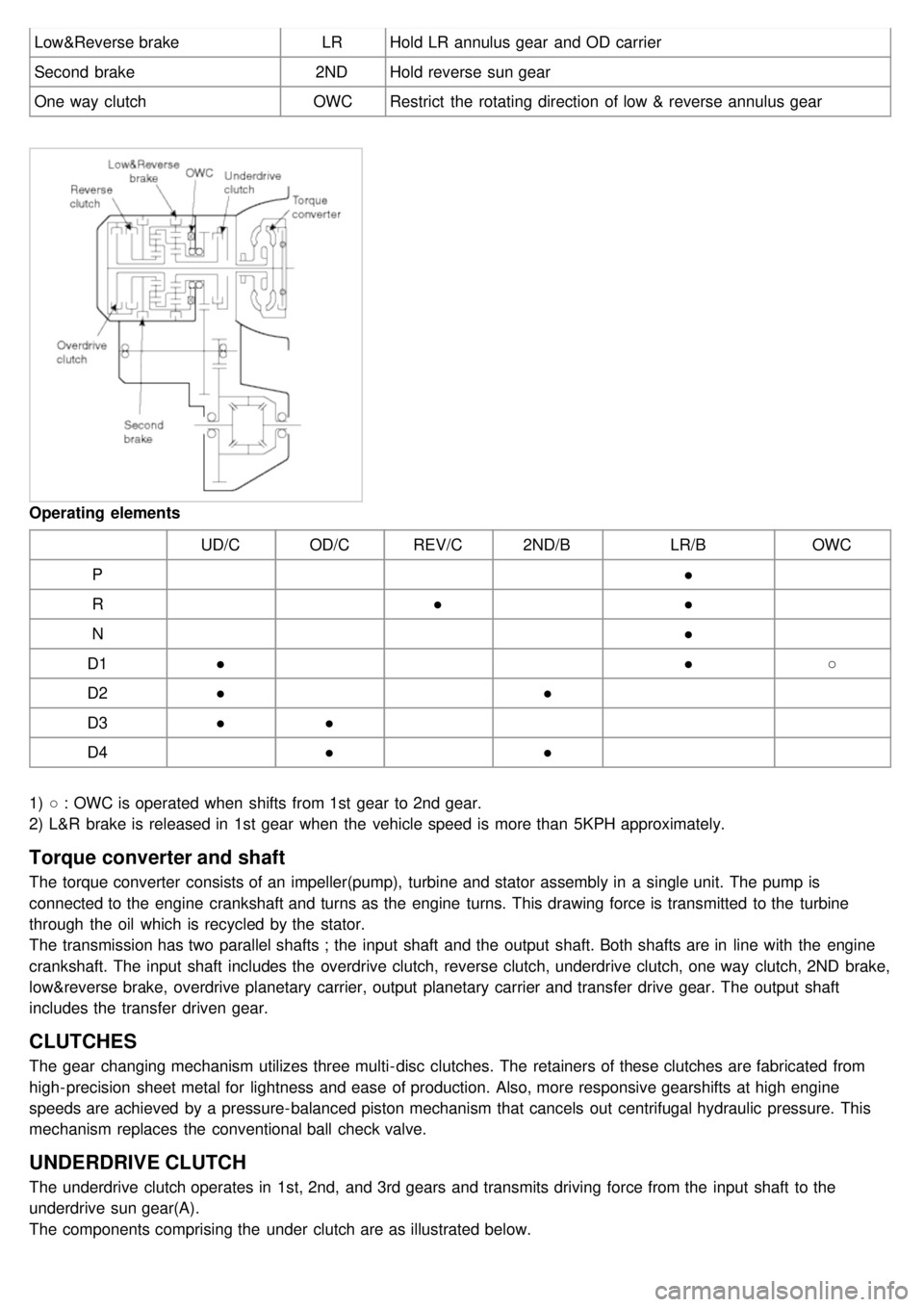
Low&Reverse brakeLRHold LR annulus gear and OD carrier
Second brake 2NDHold reverse sun gear
One way clutch OWCRestrict the rotating direction of low & reverse annulus gear
Operating elements
UD/COD/CREV/C 2ND/B LR/BOWC
P ●
R ●●
N ●
D1 ● ●○
D2 ● ●
D3 ●●
D4 ●●
1) ○ : OWC is operated when shifts from 1st gear to 2nd gear.
2) L&R brake is released in 1st gear when the vehicle speed is more than 5KPH approximately.
Torque converter and shaft
The torque converter consists of an impeller(pump), turbine and stator assembly in a single unit. The pump is
connected to the engine crankshaft and turns as the engine turns. This drawing force is transmitted to the turbine
through the oil which is recycled by the stator.
The transmission has two parallel shafts ; the input shaft and the output shaft. Both shafts are in line with the engine
crankshaft. The input shaft includes the overdrive clutch, reverse clutch, underdrive clutch, one way clutch, 2ND brake,
low&reverse brake, overdrive planetary carrier, output planetary carrier and transfer drive gear. The output shaft
includes the transfer driven gear.
CLUTCHES
The gear changing mechanism utilizes three multi- disc clutches. The retainers of these clutches are fabricated from
high- precision sheet metal for lightness and ease of production. Also, more responsive gearshifts at high engine
speeds are achieved by a pressure- balanced piston mechanism that cancels out centrifugal hydraulic pressure. This
mechanism replaces the conventional ball check valve.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
The underdrive clutch operates in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gears and transmits driving force from the input shaft to the
underdrive sun gear(A).
The components comprising the under clutch are as illustrated below.