LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 481 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-24 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Air intake duct – Gulf models from 2000MY
1Heat reflective insulation
2Supplementary air intake duct
The density of the intake air is partly dependent on altitude and temperature. Hot air has a lower density than cold air;
consequently in hot climates, the low air density can result in low power due to low volumetric efficiency.
In order to improve engine performance, Gulf specification models from 2000MY have a secondary air intake duct
which is located under the front left inner wing of the vehicle. Cooler air from the side of the vehicle is routed through
the duct to the air cleaner, where it combines with air entering via the front grille.
In addition to the secondary air duct, the vehicles are fitted with a larger front grille and have larger cooling and
condenser fans.
The MAF/IAT sensor, air cleaner and air cleaner duct are encased in insulation bags to help keep the intake air cool
and so increase the mass of air entering the engine intake manifold.
The air cleaner includes a cyclone filter and also a dump valve in the bottom of the unit. Sand and dust particles which
are carried into the air cleaner with the air flow are automatically expunged via the dump valve.
M180452
1
2
Page 482 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-25
Throttle Position (TP) sensor (C0175)
The TP sensor is located on the throttle body assembly in the engine compartment. The ECM is able to determine the
position of the throttle plate and the rate of change of its angle. The ECM processes the signal received from the TP
sensor.
The TP sensor consists of a resistance track and a sliding contact connected to the throttle plate assembly. As the
throttle is opened and closed the sliding contact moves along the resistance track to change the output voltage of the
sensor. The ECM determines throttle plate position by processing this output voltage. The connection of the sensor
to the throttle plate assembly is via a shaft.
The ECM is able to determine the closed throttle position, this enables the TP sensor to be fitted without the need for
prior adjustment. The TP sensor signal has input into the ECM's fuelling strategy and also to determine closed throttle
position for idle speed control. The TP sensor also supplies the ECM with information to enable the overrun fuel cut
off strategy to be implemented. When the ECM receives closed throttle information from the TP sensor it closes the
injectors for the duration of the closed throttle time.
The TP sensor signal is also used by the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU to determine the correct point
for gear shifts and acceleration kickdown. The ECM also supplies the SLABS ECU with this TP sensor information as
a PWM signal.
Input/Output
The TP sensor has electrical input and output. Input is a 5 volt supply via pin 10 of connector C0636 of the ECM. The
signal output is via pin 24 of connector C0636 and is a varying voltage, less than 0.5V (closed throttle) and greater
than 4.5V (wide open throttle) depending on throttle plate position. The TP sensor earth is via pin 25 of connector
C0636 of the ECM, this acts as a screen to protect the integrity of the TP sensor signal.
The connector and sensor terminals are gold plated for corrosion and temperature resistance, care must be exercised
while probing the connector and sensor terminals.
If the TP sensor signal fails, the ECM uses a default value derived from engine load and speed.
The TP sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lSignal out of parameters.
lBlocked air filter (load monitoring, ratio of the TP sensor to air flow).
lRestriction in air inlet (load monitoring, ratio of the TP sensor to air flow).
lVacuum leak
Page 483 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-26 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
In the event of a TP sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine performance concern.
lDelayed throttle response.
lFailure of emission control.
lClosed loop idle speed control inoperative.
lAutomatic gearbox kickdown inoperative.
lIncorrect altitude adaptation.
lMIL illuminated (NAS only).
There are three throttle position sensor diagnostic checks:
lTP sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold value – the engine speed must be greater than 400 rev/
min for longer than 2 seconds and the signal must be greater than 96% for longer than 50 ms.
lTP sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine speed must be greater than 400 rev/min for
longer than 2 seconds and the signal must be less than 4% for longer than 50 ms.
lRatio of throttle position to mass of air flow – the calculated throttle angle must be outside limits when the engine
speed is between 800 rev/min and 4000 rev/min, the engine load is between 2 and 6.5 and the coolant
temperature is above -10
°C (14°F).
Should a malfunction of the TP sensor occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
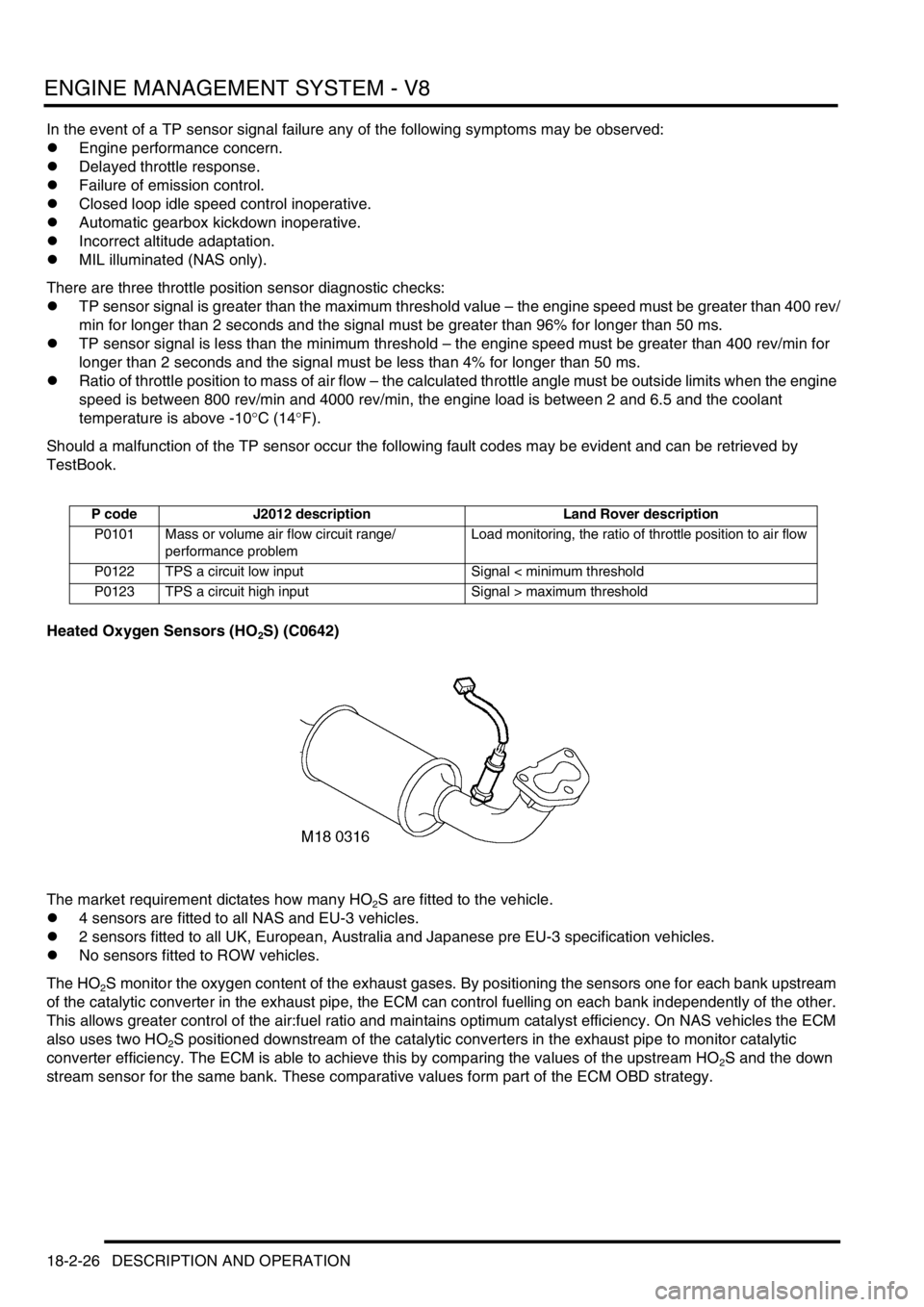
Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO
2S) (C0642)
The market requirement dictates how many HO
2S are fitted to the vehicle.
l4 sensors are fitted to all NAS and EU-3 vehicles.
l2 sensors fitted to all UK, European, Australia and Japanese pre EU-3 specification vehicles.
lNo sensors fitted to ROW vehicles.
The HO
2S monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. By positioning the sensors one for each bank upstream
of the catalytic converter in the exhaust pipe, the ECM can control fuelling on each bank independently of the other.
This allows greater control of the air:fuel ratio and maintains optimum catalyst efficiency. On NAS vehicles the ECM
also uses two HO
2S positioned downstream of the catalytic converters in the exhaust pipe to monitor catalytic
converter efficiency. The ECM is able to achieve this by comparing the values of the upstream HO
2S and the down
stream sensor for the same bank. These comparative values form part of the ECM OBD strategy.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0101 Mass or volume air flow circuit range/
performance problemLoad monitoring, the ratio of throttle position to air flow
P0122 TPS a circuit low input Signal < minimum threshold
P0123 TPS a circuit high input Signal > maximum threshold
Page 484 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-27
The HO2S uses zirconium contained in a galvanic cell surrounded by a gas permeable ceramic, this produces an
output voltage proportional to the ratio difference between the oxygen in the exhaust gases and to the ambient
oxygen.
The HO
2S operates at approximately 350 °C (662 °F). To achieve this temperature the HO2S incorporate a heating
element which is controlled by a PWM signal from the ECM. The elements are activated immediately after engine
starts and also under low engine load conditions when the exhaust gas temperature is insufficient to maintain the
required HO
2S temperature. If the heater fails, the ECM will not allow closed loop fuelling to be implemented until the
sensor has achieved the required temperature.
This value equates to an HO
2S output of 450 to 500 mV. A richer mixture can be shown as λ = 0.97, this pushes the
HO
2S output voltage towards 1000 mV. A leaner mixture can be shown as λ = 1.10, this pushes the HO2S output
voltage towards 100 mV.
From cold start, the ECM runs an open loop fuelling strategy. The ECM keeps this strategy in place until the HO
2S is
at a working temperature of 350
°C (662 °F). At this point the ECM starts to receive HO2S information and it can then
switch into closed loop fuelling as part of its adaptive strategy. The maximum working temperature of the tip of the
HO
2S is 930 °C (1706 °F), temperatures above this will damage the sensor.
HO
2S age with use, this increases their response time to switch from rich to lean and from lean to rich. This can lead
to increased exhaust emissions over a period of time. The switching time of the upstream sensors are monitored by
the ECM. If a pre-determined threshold is exceeded, a failure is detected and the MIL illuminated.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust emission control system.
Input/Output
The upstream and downstream HO
2S are colour coded to prevent incorrect fitting. The tips of the upstream sensors
are physically different to the tips of the downstream sensors.
The HO
2S are colour coded as follows:
lUpstream sensors (both banks) - orange.
lDownstream sensors (both banks) - grey.
The four HO
2S have a direct battery supply to the heater via fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box.
The heater is driven by the ECM providing an earth path for the circuit as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 19 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 13 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 7 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 1 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S output signal is measured by the ECM as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 15 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 16 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 17 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 14 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S earth path for the signal is supplied by the ECM as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 9 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 10 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 11 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 8 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S voltage is difficult to measure using a multimeter, the output can be monitored using TestBook. A rich
mixture would read 500 to 1000 mV, a weak mixture would read 100 mV to 500 mV, the reading should switch from
rich to weak. The open loop default voltage is 450 mV, this is used by the ECM to set the air/ fuel ratio until the tip of
the HO
2S reaches operating temperature.
Page 485 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-28 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The HO2S can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lSensor disconnected.
lStoichiometric ratio outside the correct operating band.
lContamination from leaded fuel.
lAir leak into the exhaust system.
lWiring loom damage.
lSensors fitted incorrectly or cross wired.
In the event of a HO
2S signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDefault to open loop fuelling on defective bank.
lIf the sensors are crossed over (LH bank to RH bank), the engine will run normally after initial start up, but
performance will become progressively worse as the sensors go towards maximum rich for one bank of cylinders
and maximum lean for the other. The ECM will eventually default into open loop fuelling.
lHigh CO reading.
lExcess emissions.
lStrong hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) smell until the ECM defaults to open loop fuelling. .
lMIL illuminated (NAS market only).
A number of diagnostic tests are performed by the ECM with regards to the HO
2sensors:
lHO
2 sensor and system diagnostics
lHO
2 sensor heater diagnostics
lHO
2 sensor switching period (ageing) diagnostics
lRear HO
2 sensor adaption diagnostic (NAS only)
lCatalyst monitoring diagnostic
For further details of the heated oxygen sensors and exhaust emission control, refer to the V8 Emission Control
section of this manual.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust emission control system.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1129 O
2 sensors swapped bank to bank (sensor 1) Front sensors transposed
P0130 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 1, sensor 1) Front sensor LH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band
P0132 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 1, sensor 1) Front sensor LH bank short circuit to battery supply
P0134 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 1,
sensor 1)Front sensor LH bank open circuit
P0150 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 2, sensor 1) Front sensor RH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band
P0152 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 2, sensor 1) Front sensor RH bank short circuit to battery supply
P0154 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 2,
sensor 1)Front sensor RH bank open circuit
P0136 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band (NAS only)
P0137 O
2 sensor circuit low voltage (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank short circuit to earth (NAS only)
P0138 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank short circuit to battery supply
(NAS only)
P0140 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 1,
sensor 2)Rear sensor LH bank open circuit (NAS only)
P0156 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band (NAS only)
P0157 O
2 sensor circuit low voltage (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank short circuit to earth (NAS only)
Page 486 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-29
Fuel injectors
The fuel injectors are located beneath the air inlet manifold. They utilise an electrical solenoid to lift the injector needle
off its seat to allow fuel injection to take place. The fuel injectors provide excellent fuel atomisation in the lower portion
of the inlet manifold, the air/fuel mixture can then be drawn into the cylinders to give good combustion characteristics
and therefore excellent driveability.
P0158 O2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank short circuit to battery voltage
(NAS only)
P0160 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 2,
sensor 2)Rear sensor RH bank open circuit (NAS only)
P0133 O
2 sensor circuit slow response (bank 1, sensor
1)Front sensor aged - period time too long/too short LH
bank
P0153 O
2 sensor circuit slow response (bank 2, sensor
1)Front sensor aged - period time too long/too short RH
bank
P1170 Downstream fuel trim malfunction (bank 1) Front sensor aged - rear HO
2S adaption too lean/too
rich LH bank (NAS and EU-3 only)
P1173 Downstream fuel trim malfunction (bank 2) Front sensor aged - rear HO
2S adaption too lean/too
rich RH bank (NAS and EU-3 only)
P0135 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 1,
sensor 1)Front sensor heater LH bank - short/open circuit
P0141 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 1,
sensor 2)Rear sensor heater LH bank - short/open circuit (NAS
and EU-3 only)
P0155 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 2,
sensor 1)Front sensor heater RH bank - short/open circuit
P0161 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 2,
sensor 2)Rear sensor heater RH bank - short/open circuit (NAS
and EU-3 only)
P0420 - Catalyst efficiency deteriorated - LH bank (NAS and
EU-3 only)
P0430 - Catalyst efficiency deteriorated - RH bank (NAS and
EU-3 only) P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
Page 487 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
There are eight fuel injectors one per cylinder that the ECM operates sequentially. All the injectors are fed from a
common fuel rail as part of the returnless fuel system. Fuel pressure is maintained at a constant 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in2) by
a regulator that is integral with the fuel pump.
+ FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
All eight fuel injectors are supplied with battery voltage via fuse number 1 located in engine compartment fuse box.
The ECM controls the individual earth path for each injector via its own pin at connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
This facility allows the ECM to control the fuel injectors so that sequential fuel injection can take place.
Typical hot engine injector pulse width values:
lIdle = 2.5 ms.
lPeak torque (3000 rev/min) = 7 ms The ECM controls injector earth as follows:
lCylinder No 1 - pin 41 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 2 - pin 1 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 3 - pin 27 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 4 - pin 40 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 5 - pin 2 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 6 - pin 15 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 7 - pin 14 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder No 8 - pin 28 of connector C0636 of the ECM multiplug.
Individual injectors can be measured for resistance using a multimeter. An acceptable injector resistance is as follows:
l14.5
± 0.7 ohms at 20 °C (68 °F).
The fuel injectors can fail in the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lInjector actuator open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBlocked injector.
lRestricted injector.
lLow fuel pressure.
In the event of fuel injector signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lRough running.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine misfire.
lPossible catalyst damage.
lHigh emissions.
lAdaptive fuelling disabled.
lAdaptive idle speed control disabled.
The ECM performs three types of fuel injector diagnostic check:
lOutput short circuit to earth
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage
lOutput open circuit
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0201 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 1 Injector 1 open circuit
P0261 Cylinder 1 injector circuit low Injector 1 short circuit to earth
P0262 Cylinder 1 injector circuit high Injector 1 short circuit to battery supply
P0301 Cylinder 1 misfire detected Injector 1 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0202 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 2 Injector 2 open circuit
P0264 Cylinder 2 injector circuit low Injector 2 short circuit to earth
P0265 Cylinder 2 injector circuit high Injector 2 short circuit to battery supply
Page 488 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-31
P0302 Cylinder 2 misfire detected Injector 2 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0203 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 3 Injector 3 open circuit
P0267 Cylinder 3 injector circuit low Injector 3 short circuit to earth
P0268 Cylinder 3 injector circuit high Injector 3 short circuit to battery supply
P0303 Cylinder 3 misfire detected Injector 3 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0204 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 4 Injector 4 open circuit
P0270 Cylinder 4 injector circuit low Injector 4 short circuit to earth
P0271 Cylinder 4 injector circuit high Injector 4 short circuit to battery supply
P0304 Cylinder 4 misfire detected Injector 4 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0205 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 5 Injector 5 open circuit
P0273 Cylinder 5 injector circuit low Injector 5 short circuit to earth
P0274 Cylinder 5 injector circuit high Injector 5 short circuit to battery supply
P0305 Cylinder 5 misfire detected Injector 5 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0206 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 6 Injector 6 open circuit
P0276 Cylinder 6 injector circuit low Injector 6 short circuit to earth
P0277 Cylinder 6 injector circuit high Injector 6 short circuit to battery supply
P0306 Cylinder 6 misfire detected Injector 6 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0207 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 7 Injector 7 open circuit
P0279 Cylinder 7 injector circuit low Injector 7 short circuit to earth
P0280 Cylinder 7 injector circuit high Injector 7 short circuit to battery supply
P0307 Cylinder 7 misfire detected Injector 7 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0208 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 8 Injector 8 open circuit
P0282 Cylinder 8 injector circuit low Injector 8 short circuit to earth
P0283 Cylinder 8 injector circuit high Injector 8 short circuit to battery supply
P0308 Cylinder 8 misfire detected Injector 8 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0171 System too rich (bank 1) Multiplication injector adaptive fuelling - rich limit
exceeded LH bank
P0172 System too lean (bank 1) Multiplication injector adaptive fuelling - lean limit
exceeded LH bank
P0174 System too rich (bank 2) Multiplication injector adaptive fuelling - rich limit
exceeded RH bank
P0175 System too lean (bank 2) Multiplication injector adaptive fuelling - lean limit
exceeded RH bank
P1171 System too rich (bank 1) Additive injector adaptive fuelling - rich limit exceeded
LH bank
P1172 System too lean (bank1) Additive injector adaptive fuelling - lean limit exceeded
LH bank
P1174 System too rich (bank 2) Additive injector adaptive fuelling - rich limit exceeded
RH bank
P1175 System too lean (bank 2) Additive injector adaptive fuelling - lean limit exceeded
RH bank
P0300 Random/multiple cylinder excess emissions
detectedExcess emissions detected on more than one cylinder
P1300 Random/multiple cylinder misfire detected Catalyst damaging level of misfire on more than one
cylinder
P1319 Misfire detected with low fuel level P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
Page 489 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
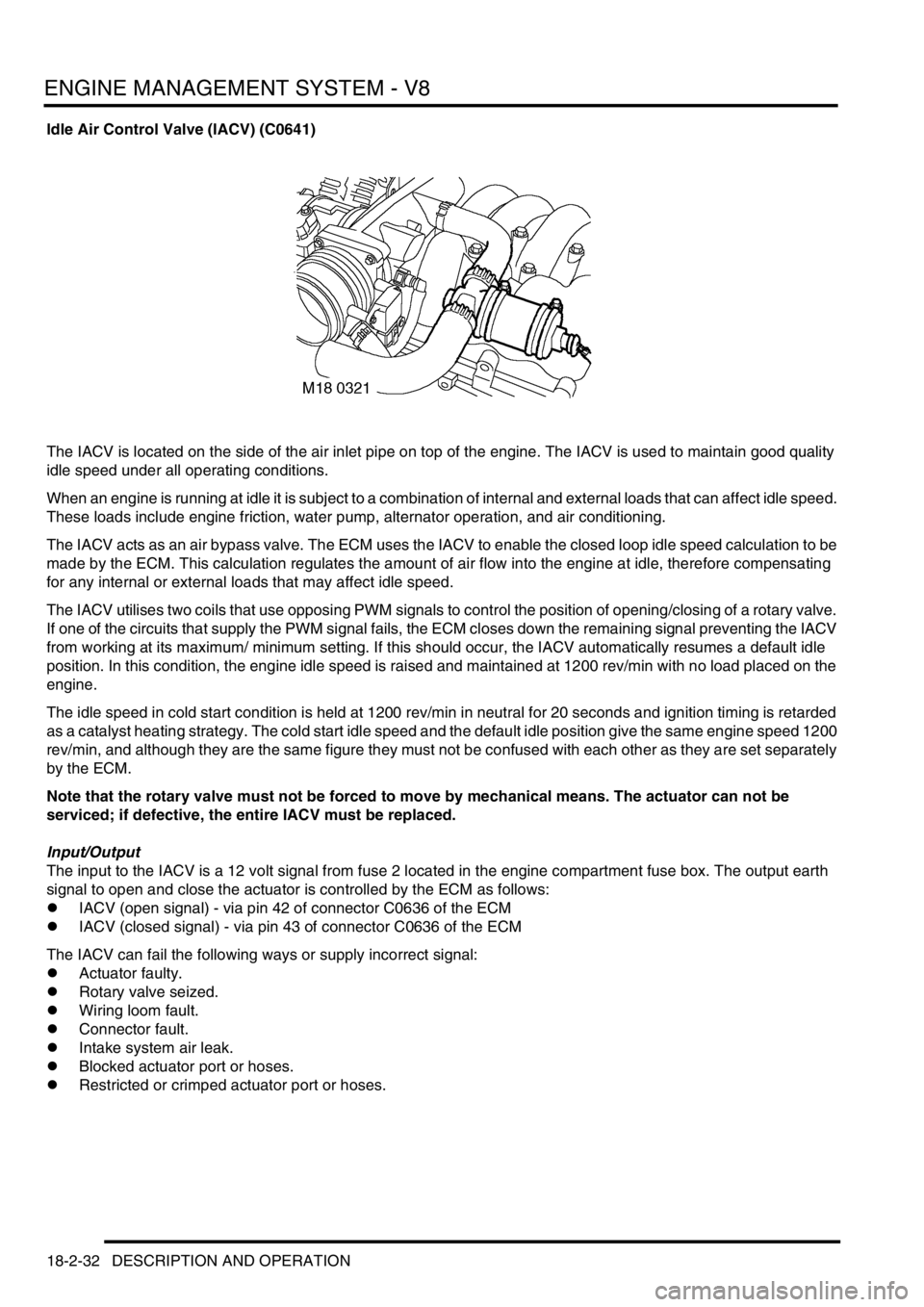
Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) (C0641)
The IACV is located on the side of the air inlet pipe on top of the engine. The IACV is used to maintain good quality
idle speed under all operating conditions.
When an engine is running at idle it is subject to a combination of internal and external loads that can affect idle speed.
These loads include engine friction, water pump, alternator operation, and air conditioning.
The IACV acts as an air bypass valve. The ECM uses the IACV to enable the closed loop idle speed calculation to be
made by the ECM. This calculation regulates the amount of air flow into the engine at idle, therefore compensating
for any internal or external loads that may affect idle speed.
The IACV utilises two coils that use opposing PWM signals to control the position of opening/closing of a rotary valve.
If one of the circuits that supply the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining signal preventing the IACV
from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the IACV automatically resumes a default idle
position. In this condition, the engine idle speed is raised and maintained at 1200 rev/min with no load placed on the
engine.
The idle speed in cold start condition is held at 1200 rev/min in neutral for 20 seconds and ignition timing is retarded
as a catalyst heating strategy. The cold start idle speed and the default idle position give the same engine speed 1200
rev/min, and although they are the same figure they must not be confused with each other as they are set separately
by the ECM.
Note that the rotary valve must not be forced to move by mechanical means. The actuator can not be
serviced; if defective, the entire IACV must be replaced.
Input/Output
The input to the IACV is a 12 volt signal from fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The output earth
signal to open and close the actuator is controlled by the ECM as follows:
lIACV (open signal) - via pin 42 of connector C0636 of the ECM
lIACV (closed signal) - via pin 43 of connector C0636 of the ECM
The IACV can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lActuator faulty.
lRotary valve seized.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector fault.
lIntake system air leak.
lBlocked actuator port or hoses.
lRestricted or crimped actuator port or hoses.
Page 490 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
In the event of an IACV signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEither low or high idle speed.
lEngine stalls.
lDifficult starting.
lIdle speed in default condition.
There are eight IACV diagnostic checks performed by the ECM:
lOutput short circuit to earth – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to battery supply – opening coil
lOutput open circuit – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to earth – closing coil
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage – closing coil
lOutput open circuit – closing coil
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error low (engine speed must be 100 rev/min less than the target speed, engine load
less than 2.5 and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h less than the expected air flow for a fault condition to
be flagged).
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error high (the engine speed must be more than 180 rev/min greater than the target
speed and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h greater than the expected air flow for a fault condition to be
flagged).
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a 4 pin normally open relay. Input from the
ECM allows the fuel pump relay to control the electrical input to the fuel pump, regulating the fuel supply to the fuel
injectors. When the ignition is switched on and the engine is cranked, the fuel pump relay is activated by the ECM,
allowing the fuel system to be pressurised to 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2). The ECM then deactivates the relay until the engine
has started.
If the fuel pump runs, but the fuel pressure is out of limits, adaptive fuel faults will be stored.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1510 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - opening winding
P1513 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - opening winding
P1514 IACV opening coil malfunction Open circuit - opening winding
P1553 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - closing winding
P1552 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - closing winding
P1551 IACV closing coil malfunction Open circuit - closing winding
P0505 Idle control system malfunction Blocked IACV - high or low rev/min error