battery MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 558 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
K2–143
K2
End Of Sie
5INSPECT LINE PRESSURE
•Start engine.
•Measure line pressure.
Specification
—D range, M (2GR) range
Idle: 290—490 kPa {3.0—4.9 kgf/cm
2, 43—69
psi}
Stall: 1,550—1,750 kPa {15.8—17.8 kgf/cm
2,
225—254 psi}
—M (1GR) range, R position
Idle:550—750 kPa {5.6—7.6 kgf/cm
2, 80—
109 psi}
Stall: 1,550—1,750 kPa {15.8—17.8 kgf/cm
2,
225—254 psi}
•Is line pressure within specification?
(See K2–72 Line Pressure Test.)Yes Go to next step.
No All ranges: Replace or overhaul oil pump or control valve
body, then go to Step 10.
Any ranges: Replace or overhaul automatic transaxle, then
go to Step 10.
(See K2–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE AND TRANSFER
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
6CLICK TEST OF SOLENOID VALVES
•Turn ignition key to OFF.
•Disconnect terminal component No.1(12-pin).
•Apply battery voltage to terminal component
No.1 (12-pin) terminals (transaxle case side).
—TCC solenoid vale: B
—Pressure control solenoid: D
•Verify the click sounds of TCC solenoid valve
and pressure control solenoid.
•Are there click sounds?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace TCC solenoid valve or pressure control solenoid,
then go to Step 10.
(See K2–105 CONTROL VALVE BODY REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
7INSPECT DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENGINE
SPEED AND TURBINE SPEED
•Inspect difference between engine speed and
turbine speed during TCC operation in 5GR
•Drive vehicle under following condition
—TR switch position: D range
—Gear position: 5GR
—TCC solenoid valve: ON
•Is difference between engine speed (RPM PID)
and turbine speed okay?
Difference
Below 99 rpmYes Go to Step
No Go to next step.
8INSPECT OPERATION OF EACH VALVE AND
EACH SPRING
•Remove control valve body.
•Disassemble control valve body.
•Is each valve operation okay and is return
spring okay?Yes Replace torque converter, then go to next step.
No Replace control valve body, then go to next step.
(See K2–105 CONTROL VALVE BODY REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
9VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING OF DTC P0740
COMPLETED
•Make sure to reconnect all disconnected
connectors.
•Clear DTC from memory using WDS or
equivalent.
•Start engine.
•Warm up ATX.
•Drive vehicle under following condition for 10
seconds or more.
—Vehicle speed (VSS PID): Within 10—87
km/h {6—54 mph}
—Gear position: 5GR
—TR switch position: D range
—TCC solenoid valve: ON
•Is there pending code present?Yes Replace TCM, then go to next step.
(See K2–96 TCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
No Go to next step.
10VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See K2–124 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE.)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
No Troubleshooting completed. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
Page 595 of 909

K2–180
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
End Of SiePID/DATA MONITOR INSPECTIONA6E5770189012301. Connect the SSTs (WDS or equivalent) to the DLC-2.
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
3. Measure the PID value.
Note
•Perform part inspection for the output device after TCM inspection.
•The PID/DATA MONITOR function monitors the calculated value of the input/output signals in the TCM.
Therefore, if a monitored value of an output device is out of specification, it is necessary to inspect the
monitored value of the input device related to the output device control. Since an output device
malfunction is not directly indicated as a malfunction of the monitored value for the output device, it is
necessary to inspect the output device individually using the simulation function, etc.
PID/DATA MONITOR AND RECORD function table
10VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See K2–124 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE.)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
No Troubleshooting completed. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
Monitor item
(Definition)Unit/
ConditionCondition/Specification ActionTCM
terminal
2-4 B Duty
(2-4 brake
solenoid vale)ON/OFFN position: ON
M range (1GR) stall: OFFInspect 2-4 brake solenoid valve.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)2V
BOO
(Brake switch)ON/OFFBrake pedal depressed: ON
Other: OFFInspect brake switch.
1U
DWN_SW
(Down switch)ON/OFFDown sift at M range: ON
Other: OFFInspect selector lever component.
1S
GEAR
(Calculated
gear range in
TCM)1ST/2ND/
3RD/4TH/
5TH1GR: 1ST
2GR: 2ND
3GR: 3RD
4GR: 4TH
5GR: 5THInspect following PIDs: THOP, TSS
–
H/C Duty
(High clutch
solenoid valve)%N position: OFF
D range 1GR to 2GR shifting: ONInspect high clutch solenoid valve.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)2U
LPS
(Pressure
control
solenoid)%Ignition switch ON: 0%
Idle: 0—100%Inspect pressure control solenoid.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)2Y
MNL_SW
(M range
switch)ON/OFFM range: ON
Other: OFFInspect selector lever component.
1AA
NSFT TIM
(Neutral shift
solenoid valve)ON/OFFN position: OFF
R position inhibition control: ONInspect main relay.
(See T–19 RELAY INSPECTION.)
Inspect battery.
(See G–6 BATTERY INSPECTION.)2D
OSS
(Intermediate
sensorrpmIgnition switch ON: 0 rpm
Idle: 700—800 rpmInspect intermediate sensor.
(See K2–86 INTERMEDIATE SENSOR
INSPECTION.)1K, 1X
PNP
(TR switch (P/
N position
switch))ON/OFFP or N position: ON
R position and all ranges: OFFInspect TR switch.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)–
RDCN TIM
(Reduction
timing solenoid
valve)ON/OFFN position: OFF
D range: ONInspect reduction timing solenoid valve.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)2G
RPM
(Engine speed)rpmIgnition switch ON: 0 rpm
Idle: 700—800 rpmInspect TCM.
(See K2–90 TCM INSPECTION.)–
SSA/SS1
(Shift solenoid
A)ON/OFFN position: ON
D range 3GR: OFFInspect shift solenoid A.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)–
Page 596 of 909
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
K2–181
K2
End Of Sie
SSB/SS2
(Shift solenoid
B)ON/OFFN position: ON
D range 4GR: OFFInspect shift solenoid B.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)–
SSC/SS3
(Shift solenoid
C)ON/OFFN position: ON
D range 2GR: OFFInspect shift solenoid C.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)–
TCCC
(TCC solenoid
valve)%TCC operating: ON
TCC non operating: OFFInspect TCC solenoid valve.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION.)2S
TFT
(ATF
temperature)°CATF 20 °C {68 °F}: 20 °C {68 °F}
ATF 60 °C {140 °F}: 60 °C {140 °F}Inspect TFT sensor.
(See K2–84 TRANSAXLE FLUID
TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR
INSPECTION.)1B, 1F
TFTV
(ATF
temperature
signal voltage)VATF 20 °C {68 °F}: 1.55 V
ATF 60°C {140 °F}: 0.7 VInspect TFT sensor.
(See K2–84 TRANSAXLE FLUID
TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR
INSPECTION.)1B, 1F
THOP
(Throttle
position)%CTP:0%
WOT: 100%Inspect TCM.
(See K2–90 TCM INSPECTION.)–
TRD
(TR switch [D
range])ON/OFFD range: ON
Other ranges and all positions: OFFInspect TR switch.
(See K2–80 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR)
SWITCH INSPECTION.)1Z
TRR
(TR switch [R
position])ON/OFFR position: ON
Other positions and all ranges: OFFInspect TR switch.
(See K2–80 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR)
SWITCH INSPECTION.)1W
TSS
(Input/turbine
speed sensor)rpmIgnition switch ON: 0 rpm
Idle: 700—800 rpmInspect input/turbine speed sensor.
(See K2–85 INPUT/TURBINE SPEED
SENSOR INSPECTION.)1N, 2F
UP_SW
(Up switch)ON/OFFUp sift at M range: ON
Other: OFFInspect selector lever component.
2C
VPWR
(Battery
voltage)VIG ON: B+
Idle: 13—14 VInspect main relay.
1P
VSS
(Vehicle
speed)km/hVehicle speed 20 km/h {12.5 mph}: 20
km/h {12.5 mph}
Vehicle speed 40 km/h {25 mph}: 40 km/
h {25 mph}Inspect vehicle speedometer sensor.
(See K2–87 VEHICLE SPEEDOMETER
SENSOR (VSS) INSPECTION.)1V, 1M Monitor item
(Definition)Unit/
ConditionCondition/Specification ActionTCM
terminal
Page 638 of 909
M–8
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
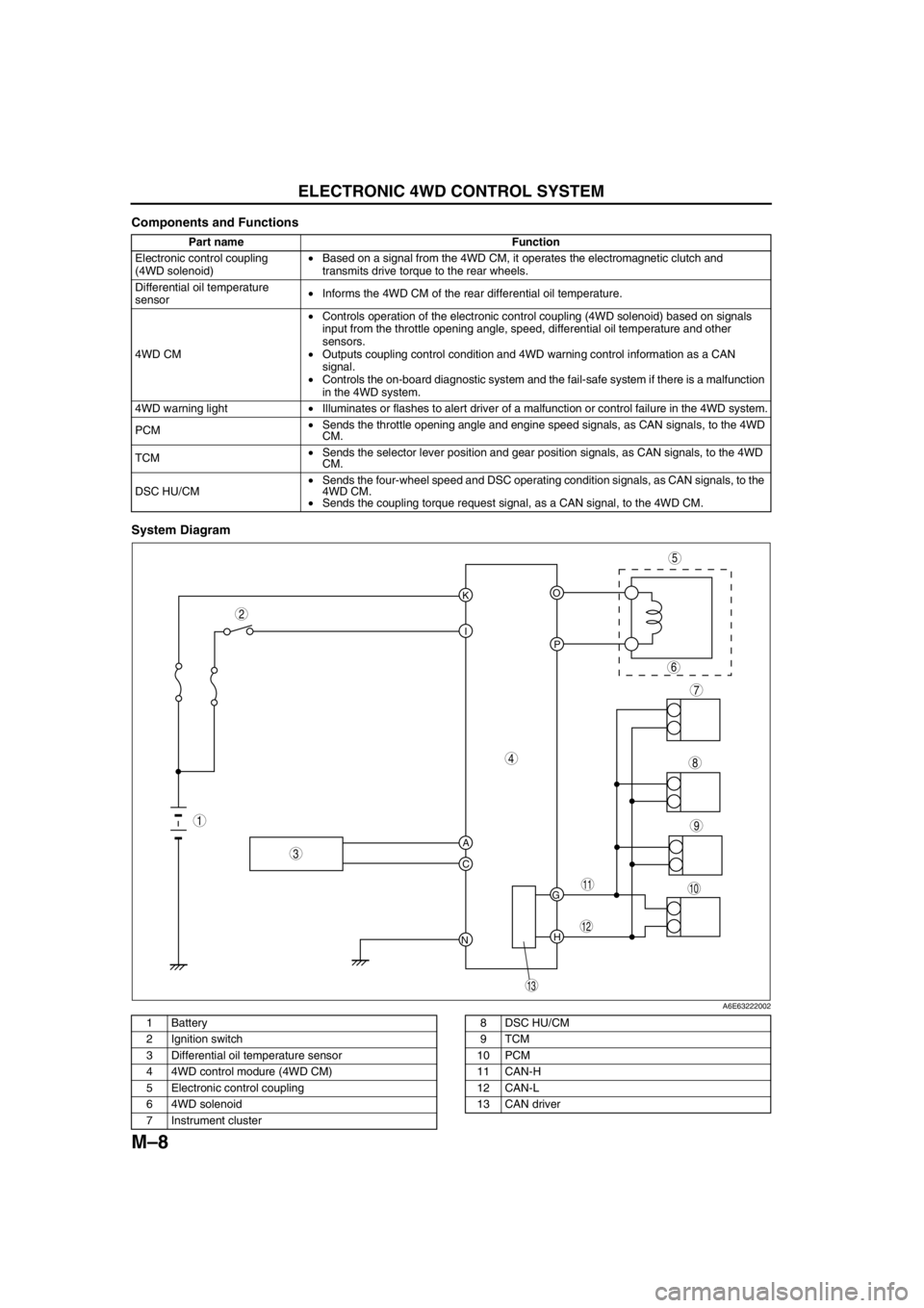
Components and Functions
System Diagram
.
Part name Function
Electronic control coupling
(4WD solenoid)•Based on a signal from the 4WD CM, it operates the electromagnetic clutch and
transmits drive torque to the rear wheels.
Differential oil temperature
sensor•Informs the 4WD CM of the rear differential oil temperature.
4WD CM•Controls operation of the electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid) based on signals
input from the throttle opening angle, speed, differential oil temperature and other
sensors.
•Outputs coupling control condition and 4WD warning control information as a CAN
signal.
•Controls the on-board diagnostic system and the fail-safe system if there is a malfunction
in the 4WD system.
4WD warning light•Illuminates or flashes to alert driver of a malfunction or control failure in the 4WD system.
PCM•Sends the throttle opening angle and engine speed signals, as CAN signals, to the 4WD
CM.
TCM•Sends the selector lever position and gear position signals, as CAN signals, to the 4WD
CM.
DSC HU/CM•Sends the four-wheel speed and DSC operating condition signals, as CAN signals, to the
4WD CM.
•Sends the coupling torque request signal, as a CAN signal, to the 4WD CM.
KO
P I
A
C
NH G
9
8
7
5
4
3
10
13
11
12
6
1
2
A6E63222002
1 Battery
2 Ignition switch
3 Differential oil temperature sensor
4 4WD control modure (4WD CM)
5 Electronic control coupling
6 4WD solenoid
7 Instrument cluster8 DSC HU/CM
9TCM
10 PCM
11 CAN-H
12 CAN-L
13 CAN driver
Page 647 of 909

ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–17
M
Memory function
•This function stores DTCs for malfunctions of the input/output signal systems as determined by the failure
detection function. Once a DTC is stored, it is not cleared even if the input/output signal system malfunction
returns to normal when the ignition key is turned to the LOCK position (engine OFF).
•Since DTCs are stored in the non-volatile memory inside the 4WD CM, they are not cleared even if the battery
is disconnected. Therefore, it is necessary to clear the memory when maintenance has been completed. For
clearing DTCs, refer to the procedures in the Workshop Manual.
•When inspecting DTCs using a WDS or equivalent, only one memory stored DTC at a time can be displayed.
Therefore, when multiple DTCs have been stored, it is necessary to inspect for DTCs again after repairing and
clearing the present DTC to ensure that there are no more DTCs present in the memory.
Fail-safe function
•When the failure detection function determines that there is a malfunction, the 4WD warning light illuminates to
alert the driver. At this time, the fail-safe function suspends control or takes other measures to ensure that
driving stability is not lost.
X:Available
*1: Does not illuminate when only the coupling torque request signal from the DSC HU/CM cannot be received.*2: Only integrated DSC control is prohibited when only the coupling torque request signal from the DSC HU/CM
cannot be received.
External tester communication function
•This function allows for the storing and clearing of DTCs due to a communication link between the 4WD CM
and an external tester.
End Of Sie
DTC Malfunction location4WD warning
lightconditionDTC stored in
memoryControl condition
P1887 System wiring Illuminated X Stop
P1888 Differential oil temperature sensor Illuminated X Stop
U0100 PCM communication system Illuminated X Stop
U0101 TCM communication system Illuminated X Stop
U0121 DSC communication system
Illuminated
*1X
Stop*2
Page 651 of 909

GENERAL PROCEDURES
M–21
M
PRECAUTION (FRONT AND REAR AXLE)A6E631001018201Wheel and Tire Removal/Installation
1. The removal and installation procedures for the wheels and tires are not mentioned in this section. When a
wheel is removed, tighten it to 88—118 N·m {9.0—12.0 kgf·m, 65.0—87.0 ft·lbf}
Brake Line Disconnection/Connection
Caution
•Brake fluid will damage painted surfaces. If brake fluid gets on a painted surface, wipe it off
immediately.
1. Tighten the brake pipe flare nut using the SST (49 0259 770B). Be sure to modify the brake pipe flare nut
tightening torque to allow for use of a torque wrench-SST combination.
2. If any brake line has been disconnected any time during the procedure, add brake fluid, bleed the brakes, and
inspect for leakage after the procedure has been completed.
Suspension Arm Removal/Installation
1. Tighten any part of the suspension that uses rubber bushings only after vehicle has been lowered and
unloaded.
Note
•Unloaded: Fuel tank is full. Engine coolant and engine oil are at specified level. Spare tire, jack, and tools
are in designated position.
Connector Disconnection
1. Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable before disconnecting connectors.
Electronic Control 4WD System Parts
1. After servicing the electronic control 4WD system parts, verify that no DTC has been stored. Clear any DTCs
remaining in the memory.
End Of Sie
GENERAL PROCEDURES
Page 695 of 909
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–65
M
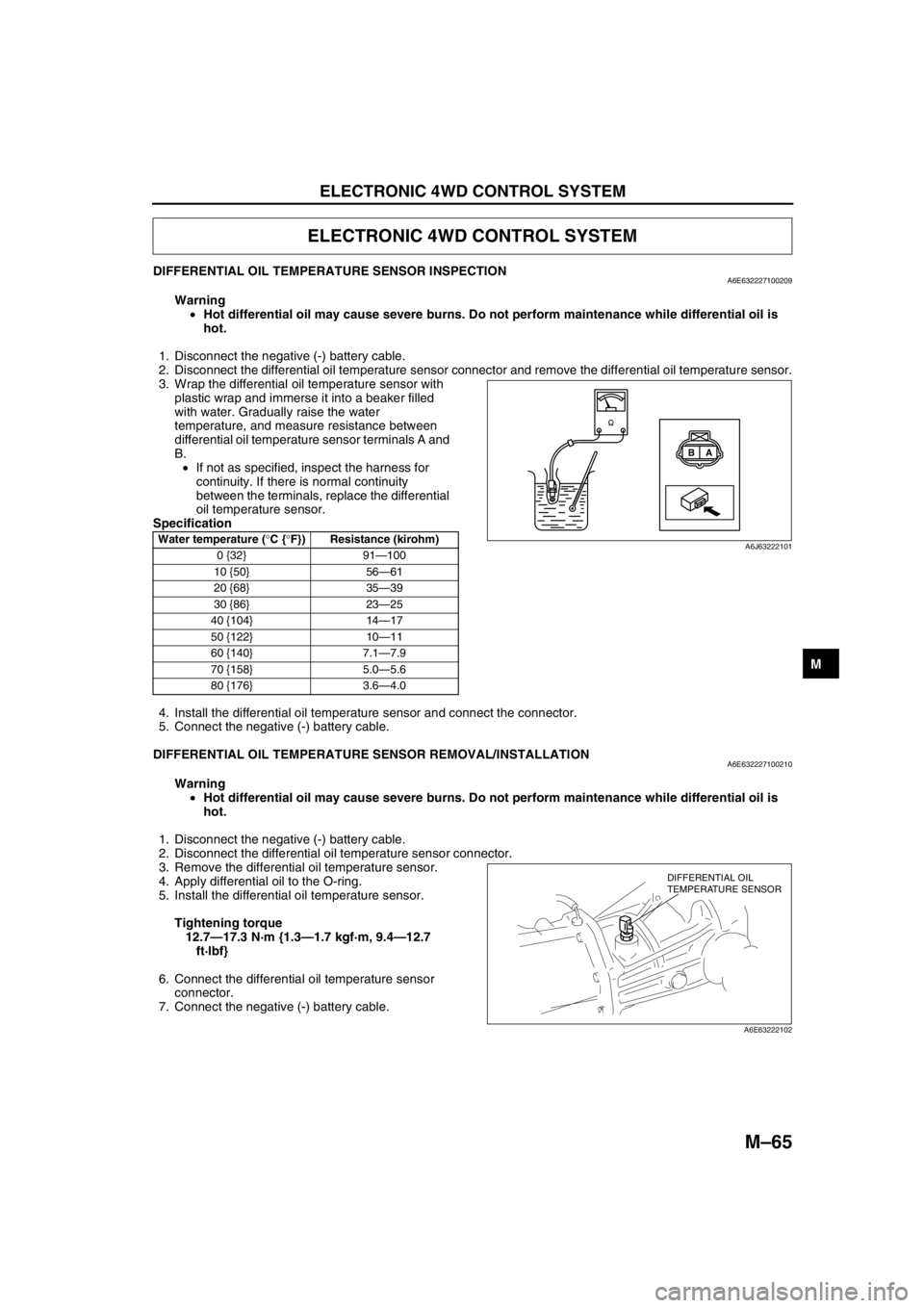
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E632227100209
Warning
•Hot differential oil may cause severe burns. Do not perform maintenance while differential oil is
hot.
1. Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
2. Disconnect the differential oil temperature sensor connector and remove the differential oil temperature sensor.
3. Wrap the differential oil temperature sensor with
plastic wrap and immerse it into a beaker filled
with water. Gradually raise the water
temperature, and measure resistance between
differential oil temperature sensor terminals A and
B.
•If not as specified, inspect the harness for
continuity. If there is normal continuity
between the terminals, replace the differential
oil temperature sensor.
Specification
4. Install the differential oil temperature sensor and connect the connector.
5. Connect the negative (-) battery cable.
End Of Sie
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E632227100210
Warning
•Hot differential oil may cause severe burns. Do not perform maintenance while differential oil is
hot.
1. Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
2. Disconnect the differential oil temperature sensor connector.
3. Remove the differential oil temperature sensor.
4. Apply differential oil to the O-ring.
5. Install the differential oil temperature sensor.
Tightening torque
12.7—17.3 N·m {1.3—1.7 kgf·m, 9.4—12.7
ft·lbf}
6. Connect the differential oil temperature sensor
connector.
7. Connect the negative (-) battery cable.
End Of Sie
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
Water temperature (°C {°F}) Resistance (kirohm)
0 {32} 91—100
10 {50} 56—61
20 {68} 35—39
30 {86} 23—25
40 {104} 14—17
50 {122} 10—11
60 {140} 7.1—7.9
70 {158} 5.0—5.6
80 {176} 3.6—4.0
A B
A6J63222101
DIFFERENTIAL OIL
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
A6E63222102
Page 696 of 909
M–66
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
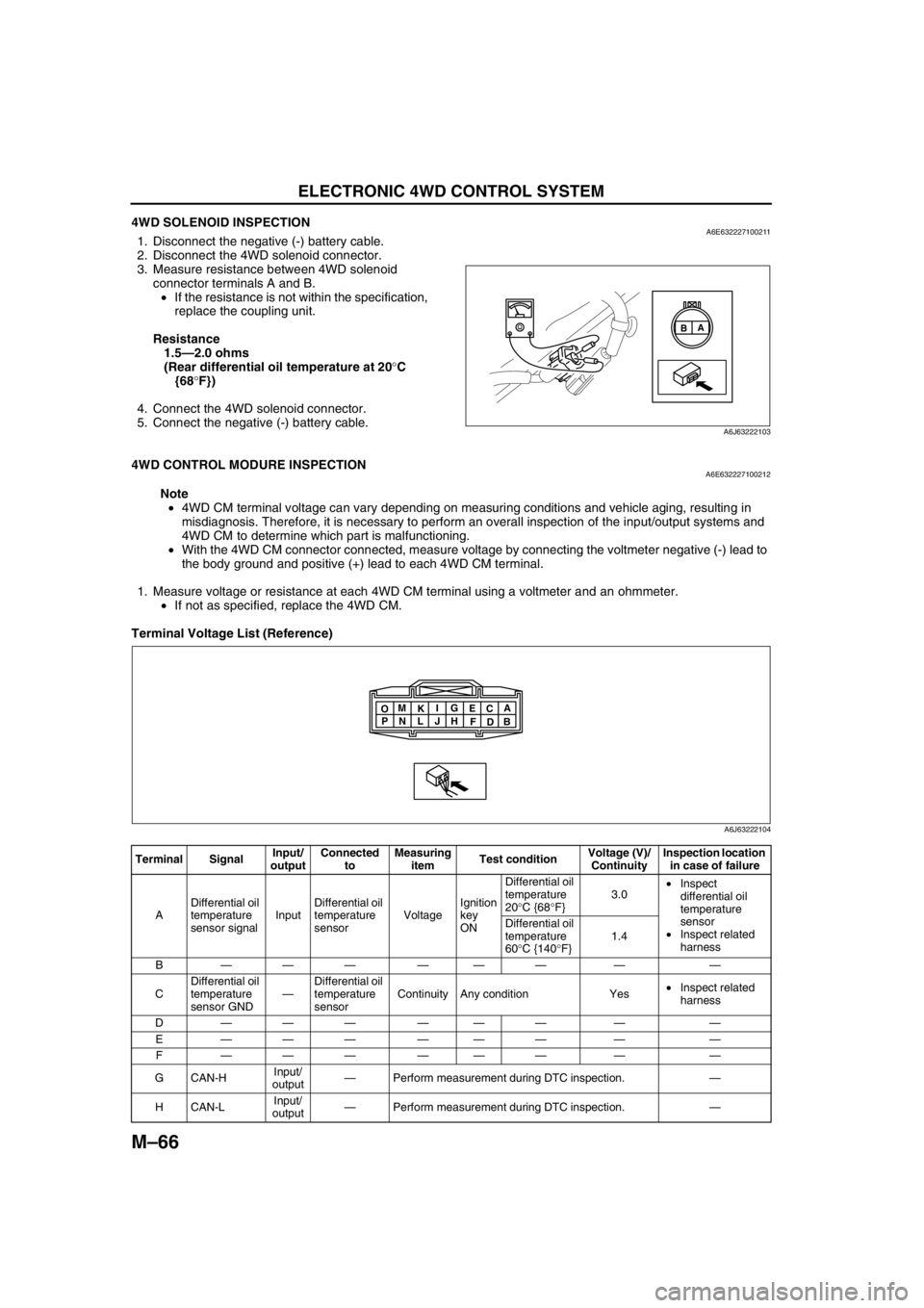
4WD SOLENOID INSPECTIONA6E6322271002111. Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
2. Disconnect the 4WD solenoid connector.
3. Measure resistance between 4WD solenoid
connector terminals A and B.
•If the resistance is not within the specification,
replace the coupling unit.
Resistance
1.5—2.0 ohms
(Rear differential oil temperature at 20°C
{68°F})
4. Connect the 4WD solenoid connector.
5. Connect the negative (-) battery cable.
End Of Sie
4WD CONTROL MODURE INSPECTIONA6E632227100212
Note
•4WD CM terminal voltage can vary depending on measuring conditions and vehicle aging, resulting in
misdiagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to perform an overall inspection of the input/output systems and
4WD CM to determine which part is malfunctioning.
•With the 4WD CM connector connected, measure voltage by connecting the voltmeter negative (-) lead to
the body ground and positive (+) lead to each 4WD CM terminal.
1. Measure voltage or resistance at each 4WD CM terminal using a voltmeter and an ohmmeter.
•If not as specified, replace the 4WD CM.
Terminal Voltage List (Reference)
A
B
A6J63222103
Terminal SignalInput/
outputConnected
toMeasuring
itemTest conditionVoltage (V)/
ContinuityInspection location
in case of failure
ADifferential oil
temperature
sensor signalInputDifferential oil
temperature
sensorVoltageIgnition
key
ONDifferential oil
temperature
20°C {68°F}3.0•Inspect
differential oil
temperature
sensor
•Inspect related
harness Differential oil
temperature
60°C {140°F}1.4
B——— ——— — —
CDifferential oil
temperature
sensor GND—Differential oil
temperature
sensorContinuity Any condition Yes•Inspect related
harness
D——— ——— — —
E——— ——— — —
F——— ——— — —
GCAN-HInput/
output—Perform measurement during DTC inspection.—
HCAN-LInput/
output—Perform measurement during DTC inspection.—
A
B C
D E
F G
H I
J K
L M
N O
P
A6J63222104
Page 697 of 909
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–67
M
End Of Sie
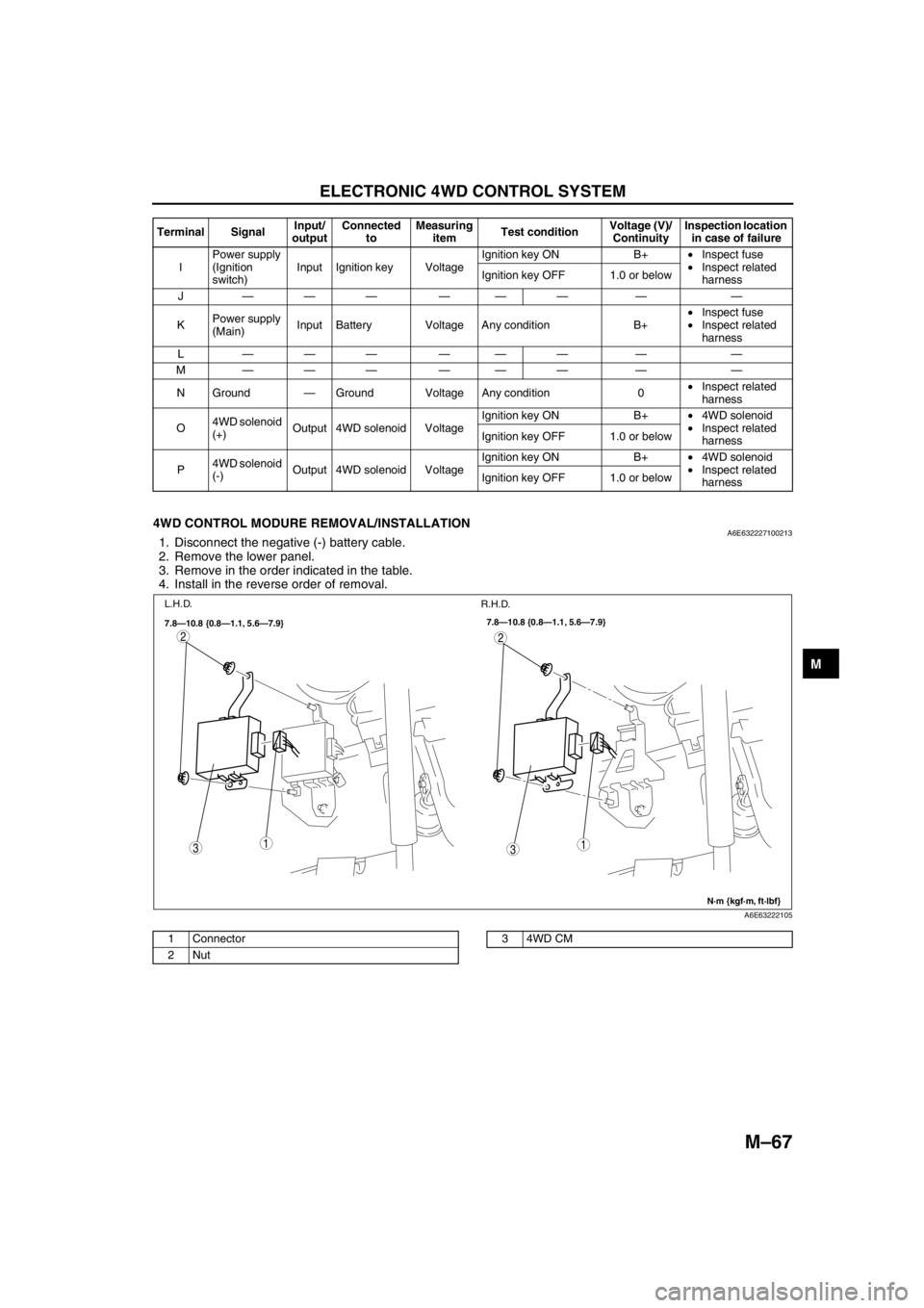
4WD CONTROL MODURE REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E6322271002131. Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable.
2. Remove the lower panel.
3. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
4. Install in the reverse order of removal.
.
End Of Sie
IPower supply
(Ignition
switch)Input Ignition key VoltageIgnition key ON B+•Inspect fuse
•Inspect related
harness Ignition key OFF 1.0 or below
J——— ——— — —
KPower supply
(Main)Input Battery Voltage Any condition B+•Inspect fuse
•Inspect related
harness
L——— ——— — —
M——— ——— — —
N Ground—Ground Voltage Any condition 0•Inspect related
harness
O4WD solenoid
(+)Output 4WD solenoid VoltageIgnition key ON B+•4WD solenoid
•Inspect related
harness Ignition key OFF 1.0 or below
P4WD solenoid
(-)Output 4WD solenoid VoltageIgnition key ON B+•4WD solenoid
•Inspect related
harness Ignition key OFF 1.0 or below Terminal SignalInput/
outputConnected
toMeasuring
itemTest conditionVoltage (V)/
ContinuityInspection location
in case of failure
31
2
31
2
7.8—10.8 {0.8—1.1, 5.6—7.9}
N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf} 7.8—10.8 {0.8—1.1, 5.6—7.9}
L.H.D.
R.H.D.
A6E63222105
1 Connector
2Nut34WD CM
Page 705 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
M–75
M
WIRING DIAGRAMA6E637027100201
End Of Sie
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
IGNITION SWITCH
BATTERY
DIFFERENTIAL OIL
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR4WD CM4WD SOLENOID ELECTRONIC CONTROL
COUPLING
CAN DRIVERINSTRUMENT CLUSTER
CAN-H
CAN-LPCM DSC HU/CM KO
P I
A
C
NH G
TCM
A6E63702002