MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 311 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
F2–159
F2
Diagnostic procedure
End Of Sie
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1PERFORM DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
•Perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure”.
(See F2–85 DTC CONFIRMATION
PROCEDURE)
•Is same DTC present during KOEO or KOER
self-test?Yes Go to next step.
No Intermittent concern exists. Go to “Intermittent Concern
Troubleshooting”.
(See F2–227 INTERMITTENT CONCERN
TROUBLESHOOTING)
2INSPECT POOR CONNECTION OF VSC
SOLENOID VALVE CONNECTOR
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect for poor connection (damaged, pulled-
out terminals, corrosion, etc.).
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Repair or replace suspected terminal, go to Step 6.
No Go to next step.
3INSPECT VSC SOLENOID VALVE CIRCUIT FOR
SHORT TO POWER
•Turn engine switch to ON (Engine switch OFF).
•Inspect voltage between VSC solenoid valve
terminal B and body GND.
•Is voltage below 1.0 V?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for short to power, go to Step 6.
4INSPECT VSC SOLENOID VALVE
•Inspect VSC solenoid valve.
(See F2–42 VARIABLE SWIRL CONTROL
(VSC) SOLENOID VALVE INSPECTION)
• Is there any malfunction?Yes Replace VSC solenoid valve, go to Step 6.
No Go to next step.
5INSPECT POOR CONNECTION OF PCM
CONNECTOR
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect for poor connection (damaged, pulled-
out terminals, corrosion, etc.).
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Repair or replace suspected terminal, go to next step.
No Go to next step.
6VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING OF DTC P0662
COMPLETED
•Make sure to reconnect all disconnected
connectors.
•Clear DTC from PCM memory using WDS or
equivalent.
•Start engine.
•Is same DTC present?Yes Replace PCM, go to next step.
(See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
No Go to next step.
7VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See F2–86 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
(See F2–87 DTC TABLE)
No Troubleshooting completed.
Page 312 of 909
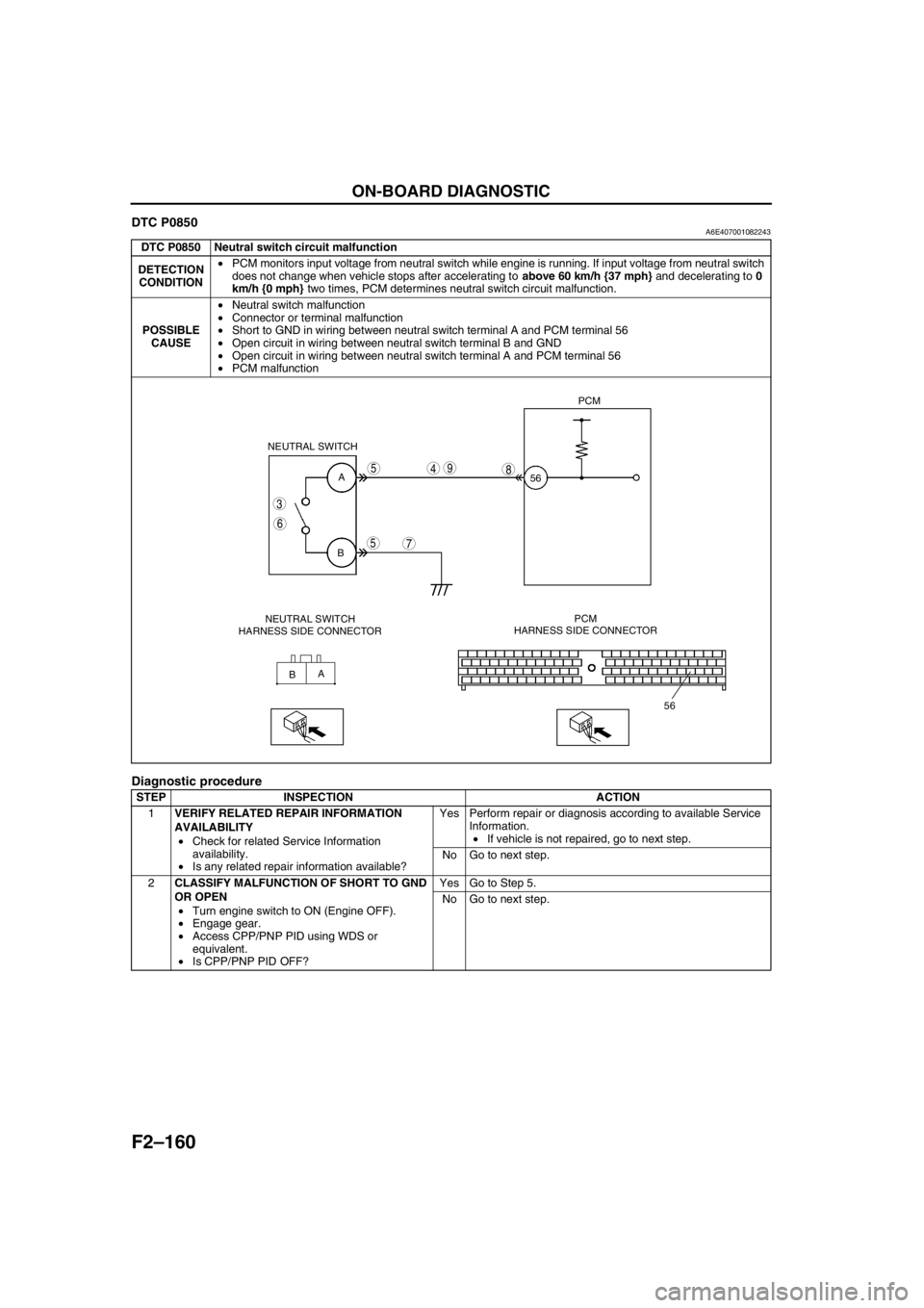
F2–160
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
DTC P0850A6E407001082243
Diagnostic procedure
DTC P0850 Neutral switch circuit malfunction
DETECTION
CONDITION•PCM monitors input voltage from neutral switch while engine is running. If input voltage from neutral switch
does not change when vehicle stops after accelerating to above 60 km/h {37 mph} and decelerating to 0
km/h {0 mph} two times, PCM determines neutral switch circuit malfunction.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Neutral switch malfunction
•Connector or terminal malfunction
•Short to GND in wiring between neutral switch terminal A and PCM terminal 56
•Open circuit in wiring between neutral switch terminal B and GND
•Open circuit in wiring between neutral switch terminal A and PCM terminal 56
•PCM malfunction
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1VERIFY RELATED REPAIR INFORMATION
AVAILABILITY
•Check for related Service Information
availability.
•Is any related repair information available?Yes Perform repair or diagnosis according to available Service
Information.
•If vehicle is not repaired, go to next step.
No Go to next step.
2CLASSIFY MALFUNCTION OF SHORT TO GND
OR OPEN
•Turn engine switch to ON (Engine OFF).
•Engage gear.
•Access CPP/PNP PID using WDS or
equivalent.
•Is CPP/PNP PID OFF?Yes Go to Step 5.
No Go to next step.
A
B
A
B NEUTRAL SWITCH
56PCM
56
3
6
5
5
7
498
NEUTRAL SWITCH
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTORPCM
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
Page 313 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
F2–161
F2
End Of Sie
3INSPECT NEUTRAL SWITCH FOR CLOSE
STUCK
•Turn engine switch to ON (Engine OFF).
•Disconnect neutral switch connector.
•Access CPP/PNP PID using WDS or
equivalent.
•Is CPP/PNP PID OFF?Yes Replace neutral switch, go to Step 10.
No Go to next step.
4INSPECT NEUTRAL SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT
FOR SHORT TO GND
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between neutral switch
terminal A and body GND.
•Is there continuity?Yes Repair or replace harness for short to GND, go to Step 10.
No Go to next step.
5INSPECT POOR CONNECTION OF NEUTRAL
SWITCH CONNECTOR
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect for poor connection (damaged, pulled-
out terminals, corrosion, etc.).
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Repair or replace suspected terminal, go to Step 10.
No Go to next step.
6INSPECT NEUTRAL SWITCH FOR OPEN
STUCK
•Turn engine switch to ON (Engine OFF).
•Disconnect neutral switch connector.
•Connect jumper wire between neutral switch
connector terminals.
•Access CPP/PNP PID using WDS or
equivalent.
•Is CPP/PNP PID ON?Yes Replace neutral switch, go to Step 10.
No Go to next step.
7INSPECT NEUTRAL SWITCH GND CIRCUIT
FOR OPEN
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between neutral switch
terminal B and body GND.
•Is there continuity?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for open, go to Step 10.
8INSPECT POOR CONNECTION OF PCM
CONNECTOR
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect for poor connection (damaged, pulled-
out terminals, corrosion, etc.).
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Repair or replace suspected terminal, go to Step 10.
No Go to next step.
9INSPECT NEUTRAL SWITCH SIGNAL CIRCUIT
FOR OPEN
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between neutral switch
terminal A and PCM terminal 56.
•Is there continuity?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for open, go to next step.
10VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING OF DTC P0850
COMPLETED
•Make sure to reconnect all disconnected
connectors.
•Clear DTC from PCM memory using WDS or
equivalent.
•Start engine.
•Is same DTC present?Yes Replace PCM, go to next step.
(See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
No Go to next step.
11VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See F2–86 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
(See F2–87 DTC TABLE)
No Troubleshooting completed. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
Page 314 of 909
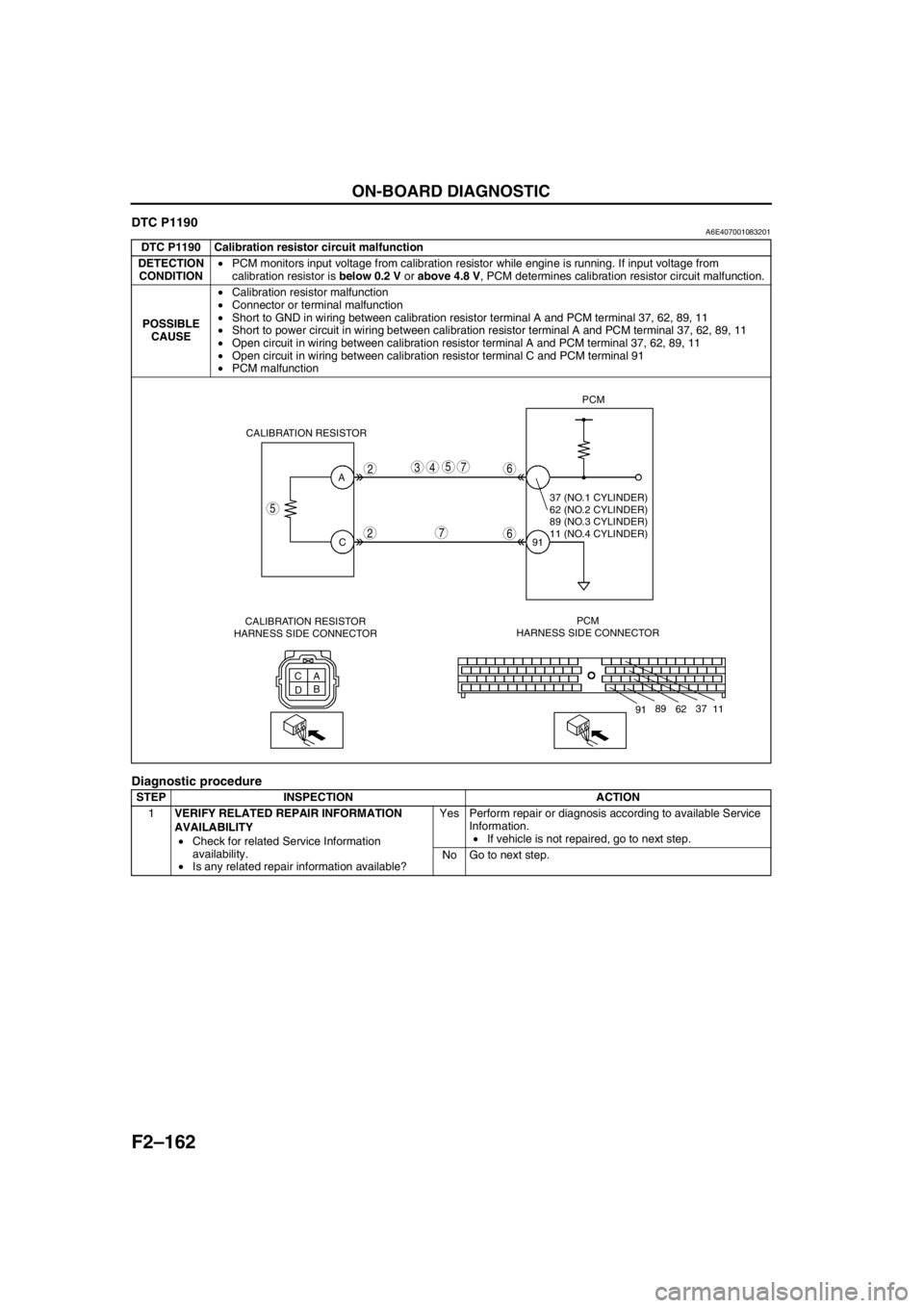
F2–162
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
DTC P1190A6E407001083201
Diagnostic procedure
DTC P1190 Calibration resistor circuit malfunction
DETECTION
CONDITION•PCM monitors input voltage from calibration resistor while engine is running. If input voltage from
calibration resistor is below 0.2 V or above 4.8 V, PCM determines calibration resistor circuit malfunction.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Calibration resistor malfunction
•Connector or terminal malfunction
•Short to GND in wiring between calibration resistor terminal A and PCM terminal 37, 62, 89, 11
•Short to power circuit in wiring between calibration resistor terminal A and PCM terminal 37, 62, 89, 11
•Open circuit in wiring between calibration resistor terminal A and PCM terminal 37, 62, 89, 11
•Open circuit in wiring between calibration resistor terminal C and PCM terminal 91
•PCM malfunction
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1VERIFY RELATED REPAIR INFORMATION
AVAILABILITY
•Check for related Service Information
availability.
•Is any related repair information available?Yes Perform repair or diagnosis according to available Service
Information.
•If vehicle is not repaired, go to next step.
No Go to next step.
A
C
C
A
DBPCM
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR91PCM
CALIBRATION RESISTOR
5
2
2
5437
7
6
6
11 37
62 89
91
37 (NO.1 CYLINDER)
62 (NO.2 CYLINDER)
89 (NO.3 CYLINDER)
11 (NO.4 CYLINDER)
CALIBRATION RESISTOR
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
Page 315 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
F2–163
F2
End Of Sie
2INSPECT POOR CONNECTION OF
CALIBRATION RESISTOR CONNECTOR
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect for poor connection (damaged, pulled-
out terminals, corrosion, etc.).
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Repair or replace suspected terminal, go to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
3INSPECT CALIBRATION RESISTOR SIGNAL
CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GND
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between calibration resistor
terminal A and body GND.
•Is there continuity?Yes Repair or replace harness for short to GND, go to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
4INSPECT CALIBRATION RESISTOR SIGNAL
CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO POWER
•Turn engine switch to ON (Engine OFF).
•Inspect voltage between calibration resistor
terminal A and body GND.
•Is voltage below 1.0V?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for short to power, go to Step 8.
5INSPECT CALIBRATION RESISTOR
•Inspect calibration resistor.
(See F2–83 CALIBRATION RESISTOR
INSPECTION)
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Replace calibration resistor, go to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
6INSPECT POOR CONNECTION OF PCM
CONNECTOR
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect for poor connection (damaged, pulled-
out terminals, corrosion, etc.).
•Is there any malfunction?Yes Repair or replace suspected terminal, go to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
7INSPECT CALIBRATION RESISTOR CIRCUIT
FOR OPEN
•Turn engine switch to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between following
harnesses:
—Calibration resistor terminal A and PCM
terminal 37, 62, 89, 11.
—Calibration resistor terminal C and PCM
terminal 91.
•Is there continuity?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for open, go to next step.
8VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING OF DTC P1190
COMPLETED
•Make sure to reconnect all disconnected
connectors.
•Clear DTC from PCM memory using WDS or
equivalent.
•Start engine.
•Is same DTC present?Yes Replace PCM, go to next step.
(See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
No Go to next step.
9VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See F2–86 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
(See F2–87 DTC TABLE)
No Troubleshooting completed. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
Page 316 of 909

F2–164
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
DTC P2228A6W407001082244
Diagnostic procedure
End Of Sie
DTC P2229A6E407001082245
Diagnostic procedure
End Of Sie
DTC P2228 BARO sensor circuit low input
DETECTION
CONDITION•PCM monitors input voltage from BARO sensor while engine is running. If input voltage from BARO sensor
is below 0.7 V, PCM determines BARO sensor circuit low input.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•BARO sensor malfunction
•PCM malfunction
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1PERFORM DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
•Perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure”.
(See F2–85 DTC CONFIRMATION
PROCEDURE)
•Is same DTC present during KOEO or KOER
self-test?Yes Go to next step.
No Intermittent concern exists. Go to “Intermittent Concern
Troubleshooting”.
(See F2–227 INTERMITTENT CONCERN
TROUBLESHOOTING)
2VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING OF DTC P2228
COMPLETED
•Clear DTC from PCM memory using WDS or
equivalent.
•Perform KOEO/KOER self-test.
(See F2–26 KOEO/KOER SELF-TEST)
•Is same DTC present?Yes Replace PCM, go to next step.
(See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
No Go to next step.
3VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See F2–86 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
(See F2–87 DTC TABLE)
No Troubleshooting completed.
DTC P2229 BARO sensor circuit high input
DETECTION
CONDITION•PCM monitors input voltage from BARO sensor while engine is running. If input voltage from BARO sensor
is above 4.5 V, PCM determines BARO sensor circuit high input.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•BARO sensor malfunction
•PCM malfunction
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1PERFORM DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
•Perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure”.
(See F2–85 DTC CONFIRMATION
PROCEDURE)
•Is same DTC present during KOEO or KOER
self-test?Yes Go to next step.
No Intermittent concern exists. Go to “Intermittent Concern
Troubleshooting”.
(See F2–227 INTERMITTENT CONCERN
TROUBLESHOOTING)
2VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING OF DTC P2229
COMPLETED
•Clear DTC from PCM memory using WDS or
equivalent.
•Perform KOEO/KOER self-test.
(See F2–26 KOEO/KOER SELF-TEST)
•Is same DTC present?Yes Replace PCM, go to next step.
(See F2–64 PCM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION)
No Go to next step.
3VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Perform “After Repair Procedure”.
(See F2–86 AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE)
•Is there any DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
(See F2–87 DTC TABLE)
No Troubleshooting completed.
Page 317 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–165
F2
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSTIC INDEXA6E408018881201
TROUBLESHOOTING
No. TROUBLESHOOTING ITEM DESCRIPTION PAGE
1 Melting of main or other fuses—(See F2–173 NO.1 MELTING
OF MAIN OR OTHER FUSES)
2 MIL illuminates MIL is illuminated incorrectly.(See F2–174 NO.2 MIL
ILLUMINATES)
3 Will not crank Starter does not work.(See F2–174 NO.3 WILL NOT
CRANK)
4Hard start/long crank/erratic start/
erratic crankStarter cranks engine at normal speed but
engine requires excessive cranking time
before starting.(See F2–176 NO.4 HARD
START/LONG CRANK/
ERRATIC START/ERRATIC
CRANK)
5 Engine stalls After start/at idleEngine stops unexpectedly at idle and/or
after start.(See F2–178 NO.5 ENGINE
STALLS-AFTER START/AT
IDLE)
6 Cranks normally but will not startStarter cranks engine at normal speed but
engine will not run.(See F2–181 NO.6 CRANKS
NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT
START)
7 Slow return to idleEngine takes more time than normal to
return to idle speed.(See F2–184 NO.7 SLOW
RETURN TO IDLE)
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idleEngine speed fluctuates between specified
idle speed and lower speed and engine
shakes excessively.(See F2–186 NO.8 ENGINE
RUNS ROUGH/ROLLING
IDLE)
9 Fast idle/runs onEngine speed continues at fast idle after
warm-up.
Engine runs after engine switch is turned to
OFF.(See F2–189 NO.9 FAST
IDLE/RUNS ON)
10 Low idle/stalls during decelerationEngine stops unexpectedly at beginning of
deceleration or recovery from deceleration.(See F2–190 NO.10 LOW
IDLE/STALLS DURING
DECELERATION)
11Engine stalls/quitsAcceleration/
cruiseEngine stops unexpectedly at beginning of
acceleration or during acceleration.
Engine stops unexpectedly while cruising.
(See F2–192 NO.11 ENGINE
STALLS/QUITS, ENGINE
RUNS ROUGH, MISSES,
BUCK/JERK, HESITATION/
STUMBLE, SURGES) Engine runs roughAcceleration/
cruiseEngine speed fluctuates during acceleration
or cruising.
MissesAcceleration/
cruiseEngine misses during acceleration or
cruising.
Buck/jerkAcceleration/
cruise/
decelerationVehicle bucks/jerks during acceleration,
cruising, or deceleration.
Hesitation/stumble AccelerationMomentary pause at beginning of
acceleration or during acceleration.
SurgesAcceleration/
cruiseMomentary minor irregularity in engine
output.
12 Lack/loss of powerAcceleration/
cruisePerformance is poor under load (e.g. power
down when climbing hills).(See F2–195 NO.12 LACK/
LOSS OF POWER-
ACCELERATION/CRUISE)
13 Knocking/pingingExcessive shrilly knocking sound from
engine.(See F2–199 NO.13
KNOCKING/PINGING)
14 Poor fuel economy Fuel economy is unsatisfactory.(See F2–202 NO.14 POOR
FUEL ECONOMY)
15 Emissions compliance Fails emissions test.(See F2–205 NO.15
EMISSION COMPLIANCE)
16 High oil consumption/leakage Oil consumption is excessive.(See F2–209 NO.16 HIGH OIL
CONSUMPTION/LEAKAGE)
17Cooling system
concernsOverheatingEngine runs at higher than normal
temperature/overheats.(See F2–210 NO.17 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS-
OVERHEATING)
Page 318 of 909

F2–166
TROUBLESHOOTING
End Of Sie
18Cooling system
concernsRuns coldEngine does not reach normal operating
temperature.(See F2–212 NO.18 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS-RUNS
COLD)
19 Excessive black smokeExcessive black smoke is observed in
exhaust gas.(See F2–213 NO.19
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE)
20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment) Fuel smell or visible leakage.(See F2–216 NO.20 FUEL
ODOR (IN ENGINE
COMPARTMENT)
21 Engine noise Engine noise from under hood.(See F2–217 NO.21 ENGINE
NOISE)
22 Vibration concerns (engine) Vibration from under hood or driveline.(See F2–220 NO.22
VIBRATION CONCERNS
(ENGINE)
23 A/C does not work sufficientlyA/C compressor magnetic clutch does not
engage when A/C is turned on.(See F2–222 NO.23 A/C
DOES NOT WORK
SUFFICIENTLY)
24A/C always on or A/C compressor runs
continuouslyA/C compressor magnetic clutch does not
disengage.(See F2–223 NO.24 A/C
ALWAYS ON OR A/C
COMPRESSOR RUNS
CONTINUOUSLY)
25A/C does not cut off under wide open
throttle conditionsA/C compressor magnetic clutch does not
disengage under wide open throttle.(See F2–224 NO.25 A/C
DOES NOT CUT OFF UNDER
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE
CONDITIONS)
26 Constant voltage Incorrect Constant voltage.(See F2–225 NO.26
CONSTANT VOLTAGE) No. TROUBLESHOOTING ITEM DESCRIPTION PAGE
Page 319 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–167
F2
SYMPTOM QUICK DIAGNOSIS CHARTA6E408018881202
×: Applicable
Troubleshooting item
1 Melting of main or other fuses
2 MIL illuminates
3 Will not crank×× ×× × ×
4 Hard start/long crank/erratic start/erratic crank×× ×
5 Engine stalls After start/at idle××
6 Cranks normally but will not start××
7 Slow return to idle
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idle××
9 Fast idle/runs on
10 Low idle/stalls during deceleration××
11Engine stalls/quits Acceleration/cruise××
Engine runs rough Acceleration/cruise××
Misses Acceleration/cruise××
Buck/jerk Acceleration/cruise/ deceleration××
Hesitation/stumble Acceleration××
Surges Acceleration/cruise××
12 Lack/loss of power Acceleration/cruise××
13 Knocking/pinging××
14 Poor fuel economy××
15 Emissions compliance×× ×
16 High oil consumption/leakage××××
17 Cooling system concerns Overheating××
18 Cooling system concerns Runs cold
19 Excessive black smoke×
20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment)
21 Engine noise×× × ×
22 Vibration concerns (engine)×
23 A/C does not work sufficiently
24 A/C always on or A/C compressor runs continuously
25 A/C does not cut off under wide open throttle conditions
26 Constant voltage
Starter motor malfunction (Mechanical or electrical)Starter circuit including engine switch is openImproper engine oil levelLow or dead bateryCharging system malfunctionLow engine compressionImproper valve timingHydrolocked egineImproper engine oil viscosityImproper dipstickBase engine malfunctionSeized flywheelImproper tension or damaged drivebelts
Page 320 of 909

F2–168
TROUBLESHOOTING
×: Applicable
Troubleshooting item
1 Melting of main or other fuses
2 MIL illuminates
3 Will not crank
4 Hard start/long crank/erratic start/erratic crank×××
5 Engine stalls After start/at idle×××
6 Cranks normally but will not start××
7 Slow return to idle×
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idle××××
9 Fast idle/runs on×
10 Low idle/stalls during deceleration××
11Engine stalls/quits Acceleration/cruise××××
Engine runs rough Acceleration/cruise×××× ×
Misses Acceleration/cruise××××××
Buck/jerk Acceleration/cruise/ deceleration××××××
Hesitation/stumble Acceleration××××××
Surges Acceleration/cruise××××××
12 Lack/loss of power Acceleration/cruise×××××××
13 Knocking/pinging×××××
14 Poor fuel economy××××
15 Emissions compliance× ××××××
16 High oil consumption/leakage
17 Cooling system concerns Overheating×× × ×
18 Cooling system concerns Runs cold××
19 Excessive black smoke××××
20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment)
21 Engine noise××
22 Vibration concerns (engine)×× ×
23 A/C does not work sufficiently
24 A/C always on or A/C compressor runs continuously
25 A/C does not cut off under wide open throttle conditions
26 Constant voltage
Improper engine coolant levelWater and anti-freeze mixture is improperCooling system malfunction (Radiator, hose,
over-flow system, thermostat, etc.)Cooling fan system malfunctionEngine or transaxle mounts are improperly installedCooling fan No.1 or No.2 seat are improperFuel qualityEngine overheatingIntake-air system clogging or restrictionAir leakage from intake-air systemVSC system malfunctionVacuum leakage