MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 611 of 909

K2–196
TROUBLESHOOTING
NO.15 ENGINE FLARES UP OR SLIPS WHEN ACCELERATING VEHICLEA6E578001030218
End Of SieNO.16 JUDDER UPON TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) OPERATIONA6E578001030219
End Of SieNO.17 EXCESSIVE SHIFT SHOCK FROM N TO D OR N TO R POSITION/RANGEA6E578001030220
Diagnostic procedure
15 Engine flares up or slips when accelerating vehicle
DESCRIPTION•Engine flares up when accelerator pedal depressed for upshifting.
•Engine flares up suddenly when accelerator pedal depressed for downshifting.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Malfunction is basically the same as for No.14 “Engine flares up or slips when upshifting or
downshifting”.
—If conditions for No.14 worsen, malfunction will develop into No.15.
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
16 Judder upon torque converter clutch (TCC) operation
DESCRIPTION•Vehicle jolts when TCC engaged.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Poor TCC engagement due to either slippage because TCC piston is stuck or line pressure is low.
Caution
•If the TCC or piston are stuck, inspect them. In addition, inspect the oil cooler for foreign
particles which may have mixed in with the ATF.
—Torque converter clutch piston slipped, burned
•Line pressure low
•Incorrect throttle position signal
•Malfunction of VSS
•Malfunction of input/turbine speed sensor
•Malfunction of sensor ground
•Malfunction of TCC solenoid valve
•Malfunction of control valve body
—Malfunction of torque converter
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
17 Excessive shift shock from N to D or N to R position/range
DESCRIPTION•Strong shock felt when shifting from N to D or N to R position/range at idle.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Shift shock may worsen when fail-safe is operating. If no DTC is output, shift shock may worsen due to
poor operation of control valve body or sticking of clutch.
—Clutch burned (N→D: Low clutch, N→R: Reverse clutch or low and reverse brake)
•Line pressure low
•Incorrect throttle position signal
•Malfunction of TFT sensor
•Malfunction of sensor ground
•Misadjustment of throttle cable
•Malfunction of control valve body
—Poor hydraulic operation (Malfunction in range change)
—Idle speed high
—Poor tightening torque of engine mount, exhaust mount
—Line pressure high
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Does shift shock occur only when engine
cold?Yes Go to next step.
No Go to Step 3.
2•Inspect TFT sensor and related harness:
vibration, intermittent open/short circuit.
•Is it okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace part if necessary.
Page 612 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
K2–197
K2
End Of SieNO.18 EXCESSIVE SHIFT SHOCK IS GIVEN WHEN UPSHIFTING AND DOWNSHIFTINGA6E578001030221
End Of SieNO.19 EXCESSIVE SHIFT SHOCK ON TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)A6E578001030222
End Of Sie
3•Is line pressure okay?
(See K2–72 Line Pressure Test.)Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace any defective parts according to
inspection results.
4•Is stall speed okay?
(See K2–74 Stall Speed Test.)Yes Go to next step.
No Go to Step 6.
5•Inspect TR switch and related harness:
vibration, intermittent open/short circuit.
•Is it okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace part if necessary.
6•Stop engine and turn ignition switch on.
•Inspect pressure control solenoid circuit.
•Is it okay?Yes•Overhaul control valve body and repair or replace any
defective parts.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
•If problem remains, replace or overhaul transaxle and
repair or replace any defective parts.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
No•Inspect for pressure control solenoid mechanical stuck.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE INSPECTION.)
7•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
18 Excessive shift shock is given when upshifting and downshifting
DESCRIPTION•Excessive shift shock felt when depressing accelerator pedal to accelerate at upshifting.
•During cruising, excessive shift shock felt when depressing accelerator pedal at downshifting.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Shift shock may worsen when fail-safe is operating. The shift shock has worsen if TP sensor, input/
turbine speed sensor, or VSS signal malfunctions.
—Clutch slipped, burned
•Line pressure low, high
•Incorrect throttle position signal
•Malfunction of VSS
•Malfunction of input/turbine speed sensor
•Malfunction of TFT sensor
•Malfunction of shift solenoid A, B, or C
•Malfunction of TCC solenoid valve
•Misadjustment of throttle cable
•Malfunction of body ground and sensor ground
•Malfunction of control valve body
—Poor hydraulic operation (Malfunction in range change)
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
19 Excessive shift shock on torque converter clutch (TCC)
DESCRIPTION•Strong shock felt when TCC engaged.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•The troubleshooting flow is the same as No.16 “Judder upon torque converter clutch (TCC) operation”.
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
Page 613 of 909

K2–198
TROUBLESHOOTING
NO.20 NOISE OCCURS AT IDLE WHEN VEHICLE IS STOPPED IN ALL POSITIONS/RANGESA6E578001030223
Diagnostic procedure
End Of SieNO.21 NOISE OCCURS AT IDLE WHEN VEHICLE IS STOPPED IN D RANGE, OR IN R POSITIONA6E578001030224
End Of SieNO.22 NO ENGINE BRAKING IN 1GR POSITION OF M RANGEA6E578001030225
Diagnostic procedure
20 Noise occurs at idle when vehicle is stopped in all positions/ranges
DESCRIPTION•Transaxle noisy in all positions and ranges when vehicle idling.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Malfunction is in pressure solenoid or oil pump which causes a high-pitched noise to be emitted from
transaxle at idle.
Note
•If a noise is emitted during shifting only, malfunction is in shift solenoid A, B, or C.
•If a noise is emitted during shifting at certain gears only or during deceleration only, it is gear noise.
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Inspect engine condition.
•Is any engine concern (e.g. Rough idle)?Yes Go to appropriate symptom troubleshooting.
(See F1–57 ENGINE SYMPTOM TROUBLESHOOTING.)
No Replace basic inspection and repair or replace any
defective parts according to inspection result.
2•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM.
21 Noise occurs at idle when vehicle is stopped in D range, or in R position
DESCRIPTION•Transaxle noisy in driving ranges when vehicle idling.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Although the malfunction is basically the same as No.20 “Noise occurs at idle when vehicle is stopped
in all positions/ranges”, other causes may be selector lever position disparity or TR switch position
disparity.
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
22 No engine braking in 1GR position of M range
DESCRIPTION•Engine speed drops to idle but vehicle coasts when accelerator pedal released during cruising at
medium to high speeds.
•Engine speed drops to idle but vehicle coasts when accelerator pedal released when in M range (1GR)
at low vehicle speed.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Clutch slipped, burned (Reduction brake)
—Line pressure low
•Malfunction of VSS
•Malfunction of input/turbine speed sensor
•Malfunction of sensor ground
•Malfunction of control valve body
—M range switch on not judged by TCM (short, or open circuit, poor operation)
•Malfunction of M range switch signal
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Inspect TR switch adjustment.
•Does TR switch adjusted properly?
•Select PNP PID.
•Is PNP PID reading okay when selecting
range?Yes Go to next step.
No Adjust TR switch as necessary.
(See K2–83 TRANSAXLE RANGE (TR) SWITCH
ADJUSTMENT.)
Inspect TR switch.
Repair or replace any defective parts.
Page 614 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
K2–199
K2
End Of SieNO.23 TRANSAXLE OVERHEATSA6E578001030226
Diagnostic procedure
End Of SieNO.24 ENGINE STALLS WHEN SHIFTED TO D RANGE, OR IN R POSITIONA6E578001030227
2•Do following symptoms concurrently occur?
—Engine flares up or slips during
acceleration
—Engine flares up or slips when shiftingYes Go to symptom troubleshooting No.14 “Engine flares up or
slips when upshifting or downshifting” or No.15 “Engine
flares up or slips when accelerating vehicle”.
No Go to next step.
3•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
23 Transaxle Overheat
DESCRIPTION•Burnt smell emitted from transaxle.
•Smoke emitted from transaxle.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Malfunction is restricted to hindrance of coolant at oil cooler. In addition, overheating of transaxle may
be caused by a malfunction of TFT sensor.
—Line pressure low
•ATF level low
•Incorrect throttle position signal
•Misadjustment of throttle cable
—Oil cooler malfunction (Foreign material mixed in with ATF)
—TFT sensor malfunction
—Excessive amount of ATF
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Is line pressure okay?
(See K2–72 Line Pressure Test.)Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace any defective parts according to
inspection results.
2•Is stall speed okay?
(See K2–74 Stall Speed Test.)Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace any defective parts according to
inspection results.
3•Inspect TFT sensor and related harness:
vibration, intermittent open/short circuit
•Is it okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace part if necessary.
4•Inspect pressure control solenoid circuit.
•Is it okay?Yes Go to next step.
No•Inspect for pressure control solenoid mechanical stuck.
(See K2–88 SOLENOID VALVE INSPECTION.)
5•Inspect for bend, damage, corrosion or kinks
of oil cooler pipes.
•Are oil cooler pipes okay?Yes•Overhaul control valve body and repair or replace any
defective parts.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
•If problem remains, replace or overhaul transaxle and
repair or replace any defective parts.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
No Replace any defective parts.
6•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM.
24 Engine stalls when shifted to D range, or in R position
DESCRIPTION•Engine stalls when shifting from N or P position to D range or R position at idle.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Malfunction is on the engine control side (e.g. IAC system). Otherwise, malfunction is in input/turbine
speed sensor (engine sometimes starts) or TCC piston circuit (engine always stalls).
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic and
Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
Page 615 of 909

K2–200
TROUBLESHOOTING
Diagnostic procedure
End Of SieNO.25 ENGINE STALLS WHEN DRIVING AT SLOW SPEED OR STOPPINGA6E578001030228
Diagnostic procedure
End Of SieNO.26 STARTER DOES NOT WORKA6E578001030229
End Of SieNO.27 GEAR POSITION INDICATOR LIGHT DOES NOT ILLUMINATE IN M RANGEA6E578001030230
Diagnostic procedure
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Go to symptom troubleshooting No.4
“Engine stalls-after start/at idle”.
(See Section F.)
•Is engine control system okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace any defective parts according to
inspection results.
2•Remove torque converter.
•Inspect torque converter.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
•Is torque converter okay?Yes•Inspect for bend, damage or kinks of oil cooler line
pipes. If okay, overhaul control valve body and repair or
replace any defective parts.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
•If problem remains, replace or overhaul transaxle and
repair or replace any defective parts.
(See ATX Workshop Manual.)
No Replace torque converter.
3•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM.
25 Engine stalls when driving at slow speeds or stopping
DESCRIPTION•Engine stalls when brake pedal depressed while driving at low speed or stopping.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Malfunction is on engine control side (e.g. Fuel injection control, IAC system)
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Go to symptom troubleshooting No.10 “Low
idle/stalls during deceleration”.
(See Section F.)
•Is engine control system okay?Yes Go to symptom troubleshooting No.24 “Engine stalls when
shifted to D range, or in R position”.
No Repair or replace any defective parts according to
inspection results.
2•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM.
26Starter does not work
DESCRIPTION•Starter does not work even when P or N position.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Selector lever misadjustment.
•TR switch misadjustment.
•Open or short circuit in TR switch.
27 Gear position indicator light does not illuminate in M range
DESCRIPTION•Gear position indicator light in instrument cluster does not illuminate in M range and ignition switch at
on.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•M range switch, gear position indicator light or related wiring harness malfunction.
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Are other indicator lights illuminated with
ignition switch on? Yes Go to next step.
No Inspect meter fuse.
Page 616 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
K2–201
K2
End Of SieNO.28 GEAR POSITION INDICATOR LIGHT ILLUMINATES IN D RANGE OR IN P, N, R POSITIONSA6E578001030231
Diagnostic procedure
End Of SieNO.29 DOES NOT SHIFT UP IN M RANGEA6E578001030232
End Of SieNO.30 DOES NOT SHIFT DOWN IN M RANGEA6E578001030233
End Of Sie
2•Inspect MNL SW PID value using WDS or
equivalent.
•Are these PIDs okay?Yes Inspect instrument cluster.
No Inspect M range switch.
If M range switch is okay, inspect for continuity between M
range switch and TCM terminal 1AA.
3•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
28 Gear position indicator light illuminates when D range or P, N, R positions
DESCRIPTION•Gear position indicator light in instrument cluster illuminates in D range or P, N, R positions and ignition
switch at on.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•M range switch or related wiring harness malfunction.
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board Diagnostic
and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1•Inspect MNL SW PID value using WDS or
equivalent.
•Are these PIDs okay?Yes Inspect instrument cluster.
No Inspect M range switch.
If M range switch is okay, inspect for continuity between M
range switch and TCM terminal 1AA.
2•Verify test results.
—If okay, return to diagnostic index to service any additional symptoms.
—If malfunction remains, inspect related Service Informations and perform repair or diagnosis.
—If vehicle repaired, troubleshooting completed.
—If vehicle not repaired or additional diagnostic information not available, replace TCM.
29Does not shift up in M range
DESCRIPTION•Gear position indicator light in instrument cluster illuminates, but vehicle does not upshift when selector
lever is pushed to “+” side.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Up switch or related harness malfunction
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board
Diagnostic and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
30 Does not shift up in M range
DESCRIPTION•Gear position indicator light in instrument cluster illuminates, but vehicle does not downshift when
selector is pushed lever to “–” side.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Down switch or related harness malfunction
Note
•Before following troubleshooting steps, make sure that Automatic Transaxle On-Board
Diagnostic and Automatic Transaxle Basic Inspection are conducted.
Page 617 of 909

L–1
L
LPROPELLER SHAFT
OUTLINE................................................................ L-2
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTION.......................... L-2
FEATURES .......................................................... L-2
SPECIFICATIONS ............................................... L-2
LOCATION INDEX................................................. L-3
PROPELLER SHAFT INDEX ............................... L-3
PROPELLER SHAFT............................................. L-4
PROPELLER SHAFT
INSPECTION ON VEHICLE ............................. L-4
PROPELLER SHAFT
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION .............................. L-5
PROPELLER SHAFT
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ............................ L-7
PROPELLER SHAFT INSPECTION .................. L-14 FEATURES
SERVICE
Page 618 of 909
L–2
OUTLINE
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTIONA6E610225002201•The Mazda6 4WD model has been adopted for European specs.
End Of Sie
FEATURESA6E610225002203Reduced noise and vibration
•The four-joint type propeller shaft with two bearing support has been adopted for the Mazda6 4WD model.
End Of Sie
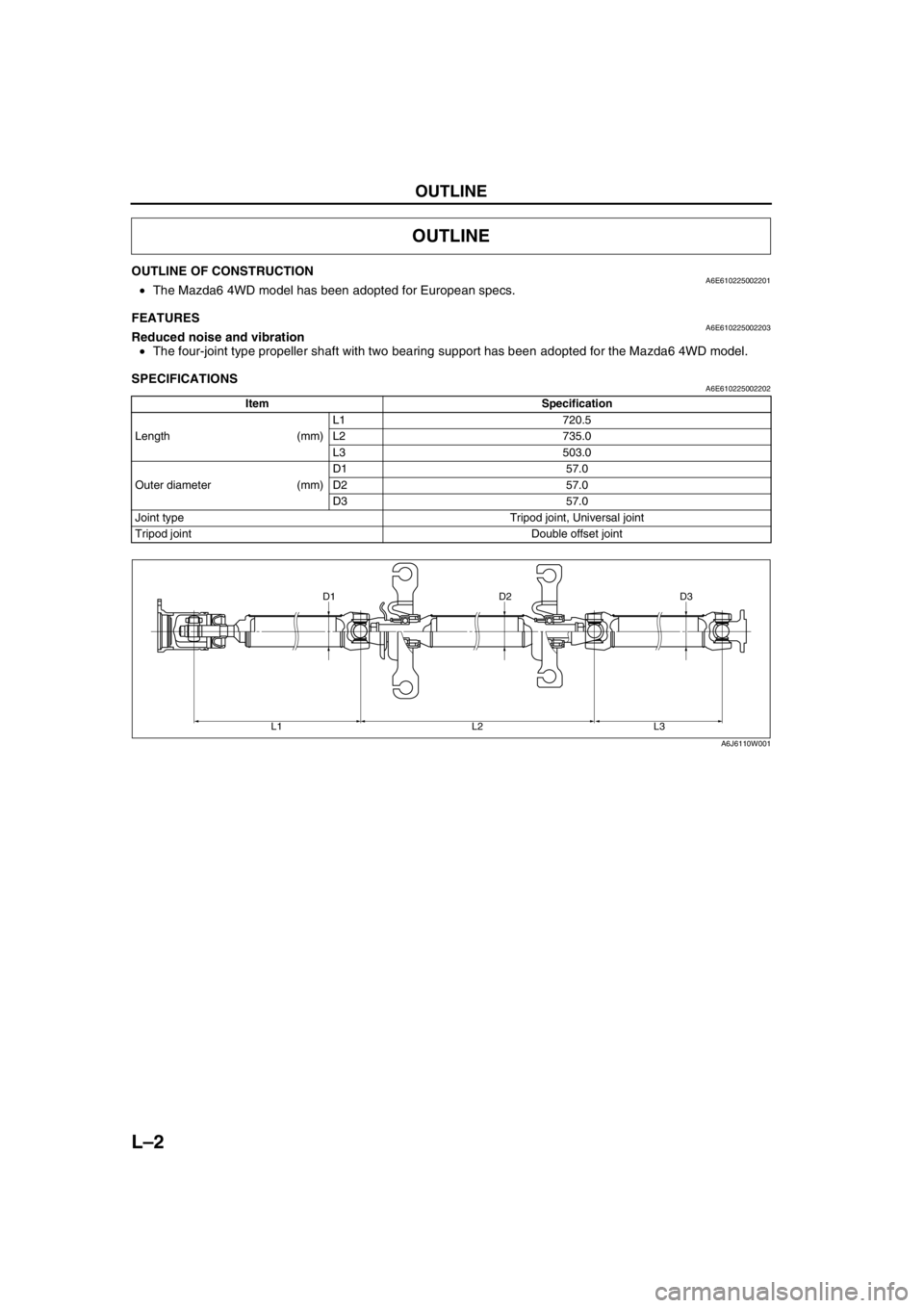
SPECIFICATIONSA6E610225002202
End Of Sie
OUTLINE
Item Specification
Length (mm)L1 720.5
L2 735.0
L3 503.0
Outer diameter (mm)D1 57.0
D2 57.0
D3 57.0
Joint type Tripod joint, Universal joint
Tripod joint Double offset joint
D3 D2 D1
L3 L2 L1
A6J6110W001
Page 619 of 909

LOCATION INDEX
L–3
L
PROPELLER SHAFT INDEXA6E610001036201
.
End Of Sie
LOCATION INDEX
1
A6E6100W001
1 Propeller shaft
(See L–4 PROPELLER SHAFT INSPECTION ON
VEHICLE)
(See L–5 PROPELLER SHAFT REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION)
(See L–7 PROPELLER SHAFT DISASSEMBLY/
ASSEMBLY)
(See L–14 PROPELLER SHAFT INSPECTION)
Page 620 of 909

L–4
PROPELLER SHAFT
PROPELLER SHAFT INSPECTION ON VEHICLEA6E611025002204Joint Play Inspection
1. Move the joint shaft by hand, and verify that there is no play.
If there is play, perform the following service operations.
•Yoke : Universal joint replacement (See L–7 PROPELLER SHAFT DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY.)
•Constant velocity joint : Propeller shaft
replacement (See L–7 PROPELLER SHAFT
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY.)
Propeller Shaft Runout Inspection
Caution
•Do not rotate the propeller shaft by starting the engine.
1. Shift the select lever to N position and release the parking brake.
2. Rotate the rear wheel by hand, and measure the
propeller shaft runout at 9 points as shown in the
figure.
Limit
0.4 mm {0.02 in}
PROPELLER SHAFT
A6J6110W002
A6J6110W003
A6J6110W004