engine MITSUBISHI 380 2005 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: 380, Model: MITSUBISHI 380 2005Pages: 1500, PDF Size: 47.87 MB
Page 887 of 1500
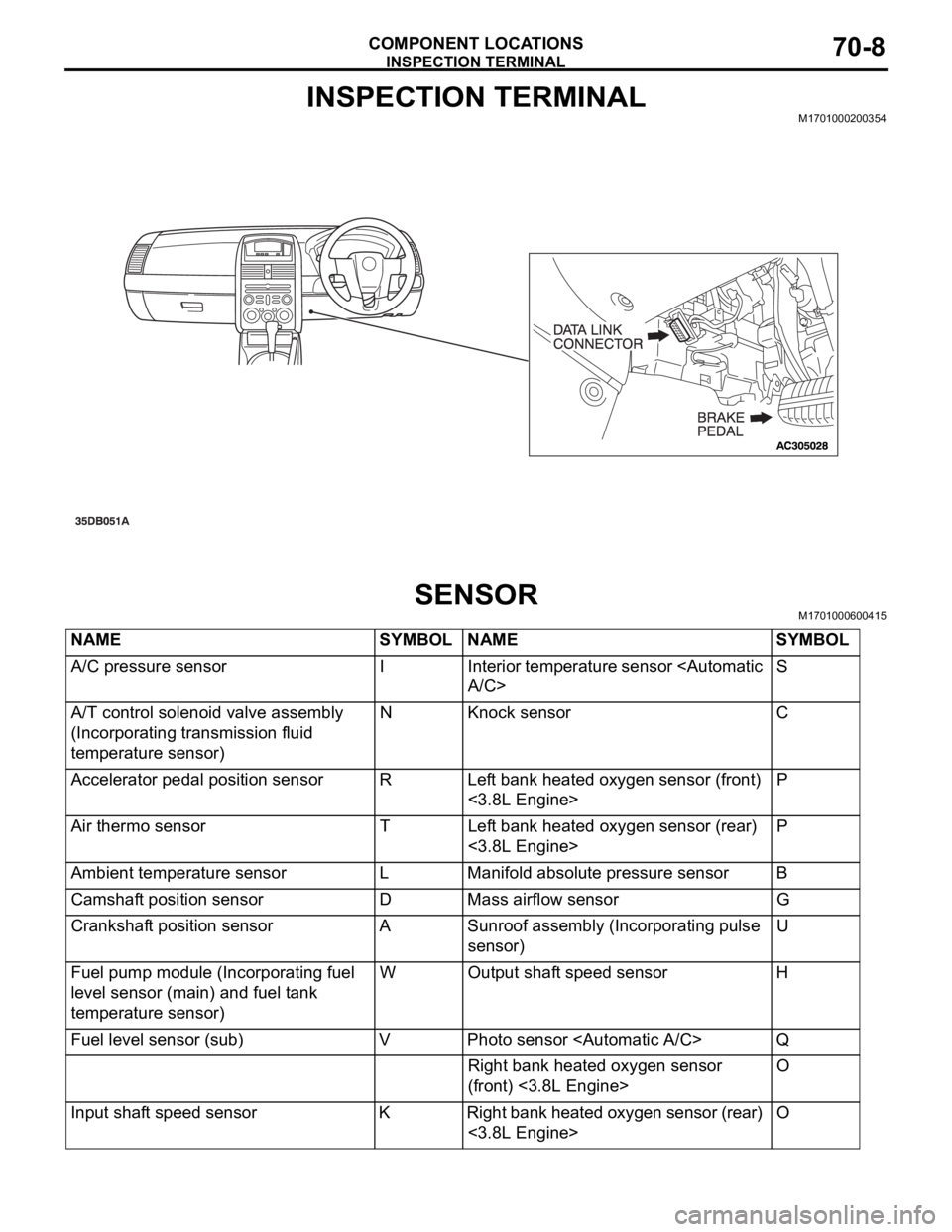
INSPECTION TERMINAL
COMPONENT LOCATIONS70-8
INSPECTION TERMINALM1701000200354
SENSORM1701000600415
NAME SYMBOL NAME SYMBOL
A/C pressure sensor I Interior temperature sensor
A/T control solenoid valve assembly
(Incorporating transmission fluid
temperature sensor)N Knock sensor C
Accelerator pedal position sensor R Left bank heated oxygen sensor (front)
<3.8L Engine>P
Air thermo sensor T Left bank heated oxygen sensor (rear)
<3.8L Engine>P
Ambient temperature sensor L Manifold absolute pressure sensor B
Camshaft position sensor D Mass airflow sensor G
Crankshaft position sensor A Sunroof assembly (Incorporating pulse
sensor)U
Fuel pump module (Incorporating fuel
level sensor (main) and fuel tank
temperature sensor)W Output shaft speed sensor H
Fuel level sensor (sub) V Photo sensor
Right bank heated oxygen sensor
(front) <3.8L Engine>O
Input shaft speed sensor K Right bank heated oxygen sensor (rear)
<3.8L Engine>O
Page 888 of 1500
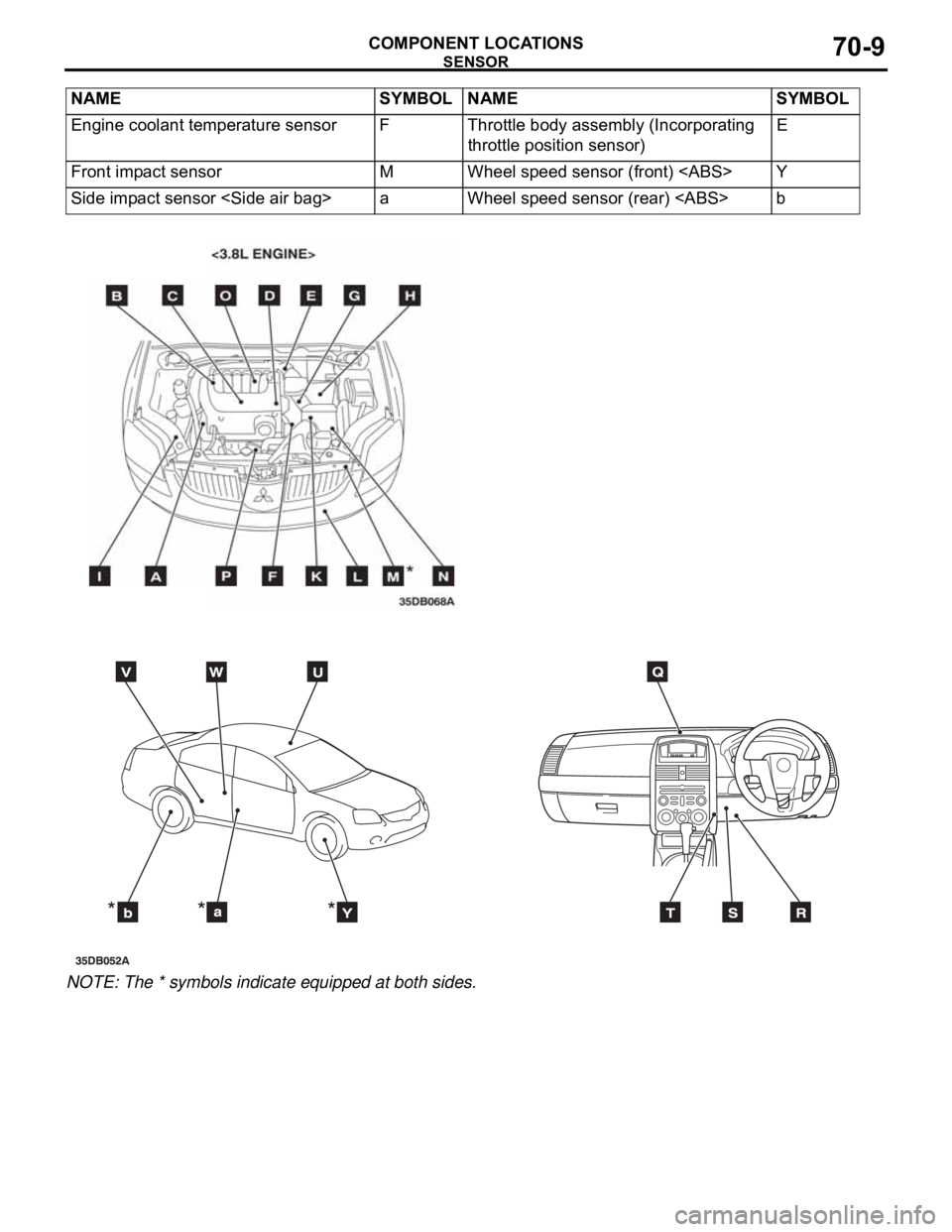
SENSOR
COMPONENT LOCATIONS70-9
NOTE: The * symbols indicate equipped at both sides.Engine coolant temperature sensor F Throttle body assembly (Incorporating
throttle position sensor)E
Front impact sensor M Wheel speed sensor (front)
Side impact sensor
Page 893 of 1500
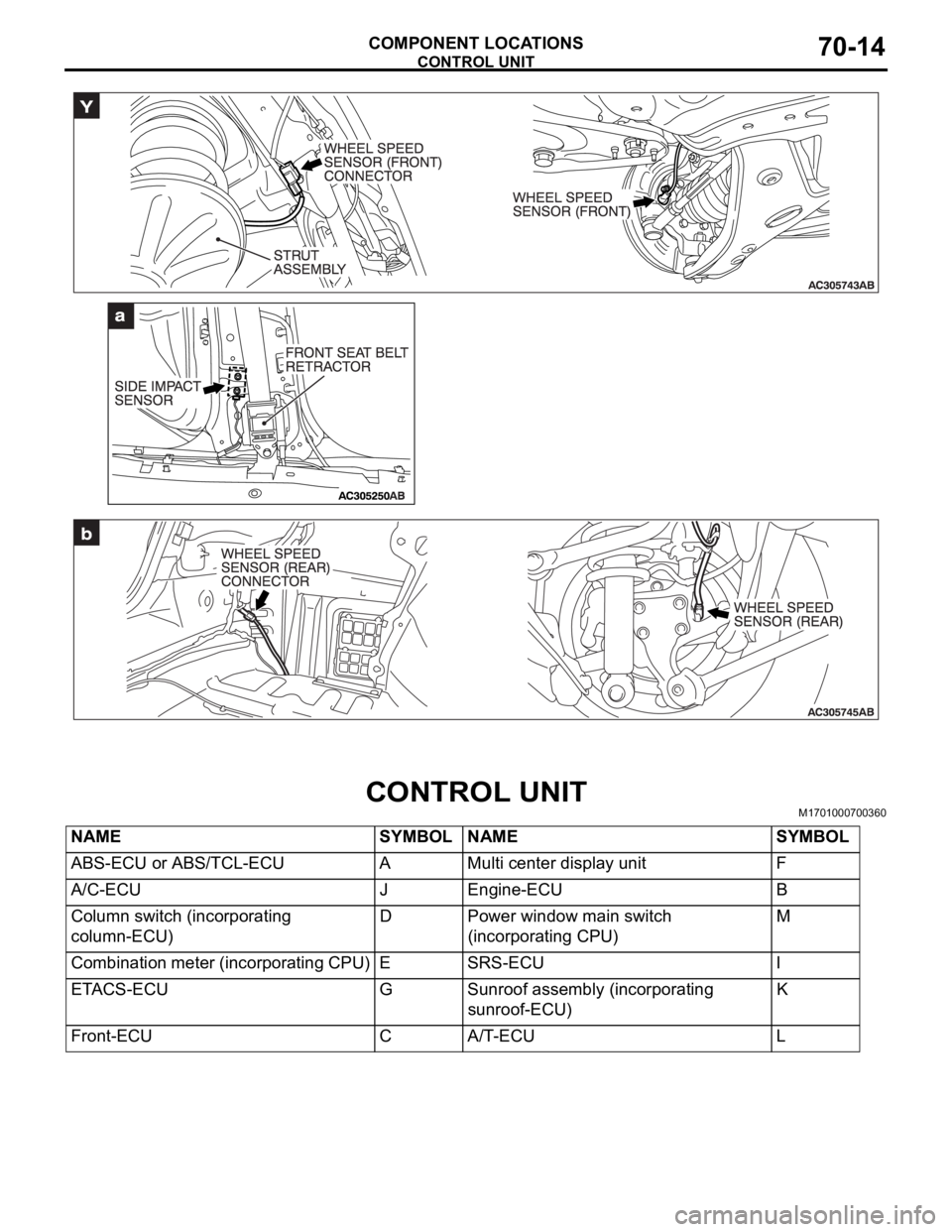
CONTROL UNIT
COMPONENT LOCATIONS70-14
CONTROL UNITM1701000700360
NAME SYMBOL NAME SYMBOL
ABS-ECU or ABS/TCL-ECU A Multi center display unit F
A/C-ECU J Engine-ECU B
Column switch (incorporating
column-ECU)D Power window main switch
(incorporating CPU)M
Combination meter (incorporating CPU) E SRS-ECU I
ETACS-ECU G Sunroof assembly (incorporating
sunroof-ECU)K
Front-ECU C A/T-ECU L
Page 910 of 1500
HOW TO DIAGNOSE
GENERAL
CABLES AND WIRES CHECKM1001005100041
1. Check connections for looseness, rust, and stains.
2. Check terminals and wires for corrosion.
3. Check terminals and wires for open circuit or impending
open circuit.
4. Check wire insulation and coating for damage, cracks, and
wear.
5. Check conductive parts of terminals for contact with other
metallic parts (vehicle body and other parts).
6. Check grounding parts to verify that there is complete
continuity between attaching bolt(s) and vehicle body.
7. Check for incorrect wiring.
8. Check that harnesses are secured to prevent contact with
sharp edges and corners or hot parts (exhaust manifold,
pipe, etc.).
9. Check that harnesses are secured firmly to provide enough
clearance from the fan pulley, fan belt, and other rotating or
moving parts.
10.Check that the harnesses between fixed parts (such as the
vehicle body) and vibrating parts (such as the engine) are
long enough to allow for vibration and movement.
BATTERY HANDLINGM1001005200048
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories con-
tain lead and lead compounds. WASH HANDS AFTER
HANDLING.
When checking or servicing does not require power from the
vehicle battery, be sure to disconnect the cable from the battery
(
) terminal. This will prevent problems that could be caused by
a short circuit. Disconnect the (
) battery terminal first and
reconnect it last.
GENERAL ELECTRICAL SYSTEM CHECKM1001005300045
A circuit consists of the power supply, switch, relay, load,
ground, etc. There are various methods to check a circuit
including an overall check, voltage check, short-circuit check,
and continuity check. Each of the methods briefly described
below applies only to circuits similar to the illustration.
Page 914 of 1500

11-1
GROUP 11
ENGINE
CONTENTS
ENGINE MECHANICAL <3.8L ENGINE> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11A
ENGINE OVERHAUL <3.8L ENGINE> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11B
Page 916 of 1500

14-1
GROUP 14
ENGINE COOLING
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . .14-2
SPECIAL TOOL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-2
ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS . . . .14-2
INTRODUCTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-2
TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY . . . . . . 14-2
SYMPTOM CHART. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-3
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-3
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . .14-26
ENGINE COOLANT LEAK CHECK . . . . . . 14-26
RADIATOR CAP PRESSURE CHECK . . . . 14-27
ENGINE COOLANT REPLACEMENT . . . . 14-27
ENGINE COOLANT CONCENTRATION TEST14-29
FAN CONTROLLER CHECK . . . . . . . . . . . 14-29
FAN CONTROL RELAY CONTINUITY CHECK14-31
RADIATOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-32
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 14-32
THERMOSTAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-35
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 14-35
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-38
WATER PUMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-39
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 14-39
WATER HOSE AND WATER PIPE . .14-40
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 14-40
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-41
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14-42
FASTENER TIGHTENING
SPECIFICATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-42
SERVICE SPECIFICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-43
CAPACITIES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-43
SEALANTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-43
Page 917 of 1500

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ENGINE COOLING14-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1141000100401
The cooling system is designed to keep every
part of the engine at appropriate temperature in
whatever condition the engine may be operated.
The cooling method is of the water-cooled, pres-
sure forced circulation type in which the water
pump pressurizes coolant and circulates it
throughout the engine. If the coolant temperature exceeds the prescribed temperature, the thermo-
stat opens to circulate the coolant through the
radiator as well so that the heat absorbed by the
coolant may be radiated into the air. The water
pump is of the centrifugal type and is driven by
the drive belt from the crankshaft. The radiator is
the corrugated fin, down flow type.
SPECIAL TOOLM1141000600279
ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTIONM1141005300347
The system cools the engine so that it does not over-
heat and maintains the engine at an optimum tem-
perature. The system components are the radiator,
water pump, thermostat, condenser and fan assem-
blies. Possible faults include low coolant, contamina-
tion, belt loosening and component damage.
TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1141005200340
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure to find
most of the engine cooling faults.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find and repair the malfunction by following the
SYMPTOM CHART.
4. Verify that the malfunction is eliminated. TOOL TOOL NUMBER AND
NAMESUPERSESSION APPLICATION
MB991871
LLC changerGeneral service tool Coolant refilling
Page 918 of 1500
ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE COOLING14-3
SYMPTOM CHARTM1141005600393
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: Coolant Leak
DIAGNOSIS
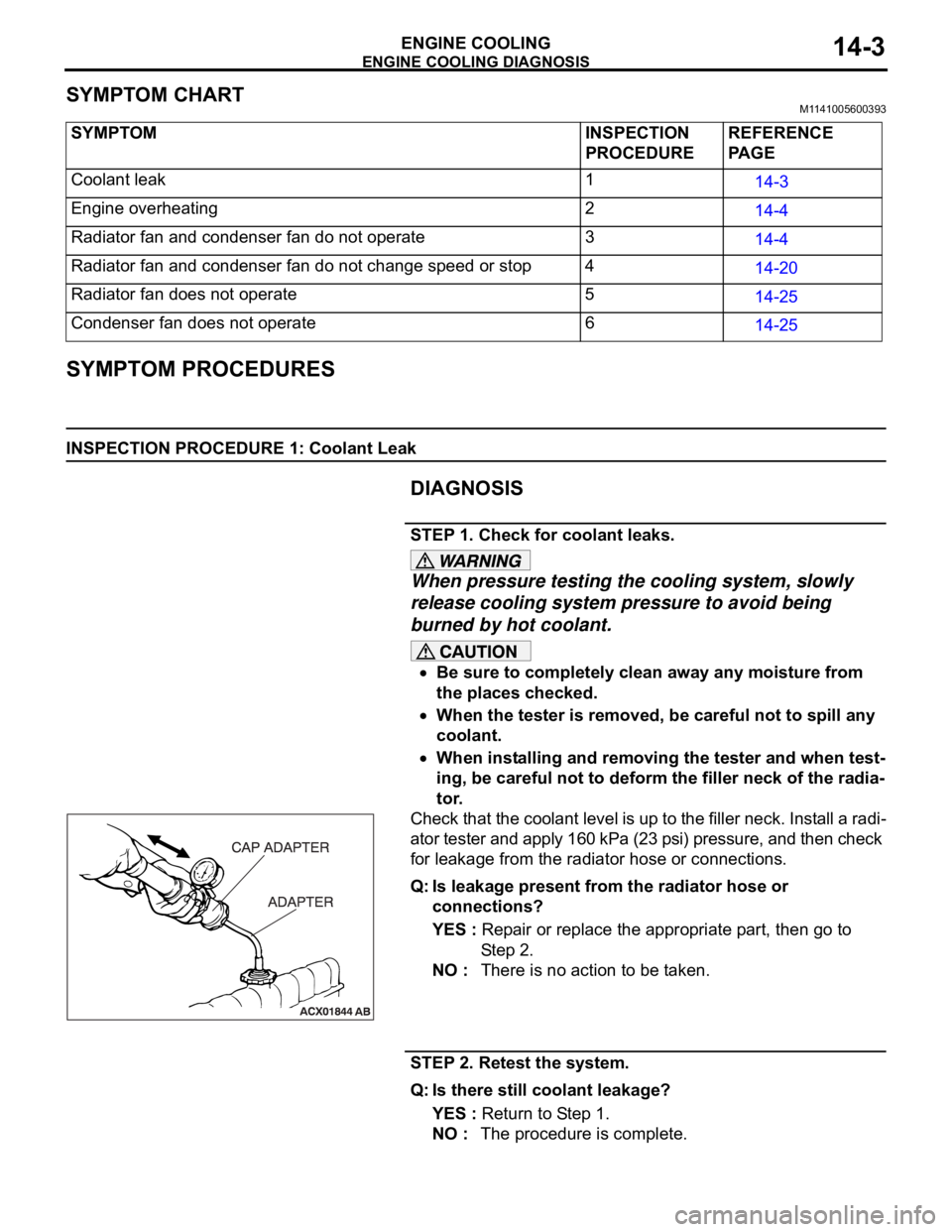
STEP 1. Check for coolant leaks.
When pressure testing the cooling system, slowly
release cooling system pressure to avoid being
burned by hot coolant.
Be sure to completely clean away any moisture from
the places checked.
When the tester is removed, be careful not to spill any
coolant.
When installing and removing the tester and when test-
ing, be careful not to deform the filler neck of the radia-
tor.
Check that the coolant level is up to the filler neck. Install a radi-
ator tester and apply 160 kPa (23 psi) pressure, and then check
for leakage from the radiator hose or connections.
Q: Is leakage present from the radiator hose or
connections?
YES : Repair or replace the appropriate part, then go to
St e p 2 .
NO : There is no action to be taken.
STEP 2. Retest the system.
Q: Is there still coolant leakage?
YES : Return to Step 1.
NO : The procedure is complete. SYMPTOM INSPECTION
PROCEDUREREFERENCE
PA G E
Coolant leak 1
14-3
Engine overheating 2
14-4
Radiator fan and condenser fan do not operate 3
14-4
Radiator fan and condenser fan do not change speed or stop 4
14-20
Radiator fan does not operate 5
14-25
Condenser fan does not operate 6
14-25
Page 919 of 1500

ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE COOLING14-4
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 2: Engine Overheating
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Remove the radiator cap and check for coolant
contamination.
Q: Is the coolant contaminated with rust and oil?
YES : Replace it. Refer to P.14-27.
NO : There is no action to be taken. Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check the radiator cap valve opening pressure.
NOTE: Be sure that the cap is clean before testing. Rust or
other foreign material on the cap seal will cause an improper
reading.
(1) Use a cap adapter to attach the cap to the tester.
(2) Increase the pressure until the gauge indicator stops
moving.
Minimum limit: 83 kPa (12 psi)
Standard value: 93
123 kPa (14 18 psi)
Q: Does the reading remain at or above the minimum limit?
YES : Go to Step 3.
NO : Replace the radiator cap. Then go to Step 5.
STEP 3. Check thermostat operation.
Refer to 38.
Q: Does the thermostat operate correctly?
YES : Go to Step 4.
NO : Replace the thermostat, then go to Step 5.
STEP 4. Check the drive belt for slippage or damage.
Refer to GROUP 00, Maintenance Service
Drive Belts
(Check Condition). <3.8L Engine>39 .
Q: Is the drive belt loose or damaged?
YES : Adjust or replace the drive belt, then go to Step 5.
NO : There is no action to be taken.
STEP 5. Retest the system.
Check the engine coolant temperature.
Q: Is the engine coolant temperature abnormally high?
YES : Return to Step 2.
NO : The procedure is complete.
Page 920 of 1500

ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE COOLING14-5
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3: Radiator Fan and Condenser Fan do not Operate
.
CIRCUIT OPERATION
The fan controller is powered from fusible link
No.2.
The engine-ECU uses input signals from the A/C
switch, the water temperature sensor unit and the
vehicle speed sensor
speed sensor to control the speed of the
radiator fan motor and the condenser fan motor.
The engine-ECU controls the fan controller to
activate the radiator fan motor and the condenser
fan motor.
.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The cause could be a malfunction of the fan con-
troller power supply or earth circuit.
If the communication line wiring harness between
the fan controller and the engine-ECU is
short-circuited to earth, the radiator fan motor
and the condenser fan motor will not rotate.
The cause could also be a malfunction of input
signal from the A/C switch, the water temperature
sensor unit and the vehicle speed sensor
or the output shaft speed sensor to the
engine-ECU.
The cause could also be a malfunction of the fan
controller or the engine-ECU.
.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Malfunction of fusible link No.2
Malfunction of fan control relay
Malfunction of cooling fan motor and fan control-
ler
Malfunction of engine-ECU.
Damaged wiring harness or connector
Refer to component locations GROUP-1
Refer to configuration diagrams GROUP-1
Refer to circuit diagrams GROUP-1