dashboard MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 43 of 408

1-44 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
INTERIOR CLEANING
Upholstery
Fabric can usually be cleaned with soapy water or
a proper detergent. For more difficult spots caused by
oil, ice cream, soda, etc., use a fabric cleaner avail-
able at most parts stores. Be sure when purchasing
the cleaner to read the label to ensure it is safe to use
on your type of fabric. A safe method of testing the
cleaner is to apply a small amount to an area usually
unseen, such as under a seat, or other areas. Wart a
while, perhaps even a day to check the spot for fad-
ing, discoloring, etc., as some cleaners will only
cause these problems after they have dried
Leather upholstery requrres special care, it can be
cleaned with a mild soap and a soft cloth. It is recom-
mended that a special leather cleaner be used to
clean but also treat the leather surfaces in your vehi-
cle. Leather surfaces can age quickly and can crack if
not properly taken care of, so it is vital that the leather
surfaces be maintained.
Floor Mats and Carpet
The floor mats and carpet should be vacuumed or
brushed regularly. They can be cleaned with a mild
soap and water. Special cleaners are available to
clean the carpeted surfaces of your vehicle, but take
care in choosing them, and again it is best to test
them in a usually unseen spot.
Dashboard, Console, Door Panels, Etc.
The dashboard, console, door panels, and other
plastic, vinyl, or wood surfaces can be cleaned using
a mild soap and water. Caution must be taken to keep
water out of electronic accessories and controls to
avoid shorts or ruining the components Again spe-
cial cleaners are available to clean these surfaces, as
with other cleaners care must taken in purchasmg
and using such cleaners.
There are protectants available which can treat the
various surfaces in your car giving them a “shiny new
look”, however some of these protectants can cause
more harm than good in the long run. The shine that
is placed on your dashboard attracts sunlight accel-
erating the aging, fading and possibly even cracking
the surfaces. These protectants also attract more dust
to stick to the surfaces they treat, Increasing the cleaning you must do to maintain the appearance of
your vehicle. Personal discretion is advised here.
On most models covered by this manual, the
wheel bearmgs used are sealed units and do not re-
quire routine maintenance. However on some Galant
and Mirage models, the rear wheel bearing do require
periodic repacking. For removal and installation in-
structions, please refer to Section 7 (for rear bear-
ings) or Section 8 (for front bearings).
REPACKING
*Sodium based grease is not compatible
with lithium based grease. Read the package
labels and be careful not to mix the two
types. If there is any doubt as to the type of
grease used, completely clean the old
grease from the bearing and hub before re-
placing.
Before handling the bearings, there are a few
things that you should remember to do and not to do.
DO the following: l Remove all outside dirt from the housing be-
fore exposing the bearing.
l Treat a used bearing as gently as you would a
new one.
l Work with clean tools in clean surroundings. l Use clean, dry gloves, or at least clean, dry
hands.
l Clean solvents and flushing fluids are a must. l Use clean paper when laying out the bearings
to dry.
l Protect drsassembled bearings from rust and
dirt. Cover them up.
l Use clean, lint-free rags to wipe the bearings. l Keep the bearings in oil-proof paper when they
are to be stored or are not in use.
l Clean the inside of the housing before replac-
ing the bearin
Do NOT do he followino: El, l Do not work in dirty sirroundings. l Do not use dirty, chipped or damaged tools. l Do not work on wooden work benches or use
wooden mallets.
l Do not handle bearings with dirty or moist
hands.
l Do not use gasoline for cleaning. Use a safe
solvent.
l Do not spin dry bearings with compressed air.
They will be damaged.
l Do not use cotton waste or dirty cloths to wipe
bearings.
l Do not scratch or nick bearing surfaces. l Do not allow the bearina to come in contact
” with dirt or rust at any time.
The rear wheel bearinas on some Galant and Mi-
rage models require periodic maintenance. A pre-
mium high melting point grease meeting Grade
Multipurpose Grease NLGI Grade #2 or equivalent
must be used. Long fiber type greases must not be
used. This service is recommended every 30,000
miles (48,000 km).
*For information on Wheel Bearing removal
and installation, refer to Section 7 of this
manual.
1. Remove the wheel bearing.
2. Clean all parts in a non-flammable solvent and
let them air dry.
*Only use lint-free rags to dry the bearings.
Never spin-dry a bearing with compressed
air, as this will damage the rollers.
3. Check for excessive wear and damage. Replace
the bearing as necessary.
*Packina wheel bearinos with arease is
best accomplished by u&g a wheel bearing
packer (available at most automotive parts
stores).
4. If a wheel bearing packer is not available, the
bearings may be packed by hand.
a. Place a “healthy’ glob of grease in the
palm of one hand.
b. Force the edge of the bearing into the
grease so that the grease fills the space between
the rollers and the bearing cage.
c. Keep rotating the bearing while continuing
to push the grease through.
d. Continue until the grease is forced out the
other side of the bearing.
5. Place the packed bearing on a clean surface
and cover it until it is time for installation.
6. Install the wheel bearing.
# See Figures 219 and 220
To prevent the bumper from deforming, these vehi-
cles cannot be towed by a wrecker using sling-type
equipment. If these vehicles require towing, use a
wheel lift or flat bed equipment. It is recommended
that the vehicle be towed from the front If a flat bed is
not available.
Manual transaxle vehicles may be towed from the
rear provided that the transaxle is in Neutral and the
driveline has not been damaged. The steering wheel
must be clamped in the straight-ahead positron with a
steering wheel clamping device designed for towing
service use.
Do not use the steering column lock to secure
the front wheel uosition for towina.
Automatic transaxle vehicles may be towed on the
front wheels at speeds not to exceed 30 mph (50
km/h) for a distance not to exceed 18 miles (30 km).
If these limits can not be met, then the front wheels
must be placed on a tow dolly.
# See Figure 221
All Wheel Drive (AWD) vehicles should only be
towed with all 4 wheels on the ground or lifted from
the road surface. This means that the vehicle is to be
towed either with flatbed equipment, with all wheels
on dollies or flat towed. Damage to the viscous cou-
pling may result if the vehicle is towed with only 2
wheels on the ground.
p See Figure 222
Whenever a vehicle is jump started, precautions
must be followed In order to prevent the possibility of
Page 87 of 408

3-26 ENGINEANDENGINEOVERHAUL
18. Remove the self-locking nuts and the small
retaining bolt holding the exhaust pipe to the bottom
of the exhaust manifold. Separate the pipe from the
manifold and remove the gasket.
19. Remove the bolts holding the support brace
to the bottom of the intake manifold.
20. Use the special hex wrench (MB 998051-01)
and loosen the head bolts in the order shown in 2 or
3 passes. When all are finger loose, remove the bolts.
21. Rock the head gently to break it loose; if tap-
ping is necessary, do so with a rubber or wooden
mallet at the corners of the head. DO NOT pry the
head up by wedging tools between the head and the
block.
22. Lift the head free of the engine. It is coming
off with both manifolds and the intake plenum at-
tached; the help of an assistant is recommended for
lifting. Support the head assembly on wooden blocks
on a suitable workbench. Refer to Cleaning and In-
spection in this section for work to be done before in-
stalling the head. If the head has been removed for
work other than gasket replacement, the rocker as-
sembly and camshaft or other components may be
removed.
Before reinstallation, the head should be com-
pletely assembled on the bench. This allows proper
location and tightening of all the external items.
To install: 23. Place a new gasket on the engine so that the
identifying mark faces up (towards the head) and is at
the timing belt end of the block. Install a new gasket
on the exhaust pipe.
Do not apply sealant to the head gasket or
mating surfaces.
24. Install the head straight down onto the block.
Try to eliminate most of the side-to-side adjust-
ments as this may move the gasket out of position.
Install the bolts by hand and just start each bolt 1 or
2 turns on the threads.
25. The head bolt torque specification is 68 ft.
Ibs. (92 Nm) for a cold engine. The bolts must be
tightened in the order shown in 3 steps. On the first
pass, tighten all the bolts to about 22 ft. Ibs. (30 Nm),
then proceed through the order tightening each bolt
to about 45 ft. Ibs. (61 Nm). The final torque is
achieved on the third pass.
26. Install the intake manifold support brace to
the manifold and tighten the bolts to 16 ft. Ibs. (22
Nm). 27. Making sure the gasket is still in place, con-
nect the exhaust pipe to the base of the exhaust man-
ifold. Use new self-locking nuts; tighten the nuts and
the small bracket bolt to 26 ft. Ibs. (35 Nm).
28. Make sure the camshaft has not changed po-
sition during repalrs. Carefully install the camshaft
sprocket and belt onto the camshaft. Tighten the re-
taining bolt to 66 ft. Ibs. (91 Nm).
29. Install the upper timing belt cover, then
tighten the bolts to 8 ft. Ibs. (11 Nm).
30. Apply sealant to the contact surfaces of the
half-circle plug and install the plug in the head In-
stall the valve cover and gasket.
31. Install the engine mount bracket to the en-
gine. Tighten the mounting nuts and bolts to 42 ft.
Ibs. (57 Nm).
32. Adjust the jack (if necessary) so that the en-
gine mount bushing aligns with the bodywork
bracket. Install the through-bolt and tighten the nuts
snug.
33. Slowly release tension on the floor jack so
that the weight of the engine bears fully on the
mount. Tighten the through-bolt to 52 ft. Ibs. (71
Nm) and the small safety nut to 26 ft. tbs. (36 Nm).
34. Install the bracket holding the power steering
hose and air conditioning hose to the top of the en-
gine mount.
35. Position the control wiring harness and in-
stall the retaining bolts. Attach each electrical con-
nector to its proper location, making sure the wires
are properly routed and firmly connected.
36. Install the spark plug wires in the distributor
cap.
37. Connect the PCV hose and the vacuum
hose(s).
38. Connect the fuel return line. Connect the
brake booster vacuum hose.
39. Install the heater hose, the coolant by-pass
hose and.the upper radiator hose. Pay close attention
to the position and routing of these hoses and insure
that they are not crimped or constricted. Install the
clamps in the same location as before removal.
40. Install a new O-ring on the high pressure fuel
line and lubricate it with a coating of gasoline. Care-
fully connect the high pressure fuel line to the fuel
rail, taking care not to damage the O-ring. Tighten the
bolts only to 4 ft. Ibs. (6 Nm).
41. Connect the accelerator cable and adjust it as
necessary.
42. Install the air intake hose.
43. Fill the cooling system with coolant.
44. Changing the oil and filter is recommended
to eliminate pollutants in the oil.
Intake side
I Front of
engine
Exhaust side
Fig. 116 Cylinder head bolt removal se-
quence-l .6L and 2.OL DDHC engines intake
side
Front of
entine
Exhaust side 7923PG18
Fig. 117 Cylinder head bolt torque se-
quence-l .6L and 2.OL DDHC engines Operating the engine without the proper
amount and type of engine oil will result in
severe engine damage.
45. Connect the negative battery cable.
46. Start the engine and check for leaks of fuel,
vacuum or oil.
47. Check the operation of all engine electrical
systems as well as dashboard gauges and lights.
48. Perform necessary adjustments to the accel-
erator cable, drive belts and engine specifications.
Adjust the coolant level after the engine has cooled
Off.
1.6L and 2.OL DDHC Engines
ti See Figures 116,117, and 116
1. Relieve fuel system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Drain the cooling system.
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
4. Disconnect the accelerator cable. There will
be 2 cables if equipped with cruise-control.
5. Remove the air cleaner with the air intake
hose.
6. Detach the electrical connectors from the the
oxygen sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor,
the engine coolant temperature gauge unit and the
engine coolant temperature switch on vehicles with
air conditioning.
7. Disconnect the wiring from the ISC motor,
throttle position sensor, crankshaft angle sensor, fuel
injectors, ignition coil, power transistor, noise filter,
knock sensor on turbocharged engines, EGR temper-
ature sensor (California vehicles), ground cable and
engine control wiring harness.
Painted mark Painted mark
Fig. 116 To ensure that the bolts are tight-
ened exactly 160 total degrees, mark the
11.6L and 2.OL DDHC engines head bolt and cylinder head as shown-
Page 363 of 408
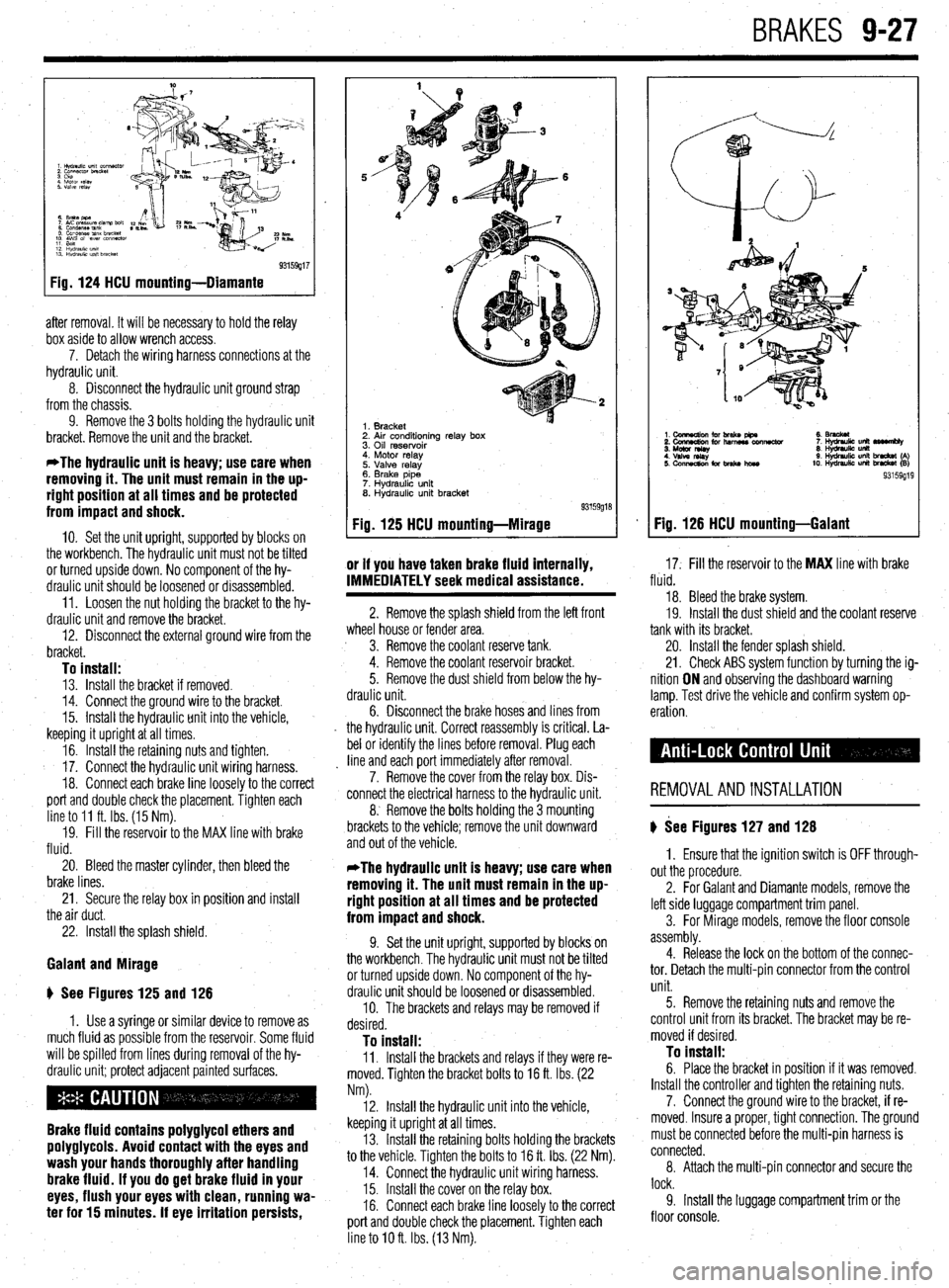
BRAKES 9-27
93159g17
Fig. 124 HCU mounting-Diamante
after removal. It will be necessary to hold the relay
box aside to allow wrench access.
7. Detach the wiring harness connections at the
hydraulic unit.
8. Disconnect the hydraulic unit ground strap
from the chassis.
9. Remove the 3 bolts holding the hydraulic unit
bracket. Remove the unit and the bracket.
*The hydraulic unit is heavy; use care when
removing it. The unit must remain in the up-
right position at all times and be protected
from impact and shock.
IO. Set the unit upright, supported by blocks on
the workbench. The hydraulic unit must not be tilted
or turned upside down. No component of the hy-
draulic unit should be loosened or disassembled.
11. Loosen the nut holding the bracket to the hy-
draulic unit and remove the bracket.
12. Disconnect the external ground wire from the
bracket.
To install: 13. Install the bracket if removed.
14. Connect the ground wire to the bracket.
15. Install the hydraulic unit into the vehicle,
keeping it upright at all times.
16. Install the retaining nuts and tighten.
17. Connect the hydraulic unit wiring harness.
18. Connect each brake line loosely to the correct
port and double check the placement. Tighten each
line to 11 ft. Ibs. (15 Nm).
19. Fill the reservoir to the MAX line with brake
fluid.
20. Bleed the master cylinder, then bleed the
brake lines.
21. Secure the relay box in position and install
the air duct.
22. Install the splash shield.
Galant and Mirage
ti See Figures 125 and 126
1. Use a syringe or similar device to remove as
much fluid as possible from the reservoir. Some fluid
will be spilled from lines during removal of the hy-
draulic unit; protect adjacent painted surfaces.
Brake fluid contains polyglycol ethers and
polyglycols. Avoid contact with the eyes and
wash your hands thoroughly after handling
brake fluid. If you do get brake fluid in your
eyes, flush your eyes with clean, running wa-
ter for 15 minutes. If eye irritation persists,
1. Bracket
2. Air conditioning relay box
3. Oil reservoir
4. Motor relay
5. Valve relay
6. Brake pipe
7. Hydraulic unit
8. Hydraulic unit bracket
Fig. 125 HCU mounting-Mirage
or if you have taken brake fluid internally,
17. Fill the reservoir to the MAX line with brake IMMEDIATELY seek medical assistance. fluid.
2. Remove the splash shield from the left front
wheel house or fender area.
3. Remove the coolant reserve tank.
4. Remove the coolant reservoir bracket.
5. Remove the dust shield from below the hy-
draulic unit.
6. Disconnect the
brake hoses and lines from
the hydraulic unit. Correct reassembly is critical. La-
bel or identify the lines before removal. Plug each
line and each port immediately after removal.
7. Remove the cover from the relay box. Dis-
connect the electrical harness to the hydraulic unit.
8. Remove the bolts holding the 3 mounting
brackets to the vehicle; remove the unit downward
and out of the vehicle. 18. Bleed the brake system.
19. Install the dust shield and the coolant reserve
tank with its bracket.
20. Install the fender splash shield.
21. Check ABS system function by turning the ig-
nition ON and observing the dashboard warning
lamp. Test drive the vehicle and confirm system op-
eration.
REMOVALANDINSTALLATION
) See Figures 127 and 128
*The hydraulic unit is heavy; use care when
removing it. The unit must remain in the up-
right position at all times and be protected
from impact and shock.
9. Set the unit upright, supported by blocks on
the workbench. The hydraulic unit must not be tilted
or turned upside down. No component of the hy-
draulic unit should be loosened or disassembled.
10. The brackets and relays may be removed if
desired.
To install: 11. Install the brackets and relays if they were re-
moved. Tighten the bracket bolts to 16 ft. Ibs. (22
Nm). 1. Ensure that the ignition switch is OFF through-
out the procedure.
2. For Galant and Diamante models, remove the
left side luggage compartment trim panel.
3. For Mirage models, remove the floor console
assembly.
4. Release the lock on the bottom of the connec-
tor. Detach the multi-pin connector from the control
unit.
12. Install the hydraulic unit into the vehicle,
keeping it upright at all times.
13. Install the retaining bolts holding the brackets
to the vehicle. Tighten the bolts to 16 ft. Ibs. (22 Nm).
14. Connect the hydraulic unit wiring harness.
15. Install the cover on the relay box.
16. Connect each brake line loosely to the correct
port and double check the placement. Tighten each
line to IO ft. Ibs. (13 Nm). 5. Remove the retaining nuts and remove the
control unit from its bracket. The bracket may be re-
moved if desired. To install: 6. Place the bracket in position if it was removed.
Install the controller and tighten the retaining nuts.
7. Connect the ground wire to the bracket, if re-
moved. Insure a proper, tight connection. The ground
must be connected before the multi-pin harness is
connected.
8. Attach the multi-pin connector and secure the
lock.
9. Install the luggage compartment trim or the
floor console.
Fig. 126 HCU mounting-Galant
Page 390 of 408

11-8 TROUBLESHOOTING
Ignition systems may be controlled by, or linked to, the engine fuel management sys-
tem. Similar to the fuel injection system, these ignition systems rely on electronic sen-
sors for information to determine the optimum ignition timing for a given engine speed
and load. Some ignition systems no longer allow the ignition timing to be adjusted.
Feedback from low voltage electrical sensors provide information to the control unit to
determine the amount of ignition advance. On these systems, if a failure occurs the failed
component must be replaced. Before replacing suspected failed electrical components,
carefully inspect the wiring and electrical connectors to the related components. Make
sure the electrical connectors are fully connected, clean and not physically damaged. If
necessary, clean the electrical contacts using electrical contact cleaner. The use of clean-
ing agents not specifically designed for electrical contacts should be avoided, as they
could leave a surface film or damage the insulation of the wiring.
1. Engine makes a knocking or pinging noise when accelerating
a. Check the octane rating of the fuel being used. Depending on the type of driving or
driving conditions, it may be necessary to use a higher octane fuel.
b. Verify the ignition system settings and operation. Improperly adjusted ignition timing
or a failed component, such as a knock sensor, may cause the ignition timing to ad-
vance excessively or prematurely. Check the ignition system operation and adjust, or
replace components as needed.
c. Check the spark plug gap, heat range and condition. If the vehicle is operated in se-
vere operating conditions or at continuous high speeds, use a colder heat range spark
plug. Adjust the spark plug gap to the manufacturer’s recommended specification and
replace worn or damaged spark plugs.
2. Sfarter motor grinds when used
a. Examine the starter pinion gear and the engine ring gear for damage, and replace dam-
aged parts.
b. Check the starter mounting bolts and housing. If the housing is cracked or damaged
replace the starter motor and check the mounting bolts for tightness.
3. Engine makes a screeching noise
a. Check the accessory drive belts for looseness and adjust as necessary.
b. Check the accessory drive belt tensioners for seizing or excessive bearing noises and
replace if loose, binding, or excessively noisy.
c. Check for a seizing water pump. The pump may not be leaking; however, the bearing
may be faulty or the impeller loose and jammed. Replace the water pump.
4. Engine makes a growling noise
a. Check for a loose or failing water pump. Replace the pump and engine coolant.
b. Check the accessory drive belt tensioners for excessive bearing noises and replace if
loose or excessively noisy.
5. Engine makes a ticking or tapping noise
a. On vehicles with hydraulic lash adjusters, check for low or dirty engine oil and top off
or replace the engine oil and filter.
b. On vehicles with hydraulic lash adjusters, check for collapsed lifters and replace failed
components.
c. On vehicles with hydraulic lash adjusters, check for low oil pressure caused by a re-
stricted oil filter, worn engine oil pump, or oil pressure relief valve.
d. On vehicles with manually adjusted valves, check for excessive valve clearance or
worn valve train parts. Adjust the valves to specification or replace worn and defective
parts.
e. Check for a loose or improperly tensioned timing belt or timing chain and adjust or re-
place parts as necessary.
f. Check for a bent or sticking exhaust or intake valve. Remove the engine cylinder head
to access and replace.
6. Engine makes a heavy knocking noise
a. Check for a loose crankshaft pulley or flywheel; replace and torque the mounting
bolt(s) to specification.
b. Check for a bent connecting rod caused by a hydro-lock condition. Engine disassem-
bly is necessary to inspect for damaged and needed replacement parts.
c. Check for excessive engine rod bearing wear or damage. This condition is also asso-
ciated with low engine oil pressure and will require engine disassembly to inspect for
damaged and needed replacement parts,
7. Vehicle has a fuel odor when driven ’ a. Check the fuel gauge level. If the fuel gauge registers full, it is possible that the odor is
caused by being filled beyond capacity, or some spillage occurred during refueling.
The odor should clear after driving an hour, or twenty miles, allowing the vapor canis-
ter to purge.
b. Check the fuel filler cap for looseness or seepage. Check the cap tightness and, if
loose, properly secure. If seepage is noted, replace the filler cap.
c. Check for loose hose clamps, cracked or damaged fuel delivery and return lines, or
leaking components or seals, and replace or repair as necessary. d. Check the vehicle’s fuel economy. If fuel consumption has increased due to a failed
component, or if the fuel is not properly ignited due to an ignition related failure, the
catalytic converter may become contaminated. This condition may also trigger the
check engine warning light. Check the spark plugs for a dark, rich condition or verify
the condition by testing the vehicle’s emissions. Replace fuel fouled spark plugs, and
test and replace failed components as necessary.
5. Vehicle has a rotten egg odor when driven
a. Check for a leaking intake gasket or vacuum leak causing a lean running condition. A
lean mixture may result in increased exhaust temperatures, causing the catalytic con-
verter to run hotter than normal. This condition may also trigger the check engine
warning light. Check and repair the vacuum leaks as necessary.
b. Check the vehicle’s alternator and battery condition. If the alternator is overcharging,
the battery electrolyte can be boiled from the battery, and the battery casing may begin
to crack, swell or bulge, damaging or shorting the battery internally. If this has oc-
curred, neutralize the battery mounting area with a suitable baking soda and water
mixture or equivalent, and replace the alternator or voltage regulator. Inspect, service,
and load test the battery, and replace if necessary.
9. Vehicle has a sweet odor when driven
a. Check for an engine coolant leak caused by a seeping radiator cap, loose hose clamp,
weeping cooling system seal, gasket or cooling system hose and replace or repair as
needed.
b. Check for a coolant leak from the radiator, coolant reservoir, heater control valve or
under the dashboard from the heater core, and replace the failed part as necessary.
c. Check the engine’s exhaust for white smoke in addition to a sweet odor. The presence
of white, steamy smoke with a sweet odor indicates coolant leaking into the combus-
tion chamber. Possible causes include a failed head gasket, cracked engine block or
cylinder head. Other symptoms of this condition include a white paste build-up on the
inside of the oil filler cap, and softened, deformed or bulging radiator hoses.
19. Engine vibraies when idling
a. Check for loose, collapsed, or damaged engine or transmission mounts and repair or
replace as necessary.
b. Check for loose or damaged engine covers or shields and secure or replace as neces-
sary.
11. Engine vibrates during acceleration
a. Check for missing, loose or damaged exhaust system hangers and mounts; replace or
repair as necessary.
b. Check the exhaust system routing and fit for adequate clearance or potential rubbing;
repair or adjust as necessary.
7. Battery goes dead while driving
a. Check the battery condition. Replace the battery if the battery will not hold a charge or
fails a battery load test. If the battery loses fluid while driving, check for an overcharg-
ing condition. If the alternator is overcharging, replace the alternator or voltage regula-
tor. (A voltage regulator is typically built into the alternator, necessitating alternator re-
placement or overhaul.)
b. Check the battery cable condition. Clean or replace corroded cables and clean the bat-
tery terminals.
c. Check the alternator and voltage regulator operation. If the charging system is over or
undercharging, replace the alternator or voltage regulator, or both.
d. Inspect the wiring and wire connectors at the alternator for looseness, a missing .
ground or defective terminal, and repair as necessary.
e. Inspect the alternator drive belt tension, tensioners and condition. Properly tension the
drive belt, replace weak or broken tensioners, and replace the drive belt if worn or
cracked.
2. Battery goes dead overnight
a. Check the battery condition. Replace the battery if the battery will not hold a charge or
fails a battery load test.
b. Check for a voltage draw, such as a trunk light, interior light or glove box light staying
on. Check light switch position and operation, and replace if defective.
c. Check the alternator for an internally failed diode, and replace the alternator if defec-
tive.
1. Engine overheats
a. Check the coolant level. Set the heater temperature to full hot and check for internal air
pockets, bleed the cooling system and inspect for leakage. Top off the cooling system
with the correct coolant mixture.
b. Pressure test the cooling system and radiator cap for leaks. Check for seepage caused
by loose hose clamps, failed coolant hoses, and cooling system components such as
the heater control valve, heater core, radiator, radiator cap, and water pump. Replace
defective parts and fill the cooling system with the recommended coolant mixture.
Page 398 of 408

II-16 TROUBLESHOOTING
c. Gauge sending unit defective. Replace gauge sending unit.
d. Gauge or sending unit improperly installed. Verify installation and wiring, and repair
1. Speedometer does not work
a. Check the speed sensor pickup and replace as necessary.
b. Check the wiring between the speed sensor and the speedometer for corroded termi-
nals, loose connections or broken wires and clean or repair as necessary.
c. Install a known good speedometer to test for proper operation. If the substituted
speedometer functions properly, replace the speedometer assembly.
2. Speedometer works intermittently
a. Check the wiring between the speed sensor and the speedometer for corroded termi-
nals, loose connections or broken wires and clean or repair as necessary.
b. Check the speed sensor pickup and replace as necessary. as necessary.
2. Gauge operates enatica//y
a. Checkfor ioose, shorted, damaged or corroded electrical connections or wiring and
repair as necessary.
b. Check gauge sending units and replace as necessary.
3. Gauge operates fully pegged
a. Sending unit-to-gauge wire shorted to ground.
b. Sending unit defective; replace sending unit.
c. Gauge or sending unit not properly grounded.
d. Gauge or sending unit improperly installed. Verify installation and wiring, and repair
as necessary.
I. Gauge does not register
a. Check for a missing or blown fuse and replace as necessary.
b. Check for an open circuit in the gauge wiring. Repair wiring as necessary.
I. No air coming from air conditioner vents
a. Check the air conditioner fuse and replace as necessary.
b. Air conditioner system discharged. Have the system evacuated, charged and leak
tested by an MVAC certified technician, utilizing approved recovery/recycling equip-
ment. Repair as necessary.
c. Air conditioner low pressure switch defective. Replace switch.
d. Air conditioner fan resistor pack defective. Replace resistor pack.
e. Loose connection, broken wiring or defective air conditioner relay in air conditioning*
electrical circuit. Repair wiring or replace relay as necessary.
2. Air conditioner blows warm air
a. Air conditioner system is discharged. Have the system evacuated, charged and leak
tested by an MVAC certified technician, utilizing approved recovery/recycling equip-
ment. Repair as necessary.
b. Air conditioner compressor clutch not engaging. Check compressor clutch wiring,
electrical connections and compressor clutch, and repair or replace as necessary.
3. Water collects on the interior floor when the air conditioner is used
a. Air conditioner evaporator drain hose is blocked. Clear the drain hose where it exits
the passenger compartment.
b. Air conditioner evaporator drain hose is disconnected. Secure the drain hose to the
evaporator drainage tray under the dashboard.
4. Air conditioner has a moldy odor when used
a. The air conditioner evaporator drain hose is blocked or partially restricted, allowing
condensation to build up around the evaporator and drainage tray. Clear the drain
hose where it exits the passenger compartment.
,
1. Blower motor does not operate
a. Check blower motor fuse and replace as necessary.
b. Check blower motor wiring for loose, damaged or corroded contacts and repair as
necessary.
c. Check blower motor switch and resistor pack for open circuits, and repair or replace
as necessary.
d. Check blower motor for internal damage and repair or replace as necessary.
2. Heater blows cool air
a. Check the engine coolant level. If the coolant level is low, top off and bleed the air
from the cooling system as necessary and check for coolant leaks.
b. Check engine coolant operating temperature. If coolant temperature is below specifica-
tion, check for a damaged or stuck thermostat.
c. Check the heater control valve operation. Check the heater control valve cable or vac-
uum hose for proper installation. Move the heater temperature control from hot to cold
several times and verify the operation of the heater control valve. With the engine at
normal operating temperature and the heater temperature control in the full hot posi-
tion, carefully feel the heater hose going into and exiting the control valve. If one
heater hose is hot and the other is much cooler, replace the control valve.
3. Heater steams the windshield when used
a. Check for a loose cooling system hose clamp or leaking coolant hose near the engine
firewall or under the dash area, and repair as necessary.
b. Check for the existence of a sweet odor and fluid dripping from the heater floor vents,
indicating a failed or damaged heater core. Pressure test the cooling system with the
heater set to the fully warm position and check for fluid leakage from the floor vents. If
leakage is verified, remove and replace the heater core assembly.
NOTE: On some vehicles, the dashboard must be disassembled and re-
moved to access the heater core.