lock MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 2 of 408

.
1-2 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Chitton’s Total Car Care manual for the 199M10
Mitsubishi Mirage, Galant and Diamante is intended
to help you learn more about the inner workings of
your vehicle while saving you money on its upkeep
and operation.
The beginning of the book will likely be referred to
the most, since that is where you will find information
for maintenance and tune-up. The other sections deal
with the more complex systems of your vehicle. Oper-
ating systems from engine through brakes are cov-
ered to the extent that the average do-it-yourselfer be-
comes mechanically involved. This book will not
explain such things as rebuilding a differential for the
simple reason that the expertise required and the in-
vestment in special tools make this task uneconomi-
cal. It will, however, give you detailed instructions to
help you change your own brake pads and shoes, re-
place spark plugs, and perform many more jobs that
can save you money, give you personal satisfaction
and help you avoid expensive problems.
A secondary purpose of this book is a reference for
owners who want to understand their vehicle and/or
their mechanics better. In this case, no tools at all are
required.
Before removing any bolts, read through the entire
procedure. This will give you the overall view of what
tools and supplies will be required. There is nothing
more frustrating than having to walk to the bus stop
on Monday morning because you were short one bolt
on Sunday afternoon. So read ahead and plan ahead.
Each operation should be approached logically and
all procedures thoroughly understood before attempt-
ing any work.
All sections contain adjustments, maintenance, re-
moval and installation procedures, and in some cases,
repair or overhaul procedures. When repair is not con-
sidered practical, we tell you how to remove the part
and then how to install the new or rebuilt replacement.
In this way, you at least save labor costs. “Backyard”
repair of some components is just not practical.
Many procedures in this book require you to “label
and disconnect. . ” a group of lines, hoses or wires.
Don’t be lulled into thinking you can remember where
everything goes-you won’t. If you hook up vacuum
or fuel lines incorrectly, the vehicle may run poorly, if
at all. If you hook up electrical wiring incorrectly, you
may instantly learn a very expensive lesson.
You don’t need to know the official or engineering
name for each hose or line. A piece of masking tape
on the hose and a piece on its fitting will allow you to
assign your own label such as the letter A or a short name. As long as you remember your own code, the
lines can be reconnected by matching similar letters
or names. Do remember that tape will dissolve in
gasolrne or other fluids; if a component is to be
washed or cleaned, use another method of identifica-
tion. A permanent felt-tipped marker or a metal scribe
can be very handy for marking metal parts. Remove
any tape or paper labels after assembly.
It’s necessary to mention the difference between
maintenance and repair Maintenance includes rou-
tine inspections, adjustments, and replacement of
parts which show signs of normal wear Maintenance
compensates for wear or deterioration. Repair implies
that something has broken or is not working. A need
for repair is often caused by lack of maintenance. Ex-
ample, draining and refilling the automatic transaxle
fluid is maintenance recommended by the manufac-
turer at specific mileage intervals. Failure to do this
can shorten the life of the transmission/transaxle, re-
quiring very expensive repairs. While no maintenance
program can prevent items from breaking or wearing
out, a general rule can be stated: MAINTENANCE IS
CHEAPER THAN REPAIR.
Two basic mechanrc’s rules should be mentioned
here. First, whenever the left side of the vehicle or en-
gine is referred to, it is meant to specify the drivers
side. Conversely, the right side of the vehicle means
the passengers side. Second, screws and bolts are
removed by turning counterclockwise, and tightened
by turning clockwrse unless specifically noted.
Safety is always the most important rule. Con-
stantly be aware of the dangers involved in working
on an automobile and take the proper precautions.
See the informatron in this section regarding SER-
VICING YOUR VEHICLE SAFELY and the SAFETY
NOTICE on the acknowledgment page.
Pay attention to the instructions provided. There
are 3 common mistakes in mechanical work:
1. Incorrect order of assembly, disassembly or
adjustment. When taking something apart or putting
it together, performing steps in the wrong order usu-
ally just costs you extra time; however, it CAN break
something. Read the entire procedure before begin-
ning disassembly. Perform everything in the order in
which the instructions say you should, even if you
can’t immedrately see a reason for it. When you’re
taking apart something that is very intricate, you
might want to draw a picture of how it looks when as-
sembled at one point in order to make sure you get everything back in its proper position. We will supply
exploded views whenever possible. When making
adjustments, perform them in the proper order. One
adjustment possibly will affect another.
2. Overtorquing (or undertorquing). While it is
more common for overtorquing to cause damage,
undertorquing may allow a fastener to vibrate loose
causing serious damage. Especially when dealing
with aluminum parts, pay attention to torque specifi-
cations and utilize a torque wrench in assembly. If a
torque figure is not available, remember that if you
are using the right tool to perform the job, you will
probably not have to strain yourself to get a fastener
tight enough. The pitch of most threads is so slight
that the tension you put on the wrench will be multi-
plied many times in actual force on what you are
tightening. A good example of how critical torque is
can be seen in the case of spark plug installation, es-
pecially where you are putting the plug into an alu-
minum cylinder head. Too little torque can fail to
crush the gasket, causing leakage of combustion
gases and consequent overheating of the plug and
engine parts. Too much torque can damage the
threads or distort the plug, changing the spark gap.
There are many commercial products available for
ensuring that fasteners won’t come loose, even if they
are not torqued just right (a very common brand is
Loctite? If you’re worried
about getting something
together tight enough to hold, but loose enough to
avoid mechanical damage during assembly, one of
these products might offer substantial insurance. Be-
fore choosing a threadlocking compound, read the
label on the package and make sure the product is
compatible with the materials, fluids, etc. involved.
3. Crossthreading. This occurs when a part such
as a bolt is screwed into a nut or casting at the wrong
angle and forced. Crossthreading is more likely to
occur if access is difficult. It helps to clean and lubri-
cate fasteners, then to start threading the bolt, spark
plug, etc. with your fingers If you encounter resis-
tance, unscrew the part and start over again at a dif-
ferent angle until it can be inserted and turned several
times without much effort. Keep in mind that many
parts, especially spark plugs, have tapered threads,
so that gentle turning will automatically bring the part
you’re threading to the proper angle. Don’t put a
wrench on the part until its been tightened a couple
of turns by hand. If you suddenly encounter resis-
tance, and the part has not seated fully, don’t force it.
Pull it back out to make sure it’s clean and threading
properly.
Be sure to take your time and be patient, and al-
ways plan ahead. Allow yourself ample time to per-
form repairs and maintenance You may find main-
taining your car a satisfying and enjoyable
experience.
b See Figures 1 thru 15
Naturally, without the proper tools and equipment
it is impossible to properly service your vehicle. It
would also be virtually impossible
to catalog every
tool that you would need to perform all of the opera-
tions in this book. Of course, It would be unwise for
the amateur to rush out and buy an expensive set of
tools on the theory that he/she may need one or more
of them at some time, The best approach is to proceed slowly, gathering savings will
be far outweighed by frustration and
a good quality set of those tools that are used most mangled knuckles.
frequently Don’t be misled by the low cost of bargain Begin accumulating those tools that are used most
tools. It is far better to spend a little more for better frequently: those associated with routine maintenance
quality. Forged wrenches, 6 or 12-point sockets and and tune-up. In addition to the normal assortment of
fine tooth ratchets are by far preferable to their less screwdrivers and pliers, you should have the follow-
expensive counterparts. As any good mechanic can ing tools:
tell you, there are few worse experiences than trying
l Wrenches/sockets and combination open
to work on a vehicle with bad tools. Your monetary end/box end wrenches in sizes from %-% in. or
Page 4 of 408

I-4 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Fig. 12 A screw-in type compression gauge- Fig. 13 A vacuum/pressure tester is neces-
is recommended for compression testing sary for many testing procedures
Fig. 14 Most modern automotive multime-
ters incorporate many helpful features
your workbench. Some useful household items are: a
large turkey baster or siphon, empty coffee cans and
ice trays (to store parts), ball of twine, electrical tape
for wiring, small rolls of colored tape for tagging lines
or hoses, markers and pens, a note pad, golf tees (for
plugging vacuum lines), metal coat hangers or a roll
of mechanic’s wire (to hold things out of the way),
dental pick or similar long, pointed probe, a strong
magnet, and a small mirror (to see into recesses and
under manifolds).
A more advanced set of tools, suitable for tune-up
work, can be drawn up easily. While the tools are
lmvl Fig. 15 Proper information is vital, so at
ways have a Chiiton Total Car Care manua
handy
l Feeler aauoes for valve adiustment
* Timing-light.
The choice of a timing fight should be made
carefully. A light which works on the DC current
supplied by the vehicle’s battery is the best choice;
it should have a xenon tube for brightness. On any
vehicle with an electronic ignition system, a timing
light with an inductive pickup that clamps around
the No. 1 spark plug cable is preferred.
In addition to these basic tools, there are several
other tools and gauges you may find useful. These
include:
l Compression gauge. The screw-in type is
slower to use, but eliminates the possibility of a
fauliy reading due to escaping pressure.
l Manifold vacuum gauge. l 12V test light. l A combination volt/ohmmeter l induction Ammeter. This is used for determin-
ing whether or not there is current in a wire. These
are handy for use if a wire is broken somewhere in a
wiring harness.
As a final note, vou will orobablv find a torque
wrench necessary for all but the most basic work.
The beam type models are perfectly adequate, al-
though the newer click types (breakaway) are easier
to use. The click type torque wrenches tend to be
more expensive. Also keep in mind that all types of
torque wrenches should be periodically checked
and/or recalibrated. You will have to decide for your-
self which better fits your pocketbook, and purpose.
ilightly more sophisticated, they need not be outra-
feously expensive. There are several inexpensive
achldwell meters on the market that are every bit as
Toad for the average mechanic as a professional
nodel. Just be sure that it goes to a least 1200-1500
pm on the tach scale and that it works on 4,6 and 8-
:ylinder engines. The key to these purchases is to
nake them with an eye towards adaptability and wide
ange. A basic list of tune-up tools could include:
l Tach/dwell meter. l Spark plug wrench and gapping tool. Normally, the use of special factory tools is
avoided for repair procedures, since these are not
readily available for the do-it-yourself mechanic.
When it is possible to perform the job with more
commonly available tools, it will be pointed out, but
occasionally, a special tool was designed to perform
a specific function and should be used. Before sub-
stituting another tool, you should be convinced that
neither your safety nor the performance of the vehicle
will be compromised.
Special tools can usually be purchased from an
automotive parts store or from your dealer. In some
cases special tools may be available directly from the
tool manufacturer.
p See Figures 16, 17, 16, and 19
It is virtually impossible to anticipate all of the haz-
ards involved with automotive maintenance and ser-
vice, but care and common sense will prevent most
accidents.
The rules of safety for mechanics range from “don’t
smoke around gasoline,” to “use the proper tool(s) for
the job.” The trick to avoiding injuries is to develop
safe work habits and to take every possible precaution.
Do keep a fire extinguisher and first aid kit
l handy.
Do wear safety glasses or goggles when cut- l ting, drilling, grinding or prying, even if you have
20-20 vision. If you wear glasses for the sake of vi-
sion, wear safety goggles over your regular glasses.
l Do shield your eyes whenever you work around
the battery. Batteries contain sulfuric acid. In case of
contact with the eyes or skin, flush the area with water
or a mixture of water and baking soda, then seek im-
mediate medical attention.
l Do use safety stands (jackstands) for any un-
dervehicle service. Jacks are for raising vehicles;
jackstands are for making sure the vehicle stays
raised until you want it to come down. Whenever the
vehicle is raised, block the wheels remaining on the
ground and set the parking brake.
l Do use adequate ventilation when working
with any chemicals or hazardous materials, Like car-
bon monoxide, the asbestos dust resulting from
some brake lining wear can be hazardous in suffi-
cient quantities.
l Do disconnect the negative battery cable when
working on the electrical system. The secondary ig- nition system contains EXTREMELY HIGH VOLT-
AGE. In some cases it can even exceed 50,000 volts.
l Do follow manufacturer’s directions whenever
working with potentially hazardous materials. Most
chemicals and fluids are poisonous if taken inter-
nally.
l Do properly maintain your tools. Loose ham-
merheads, mushroomed punches and chisels, frayed
or poorly grounded electrical cords, excessively
worn screwdrivers, spread wrenches (open end),
cracked sockets, slipping ratchets, or faulty droplight
sockets can cause accidents.
* Likewise, keep your tools clean; a greasy
wrench can slip off a bolt head, ruining the bolt and
often harming your knuckles in the process.
l Do use the proper size and type of tool for the
job at hand. Do select a wrench or socket that fits the
nut or bolt. The wrench or socket should sit straight,
not cocked.
Page 5 of 408

1-6 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Fig. 16 Screwdrivers should be kept in good
:ondition to prevent injury or damage which
:ould result it the blade slips from the screw
0
0
PP tccs1022 Fig. 16 Using the correct size wrench will
help prevent the possibility of rounding off
a nut
7
lwo.WIRE CouDuClOR TMREE-WIRE CONO”CTOI
MIRD WIRE GROUNDING GROUNDING TNRU
THE CASE A CmxlIT
.
i$Y$$pQ
p-+
TNHREE-WIRE CONDUCTOR THREE-WIRE CONDUCTOR
ONE WIRE TO 4 GROUND GROUNOlNG TMRU
AN ADAPTER PLUG
tccm21
Fig. 17 Power tools should always be prop-
erly grounded
Fig. 19 NEVER work under a vehicle unless it
is supported using safety stands (jackstands)
l Do, when possible, pull on a wrench handle l Do set the parking brake and block the drive
rather than push on it, and adjust your stance to pre-
vent a fall. wheels if the work requires a running engine.
l Do be sure that adjustable wrenches are
tightly closed on the nut or bolt and pulled so that
the force is on the side of the fixed jaw.
l Do strike squarely with a hammer; avoid glanc-
ing blows. l Don’t run the engine in a garage or anywhere
else without proper ventilation-EVER! Carbon monoxide is poisonous; it takes a long time to leave
the human body and you can build up a deadly sup-
ply of it in your system by simply breathing in a !ittle
every day. You may not realize you are slowly poi-
soning yourself. Always use power vents, windows,
fans and/or open the garage door.
l Don’t work around moving parts while wearing
loose clothing. Short sleeves are much safer than
long, loose sleeves. Hard-toed shoes with neoprene
soles protect your toes and give a better grip on slip-
pery surfaces. Jewelry such as watches, fancy belt
buckles, beads or body adornment of any kind is not
safe working around a vehicle. Long hair should be
tied back under a hat or cap.
l Don’t use pockets for toolboxes. A fall or bump
can drive a screwdriver deep into your body. Even a
rag hanging from your back pocket can wrap around
a spinning shaft or fan.
l Don’t smoke when working around gasoline,
cleaning solvent or other flammable material.
l Don’t smoke when workrng around the battery.
When the battery is being charged, it gives off explo-
sive hydrogen gas.
l Don’t use gasoline to wash your hands; there
are excellent soaps available. Gasoline contains dan-
gerous additives which can enter the body through a
cut or through your pores. Gasoline also removes all
the natural oils from the skin so that bone dry hands
will suck up oil and grease.
l Don’t service the air conditioning system un-
less you are equipped with the necessary tools and
trainmg. When liquid or compressed gas refrigerant
is released to atmospheric pressure it will absorb
heat from whatever it contacts. This will chill or freeze
anything it touches.
l Don’t use screwdrivers for anything other than
driving screws! A screwdriver used as an prying tool
can snap when you least expect it, causing injuries.
At the very least, you’ll ruin a good screwdriver.
. Don’t use an emergency jack (that little ratchet,
scissors, or pantograph jack supplied with the vehi-
cle) for anything other than changing a flat! These
jacks are only Intended for emergency use out on the
road; they are NOT designed as a maintenance tool. If
you are serious about mamtaining your vehicle your-
self, invest in a hydraulic floor jack of at least a 1%
ton capacity, and at least two sturdy jackstands.
sion which can increase the torque necessary to proper installation and safe operation of the vehicle
achieve the desired clamp load for which that fastener afterwards.
was originally selected. Additionally, be sure that the Thread gauges are available to help measure a bolt
p See Figures 20, 21, 22, and 23 driver surface of the fastener has not been compro- or stud’s thread. Most automotive and hardware
mised by rounding or other damage. In some cases a stores keep gauges available to help you select the
Although there are a great variety of fasteners found driver surface may become only partially rounded, al- proper size. In a pinch, you can use another nut or
in the modern car or truck, the most commonly used lowing the driver to catch in only one direction. In bolt for a thread gauge. If the bolt you are replacing is
retainer is the threaded fastener (nuts, bolts, screws, many of these occurrences, a fastener may be in- not too badly damaged, you can select a match by
studs, etc.). Most threaded retainers may be reused, stalled and tightened, but the driver would not be able finding another bolt which will thread in its place. If
provided that they are not damaged in use or during to grip and loosen the fastener again. (This could lead you find a nut which threads properly onto the dam-
the repair. Some retainers (such as stretch bolts or J to frustration down the line should that component aged bolt, then use that nut to help select the replace-
torque prevailing nuts) are designed to deform when ever need to be disassembled again). ment bolt If however, the bolt you are replacing is so
tightened or in use and should not be reinstalled. If you must replace a fastener, whether due to de- badly damaged (broken or drilled out) that its threads
Whenever possible, we will note any special re- sign or damage, you must ALWAYS be sure to use cannot be used as a gauge, you might start by look-
tainers which should be replaced during a procedure. the proper replacement In all cases, a retainer of the ing for another bolt (from the same assembly or a
But you should always inspect the condition of a re- same design, material and strength should be used. similar location on your vehicle) which will thread
tainer when It is removed and replace any that show Markings on the heads of most bolts will help deter- into the damaged bolt’s mounting. If so, the other bolt
signs of damage. Check all threads for rust or corro- mine the proper strength of the fastener. The same
can be used to select a nut; the nut can then be used
material, thread and pitch must be selected to assure
to select the replacement bolt.
Page 6 of 408
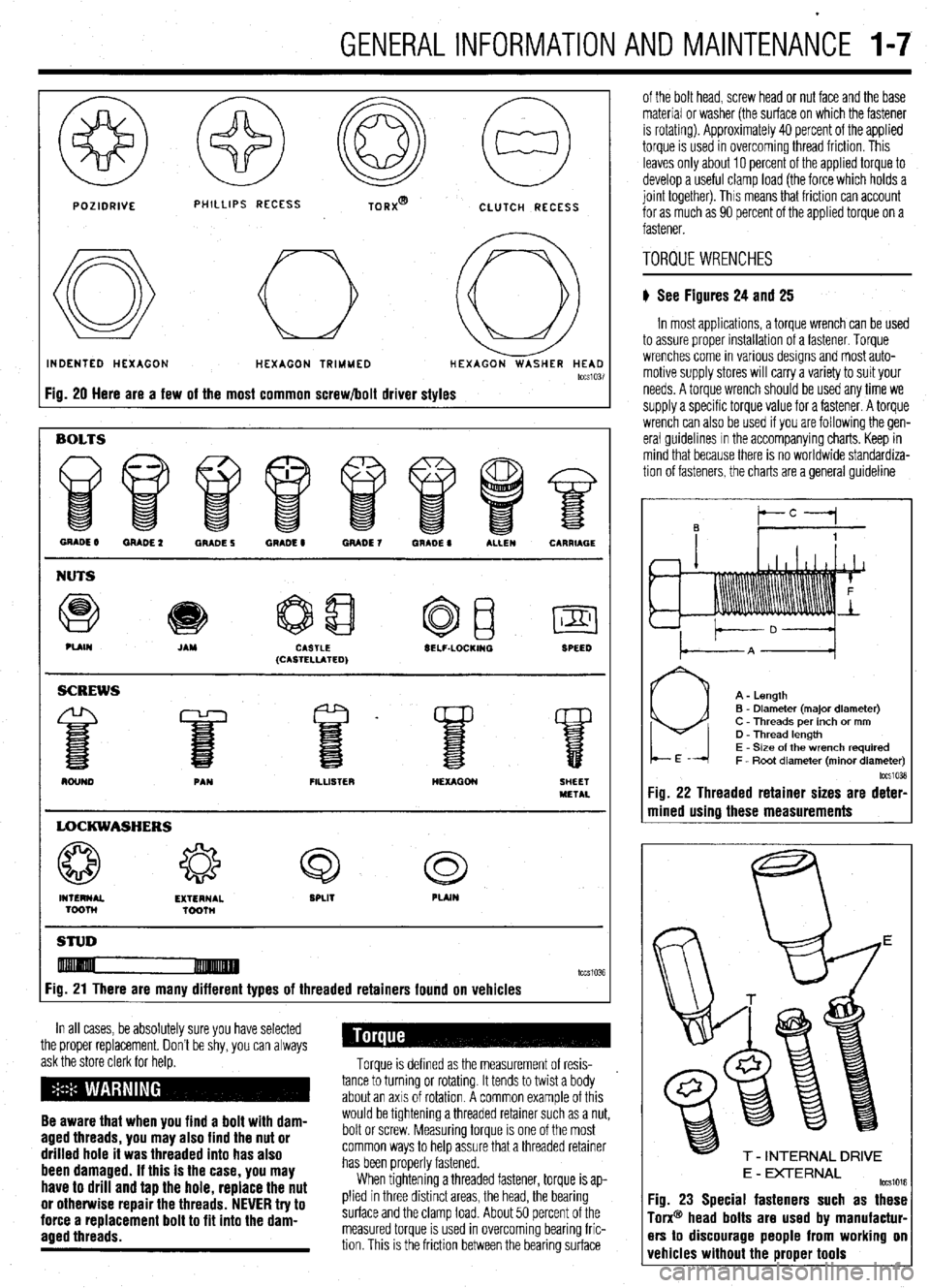
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAlNTENAiCE I-7
POZIDRIVE PHILLIPS RECESS
TORX@
CLUTCH RECESS
INDENTED HEXAGON HEXAGON TRIMMED HEXAGON WASHER HEAD
tccs1037
Fig. 20 Here are a few of the most common screw/bolt driver styles
GRADE 8 MADE 2 GRADE 5 QRADE 8 GRADE 7 WADE 0 ALLEN CARRIAGE
NUTS
Q e
PUIN JAM CASTLE
(CASTELLATED) SELF-LOCKINQ
SPEED
FILLISTER
LOCKWASHERS
4% 43 Q c3
INTERNAL EXTERNAL SPLIT PLAIN
Toonl
TQonl
STUD
Fig. 21 There are many different types of threaded retainers found on vehicles
In all cases, be absolutely sure you have selected
the proper replacement. Don’t be shy, you can always
ask the store clerk for helo.
Be aware that when you find a bolt with dam-
aged threads, you may also find the nut or
drilled hole it was threaded into has also
been damaged. If this is the case, you may
have to drill and tap the hole, replace the nut
or otherwise repair the threads. NEVER try to
force a replacement bolt to fit into the dam-
aaed threads.
Torque is defined as the measurement of resis-
.
tance to turning or rotating. It tends to twist a body
about an axis of rotation. A common example of this
would be tightening a threaded retainer such as a nut,
bolt or screw. Measuring torque is one of the most
common ways to help assure that a threaded retainer
has been properly fastened.
When tightening a threaded fastener, torque is ap-
plied in three distinct areas, the head, the bearing
surface and the clamp load. About 50 percent of the
measured torque is used in overcoming bearing fric-
tion This is the friction between the bearing surface of the bolt head, screw head or nut face
and the base
material or washer (the surface on which the fastener
is rotating). Approximately 40 percent of the applied
torque is used in overcoming thread friction. This
leaves only about 10 percent of the applied torque to
develop a useful clamp load (the force which holds a
joint together). This means that friction can account
for as much as 90 percent of the applied torque on a
fastener.
TORQUE WRENCHES
ti See Figures 24 and 25
In most applications, a torque wrench can be used
to assure proper installation of a fastener. Torque
wrenches come in various designs and most auto-
motive supply stores will carry a variety to suit your
needs. A torque wrench should be used any time we
supply a specific torque value for a fastener. A torque
wrench can also be used if you are following the gen-
eral guidelines In the accompanying charts. Keep in
mind that because there is no worldwide standardiza-
tion of fasteners, the charts are a general guideline
A - Length
B - Diameter (major diameter)
C - Threads per inch or mm
D - Thread length
E - Size of the wrench required
F - Root diameter (minor diameter)
IccSlO3l
Fig. 22 Threaded retainer sizes are deter
mined using these measurements
E - DCTERNAL tm1016 Yg. 23 Special fasteners such as these
font@’ head bolts are used by manufactur-
?rs to discourage people from working on
rehicles without the proper tools
Page 9 of 408

.
l-10 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
which are available today will have two scales so the
The conversion factor chart is used by taking the
Standard or Metric measurements may easily be given specification and multiplying it by the neces-
taken. If any of the various measuring tools which are sary conversion factor. For instance, looking at the
available to you do not contain the same scale as first line, if you have a measurement in inches such
listed in the specifications, use the accompanying
as “free-play should be 2 in.” but your ruler reads
conversion factors to determine the proper value. only in millimeters, multiply 2 in. by the conversion factor of 25.4 to get the metric equivalent of 50.8mm.
Likewise, if the specification was given only in a Met-
ric measurement, for example in Newton Meters
(Nm), then look at the center column first. If the mea-
surement is 100 Nm, multiply it by the conversion
factor of 0.738 to get 73.8 ft. Ibs.
b See Figures 32,33, and 34
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is located
on a plate which is attached to the left top side of the
instrument panel. These numbers are visible from the
outside of the vehicle. All Vehicle Identification Num-
bers contain 17 digits. The vehicle number is a code
which tells country, make, vehicle type, engine, body
and many other important characteristics of that spe-
cific vehicle.
There is also a vehicle information code plate
which is riveted to the bulkhead in the engine com-
partment. The plate shows the VIN, model code, en-
gine model, transaxle model and body color codes.
The engine code used on this plate differs from the
code letter used in the 8th position of the Vehicle
Identification Number (VIN). Either code can be used
to identify the particular engine in the vehicle. Since
the vehicle owners card is usually carried, it may be if the engine is equipped with a turbocharger. If the
8th VIN number is a U, there is no doubt that the en-
gine in question is a 2.OL DOHC engine equipped
with a turbocharger.
The engine codes found on the vehicle information
code plate are as follows:
l 4G15--1.5L SOHC engine l 4G61-1.6L DOHC engine l 4G93-1.8L SOHC engine l 4G63-2.OL (SOHC or DOHC) engine l 4G64-2.4L (SOHC or DOHC) engine l 6G72-3.OL (SOHC or DOHC) engine l 6G74-3.5L DOHC engine
A vehicle safety certification label is attached to
the face of the left door pillar post. This label indi-
cates the month and year of manufacture, Gross Ve-
hicle Weight Rating (GRVW) front and rear, and Ve-
hicle Identification Number (VIM). 4 character code as on the vehicle information code
plate is used. The engine serial number is also
stamped near the engine model number. As men-
tioned above, the engine can also be identified by the
8th digit in the VIN number.
The transaxle model code is located on the vehicle
information code plate. The transaxle identification
number is etched on a boss located on the front up-
per portion of the case.
The code for the drive axle is etched on a boss lo-
cated on the case of the differential carrier.
easier to use the code letter in the VIN for engine ref-
erence. A second reason for referring to the VIN for
engine identification is that code 4663, located on
the vehicle information code plate, does identify the
engine as a 2.OL DOHC engine, but does not tell you ) See Figure 35
The engine model number is stamped at the front
side on the top edge of the cylinder block. The same
Fig. 32 The Vehicle Identification Number
g3’51p’o of the instrument panel _I:^1 / Fig. 33 The vehicle model, engine model,
(VIN) plate is attached to the top left side
bansaxle model, and body color code are all
noted on the vehicle information code plate
ENGINE AND VEHiCLE IDENTlFlCATlON
EnglnCode
ModelYerr
todeal
LIten (cc)
Cu. In. W. Fuel+ Type m.hWg. Code@ Year ,G15JA 1.5 (1468) 92 4 MFI SOHC Mitsubishi
L 1990
IG61N 1.6(15QQ) 98 4 MFI DOHC
Mitsubishi M 1991
1G93lC 1.8 (1834) 112 4 MFI SOHC Mitsubishi N 1992
IG63N 2.0 (1997) 122 4 MFI SOHC “-Mitsubishi P
1993
!G63Fi 2.0 (1997) 122 4 MFI DOHC Mitsubishi
R 1994
,G63iU 2.0 (1997) 122 4 MFI-Tuibo DOHC Mitsubishi
S 1995
.GMffi 2.4 (2351) 143 4 MFI SOHC
Mitsubishi T 1996
iG64L 2.4 (2351) 143 4 MFI DOHC Mitsubishi V
lEzH 3.0 1997
(2972) 161 6 MFI SOHC Mitsubishi W 1998
;G7ZJ 3.0 (2Q72) 161 6 MFI GQHC Mitsubishi
~.. X 1999
iG7zL 3.0 (2972) 181
~ 6 MFI SOHC ___-___ Miisubishi
Y 2000
iG74lP 3.5 (3497) 213 6 MFI SOHC Miisubishi
The transfer case has no separate model code, the
code is located on the transaxle. The transfer case is
onlv eoUiODed on manual transaxle All Wheel Drive
(AWD)‘mbdels.
Fig. 34 Your car should have a vehicle
Fig. 35 Engine model number location-
4663 (2.OL) engine shown
Page 17 of 408

l
1-18 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
the clamps and remove the cables, negative cable
first. On batteries with posts on top, the use of a
puller specially made for this purpose is recom-
mended. These are inexoensive and available in most alternator or turn the adjusting bolt to adjust belt ten-
sion. Once the desired value is reached, secure the
bolt or locknut and recheck tension.
d”t” lJdlL> X”lt;>. 31°C LtXlllllldl lJdllt2)’ MLJIC, dlt’ X- cured with a small bolt. ST& I REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Clean the cable clamps and the battery terminal I
with a wire brush, until all corrosion, grease, etc., is
removed and the metal is shinv. It is esneciallv imnnr-
tant to c
knife is useful nere), since a smart
material or oxidation there will pre Clean the cable clamps and the battery terminal
with a wire brush, until all corrosion, grease, etc., is
removed and the metal is shiny. It is especially impor-
tant to clean the inside of the clamp thoroughly (an old
knife is useful here), since a small deposit of foreign
material or oxidation there will prevent a sound electri-
cal connection and inhibit either starting or charging.
Special tools are available for cleaning these parts,
one type for conventional top post batteries and an-
other type for side terminal batteries. It is also a good
idea to apply some dielectric grease to the terminal, as
this will aid in the prevention of corrosion,
After the clamps and terminals are clean, reinstall
the cables, negative cable last; DO NOT hammer the
clamps onto battery posts. Tighten the clamps se-
curely, but do not distort them. Give the clamps and
terminals a thin external coating of grease after in-
stallation, to retard corrosion.
Check the cables at the same time that the terminals
are cleaned. If the cable insulation is cracked or bro-
ken, or if the ends are frayed, the cable should be re-
placed with a new cable of the same length and gauge.
CHARGING
the cables, negative cable last; DO NOT hammer the
curely, but do not distort them. Give the clamps and
terminals a thin external coating of grease after in-
stallation, to retard corrosion.
Check the cables at the same time that the terminals
are cleaned. If the cable insulation is cracked or bro-
ken, or if the ends are frayed, the cable should be re-
placed with a new cable of the same length and aauae.
CHARGING
Fig. 62 mere are typically 3 types of ac-
cessory drive belts found on vehicles today 1. Loosen the alternator support nut.
2. Loosen the adjuster lock bolt.
3. Rotate the adjuster bolt counter clockwise to
I .I , . . . * . .
I Tn i”et*ll* Fig. 62 There are typically 3 types of ac-
Fig. 64 Deep cracks in this belt will cause
flex, building up heat that will eventually 11, 1.8L, 2.OL and 2.4L Engines
cal connection and inhibit either starting or charging.
Special tools are available for cleaning these parts,
one type for conventional top post batteries and an-
other type for side terminal batterin, I+ if QI@* 3 nnnd
idea to apply some dielectric grr
this will aid in the prevention of ,,vIIuaIUII.
After the clamps and terminals are clean, reinstall 1.5L, 1.6
AL TERNA TOR BE1 T
e See Figures 67,68, and 69
1. Loosen the alternator support nut.
2. Loosen the adjuster lock bolt.
3. Rotate the adjuster bolt counter clockwise to
release the tension on the belt.
4. Remove the belt.
To install:
5. Install the belt on the pulleys.
6. Rotate the adjuster bolt clockwise until the
proper tension is reached.
7. Tighten the adjuster lock bolt and the alternator
support nut.
POWER STEERING BELT
8 See Figures 70 and 71
1. Remove the alternator belt as described above.
2. Loosen the power steering pump adjusting
bolts.
3. Remove the power steering oumo fixed bolt on
R Rntatn the cxiillrtm hnit A&+,& until the r -r- .- .- ._.. ._ .______
7. Tighten the adjuster lock bolt and the alternator
support nut.
POWER STEERING BELT
1 ..“‘.I ““..Y...Y up II”“. ..IU. ..m.*
1 lead to belt failure V.
I
I
The chemical reaction which takes place in - 1 the rear of the bracket.
4. Rotate the pump toward the engine and remove
the belt.
all batteries generates explosive hydrogen
gas. A spark can cause the battery to explode
and splash acid. To avoid serious personal
injury, be sure there is proper ventilation and
take appropriate fire safety precautions when
connecting, disconnecting, or charging a bat-
tery and when using jumper cables. To fnstall:
5. Install the belt on the pulleys.
A battery should be charged at a slow rate to keep
the plates inside from getting too hot. However, if
some maintenance-free batteries are allowed to dis-
charge until they are almost “dead,” they may have to
be charged at a high rate to bring them back to “life.”
Always follow the charger manufacturers instructions
on charging the battery. 85 The cover of this belt ex-
Fig. is worn,
REPLACEMENT
When it becomes necessary to reolace thn haeoN
‘” yyL’“‘J’ I or oreMer
select one with an amperage rating equal tc .
a ----
than the battery originally installed. Deterioration and
just plain aging of the battery cables, starter motor,
and associated wires makes the battery’s job harder
in successive years. The slow increase in electrical
resistance over time makes it prudent to install a new
battery with a greater capacity than the old. 1 Fig. 67 Loosen the adjuster lock bolt . . .
I ‘-
I -. -_ tm1217 Fig. 66 Installing too wide a belt can resylt
in serious belt wear and/or breakage
the belt and run outward. All worn or damaged drive
belts should be replaced immediately. It is best to re-
place all drive belts at one time, as a preventive
uring this service operation. maintenance measure, d
- ADJUSTMENT : *
INSPECTION Excessive belt tension will cause damage to the al-
e See Figures 62, 83, 64, 65, and 88
Inspect the belts for signs of glazing or cracking. A
glazed belt will be perfectly smooth from slippage,
while a good belt will have a slight texture of fabric
visible. Cracks will usually start at the inner edge of pulley bearings, while, on
It tension will
Droduce slin ternator and water pump
the other hand, loose be
r ------ r
and premature wear on the belt. Therefore, be sure to
adjust the belt tension to the proper level.
To
adjust the tension ’ ’ ’ ” ’ ‘* adjusting bolt or fixing b
alternator bracket or tens on a onve Den. loosen me I Fig. 68 . . . then
from the engine remove the alternator
bolt locknut on the alternator,
iion pulley. Then move the
Page 18 of 408

GENERAL INFORMATION AND MAlNTENANdE l-19
792UQ4 Fig. 69 Accessory V-belt routing-Mii
subishf 1.6L, 1.6L,-1.6L, 2.OL and 2.4L en
gines
33151PM Fig. 70 After the adjusting and fixed bolt!
are loosened, rotate the pump . . .
/ F$71t immtl$mm&a the power ::: 6. Rotate the pump until the proper tension is
reached.
7. Tighten the adjusting bolts on the pump.
8. Tighten the fixed bolt on the rear of the bracket.
9. Install the alternator belt.
A/r: COMPRESSOIl BEL f
1. Loosen the tension oullev and remove the belt.
2. The installation is the reverse of the removal.
.3.gL DGHC, 3.OL SOHC (Gaiant models
only) and 3.5L Engines 4. Remove the belt.
To install:
5. Install the belt on the crankshaft and alternator
pulleys.
6. Using the adjusting bolt on the tensioner,
tighten the belt to the desired tension.
7. Tighten the fixing nut to hold the adjustment.
8. Install the undercover and lower the vehicle to
_,
the tloor.
9. Connect the negative battery cable.
POWER SliEERlNG BEL f
6 See Figures 72 and 73 1. Disconnect the neaative batteN cah+P
-I
Wait at least 60 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent poS-
sibie deployment of the air bag.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle and re-
mob re the undercover.
3. Remove the alternator and NC compressor
belt.
4. Lower the vehicle and remove the cruise con-
trol oumn link iW%mblV. 79244Q.37
-- I-- r ---- - _I
Fig. 72 Serpentine belt routing-Mitsubishi 5. Place the power steering hose under the oil
reservoir.
3.OL engines (except 1696-00 Galant mod-
6.
Loosen the tension pulley fixing bolts and re-
els)
Generator pulP
1 move the power steering pump drive belt.
To install:
1 7. install the Dower steerina oumu r+r+v~ hp++
8. Insert an extension bar &eoufvaik;;t”f;;id‘he
opening at the end of the tension pulley bracket and
pivot the pulley to apply tension to the belt.
9. Tighten the fixing bolts.
10. Raise the vehicle and install the alternator and
compressor belt.
Il. Install the undercover and lower +hfi vph+r+p
.I,., .VII.“.Y.
12. Connect the negative battery cable.
I 3.OL SGHC (Diamante Models Onivl Enotne
I ,r ” 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.’ Loosen the lockbolt on the face nf the A/C _ __.- tensioner pulley.
3
Turn the adiustina bolt of the A/C +fincrnner
pulley to loosen the tension of the A/C belt.
4. Remove the A/C compressor belt.
5.
Loosen the locknut on the face of the power
to loosen the tc
7. Remov
Fig. 73 Accessory V-belt routing-Mitsubishi
3.5L and 1996-00 3.OL SOHC Galant en-
gines steering/alternator tensloner pulley.
6. Turn the adjusting bolt of the tensioner pulley
msion of the belt.
‘e the power steering/alternator belt.
To install:
8. Install the power steering/alternator belt first
.* .* . ,^
ssor drive belt. ana tnen tne A/ti compre:
9. Adjust the belts t+
ing the adjusting bolts anu
II~IIWII pueey tlxmg I the proper tension by turn-
A.:-L I-..-.. I,^, .’
nut/bolt.
10. Tighten the mounting nut of the power steer-
ing/alternator tensioner pulley to 36 ft. Ibs. (50 Nm).
Wait at least 60 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent pos-
sible deployment of the air bag. -The manufacturer does not provide a
torque specification for the bolt that secures
A/C tensioner pulley.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle and re- 11. Connect the negative battery cable.
move the front undercover.
3. Loosen the tension pulley fixing nut and relieve
the tension on the belt by turning the adjusting bolt.
Page 21 of 408

l-22 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
tears. If the boot is damaged, it should be replaced
trode is to the block’s cooling passages) the cooler it
your driving is long distance, high speed travel, use a
immediately. Please refer to Section 7 for procedures.
will operate. A plug that absorbs little heat and re-
colder plug; if most of your driving is stop and go,
mains too cool will quickly accumulate deposits of
use a hotter plug. Original equipment plugs are gen-
oil and carbon since it is not hot enough to burn
erally a good compromise between the 2 styles and
them off. This leads to plug fouling and consequently
most people never have the need to change their
to misfiring. A plug that absorbs too much heat will
plugs from the factory-recommended heat range.
ti See Figure 88 have no deposits but, due to the excessive heat, the
,electrodes will burn away quickly and might possibly
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
A typical spark plug consists of a metal shell sur- lead to preignition or other ignition problems. Preig-
rounding a ceramic insulator. A metal electrode ex- nition takes place when plug tips get so hot that they
ti See Figures 90 thru 95
tends downward through the center of the insulator glow sufficiently to ignite the air/fuel mixture before
and protrudes a small distance. Located at the end of the actual spark occurs. This early ignition will usu- A set of spark plugs usually requires replacement
the plug and attached to the side of the outer metal ally cause a pinging during low speeds and heavy after about 20,000-30,000 miles (32,000-48,000
shell is the side electrode. The side electrode bends loads. km), depending on your style of driving. In normal
in at a 90” angle so that its tip is just past and paral- The general rule of thumb for choosing the correct operation plug gap increases about 0.001 in.
lel to the tio of the center electrode. The distance be- heat range when picking a spark plug is: if most of (0.025mrn) for every 2,500 miles
(4,000 km). As the
tween these two electrodes (measured in thousandths
of an inch or hundredths of a millimeter) is called the
spark piug gap.
The spark plug does not produce a spark, but in-
steed provides a gap across which the current can
arc. The coil produces anywhere from 20,000 to
50,000 volts (depending on the type and application)
which travels through the wires to the spark plugs.
The current passes along the center electrode and
jumps the gap to the side electrode, and in doing so,
ignites the air/fuel mixture in the combustion charn-
ber.
SPARKPLUG HEATRANGE
ti See Figure 89
Spark plug heat range is the ability of the plug to
dissipate heat. The longer the insulator (or the farther
INSULATOR CRACKS
OFTEN OCCUR HERE
SIDE ELECTRODE ENTER ELECTRODE:
(SEND TO ADJUST GAP) FILE FLAT WHEN
ADJUSTING GAP;
DO NOT BEND
Fig. 88 Cross-section of a spark plug
it extends into the engine), the hotter the plug will
operate; the shorter the insulator (the closer the elec- Fig. 90 Carefully twist the boot end of the
I
spark plug wire and withdraw the spark plug
wire boot from the cylinder head
Fig. 92 A locking extension such as this is
extremely helpful when removing spark
plugs that are centrally located in the cyhn-
Fig. 94 . . .
then carefully withdraw the
spark plug from the engine Fig. 91 A special spark plug socket with a
rubber insert is required to remove the
spark plugs. Typically the spark plugs
re-
quire a Ya spark plug socket
Fig, 93 Using the appropriate sized spark
plug socket, necessary extensions and drive
tools, loosen the spark plug . . .
93151ptxl Fig. 95 After removing the plug from the en-
gine, inspect it using the spark plug condi-
tion chart in this section to determine the
running condition of your engine
Page 22 of 408

t
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE l-23
gap increases, the plug’s voltage requirement also in-
creases. It requires a greater voltage to jump the the spark plug counterclockwise to loosen and re-
move the spark plug from the bore.
wider gap and about &o to three times as much volt-
age to fire the plug at high speeds than at idle. The
improved air/fuel ratio control of modern fuel injec-
tion combined with the higher voltage output of mod- Be sure not to use a flexible extension on the place. The click may be felt or heard, then gently pull
ern ignition systems will often allow an engine to run socket. Use of a flexible extension may allow back on the boot to assure proper contact.
.___. . _
significantly longer on a set of standard spark plugs, a shear force to be agptf’ ea to me plug.
A 12. On the 3.OL fSOHC and DOHC) and 3.5L en-
LL_ _I___ -u I_ IL-
but keep in mind that efficiency will drop as the gap shear force could break tne pug on III me
tion 3 for the installation procedure.
widens (along with fuel economy and power). cylinder head, leading to costly and frustrat-
13. If equipped, install the center cover.
When you’re removing spark plugs, work on one ing repairs.
at a time. Don’t start by removing the plug wires all at
once, because, unless you number them, they may To install:
INSPECTION & GAPPING
11. Apply a small amount of silicone dielectric
compound to the end of the spark plug lead or inside
the spark plug boot to prevent sticking, then install
the boot to the spark plug and push until it clicks into
gines, install the upper intake manifold. Refer to Sec-
,,Y” ..1111 uy”’ 1 the neaative bat&v cable and if become mixed up. Take a minute before you begin
and number the wrrpc with +sne
1. Disconnect. ~~.~
--..-., -..-.-, -..-
thevehicle has been run recently, allow the engine to
thoroughly cool.
2. If equipped, remove the center cover.
3. On the 3.OL (SOHC and DOHC) and 3.5L en-
gines, the upper intake manifold must be removed to
access the rear spark plugs. Refer to Section 3 for the
removal procedure.
4. Carefully twist the spark plug wire boot to
loosen it, then pull upward and remove the boot from
the plug. Be sure to pull on the boot and not on the
wire, otherwise the connector located inside the boot
may become separated.
5. Using compressed air, blow any water or de-
bris from the spark plug well to assure that no harm-
ful contaminants are allowed to enter the combustion
chamber when the spark plug is removed. If com-
pressed air is not available, use a raa or a brush to must be replaced.
Check the plugs for deposits and wear, If they are 7. Inspect the spark plug boot for tears or dam-
age. If.a damaged boot is found, the spark plug wire
8. Using a wire feelergauge, check and adjust
the spark plug gap. When using a gauge, the proper
size should pass between the electrodes with a slight
drag. The next larger size should not be able to pass
while the next smaller size should pass freely.
9. Carefully thread the plug into the bore by
hand. If resistance is felt before the plug is almost
completely threaded, back the plug out and begin
threading again. In small, hard to reach areas, an old
spark plug wire and boot could be used as a thread-
ing tool. The boot will hold the plug while you twist
the end of the wire and the wire is supple enough to
twist before it would allow the plug to crossthread.
Do not use the spark plug sock?
l -- K-rrA tha nhme Alwmm rarntdlv thw GL I” IlllGa”
the possibility of crossthreading and damag- lad the plug
. ..Y f..“YY. rn”Y,‘““mY*“.‘, .I**” by hand or using an old plug wire to prevent
ing the cylinder head bore.
10. Carefully tighten the spark plug. If the plug
you are installing is equipped with a crush washer,
seat the plug, then tighten about I/, turn to crush the
washer. If you are installing a tapered seat plug,
tighten the plug to specifications provided by the ve-
hicle or plug manufacturer. b See Figures 98, 97, 98, 99, and 100
not going to be replaced, clean the plugs thoroughly.
Remember that any kind of deposit will decrease the
efficiency of the plug. Plugs can be cleaned on a
spark plug cleaning machine, which can sometimes
be found in service stations, or you can do an accept-
able job of cleaning with a stiff brush. If the plugs are’
cleaned, the electrodes must be filed flat. Use an ig-
nition points file, not an emery board or the like,
which will leave deposits. The electrodes must be
filed perfectly flat with sharp edges; rounded edges
reduce the spark plug voltage by as much as 50%.
Check spark plug gap before installation. The
ground electrode (the L-shaped one connected to the
body of the plug) must be parallel to the center elec-
trode and the specified size wire gauge (please refer
to the Tune-Up Specifications chart for details) must
pass between the electrodes with a slight drag:
*,NEVER adjust the gap on a used platinum
. clean the area.
*Remove the spark plugs when the engine
is cold, if possible, to prevent damage to the
threads. If removal of the plugs is difficult,
apply a few drops of penetrating oil or sili-
cone spray to the area around the base of the
plug, and allow it a few minutes to work.
6. Using a spark plug socket that is equipped
with a rubber insert to properly hold the plug, turn type spark plug.
Always check the gap on new plugs as they are
not always set correctly at the factory. Do not use a
flat feeler gauge when measuring the gap on a used
plug, because the reading may be inaccurate. A
round-wire type gapping tool is the best way to check
the gap. The correct gauge should pass through the
electrode gap with a slight drag. If you’re in doubt, try
one size smaller and one laraer. The smaller aauqe
Page 26 of 408
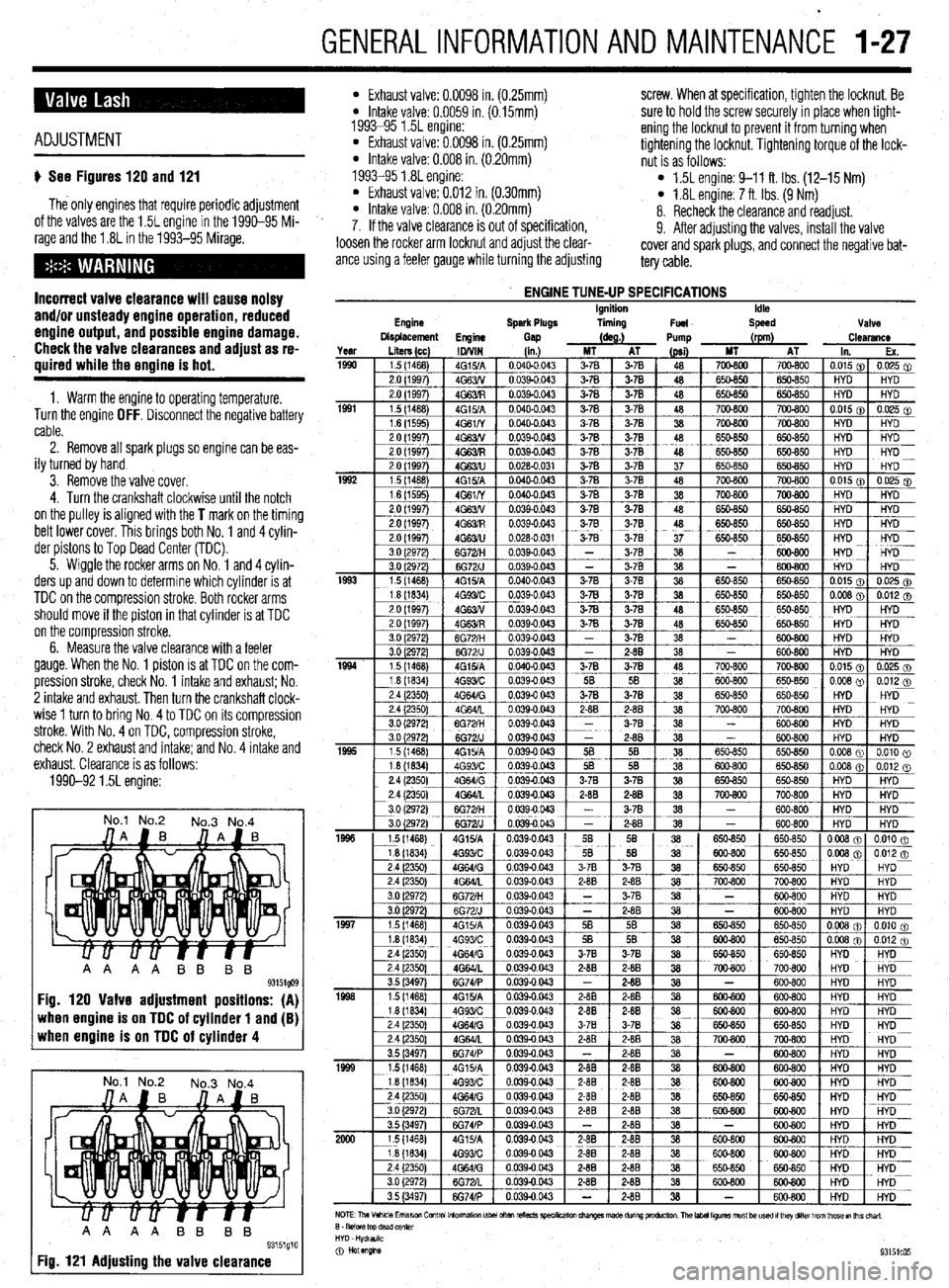
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAlNTENANdE I-27
ADJUSTMENT
u See Figures 120 and 121
The only engines that require periodic adjustment
of the valves are the 1.5L engine in the 1990-95 Mi-
rage and the 1.8L in the 1993-95 Mirage.
Incorrect valve clearance will cause noisy
and/or unsteady engine operation, reduced
engine output, and possible engine damage.
Check the valve clearances and adjust as re-
quired while the engine is hot.
1. Warm the engine to operating temperature.
Turn the engine OFF. Disconnect the negative battery
cable.
2. Remove all spark plugs so engine can be eas-
ily turned by hand
3. Remove the valve cover.
4. Turn the crankshaft clockwise until the notch
on the pulley is aligned with the
T mark on the timing
belt lower cover. This brings both No. 1 and 4 cylin-
der pistons to Top Dead Center (TDC).
5. Wiggle the rocker arms on No. 1 and 4 cylin-
ders up and down to determine which cylinder is at
TDC on the compression stroke. Both rocker arms
should move if the piston in that cylinder is at TDC
on the compression stroke.
6. Measure the valve clearance with a feeler
gauge. When the No. 1 piston is at TDC on the com-
pression stroke, check No. 1 intake and
exhaust; No.
2 intake and exhaust. Then turn the crankshaft clock-
wise 1 turn to bring No. 4 to TDC on its compression
stroke. With No. 4 on TDC, compression stroke,
check No. 2 exhaust and intake; and No. 4 intake and
exhaust. Clearance is as follows:
1990-92 1.5L engine:
No.1 No.2
No.3 No.4
when engine is on TDC of cylinder 1 and (B) when engine is on TDC of cylinder 4
No.1 No.2
No.3 No.4
AA AA BB BB
93151g10 Fig. 121 Adjusting the valve clearance
l Exhaust valve: 0.0098 in. (0.25mm) screw. When at specification, tighten the locknut. Be l Intake valve: 0.0059 in. (0.15mm)
1993-95 1.5L engine: sure to hold the screw securely in place when tight-
l Exhaust valve: 0.0098 in. (0.25mm) ening the locknut to prevent it from turning when
* Intake valve: 0.008 in. (0.20mm) tightening the locknut. Tightening torque of the lock-
nut is as follows:
1993-95 1.8L engine:
l Exhaust valve: 0.012 in. (0.30mm) l 1.5L engine: 9-11 ft. Ibs. (12-15 Nm)
l Intake valve: 0.008 in. (0.20mm) l 1.8L engine: 7 ft. Ibs. (9 Nm)
8. Recheck the clearance and readjust.
7. If the valve clearance is out of specification,
9. After adjusting the valves, install the valve
loosen the rocker arm locknut and adjust the clear-
ante using a feeler gauge while turning the adjusting cover and spark plugs, and connect the negative bat-
tery cable.
Engine
ENGINE TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS Ignition
Spark Plugs liming
Fuel Idle
Speed Valve
Displacement
Engine
Gap (as.) Pump (rpm)
Clearance