MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1990, Model line: SPYDER, Model: MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990Pages: 2103, PDF Size: 68.98 MB
Page 461 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
Scan tool 183
Code General scan tool Evaporative Emission
No.tion Solenoid Circuit
31
[Comment]l Open or short control drcuitBackgroundl Open fused ignition MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
Scan tool 183
Code General scan tool Evaporative Emission
No.tion Solenoid Circuit
31
[Comment]l Open or short control drcuitBackgroundl Open fused ignition](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-460.png)
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
Scan tool 183
Code General scan tool Evaporative Emission
No.tion Solenoid Circuit
31
[Comment]l Open or short control drcuitBackgroundl Open fused ignition l The PCM provides a switched ground path to the sole noid. Open or shorted solenoid lThis DTC indicates an open or short-circuit condition in the evaporative emission l PCM failed
solenoid control circuit.
Range of Check
l Battery voltage:
or more
l Ignition switch: ON
ConditionlOpen or short circuit is detected in the evaporativ e emission ventilation solenoid for 3seconds.
N GMeasure at the evaporative emission ventilation sol enoid connectorCheck the following connectors:
lDisconnect the connector and measure at the harness side.
l Voltage between 2 and ground
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK: Battery positive voltage
OKCheck the harness wire between ignition switch and emission ventilation solenoid connector. Repair,if
NGMeasure at the PCM connector Check the following connectors: lDisconnect the connector and measure at the harness side.
l Voltage between 77 and ground
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK: Battery positive voltage
OKCheck the harness wire between PCM and emissionventilation solenoid connector. Repair, if necessar y.
Check the following connector: Repair
Check trouble symptom.
N G
Replace the PCM.
TSB Revision
Page 462 of 2103
E N G I N E ( N O N - T U R B O ) > .
Scan tool 184. .
C o d e G e n e r a l s c a n t o o l E v a p o r a t i v e E m i s s i o n V e n t i l a-
No.tion Switch or Mechanical Fault
31
[Comment]
Backgroundl Evaporative emission failedlWhen the solenoid diaphragm moves up and down by ac tivating the evaporative emission the solenoid switch turns on and off. l
Open or short circuit lThe PCM detects how often the solenoid is activated by counting the ON and OFF conditionsl c l o g g e d
l PCM failed
of the solenoid switch.Range of Check, Set Conditionl The solenoid is activated, but the solenoid switch does not turn on and off.
‘ I
NG.
Repair
Check trouble symptom.
NG
NG
emission ventilation Repairsolenoidconnector.
OK
Replace the PCM.
Scan tool 187
Code General scan tool EVAP Leak Monitor Pinched
NO.
Hose Found
31
‘Backgroundl The PCM monitors that the fuel tank, purge lines, e tc. are sealed well.
lWhen monitoring, the PCM byactivatingtheevaporativeemission
ventilation solenoid with the canister ventilation valve (incorporated in the solenoid) closed.
lIf the fuel tank and purge lines are sealed correct ly, the pressure will rise well by activatingthe solenoid specific times.
l After the pressure rises well, the diaphragm inside the solenoid will not work any more.
l If the hoses are pinched, the pressure will rise we ll by activating the solenoid only fewer
times.Range of Check, Set Condition
lThe evaporative emission ventilation solenoid has b een activated less than specific times.
TSB Revision
lClogged hoses between the ventilation solenoid and the fuel tank
l Evaporative emission ventilation solenoid
failed
l P C M f a i l e d
Checktheclogged
tion solenoid and the fuel tank. Clean. if Replace the PCM.
Page 463 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting’
INSPECTION CHART FOR TROUBLE SYMPTOMS
Trouble symptom
Communication with all systems is not possible.1tion with scan,
tool is
Communication with PCM only is not possible.2
malfunctionThe check engine/malfunction indicator lamp does no t illuminate right after the ignition
indicator lamp switch is turned to the ON position.3
and related
parts The check engine/malfunction indicator lamp remains
illuminated and never goes 4
Cranks, won’t start
5
StartingFires up and dies6
Hard starting7
Idling stability Unstable idle. (Rough idle, hunting)6
(Improper
Idle speed is high. (Improper idle speed)9idling)Idle speed is low. (Improper idle speed)1 0
When the engine is cold, it stalls at idle (Die out )11
stabilityWhen the engine becomes hot, it stalls at idle. (Di e 12
(Engine stalls)Th engine stalls when accelerating. (Pass out)13
The engine stalls when decelerating.14
Hesitation, sag or stumble15
Acceleration shock1 6
Deceleration shock 17DrivingPoor acceleration 16
Surge19
Knocking 20
21
Too high CO and HC concentration when idling22
Revision
Page 464 of 2103
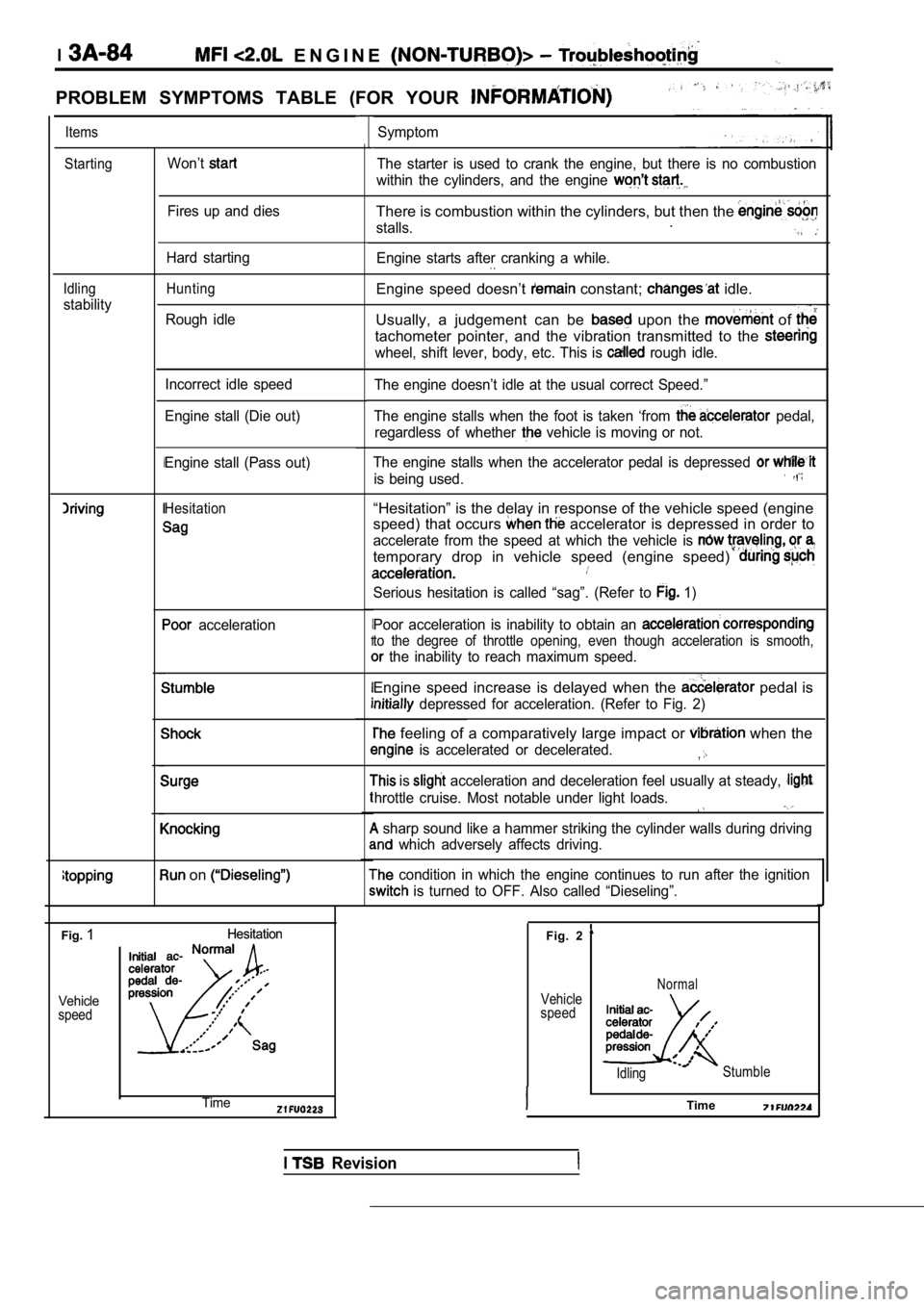
I E N G I N E
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE (FOR YOUR
ItemsSymptom
StartingWon’tThe starter is used to crank the engine, but there is no combustion
within the cylinders, and the engine
Fires up and diesThere is combustion within the cylinders, but then the
stalls..
Engine starts after cranking a while.Hard starting
Idling
stability
HuntingEngine speed doesn’t constant; idle.
Usually, a judgement can be
upon the of
tachometer pointer, and the vibration transmitted to the
wheel, shift lever, body, etc. This is rough idle.
Rough idle
The engine doesn’t idle at the usual correct Speed. ”
The engine stalls when the foot is taken ‘from
pedal,
regardless of whether
vehicle is moving or not.
Incorrect idle speed
Engine stall (Die out)
The engine stalls when the accelerator pedal is dep ressed
is being used.
Engine stall (Pass out)
Hesitation“Hesitation” is the delay in response of the vehicle speed (engine
speed) that occurs
accelerator is depressed in order to
accelerate from the speed at which the vehicle is
temporary drop in vehicle speed (engine speed)
Serious hesitation is called “sag”. (Refer to 1)
Poor acceleration is inability to obtain an
to the degree of throttle opening, even though acce leration is smooth,
the inability to reach maximum speed.
acceleration
Engine speed increase is delayed when the pedal is
depressed for acceleration. (Refer to Fig. 2)
feeling of a comparatively large impact or when the
is accelerated or decelerated.,
is acceleration and deceleration feel usually at steady,
hrottle cruise. Most notable under light loads.
sharp sound like a hammer striking the cylinder wa lls during driving
which adversely affects driving.
condition in which the engine continues to run after the ignition
is turned to OFF. Also called “Dieseling”.
on
Fig.1Hesitation
Hesitation
Vehicle
speed
Fig. 2
Vehicle
speedNormal
Idling Stumble
ITimeTime
I Revision
Page 465 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
INSPECTION PROCEDURE FOR TROUBLE SYMPTOMS
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1Communication with scan tool is not possible. (Comm unication
with all systems is not possible.)
The cause is probably a defect in the power supply system (including ground) for the on-board
Measure at the data link connector
OK
. Check the following connectors: 5 7 5
Check troubleNG. Check between and
Replace the scan tool.
. .
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 2
Scan tool communication with PCM is not possible.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]One of the following causes may be suspected. l No power supply to PCM
* Defective ground circuit of PCM
l Defective PCM
l Improper communication line between PCM and scan to olMalfunctionof- power supply o f lOpen circuit between PCM and data link con-
Check the following connectors:
OK
NG Repair
Check trouble symptom.IN G
Check the harness wire between PCM and data link connector.
OK
Check the power supply and ignition circuit.
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 23.)
N G Repair
Revision
Page 466 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3,
T h e c h e c k i n d i c a t o r . l a m p n o t
illuminate right after the ignition switch is turned to the
position. ,
[Comment]l bulbThe PCM ca MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3,
T h e c h e c k i n d i c a t o r . l a m p n o t
illuminate right after the ignition switch is turned to the
position. ,
[Comment]l bulbThe PCM ca](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-465.png)
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3,
T h e c h e c k i n d i c a t o r . l a m p n o t
illuminate right after the ignition switch is turned to the
position. ,
[Comment]l bulbThe PCM causes the check engine/malfunction indicator lamp to illuminate for three seconds, l Defective check engine/malfunction immediately after the ignition switch is turned to ON.
If the check engine/malfunction indicator lamp does not illuminate immediately after the ignition llamp circuit of the switch is turned to ON, one of the malfunctions lis
ted at right probably occurred.
NG
10Battery voltage (Refer toCheck the power supply and ignition circuit.
(Refer to I N S P E C T I O N
Measure at the PCM connector,
OK: The check engine/malfunction indicator lamp
NG
Check a burnt-out bulb.
OK
N G Replace
Measure at the combination meter connector
lDisconnect the connector, and measure at the harnes s
side.
lVoltage between 10 and ground (Ignition switch: ON)
OK: Battery positive voltage
OK
Replace the PCM.I
NGCheck the check engine/malfunction indicator power supply circuit. Repair, if necessary.; ,
Check the
OK
Repair
Check trouble symptom.I
Check the harness wire between combination meter an d
PCM connector. Repair, if necessary.
TSB Revision
Page 467 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 4
The check engine/malfunction indicator lamp remains
illuminated and never goes out.
[Comment]In cases such as the above, the cause MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 4
The check engine/malfunction indicator lamp remains
illuminated and never goes out.
[Comment]In cases such as the above, the cause](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-466.png)
ENGINE Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 4
The check engine/malfunction indicator lamp remains
illuminated and never goes out.
[Comment]In cases such as the above, the cause is probably t hat the PCM is
detecting a problem in a sensor or actuator, or tha t one of the malfunctions listed at right has
occurred.
Probable cause
l Short-circuit between the check indicator lamp and l Malfunction of the PCM
SCAN TOOL DTC Refer to
INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC
Are diagnostic trouble codesoutput? TROUBLE CODES
Measure at the combination meter connector lDisconnect the connector, and measure at the harnes s
side.Check the harness wire between meter and PCM
connector. Repair, if necessary.
l Disconnect the PCM connector.
l Continuity between 51 and ground
OK: No continuity
O K
Replace the PCM.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 5
Cranks, won’t start Probable cause
[Comment]l Malfunction of the ignition system
In cases such as the above, the cause is probably t hat a spark plugs are fouled defective,l Malfunction of the fuel pump system
or that the supply of fuel to the combustion chambe r is defective.
l Malfunction of the injector system
in addition, foreign materials (water, kerosene, et c.) may be mixed with the fuel.
l Malfunction of the PCM
l Foreign materials in fuel
,
Check battery positiv
OK: 8 or hiaher Check the battery. (Refer to GROUP 54 Battery)
OK
Scan tool: Inspection when no initial combustion oc
curs.
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 29.)
OK
Can any sound be heard
.
(Refer to
Yes
Check ignition circuit system.
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 28.)
OK
Check the injector control circuit. Carry out proce dures 19, 20, 21, in “INSPECTION PROCEDURE
FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES”.,
Check the following items. l Check the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug ca bles.
l Clean the injectors.
l Check if foreign materials (water, alcohol, etc.) g ot into fuel.
l Check the compression pressure.
TSB Revision
Page 468 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)=,
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 6
Fires up and dies.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]l of the ignition system
In such cases as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark plugs are MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)=,
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 6
Fires up and dies.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]l of the ignition system
In such cases as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark plugs are](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-467.png)
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)=,
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 6
Fires up and dies.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]l of the ignition system
In such cases as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark plugs are generating sparkslbut the sparks are weak, or the initial mixture for starting is not appropriate.Malfunction of the injector system
l Foreign fuel
l Poor compression
l
of the PCM
Check the battery. (Refer to GROUP 54
OK:8 or higher
Scan tool: Inspection when incomplete combustion oc curs.(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 30.)
OK
Canany sound be heard (Refer to
Yes
Check the injector control circuit. Carry out procedures in “INSPECTION PROCEDURE
FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES”.
Is starting good if the engine is cranked with the acceleratorpedal slightly depressed?
No
motor circuit INSPECTION
PROCEDURE FOR
TROUBLECODE
Check the following items.
l Check the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug ca bles.
l Clean the injectors.
l Check the compression pressure.
l Check fuel lines for
l Check if foreign (water, alcohol, etc.) got into fuel.
TSB Revision
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 7
Hard startingIProbable cause I
[Comment]l Malfunction of the ignition systemIn cases such as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark is weak and ignition is difficult,lMalfunction of the injector system
the initial mixture for starting is not appropriate , or sufficient compression pressure is not beinglInappropriate gasoline useobtained.l P o o r
Check battery positive vo
OK: 8 or higherOK
Scan tool: Inspection when incomplete combustion oc curs.
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 30.)Check the battery. (Refer to GROUP 54
Battery)1
Can any sound be heard fro
No Check the injector control circuit. Carry out proc
edures 19, 20, 21,
(Refer to in “INSPECTION PROCEDURE
YesFOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES”.
Check the following items.
l Check the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug ca bles.
l Clean the
l Check the pressure.
l Check if foreign materials (water, alcohol, etc.) g ot into fuel.
Page 469 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 8
Unstable idle (Rough idle, hunting)Probable cause
[Comment] Malfunction of the ignition system
In cases such as the abo MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 8
Unstable idle (Rough idle, hunting)Probable cause
[Comment] Malfunction of the ignition system
In cases such as the abo](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-468.png)
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 8
Unstable idle (Rough idle, hunting)Probable cause
[Comment] Malfunction of the ignition system
In cases such as the above, the cause is probably t hat the ignition system,l Malfunction of air-fuel ratio system
idle air control motor or compression pressure is d efective.
l Malfunction of the system
Because the range of possible causes is broad, insp ection is narrowed down to simple items.
l Malfunction of the evaporative emission
purge solenoid system
l Malfunction of the EGR system
l Poor compression
l Drawing air into exhaust system
W ere the battery terminals disconnected recently?
SCAN TOOL DTC
Are diagnostic trouble codes output
NO Refer to
INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTICTROUBLE CODES.
YES
Inspection when hunting occurs.
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 31.)
SCANTOOL Actuator test
07 motor (Refer to
OK
NG Check the idle air control motor (Refer to P. INSPECTION PROCEDURE FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
SCAN TOOL Specialfunction
“Reset
I
Check trouble symptoms.
OK
Scan tool: Inspection when idle speed is unstable. (Refer
to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 32.)
OK
Check the injector control circuit: (Carry out pro cedures 19, 20, 21, in “INSPECTION PROCEDURE
FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES”.)
Check the following items. l Check the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug ca bles.
l Check the purge control system.
l Check the EGR svstem.
l Check the compression pressure.
l Check if foreign materials (water, alcohol, etc.) g ot into fuel.
TSB Revision
Page 470 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual E N G I N E
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 9
Idle speed is high. (Improper idle speed)
[Comment] lIn such cases as the above, the cause is probably that the intake air volume during MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual E N G I N E
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 9
Idle speed is high. (Improper idle speed)
[Comment] lIn such cases as the above, the cause is probably that the intake air volume during](/img/19/57345/w960_57345-469.png)
E N G I N E
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 9
Idle speed is high. (Improper idle speed)
[Comment] lIn such cases as the above, the cause is probably that the intake air volume during idle is’ ltoo great. Intake manifold vacuum leak b o d y
SCAN TOOL DTC
Are diagnostic trouble codes output
NO
07 motor (Refer to
NG
Refer to INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTICTROUBLE CODES.
Checktheidleaircontrolmotorcircuit.PROCEDURE FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
OK
SCAN TOOLSpecial function
“Reset
Check trouble symptoms.
NG
SCAN TOOL SENSOR NGCheck the engine coolant temperature circuit.(Refer to INSPECTION
OK
SCAN TOOL OUTPUT clutch relay (Refer to
OK
NGCheck the switch and compressor clutch relay to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 26.)
Check the throttle body minimum air flow.
(Refer to
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 10
Idle speed is low. (Improper idle speed) Probable ca use
,
[Comment]l control motor In cases such as the above, the cause is probably that the intake air volume during idling is l
Malfunction of the’ throttle body
too small.
SCAN TOOL DTC
YESRefer to INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC
Are diagnostic troublecodesoutputTROUBLE CODES.
SCAN TOOL Actuator test
07 motor. (Refer to
OK
NG
PROCEDURE FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
SCAN TOOL Special function
“Reset
Check trouble
OK
Check the engine coolant temperature circuit. (Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 36.)
SCAN TOOL INPUT STATE TESTS
list) position switch (transaxle range switch)
(Refer to
OK Checktransaxle range sensorcircuit.
INSPECTION
PROCEDURE 25.)
Check the throttle body minimum air flow.
(Refer to
TSB Revision