Gas OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1041 of 6000

6A–85
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Block and Associated Parts
012RW010
Legend
(1) Cylinder Head Assembly
(2) Cylinder Head Gasket
(3) Crankcase with Oil Pan
(4) Oil Pipe and O-Ring
(5) Oil Strainer and O-Ring
(6) Oil Pump Assembly
(7) Cylinder Block Side Bolts(8) Oil Gallery
(9) Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
(10) Flywheel
(11) Rear Oil Seal Retainer Assembly
(12) Main Bearing Cap
(13) Crankshaft
(14) Cylinder Block
Disassembly
1. Remove cylinder head assembly.
2. Remove cylinder head gasket.
3. Remove crankcase with oil pan.
4. Remove oil pipe and O-ring.5. Remove oil strainer and O-ring.
6. Remove oil pump assembly.
7. Remove crankcase side bolts.
8. Remove oil gallery.
9. Remove piston and connecting rod assembly.
10. Remove flywheel.
Page 1042 of 6000

6A–86
ENGINE MECHANICAL
11. Remove rear oil seal retainer assembly.
12. Remove main bearing cap.
13. Remove crankshaft.
14. Remove cylinder block.
Inspection and Repair
1. Remove the cylinder head gasket and any other
material adhering to the upper surface of the cylinder
block. Be very careful not to allow any material to
accidentally drop into the cylinder block. Be very
careful not to scratch the cylinder block.
2. Carefully remove the oil pump, rear oil seal retainer,
and crankcase assembly installation surface seal.
3. Wipe the cylinder block clean.
4. Visually inspect the cylinder block. If necessary, use a
flaw detector to perform a dye penetrate and
hydraulic (or air pressure) test. If cracking or other
damage is discovered, the cylinder block must either
be repaired or replaced.
Flatness
1. Using a straight–edge and feeler gauge, check that
the upper surface of the cylinder block is not warped.
CAUTION: Be very careful not to allow any material
to accidentally drop into the upper surface of the
cylinder block. Be very careful not to scratch the
upper surface of the cylinder block.
2. The cylinder block must be reground or replaced if the
warpage exceeds the limit.
Warpage
Limit : 0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
Maximum repairable limit: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
012RS004
Cylinder Bore
Use a cylinder gauge to measure the cylinder bore
diameter in both the axial and thrust directions. Each
measurement should be made at six points.CAUTION: Be very careful not to allow any material
to accidentally drop into the upper surface of the
cylinder block. Be very careful not to scratch the
upper surface of the cylinder block.
Cylinder Bore Inside Diameter
Limit : 93.530 (3.6823)
If the measurement exceed the specified limit, the
cylinder block must be replaced.
Diameter
Grade A : 93.400 mm–93.410 mm
(3.6772 in–3.6776 in)
Grade B : 93.411 mm–93.420 mm
(3.6776 in–3.6779 in)
Grade C : 93.421 mm–93.430 mm
(3.6780 in–3.6783 in)
012RS005
NOTE: For information on piston diameter, please refer
to the section ”Inspection of the Piston and Connecting
Rod Assembly” in this manual.
The ”Grade” mark (1) is stamped at the position
illustrated.
Page 1045 of 6000

6A–89
ENGINE MECHANICAL
012RS007
7. Install cylinder block side bolts (1) and tighten
crankcase bolts in sequence shown in the illustration.
Torque : 39 Nꞏm (4.0 Kgꞏm/29 lb ft)
012RW005
8. Install oil pump assembly. Refer to “Oil Pump” in this
manual.
9. Install oil strainer and O-ring.
10. Install oil pipe and O-ring.
11. Install crankcase with oil pan.
1. Completely remove all residual sealant, lubricant
and moisture from the sealing surfaces. The
surfaces must be perfectly dry.
2. Apply a correct width bead of sealant (TB– 1207C
or its equivalent) to the contact surfaces of the
crankcase. There must be no gaps in the bead.
3. The oil pan must be installed within 5 minutes
after sealant application to prevent premature
hardening of sealant.
4. Tighten the bolts and nuts to the specified torque.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0 Kgꞏm/89 lb in)
013RW010
Legend
(1) Portion Between Both Holes
(2) Bolt Hole Portions
12. Install cylinder head gasket.
13. Install cylinder head assembly. Refer to “Cylinder
Head” in this manual.
Page 1058 of 6000
ENGINE COOLING6B–5
Diagnosis
Engine Cooling Trouble
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Engine overheatingLow Engine Coolant levelReplenish
Incorrect fan installedReplace
Thermo meter unit faultyReplace
Faulty thermostatReplace
Faulty Engine Coolant temperature
sensorRepair or replace
Clogged radiatorClean or replace
Faulty radiator capReplace
Low engine oil level or use of
improper engine oilReplenish or change oil
Clogged exhaust systemClean exhaust system or replace
faulty parts
Faulty Throttle Position sensorReplace throttle valve assembly
Open or shorted Throttle Position
sensor circuitRepair or replace
Damaged cylinder head gasketReplace
Engine overcoolingFaulty thermostatReplace
Engine slow to warm–upFaulty thermostatReplace
Thermo unit faultyReplace
Page 1060 of 6000
ENGINE COOLING6B–7
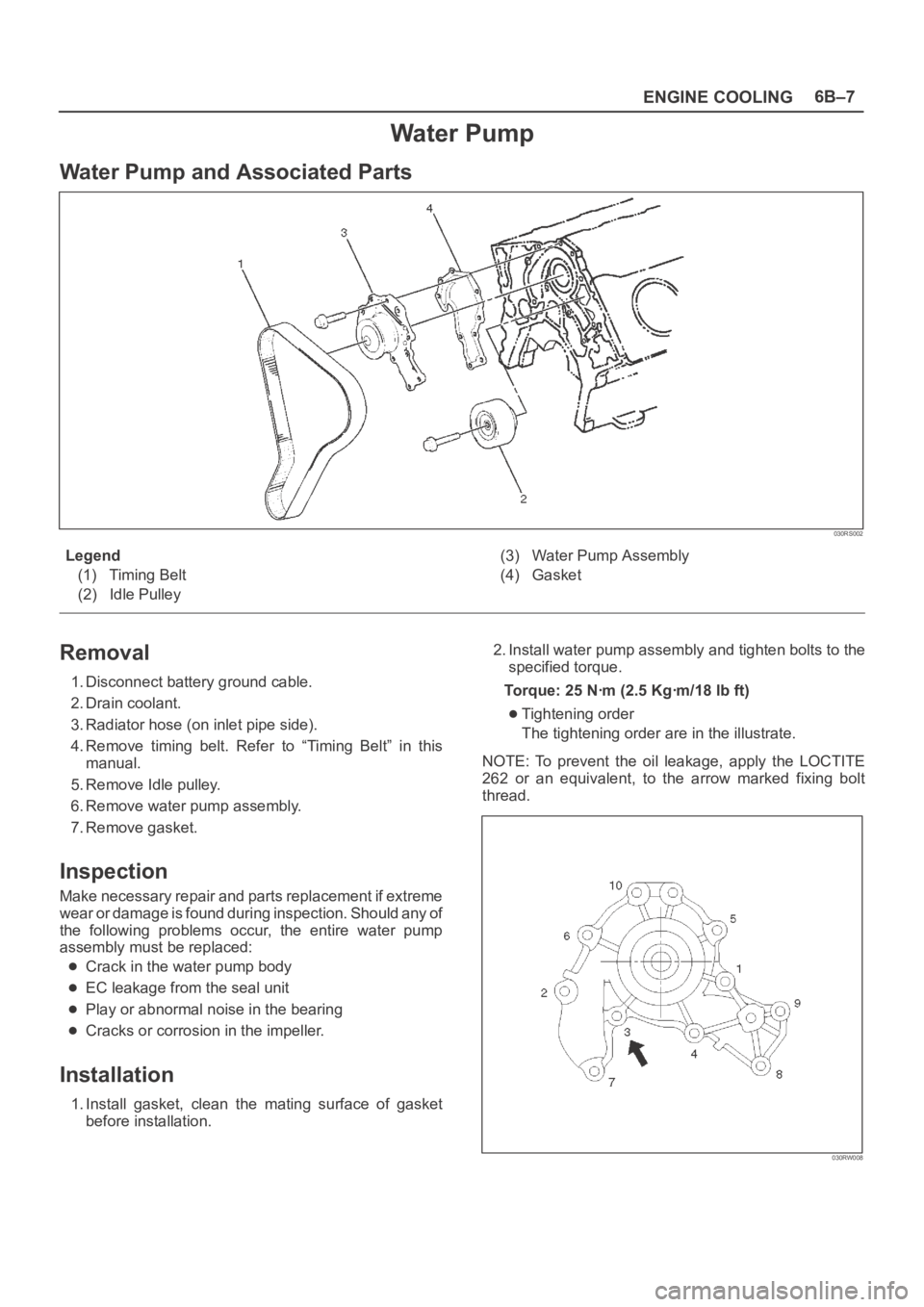
Water Pump
Water Pump and Associated Parts
030RS002
Legend
(1) Timing Belt
(2) Idle Pulley(3) Water Pump Assembly
(4) Gasket
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Drain coolant.
3. Radiator hose (on inlet pipe side).
4. Remove timing belt. Refer to “Timing Belt” in this
manual.
5. Remove Idle pulley.
6. Remove water pump assembly.
7. Remove gasket.
Inspection
Make necessary repair and parts replacement if extreme
wear or damage is found during inspection. Should any of
the following problems occur, the entire water pump
assembly must be replaced:
Crack in the water pump body
EC leakage from the seal unit
Play or abnormal noise in the bearing
Cracks or corrosion in the impeller.
Installation
1. Install gasket, clean the mating surface of gasket
before installation.2. Install water pump assembly and tighten bolts to the
specified torque.
Torque: 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
Tightening order
The tightening order are in the illustrate.
NOTE: To prevent the oil leakage, apply the LOCTITE
262 or an equivalent, to the arrow marked fixing bolt
thread.
030RW008
Page 1065 of 6000

6B–12
ENGINE COOLING
Drive Belt and Cooling Fan
Drive Belt and Associated Parts
015RW005
Legend
(1) Crankshaft Pulley
(2) Generator
(3) Power Steering Pump(4) Water Pump and Cooling Fan Pulley
(5) Idle Pulley
(6) Tension Pulley
(7) Drive Belt
The drive belt adjustment is not required as automatic
drive belt tensioner is equipped.
Inspection
Check drive belt for wear or damage, and replace with a
new one as necessary.
Installation
Install cooling fan assembly and tighten bolts/nuts to the
specified torque.
Torque : 22 Nꞏm (2.2 Kgꞏm/16 lb ft) for fan pulley
and fan bracket.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0 Kgꞏm/88.5 lb in) for fan and
clutch assembly.
NOTE: Fan belts for 6VE1 Gasoline Engine mounted on
98MY (UX) have been brought into one. As a result, the
rotating direction of a fan belt is opposite to the direction
o f c o o l i n g f a n f o r 9 2 t o 9 7 M Y 6 V D 1 w i t h n o
interchangeability.
Therefore, incorrect installation of a fan may cause the air
for cooling to flow in the opposite direction, this resulting
in the poor performance of the air-conditioner and a rise
temperature in engine cooling water.
Page 1070 of 6000

6C–3
ENGINE FUEL
Adhere to all Notices and Cautions.
All gasoline engines are designed to use only unleaded
gasoline. Unleaded gasoline must be used for proper
emission control system operation.
Its use will also minimize spark plug fouling and extend
engine oil life. Using leaded gasoline can damage the
emission control system and could result in loss of
emission warranty coverage.
All cars are equipped with an Evaporative Emission
Control System. The purpose of the system is to minimize
the escape of fuel vapors to the atmosphere.
Fuel Metering
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is in complete control
of this fuel delivery system during normal driving
conditions.
The intake manifold function, like that of a diesel, is used
only to let air into the engine. The fuel is injected by
separate injectors that are mounted over the intake
manifold.
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load and speed changes, which the MAP
sensor converts to a voltage output.
This sensor generates the voltage to change
corresponding to the flow of the air drawn into the engine.
The changing voltage is transformed into an electric
signal and provided to the ECM.
With receipt of the signals sent from the MAP sensor,
Intake Air Temperature sensor and others, the ECM
determines an appropriate fuel injection pulse width
feeding such information to the fuel injector valves to
effect an appropriate air/fuel ratio.
The Multiport Fuel Injection system utilizes an injection
system where the injectors turn on at every crankshaft
re vol u tion . Th e EC M con tro ls t he in je cto r on tim e so t ha t
the correct amount of fuel is metered depending on
driving conditions.
Two interchangeable “O” rings are used on the injector
that must be replaced when the injectors are removed.
The fuel rail is attached to the top of the intake manifold
and supplies fuel to all the injectors.
Fuel is recirculated through the rail continually while the
engine is running. This removes air and vapors from the
fuel as well as keeping the fuel cool during hot weather
operation.
The fuel pressure control valve that is mounted on the fuel
rail maintains a pressure differential across the injectors
under all operating conditions. It is accomplished by
controlling the amount of fuel that is recirculated back to
the fuel tank based on engine demand.
See Section “Driveability and Emission” for more
information and diagnosis.
Page 1081 of 6000
6D1–2
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
Battery
General Description
There are six battery fluid caps on top of the battery.
These are covered by a paper label.
The battery is completely sealed except for the six small
vent holes on the side. These vent holes permit the
escape of small amounts of gas generated by the battery.
This type of battery has the following advantages over
conventional batteries:
1. There is no need to add water during the entire
service life of the battery.
2. The battery protects itself against overcharging.
The battery will refuse to accept an extensive charge.
(A conventional battery will accept an excessive
charge, resulting in gassing and loss of battery fluid.)
3. The battery is much less vulnerable to self discharge
than a conventional type battery.
Diagnosis
1. Visual Inspection
Inspect the battery for obvious physical damage, such as
a cracked or broken case, which would permit electrolyte
loss.
Replace the battery if obvious physical damage is
discovered during inspection.
Check for any other physical damage and correct it as
necessary.
2. Hydrometer Check
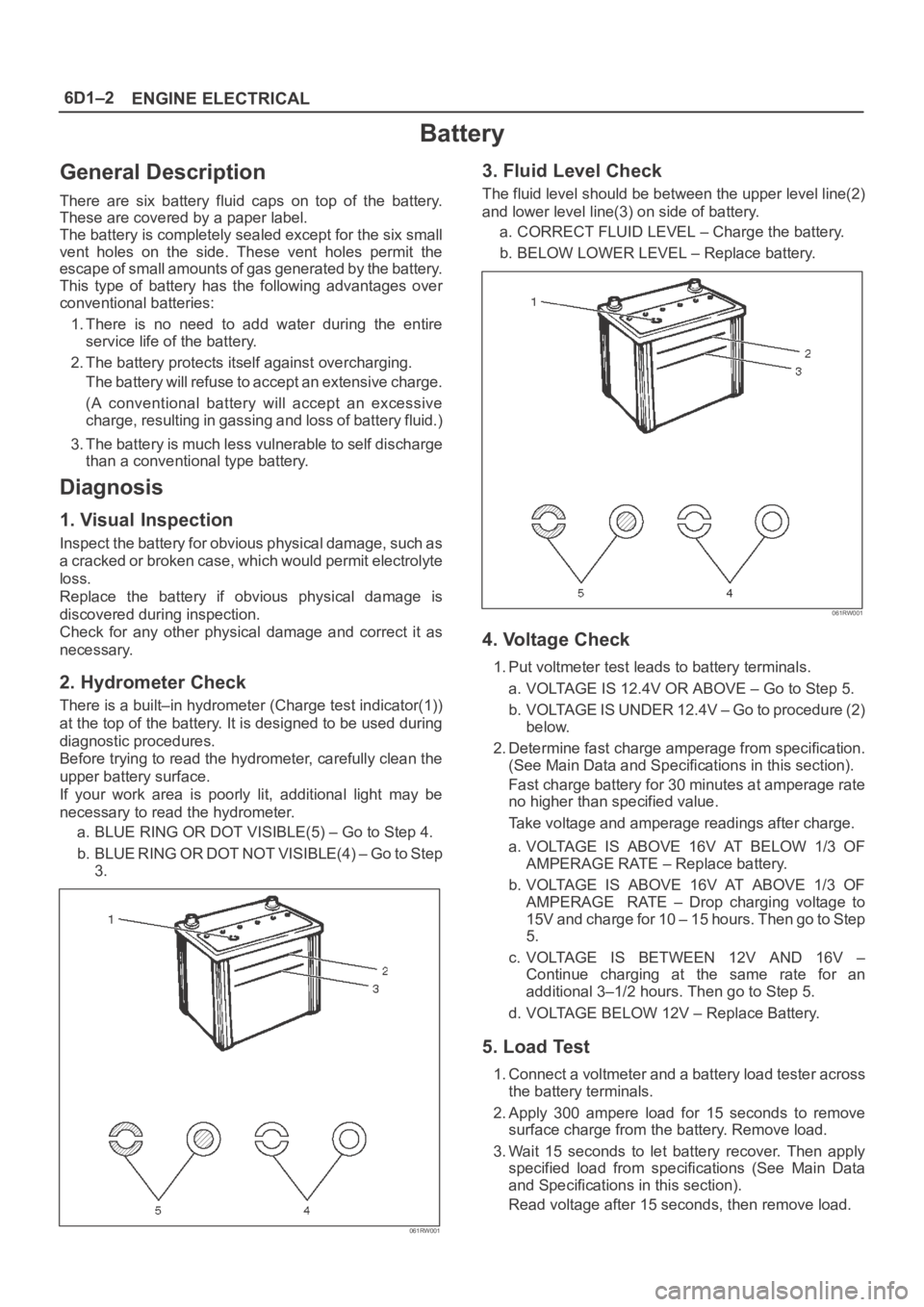
There is a built–in hydrometer (Charge test indicator(1))
at the top of the battery. It is designed to be used during
diagnostic procedures.
Before trying to read the hydrometer, carefully clean the
upper battery surface.
If your work area is poorly lit, additional light may be
necessary to read the hydrometer.
a. BLUE RING OR DOT VISIBLE(5) – Go to Step 4.
b . B L U E R I N G O R D O T N O T V I S I B L E ( 4 ) – G o t o S t e p
3.
061RW001
3. Fluid Level Check
The fluid level should be between the upper level line(2)
and lower level line(3) on side of battery.
a. CORRECT FLUID LEVEL – Charge the battery.
b. BELOW LOWER LEVEL – Replace battery.
061RW001
4. Voltage Check
1. Put voltmeter test leads to battery terminals.
a. VOLTAGE IS 12.4V OR ABOVE – Go to Step 5.
b. VOLTAGE IS UNDER 12.4V – Go to procedure (2)
below.
2. Determine fast charge amperage from specification.
(See Main Data and Specifications in this section).
Fast charge battery for 30 minutes at amperage rate
no higher than specified value.
Take voltage and amperage readings after charge.
a. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT BELOW 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Replace battery.
b. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT ABOVE 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Drop charging voltage to
15V and charge for 10 – 15 hours. Then go to Step
5.
c. VOLTAGE IS BETWEEN 12V AND 16V –
Continue charging at the same rate for an
additional 3–1/2 hours. Then go to Step 5.
d. VOLTAGE BELOW 12V – Replace Battery.
5. Load Test
1. Connect a voltmeter and a battery load tester across
the battery terminals.
2. Apply 300 ampere load for 15 seconds to remove
surface charge from the battery. Remove load.
3. Wait 15 seconds to let battery recover. Then apply
specified load from specifications (See Main Data
and Specifications in this section).
Read voltage after 15 seconds, then remove load.
Page 1082 of 6000

ENGINE ELECTRICAL6D1–3
a. VOLTAGE DOES NOT DROP BELOW THE
MINIMUM LISTED IN THE TABLE – The battery is
good and should be returned to service.
b. VOLTAGE IS LESS THAN MINIMUM LISTED –
Replace battery.
ESTIMATED TEMPERATURE
MINIMUM
VOLTAGE
FCV
70219.6
60169.5
50109.4
4049.3
30–19.1
20–78.9
10–128.7
0–188.5
The battery temperature must be estimated by feel
and by the temperature the battery has been
exposed to for the preceding few hours.
Battery Charging
Observe the following safety precautions when charging
the battery:
1. Never attempt to charge the battery when the fluid
level is below the lower level line on the side of the
battery. In this case, the battery must be replaced.
2. Pay close attention to the battery during charging
procedure.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate of
charge reduced if the battery feels hot to the touch.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the rate of
charge reduced if the battery begins to gas or spew
electrolyte from the vent holes.
3. In order to more easily view the hydrometer blue dot
or ring, it may be necessary to jiggle or tilt the battery.
4. Battery temperature can have a great effect on
battery charging capacity.
5. The sealed battery used on this vehicle may be either
quick charged or slow charged in the same manner as
other batteries.
Whichever method you decide to use, be sure that
you completely charge the battery. Never partially
charge the battery.
Jump Starting
Jump Starting with an Auxiliary (Booster)
Battery
CAUTION: Never push or tow the vehicle in an
attempt to start it. Serious damage to the emission
system as well as other vehicle parts will result.Treat both the discharged battery and the booster
battery with great care when using jumper cables.
Carefully follow the jump starting procedure, being
careful at all times to avoid sparking.
WARNING: FAILURE TO CAREFULLY FOLLOW THE
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE COULD RESULT IN
THE FOLLOWING:
1. Serious personal injury, particularly to your eyes.
2. Property damage from a battery explosion, battery
acid, or an electrical fire.
3. Damage to the electronic components of one or both
vehicles particularly.
Never expose the battery to an open flame or electrical
spark. Gas generated by the battery may catch fire or
explode.
Remove any rings, watches, or other jewelry before
working around the battery. Protect your eyes by wearing
an approved set of goggles.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with your eyes
or skin.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with fabrics or
painted surfaces.
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.
Should battery fluid come in contact with your eyes, skin,
fabric, or a painted surface, immediately and thoroughly
rinse the affected area with clean tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come in
contact with the positive battery terminal, or any other
metal surface of the vehicle. This will protect against a
short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of reach of young children.
Jump Starting Procedure
1. Set the vehicle parking brake.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the selector level in the “PARK”
position.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission,
place the shift lever in the “NEUTRAL” position.
Turn “OFF” the ignition.
Turn “OFF” all lights and any other accessory
requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built–in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built–in hydrometer is
completely clear, do not try to jump start.
3. Attach the end of one jumper cable to the positive
terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive
terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other. This will
cause a ground connection, effectively neutralizing
the charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt rating.
Page 1089 of 6000

6D2–4
IGNITION SYSTEM
Spark Plug
Removal
1. Remove spark plugs.
Inspection and Repair
The spark plug affects entire engine performance and
therefore its inspection is very important.
Check electrode and insulator for presence of cracks,
and replace if any.
Check electrode for wear, and replace if necessary.
Check gasket for damage, and replace if necessary.
Measure insulation resistance with an ohmmeter, and
replace if faulty.
Adjust spark plug gap to 1.0 mm (0.04 in) 1.1 mm
(0.043 in).
Check fuel and electrical systems if spark plug is
extremely dirty.
Use spark plugs having low heat value (hot type plug)
if fuel and electrical systems are normal.
Use spark plugs having high heat value (cold type
plug) if insulator and electrode are extremely burned.
Sooty Spark Plugs
Much deposit of carbon or oil on the electrode and
insulator of spark plug reduces the engine performance.
Possible causes:
Too rich mixture
Presence of oil in combustion chamber
Incorrectly adjusted spark plug gap
Burning Electrodes
This fault is characterized by scorched or heavily oxidized
electrode or blistered insulator nose.
Possible causes:
Too lean mixture
Improper heat value
Measuring Insulation Resistance
Measure insulation resistance using a 500 volt
megaohm meter.
Replace spark plugs if measured value is out of
standard.
Insulation resistance: 50 M
or more
011RS010
Cleaning Spark Plugs
Clean spark plugs with a spark plug cleaner.
Raise the ground electrode to an angle of 45 to 60
degrees. If electrode is wet, dry it before cleaning.
After spark plug is thoroughly cleaned, check
insulator for presence of cracks.
Clean threads and metal body with a wire brush.
File the electrode tip if electrode is extremely worn.
Bend the ground electrode to adjust the spark plug
gap.
011RS011
Installation
1. Spark plugs
Tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Torque: 18 Nꞏm (1.8 Kgꞏm/13 lb ft)