Gas OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1119 of 6000
6E–2
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Primary System-Based Diagnostic 6E–50. . . . . . . . .
Primary System-Based Diagnostic 6E–50. . . . . . .
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor 6E–50. . . . .
HO2S Heater 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim Cell Diagnostic Weights 6E–50. . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check 6E–51.
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis 6E–54. . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis 6E–60. . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System Check 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Pressure Test 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and Fuel
Injector Balance Test Procedure 6E–60. . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor Diagnosis 6E–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Diagnosis 6E–65
Multiple PCM Information Sensor DTCS Set 6E–65
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Diagnosis
(For except EXPORT and
SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Tech 2 Data Definitions and Ranges 6E–68
Typical Scan Data Values 6E–70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–74. . . . . . .
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) “ON”
Steady 6E–77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run 6E–79. . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Electrical Test 6E–85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Diagnosis 6E–88. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check 6E–93. . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) System Check
(Engine Knock, Poor Performance, or Poor
Economy) 6E–95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
Check 6E–97. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Output
Check 6E–99. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes 6E–101. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0101
MAF System Performance 6E–104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0102
MAF Sensor Circuit Low Frequency 6E–107. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0103
MAF Sensor Circuit High Frequency 6E–110. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–112. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108
MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–115. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0112
IAT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–118. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0113
IAT Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–121. . . . . . . . . . Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0117
ECT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–124. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0118
ECT Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–127. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0121
TP System Performance 6E–130. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0122
TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–133. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123
TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–136. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131
HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–139. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0132
HO2S Circuit High Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0134
HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0151
HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–148. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0152
HO2S Circuit HIGH Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0171
Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 1 6E–154. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0172
Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 1 6E–158. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0174
Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 6E–162. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0175
Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 2 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0201
Injector 1 Control Circuit 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0202
Injector 2 Control Circuit 6E–173. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0203
Injector 3 Control Circuit 6E–176. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0204
Injector 4 Control Circuit 6E–179. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0205
Injector 5 Control Circuit 6E–182. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0206
Injector 6 Control Circuit 6E–185. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0325
KS Module Circuit 6E–188. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0327
KS Sensor Circuit 6E–190. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336
58X Reference Signal Circuit 6E–193. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0337
CKP Sensor Circuit Low Frequency 6E–195. . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0341
CMP Sensor Circuit Performance 6E–198. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0342
CMP Sensor Circuit Low 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1120 of 6000

6E–3 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351
Ignition 1 Control Circuit 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0352
Ignition 2 Control Circuit 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0353
Ignition 3 Control Circuit 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0354
Ignition 4 Control Circuit 6E–215. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0355
Ignition 5 Control Circuit 6E–218. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0356
Ignition 6 Control Circuit 6E–221. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0402
EGR Pintle Crank Error 6E–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0404
EGR Open Stuck 6E–226. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0405
EGR Low Voltage 6E–228. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0406
EGR High Voltage 6E–231. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0502
VSS Circuit Low Input 6E–234. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0562
System Voltage Low 6E–237. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0563
System Voltage High 6E–239. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601
PCM Memory 6E–240. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1154
HO2S Circuit Transition Time Ratio Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1171
Fuel System Lean During Acceleration 6E–245. . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1380
ABS Rough Road ABS System Fault 6E–248. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1404
EGR Closed Stuck 6E–249. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1508
IAC System Low RPM 6E–251. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1509
IAC System High RPM 6E–254. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1618
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) PCM
Interprocessor Communication Error 6E–257. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1625
PCM Unexpected Reset 6E–258. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1640
Driver-1-Input High Voltage 6E–259. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 6E–262. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Default Matrix Table 6E–288. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 6E–291. . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–292. . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–292.
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) 6E–293. . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–295. . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) 6E–296. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor 6E–297. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–297.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–298. . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–298. . . . . . . . .
EEPROM 6E–300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Steering Pressure (PSP) Switch 6E–300
. . . .
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 6E–301. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–302. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Cleaner/Air Filter 6E–303. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–304. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common Chamber 6E–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Cable Assembly 6E–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Pedal Replacement 6E–308. . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter Cap 6E–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter 6E–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Gauge Unit 6E–313. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injectors 6E–314. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pressure Regulator 6E–315. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System 6E–317. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Assembly 6E–318. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Relay 6E–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Rail Assembly 6E–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank 6E–321. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Body (TB) 6E–323. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System 6E–324. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Catalytic Converter 6E–325. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Conditioning Relay 6E–325. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister Hoses 6E–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister 6E–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid 6E–327. . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank Vent Valve 6E–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve 6E–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve 6E–329.
Wiring and Connectors 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Connectors and Terminals 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . .
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted Shielded
Cable 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Twisted Leads 6E–331. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Weather-Pack Connector 6E–332. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Com-Pack III 6E–333. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Metri-Pack 6E–333. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (PCM and Sensors) 6E–335. . .
58X Reference PCM Input 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Request Signal 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–335. . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor and
Signal 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–335
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EEPROM) 6E–336. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensors 6E–336. . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–336. . . . .
Page 1121 of 6000

6E–4
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Knock Sensor 6E–337. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Control 6E–337. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor 6E–337. . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–338
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–338. . . . . . .
PCM Function 6E–338. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Components 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Voltage Description 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Input/Outputs 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Service Precautions 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reprogramming The PCM 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
Sensor 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Range Switch 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . .
Use of Circuit Testing Tools 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrostatic Discharge Damage 6E–341. . . . . . . . .
Upshift Lamp 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Air Induction) 6E–341. . . . . . . .
Air Induction System 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Fuel Metering) 6E–341. . . . . . .
Acceleration Mode 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Controls 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Voltage Correction Mode 6E–341. . . . . . . .
CMP Signal 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clear Flood Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Deceleration Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Speed/Vehicle Speed/Fuel
Disable Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Cutoff Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injector 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System Components 6E–342. . . . . . Fuel Metering System Purpose 6E–342. . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pressure Regulator 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Rail 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Run Mode 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Starting Mode 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Body Unit 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Electronic Ignition
System) 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 6E–344. . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–345. . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition 6E–345. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition Coils 6E–345. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition Control 6E–345. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition Control PCM Output 6E–347. . . . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) PCM Input 6E–347
. . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–347. . . . . . .
Spark Plug 6E–347. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Clutch Diagnosis 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Request Signal 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System) 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Purpose 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear EGR Valve 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear EGR Control 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear EGR Valve Operation and Results
of Incorrect Operation 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Pintle Position Sensor 6E–350. . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) System) 6E–350. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose 6E–350. . .
Crankcase Ventilation System Operation 6E–350.
Page 1136 of 6000
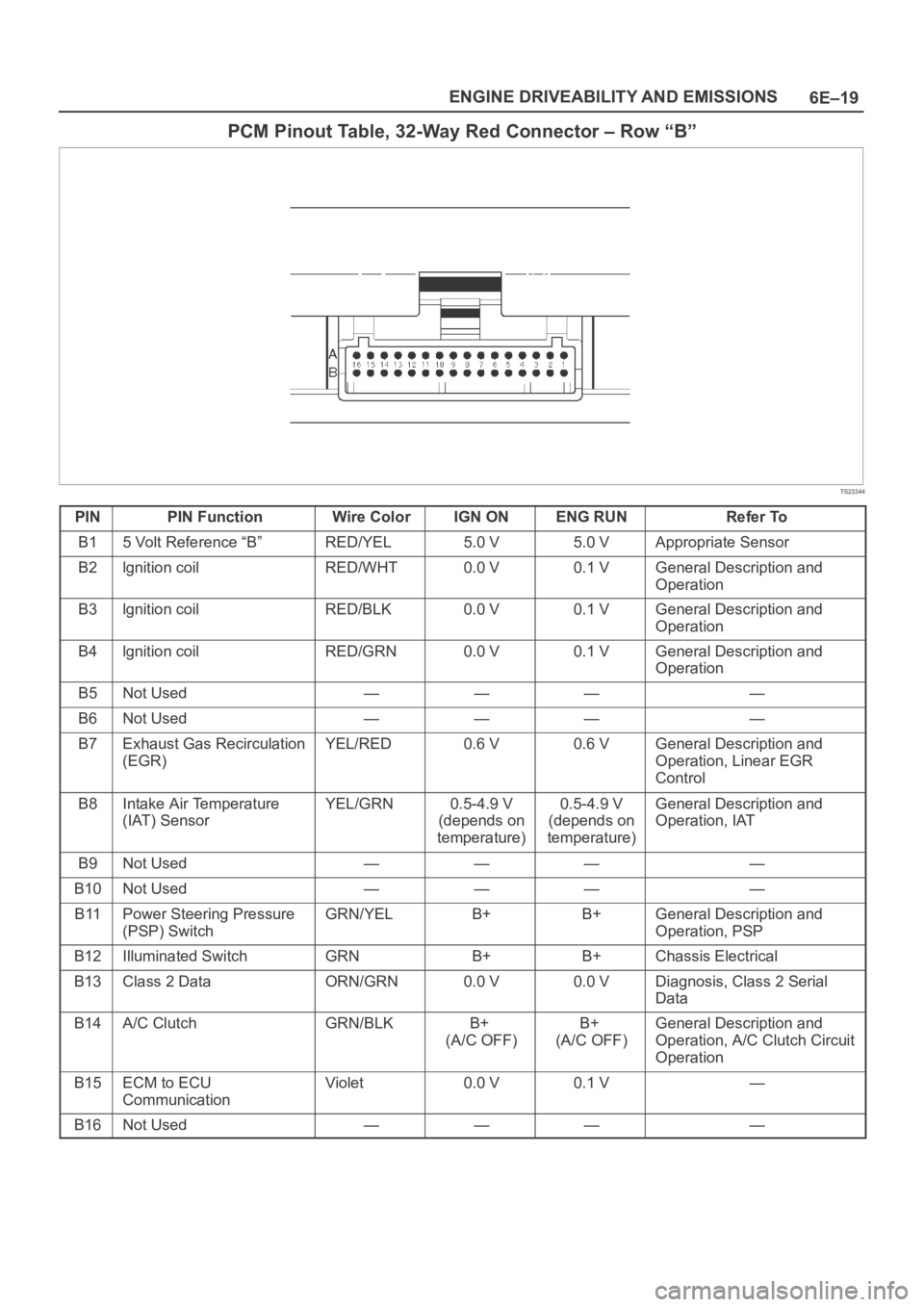
6E–19 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red Connector – Row “B”
TS23344
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
B15 Volt Reference “B”RED/YEL5.0 V5.0 VAppropriate Sensor
B2lgnition coilRED/WHT0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B3lgnition coilRED/BLK0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B4lgnition coilRED/GRN0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B5Not Used————
B6Not Used————
B7Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR)YEL/RED0.6 V0.6 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Linear EGR
Control
B8Intake Air Temperature
(IAT) SensorYEL/GRN0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)General Description and
Operation, IAT
B9Not Used————
B10Not Used————
B11Power Steering Pressure
(PSP) SwitchGRN/YELB+B+General Description and
Operation, PSP
B12Illuminated SwitchGRNB+B+Chassis Electrical
B13Class 2 DataORN/GRN0.0 V0.0 VDiagnosis, Class 2 Serial
Data
B14A/C ClutchGRN/BLKB+
(A/C OFF)B+
(A/C OFF)General Description and
Operation, A/C Clutch Circuit
Operation
B15ECM to ECU
CommunicationViolet0.0 V0.1 V—
B16Not Used————
Page 1141 of 6000

6E–24
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue Connector – Row “E”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA)
TS23346
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
E1Transmission Output Shaft
Sensor (TOSS) HighRED0.0 V0.1 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
E2Transmission Output Shaft
Sensor (TOSS) LowWHT0.0 V0.0 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
E3Pressure Control Solenoid
LowPPL/RED0.0 V1.1 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
E4Pressure Control Solenoid
HighPPL/WHT0.0 V4.9 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
E5Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Control HighBLK/YELB+B+General Description and
Operation, EGR Control
E6Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Control LowYELB+B+General Description and
Operation, EGR Control
E7Transmission Range
Signal “B”BLU/YEL0.0 V0.0 VAutomatic Transmission
(4L30E)
E8Throttle Position (TP)
SensorBLU0.5-0.8 V0.5-0.8 V
(at idle)General Description and
Operation, Throttle Position
Sensor
E9Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT)
SensorBLU/RED0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)General Description and
Operation, Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) Sensor
E10Not Used————
E11Crankshaft Position (CKP)
Sensor +5 Volt ReferenceYEL/RED5.0 V or less
than 1.0 V5.0 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Crankshaft
Position Sensor
E12Transmission Range
Signal “A”BLU/WHTB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
E13Fuel Pump (FP) RelayRED/WHT0.0 VB+On-Vehicle Service, Fuel
Pump Relay
E14Shift High (BAND APPLY)BRN/WHTB+B+Automatic Transmission
(4L30E)
Page 1146 of 6000
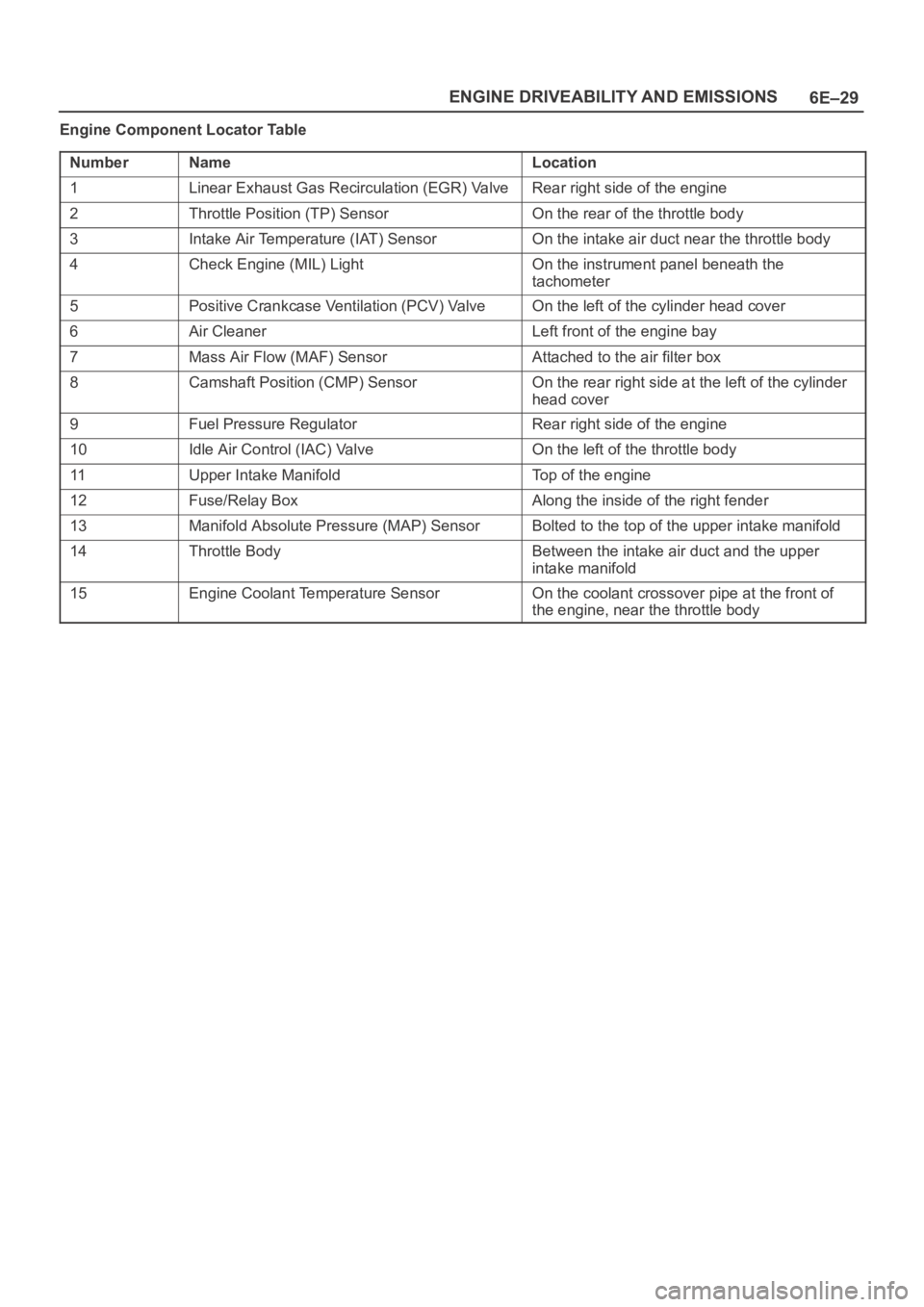
6E–29 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body
Page 1148 of 6000
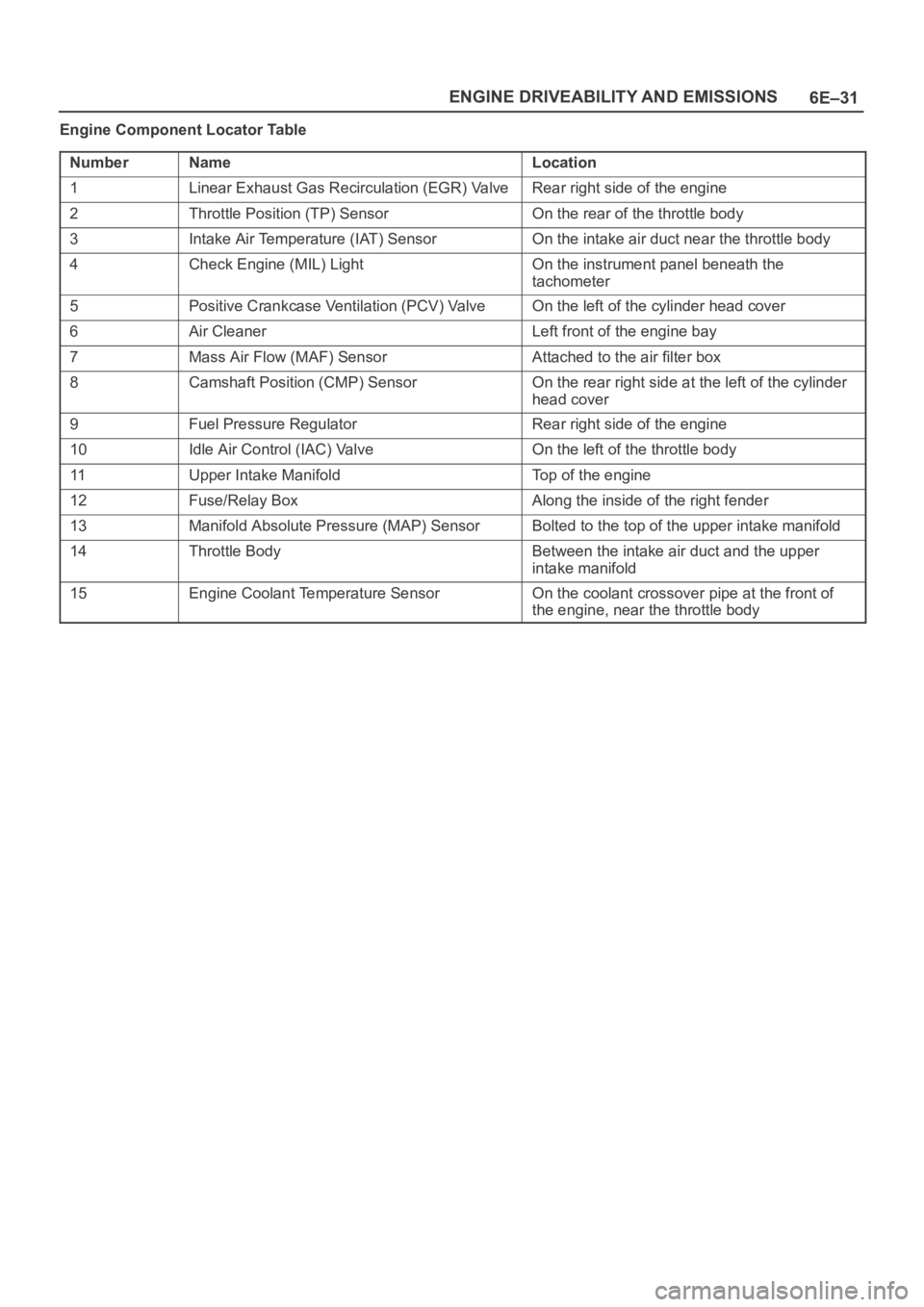
6E–31 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body
Page 1155 of 6000

6E–38
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Service Information
OBD Serviceablity Issues
The list of non-vehicle faults that could affect the
performance of the OBD system has been compiled.
These non-vehicle faults vary from environmental
conditions to the quality of fuel used.
The illumination of the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) due to
a non-vehicle fault could lead to misdiagnosis of the
vehicle, increased warranty expense and customer
dissatisfaction. The following list of non-vehicle faults
does not include every possible fault and may not apply
equally to all product lines.
Fuel Quality
Using fuel with the wrong octane rating for your vehicle
may cause driveability problems. Many of the major fuel
companies advertise that using “premium” gasoline will
improve the performance of your vehicle. Most premium
fuels use alcohol to increase the octane rating of the fuel.
Although alcohol-enhanced fuels may raise the octane
rating, the fuel’s ability to turn into vapor in cold
temperatures deteriorates. This may affect the starting
ability and cold driveability of the engine.
Low fuel levels can lead to fuel starvation, lean engine
operation, and eventually engine misfire.
Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Something as simple as a
high-performance exhaust system that affects exhaust
system back pressure could potentially interfere with the
operation of the EGR valve and thereby turn on the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp). Small leaks in the exhaust
system near the post catalyst oxygen sensor can also
cause the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the MIL (“Check
Engine” lamp).
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain-soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL (“Check Engine”
lamp).
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the MIL
(“Check Engine” lamp) to turn on if the vehicle is not
maintained properly. Restricted air filters, fuel filters, and
crankcase deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper
oil viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics, vehicle
maintenance schedules must be more closely followed.Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
PCM detects a fault on a related system or component.
One example would be that if the PCM detected a Misfire
fault, the diagnostics on the catalytic converter would be
suspended until Misfire fault was repaired. If the Misfire
fault was severe enough, the catalytic converter could be
damaged due to overheating and would never set a
Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault was repaired and the
Catalyst diagnostic was allowed to run to completion. If
this happens, the customer may have to make two trips to
the dealership in order to repair the vehicle.
Maintenance Schedule
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule.
Visual / Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any diagnostic
procedure or diagnosing the cause of an emission test
failure. This can often lead to repairing a problem without
further steps. Use the following guidelines when
performing a visual/physical inspection:
Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts,
disconnects, and correct routing.
Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other
components.
Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper
connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched wires,
contact with sharp edges or contact with hot exhaust
manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain when
performing diagnostic procedures could result in an
incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to effec-
tively use this section of the Service Manual.
Serial Data Communications
Class II Serial Data Communications
This vehicle utilizes the “Class II” communication system.
Each bit of information can have one of two lengths: long
or short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by
transmitting and receiving multiple signals over a single
wire. The messages carried on Class II data streams are
also prioritized. If two messages attempt to establish
communications on the data line at the same time, only
the message with higher priority will continue. The device
with the lower priority message must wait. The most
significant result of this regulation is that it provides Tech 2
manufacturers with the capability to access data from any
make or model vehicle that is sold.
Page 1167 of 6000

6E–50
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Primary System-Based Diagnostic
Primary System-Based Diagnostic
There are primary system-based diagnostics which
evaluate system operation and its effect on vehicle
emissions. The primary system-based diagnostics are
listed below with a brief description of the diagnostic
function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control heated oxygen sensors (Bank 1 HO2S 1
and Bank 2 HO2S 1) are diagnosed for the following
conditions:
Inactive signal (output steady at bias voltage – approx.
450 mV)
Signal fixed high
Signal fixed low
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must
be replaced. DO NOT attempt to repair the wiring,
connector or terminals. In order for the sensor to function
properly, it must have clean reference air provided to it.
This clean air reference is obtained by way of the oxygen
sensor wire(s). Any attempt to repair the wires, connector
or terminals could result in the obstruction of the
reference air and degrade oxygen sensor performance.
Refer to
On-Vehicle Service, Heated Oxygen Sensors.
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor
The main function of the fuel control heated oxygen
sensors is to provide the control module with exhaust
stream oxygen content information to allow proper fueling
and maintain emissions within mandated levels. After it
reaches operating temperature, the sensor will generate
a voltage, inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen
present in the exhaust gases. The control module uses
the signal voltage from the fuel control heated oxygen
sensors while in closed loop to adjust fuel injector pulse
width. While in closed loop, the PCM can adjust fuel
delivery to maintain an air/fuel ratio which allows the best
combination of emission control and driveability.
HO2S Heater
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the amount
of time required for closed loop fuel control to begin
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The
oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of
time required for fuel control sensors (Bank 1 HO2S 1 and
Bank2 HO2S 1) to become active. Oxygen sensor
heaters are required to maintain a sufficiently high
temperature which allows accurate exhaust oxygen
content readings further away from the engine.
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation
This system monitors the averages of short-term and
long-term fuel trim values. If these fuel trim values stay at
their limits for a calibrated period of time, a malfunction is
indicated. The fuel trim diagnostic compares the
averages of short-term fuel trim values and long-term fuel
trim values to rich and lean thresholds. If either value is
within the thresholds, a pass is recorded. If both values
are outside their thresholds, a rich or lean DTC will be
recorded.
The fuel trim system diagnostic also conducts an intrusive
test. This test determines if a rich condition is being
caused by excessive fuel vapor from the EVAP canister.
In order to meet OBD requirements, the control module
uses weighted fuel trim cells to determine the need to set
a fuel trim DTC. A fuel trim DTC can only be set if fuel trim
counts in the weighted fuel trim cells exceed
specifications. This means that the vehicle could have a
fuel trim problem which is causing a problem under
certain conditions (i.e., engine idle high due to a small
vacuum leak or rough idle due to a large vacuum leak)
while it operates fine at other times. No fuel trim DTC
would set (although an engine idle speed DTC or HO2S
DTC may set). Use a Tech 2 to observe fuel trim counts
while the problem is occurring.
A fuel trim DTC may be triggered by a number of vehicle
faults. Make use of all information available (other DTCs
stored, rich or lean condition, etc.) when diagnosing a fuel
trim fault.
Fuel Trim Cell Diagnostic Weights
N o f u e l t r i m D T C w i l l s e t r e g a r d l e s s o f t h e f u e l t r i m c o u n t s
in cell 0 unless the fuel trim counts in the weighted cells
are also outside specifications. This means that the
vehicle could have a fuel trim problem which is causing a
problem under certain conditions (i.e. engine idle high due
to a small vacuum leak or rough due to a large vacuum
leak) while it operates fine at other times. No fuel trim
DTC would set (although an engine idle speed DTC or
HO2S DTC may set). Use a Tech 2 to observe fuel trim
counts while the problem is occurring.
Page 1177 of 6000

6E–60
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis
If the engine cranks but will not run or immediately stalls,
the Engine Cranks But Will Not Start chart must be used
to determine if the failure is the ignition system or the fuel
system. If DTC P0341, or P0336 is set, the appropriate
diagnostic trouble code chart must be used for diagnosis.
If a misfire is being experienced with no DTC set, refer to
the
Symptoms section for diagnosis.
Fuel Metering System Check
Some failures of the fuel metering system will result in an
“Engine Cranks But Will Not Run” symptom. If this
condition exists, refer to the
Cranks But Will Not Run
chart. This chart will determine if the problem is caused
by the ignition system, the PCM, or the fuel pump
electrical circuit.
Refer to
Fuel System Electrical Test for the fuel system
wiring schematic.
If there is a fuel delivery problem, refer to
Fuel System
Diagnosis
, which diagnoses the fuel injectors, the fuel
pressure regulator, and the fuel pump. If a malfunction
occurs in the fuel metering system, it usually results in
either a rich HO2S signal or a lean HO2S signal. This
condition is indicated by the HO2S voltage, which causes
the PCM to change the fuel calculation (fuel injector pulse
width) based on the HO2S reading. Changes made to the
fuel calculation will be indicated by a change in the long
term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a Tech
2. Ideal long term fuel trim values are around 0%; for a
lean HO2S signal, the PCM will add fuel, resulting in a fuel
trim value above 0%. Some variations in fuel trim values
are normal because all engines are not exactly the same.
If the fuel trim values are greater than +23%, refer to
DTC
P0131, DTC P0151, DTC P0171, and DTC 1171
f o r i t e m s
which can cause a lean HO2S signal.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The Tech 2 displays the IAC pintle position in counts. A
count of “0” indicates the PCM is commanding the IAC
pintle to be driven all the way into a fully-seated position.
This is usually caused by a large vacuum leak.
The higher the number of counts, the more air is being
commanded to bypass the throttle blade. Refer to IAC
System Check in order to diagnose the IAC system.
Refer to
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling in
Symptoms for other possible causes of idle problems.
Fuel System Pressure Test
A fuel system pressure test is part of several of the
diagnostic charts and symptom checks. To perform this
test, refer to
Fuel Systems Diagnosis.
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and
Fuel Injector Balance Test Procedure
T32003
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Relieve the fuel pressure by connecting the
5-8840-0378-0 Fuel Pressure Gauge to the fuel
pressure connection on the fuel rail.
CAUTION: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the fuel
pressure connection. The towel will absorb any fuel
leakage that occurs during the connection of the fuel
pressure gauge. Place the towel in an approved
container when the connection of the fuel pressure
gauge is complete.
Place the fuel pressure gauge bleed hose in an
approved gasoline container.
With the ignition switch “OFF,” open the valve on the
fuel pressure gauge.
3. Record the lowest voltage displayed by the DVM
after the first second of the test. (During the first
second, voltage displayed by the DVM may be
inaccurate due to the initial current surge.)
Injector Specifications:
Resistance Ohms
Voltage Specification at
10
C-35C (50F-95F)
11.8 – 12.65.7 – 6.6
The voltage displayed by the DVM should be within
the specified range.
The voltage displayed by the DVM may increase
throughout the test as the fuel injector windings
warm and the resistance of the fuel injector windings
changes.