engine OPEL GT-R 1973 Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: GT-R, Model: OPEL GT-R 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 327 of 625
6C- 361973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
FUEL SYSTEM
ALL MODELS
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
Fuel Pump. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . .Evaporation Control System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .DIAGNOSIS:
(Not Applicable)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS:
Cleaning Fuel Pump Strainer.,....................................
*.Evaporation Control System
. . . . . . . . . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAJOR REPAIR:
Fuel Tank
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Fuel Lines and Fuel Tank Gauge Units
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS:
Fuel System Specifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page No.6C-366C-376C-376C-386C-396C-416C-41
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL PUMPThe 1.9 liter engine uses a push rod type fuel pump.
The push rod is actuated by an eccentric on the
distributor shaft. The push rod is held in contact
with the eccentric at all times by a push rod spring.
Each time the push rod is on the high part of the
eccentric, the lighter diaphragm spring will push the
diaphragm to replace any fuel used in the carburetor.
The diaphragm seldom operates through a full
stroke; under normal driving conditions, the dia-
phragm moves only a few tenths of an inch.
Fuel pump pressure is determined by the compres-
sion of the diaphragm spring. Low pressure or pres-
sure leak- down generally indicates a leaky
diaphragm or check valves.
Two holes in the lower part of the fuel pump serve
to ventilate the space below the diaphragm and to
drain any fuel which may have entered. If any fuel
comes from these holes, this indicates a defective
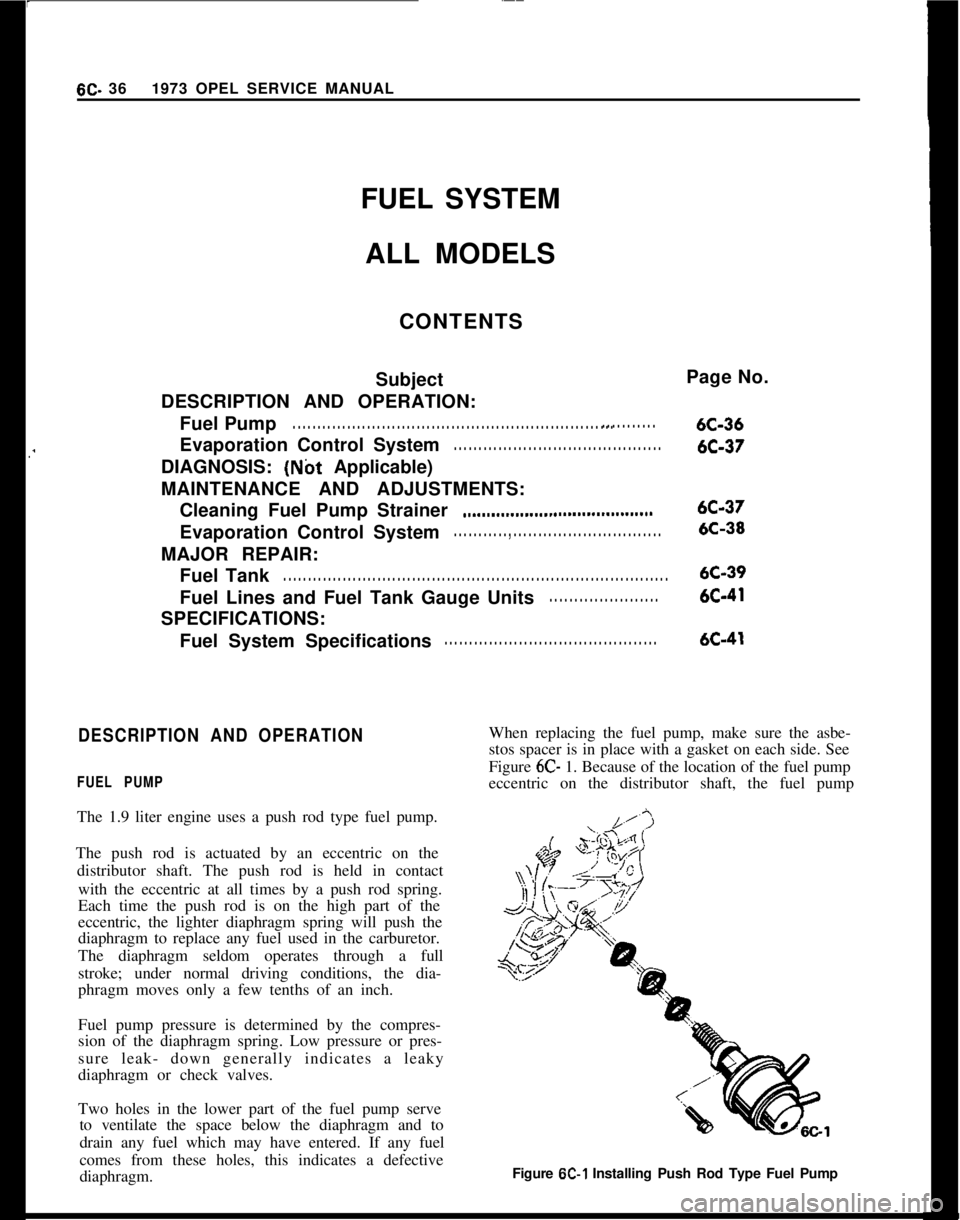
diaphragm.When replacing the fuel pump, make sure the asbe-
stos spacer is in place with a gasket on each side. See
Figure 6C- 1. Because of the location of the fuel pump
eccentric on the distributor shaft, the fuel pump
Figure
6C-1 Installing Push Rod Type Fuel Pump
Page 328 of 625
FUEL SYSTEMSC- 37
must always be removed before the distributor can be
removed.
EVAPORATION CONTROL SYSTEM1. The function of the fuel evaporation control sys-
tem is to absorb the fuel vapors developing in the fuel
tank, especially when vehicle is parked, due to at-
mospheric pressure and temperature influences, and
to release these fuel vapors during vehicle operation.
2. This system utilizes the property of the activated
carbon to absorb and expel fuel vapors. The activated
carbon container is installed on the left front side of
the engine compartment. The fuel tank has a
non-vented tiller cap. Vent hoses are joined in the area of
the tank. A plastic evaporation line leads from there
along vehicle underbody to the activated carbon con-
tainer.
3. A small tube above the throttle valve body con-
nects the carburetor to the activated carbon con-
tainer. In this way, the fuel vapor collected in the
activated carbon container is fed through the carbu-
retor into the combustion chambers during engine
operation.
4. The carburetor is provided with an internal and
outside ventilation, the activated carbon container is
also connected to the outside ventilation (only effec-
tive when engine is idling). In this way, the fuel
vapors escaping to the outside during engine idle are
collected by the activated carbon container and fed
into the combustion chambers.
5. The vent lines are connected to the upper part of
the activated carbon container. Fresh air enters
through a foam rubber filter at the lower part andflows, together with the fuel vapor, to the carburetor.
Metered bores in the hose fittings of the fuel tank
control the air
- and fuel vapor flow through the
activated carbon container to the carburetor, and the
pressure release in the fuel tank and ensure complete
purging of the carbon container.
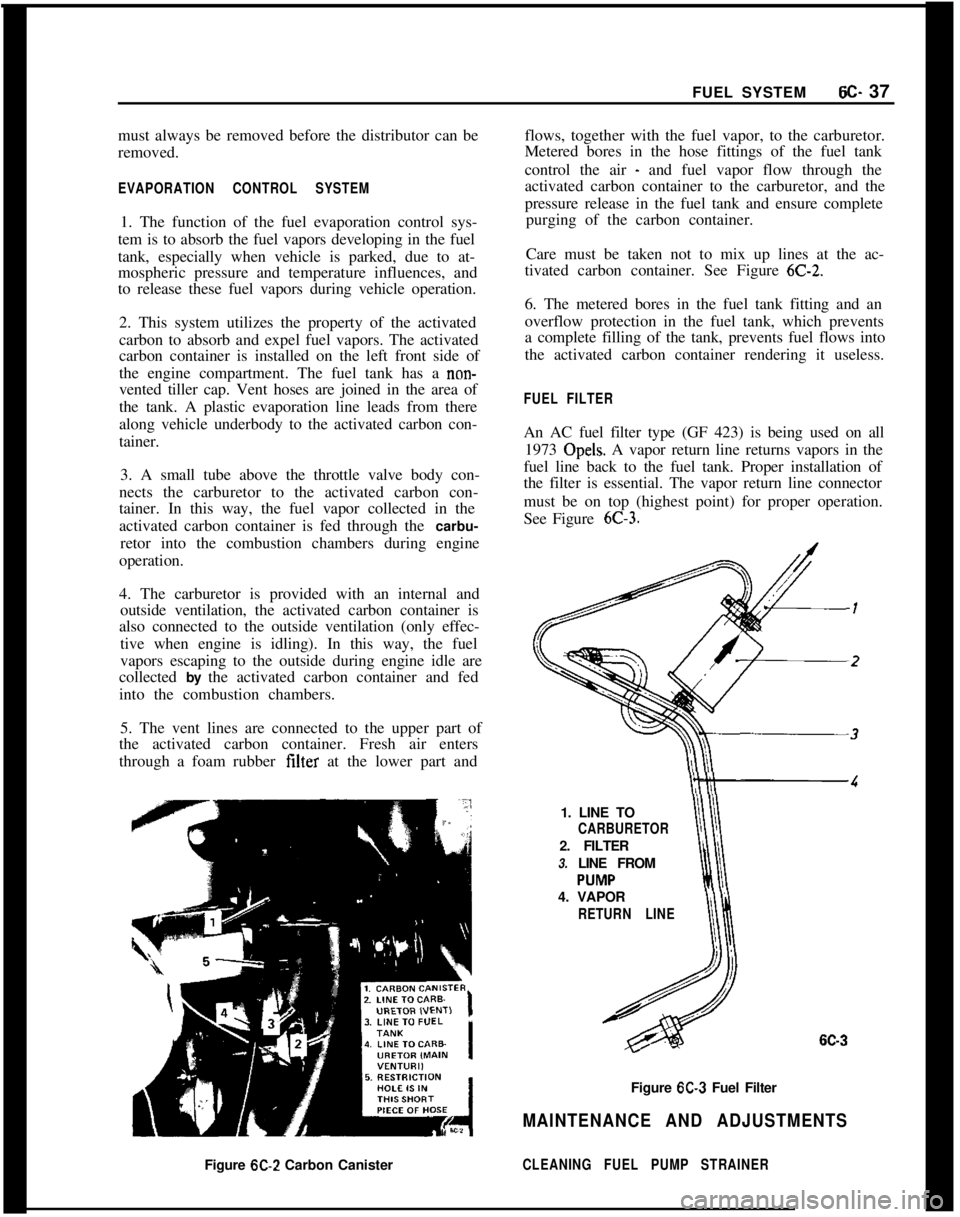
Care must be taken not to mix up lines at the ac-
tivated carbon container. See Figure
6C-2.6. The metered bores in the fuel tank fitting and an
overflow protection in the fuel tank, which prevents
a complete filling of the tank, prevents fuel flows into
the activated carbon container rendering it useless.
FUEL FILTERAn AC fuel filter type (GF 423) is being used on all
1973 Opels. A vapor return line returns vapors in the
fuel line back to the fuel tank. Proper installation of
the filter is essential. The vapor return line connector
must be on top (highest point) for proper operation.
See Figure
6C-3.1. LINE TO
CARBURETOR2. FILTER
3. LINE FROM
4. VAPOR
RETURN LINE
6C-3Figure
6C-3 Fuel Filter
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTSFigure
6C-2 Carbon CanisterCLEANING FUEL PUMP STRAINER
Page 329 of 625
6C- 381973 OPEL SERVICE MANUALCAUTION:Because the fuel pump is below fuel tank
level, fuel
will drain from the tank. when the supply
hne is disconnected from the fuel pump.1. Pull fuel supply line and rubber connector from
fuel pump. Plug rubber connector to prevent fuel
loss.2. Remove fuel pump cap, gasket and plastic
strainer.
3. Cover center opening in sediment bowl with finger
and blow out sediment bowl with compressed air.
4. Wash plastic strainer in solvent; if strainer does
not clean-up or is damaged, replace strainer.
5. Install clean parts, noting the following:
(a) Strainer must be properly seated with projections
facing upward.(b) A new cap gasket must be positioned over
strainer.
(c) Sealing ring must be in place on cap retaining
screw.6. Reconnect fuel supply line. Start engine and check
for leaks.
EVAPORATION CONTROL SYSTEMProper performance of the system requires the use of
a non-vented fuel tank cap, hose connections be leak-
free, and all hoses routed correctly to avoid a
pinched or blocked line.
Maintenance requirements demand only that the ac-
cumulator purge air tilter, an oiled foam filter assem-
bled in the bottom of the canister, be replaced at
12,CKO mile intervals. Under extremely dusty condi-
tions, more frequent attention may be required.
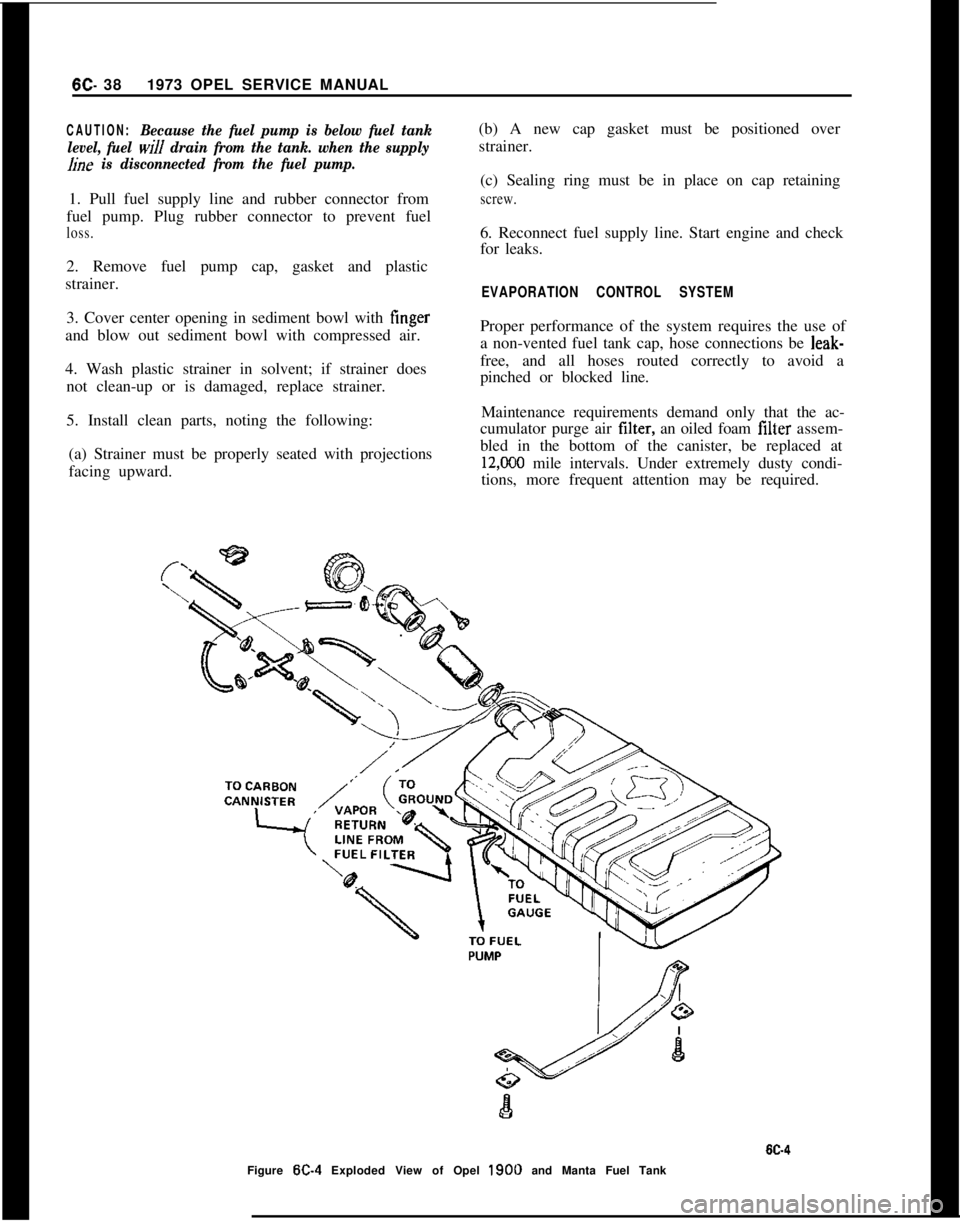
Figure
W-4 Exploded View of Opel 1900 and Manta Fuel Tank
Page 335 of 625

SE- 441973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
CARBURETOR AND THROTTLE LINKAGE
ALL MODELS
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
Carburetor
. . . . . . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .DIAGNOSIS:
Carburetor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS:
Idle Speed and Mixture Adjustments
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Fast Idle Speed Adjustment
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Throttle Linkage Adjustment
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . , . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAJOR REPAIR:
RemoveandInstallCarburetor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . I...Throttle Linkage Removal
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .OverhaulCarburetor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS:
Carburetor
Specifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page No.
6E-44
6E-49
6E-50
6E-51
6E-51
6E-52
6E-53
6E-53
6E-58
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CARBURETORThe two-barrel carburetor for all 1973 Opel1
19G0,Manta and GT models is a down-draft carburetor
with two barrels of 1.25 inch diameter each. It has
an automatic choke and a secondary valve operated
by a vacuum diaphragm, except when installed in an
Opel GT. In the GT, the secondary throttle valve is
operated by mechanical linkage from the primary
throttle valve.
The two-barrel carburetor consists of three main
parts
- throttle body, float chamber and air horn.
Each barrel is a separate system, but both barrels
discharge into a common inlet in the intake mani-
fold. The secondary barrel does not have a choke
valve or an accelerator pump. See Figure
6E-2.The throttle valve of the primary barrel is opened
through the throttle linkage. When the primary
throttle valve is almost open, at approximately half
of the maximum engine RPM, the secondary throttlevalve is opened by vacuum applied through a
vacuum diaphragm case. See Figure
6E-3. The sec-
ondary throttle valve on the GT model is opened by
mechanical linkage from the primary throttle shaft.
Choke SystemThe automatic choke is operated by a bi-metal
spring. The tension of the spring
- depending on
temperature of the heater coil
- decreases with rising
temperature and the choke valve opens progressively
until it is completely opened at engine operating tem-
perature. The choke valve is off-set so that choke
valve opening increases as air flow increases.
If the choke valve is closed, the throttle valve is
opened slightly to provide a fast idle speed. This is
done through a cam, abutment lever and throttle
connecting link. With the throttle valve opened
slightly, the vacuum during cranking can take effect
up to the choke valve, thereby drawing ample fuel
out of the main nozzle. See Figure
6E-4.With rising temperature of the heater coil, the choke
Page 336 of 625

CARBURETOR AND THROTTLE LINKAGE6E- 4512345678Sectional View Of 19 US Carburetor (both barrels)
1 PIug(transition channels, secondary barrel)
6 Float chamber
2Carburetor
cover7Idleairpassage
3Vent tube
8Idleairiet4Transit’
,n iet9 Idle air adjusting screw
5 Transition air iet10 Mixture adjusting screw
6E-1Figure 6E-1 Sectional View of Primary and Secondary Barrels
valve gradually opens and the mixture
become+leaner. During this process, the abutment lever
changes position on the fast idle cam, further closingBefore starting a cold engine slowly, depress the ac-celerator pedal three times before engaging the
starter.
the throttle valve until, the engine is at normal oper-
ating temperature, the choke valve is wide open and
the throttle valve is in slow idle position.
Idle and Part Throttle SystemA choke diaphragm is connected to the intermediate
lever of the choke valve spindle through a pull rod.
The vacuum, which develops below the throttle
valve, takes effect on the diaphragm through a
vacuum passage. See Figure
6E-4. As soon as the
engine starts, this vacuum pulls the choke valve
slightly open; the amount of choke valve opening
depends on the amount of vacuum, which depends
on the engine load. Therefore, with a light engine
load, the choke valve will open slightly; with a heavy
engine load, the valve will close slightly to give a
richer mixture as required for this engine load.At engine idle grid during low speed (part throttle)
operation, fuel is drawn from the emulsion tube bore,
controlled by the idle jet and mixed with air entering
through idle air bleeds (Figure 6E-1) and ports in thethrottle body. This mixture is drawn downward to
the three ports near the throttle valve. When the
throttle valve is closed, the mixture is drawn from
the lowest port and mixed with air by-passing the
throttle valve to form the idle mixture.
Turning the idle mixture screw (Figure
6E-1) inward
results in a leaner mixture, and turning it out results
Page 338 of 625

CARBURETOR AND THROTTLE LINKAGE65 47
Figure 6E.3 Secondary Vacuum Diaphragm
Figure
6E-4 Automatic Choke System
Figure
6E-5 Idle Systemin a richer mixture. When the throttle valve is
opened, fuel is also drawn from the upper ports,
providing a good transfer from the idle system to the
main metering jet system. See Figure
6E-5.Main Metering Jet System
During high-speed operation, fuel is drawn from the
float chamber through the main metering jet (Figure6E-2) into the emulsion tube bore. The emulsion
tube, which is provided with transverse bores, is in-
serted in the emulsion tube bore. Vacuum in the
primary venturi (Figure 6E-2) draws fuel from the
main nozzle. As the vacuum increases, the tendency
is to draw too much fuel from the main nozzle, mak-
ing the mixture too rich. To compensate for this
tendency, the fuel level drops in the emulsion tube
bore and more emulsion tube transverse bores are
exposed. Air from the high speed air jet (Figure6E-2) enters the emulsion tube through these trans-
verse bores and mixes with the fuel. The more the
fuel level drops, the more the transfer bores are ex-
posed. This causes the air-fuel ratio to remain con-
stant over the whole engine speed range. See Figure
6E-6.Figure
6E-6 High Speed System
The secondary valve diaphragm is operated by
vacuum taken from the mixing chamber of the pri-
mary barrel on the Opel 1900 and Manta only. With
the primary throttle valve almost open and with en-
gine speed at approximately half of the maximum
engine RPM, vacuum increases to such an extent
that the secondary throttle valve starts opening from
vacuum applied in the vacuum diaphragm case act-
ing through a connecting rod and throttle valve
lever. See Figure
6E-3.
Primary to Secondary Transfer SystemIn order to have a smooth engagement of the
second-
Page 339 of 625

6~. 46,1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
ary barrel, it is provided with g transfer system.
When the secondary throttle valve starts to open,
two‘ports (which are normally just above the closed
valve) are uncovered, causing fuel to feed into the
secondary bore just before the secondary nozzle
starts feeding. This provides for an additional enrich-
ment of the air-fuel mixture at the beginning of full
throttle operation. See Figure
6E-7.
nInFlFigure
6E-7 Primary to Secondary Transfer System
Full Thrdttle Enrichment SystemIf the secondary throttle valve is fully opened, the
vacuum in the throttle valve area is reduced so that
the transfer ports (mentioned above) stop feeding.
However, the vacuum increases greatly in the sec-
ondary venturi area. An enrichment tube which pro-
trudes into the primary venturi area, feeds fuel
continuously during full throttle operation. See Fig-
ure
6E-2.
Acceleration SystemWhenever the throttle is closing, the suction stroke
of the diaphragm pump causes fuel to flow from the
float chamber through the inlet ball valve into the
pump chamber. When the throttle valve is opened
the diaphragm is moved inward by the pump con-
necting rod and the pump lever. Fuel is injected into
the primary bore through the injector tube. The
amount of fuel is determined by the pump stroke.
The inlet ball valve in the pump chamber prevents
fuel from flowing back into the float chamber during
the pressure stroke of the pump. The outlet ball valve
prevents air from being drawn into the injector tube
during the suction stroke of the pump. See Figure6E- 8.
Float Bowl VentilationWhile driving, the float bowl is ventilated from insideFigure
6E-8 Acceleration System
the carburetor. That is, the float bowl is connected
through the vent valve with the area under the air
cleaner.
When the engine is idling or off, the ventilation from
inside is cut off and ventilation from the charcoal
canister is cut in. The upper spring now seats the
valve on the upper seat. See Figure
6E-9.
-6E-9
Figure
6E-9 Float Bowl VentilationThe advantage of an inside vent while driving is that
air cleaner restriction does not enrichen the air fuel
mixture. The purpose of the charcoal canister vent
while idling or after shutting-off a hot engine, is to
prevent excess fuel vapors from entering the intakemanifold and outside air. Excess fuel vapors may
cause an idling engine to stall, or may make it dif-
ficult to restart a hot engine.
Page 340 of 625
CARBURETOR AND THROTTLE LINKAGE6E- 49DIAGNOSIS
CARBURETORCondition I
Hesitation or Stall Upon Light AccelerationCorrection
1. Check spark plugs and plug gap. Plug gap should
be
,030 in.
2. Check dwell and timing.
3. Adjust carburetor.
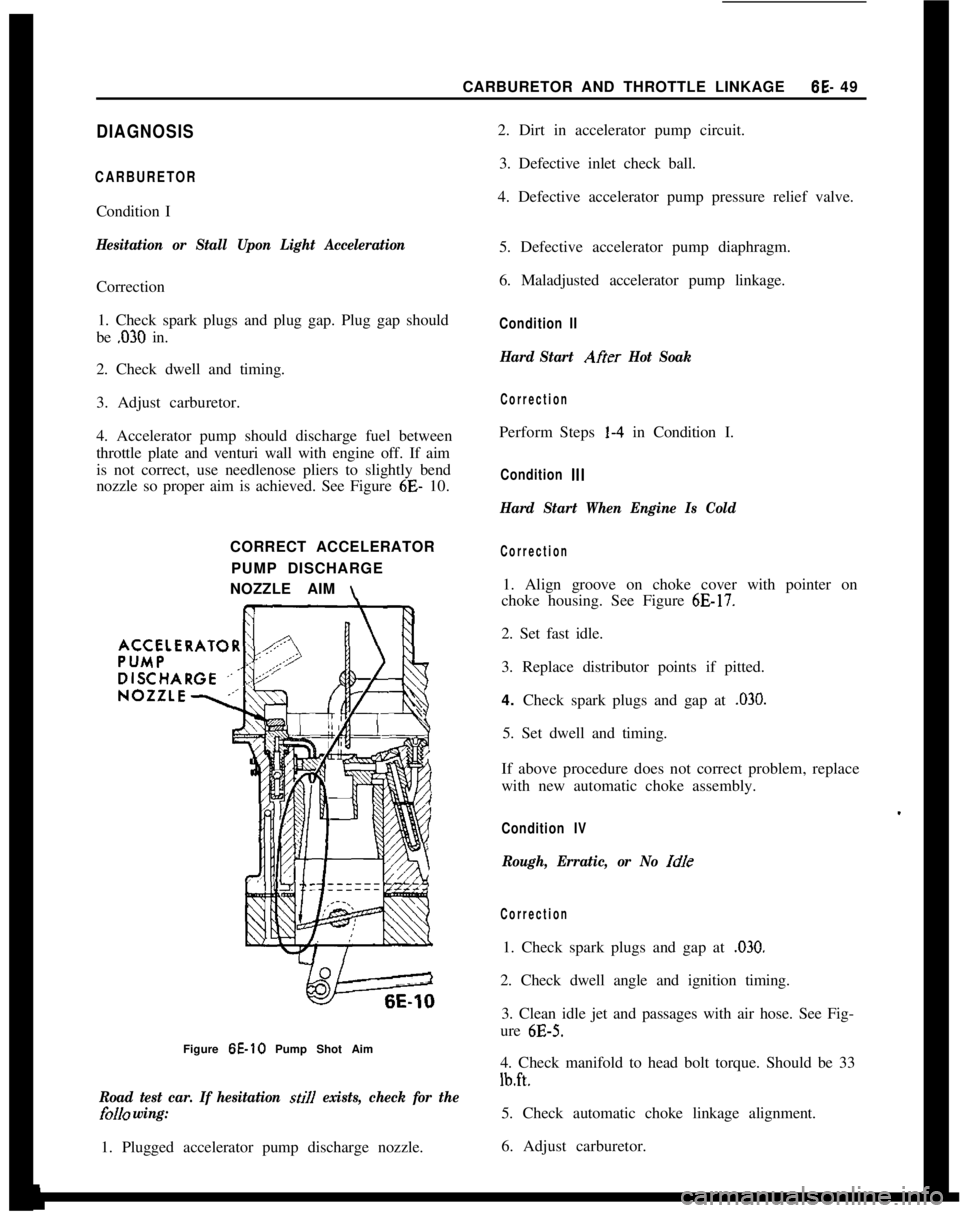
4. Accelerator pump should discharge fuel between
throttle plate and venturi wall with engine off. If aim
is not correct, use needlenose pliers to slightly bend
nozzle so proper aim is achieved. See Figure 6E- 10.
CORRECT ACCELERATOR
PUMP DISCHARGE
NOZZLE AIM
\Figure 6E-10 Pump Shot Aim
Road test car. If hesitation still exists, check for the
folI0 wing:1. Plugged accelerator pump discharge nozzle.2. Dirt in accelerator pump circuit.
3. Defective inlet check ball.
4. Defective accelerator pump pressure relief valve.
5. Defective accelerator pump diaphragm.
6. Maladjusted accelerator pump linkage.
Condition II
Hard Start Afier Hot Soak
CorrectionPerform Steps l-4 in Condition I.
Condition Ill
Hard Start When Engine Is Cold
Correction1. Align groove on choke cover with pointer on
choke housing. See Figure
6E-17.2. Set fast idle.
3. Replace distributor points if pitted.
4. Check spark plugs and gap at
,030.5. Set dwell and timing.
If above procedure does not correct problem, replace
with new automatic choke assembly.
Condition IV
Rough, Erratic, or No Idle
Correction1. Check spark plugs and gap at
,030.2. Check dwell angle and ignition timing.
3. Clean idle jet and passages with air hose. See Fig-
ure
6E-5.4. Check manifold to head bolt torque. Should be 33
lb.ft.5. Check automatic choke linkage alignment.
6. Adjust carburetor.
Page 341 of 625

6E- 501973 OPEL SERVICE MANUALMAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
IDLE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
Note:
Idle speeds of 600 to 800 R.P.M. are normal
for engines with less than
3,ooO miles.Prior to making any adjustment to the carburetor,
the following items must be checked for proper oper-
ation and/or setting:
1. Valve Adjustment (Hydraulic lifters can be im-
properly adjusted.)
2. Dwell Angle.
3. Ignition Timing.
4. Spark Plug Gap.
5. Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve (See “Check-
ing” under EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
SYSTEM.)
After it has been ascertained that the above items are
properly adjusted and operating correctly and idle
R.P.M. is still not within specifications, proceed as
follows:
1. With air cleaner installed, run engine until normal
operating temperature is reached.
2. Remove plastic caps from the idle mixture screw
and air speed screw. See Figure
6E-11.Figure
6E-1 1 Carburetor Adjusting Screws
3. To raise R.P.M., turn air speed screw counter-
clockwise. To lower R.P.M., turn air speed screw
clockwise, thereby reducing the amount of air going
through the system.4.
Ad,just idle mixture screw until highest R.P.M. is
obtained. Alternately adjust idle mixture screw and
air speed screw until R.P.M. is obtained that is 50
R.P.M. higher than the desired final setting. This is
to be accomplished with the idle mixture screw at
best idle.
5. Turn idle mixture screw clockwise (lean) until a
decrease of 50 R.P.M. is obtained. The idle R.P.M.
will
n.ow be within specifications and proper emis-
sion control maintained.
6. Install red plastic caps over the air speed screw
and idle mixture screw.
Basic Idle AdjustmentA basic idle adjustment is to be made only if engine
idle R.P.M. correction does not result in correct idle
R.P.M. setting and engine has more than
3,OOO miles
of operation. If necessary, proceed as follows:
1. Remove plastic cap from the throttle valve stop
screw. See Figure
6E-11.2. Place the Manometer (J-23951) in a vertical posi-
tion. Turn the 2 vents on top open to equalize pres-
sure and balance gauge to read zero. With engine
idling, unplug the vacuum advance hose from the
carburetor and connect the manometer hose in its
place. See Figure 6E- 12.
Figure 6E-12 Throttle Plate Calibrator J-23951
Installed3. If the manometer does not read 1 to 8 inches of
Page 342 of 625
CARBURETOR AND THROTTLE LINKAGE6E- 51
water, adjust the throttle stop screw to read 6 inches
of water (3 inches down and 3 inches up).
4. Disconnect manometer and reconnect the vacuum
advance hose.
5. Adjust idle air speed screw and mixture screw to
obtain maximum idle at 850 to 900 R.P.M. (auto-
matic transmission) or 900 to 950 R.P.M. (manual
transmission).
6. Make final adjustment by turning idle mixture
screw in to reduce idle speed 50 R.P.M.
7. Install red plastic caps over the air speed screw
and idle mixture screw. Replace plastic cap over the
throttle valve stop screw and secure in place with
Loctite.
Fast Idle Speed Adjustment
1. Remove air cleaner cover.
2. With engine off, open the throttle halfway and
close the choke valve, release the throttle, then re-
lease the choke.
3. Start engine without moving the throttle. Adjust
to 3200 to 3300 R.P.M. using 2 nuts on fast idle rod.
See Figures 6E-13 and
6E-14.Figure
6E-13 Decreasing Fast Idle Speed
CARBURETOR LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
GT Series1. Remove air cleaner.
2. Have helper depress accelerator pedal to floor and
check to see if wide open throttle is reached at carbu-
retor.
3. If adjustment is necessary, proceed as follows:
6E-14Figure
6E-14 Increasing Fast Idle Speed
(a) Unhook accelerator pedal return spring.
(b) Remove lock spring at upper end of vertical con-
trol rod and detach rod.
(c) Lengthen or shorten control rod so that wide
open throttle is obtained at the carburetor when ac-
celerator pedal is
l/4” - l/2” from floor mat.
(d) Reinstall rod, lock spring and pedal return
spring.
Opel 19W and Manta SeriesThe carburetor bowden control wire is properly ad-
justed if, with correctly-adjusted engine idle speed,
engine at operating temperature and accelerator
pedal at an angle of 25 degrees to the vertical plane,
the ball (A) of the carburetor bowden control wire
rests against the accelerator pedal lever. See Figure
6E-15.
1. Position accelerator pedal at an angle of 25 degrees
to the vertical plane. To do this, loosen lock nut of
adjusting bolt (c) and unscrew adjusting bolt a few
turns.
Squeeze a 1 3/S” wood block (D) between accelera-
tor pedal and dash panel. See Figure
6E-15.Screw in adjusting bolt until the accelerator pedal
lever releases the wood block (D). Tighten lock nut.
2. Adjust bowden control wire at adjuster. See Figure
6E-16. Prior to doing this, adjust engine idle speed
with engine at operating temperature.
Set carburetor bowden control wire adjuster at the
bracket so that the ball (A) of the control wire rests
against part (B) of the accelerator pedal lever and the
wire core between bracket and segmental disc is not
sagging.