warning light RENAULT KANGOO 1997 KC / 1.G Engine And Peripherals Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RENAULT, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KANGOO, Model: RENAULT KANGOO 1997 KC / 1.GPages: 208
Page 3 of 208
Contents
Consumables
Identification
Oil consumption
Oil pressure
Engine - Gearbox
Engine and transmission assembly
Sump
Crankshaft seal, timing end
Oil pump10-1
10-1
10-2
10-3
10-4
10-9
10-25
10-29
10-30
TOP AND FRONT OF ENGINE
Timing belt
Cylinder head gasket
Replacement of valve adjustersPage Page
11
Engine and
peripherals
11-1
11-11
11-29 ENGINE AND PERIPHERALS
10FUEL SUPPLY -
DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Fuel supply
Fuel cut off in case of an impact
Injector gallery
Fuel filter
Pump flow
Fuel pressure
Antipercolation device
Diesel equipment
General
Specifications
Location of components
Advance solenoid valve
Altimetric corrector
Fast idle LDA
Coded solenoid valve
Load potentiometer
Computer configuration
Injector with sensor (needle
lift)
Injection warning light
Pre-postheating control
Fast idle control
Injection/air conditioning
programming
Computer
Defect modes
Pump
Pump -Timing
Idle speed settings13-1
13-2
13-6
13-7
13-8
13-12
13-13
13-14
13-16
13-19
13-22
13-25
13-26
13-28
13-29
13-31
13-32
13-33
13-35
13-36
13-36
13-37
13-38
13-39
13-41
13-4613
FUEL MIXTURE
Specifications
Throttle body
Inlet manifold
Exhaust manifold
Inlet-exhaust manifolds12-1
12-7
12-15
12-18
12-2012
Page 4 of 208

Page
Cooling
Specifications
Filling and bleeding
Testing
Diagram
Water pump
Exhaust
General
Exhaust pipe assembly
Fuel tank
Tank
Sender unit
Pump and sender unit assembly
Engine suspension
Suspended engine mountings19-1
19-2
19-3
19-4
19-7
19-12
19-15
19-17
19-29
19-30
19-32 COOLING - EXHAUST - FUEL TANK -
ENGINE SUSPENSION
19
16-1
16-7 STARTING - CHARGING
Alternator
Starter
16
IGNITION - INJECTION
Ignition
Static ignition
Plugs
Injection
General
Location of components
Centralised coolant temperature
management
Injection fault warning light
Immobiliser function
Computer configuration depending
on gearbox type17
14-1
14-2
14-7
14-11 ANTIPOLLUTION
Test for the presence of lead
Fuel vapour rebreathing
Oil vapour rebreathing
Exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR)
14
17-17
17-18
17-19
17-20
17-22 IGNITION - INJECTION
(continued)
Injection/air conditioning
programming
Idle speed correction
Adaptive idle speed
correction
Richness regulation
Adaptive richness correction
17
Page
17-1
17-3
17-4
17-8
17-13
17-14
17-15
17-16
Contents
Page 93 of 208

DIESEL EQUIPMENT
General
13
The use of electronic injection in Diesel engines has allowed the operational power of these engines to be
optimised, thus reducing the emission rate of pollutant gases.
The system consists of a computer, which receives information from:
- the coolant temperature sensor,
- the air temperature sensor,
- the engine speed sensor,
- the vehicle speed sensor,
- the load potentiometer,
- the injection start sensor, which forms part of the injector of cylinder n° 3 (injector with sensor).
It controls :
- the injection pump :
• the altimetric corrector (F8Q 630) via a relay
• the advance solenoid valve.
- the cold engine starting system (heater plugs and pre-postheating unit),
- the exhaust gas recycling system (EGR),
- the diesel injection fault warning light,
- the preheating warning light,
- the solenoid valve controlling the fast idle speed LDA,
- the relay controlling the power assisted steering electric pump assembly (for vehicles with air conditio-
ning), the pump assembly is supplied once the engine speed exceeds 650 rpm.
It carries out a self diagnosis procedure which may be visualised through the
XR25.
SPECIAL FEATURES
On the injection pump it is possible to replace:
- the load potentiometer,
- the advance solenoid valve,
- the altimetric corrector,
- the electrical solenoid.
13-13
Page 98 of 208

DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Location of components
13
20 EGR valve
13047-1R
7Engine speed sensor
13048R
87970R
17Diesel injection fault warning light
18Preheating warning light
Warning light illuminates when ignition is
switched on during preheating phase.
12839S
C Power assisted steering pump assembly relay
HAltimetric corrector relay
LInjection locking relay
MDiesel heating relay
13-18
Page 112 of 208

DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Injection warning light
13
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF THE DIESEL INJECTION WARNING LIGHT ON THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
On switching on the ignition, the diesel injection fault warning light is illuminated. It extinguishes as the en-
gine begins to run.
•Fault in a component of the injection assembly
Faults in the following components may cause the warning light to illuminate :
- injector with sensor
- advance solenoid valve,
- engine speed sensor ,
- load lever potentiometer,
- pre-postheating (according to version).
13-32
Page 113 of 208
DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Pre-postheating control
13
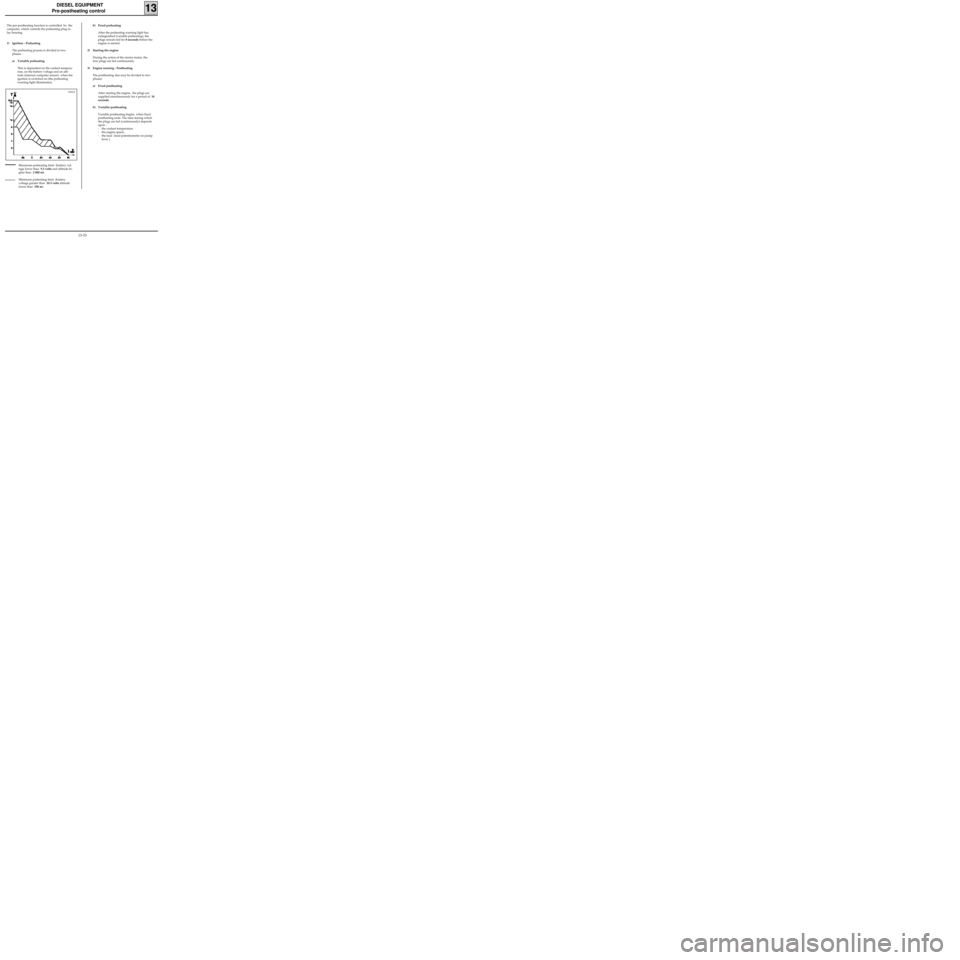
The pre-postheating function is controlled by the
computer, which controls the preheating plug re-
lay housing.
1) Ignition - Preheating
The preheating process is divided in two
phases :
a) Variable preheating
This is dependent on the coolant tempera-
ture, on the battery voltage and on alti-
tude (internal computer sensor) when the
ignition is switched on (the preheating
warning light illuminates).b) Fixed preheating
After the preheating warning light has
extinguished (variable preheating), the
plugs remain fed for 8 seconds before the
engine is started.
2) Starting the engine
During the action of the starter motor, the
four plugs are fed continuously.
3) Engine running - Postheating
The postheating also may be divided in two
phases:
a) Fixed postheating
After starting the engine, the plugs are
supplied simultaneously for a period of 10
seconds.
b) Variable postheating
Variable postheating begins when fixed
postheating ends. The time during which
the plugs are fed (continuously) depends
upon :
- the coolant temperature
- the engine speed ,
- the load (load potentiometer on pump
lever ).
Maximum preheating limit (battery vol-
tage lower than 9.3 volts and altitude hi-
gher than 2 000 m).
Minimum preheating limit (battery
voltage greater than 10.5 volts altitude
lower than 350 m).
13041S
13-33
Page 117 of 208

DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Computer
13
PRM1316
CONNECTION
1-<-
2-----
3-----
4-->-
5-->-
6-->-
7-<--
8-<--
9-->-
10-<--
11-<--
12-<--
13-><-Computer supply
Computer earth
Sensor earth
Potentiometer lever supply
EGR solenoid control
Advance corrector control
Needle lift signal
Engine speed signal
Preheating warning light control
Fault finding information line L
AC status
Vehicle speed signal
Fault finding information line KPlug relay control
Altimetric corrector relay control
Fast idle speed control
Load lever position information
Fault finding warning light control
AC prevention control
Power assisted steering pump assembly
relay control
Engine speed information
Not used
Load lever signal
Air temperature signal
Coolant temperature signal14-->-
15-->-
16-->-
17-->-
18-->-
19-->-
20 -->-
21-----
22
23-<--
24-<--
25-<--
13-37
Page 141 of 208

STARTING - CHARGING
Alternator
16
OPERATION - FAULT FINDING
These vehicles are equipped with alternators with
internal ventilation and integral regulator, also
with a warning light on the instrument panel
which has the following functions :
- when the ignition is switched on, the light illu-
minates
- when the engine is started the light extin-
guishes,
- if the light illuminates whilst the engine is
running there is a "charging "fault.
LOOKING FOR FAULTS
The warning light does not illuminate when the
ignition is switched on.
Check:
- all electrical connections are good.
- the bulb has not blown. (Earth the circuit and
the bulb should illuminate).
The warning light illuminates when the engine is
running.
This indicates a charging fault which could be
caused by :
- the alternator drive belt being broken or the
charging wiring being cut,
- internal alternator damage (rotor, stator,
diodes or brush),
- a regulator fault,
- excess voltage.The customer complains of a lack of charge and
the warning light is operating correctly.
If the regulated voltage is less than 13.5 V, check
the alternator. The fault could be caused by :
- a diode which has been damaged,
- a phase which is cut,
- contaminated or worn tracks.
Checking the voltage
Connect a voltmeter across the battery terminals
and read the battery voltage.
Start the engine and increase the engine speed
until the needle registers a stable regulated
voltage.
This voltage should be between 13.5 V and 14.8 V.
Connect as many consumers as possible, the
regulated voltage should be between 13.5 V and
14.8 V.
IMPORTANT: if arc welding work is to be carried
out on the vehicle, the battery and regulator
must be disconnected.
16-2
Page 154 of 208

INJECTION
General
17
SPECIAL NOTES FOR MULTIPOINT INJECTION
• 35 track SAGEM or MAGNETI MARELLI computer for vehicles without options.
• 55 track SAGEM computer ,
SAFIR or MAGNETI MARELLI type for versions with air conditioning.
•Semi-sequential multipoint injection. Injectors controlled two by two (injectors for cylinders 1 and 4 fol-
lowed by injectors for cylinders 2 and 3).
•Semi-static ignition with dual single unit coils.
•Canister bleed solenoid valve controlled by RCO signal.
•Computer configuration depending on gearbox type (manual gearbox or automatic transmission).
•The maximum engine speed permitted is 6 200 rpm.
•Idle speed correction depending on :
- battery voltage,
- air conditioning
- power assisted steering pressostat.
•Injection warning light on instrument panel not operational.
•Use fault finding fiche n° 27. D7F Engine
FITTING A 2ND GENERATION ENGINE IMMOBILISER REQUIRES A SPECIAL PROCEDURE FOR REPLACING THE
COMPUTER.
17-4
Page 155 of 208

INJECTION
General
17
SPECIAL NOTES FOR MULTIPOINT INJECTION
• 55 track SIEMENS FENIX 5 computer.
•Semi-sequential multipoint injection. Injectors are controlled two by two (injectors for cylinders 1 and 4
followed by cylinders 2 and 3).
•Semi-static ignition with dual coils.
•Canister bleed solenoid controlled by RCO signal.
•Computer configuration depending on gearbox type (manual gearbox or automatic transmission)
•Idle speed correction depending on :
- air conditioning,
- power assisted steering pressostat,
- battery voltage.
•Injection warning light on instrument panel operational.
•Use fault finding fiche n° 27.
•Maximum speed :
-6 200 rpm if 1st , 2nd or 3rd gears
-6 000 rpm if 4th,or 5th gears. E7J Engine
FITTING A 2ND GENERATION ENGINE IMMOBILISER REQUIRES A SPECIAL PROCEDURE FOR REPLACING THE
COMPUTER.
17-5