SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 981 of 2053

REAR BRAKES 4E-21
SSANGYONG MY2002
7. Connect the brake pipe to the wheel cylinder.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque15 - 19 Nm
(11 - 14 lb-ft)
8. Bleed the brake system and verify the parking
brake operation.
Install the tire.
YAD4C450
Page 982 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4E-22 REAR BRAKES
UNIT REPAIR
WHEEL CYLINDER
Disassembly Procedure
1. Remove the upper brake return spring and remove
the wheel cylinder with pulling the upper lining
outside.
2. Disassembly the wheel cylinder assembly.
Remove the dust boot and do not reuse them
(1).
Remove the piston (2).
Remove the piston cup and do not reuse it (3).
Remove the spring assembly (4).
Remove the bleeder screw (5).
3. Clean all the parts with the denatured alcohol. Dry
the parts with unlubricated compressed air.
Bleeder Screw7 - 10 Nm
(62 - 89 lb-in)
8 - 12 Nm
(71 - 106 lb-in)
Wheel Cylinder
Mounting Bolt
Notice: Lubricate the new seals, the piston, the
piston cup and the wheel cylinder bore with clean
brake fluid before assembly. 4. Installation should follow the removal procedure
in the reverse order.
5. Tighten the bleeder screw and wheel cylinder as
specified torque.
YAD4C460
YAD4C470
YAD4C480
Page 983 of 2053

REAR BRAKES 4E-23
SSANGYONG MY2002
2. Pull out the lever pin (arrow) and Disconnect the
the parking brake lever and the adjuster lever.
3. Installation should follow the removal procedure
in the reverse order.
YAD4C500
PARKING BRAKE LEVER
1. Disconnect the parking brake lever and the
adjuster lever from the lining.
YAD4C490
Page 984 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4E-24 REAR BRAKES
14
20
70
- Brake Hose Bolt
Caliper Guide Bolt
Caliper Mounting Bolts
Splash Shield-to-Knuckle BoltsN•m Application
Lb-In
SPECIFICATIONS
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
Lb-Ft
19
27
95
6-
-
-
53
Page 985 of 2053

SECTION 4F
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM AND
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Description and System Opertion..........4F-3
Basic Knowledge Required...................................4F-3
ABS System Components...................................4F-3
Traction Control System (TCS) Description...........4F-3
EBD System........................................................4F-5
EBD Failure Matrix...............................................4F-6
Tires and ABS/TCS..............................................4F-7
Hydraulic Circuit...................................................4F-8
ABS 5.3...............................................................4F-8
ABS/TCS 5.3.....................................................4F-11
Component Locator...........................................4F-14
ABS, ABS/TCS 5.3............................................4F-14
Diagnosis............................................................4F-15
Diagnostic Circuit Check....................................4F-15
ABS Indicator Lamp Inoperative.........................4F-18
Traction Control System (TCS) Indicator Lamp
Inoperative.....................................................4F-22
EBD Indicator Lamp Inoperative.........................4F-26
Power Supply to Control Module,
No DTCs Stored..............................................4F-30
ABS Indicator Lamp Illuminated Continuously,
No DTCs Stored..............................................4F-34
Self-Diagnostics................................................4F-36
Displaying DTCs................................................4F-36
Clearing DTCs...................................................4F-36
Intermittents and Poor Connections....................4F-36
DTC 03 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault ...4F-38
DTC 07 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-40
DTC 04 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fault...............................................................4F-42DTC 08 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-44
DTC 05 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault....4F-46
DTC 09 - Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-48
DTC 06 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Fault .4F-50
DTC 10 - Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Continuity Fault...............................................4F-52
DTC 11 - Wheel Speed Sensor Frequency Error ..4F-54
DTC 42 - Acceleration Sensor Fault....................4F-58
DTC 43 - Acceleration Sensor Continuity Fault.....4F-60
DTC 13/14 - Left Front Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-62
DTC 15/16 - Right Front Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-64
DTC 17/18 - Left Rear Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-66
DTC 19/20 - Right Rear Inlet and Outlet Valve
Solenoid Fault.................................................4F-68
DTC 21/22 - Left Rear Prime Line and Traction
Control System (TCS) Pilot Valve Fault............4F-70
DTC 23/24 - Right Rear Prime Line and Traction
Control System (TCS) Pilot Valve Fault............4F-72
DTC 12 - Valve Relay Circuit Fault......................4F-74
DTC 24 - Pump Motor or Pump Motor
Relay Fault.....................................................4E-76
DTC 27 - Stoplamp Switch Fault.........................4E-80
DTC 28 - Low Voltage Fault................................4E-84
DTC 02 - ABS Control Module Internal Fault........4E-88
Scheatic and Routing Diagrams........................4E-90
ABS Circuit (Without TCS): Gasoline...................4E-90
ABS/TCS Circuit: Gasoline.................................4E-91
ABS/ABD (Automatic Brake
Differential Lock): Diesel.................................4E-93
Page 986 of 2053

EBCM Connection Fact View.............................4E-95
EBCM Connector...............................................4E-95
Hydraulic Modulator Connector..........................4E-96
Repair Instructions..............................................4E-99
On-Vehicle Service...............................................4E-99
Service Precautions...........................................4E-99
ABS 5.3 Assembly..........................................4E-100
ABS/TCS Unit..................................................4E-100
Front Wheel Speed Sensor..............................4E-101Rear Wheel Speed Sensor...............................4E-101
Acceleration Sensor .........................................4E-102
System Fuse...................................................4E-102
Indicators........................................................4E-102
Unit Repair........................................................4E-103
ABS Front Tooth Wheel....................................4E-103
Special Tools and Equipment..........................4E-104
Special Tools Table..........................................4E-104
Page 987 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have
a basic knowledge of the following items. Without this
knowledge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic
procedures contained in this section.
•Basic Electrical Circuits - You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the meaning
of voltage, current (amps), and resistance (ohms).
You should understand what happens in a circuit
with an open or shorted wire. You should be able to
read and understand a wiring diagram.
Use of Circuit Testing Tools - You should know
how to use a test light and how to bypass
components to test circuits using fused jumper
wires. You should be familiar with a digital
multimeter. You should be able to measure voltage,
resistance, and current, and be familiar with the
controls and how to use them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists
of a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock
components. The conventional brake system includes
a vacuum booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes,
rear disc brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake pipes
and hoses, brake fluid level switch and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator
and the TCS indicator. See “ABS Component Locator”
in this section for the general layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located
between the surge tank and the bulkhead on the left
side of the vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hy-
draulic check valves, two solenoid valves for each
wheel, a hydraulic pump, and two accumulators. The
hydraulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front
calipers and rear calipers by modulating hydraulic
pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Units equipped with TCS add two more valves for each
drive wheel for the purpose of applying the brake to a
wheel that is slipping. This is done with pressure from
the hydraulic pump in the unit. There is also a TCS
indicator lamp on the instrument panel to alert the driver
to the fact that the TCS system is active. The
components identified in the drawing are those added
to the basic ABS 5.3 system to provide traction control.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit withattached EBCM must be replaced. For more
information, refer to “Base Braking Mode” and
“Antilock Braking Mode” in this section.
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(TCS) DESCRIPTION
General Information
The traction control system (TCS) is a traction system
by means of brake intervention only, available in a low
speed range (< 60kph).
It workes on µ - split roads with sidewise different friction
coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive
torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high-µ
side. During TCS active, the TCS information lamp is
blinking.
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a mathe-
matical model and TCS is switched passive if the calcu-
lated temperature is greater than a threshold value (500
°C).
TCS is permitted again, when the calculated tempera-
ture is less than 350 °C.
Control Algorithm
The input signals for the control algorithm are the
filtered wheel speed signals from the ABS speed
processing.
With the speed difference of the driven wheels, the
control deviation is calculated.
If the control deviation exceeds a certain threshold
value, the wheel with the greater slip is braked actively.
The threshold value depends on the vehicle speed:
It is reduced with increasing vehicle speed down to a
constant value.
KAA4F010
Page 988 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-4 ABS AND TCS
Pressure Modulation
Depending on the control deviation and the wheel accel-
eration of the spinning wheel, pressure increase, hold
and decrease are made.
The pressure modulation is done with the conventional
control with the valves. Prime valve, pilot valve, inlet
valve and outlet valve according to the following table:
Speed Range
TCS is available in the speed range ≤ 60 kph.
Above 60 kph vehicle speed, TCS is passive.
It is possible to initiate TCS operation up to a vehicle
speed of 55 kph.
Prime Valve
Pilot Valve
Inlet Valve
Outlet Valve
Increase
Open
Closed
Open
ClosedHold
Open
Closed
Closed
ClosedDecrease
Open
Closed
Closed
Open
System Failure (EBD,
ABS or TCS are Not
Distinguished)
ABS Warning
LampIgnition ONABS
OperationTCS
OperationTCS Passive Due to
Temperature Model
2 second on
for lamp
checkOFF OFF ON OFF
TCS Info
Lamp2 second on
for lamp
checkOFFBlinking
(FLASHING)OFF ON
EBD Warning
Lamp2 second on
for lamp
checkEBD
operation/OFFOFF ON OFF
Temperature Model
TCS operation is a high thermal load for the brakes.
To avoid any damages at the brakes, the disk tempera-
ture is calculated with a mathematical model for each
driven wheel separately. After ignition on, the
calculation starts with 30°C and then three different
phases are evaluated separately and added:
TCS operation, braking and coling phase.
If the temperature is highter than 500°C, TCS is dis-
abled for this wheel.
It is permitted again, if the model has calculated down
the 350°C.
Lamp Concepts
The system is equipped with an TCS information lamp,
which is blinking during TCS operation.
The activation of the EBD, TCS warning lamp and the
TCS info lamp issummarized in thefollowing table:
Page 989 of 2053
ABS AND TCS 4F-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
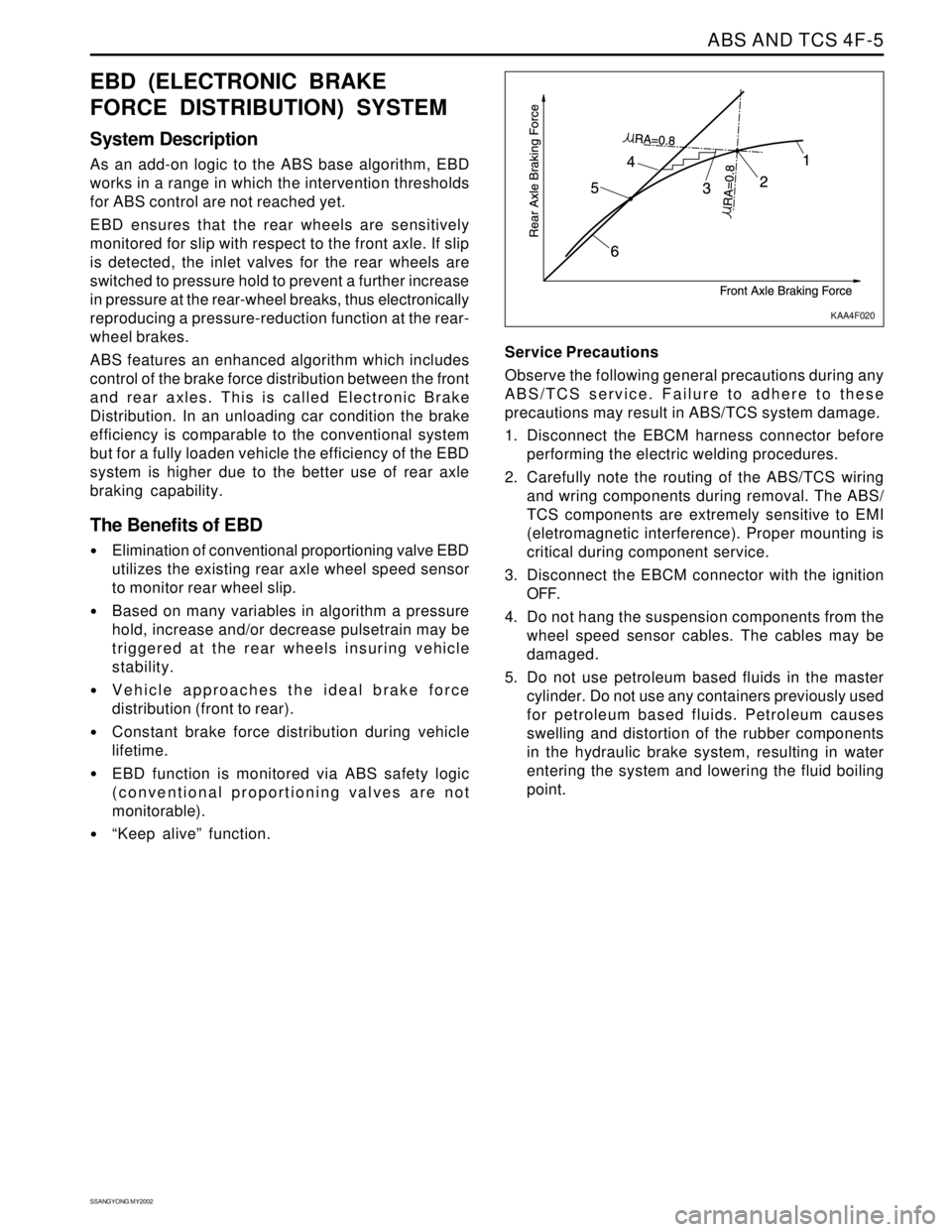
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE
FORCE DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
System Description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD
works in a range in which the intervention thresholds
for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively
monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip
is detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are
switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically
reproducing a pressure-reduction function at the rear-
wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes
control of the brake force distribution between the front
and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake
Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system
but for a fully loaden vehicle the efficiency of the EBD
system is higher due to the better use of rear axle
braking capability.
The Benefits of EBD
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD
utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed sensor
to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle
stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable).
“Keep alive” function.Service Precautions
Observe the following general precautions during any
ABS/TCS service. Failure to adhere to these
precautions may result in ABS/TCS system damage.
1. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector before
performing the electric welding procedures.
2. Carefully note the routing of the ABS/TCS wiring
and wring components during removal. The ABS/
TCS components are extremely sensitive to EMI
(eletromagnetic interference). Proper mounting is
critical during component service.
3. Disconnect the EBCM connector with the ignition
OFF.
4. Do not hang the suspension components from the
wheel speed sensor cables. The cables may be
damaged.
5. Do not use petroleum based fluids in the master
cylinder. Do not use any containers previously used
for petroleum based fluids. Petroleum causes
swelling and distortion of the rubber components
in the hydraulic brake system, resulting in water
entering the system and lowering the fluid boiling
point.
KAA4F020
Page 990 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-6 ABS AND TCS
EBD (Electronic Brake-Force Distribution) FAILURE MATRIX
KAA4F030