torque SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1998, Model line: MUSSO, Model: SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998Pages: 1463, PDF Size: 19.88 MB
Page 946 of 1463

REAR DISC BRAKES 4E-3
Tightening Torque 15 - 18 Nm
Tightening Torque 85 - 105 Nm
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the eye-hose bolt and disconnect the hose.
Installation Notice
2. Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the brake caliper
assembly.
Installation Notice
3. Pull out the brake pads. Replace pads if necessary.
Notice
Always change the all pads on one wheel at a time.
4. Installation should follow the removal precedure in the
reverse order.
5. Bleed the air from the system.
Page 954 of 1463
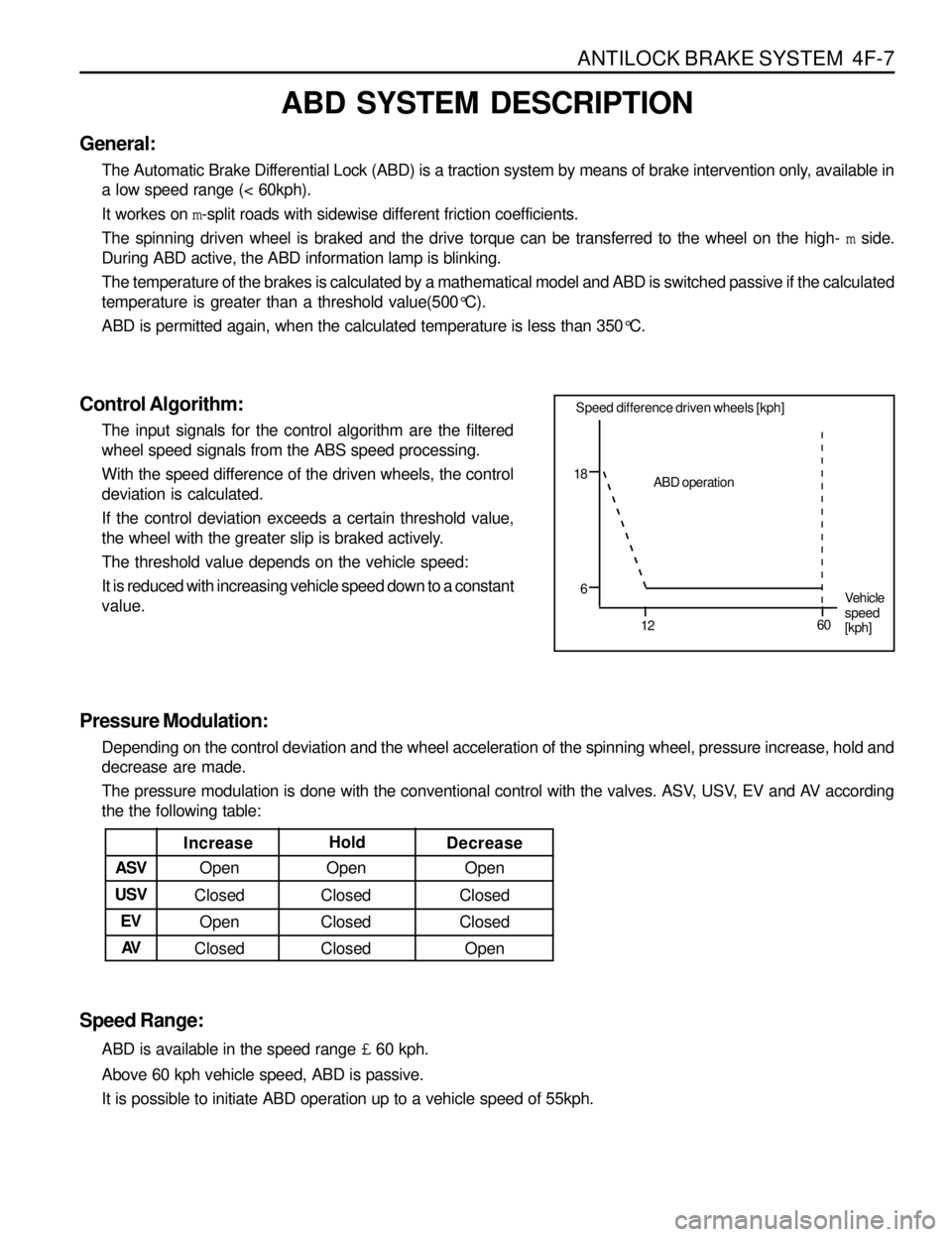
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F-7
ABD SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
General:
The Automatic Brake Differential Lock (ABD) is a traction system by means of brake intervention only, available in
a low speed range (< 60kph).
It workes on m-split roads with sidewise different friction coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high- m side.
During ABD active, the ABD information lamp is blinking.
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a mathematical model and ABD is switched passive if the calculated
temperature is greater than a threshold value(500°C).
ABD is permitted again, when the calculated temperature is less than 350°C.
Control Algorithm:
The input signals for the control algorithm are the filtered
wheel speed signals from the ABS speed processing.
With the speed difference of the driven wheels, the control
deviation is calculated.
If the control deviation exceeds a certain threshold value,
the wheel with the greater slip is braked actively.
The threshold value depends on the vehicle speed:
It is reduced with increasing vehicle speed down to a constant
value.
Pressure Modulation:
Depending on the control deviation and the wheel acceleration of the spinning wheel, pressure increase, hold and
decrease are made.
The pressure modulation is done with the conventional control with the valves. ASV, USV, EV and AV according
the the following table:
Speed Range:
ABD is available in the speed range £ 60 kph.
Above 60 kph vehicle speed, ABD is passive.
It is possible to initiate ABD operation up to a vehicle speed of 55kph.
Increase
Open Open Open ASVDecrease Hold
Closed Closed Closed
Closed Closed Open
Open Closed Closed USV
EV
AV
Speed difference driven wheels [kph]
18
6
1260ABD operation
Vehicle
speed
[kph]
Page 967 of 1463
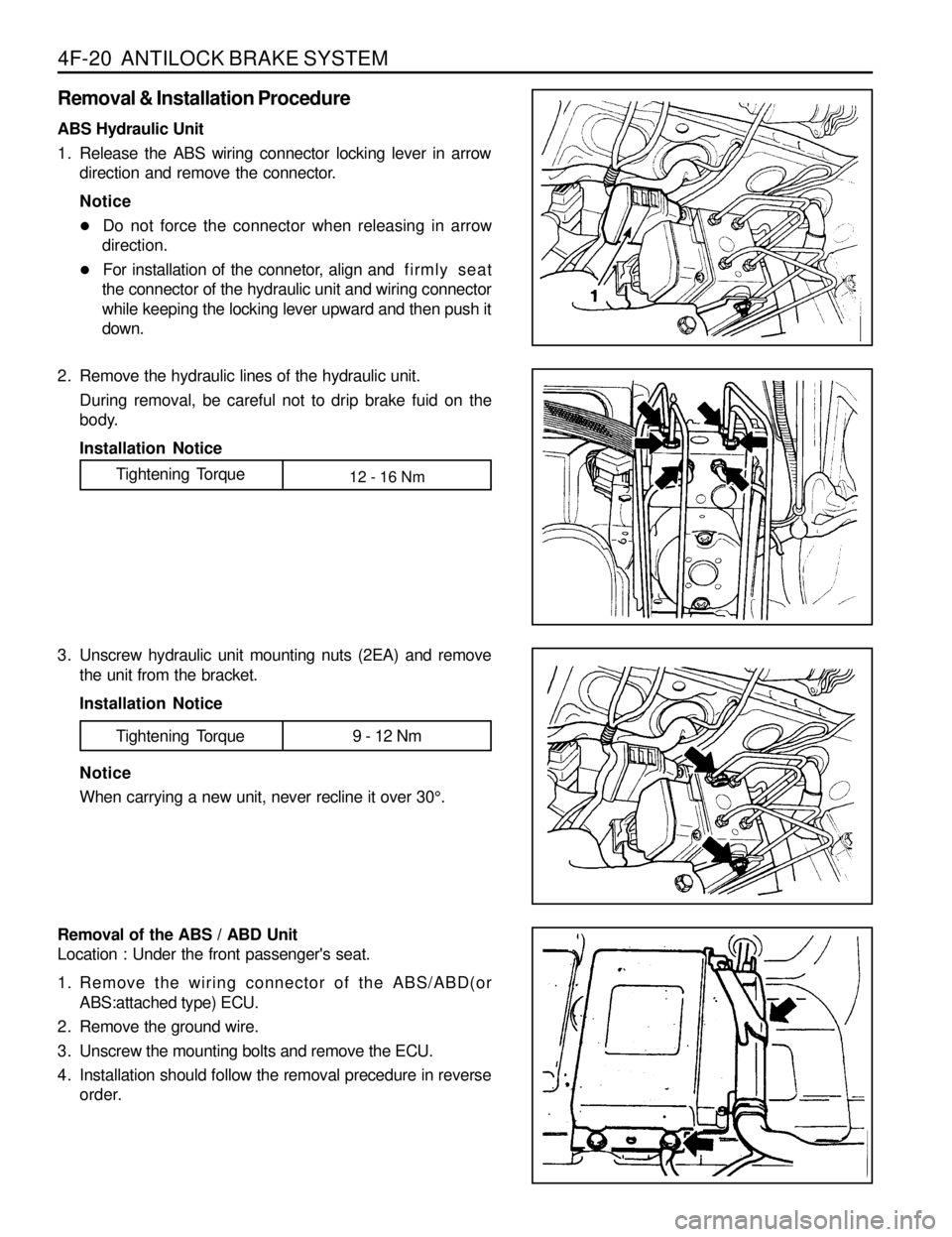
4F-20 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
Removal & Installation Procedure
ABS Hydraulic Unit
1. Release the ABS wiring connector locking lever in arrow
direction and remove the connector.
Notice
lDo not force the connector when releasing in arrow
direction.
lFor installation of the connetor, align and firmly seat
the connector of the hydraulic unit and wiring connector
while keeping the locking lever upward and then push it
down.
2. Remove the hydraulic lines of the hydraulic unit.
During removal, be careful not to drip brake fuid on the
body.
Installation Notice
3. Unscrew hydraulic unit mounting nuts (2EA) and remove
the unit from the bracket.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 9 - 12 Nm
Removal of the ABS / ABD Unit
Location : Under the front passenger's seat.
1. Remove the wiring connector of the ABS/ABD(or
ABS:attached type) ECU.
2. Remove the ground wire.
3. Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the ECU.
4. Installation should follow the removal precedure in reverse
order.
Tightening Torque12 - 16 Nm
Notice
When carrying a new unit, never recline it over 30°.
Page 976 of 1463

PARKING BRAKE 4G-3
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
PARKING BRAKE
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Disconnect the parking brake indicator switch connector.
2. Disconnect the right and left cable from equalizer while
parking brake lever is released.
3. Unscrew 8 bolts and remove the parking brake lever
assembly.
Installation Notice
Notice
Tighten the bolts with sequence number while the lever is
pulled up 4 to 6 notches.
Tightening Torque 8 - 18 Nm
4. Unscrew the frame and lower arm side cable mounting
bracket bolts.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 8 - 18 Nm
Page 978 of 1463

SECTION 5A
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
Model Part Numbers and Applications . . . . . . 5A-2
Model Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
Clutch Pack Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-3
Special Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-4
Special Tools Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-4
Schematic and Routing Diagrams . . . . . . . . 5A-5
TCU Circuit (Diesel) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-5
TCU Circuit (Gasoline) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-6
Shift Pattern Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-7
661LA Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-7
661LA Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-8
662LA Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-9
662LA Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-10
662LA Low Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-11
E32 Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-12
E32 Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-13
E32 Low Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-14
E23 Power Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-15
E23 Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-16
E23 Low Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-17
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-18
Operator Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-20
Gear Select Lever Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-20
Driving Mode Selector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-21
Control Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
Electronic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
Hydraulic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-31
Power Train System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-42
Torque Converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-43
Clutch Packs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-44Bands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-45
One Way Clutches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-45
Planetary Gear Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-45
Parking Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-46
Power Flows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-47
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-47
Power Flow - Park and Neutral . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Power Flow - Reverse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-49
Power Flow - Manual 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Power Flow - Drive 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-51
Power Flow - Drive 2 and Manual 2 . . . . . . . 5A-52
Power Flow - Drive 3 and Manual 3 . . . . . . . 5A-54
Power Flow - Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual
3 Lock Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-56
Power Flow - Drive 4 (Overdrive) . . . . . . . . . 5A-57
Power Flow - Drive 4 Lock Up . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-59
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-60
Diagnostic System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-60
Mechanical Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-69
Self Diagnosis Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-75
Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-79
Hydraulic System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-79
Transmission Fluid Test Procedure . . . . . . . . 5A-79
Electronic Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-80
Maintenance and Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-82
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-82
Removal and Installation of Transmission . . . 5A-82
Unit Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-85
Rebuild Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-85
Disassembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-85
Assembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-94
Front and Rear Band Adjustment . . . . . . . . 5A-128
Page 979 of 1463

5A-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL PART NUMBERS AND APPLICATIONS
Transmission
0574-000001 (9)
0574-000002 (8)
0574-000004 (10)
0574-000005 (7)Torque Converter
179K
160K
160K
179KEngine Version
661LA
E32
662LA(Turbo)
E23
MODEL SPECIFICATIONS
Application
Torque Converter
Mean diameter of fluid circuit
Maximum torque multiplication
Stall speed (rpm)
0574-000001 (D23LA)
0574-000002 (E32)
0574-000004 (D29LA)
0574-000005 (E23)
0574-000020
0574-000021
Gear Ratios
First
Second
Third
Fourth
Reverse
Lubricant
Type
Capacity
Dry System
Service Refill
Gear Train End Float
Gear Set Pinion End FloatDescriprtion
260
2.0 : 1
2100 - 2250
2050 - 2250
2100 - 2200
1800 - 2100
2.741 : 1
1.508 : 1
1.000 : 1
0.708 : 1
2.429 : 1
Castrol TQ95 or other approved fluid
9.0 Litres (approx)
4.5 Litres (approx)
0.50 - 0.65 mm
0.10 - 0.50 mm DWMC P/NO
36100-05420 (1)
36100-05430 (1)
36100-05410 (1)
36100-05440 (1)
Page 995 of 1463
5A-18 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
INTRODUCTION
The BTR Automotive Model 74 Four Speed Automatic Transmission is an electronically controlled overdrive four
speed unit with a lock-up torque converter. The lock-up torque converter results in lower engine speeds at cruise and
eliminates unnecessary slippage. These features benefit the customer through improved fuel economy and noise
reduction. Refer to table 1.1 for details of power, torque and configuration.
Of primary significance is the transmission control unit (TCU) which is a microprocessor based control system. The
TCU utilizes throttle position, rate of throttle opening, engine speed, transmission output speed, transmission sump
temperature, gear selector position and mode selector inputs, and in some applications a ‘kickdown’ switch to control
all shift feel and shift schedule aspects.
The TCU drives a single proportional solenoid multiplexed to three regulator valves to control all shift feel aspects.
The output pressure of this solenoid is controlled as a function of transmission sump temperature to maintain consistent
shift feel throughout the operating range.
Shift scheduling is highly flexible, and several independent schedules are programmed depending on the vehicle.
Typically the ‘NORMAL’ schedule is used to maximise fuel economy and driveability, and a ‘POWER’ schedule is used
to maximise performance. ‘WINTER’ schedule is used to facilitate starting at second gear.
Figure 1.1 details the differences between conventional and electronic transmission control systems.
Max Torque (Nm)
320Configuration
260 mm Torque Converter
Wide Ratio Gear Set
Splined Output for Transfer CaseMin Torque (Nm)
160 Model
M74 4WD
Transmission Table 1.1 - M74 Torque, Power and Configuration
Page 999 of 1463
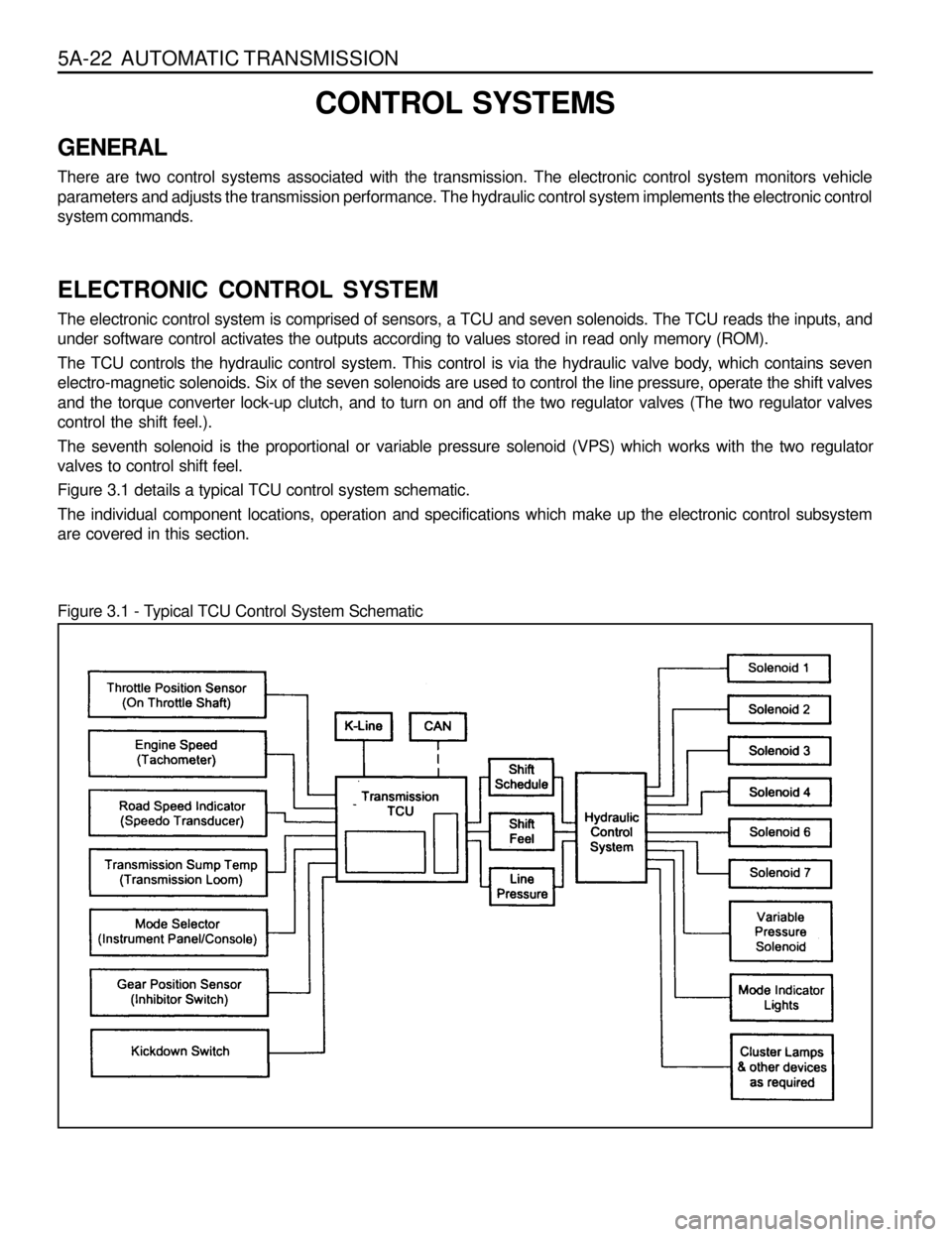
5A-22 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
CONTROL SYSTEMS
GENERAL
There are two control systems associated with the transmission. The electronic control system monitors vehicle
parameters and adjusts the transmission performance. The hydraulic control system implements the electronic control
system commands.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The electronic control system is comprised of sensors, a TCU and seven solenoids. The TCU reads the inputs, and
under software control activates the outputs according to values stored in read only memory (ROM).
The TCU controls the hydraulic control system. This control is via the hydraulic valve body, which contains seven
electro-magnetic solenoids. Six of the seven solenoids are used to control the line pressure, operate the shift valves
and the torque converter lock-up clutch, and to turn on and off the two regulator valves (The two regulator valves
control the shift feel.).
The seventh solenoid is the proportional or variable pressure solenoid (VPS) which works with the two regulator
valves to control shift feel.
Figure 3.1 details a typical TCU control system schematic.
The individual component locations, operation and specifications which make up the electronic control subsystem
are covered in this section.
Figure 3.1 - Typical TCU Control System Schematic
Page 1001 of 1463

5A-24 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Transmission Control Unit(TCU)
The TCU is an in-vehicle micro-processor based transmission management system. It is usually mounted in the
vehicle cabin, under the instrument panel, under the seat, behind the side kick panels or under the floor in the
footwell on the passenger side. Different control units are supplied for different vehicle applications.
The TCU contains:
lProcessing logic circuits which include a central microcontroller and a back-up memory system.
lInput circuits.
lOutput circuits which control external devices such as the variable pressure solenoid (VPS), on/off solenoid
drivers, a diagnostics output and the driving mode indicator light.
The various items which make up the TCU are discussed below.
Processing Logic
Shift schedule and calibration information is stored in an erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM).
Throttle input calibration constants and the diagnostics information are stored in electrically erasable programmable
read only memory (EEPROM) that retains the memory even when power to the TCU is disconnected.
In operation the software continuously monitors the input values and uses these, via the shift schedule, to determine
the required gear state, At the same time it monitors, via the solenoid outputs, the current gear state. Whenever the
input conditions change such that the required gear state is different to the current gear state, the TCU initiates a
gear shift to bring the two states back into line.
Once the TCU has determined the type of gear shift required the software accesses the shift logic, estimates the
engine torque output, adjusts the variable pressure solenoid ramp pressure then executes the shift.
The TCU continuously monitors every input and output circuit for short or open circuits and operating range. When
a failure or abnormal operation is detected the TCU records the condition code in the diagnostics memory and
implements a limp mode, The actual limp mode used depends upon the failure detected with the object to maintain
maximum driveability without damaging the transmission. In general input failures are handled by providing a default
value. Output failures, which are capable of damaging the transmission, result in full limp mode giving only third or
fourth gear and reverse. For further details of limp modes and memory retention refer to the Diagnostic Section.
The TCU is designed to operate at ambient temperatures between -40 and 85°C . It is also protected against
electrical noise and voltage spikes, however all the usual precautions should be observed, for example when arc
welding or jump starting.
TCU Inputs
To function correctly, the TCU requires engine speed, road speed, transmission sump temperature, throttle position
and gear position inputs to determine the variable pressure solenoid current ramp and on/off solenoid states. This
ensures the correct gear selection and shift feel for all driving conditions.
The inputs required by the TCU are as follows:
lEngine Speed
The engine speed signal is derived from the tachometer signal line, a dedicated sensor or a Controlled Area
Network (CAN).
lRoad Speed
4WD (Diesel) - The shaft speed signal is derived from the speedo sensor located on the transfer case. This signal
is transmitted directly to the TCU.
4WD (Gasoline) - The speedo sensor sends the shaft speed signal to the engine control module (ECM). The
information is then transferred to the TCU via the CAN.
lTransmission Sump Temperature
The transmission sump temperature sensor is a thermistor located in the solenoid wiring loom within the transmission.
This sensor is a typical NTC resistor with low temperatures producing a high resistance and high temperatures
Page 1002 of 1463
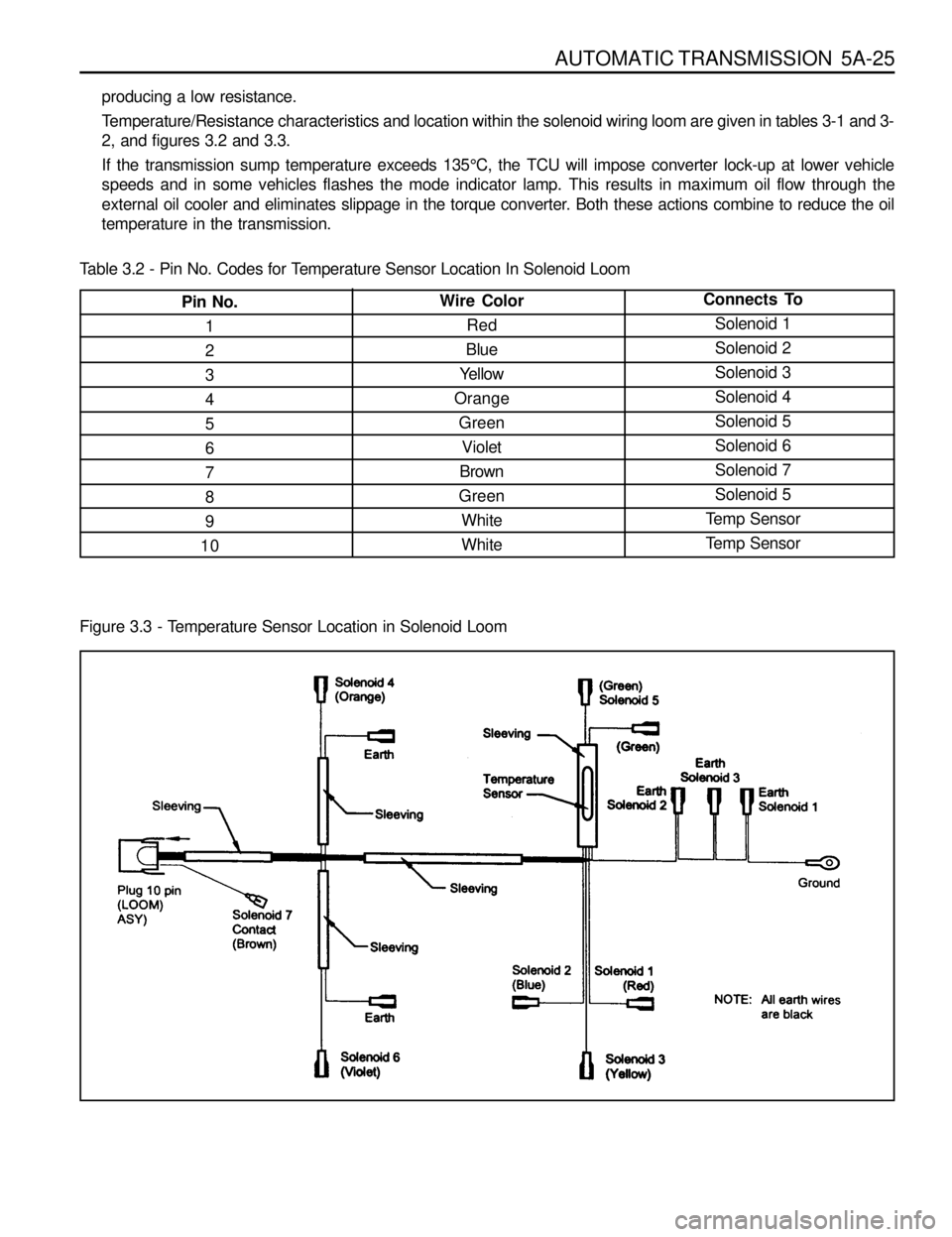
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-25
producing a low resistance.
Temperature/Resistance characteristics and location within the solenoid wiring loom are given in tables 3-1 and 3-
2, and figures 3.2 and 3.3.
If the transmission sump temperature exceeds 135°C, the TCU will impose converter lock-up at lower vehicle
speeds and in some vehicles flashes the mode indicator lamp. This results in maximum oil flow through the
external oil cooler and eliminates slippage in the torque converter. Both these actions combine to reduce the oil
temperature in the transmission.
Connects To
Solenoid 1
Solenoid 2
Solenoid 3
Solenoid 4
Solenoid 5
Solenoid 6
Solenoid 7
Solenoid 5
Temp Sensor
Temp SensorWire Color
Red
Blue
Yellow
Orange
Green
Violet
Brown
Green
White
WhitePin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Table 3.2 - Pin No. Codes for Temperature Sensor Location In Solenoid Loom
Figure 3.3 - Temperature Sensor Location in Solenoid Loom