TOYOTA CELICA 1987 Service Owner's Guide
Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 1987, Model line: CELICA, Model: TOYOTA CELICA 1987Pages: 346, PDF Size: 35.13 MB
Page 31 of 346
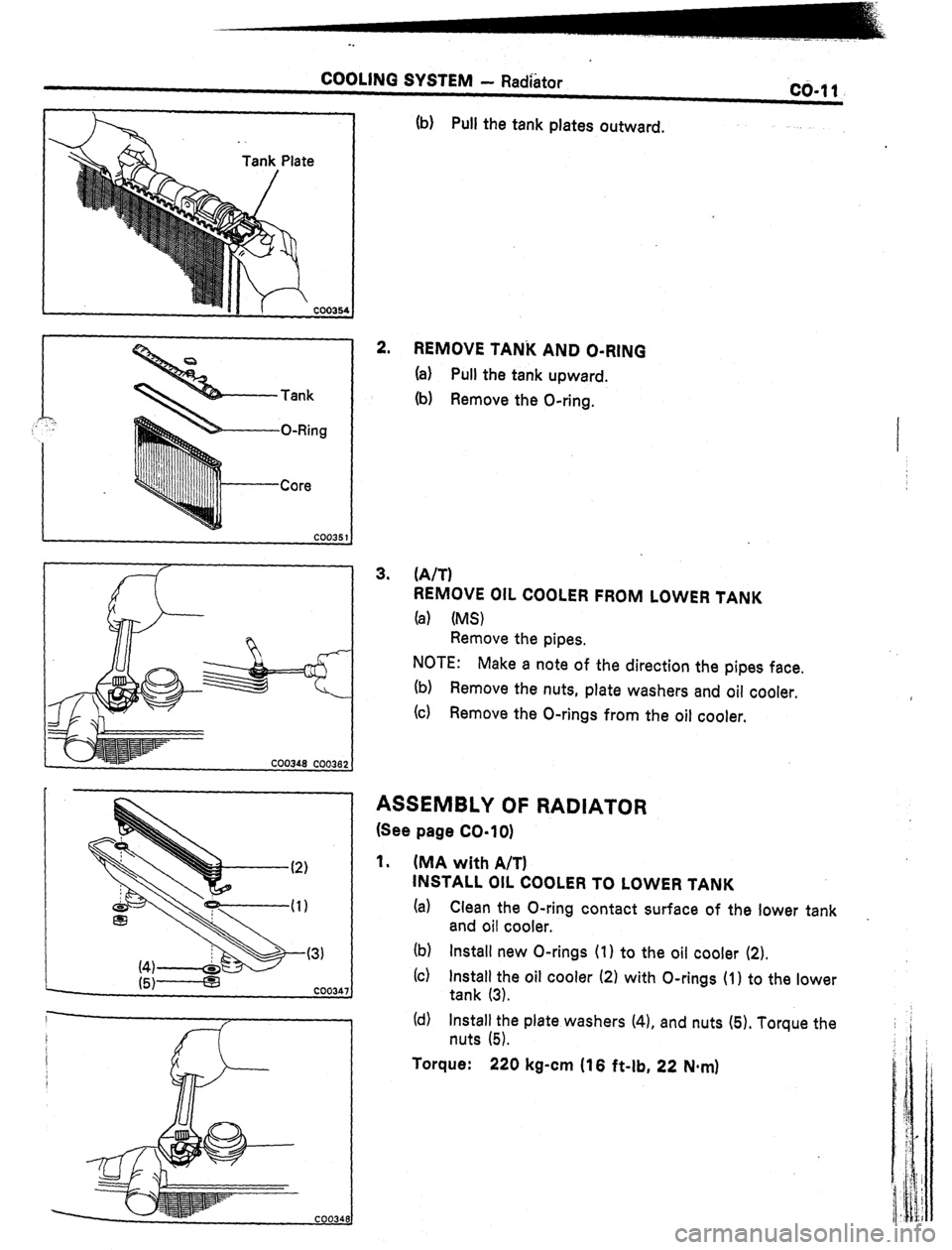
COOLING SYSTEM - Radhtor co-11
Tank
O-Ring
Core
(b) Pull the tank plates outward.
2.
REMOVE TANi( AND O-RING
(a) Pull the tank upward.
(b) Remove the O-ring.
3. (A/T)
REMOVE OIL COOLER FROM LOWER TANK
(a) (MS)
Remove the pipes.
NOTE:
Make a note of the direction the pipes face.
(b) Remove the nuts, plate washers and oil cooler.
(c) Remove the O-rings from the oil cooler.
ASSEMBLY OF RADIATOR
(See page CO-lo)
1. (MA with A/T)
INSTALL OIL COOLER TO LOWER TANK
(a) Clean the O-ring contact surface of the lower tank
and oil cooler. _
(b) Install new O-rings (1) to the oil cooler (2).
(c) Install the oil cooler (2) with O-rings (1) to the lower
tank (3).
(d) Install the plate washers (4). and nuts (5). Torque the
nuts (5).
Torque: 220 kg-cm (16 f&lb, 22 Nqn)
Page 32 of 346
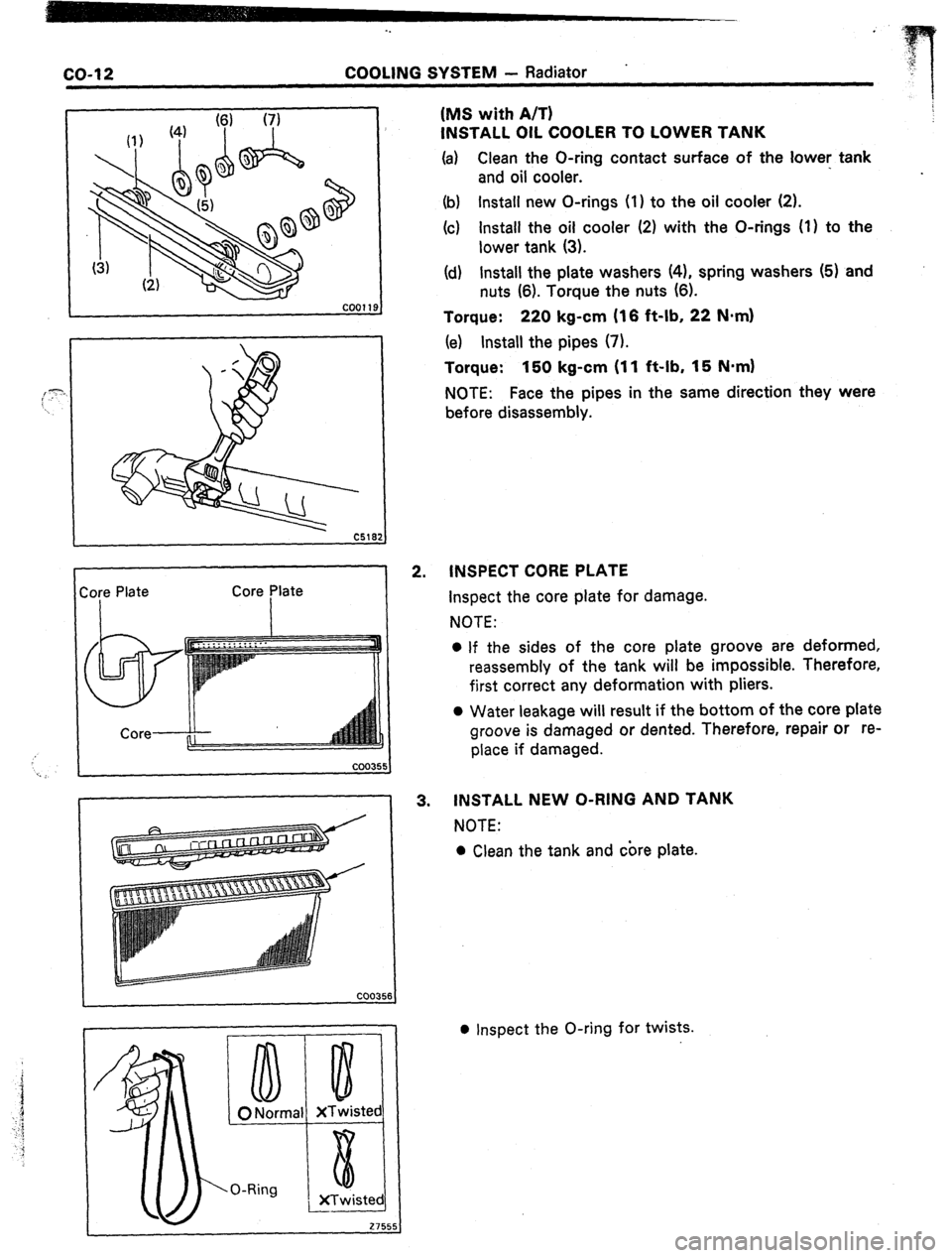
-.
COOLING SYSTEM - Radiator
.
ore
Plate
Core plate
XTwisteq
XTwistedl
- 2755:
2. (MS with A/T)
INSTALL OIL COOLER TO LOWER TANK
(a)
Clean the O-ring contact surface of the
lower: tank
and oil cooler.
(b) Install new O-rings (1) to the oil cooler (2).
(c) Install the oil cooler (2) with the O-rings (1) to the
lower tank (3).
(d) Install the plate washers (41, spring washers (5) and
nuts (6). Torque the nuts (6).
Torque: 220 kg-cm (16 ft-lb, 22 N*m)
(e) Install the pipes (7).
Torque: 150 kg-cm (11 ft-lb, 15 N.mI
NOTE: Face the pipes in the same direction they were
before disassembly.
INSPECT CORE PLATE
Inspect the core plate for damage.
NOTE:
l If the sides of the core plate groove are deformed,
reassembly of the tank will be impossible. Therefore,
first correct any deformation with pliers.
0 Water leakage will result if the bottom of the core plate
groove is damaged or dented. Therefore, repair or re-
place if damaged.
3. INSTALL NEW O-RING AND TANK
NOTE:
l Clean the tank and core plate.
l Inspect the O-ring for twists.
Page 33 of 346
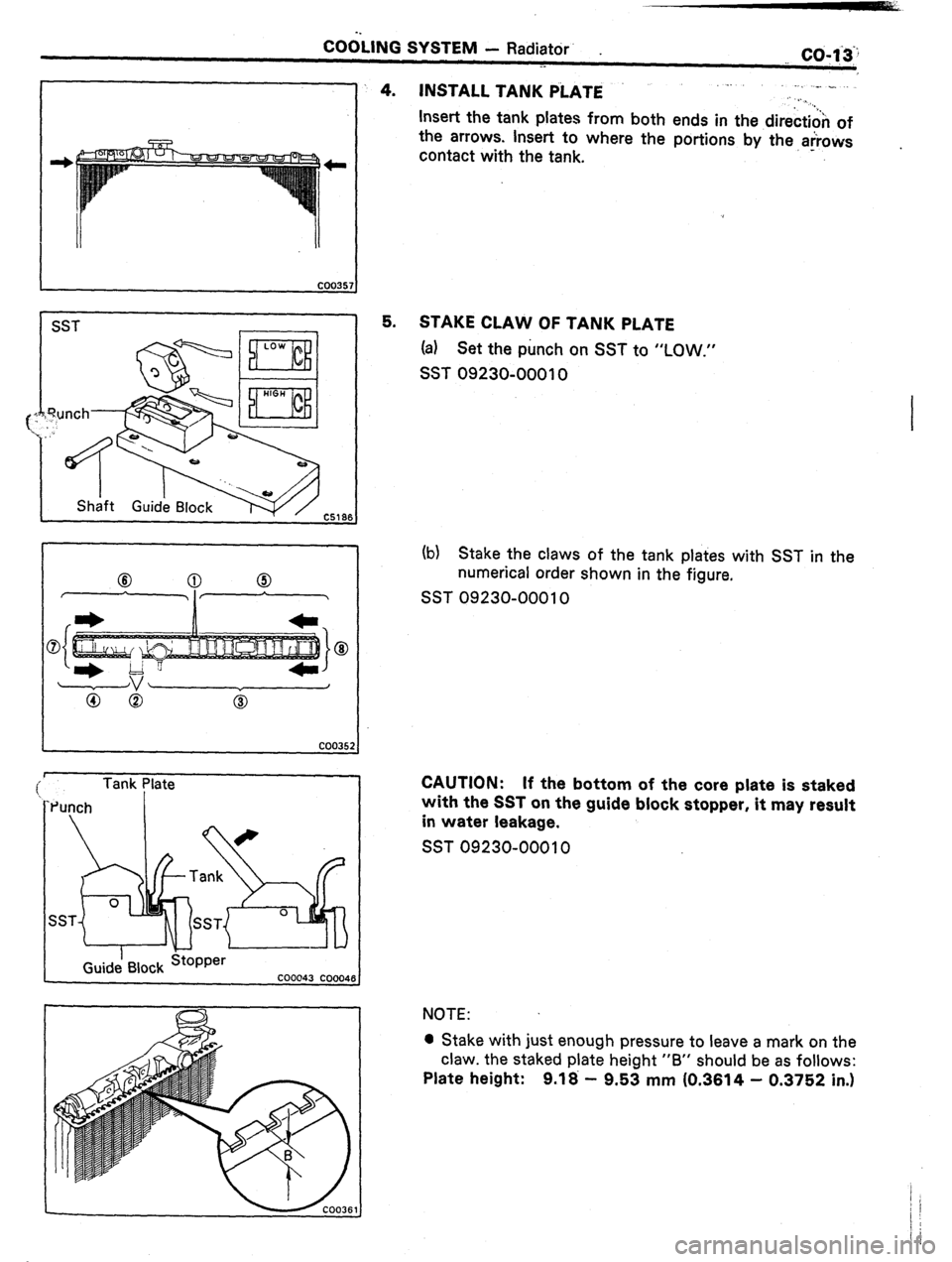
COGLING SYSTEM - Radiator’ .
__ co- 1.3::
.-
1 SST
r
i
Tank Plate
Punch I
I
4. INSTALL TANK PiATE .
., _. .,
. ._
Insert the tank plates from both ends in the direction of
the arrows. Insert to where the portions by the arrows
contact with the tank. - .
5. STAKE CLAW OF TANK PLATE
(a) Set the punch on SST to “LOW.”
SST 09230-00010
(b) Stake the claws of the tank plates with SST in the
numerical order shown in the figure.
SST 09230-00010
CAUTION: If the bottom of the core plate is staked
with the SST on the guide block stopper, it may result
in water leakage.
SST 09230-00010
NOTE:
l Stake with just enough pressure to leave a mark on the
claw. the staked plate height “B” should be as follows:
Plate height: 9.18 - 9.53 mm (0.3614 - 0.3752 in.)
Page 34 of 346
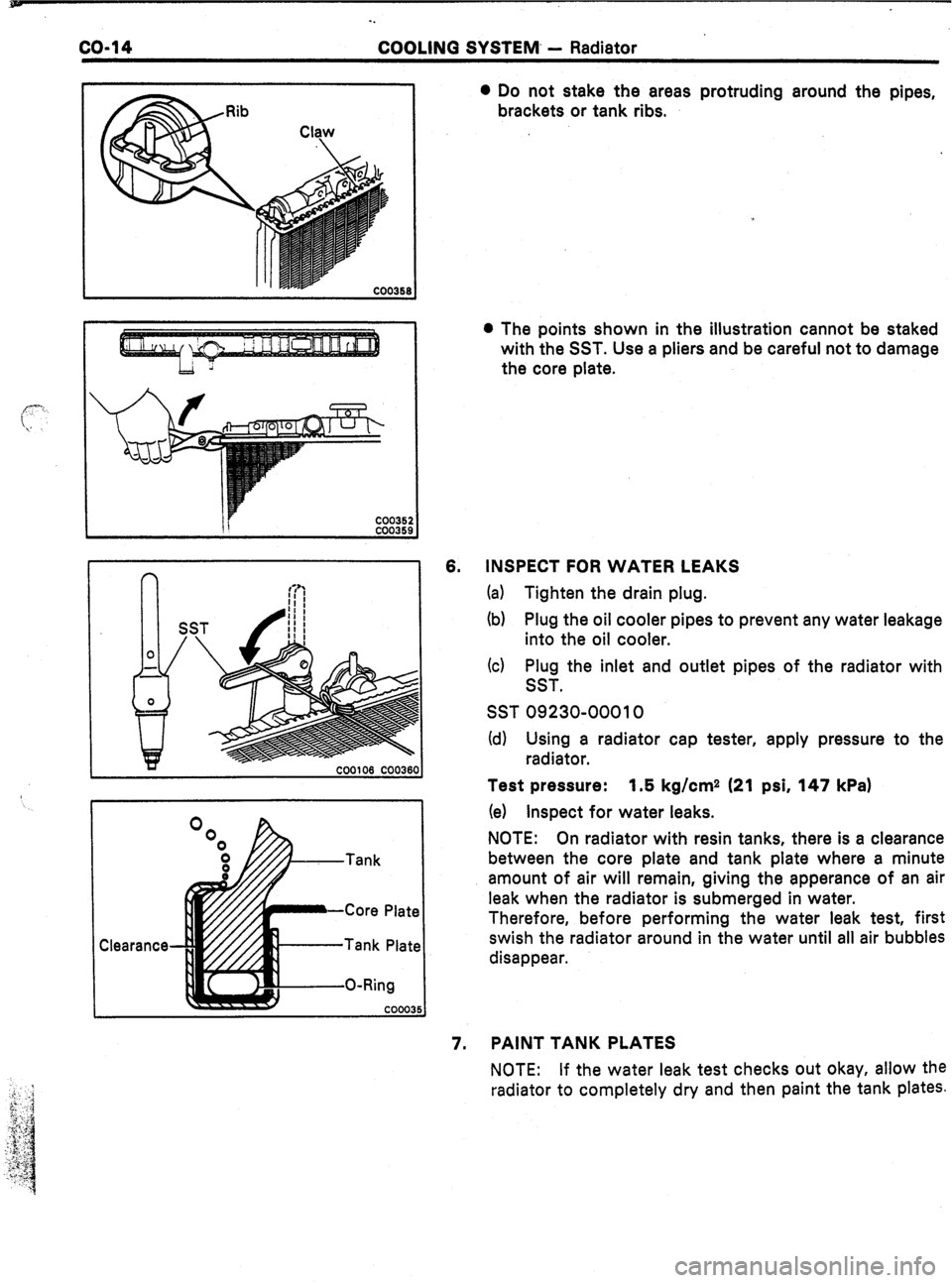
co-14
-.
COOLINQ SYSTEM. - Radiator
Tank Plate
O-Ring 6. 0 Do not stake the areas protruding around the pipes,
brackets or tank ribs.
l The points shown in the illustration cannot be staked
with the SST. Use a pliers and be careful not to damage
the core plate.
INSPECT FOR WATER LEAKS
(a) Tighten the drain plug.
(b) Plug the oil cooler pipes to prevent any water leakage
into the oil cooler.
(c) Plug the inlet and outlet pipes of the radiator with
SST.
SST 09230-00010
(d) Using a radiator cap tester, apply pressure to the
radiator.
Test pressure: 1.5 kg/cm2 (21 psi, 147 kPa)
(e) Inspect for water leaks.
NOTE: On radiator with resin tanks, there is a clearance
between the core plate and tank plate where a minute
amount of air will remain, giving the apperance of an air
leak when the radiator is submerged in water.
Therefore, before performing the water leak test, first
swish the radiator around in the water until all air bubbles
disappear.
7. PAINT TANK PLATES
NOTE: If the water leak test checks out okay, allow the
radiator to completely dry and then paint the tank plates.
Page 35 of 346

FI-1
i’.. ;
-EFI SYSTEM
i
‘x
. .
Page
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
....................... Fl-i.&.
PRECAUTIONS
;;:“, F,-, ;a”“- .............................. . ....
INSPECTION PRECAUTIONS
FI-7 . ....................
TROUBLESHOOTING
.......................... FI-12
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
.................... .
.... FI-25
TROUBLESHOOTING WITH
VOLT/OHMMETER (MA)
.................... FI-34
m
.:
TROUBLESHOOTING WITH
VOLT/OHMMETER (MS)
.................... FI-57
FUEL SYSTEM
................................ FI-73,
Fuel Pump ..................................
FI-73
Cold Start Injector ...........................
Fl-80
Pressure Regulator
.......................... FI’i84 ..
Injectors
.............................. ..i ..
FI-86
AIR INDUCTION SYSTEM
..................... FI-96
Air Flow Meter (7M-GE)
..................... FI-96
Air Flow Meter (7M-GTE)
................... FI-98
Throttle Body
.............................. FI-102
Idle Speed Control (ISC) Valve
............... FI-108
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM .............. FI-110
Location of Electronic Control Parts .......... FI-110
l EFI Main Relay
............................. Fl-112
. Circuit Opening Relay ....................... FI-113
Solenoid Resistor
........................... Fl-114
Cold Start Injector Time Switch ...............
FI-115
Water Temperature Sensor ..................
FI-116
Fuel Pump Relay and Resistor ............... FI-117
High Temperature Line Pressure -
Up System ............................... FIi119
High Altitude Compensation (HACK
System (7M-GTE)
........................ FI-121
Oxygen Sensor .............................
FI-122
Electronic Controlled Unit (ECU) .............
FI-125
Fuel Cut RPM
.............................. FI-128
Page 36 of 346
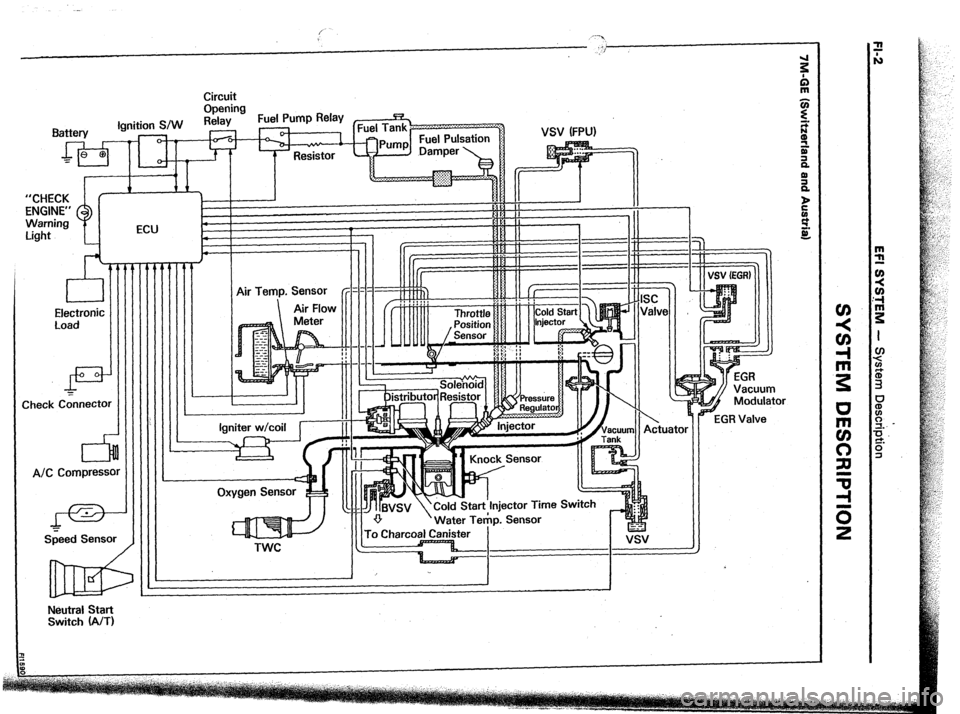
Circuit
Opening
Fuel Pump Relay
I
Warning 1
I :..I-, -7-I ECU
P 1
L-
VSV (FPU)
Electronic
Load
di!=
Check C&tnector
A/C Compressc
I-=-
Szeed Sensor
IIIII:IIlI Igniter w/coil
l---it-
Start‘lnjector Time Switch
Water Te&p. Sensor
TWC
Neutral Start
Switch (A/T)
Page 37 of 346
![TOYOTA CELICA 1987 Service Owners Guide Circuit
Opening
Relay Fuel Pump Relay
“CHECK 1 f-- 1 ] : :
llll II :
: :
ENGINE”
Warning
Light ECU
I iIll
+-,llllllllllll
Electronic
Load Air Temp. Sensor
Check Connector 1 1 1 / 1 TOYOTA CELICA 1987 Service Owners Guide Circuit
Opening
Relay Fuel Pump Relay
“CHECK 1 f-- 1 ] : :
llll II :
: :
ENGINE”
Warning
Light ECU
I iIll
+-,llllllllllll
Electronic
Load Air Temp. Sensor
Check Connector 1 1 1 / 1](/img/14/57451/w960_57451-36.png)
Circuit
Opening
Relay Fuel Pump Relay
“CHECK 1 f-- 1 ] : :
llll II :
: :
ENGINE”
Warning
Light ECU
I iIll
+-,llllllllllll
Electronic
Load Air Temp. Sensor
Check Connector 1 1 1 / 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
:uator
Igniter w/r-:’ ’
A/C Compressor
& 1 wTwy 1 To Charcoal Canister
Neutral Start
Switch (A/T)
Page 38 of 346
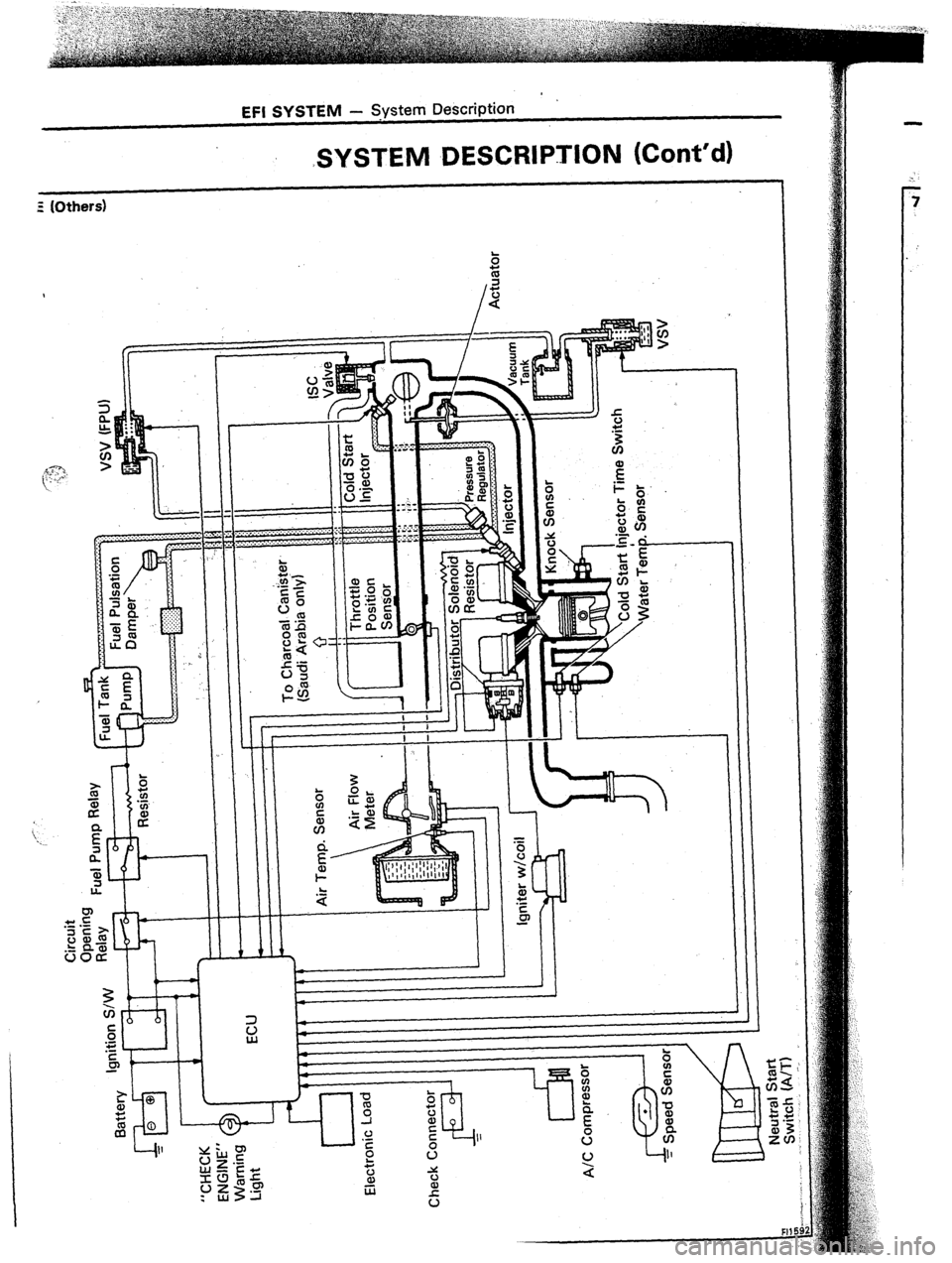
EFI SYSTEM - STystem Description
;SYSTEM DESCRIPTION (Cont’d)
5 (Others)
,
.
I
I I I
I .5:
a
J I
Page 39 of 346
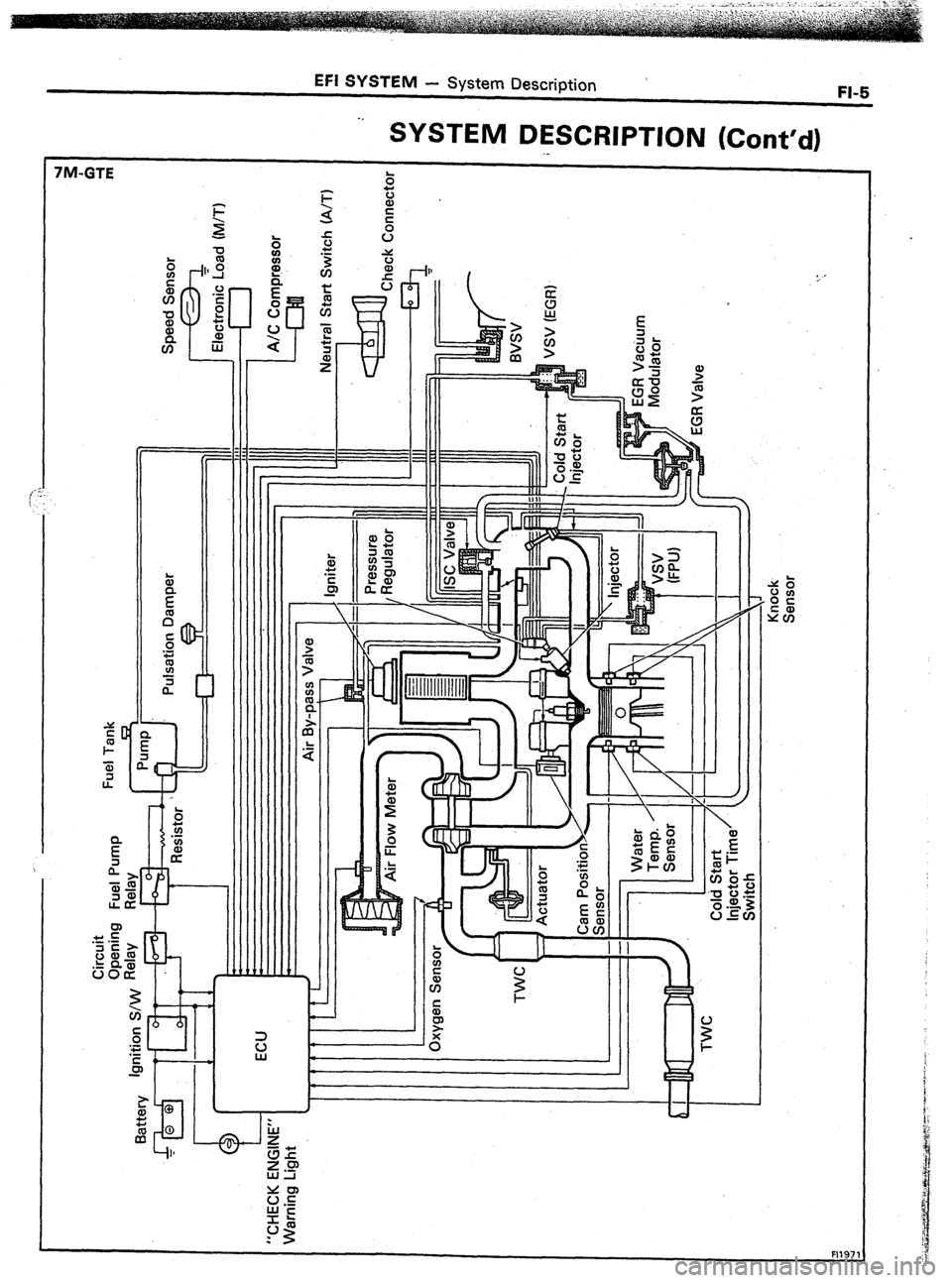
EFI SYSTEM
- System Description
’
FI-5
FM-GTE -.
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION (Cont’d)
._
1
Page 40 of 346

1-6 EFI SYSTEM - System Description
‘he .EFI system is composed of 3 basic sub
;ystems; Fuel Induction, Air Induction and
Ziectronic Control.
FUEL SYSTEM
An electric fuel pump supplies sufficient fuel,
under a constant pressure, to the injectors. These
injectors inject a metered quantity of fuel into the
intake manifold in accordance with signals from
the ECU (Electronic Control Unit).
AIR INDUCTION SYSTEM
The air induction system provides sufficient air for
engine operation.
[3: ‘I
i&TRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The 7M-GE, 7M-GTE engines are equipped wifh a
Toyota Computer Control System (TCCS) which
centrally controls the EFI, ESA, Diagnosis systems,
etc. by means of an Electronic Control Unit (ECU -
for-merly EFI computer) employing a microcom-
puter.
By means of the ECU, the TCCS controls the
following functions:
1. Electronic Fuel injection (EFI)
The ECU receivers signals from,various sen-
sors indicating changing engine operating
conditions such as:
Exhaust oxygen content (w/ TWC)
Intake air volume
i Intake air temperature
Coolant temperature
Engine rpm
Vehicle speed
Acceleration/deceleration etc.
These signals are utilized by the ECU to
determine the injection duration necessary for
an optimum air-fuel ratio.
2. Electronic Spark Advance (ESA)
The ECU is programmed with data for
optimum ignition timing under any and all
operating conditions. Using data provided by
sensors which monitor various engine func-
tions (rpm, A/C signal, coolant temperature,
etc.), the microcomputer (ECU) triggers the
spark at precisely the right instant. (See IG
section) 3. Idle Speed Control (IX)
The ECU is programmed with, target idling
speed values to respond to different engine
conditions (coolant temperature, air condi-
tioner on/off, etc.). Sensors transmit signals
to the ECU which control the flow of air
through the bypass of the throttle valve and
adjust idle speed to the target value.
(See pages FI-53, 7 1, 108) ’
4. Diagnosis
The ECU detects any malfunctions or abnor-
malities in the sensor network and tights the
“CHECK ENGINE” warning light on the instru-
ment panel. At the same time, the trouble is
identified and a diagnostic code is recorded
by the ECU.
5. Fail-Safe Function ’
In the event of computer malfunction, a back-
up circuit will take over to provide minimal
drivability. Simultaneously, the “CHECK
ENGINE” warning light will come on.