air condition DATSUN 210 1979 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 156 of 548

3
way
connector
ck
Air
@
Manometer
Carbon
canister
Emission
Control
System
400
mmH20
15
75
inH20
Check
valve
Fuel
filler
cap
r
EC091A
Fig
EC
I09
Checking
Evaporative
Emiuion
Control
Syatem
FUEL
CHECK
VALVE
I
Blow
air
through
connector
on
fuel
tank
side
A
considerable
resistance
should
be
felt
at
the
mouth
and
a
portion
of
air
flow
be
directed
toward
the
engine
2
Blow
air
through
connector
on
engine
side
Air
flow
should
be
smoothly
direct
ed
toward
fuel
tank
3
If
fuel
check
valve
is
suspected
of
not
being
properly
functioning
in
steps
I
and
2
above
replace
Engine
side
Fuel
tank
side
Q
Evaporative
fuel
flow
Fresh
air
flow
EC090A
Fig
EC
110
Checking
Fuel
Check
Valve
CARBON
CANISTER
PURGE
CONTROL
VALVE
Check
for
fuel
vapor
leakage
in
the
distributor
vacuum
line
at
diaphragm
of
carbon
canister
purge
control
valve
To
check
for
leakage
proceed
as
follows
I
Disconnect
rubber
hose
in
the
line
between
T
connector
and
carbon
canister
at
T
connector
2
Inhale
air
into
the
opening
of
rubber
hose
running
to
vacuum
hole
in
carbon
canister
and
ensure
that
there
is
no
leak
ET349
Fig
EC
lll
Checking
Carbon
Canister
Purge
Control
Valve
EC37
3
If
there
is
a
leak
remove
top
cover
from
purge
control
valve
and
check
for
dislocated
or
cracked
dia
phragm
If
necessary
replace
dia
phragrrt
kit
which
is
made
up
of
a
retainer
diaphragm
and
spring
i
ii
1
Cover
2
Diaphragm
3
Retainer
4
Diaphragm
spring
ET350
Fig
EC
112
Carbon
Canister
Purge
Control
Valve
FUEL
TANK
VACUUM
RELIEF
VALVE
Remove
fuel
filler
cap
and
see
it
functions
properly
I
Wipe
clean
valve
housing
and
have
it
in
your
mouth
2
Inhale
air
A
slight
resistance
ac
companied
by
valve
indicates
that
valve
is
in
good
mechanical
condition
Note
also
that
by
further
inhaling
air
the
resistance
should
be
disappeared
with
valve
clicks
3
If
valve
is
clogged
or
if
no
resist
ance
is
felt
replace
cap
as
an
assem
bled
unit
O
ET500
Fig
EC
1l3
Fuel
Filler
Cap
Page 178 of 548
DESCRIPTION
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
igni
tion
switch
Ie
ignition
unit
dis
tributor
winng
ipark
plugs
and
battery
The
distributor
is
of
the
contactless
type
and
is
equipped
with
a
pick
up
coil
which
electrically
detects
the
igni
tion
timing
signal
in
place
of
the
ircuit
I
rea
r
of
the
conventional
distributor
The
IC
ignition
unit
is
a
new
addition
which
generates
the
signal
required
for
the
make
and
break
of
the
primary
current
for
the
ignition
coil
The
primary
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
primary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
IC
ignition
unit
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
secondary
current
is
produced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
resulting
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distribu
tor
high
tension
cables
to
coil
and
spark
plugs
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
reluctor
rotates
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
IC
ignitionu
nit
to
ground
When
the
primary
circuit
is
opened
by
circuit
of
IC
ignition
unit
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
in
ducing
high
voltage
This
high
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
primary
circuit
opens
EngineElect
ical
System
IGNITfON
CIRCUIT
The
secondary
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
cable
to
the
distributor
cap
then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distrubutor
cap
Then
the
spark
occurs
while
the
secondary
current
jumps
the
gap
be
tween
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
t
e
engine
The
spark
plug
should
be
inspected
cleaned
and
regapped
at
tune
up
Spark
plugs
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Schedule
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
component
parti
should
be
inspected
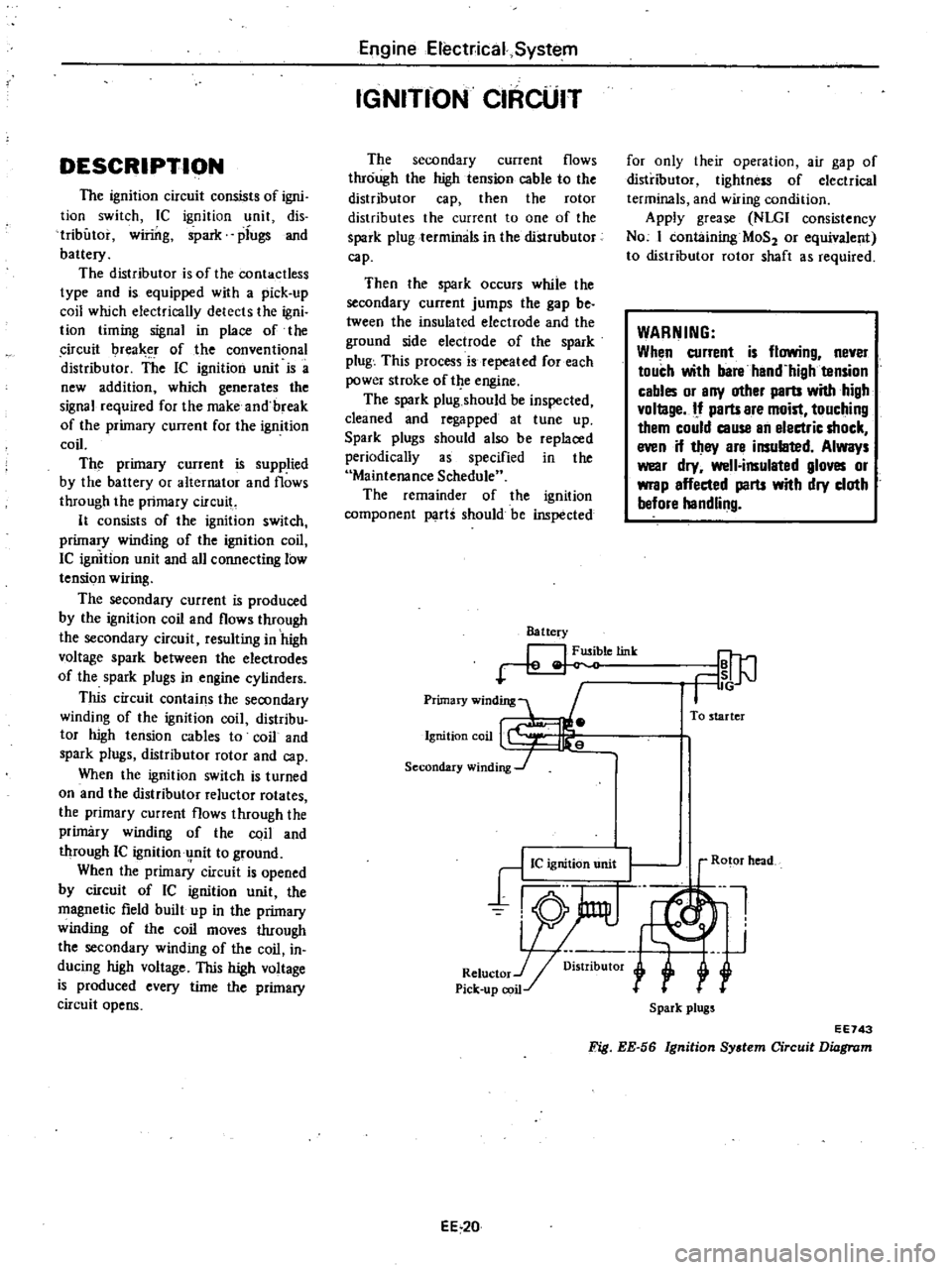
Battery
letink
Primary
winding
1
Ignition
coil
Secondary
winding
J
for
only
their
operation
air
gap
of
distributor
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
condition
Apply
grease
NLGI
consistency
No
I
containing
MaS
or
equivalent
to
distributor
rotor
shaft
as
required
WARNING
When
current
is
flowing
never
touch
with
bare
hand
high
tension
cables
or
any
other
parts
with
high
vollage
If
parts
are
moist
touching
them
could
cause
an
electric
shock
even
if
they
are
insulated
Always
wear
dry
well
insulated
gloves
or
wrap
affected
parts
with
dry
cloth
before
handling
To
starter
EE
20
Ro
or
head
Ul
J
r
Spark
plugs
EE743
Fig
EE
56
Ignition
System
Circuit
Diagram
Page 181 of 548

CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CAP
AND
ROTOR
HEAD
Cap
and
rotor
head
should
be
in
spected
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Main
teoanee
Schedule
Remove
cap
and
clean
all
dust
and
carbon
deposits
from
cap
and
rotor
from
time
to
time
If
cap
is
cracked
or
is
leaking
replace
wi
th
a
new
one
ADVANCE
MECHANISMS
SpecHlcatlons
Refer
to
Service
Data
and
Specifica
tions
for
distributor
Vacuum
advance
mechanism
mechanical
parts
If
vacuum
advance
mechanism
fails
to
operate
properly
check
for
the
followin
B
items
and
correct
the
mal
function
as
required
I
Check
vacuum
inlet
for
signs
of
leakage
at
its
connection
If
necessary
retighten
or
replace
with
a
new
one
2
Check
vacuum
diaphragm
for
air
leak
If
leak
is
found
replace
vacuum
controUer
assembly
3
Inspect
breaker
plate
for
smooth
moving
If
plate
does
not
move
smoothly
this
condition
could
be
due
to
sticky
steel
balls
or
pivot
Apply
grease
to
steel
halls
or
if
necessary
replace
breaker
plate
as
an
assembly
Centrifugal
advance
mechanical
parts
When
cause
of
engine
malfunction
is
traced
to
centrifugal
advance
mecha
nical
parts
use
distributor
tester
to
check
its
characteristics
If
nothing
is
wrong
with
its
charac
teristics
conceivable
causes
are
faulty
or
abnormal
wear
of
driving
part
or
others
So
do
not
disassemble
it
In
the
event
of
improper
character
istics
check
closely
rotor
shaft
assem
bly
governor
weight
and
shaft
If
any
of
the
above
parts
are
mal
functioning
replace
the
parts
Engine
Electrical
System
DISASSEMBLY
AND
ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY
I
Take
off
cap
and
remove
rotor
head
2
Remove
Ie
ignition
unit
Refer
to
IC
Ignition
Unit
for
removal
and
in
stallation
3
Remove
stator
and
magnet
by
removing
stator
securing
screws
4
Remove
vacuum
controller
by
removing
securing
screws
EE746
Fig
EE
59
Removing
Vacuum
Controller
5
Using
two
pry
bars
or
suitable
puller
pry
reluctor
from
shaft
CAUTION
When
removing
reluctor
be
careful
not
10
distort
or
damage
the
teeth
6
Remove
roll
pin
7
Remove
pick
up
coil
assembly
8
Remove
breaker
plate
setscrews
and
remove
breaker
plate
assembly
EE703
Fig
EE
60
Removing
Breaker
Plate
Setscrews
9
Punch
knock
pin
out
and
remove
pinion
EE
23
EE704
Fig
EE
61
Removing
Knock
Pin
10
Remove
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
assembly
EE705
Fig
EE
62
Removing
Rotor
Shaft
and
Drive
Shaft
Assembly
11
Mark
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
Remove
packing
from
the
top
of
rotor
shaft
and
unscrew
rotor
shaft
setscrew
Remove
rotor
shaft
EE706
Fig
EE
63
Removing
Rotor
Shaft
12
Mark
one
of
the
governor
springs
and
its
bracket
Also
mark
one
of
the
governor
weights
and
its
pivot
pins
13
Carerully
unhook
and
remove
governor
springs
14
Remove
governor
weights
A
r
ply
grease
to
guvernor
weights
after
disassembling
Page 187 of 548

INSPECTION
I
Disconnect
high
tension
cables
from
spark
plugs
by
pulling
on
boot
not
on
cable
itself
2
Remove
spark
plugs
3
Check
electrodes
and
inner
and
outer
porcelains
of
plugs
noting
the
type
of
deposits
and
the
degree
of
electrode
erosion
Refer
to
Fig
EE
76
Normal
Brown
to
grayish
Ian
de
posits
and
slighl
electrode
wear
indicate
correct
spark
plug
heat
range
Carbon
fouled
Dry
fluffy
carbon
de
posits
on
the
insulator
and
elec
trode
are
mostly
caused
by
slow
speed
driving
in
city
weak
ignition
too
rich
fuel
mixture
dirty
air
cleaner
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
hotter
heat
range
Oil
fouled
Wet
black
deposits
show
excessive
oil
entrance
into
comb
us
tion
chamber
through
worn
rings
and
pistons
or
excessive
clearance
between
valve
guides
and
stems
If
the
same
condition
remains
after
repair
use
a
hotter
plug
Overheating
White
or
light
gray
insu
lator
with
black
or
gray
brown
spots
and
bluish
burnt
electrodes
indicate
engine
overheating
More
over
the
appearance
results
from
incorrect
ignition
timing
loose
spark
plugs
low
fuel
pump
pres
sure
wrong
selection
of
fuel
a
hotter
range
plug
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
colder
heat
range
4
After
cleaning
dress
electrodes
with
a
smaU
fme
file
to
flatten
the
surfaces
of
both
center
and
side
elec
trodes
in
parallel
Set
spark
plug
gap
to
specification
5
Install
spark
plugs
and
torque
each
plug
6
Connect
spark
plug
wires
CLEANING
AND
REGAP
Clean
spark
plugs
in
a
sand
blast
Engine
Electrical
System
SPARK
PLUG
Conventional
type
Normal
Overheating
Multi
gap
type
Nonnal
Overheating
type
cleaner
Avoid
excessive
blasting
Clean
and
remove
carbon
or
oxide
deposits
but
do
not
wear
away
porce
lain
If
deposits
are
too
stubborn
discard
plugs
After
cleaning
spark
plugs
renew
firing
surface
of
electrodes
with
file
mentioned
above
Then
check
spark
plug
gap
with
wire
feeler
gauge
All
spark
plugs
new
or
used
should
have
the
gap
checked
and
reset
by
bending
ground
electrode
EEOSO
Fig
EE
77
Setting
Spark
Plug
Gap
Except
FU
model
EE
29
Carbon
fouled
EE079
Worn
Carbon
fouled
Worn
EE601
Fig
EE
76
Spark
Plug
EE586
Fig
EE
78
Setting
Spark
Plug
Gap
FU
models
Page 193 of 548

Engine
Electrical
System
II
STARTING
MOTOR
Condition
Starting
motor
will
not
operate
Noisy
starting
motor
Starting
motor
cranks
lowly
Starting
motor
cranks
slowly
Starting
motor
operate
but
does
not
crank
engine
Starting
motor
will
not
disengage
even
if
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
Probable
cause
Discharged
battery
Damaged
solenoid
witch
Loose
connections
of
terminal
Damaged
field
coil
Damaged
brushes
Damaged
bearing
Damaged
annature
Loose
securing
bolt
Worn
pinion
gear
Poor
lubrication
Worn
commutator
Worn
brushes
Discharged
battery
Loose
connection
of
terminal
Worn
brushes
Locked
brushes
Loose
connections
of
terminal
Damaged
field
coil
Damaged
brushes
Damaged
bearing
Damaged
armature
Dirty
or
worn
commutator
Armature
rubs
field
coil
Damaged
splenoid
switch
Worn
pinion
Locked
pinion
guide
Worn
ring
gear
Damaged
sOlenoid
switch
Damaged
gear
teeth
EE
35
Corrective
action
Charge
or
repiace
battery
Repair
or
replace
solenoid
switch
Clean
and
tighten
terminal
Replace
yoke
Replace
brushes
Replace
bearing
Replace
armature
Tighten
Replace
Add
oil
Replace
Replace
Charge
Clean
and
tighten
Replace
Inspect
brush
pring
tension
or
repair
brush
holder
Clean
and
tighten
terminal
Replace
yoke
Replace
brushe
Replace
bearing
Replace
armature
Clean
and
repair
Repalce
assembly
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Replace
damaged
gear
Page 194 of 548

Engine
Electrical
System
III
ALTERNATOR
Including
voltage
regulator
Condition
No
output
Excessive
output
Low
output
Noisy
alternator
Probable
cause
Sticking
brushes
Dirty
brushes
and
slip
rings
Loose
connections
or
broken
leads
Open
stator
winding
Open
rotor
winding
Open
diodes
Shorted
diodes
Shorted
rotor
Shorted
stator
Ground
BAT
terminal
Broken
fan
belt
Voltage
regulator
breakdown
Poor
connection
of
alternator
S
terminal
Open
diode
Loose
or
worn
fan
belt
Slicking
brushes
Low
brush
spring
tension
Voltage
regulator
breakdown
Dirty
slip
ring
Partial
hort
ground
or
open
in
stator
winding
Partially
shorted
or
grounded
rotor
winding
Open
or
damaged
diode
Loose
mounting
Loose
drive
pulley
Broken
ball
bearing
Improperly
seated
brushes
EE
36
Corrective
action
Correct
or
replace
bru
hes
and
brush
springs
Clean
Retigliten
or
older
connection
Replace
leads
if
necessary
Repair
or
replace
stator
Replace
rotor
Replace
Replace
Replace
rotor
Replace
Replace
insulator
Replace
Check
regulator
operation
and
repair
or
replace
a
required
Correct
Replace
Retighten
or
replace
Correct
or
replace
brushes
and
springs
if
necessary
Replace
brush
spring
Check
regulator
operation
and
repair
or
replace
as
required
Clean
Replace
tator
Replace
rotor
Replace
diode
Retighten
bolts
Retighten
Replace
Seat
correctly
Page 195 of 548

Engine
Electrical
System
IV
IGNITION
CIRCUIT
When
engine
does
not
start
If
there
is
no
problem
in
fuel
system
ignition
system
should
be
checked
This
can
be
easily
done
by
detaching
a
high
tension
cable
from
distributor
starting
engine
and
ob
serving
oondition
of
spark
that
occurs
between
high
tension
cable
and
engine
block
After
checking
this
repair
as
necessary
tery
and
anti
dieseliilg
wlenoid
valve
connector
to
cuI
off
supply
of
fuel
10
engine
Then
observe
the
condition
of
sparks
while
starter
motor
is
in
operation
Note
Turn
ignilion
switch
off
and
disconnect
ground
cable
from
bat
Condition
Location
Probable
cause
Corrective
action
No
spark
at
all
Distributor
Breakage
of
lead
wire
on
low
tension
side
Repair
Poor
insulation
of
cap
and
rotor
head
Replace
Open
pick
up
coil
Replace
Air
gap
wider
than
specification
Adjust
Ignition
coil
Wire
breakage
or
short
circuit
of
coil
Replace
with
new
one
High
tension
cable
Wire
coming
off
Repair
Faulty
insulation
Replace
IC
ignition
unit
Faulty
IC
ignition
unit
Replace
Breakage
of
circuit
Replace
Detached
connection
Repair
Spark
length
Spark
plugs
Spark
plug
gap
too
wide
Correct
or
replace
More
than
6
mm
Too
much
carbon
Clean
or
replace
0
24
in
Broken
neck
of
insulator
Replace
Expiration
of
plug
life
Replace
Distributor
Air
gap
too
wide
Correct
IC
ignition
unit
Faulty
IC
ignition
unit
Replace
Breakage
of
circuit
Replace
Detached
connection
Repair
EE
37
Page 196 of 548

2
Engine
rotates
but
does
not
run
smoothly
This
may
be
caused
by
the
ignition
Condition
Location
Engine
misses
Distributor
Ignition
coil
High
tension
cable
Spark
plugs
IC
ignition
unit
Engine
causes
knocking
very
often
Distributor
Spark
plugs
Engine
does
not
deliver
enough
power
Distributor
Spark
plugs
Engine
Electrical
System
system
or
other
engine
conditions
not
related
to
ignition
system
Therefore
first
complete
inspection
of
ignition
system
should
be
carried
out
Probable
cause
Foreign
matter
onpicl
up
coil
Improper
air
gap
Leak
of
electricity
at
cap
and
rotor
head
Breakage
of
pick
up
coil
lead
wire
Worn
or
shaky
breaker
plate
Worn
or
shaky
distributor
driVing
shaft
Layer
short
circuit
or
inferior
quality
coil
Deterioration
of
insulation
with
cense
quenlleak
of
electricity
Fouled
Leak
of
electricity
at
upper
porcelain
insulator
Spark
plug
gap
too
narrow
Faulty
IC
ignition
unit
Breakage
of
circuit
Detached
connection
Improper
ignition
timing
too
advanced
Coming
off
or
breakage
of
governor
spring
Worn
pin
or
hole
of
governor
Burnt
too
much
Improper
ignition
timing
too
retarded
Improper
functioning
governor
Foreign
particles
stuck
in
air
gap
Fouled
EE
38
Corrective
action
Clean
Correct
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Replace
assembly
Replace
aSsembly
Replace
with
good
one
Replace
Clean
Repair
or
replace
Correct
or
replace
Replace
Replace
Repair
Correct
Correct
or
replace
Replace
Replace
Correct
Replace
assembly
Clean
Clean
Page 199 of 548

REMOVAL
It
is
much
easier
to
remove
engine
and
transmission
as
a
single
unit
than
to
remove
alone
After
removal
engine
can
be
separated
from
the
transmission
assembly
WARNING
a
Place
wheel
chocks
in
fronl
of
front
wheels
and
in
rear
of
rear
wheels
b
Be
sure
to
hoist
engine
in
a
safe
manner
c
You
should
not
remove
engine
until
exhaust
system
has
com
pletely
cooled
off
Otherwise
you
may
burn
your
self
and
or
fire
may
break
out
in
fuel
line
Note
Fender
coven
should
be
used
to
protect
car
body
1
Disconnect
battery
ground
cable
from
battery
terminal
and
fusible
link
at
wire
connector
2
Remove
hood
as
follows
CAUTION
Have
an
assistant
help
you
so
as
to
prevent
damage
to
body
I
Mark
hood
hinge
locations
on
hood
to
facilitate
reinstallation
2
Support
hood
by
ltand
and
re
move
bolts
securing
it
to
hood
hinge
being
careful
not
to
let
hood
slip
when
bolts
are
removed
See
Fig
ER
2
3
Remove
hood
from
hood
hinge
f
Il
I
BF133A
Fig
ER
2
Removing
Hood
Remove
under
cover
Drain
radiator
coolant
and
engine
3
4
oil
5
Disconnect
upper
and
lower
hoses
from
radiator
and
disconnect
oil
cooler
hoses
automatic
transmission
only
6
Remove
four
bolts
securing
radia
Engine
Removal
Installation
tor
to
body
and
detach
radiator
after
removing
radiator
shroud
7
Remove
air
cleaner
assembly
from
carburetor
as
follows
1
Remove
fresh
air
duct
from
air
cleaner
2
Remove
hot
air
duct
from
air
cleaner
3
Loosen
air
cleaner
band
bolt
4
Disconnect
air
cleaner
to
air
pump
hose
at
air
cleaner
5
Disconnect
air
cleaner
ta
rocker
cover
hose
at
rocker
cover
6
Disconnect
air
cleaner
to
A
B
valve
hose
at
air
cleaner
7
Disconnect
air
cleaner
to
related
vacuum
hoses
at
air
cleaner
8
Disconnect
accelerator
control
wire
from
carburetor
9
Disconnect
the
following
cables
wires
and
hoses
Wire
to
auto
choke
heater
Wire
to
throttle
opener
cut
solenoid
or
throttle
switch
Wire
to
fuel
cut
solenoid
Wire
to
vacuum
switching
valve
High
tension
cable
between
igni
tion
coil
and
distributor
Battery
cable
to
starter
motor
Wire
to
distributor
Wire
to
thermal
transmitter
Wire
to
alternator
Engine
ground
cable
oil
pressure
switch
and
engine
harness
No
2
See
Fig
ER
3
o
1
Ground
cable
2
Engine
harness
No
2
3
Oil
pressure
switch
Fig
ER
3
EA368
Disconnecting
Cable
and
Wire
Fuel
hose
at
fuel
pump
and
fuel
return
hose
at
connection
Air
pump
air
cleaner
hose
Carbon
canister
hoses
Heater
inlet
and
outlet
hoses
if
so
equipped
ER
3
Vacuum
hose
of
brake
booster
at
intake
manifold
Air
conditioner
equipped
model
10
Remove
compressor
belt
To
remove
loosen
idler
pulley
nut
and
adjusting
bolt
1
Remove
air
pump
2
Remove
compressor
retaining
bolts
and
move
compressor
toward
fender
to
facilitate
removal
of
engine
Nole
Never
discharge
gas
from
com
pressor
while
work
is
being
per
formed
II
Compressor
EA478
Fig
ER
4
Location
of
Air
Compressor
3
Disconnect
vacuum
hose
of
air
conditioner
from
connector
of
intake
manifold
4
Remove
F
i
C
D
actuator
from
bracket
II
Remove
clutch
operating
cylin
der
from
clutch
housing
manual
trans
mission
only
dJ
Tightening
torque
Clutch
operating
cylinder
E
A3
to
clutch
housing
3
1
to
4
1
kg
22
to
30
ft
lbl
Fig
ER
5
Removing
Clutch
Operating
Cylinder
Page 201 of 548

INSTALLATION
Install
in
the
reverse
order
of
re
moval
observing
the
following
Note
When
inslal1ing
be
sure
to
check
thaI
electrical
harnesses
are
connected
ly
1
When
installing
first
secure
rear
engine
mounting
member
to
body
2
Refer
to
applicable
section
when
installing
and
adjusting
any
parts
Adjust
clutch
pedal
free
travel
Re
fer
to
Clutch
Pedal
Free
Travel
Section
CL
for
installation
and
adjustment
Adjust
accelerator
control
system
Refer
to
Engine
Control
System
Section
FE
for
adjustment
For
installation
of
air
conditioner
compressor
and
belt
adjustment
Refer
to
Idler
Pulley
and
Com
pressor
Drive
Belt
for
adjustment
of
belt
tension
3
When
installing
exhaust
front
tube
on
exhaust
manifold
be
sure
to
use
new
gasket
4
When
installing
hood
following
engine
installation
be
sure
that
it
is
properly
centered
and
that
hood
lock
operates
securely
Refer
to
Hood
See
tion
BF
for
adjustment
Engine
Removal
Installation
ENGINE
MOUNTING
INSULATOR
FRONT
INSULATOR
Removal
Disconnect
battery
ground
cable
2
Suspend
engine
with
wire
or
chain
3
Remove
front
engine
mounting
insulator
lower
and
upper
nuts
on
both
sides
4
Make
sure
that
wire
or
chain
used
to
suspend
engine
is
positioned
prqper
ly
so
that
no
load
is
applied
to
insulators
and
remove
nuts
complete
ly
5
Lift
up
engine
and
separate
in
sulators
from
engine
mounting
rack
ets
Inspection
If
there
is
damage
deterioration
or
separation
of
bounded
surface
re
place
Installation
Install
front
insulators
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
noting
the
fol
lowing
1
Do
not
confuse
right
and
left
insulators
R
right
side
or
L
left
side
identification
mark
is
stamp
ed
on
each
insulator
2
Install
front
insulator
so
that
ER
5
position
pin
is
projected
upward
3
Tighten
the
bolts
and
nut
correct
ly
and
securely
See
Fig
ER
I
REAR
INSULATOR
Removal
l
Support
transmission
weight
with
ajack
2
Remove
nuts
securing
rear
engine
mounting
insulator
to
mounting
mem
ber
3
Remove
bolts
connecting
rear
en
gine
mounting
insulator
to
transmis
sion
reaf
extension
housing
4
Jack
up
the
transmission
a
little
and
remove
insulator
Inspection
If
there
is
damage
deterioration
or
separation
of
mating
surface
replace
Installation
Install
rear
engine
mounting
mem
ber
and
insulator
in
reverse
order
of
removal
noting
the
following
I
Install
insulator
in
place
so
that
direction
of
mounted
insulator
is
same
as
that
in
Fig
ER
2
Tighten
nuts
and
bolts
correctly
and
securely
As
for
tightening
torque
see
Fig
ER
l