air condition DATSUN 210 1979 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 207 of 548
are
clean
and
free
from
foreign
matter
Cearance
between
cylinder
bore
and
piston
Leu
than
0
15
mm
0
0059
in
ASSEMBLY
Assemble
clutch
master
cylinder
in
the
reverse
order
of
disassembly
Ob
serve
the
following
I
Dip
piston
cup
in
brake
fluid
before
installing
Make
sure
that
it
is
correctly
faced
in
position
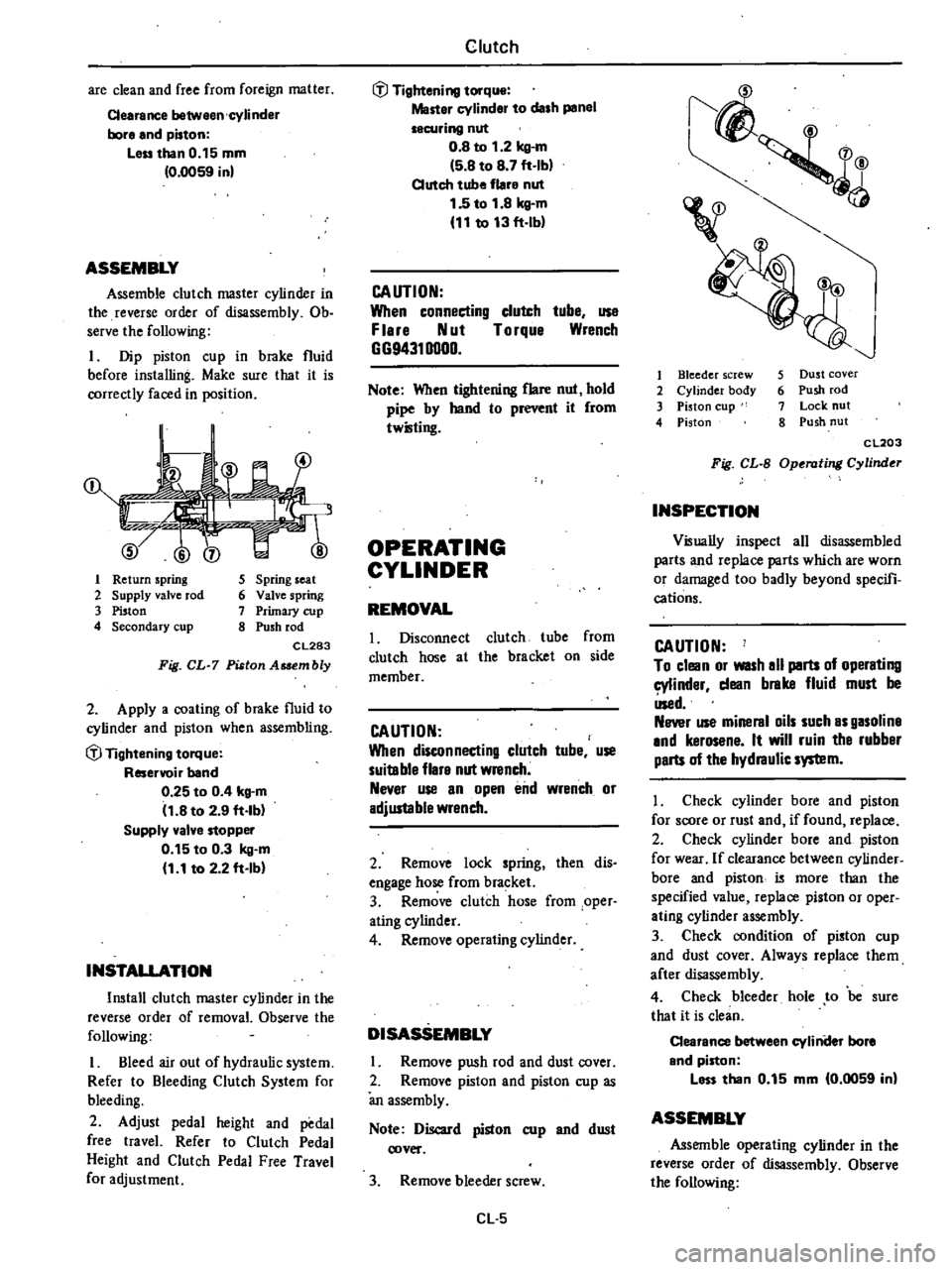
1
Return
spring
2
Supply
valve
rod
3
Piston
4
Secondary
cup
5
Spring
seat
6
Valve
spring
7
Primary
cup
8
Push
rod
CL283
Fig
CL
7
Piston
Asaembly
2
Apply
a
coating
of
brake
fluid
to
cylinder
and
piston
when
assembling
if
Tightening
torque
Reservoir
band
0
25
to
0
4
kg
m
11
8
to
2
9
ft
lb
Supply
valve
stopper
0
15
to
0
3
kg
m
1
1
to
2
2
ft
Ib
INSTALLATION
Install
clutch
master
cylinder
in
the
reverse
order
of
removal
Observe
the
following
I
Bleed
air
out
of
hydraulic
system
Refer
to
Bleeding
Clutch
System
for
bleeding
2
Adjust
pedal
height
and
pedal
free
travel
Refer
to
Clutch
Pedal
Height
and
Clutch
Pedal
Free
Travel
for
adjustment
Clutch
if
Tightening
torque
Master
cylinder
to
dash
panel
securing
nut
0
8
to
1
2
kg
m
5
8
to
8
7
ft
Ib
Clutch
tube
flare
nut
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
11
to
13
ft
lb
CAUTION
When
connecting
clutch
tube
use
F
lere
Nut
Torque
Wrench
GG94310000
Note
When
tightening
flare
nut
hold
pipe
by
hand
to
r
it
from
twilling
OPERATING
CYLINDER
REMOVAL
I
Disconnect
clutch
tube
from
clutch
hose
at
the
bracket
on
side
member
CAUTION
When
disconnecting
clutch
tube
use
suitable
flare
nut
wrench
Never
use
an
open
end
wrench
or
adjustable
wrench
2
Remove
lock
spring
then
dis
engage
hose
from
bracket
3
Remove
clutch
hose
from
oper
ating
cylinder
4
Remove
operating
cylinder
DISASSEMBLY
Remove
push
rod
and
dust
cover
2
Remove
piston
and
piston
cup
as
an
assembly
Note
Discard
piston
cup
and
dust
cover
3
Remove
bleeder
screw
Cl
5
1
4
v
I
Bleeder
screw
2
Cylinder
body
3
Piston
cup
4
Piston
5
Dust
cover
6
Push
rod
7
Lock
nut
8
Push
nut
CL203
Fig
CL
B
Operating
Cylinder
INSPECTION
Visually
inspect
all
disassembled
parts
and
replace
parts
which
are
worn
or
damaged
too
badly
beyond
specifi
cations
CAUTION
To
clean
or
WISh
all
parts
of
operating
cylinder
dean
brake
fluid
must
be
Used
Never
use
mineral
oils
such
as
gasoline
and
kerosene
It
will
ruin
the
rubber
parts
of
the
hydraulic
system
I
Check
cylinder
bore
and
piston
for
score
or
rust
and
if
found
replace
2
Check
cylinder
bore
and
piston
for
wear
If
clearance
between
cylinder
bore
and
piston
i5
more
than
the
specified
value
replace
piston
or
oper
ating
cylinder
assembly
3
Check
condition
of
piston
cup
and
dust
cover
Always
replace
them
after
disassembly
4
Check
bleeder
hole
to
be
sure
that
it
is
clean
Clearance
between
cyliniler
bore
and
piston
less
than
0
15
mm
0
0059
in
ASSEMBLY
Assemble
operating
cylinder
in
the
reverse
order
of
disassembly
Observe
the
following
Page 214 of 548

Condition
Clutch
slips
Clutch
drags
Clutch
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Probable
cause
and
testing
Corrective
action
Slipping
of
clutch
may
be
noticeable
when
any
of
the
following
symptoms
is
encountered
during
operation
I
Car
will
not
respond
to
erigine
speed
during
acceleration
2
Insufficient
car
speed
3
Lack
of
power
during
uphill
driving
Some
of
the
above
conditions
may
also
be
attributable
to
engine
problem
First
determine
whether
engine
or
clutch
is
causing
the
problem
If
slipping
clutch
is
left
unheeded
wear
and
or
overheating
will
occur
on
clutch
facing
to
such
an
extent
that
it
is
no
longer
serviceable
TO
TEST
FOR
SLIPPING
CLurCH
proceed
as
follows
During
upgrade
havelling
run
engine
at
about
40
to
50
km
h
25
to
31
MPH
with
gear
shift
lever
in
3rd
speed
position
shift
into
highest
gear
and
t
the
same
time
rev
up
engine
If
clutch
is
slipping
car
willnot
readily
respond
to
depression
of
accelerator
pedal
Clutch
facing
warn
excessively
Oil
or
grease
on
clutch
facing
Warped
clutch
cover
or
pressure
plate
Replace
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Dragging
clu
tch
is
particularly
noticeable
when
shifting
gears
especially
into
low
gear
TO
TEST
FOR
DRAGGING
CLurCH
proceed
as
follows
I
Start
engine
Disengage
clutch
Shift
into
reverse
gear
and
then
into
Neutral
Gradually
increase
engine
speed
and
again
shift
into
reverse
gear
If
clutch
is
dragging
gear
grating
is
heard
when
shifting
gears
from
Neutral
into
Reverse
2
Stop
engine
and
shift
gears
Conduct
this
test
at
each
gear
position
3
In
step
2
gears
are
shifted
smoothly
except
1st
speed
position
at
idling
a
If
dragging
is
encountered
at
the
end
of
shifting
check
condition
of
synchro
mechanism
in
transmission
b
If
dragging
is
encountered
at
the
beginning
of
shifting
proceed
to
step
4
below
4
Push
change
lever
toward
Reverse
ide
depress
pedal
to
check
for
free
travel
of
pedal
a
If
pedal
can
be
depressed
further
check
clutch
for
condition
b
If
pedal
cannot
be
depressed
further
proceed
to
step
5
below
5
Check
clutch
control
pedal
height
pedal
free
play
free
travel
withdrawal
lever
play
etc
If
any
abnormal
condition
does
not
exist
and
if
pedal
cannot
be
depressed
further
check
clutch
for
condition
Clutch
disc
runout
or
warped
Wear
or
rust
on
hub
splines
in
clutch
disc
Diaphragm
spring
toe
height
out
of
adjustment
or
toe
tip
worn
Worn
or
improperly
installed
parts
Replace
Clean
and
lubricate
with
grease
or
replace
Adjust
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
CL12
Page 215 of 548

Condition
Clutch
chatters
Noisy
clutch
Clutch
grabs
Clutch
Probable
cause
and
testing
Corr
ctive
action
Clutch
chattering
is
usually
noticeable
when
car
is
just
rolled
off
with
clutch
parlially
engaged
Weak
or
broken
clutch
disc
torsion
spring
Oil
or
grease
on
clutch
facing
Clutch
facing
out
of
proper
contact
or
clutch
disc
runout
Loose
rivets
Warped
pressure
plate
or
clutch
cover
surface
Unevenness
of
diaphragm
spring
toe
height
Loose
engine
mounting
or
deteriorated
rubber
A
noise
is
heard
after
clutch
is
disengaged
Damaged
release
bearing
A
noise
is
heard
when
clutch
is
disengaged
Insufficient
grease
on
the
sliding
surface
of
bearing
sleeve
Clutch
cover
and
bearing
are
not
in
stalled
correctly
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Adjust
or
replace
Retighten
or
replace
I
Replace
Apply
grease
Adjust
A
noise
is
heard
when
car
is
suddenly
rolled
off
with
clutch
partially
engaged
Damaged
pilot
bushing
I
Replace
When
grabbing
of
clutch
occurs
car
will
not
roll
off
smoothly
from
a
standing
start
or
clutch
will
be
engaged
before
clutch
pedal
is
fully
depressed
Oil
or
grease
on
clutch
facing
Clutch
facing
worn
or
loose
rivets
Wear
or
rust
on
splines
in
drive
shaft
and
clutch
disc
Warped
flywheel
or
pressure
plate
Loose
mountings
for
engine
or
power
train
units
CL13
Replace
Replace
Clean
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Retighten
Page 225 of 548
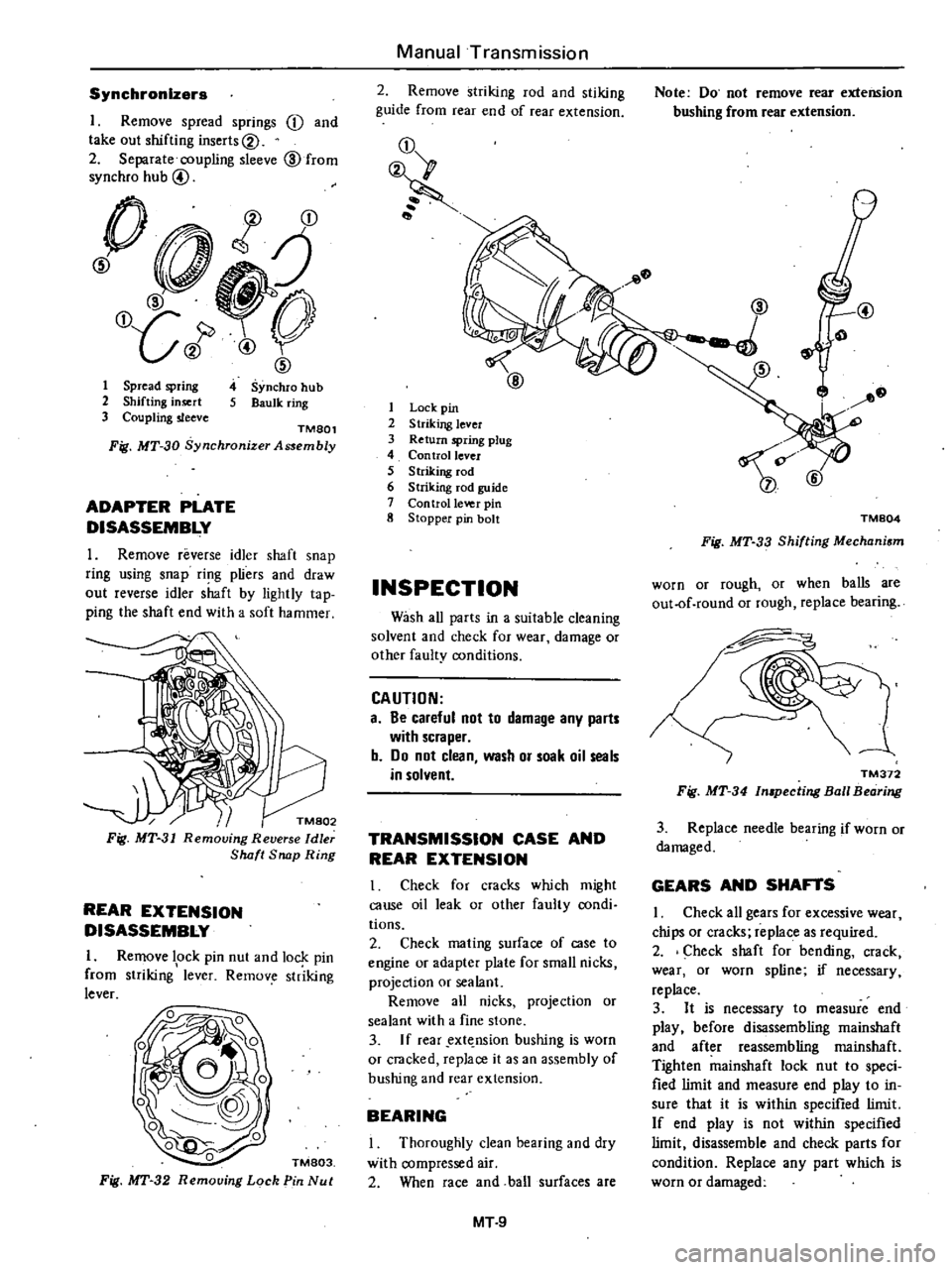
Synchronizers
I
Remove
spread
springs
j
and
take
out
shifting
inserts@
2
Separate
coupling
sleeve
@
from
synchro
hub
@
0
t
j
@
O
LJ
J
1
ID
4
Synchro
hub
S
Baulk
ring
1
Spread
spring
2
Shifting
insert
3
Coupling
sleeve
TMSOl
Fig
MT
30
Synchronjzer
Assembly
ADAPTER
PLATE
DISASSEMBLY
1
Remove
reverse
idler
shaft
snap
ring
using
snap
ri
1g
pliers
and
draw
out
reverse
idler
shaft
by
lightly
tap
ping
the
shaft
end
with
a
soft
hammer
k
Fig
MT
31
Removing
Reverse
Idler
Shaft
Snap
Ring
REAR
EXTENSION
DISASSEMBLY
I
Remove
lock
pin
nut
and
lock
pin
from
striking
1
lever
Remov
str
iking
lever
TM803
Fig
MT
32
Removing
Lock
Pin
Nut
Manual
Transmission
2
Remove
striking
rod
and
stiking
guide
from
rear
end
of
rear
extension
j
1
Lock
pin
2
Striking
lever
3
Return
spring
plug
4
Con
trollevcr
5
Striking
rod
6
Striking
fod
guide
7
Control
Ie
o
eI
pin
8
Stopper
pin
bolt
INSPECTION
Wash
all
parts
in
a
suitable
cleaning
solvent
and
check
for
wear
damage
or
other
faulty
conditions
CAUTION
a
Be
careful
not
to
damage
any
parts
with
scraper
b
Do
not
clean
wash
or
soak
oil
seals
in
solvent
TRANSMISSION
CASE
AND
REAR
EXTENSION
I
Check
for
cracks
which
might
cause
oil
leak
or
other
faulty
condi
tions
2
Check
mating
surface
of
case
to
engine
or
adapter
plate
for
small
nicks
projection
or
sealant
Remove
all
nicks
projection
or
sealant
with
a
fine
stone
3
If
rear
ext
nsion
bushing
is
worn
or
cracked
replace
it
as
an
assembly
of
bushing
and
rear
extension
BEARING
Thoroughly
clean
bearing
and
dry
with
compressed
air
2
When
race
and
ball
surfaces
are
MT
9
Note
Do
not
remove
rear
extension
bushing
from
rear
extension
@
TM804
Fig
MT
33
Shifting
Mechanism
worn
or
rough
or
when
balls
are
out
of
round
or
rough
replace
bearing
TM372
Fig
MT
34
In
pecting
Ball
Bearing
3
Replace
needle
bearing
if
worn
or
damaged
GEARS
AND
SHAFTS
I
Check
all
gears
for
excessive
wear
chips
or
cracks
replace
as
required
2
Check
shaft
for
bending
crack
wear
or
worn
spline
if
necessary
replace
3
It
is
necessary
to
measure
end
play
before
disassembling
mainshaft
and
after
reassembling
rnainshaft
Tighten
mainshaft
lock
nut
to
speci
fied
limit
and
measure
end
play
to
in
sure
that
it
is
within
specified
limit
If
end
play
is
not
within
specified
limit
disassemble
and
check
parts
for
condition
Replace
any
part
which
is
worn
or
damaged
Page 239 of 548
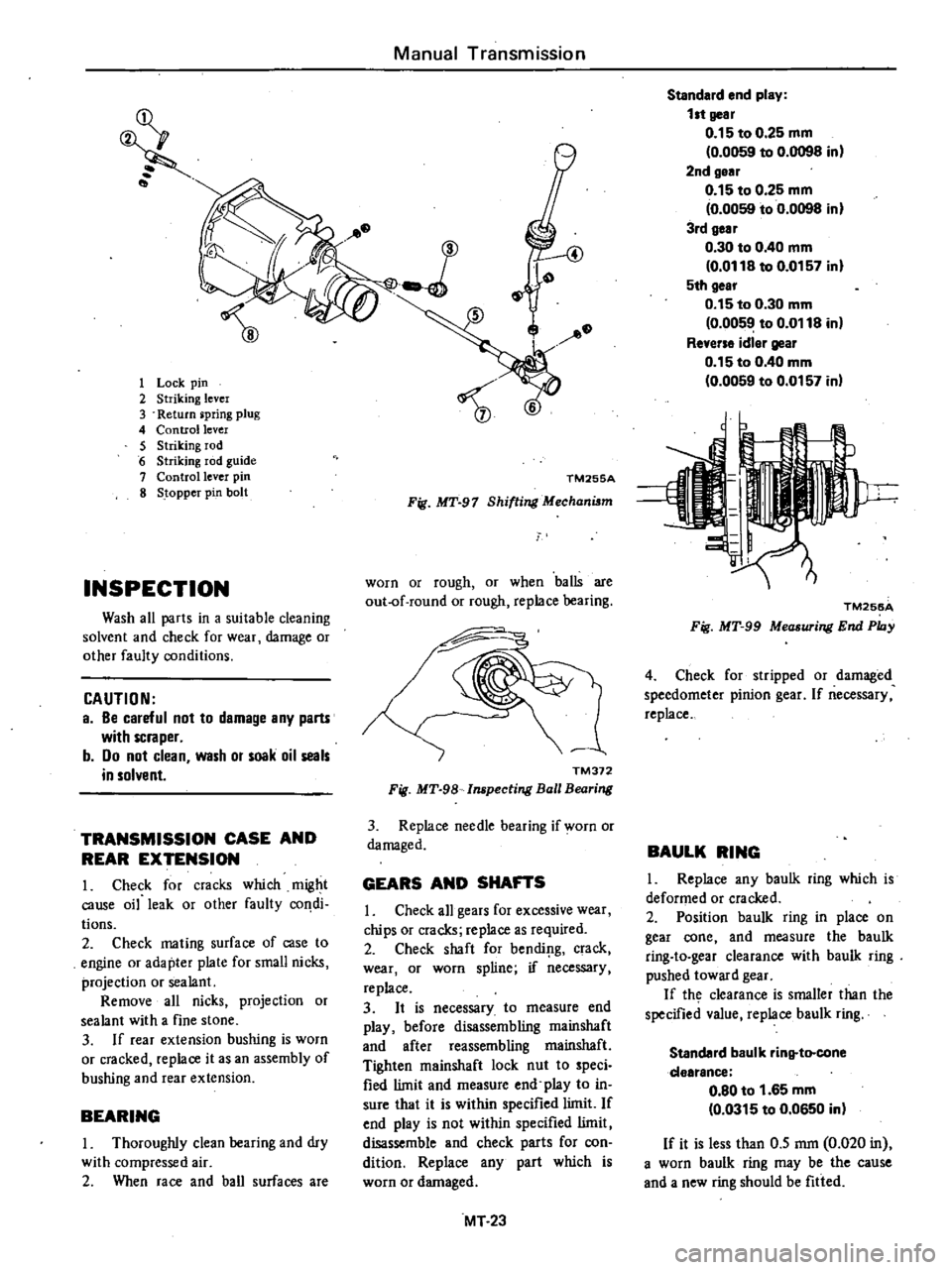
1
Lock
pin
2
Striking
lever
3
Return
pring
plug
4
Control
lever
5
Striking
rod
6
Striking
rod
guide
7
Control
lever
pin
8
Stopper
pin
bolt
INSPECTION
Wash
all
parts
in
a
suitable
cleaning
solvent
and
check
for
wear
damage
or
other
faulty
conditions
CAUTION
a
Be
careful
not
to
damage
any
parts
with
scraper
b
Do
not
clean
wash
or
soak
oil
seals
in
solvent
TRANSMISSION
CASE
AND
REAR
EXTENSION
1
Check
for
cracks
which
might
cause
oil
leak
or
other
faulty
condi
tions
2
Check
mating
surface
of
case
to
engine
or
adapter
plate
for
small
nicks
projection
or
sealant
Remove
all
nicks
projection
or
sealant
with
a
fine
stone
3
If
rear
extension
bushing
is
worn
or
cracked
replace
it
as
an
assembly
of
bushing
and
rear
extension
BEARING
I
Thoroughly
clean
bearing
and
dry
with
compressed
air
2
When
race
and
ball
surfaces
are
Manual
Transmission
1
TM255A
Fig
MT
97
Shifting
Mechanism
worn
or
rough
or
when
balls
are
out
of
round
or
rough
replace
bearing
TM372
Fig
MT
98
Inspecting
Ball
Bearing
3
Replace
needle
bearing
if
worn
or
damaged
GEARS
AND
SHAFTS
I
Check
all
gears
for
excessive
wear
chips
or
cracks
replace
as
required
2
Check
shaft
for
bendillg
crack
wear
or
worn
spline
if
necessary
replace
3
It
is
necessary
to
measure
end
play
before
disassembling
mainshaft
and
after
reassembling
mainshaft
Tighten
mainshaft
lock
nut
to
speci
fied
limit
and
measure
end
play
to
in
sure
that
it
is
within
specified
limit
If
end
play
is
not
within
specified
limit
disassemble
and
check
parts
for
con
dition
Replace
any
part
which
is
worn
or
damaged
MT
23
Standard
end
play
1
t
gear
0
15
to
0
25
mm
0
0059
to
0
0098
in
2nd
gear
0
15
to
0
25
mm
0
0059
to
0
0098
in
3rd
gear
0
30
to
0
40
mm
0
0118
to
0
0157
in
5th
gear
0
15
to
0
30
mm
0
0059
to
0
0118
in
Reverse
idler
gear
0
15
to
0
40
mm
0
0059
to
0
0157
in
TM256A
Fig
MT
99
Measuring
End
Phly
4
Check
for
stripped
or
damaged
speedometer
pinion
gear
If
necessary
replace
BAULK
RING
I
Replace
any
baulk
ring
which
is
deformed
or
cracked
2
Position
baulk
ring
in
place
on
gear
cone
and
measure
the
baulk
ring
to
gear
clearance
with
baulk
ring
pushed
toward
gear
If
th
clearance
is
smaller
than
the
specified
value
replace
baulk
ring
Standard
baulk
rinltto
cone
dearance
0
80
to
1
65
mm
0
0315
to
0
0650
in
If
it
is
less
than
0
5
mm
0
020
in
a
worn
baulk
ring
may
be
the
cause
and
a
new
ring
should
be
fitted
Page 250 of 548

Manual
Transmission
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Difficult
to
intermesh
gears
Causes
for
difficult
gear
shifting
are
classi
fie
t
o
ro
lb
c
QncerlJing
coJltr
1
syste
and
transmission
When
gear
shift
lever
is
heavy
and
it
is
difficult
to
shift
gears
clutch
disengagement
may
also
be
unsmooth
First
make
sure
that
clutch
operates
correctly
and
inspect
transmjssion
Gear
slips
out
of
mesh
In
most
cases
this
troubk
occurs
when
check
baD
and
or
spring
is
waIn
or
weaken
ed
or
when
control
system
is
faulty
In
this
case
the
troubk
cannot
be
correct
by
replacing
gears
and
therefore
trouble
shoot
ing
must
be
carried
out
carefuDy
It
should
also
be
noted
that
gear
slips
out
of
mesh
due
to
vibration
generated
by
weakened
front
and
rear
enigne
mounts
Noise
When
noise
occurs
with
engine
idling
and
ceases
when
clutch
is
disengaged
or
when
noise
occurs
while
shifting
gears
it
is
an
indication
that
the
noise
is
from
trans
mission
Transmission
may
rallk
during
engine
idling
Check
air
fuel
mixture
and
ignition
timing
After
above
procedure
readjust
engine
idling
Probable
cause
Worn
gears
shaft
and
or
bearing
Insufficient
operating
stroke
due
to
worn
or
loose
sliding
part
Worn
or
damaged
syncluonizer
Worn
check
baD
and
or
weakened
or
broken
spring
Worn
fork
rod
baU
groove
Worn
or
damaged
bearing
Worn
or
damaged
gear
Insufficient
or
improper
lubricant
Oil
leaking
due
to
damaged
oil
seal
or
sealant
clogged
breather
etc
Worn
bearing
High
humming
occurs
at
a
high
speed
Damaged
bearing
Cyclic
knocking
sound
occurs
also
at
a
low
speed
Worn
spline
Worn
bushing
MT34
Corrective
action
Replace
Repair
ClI
replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Add
oil
or
replace
with
designated
oil
Clean
or
replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
as
a
rear
ex
tension
assembly
Page 286 of 548
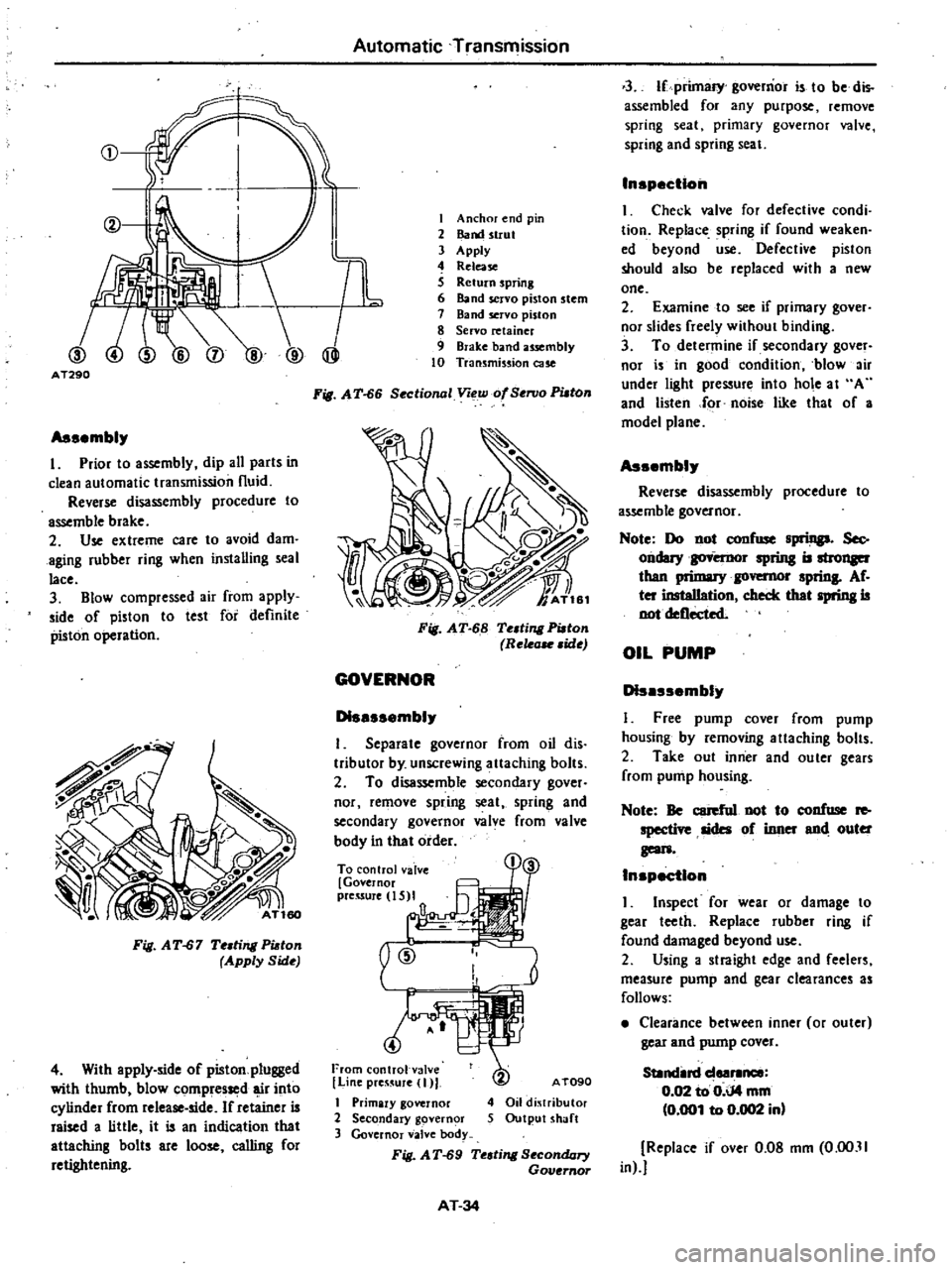
CD
@
I
I
TL
@
@
AT290
Assembl
I
Prior
to
assembly
dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
Reverse
disassembly
procedure
to
assemble
brake
2
Use
extreme
care
to
avoid
dam
aging
rubber
ring
when
installing
seal
lace
3
Blow
compressed
air
from
apply
side
of
piston
to
test
for
definite
piston
operation
Fig
AT
67
Te
ling
Pi
ton
Apply
Side
4
With
apply
side
of
piston
plugged
with
thumb
blow
compressed
r
into
cylinder
from
release
side
If
retainer
is
raised
a
little
it
is
an
indication
that
attaching
bolts
are
loose
calling
for
retightening
Automatic
Transmission
I
Anchor
end
pin
2
Band
strut
3
Apply
4
Release
S
Return
spring
6
Band
servo
piston
stem
7
Band
servo
piston
8
Servo
retainer
9
Brake
band
usembly
10
Transmission
cue
Fig
A
T
66
Sectional
Voew
of
SenJo
PUlOn
Fig
AT
68
Te
ting
Pi
ton
Rele
ide
GOVERNOR
D1sessembl
I
Separate
governor
from
oil
dis
tributor
by
unscrewing
attaching
bolts
2
To
disassemble
secondary
gover
nor
remove
spring
seat
spring
and
secondary
governor
valve
from
valve
body
in
that
order
To
control
valve
Governor
preuure
IS
I
a
@
From
control
val
e
I
Line
preS
UJe
I
I
Primary
governor
2
Secondary
govern
r
3
Governor
valve
body
Fig
AT
69
Te
ling
SecondQry
Governor
AT090
4
Oil
dj
tributor
5
Output
shaft
AT
34
3
If
primary
governor
is
to
be
dis
assembled
for
any
purpose
remove
spring
seat
primary
governor
valve
spring
and
spring
seal
Inspection
I
Check
valve
for
defective
condi
tion
Replace
spring
if
found
weaken
ed
beyond
use
Defective
piston
should
also
be
replaced
with
a
new
one
2
Examine
to
see
if
primary
gover
nor
slides
freely
without
binding
3
To
determine
if
secondary
gover
nor
is
in
good
condition
blow
ir
under
light
pressure
into
hole
at
A
and
listen
for
noise
like
thaI
of
a
model
plane
Assembl
Reverse
disassembly
procedure
to
assemble
governor
Note
Do
not
confuse
spriDp
Sec
ondary
spring
is
than
1
governor
sprinS
Af
ter
insteIIation
check
thet
spring
is
not
deflected
OIL
PUMP
D1sessembl
I
Free
pump
cover
from
pump
housing
by
removing
allaching
bolts
2
Take
out
inner
and
ouler
gears
from
pump
housing
Note
Be
cerefnl
not
to
confuse
Ie
specti
sides
of
inner
end
outer
geon
Inspection
I
Inspect
for
wear
or
damage
to
gear
teeth
Replace
rub
bel
ring
if
found
damaged
beyond
use
2
Using
a
straight
edge
and
feelers
measure
pump
and
gear
clearances
as
follows
Clearance
between
inner
or
outer
gear
and
pump
cover
SUndin
deer1lnee
0
02
to
0
iJ4
mm
0
001
to
0
002
in
Replace
if
over
0
08
mm
0
00
11
in
Page 291 of 548

Automatic
Transmission
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
AND
ADJUSTMENT
Since
mo
automatic
transmission
troubles
can
be
repaired
by
simple
adjustment
do
not
disassemble
im
media
tely
Firstly
inspect
and
adjust
the
auto
D1
3tic
transmission
in
place
utilizing
the
Trouble
Shooting
Chart
If
the
trouble
can
not
be
solved
by
this
procedure
remove
and
disas
semble
the
automatic
tlllnsmission
It
is
advisable
to
check
overhaul
and
repair
each
part
in
the
order
listed
in
the
Trouble
Shooting
Chart
In
the
Trouble
Shooting
Chart
the
diagnosis
items
are
arranged
ac
cording
to
difficulty
from
easy
to
difficult
therefore
please
follow
these
items
The
tlllnsmission
should
riot
be
removed
unless
necessary
2
Tests
and
adjustments
should
be
inade
on
the
basil
of
standard
values
and
the
data
Should
be
recorded
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
BEFORE
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
TESTING
INSTRUMENT
FOR
INSPECTION
I
Engine
t
chometer
2
Vacuum
gauge
3
Oil
pressure
gauge
It
is
convenieni
to
install
these
instruments
in
a
way
that
allows
meas
urements
to
be
made
from
the
driver
s
seat
CHECKING
OIL
LEVEL
In
checkIng
the
automatic
transmis
sion
the
oil
level
and
the
condition
of
oil
around
the
oil
level
gauge
should
be
examined
every
S
ooo
Ion
3
000
miles
This
is
an
easy
and
effective
trouble
shooting
procedure
since
some
changes
in
oil
condition
are
often
linked
with
developed
troubles
For
instance
Lack
of
oil
causes
defective
opera
tion
by
making
the
clutches
and
brakes
slip
resulting
in
severe
wear
This
is
because
the
oil
pump
sucks
air
causing
oil
foaming
thus
rapidly
deteriorating
the
oil
quality
and
pro
ducing
sludge
and
varnish
Excessive
oil
is
also
bad
because
of
oil
foaming
caused
by
the
gears
stirring
up
the
oil
During
high
speed
driving
excessive
oil
in
the
transmission
often
hlows
out
from
the
brealher
Me
urlns
011
level
To
check
the
nuid
leyel
sian
Ihe
engine
and
run
it
until
normal
operat
ing
temperatures
oil
temperature
SO
to
800C
122
to
1160F
Approxi
mately
ten
minute
of
operation
will
raise
the
temperature
to
this
range
and
engine
idling
conditions
are
stabi
lized
Then
apply
the
brakes
and
move
the
transmission
shift
lever
through
aU
drive
positions
and
place
it
in
park
P
position
In
his
inspec
tion
the
car
must
be
placc
d
on
a
level
surface
The
amount
of
the
oil
varies
with
the
temperature
As
a
rule
the
oil
level
must
be
measured
after
its
tempera
ture
becomes
sufficiently
high
I
Fill
the
oil
to
the
line
H
The
difference
of
capacities
between
both
H
and
L
is
approximately
0
4
liter
J
U
S
pt
Y
Imp
pt
and
therefore
do
not
fill
beyond
the
line
H
2
When
topping
up
and
changing
oil
care
should
be
taken
to
prevent
mixing
the
oil
with
dusl
and
water
In
pectlns
oU
condition
The
condition
of
oil
sticking
to
the
level
gauge
indicates
whether
to
OVOl
haul
and
repair
the
transmission
or
luok
for
Ihe
defective
part
If
the
oil
has
deteriorated
to
a
varnish
ike
quality
it
causes
the
con
trol
valve
to
stick
Blackened
oil
indi
cates
a
burned
clutch
brake
band
etc
AT
39
In
these
cases
the
transmission
must
be
repaired
CAUTION
I
In
checking
oil
IlVal
use
special
piper
Cloth
tohandla
the
18V81
llIugi
Ind
be
careful
not
to
let
the
scraps
of
paper
end
cloth
stick
to
the
IlIUp
b
U
lutomatic
transmission
fluid
having
OEXRON
ida
ons
only
in
the
3N71
B
eutomatic
trans
mission
c
Pay
IttBntion
blcau
the
oil
to
be
used
differs
from
that
used
in
the
Nissen
Full
Autometic
TllInsmis
sion
3N71A
N8V8r
mill
thl
oils
Note
Insert
the
gauge
fully
and
take
it
out
quickly
before
splesbing
oil
edheres
to
the
gauge
Then
observe
the
level
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
OF
OIL
LEAKAGE
When
oil
leakage
takes
place
the
portion
near
the
leakage
is
covered
with
oil
presenting
difficulty
in
detecting
the
spot
Therefore
the
places
where
oil
seals
and
gaskets
are
equipped
are
enumerated
below
Converter
housing
Rubber
ring
of
oil
pump
housing
Oil
seal
of
oil
pump
housing
Oil
seal
of
engine
crankshaft
Bolts
of
converter
housing
to
case
2
Transmission
and
rear
extension
Junction
of
transmission
and
rear
extension
Oil
cooler
tube
connectors
Oil
pan
Oil
pressure
inspection
holes
See
Fig
AT
81
Mounting
portion
of
vacuum
dia
phragm
and
downshift
solenoid
Breather
and
oil
charging
pipe
Speedometer
pinion
sleeve
Oil
seal
of
rear
extension
To
exactly
locate
Ihe
place
of
oil
leakage
proceed
as
follows
Page 311 of 548

they
are
worn
damaged
or
otherwise
faulty
and
how
they
are
affected
Re
pair
or
replace
all
faulty
parts
which
ever
is
necessary
1
Check
gear
teeth
for
scoring
cracking
or
chipping
and
make
sure
that
tooth
contact
pattern
indicates
correct
meshing
depth
If
any
fault
is
evident
replace
parts
as
required
Note
Drive
pinion
and
ring
gear
are
supplied
for
replacement
as
a
set
therefore
should
either
part
be
damaged
replece
as
a
set
2
Check
pinion
shaft
and
pinion
mates
for
scores
and
signs
of
wear
and
replace
as
required
F
oUow
the
same
procedure
for
side
gear
and
their
seats
on
differential
case
3
Inspect
all
bearing
races
and
roU
ers
for
scoring
chipping
or
evidence
of
excessive
wear
They
should
be
in
tiptop
condition
such
as
not
worn
and
with
mirror
like
surfaces
Replace
if
there
is
a
shadow
of
doubt
on
their
efficiency
as
an
incorrect
bearing
op
eration
may
result
in
noises
and
gear
seizure
4
Inspect
thrust
washer
faces
SmaU
faults
can
be
corrected
with
sand
paper
If
pinion
mate
to
de
gear
backlash
exceeds
specified
value
re
place
thrust
washers
Pinion
mate
to
side
gear
backlash
0
10
to
0
20
mm
0
0039
to
0
0079
in
5
Inspect
gear
carrier
and
differ
ential
case
for
cracks
or
distortion
If
either
condition
is
evident
replace
Jaulty
parts
6
As
a
general
rule
oil
seal
should
be
replaced
at
each
disassembly
ASSEMBLY
AND
ADJUSTMENT
Assembly
can
be
done
in
the
reverse
order
of
disassembly
The
foUowing
directions
for
adjustment
and
usage
of
special
tools
enable
to
obtain
a
perfect
differential
operation
Propeller
Shaft
Differential
Carrier
PRECAUTIONS
IN
REASSEMBLY
I
Arrange
shims
washers
and
the
like
to
install
them
correctly
2
Thoroughly
clean
the
surfaces
on
which
shims
washers
bearings
and
bearing
caps
are
installed
3
Apply
gear
oil
when
installing
bearings
4
Pack
grease
cavity
between
lips
when
fitting
oil
seal
ASSEMBLY
OF
DIFFERENTIAL
CASE
1
Assemble
pinion
mates
side
gears
and
thrust
washers
in
differential
case
2
Fit
pinion
shaft
to
differential
case
so
that
it
meets
lock
pin
hole
3
Adjust
pinion
mate
to
ide
gear
backlash
or
the
clearance
between
the
rear
face
of
side
gear
and
thrust
washer
to
the
specified
value
by
selecting
side
gear
thrust
washer
Pinion
mate
to
side
gear
backlash
0
10
to
0
20
mm
10
0039
to
0
0079
in
PD023
Fig
PD
l1
Measuring
Clearance
Side
gear
thrust
washer
Thickness
mm
in
0
785
0
0309
0
835
0
0329
0
885
0
0348
4
Lock
pinion
shaft
lock
pin
using
a
punch
after
it
is
secured
into
place
5
Apply
oil
to
gear
tooth
surfaces
and
thrust
surfaces
and
check
if
they
turn
properly
6
Place
ring
gear
on
differential
case
and
install
bolts
and
lock
straps
Tor
que
bolts
to
specification
and
bend
up
lock
straps
PO
5
tiJ
Tightening
torque
Ring
gear
bolt
6
0
to
7
0
kg
m
43
to
51
ft
Ib
CAUTION
e
Use
only
genuine
ring
gear
bolts
end
new
lock
straps
b
Tighten
bolts
in
criss
crilss
fashion
lightly
tapping
around
bolt
heads
with
a
hammer
7
When
replacing
side
bearing
measure
bearing
width
using
Side
Bear
ing
Adjust
Weight
ST3250S000
Weight
mock
ST3250
I
000
and
Master
Gauge
ST325020oo
or
suit
able
standard
gauge
17
5
nun
0
689
in
thickness
and
a
weight
block
2
5
kg
5
5
Ib
prior
to
installation
Standald
bearing
width
17
5
mm
10
689
in
y
ST32501000
8
Select
side
bearing
shims
re
ferring
to
Adjustment
of
Side
Bearing
Shims
9
Press
fit
side
bearing
cone
into
differential
case
using
Gear
Carrier
Side
Bearing
Drift
ST33220oo0
and
Adapter
ST33052000
w
I
ST33220000
PD244
1000
ST33052000
Fig
PD
13
lnatalling
Side
Bearing
Cone
Page 319 of 548
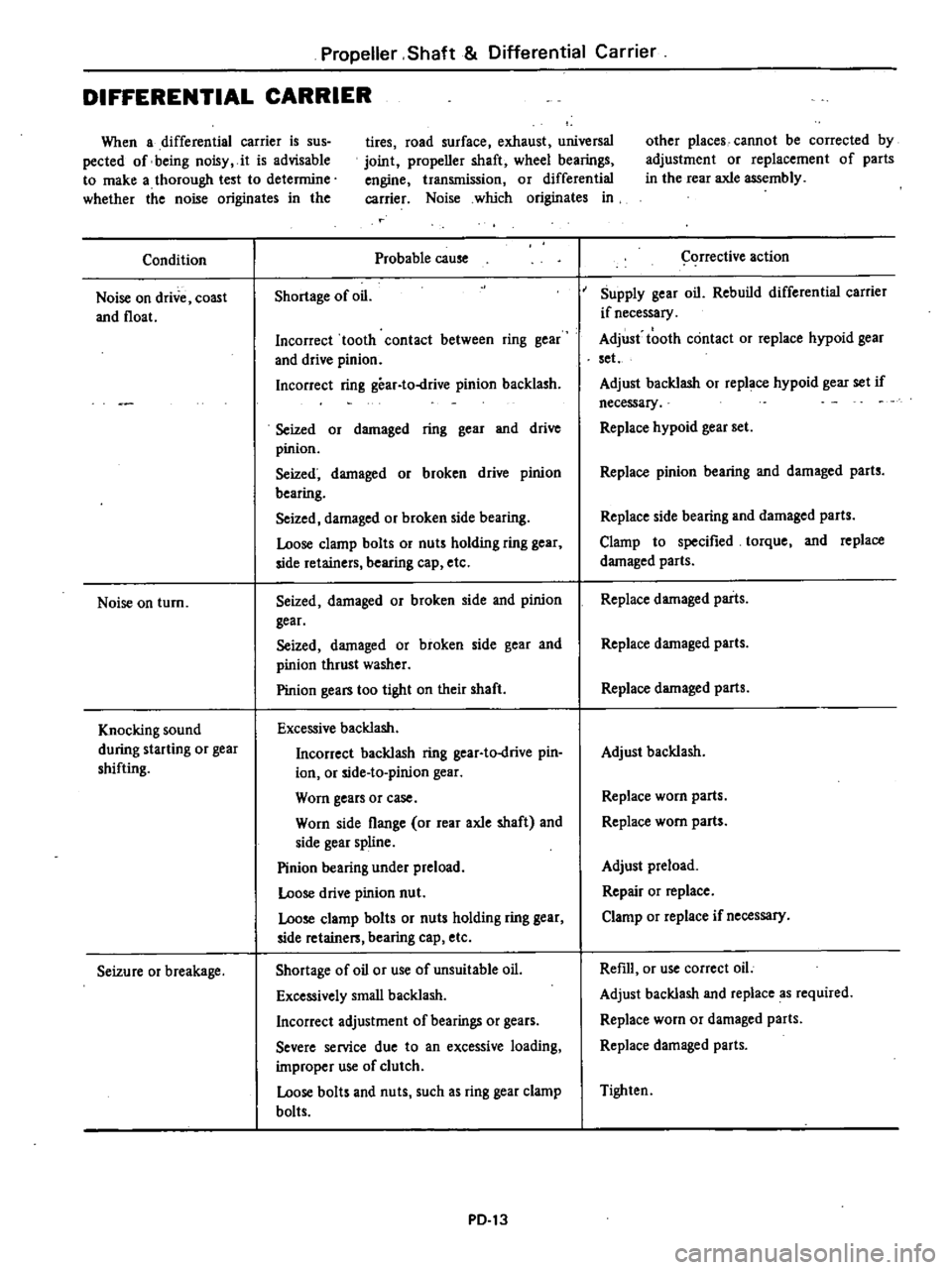
Propeller
Shaft
Differential
Carrier
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
When
a
differential
carrier
is
sus
pected
of
being
noisy
it
is
advisable
to
make
a
thorough
test
to
determine
whether
the
noise
originates
in
the
tires
road
surface
exhaust
universal
joint
propeller
shaft
wheel
bearings
engine
transmission
or
differential
carrier
Noise
which
originates
in
Condition
Noise
on
drive
coast
and
float
Noise
on
turn
Knocking
sound
during
starting
or
gear
shifting
Seizure
or
breakage
Probable
cause
Shortage
of
oil
Incorrect
tooth
contact
between
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
Incorrect
ring
gear
to
drive
pinion
backlash
Seized
or
damaged
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
Seized
damaged
or
broken
drive
pinion
bearing
Seized
damaged
or
broken
side
bearing
Loose
clamp
bolts
or
nuts
holding
ring
gear
side
retainers
bearing
cap
etc
Seized
damaged
or
broken
side
and
pinion
gear
Seized
damaged
or
broken
side
gear
and
pinion
thrust
washer
Pinion
gears
too
tight
on
their
shaft
Excessive
backlash
Incorrect
backlash
ring
gear
to
drive
pin
ion
or
side
ta
pinion
gear
Worn
gears
or
case
Worn
side
flange
or
rear
axle
shaft
and
side
gear
spline
Pinion
bearing
under
preload
Loose
drive
pinion
nut
Loose
clamp
bolts
or
nuts
holding
ring
gear
side
retainers
bearing
cap
etc
Shortage
of
oil
or
use
of
unsuitable
oil
Excessively
small
backlash
Incorrect
adjustment
of
bearings
or
gears
Severe
service
due
to
an
excessive
loading
improper
use
of
clutch
Loose
bolts
and
nuts
such
as
ring
gear
clamp
bolts
PD
13
other
places
cannot
be
corrected
by
adjustment
or
replacement
of
parts
in
the
rear
axle
assembly
orrective
action
Supply
gear
oil
Rebuild
differential
carrier
if
necessary
Adjust
tooth
contact
or
replace
hypoid
gear
set
Adjust
backlash
or
replace
hypoid
gear
set
if
necessary
Replace
hypoid
gear
set
Replace
pinion
bearing
and
damaged
parts
Replace
side
bearing
and
damaged
parts
Clamp
to
specified
torque
and
replace
damaged
parts
Replace
damaged
parts
Replace
damaged
parts
Replace
damaged
parts
Adjust
backlash
Replace
worn
parts
Replace
worn
parts
Adjust
preload
Repair
or
replace
Clamp
or
replace
if
necessary
Refill
or
use
correct
oil
Adjust
backlash
and
replace
as
required
Replace
worn
or
damaged
parts
Replace
damaged
parts
Tighten