DATSUN B110 1969 Service Service Manual
Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1969, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1969Pages: 136, PDF Size: 5.64 MB
Page 41 of 136

i
J
J
1
1
1
i
j
l
1
d
1
f
t
1k
4
I
rt
I
v
401
of
t
t
Wf
P
p
r
l
iltA
4
fl
i
r
i
JIA
l
ill
t
I
i
1
J
7lt
1
jj
l
a
lfI
J
A
L
r
c
Page 42 of 136
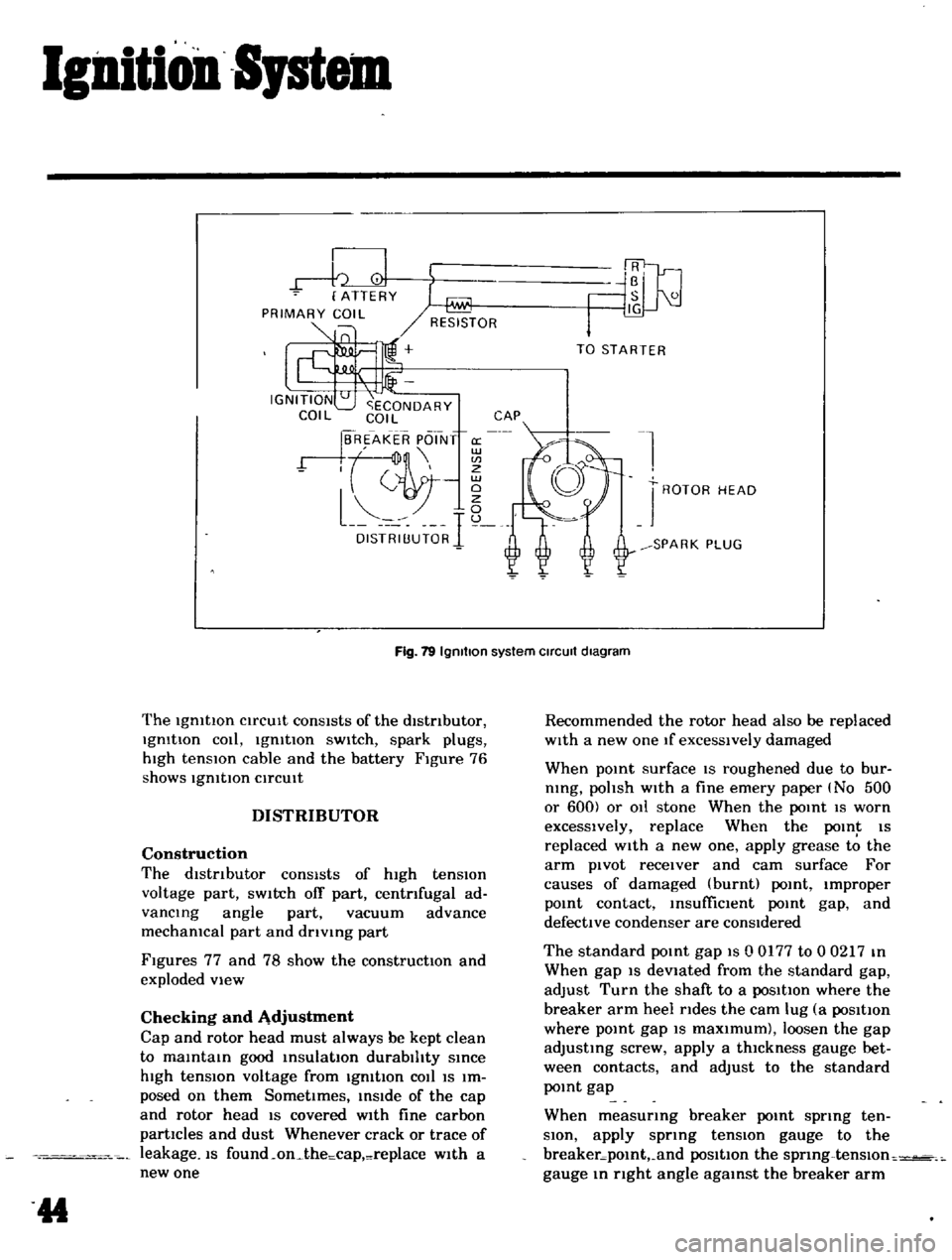
lenition
Sptem
IGNITION
SECONDARY
COI
L
COI
L
CAP
BREAKER
POTNT
cr
r
7
W
tc
l
uToRI
8
TO
STARTER
l
J
ROTOR
HEAD
SPARK
PLUG
Fig
19
Igmtlon
system
Circuit
diagram
The
IgmtlOn
CirCUIt
conSIsts
of
the
distributor
IgmtIon
cOli
IgmtIon
sWitch
spark
plugs
hIgh
tensIOn
cable
and
the
battery
Figure
76
shows
IgmtlOn
CirCUIt
DISTRIBUTOR
Construction
The
dIstributor
consists
of
high
tension
voltage
part
SWitch
off
part
centrifugal
ad
vancing
angle
part
vacuum
advance
mechamcal
part
and
drlvmg
part
Figures
77
and
78
show
the
constructIOn
and
exploded
view
Checking
and
Adjustment
Cap
and
rotor
head
must
always
be
kept
clean
to
maintain
good
insulation
durability
since
high
tensIOn
voltage
from
IgmtIon
cOil
IS
Im
posed
on
them
SometImes
inside
of
the
cap
and
rotor
head
IS
covered
wIth
fine
carbon
partIcles
and
dust
Whenever
crack
or
trace
of
leakage
IS
found
on
the
cap
replace
w1th
a
new
one
44
Recommended
the
rotor
head
also
be
replaced
wIth
a
new
one
If
excessively
damaged
When
pomt
surface
IS
roughened
due
to
bur
nlng
polish
with
a
fine
emery
paper
No
500
or
600
or
011
stone
When
the
point
IS
worn
excessively
replace
When
the
POIn
IS
replaced
with
a
new
one
apply
grease
to
the
arm
pivot
receiver
and
cam
surface
For
causes
of
damaged
burnt
point
Improper
pomt
contact
msufficlent
point
gap
and
defective
condenser
are
conSidered
The
standard
pomt
gap
IS
0
0177
to
0
0217
m
When
gap
IS
devIated
from
the
standard
gap
adjust
Turn
the
shaft
to
a
posItIon
where
the
breaker
arm
heel
rides
the
cam
lug
a
posItIon
where
pomt
gap
IS
maxImum
loosen
the
gap
adjusting
screw
apply
a
thIckness
gauge
bet
ween
contacts
and
adjust
to
the
standard
pomt
gap
When
measurmg
breaker
pomt
spring
ten
SIOn
apply
sprmg
tensIOn
gauge
to
the
breaker
pomt
and
posItIon
the
sprmg
tenslOn
gauge
m
right
angle
agamst
the
breaker
arm
Page 43 of 136
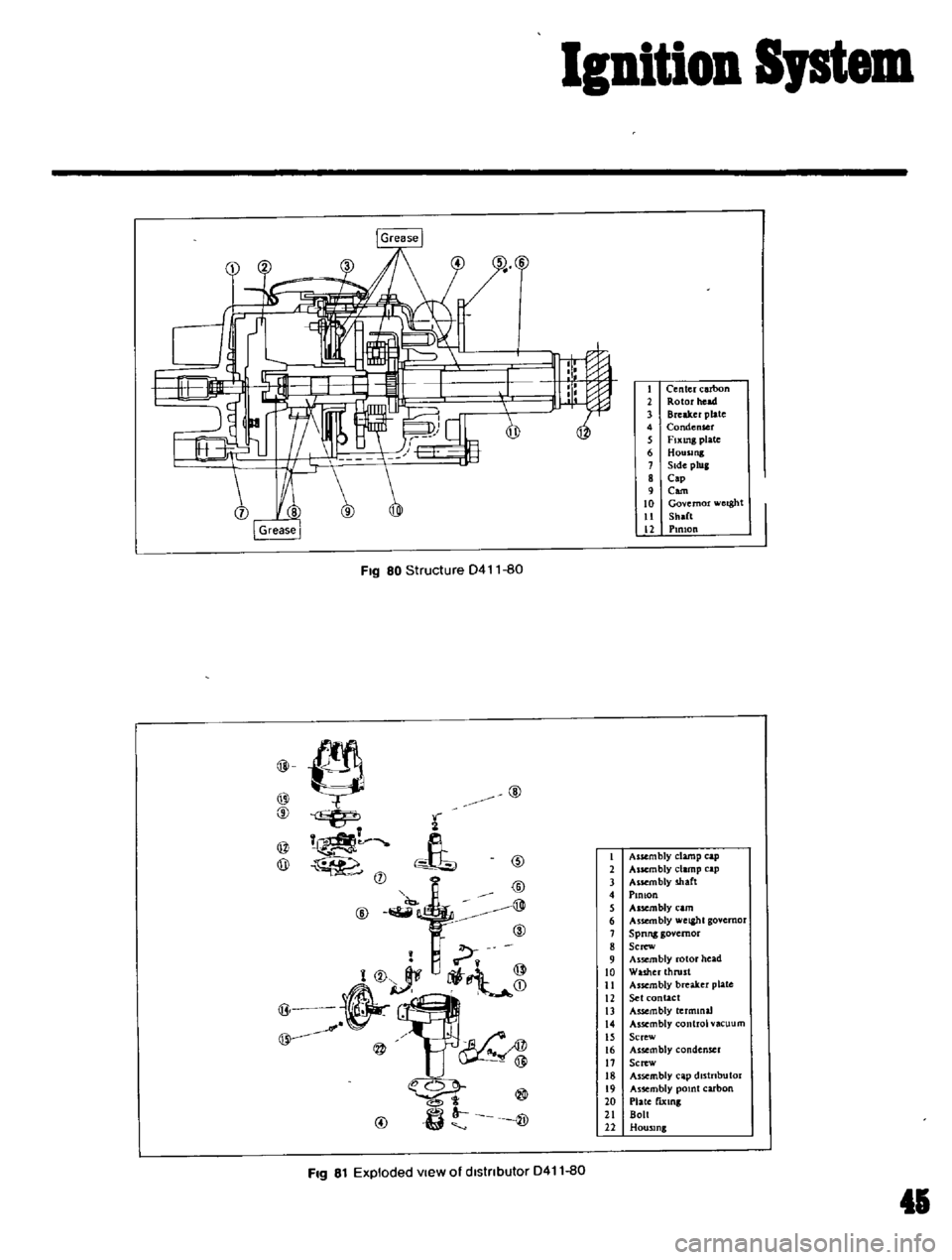
Ignition
Iptem
FIg
80
Structure
D411
80
CID
0
A
t
CID
l@J
rf
@
@
@
2
@
@
ID
@
FIg
81
Exploded
View
of
dlstnbutor
D411
80
1
Center
carbon
2
Rotor
head
3
Breaker
plate
4
Condenser
5
FIxing
plate
6
Housing
1
Side
plug
8
Cap
9
Com
10
Governor
werght
11
Sh
lft
l2
PIRIOn
1
Assembly
clamp
cap
2
Aucmbly
clamp
cap
3
Assembly
shaft
4
PlOlon
5
A
uembly
eam
6
Assembly
weight
governor
7
Spnng
governor
8
Screw
9
Assembly
rotor
head
10
Washer
thrust
II
Assembly
breaker
plate
12
Set
contact
13
Assembly
termmaJ
14
Assembly
control
vacuum
IS
Screw
16
AssembJy
condenser
17
Screw
J
8
Assembly
cap
dJstnbutor
19
Assembly
pomt
carbon
20
Plate
fixing
21
Bolt
22
Housing
45
Page 44 of 136
Ignition
Sptem
The
standard
breaker
pOint
spring
tensIOn
IS
1
1
to
1
4
lb
Replace
If
devIated
Performance
of
condenser
IS
affected
by
Im
proper
setting
contaminatIOn
and
reductIOn
of
In
ulatlOn
resIstance
Thus
pellOdlcal
checking
I
I
eqlJ
lred
to
maintain
the
outlet
of
lead
wire
clean
and
to
prevent
et
screw
from
loosening
Checking
the
condenser
capacIty
IS
checked
USing
a
capacity
meter
It
may
be
also
checked
condenser
Isolate
resl
tance
USing
a
tester
by
adjusting
ItS
I
ange
to
measure
large
I
eSlstance
value
When
the
condenser
IS
normal
the
tester
pOinter
SWings
1m
gely
and
rapIdly
and
moves
gradually
back
to
the
Infimte
SIde
When
the
pOinter
does
not
stay
stili
or
It
points
Zero
In
reSIstance
replacement
IS
necessary
Fig
82
AdJusllng
POint
gap
Fig
83
Measunng
breaker
POint
spnng
tension
g
SPARK
PLUGS
Description
The
spark
plugs
are
of
the
re
lster
type
haVing
0
551
In
threads
and
0031
to
0035
11i
gap
Note
All
spark
plugs
installed
on
an
engme
must
be
of
the
same
brand
and
number
of
heat
range
Inspection
Remove
spark
plug
wIre
by
pulhng
on
boot
not
on
WIre
Itself
Remove
spark
plugs
Check
electrodes
and
Inner
and
outer
por
celams
of
plugs
noting
the
type
of
depOSits
and
the
degree
of
electrode
erO
lOn
Refer
to
Figure
85
Normal
Brown
to
gl
aYlsh
tan
depoSits
and
shght
electrode
wear
indIcate
correct
spark
@
I
Pnmary
terminal
2
Secondary
terminal
3
Cdp
4
Sprang
5
SIde
core
6
Prrmary
coil
7
Secondary
COIl
8
Insulator
011
9
enter
lore
10
Segment
II
Case
Fig
84
Construction
Page 45 of 136

Icnition
Sptem
Ovcrhc
Jtmg
Norm
Jl
i
r
rJ
I
ttr
I
i
V
Carbon
fould
Fig
85
Spark
plug
Life
plug
heat
range
Carbon
fouled
Dry
fluffy
carbon
depo
lts
on
the
Insulator
and
electrode
were
mostly
caused
by
slow
speed
dnvlng
In
cIty
weak
Ig
nltlOn
too
nch
fuel
mixture
dirty
aIr
cleaner
etc
It
IS
advIsable
to
replace
WIth
plugs
havmg
hotter
heat
range
011
fouled
Wet
black
depoSits
show
excesSive
oIl
entrance
Into
combusllon
chamber
through
worn
rmgs
and
pIstons
or
excessIve
clearance
between
valve
gUIdes
and
stems
If
the
same
condition
remams
after
repair
use
a
hotter
plug
Overheatmg
WhIte
or
hght
gray
msulator
WIth
black
or
gray
brown
spots
and
blUIsh
burnt
electrodes
indIcate
engme
overheatIng
Moreover
th
e
appearance
results
from
in
correct
IgnitIon
tIming
loose
spark
plugs
low
guel
pump
pressure
wrong
selectIOn
of
fuel
a
hotter
plug
etc
It
IS
adVisable
to
replace
WIth
plugs
havmg
colder
heat
range
After
cleaning
dress
electrodes
With
a
small
fine
file
to
flatten
the
surfaces
of
both
center
and
Side
electrodes
In
parallel
Set
spark
plug
gap
to
specification
FIg
86
Settmg
spark
plug
gap
Install
spark
plugs
and
torque
each
plug
to
11
to
15
ft
Ib
Connect
spark
plug
wires
Cleaning
and
Regap
Clean
spark
plugs
In
a
sand
blast
type
cleaner
A
VOId
excessIve
blasting
Clean
and
remove
carbon
or
OXide
depoSits
but
do
not
wear
away
porcelain
If
depos1ts
are
too
stub
born
discard
plugs
After
cleaning
spark
plugs
renew
firing
sur
face
of
electrodes
With
file
mentioned
above
Then
gap
spark
plugs
to
0
030
to
0
035
In
uSing
a
round
wire
feeler
gauge
All
spark
plugs
new
or
used
should
have
the
gap
checked
and
reset
by
bending
ground
electrode
II
Page 46 of 136

A
1n
v
v
1
l
J
i
r
y
t
r
t
fJ
1r
r
J
f
c
1
t
ii
V
Page 47 of 136
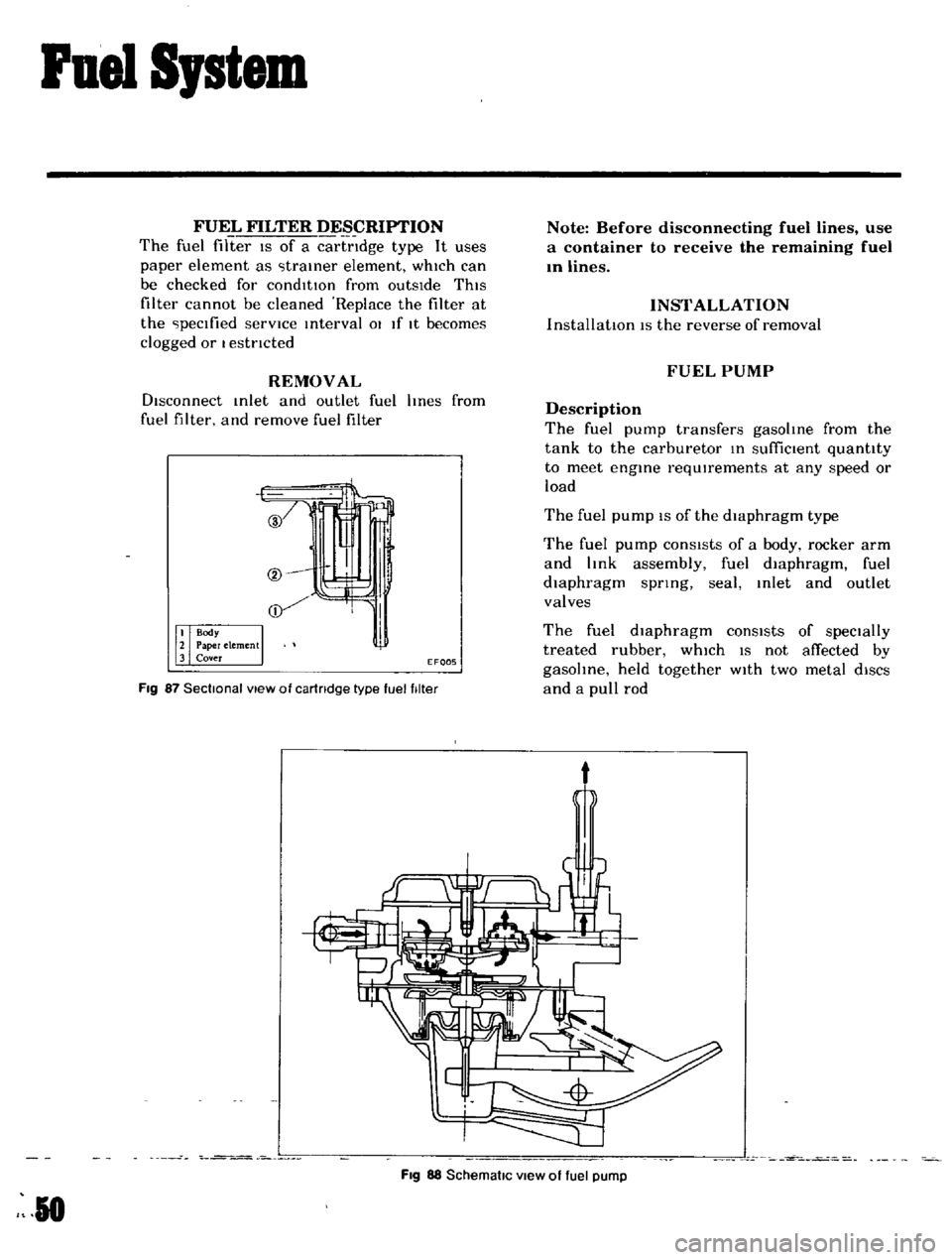
ruel
Sptem
FUEL
FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
filter
IS
of
a
cartndge
type
It
uses
paper
element
as
traIner
element
which
can
be
checked
for
condItIOn
from
outsIde
ThIS
filter
cannot
be
cleaned
Replace
the
filter
at
the
peclfied
servICe
Interval
01
If
It
becomes
clogged
or
I
estncted
REMOVAL
DIsconnect
Inlet
and
outlet
fuel
hnes
from
fuel
filter
and
remove
fuel
filter
if
EF005
Fig
87
Sectional
view
of
cartridge
type
fuel
filter
Note
Before
disconnecting
fuel
lines
use
a
container
to
receive
the
remaining
fuel
In
lines
INSTALLATION
InstallatIOn
IS
the
reverse
of
removal
FUEL
PUMP
Description
The
fuel
pump
transfers
gasoline
from
the
tank
to
the
carburetor
In
suffiCient
quantity
to
meet
engine
requIrements
at
any
speed
or
load
The
fuel
pump
IS
of
the
diaphragm
type
The
fuel
pump
conSIsts
of
a
body
rocker
arm
and
link
assembly
fuel
diaphragm
fuel
diaphragm
spnng
seal
Inlet
and
outlet
valves
The
fuel
diaphragm
consists
of
specially
treated
rubber
whIch
IS
not
affected
by
gasohne
held
together
WIth
two
metal
diSCS
and
a
pull
rod
t
Fig
88
SchematiC
view
of
fuel
pump
R
0
Page 48 of 136
Fuel
Sptem
Testing
A
fuel
pump
IS
operatIng
properly
when
1tS
pressure
IS
Within
specifications
and
ItS
capacIty
IS
equal
to
the
engine
s
reqUIrements
at
all
speeds
Pressure
and
capacity
must
be
determined
by
two
tests
With
the
pump
mounted
on
the
engIne
Be
sure
that
there
IS
gasohne
m
the
tank
when
conductIng
these
tests
Fig
89
Pull
rod
removal
StatIc
Pressure
Test
The
static
pressure
test
IS
conducted
as
follows
Disconnect
the
carburetor
fuel
line
at
the
car
buretor
Install
the
necessary
adapter
and
tee
fitting
to
the
fuel
Ime
and
attach
a
SUitable
pressure
gauge
Start
and
run
engme
at
varymg
speeds
The
readIng
on
the
gauge
IS
the
static
fuel
pressure
and
thIS
should
remam
wlthm
the
follOWing
Itmlts
2
61b
sq
m
Pressure
below
the
lower
hmlt
IndlCates
ex
treme
wear
on
one
part
of
a
small
amount
of
wear
on
each
working
part
They
also
md1cate
a
ruptured
dIaphragm
worn
warped
dirty
or
gummmg
valves
and
seats
or
weak
dIaphragm
return
spring
Pressure
above
the
upper
hmlt
Indicates
an
excessIVely
strong
dIaphragm
that
IS
too
tight
ThIS
condItIOn
reqUIres
removal
of
the
fuel
pump
assembly
for
replacement
or
repair
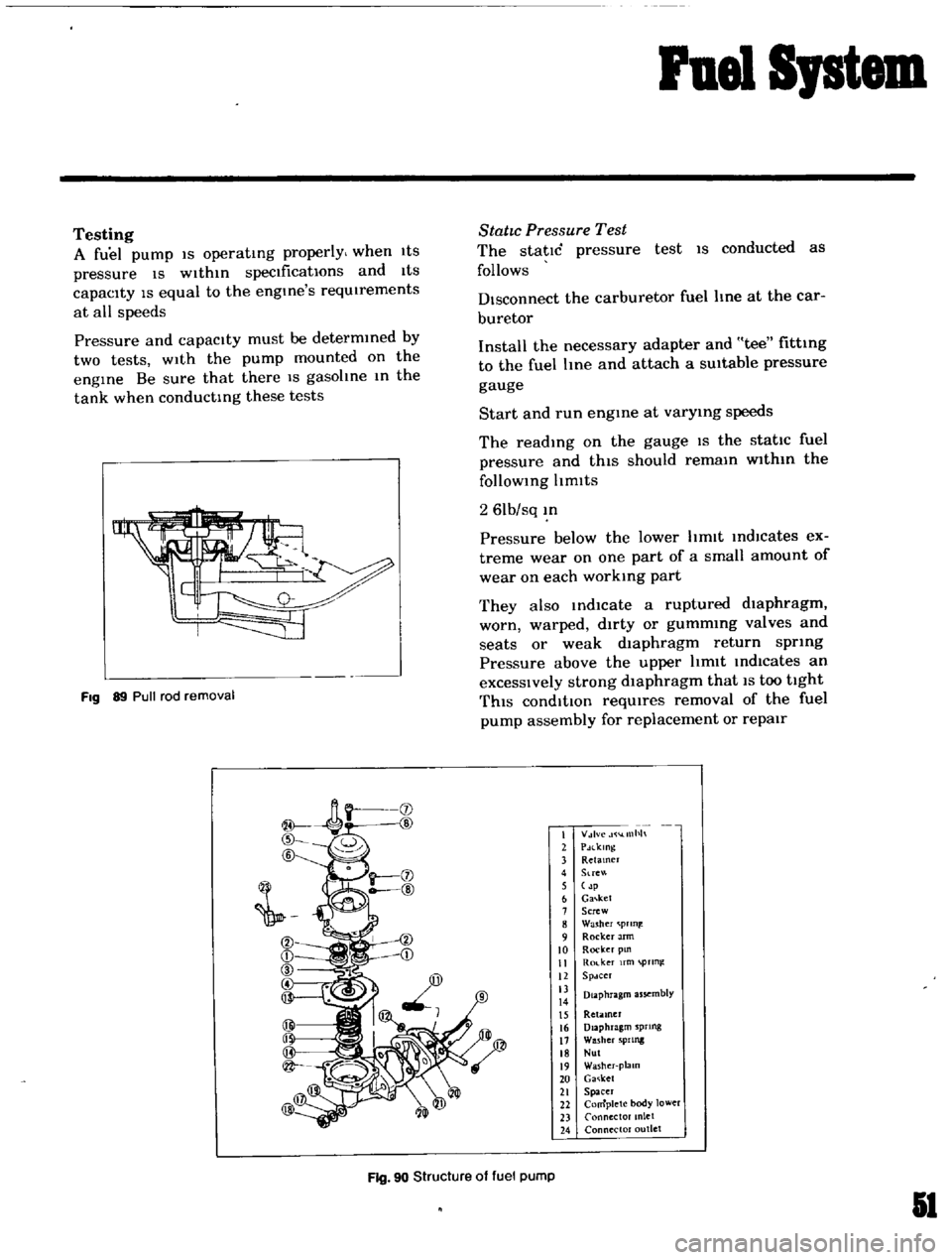
I
V
lvc
llllh
2
PdlklOg
3
Retamer
4
Stre
5
p
6
Ga
ket
7
Screw
8
Washer
prln
9
Rocker
Jrm
10
Rocker
pm
II
Ro
ker
fm
pTln
12
Spdcer
13
Diaphragm
assembly
14
15
Retiuner
16
Diaphragm
sprtng
17
Washer
5PIlllg
18
Nul
19
Washer
plalO
20
Ga
ket
21
Spacer
22
Complete
body
lower
23
Connector
anlet
24
Connector
outlet
Fig
90
Structure
of
fuel
pump
51
Page 49 of 136

Fuel
Sptem
Capacity
Test
The
capaclty
test
IS
used
only
when
the
statIc
plessure
IS
wlthm
specIficatIOns
The
capacity
test
IS
conducted
as
follows
Disconnect
the
fuel
p1pe
at
the
carburetor
Place
a
bUltable
contamer
at
the
end
of
the
pIpe
Start
the
engme
and
run
at
1
000
rpm
The
pump
should
delIver
1
US
pt
of
fuel
In
one
mmute
or
less
If
no
gasolme
or
only
a
lIttle
flows
flOm
open
end
of
pIpe
the
fuel
pIpe
IS
clogged
or
the
pump
I
malfunctlOntng
Before
removing
the
pump
remove
the
gas
tank
cap
dIsconnect
both
Inlet
dnd
outlet
pIpes
and
blow
through
them
wIth
an
aIr
hose
to
make
sure
that
they
are
clear
Thl
wIll
elImmate
pOSSible
clogged
gas
tramer
In
the
fuel
tank
Reconnect
the
pIpes
to
the
pump
and
rete
t
flow
Removal
and
DisassenbIy
Remove
the
fuel
pump
assembly
by
un
screwmg
two
mounting
nuts
and
dIsassemble
In
the
follOWing
order
Separate
the
upper
body
and
the
lower
body
by
unscrewmg
the
body
set
screws
Take
off
the
cap
and
the
cap
gasket
by
I
emOVIng
the
cap
screw
Unscrew
the
elbow
and
the
connector
Take
off
the
valve
retainer
by
unscrewmg
two
valve
retamer
screws
Two
valves
are
eaSIly
removed
To
remove
the
diaphragm
diaphragm
sprmg
lower
body
seal
washer
and
lower
body
seal
from
the
lower
body
press
down
the
dIaphragm
counter
to
the
force
of
the
dIaphragm
spring
and
while
dOIng
thIS
cant
the
dIaphragm
so
that
the
rectangular
part
m
the
lower
end
of
the
pull
rod
IS
unhooked
from
the
rocker
arm
lInk
Inspection
Check
the
upper
and
lower
bodIes
for
cracks
2
Check
the
valve
assembly
for
wear
of
the
valve
and
valve
sprmg
Blow
the
valve
assem
bly
by
breath
to
examme
ItS
functIOn
Check
the
dIaphragm
for
small
holes
cral
ks
and
wear
Check
the
rocker
dl
m
for
wear
at
the
portIOn
In
contact
With
the
camshaft
Check
the
rocker
arm
pin
for
wear
since
a
worn
pm
may
cause
011
leakage
Check
all
other
components
for
any
abnor
mahtIes
and
replace
With
new
parts
as
requIred
Assembly
Assembly
IS
done
In
reverse
order
of
disassem
bly
For
reassembly
and
remstallatlOn
the
followmg
matters
should
be
noted
Use
new
gasket
Lubricate
the
rocker
arm
link
rocker
arm
pm
and
lever
pm
before
mstallatlOlI
To
test
the
functIOn
poSItIOn
the
fuel
pump
assembly
about
33ft
above
fuel
level
WIth
a
pipe
connecting
the
fuel
pump
and
the
fuel
filter
and
operate
the
rocker
arm
by
hand
If
fuel
IS
drawn
up
soon
after
the
rocker
arm
IS
released
the
functIOn
of
the
pump
IS
satIsfactory
CARBURETOR
Description
The
carburetors
are
of
a
downdraft
type
whIch
IS
deSIgned
and
bUIlt
to
Increase
power
and
fuel
economy
as
well
as
to
reduce
the
em1SSlon
of
exhaust
gases
These
carburetors
present
several
dIstinct
features
of
Importance
to
the
car
owners
A
summary
of
features
IS
as
follows
Secondary
throttle
valve
IS
operated
by
throt
tie
lever
The
hIgh
power
and
good
ac
celeratIon
are
gained
With
combmatlOn
of
the
auxlhary
valve
Acceleratmg
pump
glves
excellent
ac
celeratIon
Page 50 of 136

Fuel
Sptem
The
power
valve
mechanIsm
IS
of
a
vacuum
actuated
boost
type
and
Improves
hIgh
speed
drivIng
The
throttle
opener
control
system
Incor
porates
a
servo
diaphragm
The
servo
dIaphragm
helps
open
the
throttle
valve
at
a
decreasIng
speed
so
as
to
reduce
the
emISSIOn
of
hydrocarbons
to
a
minImum
An
antI
dlesehng
olen01d
IS
used
as
a
means
of
preventIng
dlesehng
When
the
IgnItIOn
key
IS
turned
ofT
the
fuel
passage
Involved
In
the
slow
system
IS
closed
and
the
fuel
supply
IS
shut
down
completely
In
the
chok
mechanIsm
an
electric
automatIc
choke
IS
used
to
automatically
con
trol
the
choke
valve
operatIOn
durIng
the
war
m
up
of
the
engIne
The
carburetor
for
automatic
transmiSSIOn
IS
eqUIpped
WIth
so
called
dash
pot
that
IS
It
makes
smooth
deceleratIng
WIthout
engIne
stall
at
any
operatIng
conditIOn
These
carburetors
are
qUIte
SImIlar
In
ap
pearance
as
explaIned
above
except
the
dash
pot
for
the
automatIc
transmISSion
model
Adjustment
Idhng
Adjustment
Idle
mixture
adjustment
requIres
the
use
of
a
CO
meter
When
prepatlng
to
adjust
Idle
mIxture
It
IS
essentIal
to
have
the
meter
thoroughly
warmed
and
cahbrated
Warm
up
the
engIne
suffiCiently
ContInue
engme
operatIOn
for
one
mmute
un
der
ldhng
speed
Adjust
throttle
adjustIng
screw
so
that
engme
speed
IS
800
rpm
m
N
pos1tIon
for
automatic
transmiSSIOn
Check
IgmtlOn
tl
If
necessary
adjust
It
to
the
speCificatIOns
IgnItIOn
tImlo
800
rpm
Adjust
Idle
adJustmg
screw
so
that
CO
percen
tage
IS
1
5
0
50
at
800
ns
a
On
automatIc
transmiSSIOn
eqUipped
model
check
must
be
done
In
the
D
poSItIon
Be
sure
to
apply
parkmg
brake
and
to
lock
both
front
and
rear
wheels
With
wheel
chocks
b
Hold
brake
pedal
while
steppIng
down
on
accelerator
pedal
OtherWise
car
Will
rush
out
dangerously
On
automatIc
transmiSSIOn
eqUIpped
model
make
sure
that
the
adjustment
has
been
made
With
the
selector
lever
In
N
posItIon
And
then
check
the
specificatIOns
With
the
lever
In
D
pOSitIOn
Insure
that
CO
percent
and
Idle
speed
are
as
follows
Idle
rpm
650
for
Manual
transmISSion
for
Automatic
transmISSion
Fig
91
External
view
of
carburetor
3