light DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 175 of 537

CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Clean
all
disassembled
parts
but
do
not
use
grease
dissolving
solvents
for
cleaning
overrunning
clutch
annature
assembly
magnetic
switch
assembly
and
field
coils
since
such
a
solvent
would
dissolve
grease
packed
in
c1u
tch
mechanism
and
would
damage
coils
or
other
insulators
Check
them
for
excessive
damage
or
wear
and
replace
if
necessary
TERMINAL
Check
terminal
for
damage
and
wear
and
replace
magnetic
switch
assembly
if
necessary
FIELD
COIL
Check
field
coil
for
insulation
If
the
insulation
of
coil
is
damaged
or
worn
it
should
be
replaced
Testing
field
coil
for
continuity
Connect
the
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
or
an
ohmmeter
to
field
coil
positive
terminal
and
positive
brush
holder
If
tester
shows
no
continuity
field
circuit
or
coil
is
open
EE016
Fig
EE
I2
Testing
field
coil
for
continuity
TestIng
field
coD
for
ground
Place
one
probe
of
circuit
tester
onto
yoke
and
the
other
onto
field
coil
lead
positive
tenninal
If
very
little
resistance
is
read
field
coil
is
grounded
Engine
Electrical
System
EE017
Fig
EE
I3
Testing
rU
ld
coil
for
ground
BRUSHES
AND
BRUSH
LEAD
WIRE
Check
the
surface
condition
of
brush
contact
and
wear
of
brush
If
a
loose
contact
is
found
it
should
be
replaced
If
brush
is
worn
so
that
its
length
is
less
than
12
mm
0
472
in
replace
Check
the
connection
of
lead
clip
and
lead
wire
o
@
EE
8
Check
brush
holders
and
spring
cUp
to
see
if
they
are
not
deformed
or
bent
and
will
properly
hold
brushes
against
the
commutator
If
brushes
or
brush
holders
are
dirty
they
should
be
cleaned
BRUSH
SPRING
TENSION
Check
brush
spring
tension
by
a
spring
scale
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
13
The
reading
should
be
1
6
kg
3
5
Ib
Replace
spring
if
tension
is
lower
than
I
4
kg
3
1
Ib
ARMATURE
ASSEMBLY
Check
external
appearance
of
armature
and
commutator
1
Inspect
commutator
If
the
sur
face
of
commutator
is
rough
it
must
be
sanded
lightly
with
a
No
500
emery
cloth
If
the
depth
of
insulating
mica
is
less
than
0
2
mm
0
0079
in
from
commutator
surface
insulating
mica
should
also
be
undercut
so
that
its
depth
is
0
5
to
0
8
mm
0
01
97
to
0
0315
in
The
wear
limit
of
commutator
dia
meter
is
2
mm
0
0787
in
If
the
diameter
of
cammu
tator
is
less
than
31
mm
1
220
in
replace
annature
assembly
EE018
Fig
EE
14
Inspecting
brush
spring
tension
Page 176 of 537

L
0
5
to
0
8
mm
71j
Correct
2
Inspect
soldered
connection
of
armature
lead
and
commutator
If
loose
connection
is
found
solder
it
using
resin
flux
3
Armature
test
for
ground
Using
a
circuit
tester
place
one
test
probe
onto
armature
shaft
and
other
onto
each
commutator
bar
If
tester
shows
continuity
armature
is
grounded
and
must
be
replaced
EE022
Fig
EE
16
Testing
annature
for
ground
4
Check
armature
for
short
by
placing
it
on
armature
tester
growler
with
a
piece
of
iron
over
armature
core
rotating
armature
If
the
plate
vibrates
armature
is
shorted
j
l
EE023
Fig
EE
17
Testing
annature
for
ahort
Engine
Electrical
System
L
File
l
0
Commutator
Segmen
t
IWMica
Incorrect
EE021
Fig
EE
15
Undercutting
i118ulating
mica
5
Check
armature
for
continuity
by
placing
probes
of
tester
on
two
seg
ments
side
by
side
If
tester
shows
no
continuity
the
circuit
is
open
OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH
ASSEMBLY
Inspect
pinion
assembly
and
screw
sleeve
Screw
sleeve
must
slide
freely
along
armature
shaft
splines
If
damage
is
found
or
resistance
is
felt
when
sliding
it
must
be
repaired
Inspect
pinion
teeth
If
excessive
rub
bing
is
found
on
teeth
replace
Flywheel
ring
gear
also
must
be
in
spected
l
EE278
Fig
EE
18
Overrunning
clutch
auem
bly
BRUSH
HOLDER
TEST
FOR
GROUND
Using
a
circuit
tester
place
one
test
probe
onto
negative
side
of
brush
holder
and
another
onto
positive
side
If
tester
shows
continuity
brush
holder
is
shorted
to
ground
Replace
brush
holder
EE
9
Ee026
Fig
EE
19
Testing
brush
for
round
BEARING
METAL
Inspect
bearing
metal
for
wear
or
side
play
If
the
clearance
between
bearing
metal
and
armature
shaft
is
more
than
0
2
mm
0
0079
in
replace
metal
MAGNETIC
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
1
Using
a
circuit
tester
l
check
con
tinuity
between
S
terminal
of
mag
netic
switch
and
switch
body
metal
If
continuity
does
not
exist
shunt
coit
is
opened
Replace
switch
assembly
2
In
the
same
manner
as
above
check
continuity
between
terminals
S
and
M
If
continuity
does
not
exist
series
coil
is
opened
Replace
switch
assembly
ASSEMBLY
Reassemble
starting
motor
in
re
verse
sequence
of
disassembly
When
assembling
be
sure
to
apply
grease
to
gear
case
and
rear
cover
bearing
metal
and
apply
oil
lightly
to
pinion
TEST
PERFORMANCE
TEST
Starter
motor
should
be
subjected
to
a
no
load
test
whenever
it
has
been
overhauled
to
ensure
that
its
performance
will
be
satisfactory
when
installed
on
engine
Starter
motor
should
also
be
subjected
to
the
test
when
the
cause
of
abnormal
operation
is
to
be
determined
A
brief
outline
of
the
test
is
given
below
Page 179 of 537

Condition
Engine
Electrical
System
Probable
cause
Starting
motor
cranks
slowly
Dirty
or
worn
commutator
Armature
rubs
field
coil
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Starting
motor
operates
but
does
not
crank
engine
Worn
pinion
Locked
pinion
guide
Worn
ring
gear
Starting
motor
will
not
disengage
even
if
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Damaged
gear
teeth
The
charging
circuit
consists
of
the
battery
alternator
regulator
and
necessary
wiring
to
connect
these
parts
The
purpose
of
this
system
is
to
convert
mechanical
energy
from
the
engine
into
electrical
energy
which
is
used
to
operate
all
electrically
operat
ed
units
and
to
keep
the
battery
fully
charged
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
voltage
regulator
IG
terminal
primary
side
contact
point
PI
movable
contact
point
P2
voltage
regulator
IF
terminal
alternator
IF
terminal
rotor
field
coil
and
alternator
E
terminal
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
23
by
full
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
rotor
in
the
alternator
is
excited
On
the
other
hand
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
warning
lamp
voltage
regula
tor
L
terminal
lamp
side
contact
point
P4
movable
contact
point
P5
and
voltage
regulator
E
termi
nal
as
shown
by
dotted
line
arrow
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
marks
Then
the
warning
lamp
lights
When
the
alternator
begins
to
op
erate
three
phase
alternating
current
is
induced
in
the
stator
armature
coil
This
alternating
current
is
rectified
by
the
positive
and
negative
silicon
diodes
The
rectified
direct
current
output
reaches
the
alternator
A
and
E
terminals
On
the
other
hand
the
neutral
point
voltage
reaches
N
and
E
terminals
nearly
a
half
of
the
output
voltage
and
current
flows
from
voltage
regulator
N
terminal
to
E
terminal
or
ground
through
the
coil
VCI
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
24
by
the
dotted
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
coil
VCI
is
excited
and
the
movable
contact
point
IPS
comes
into
contact
with
voltage
winding
side
contact
point
P6
This
action
causes
to
turn
off
the
warning
lamp
and
complete
the
voltage
winding
circuit
as
shown
by
the
full
line
arrow
marks
When
the
alternator
speed
is
in
creased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
EE
12
Corrective
action
Clean
and
repair
Replace
assembly
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Replace
damaged
gear
P2
is
separated
from
the
primary
side
contact
PI
by
the
magnetic
force
of
coil
VC2
Therefore
registor
RI
is
applied
into
the
rotor
circuit
and
output
voltage
is
decreased
AJ
the
output
voltage
is
decreased
the
movable
contact
point
P2
and
primary
side
contact
Pin
comes
into
contact
once
again
and
the
alternator
voltage
increases
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
IPl
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
constant
When
the
alternator
speed
is
further
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
comes
into
contact
with
secondllJ
side
contact
point
P3
Then
the
rotor
current
is
shut
off
and
alternator
output
voltage
is
decreased
immediately
This
action
causes
movable
contact
n
to
separate
from
secondary
contact
P3
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
or
breaking
and
completing
the
rotor
circuit
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
constant
Page 182 of 537
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ROTOR
INSPECTION
INSPECTION
OF
STATOR
DESCRIPTION
In
the
alternator
a
magnetic
field
is
produced
by
the
rotor
which
consists
of
alternator
shaft
field
coil
pole
pieces
and
slip
rings
The
slip
rings
pressed
in
the
shaft
conduct
only
a
small
field
current
Output
current
is
generated
in
the
armature
coils
located
in
the
stator
The
stator
has
three
windings
and
generates
three
phase
alternating
current
Silicon
diodes
act
@God
A
tfff
Engine
Electrical
System
ALTERNATOR
CONTENTS
EE
15
EE
16
EE
16
EE
16
EE
17
EE
17
INSPECTION
OF
DIODE
INSPECTION
OF
BRUSH
SPRING
PRESSURE
TEST
ASSEMBL
Y
ALTERNATOR
TEST
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
EE
17
EE
1B
EE1B
EE
1B
EE19
EE
19
like
a
one
way
valve
for
electricity
so
that
charging
current
passes
easily
but
reverse
current
is
shut
out
In
this
alternator
pack
type
silicon
di
odes
are
used
Six
diodes
three
negative
and
three
positive
are
installed
in
positive
and
negative
plates
as
an
assembly
These
diodes
are
direct
soldered
at
their
tips
and
constructed
with
posi
3
2
I
4
e
o
e
9
tive
and
negative
conjunction
They
are
mounted
on
the
two
plates
which
combine
the
function
of
heat
dissipating
plate
and
positive
negative
terminals
and
are
light
in
weight
and
easy
to
service
The
pulley
mounted
on
the
air
conditioner
models
is
different
from
that
on
the
standard
models
without
air
conditioner
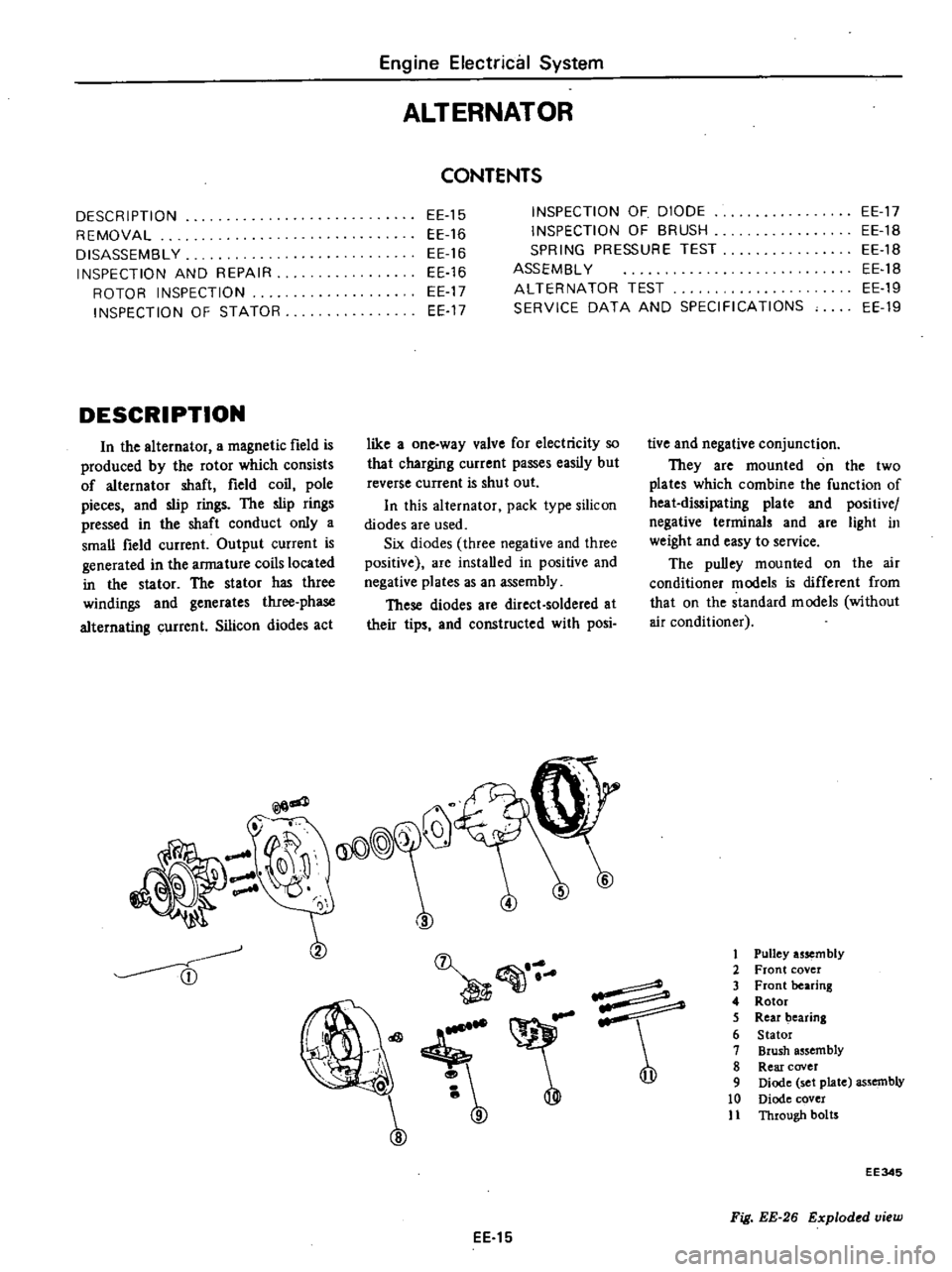
1
Pulley
usem
bly
2
Front
cover
3
Front
bearing
4
Rotor
5
Rear
bearing
6
Stator
7
Brush
assembly
8
Rear
cover
9
Diode
set
plate
assembly
10
Diode
cover
11
Through
botrs
EE
15
EE345
Fig
EE
26
Exploded
view
Page 183 of 537

REMOVAL
1
Disconnect
negative
battery
ter
minaL
2
Disconnect
two
lead
wires
and
connector
from
alternator
3
loosen
adjusting
bolt
4
Remove
alternator
drive
belt
5
Remove
parts
associated
with
alternator
from
engine
6
Remove
alternator
from
vehicle
DISASSEMBLY
1
Remove
pulley
nut
and
pulley
assembly
11
C
@@@
EE033
Fig
EE
27
Removing
pulley
ond
fan
2
Remove
brush
holder
fIxing
screws
and
remove
brush
holder
cover
Pull
brush
holder
fOIWard
and
remove
brushes
together
with
brush
holder
Note
Do
not
disconnect
N
tenninaJ
from
stator
coil
lead
wire
EE346
1
N
terminal
2
Brush
holder
3
Brush
holder
co
r
Fig
EE
28
Remouing
brush
Engine
Electrical
System
3
Remove
through
bolts
Separate
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
with
stator
by
lightly
tapping
front
bracket
with
a
wooden
mallet
J
J
4
C
EE035
Fig
EE
29
Separating
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
4
Remove
three
set
screws
from
bearing
retainer
and
separate
rotor
from
front
cover
DO
Q
EE036
Fig
EE
3D
Removing
rotor
5
Pull
rear
bearing
out
from
rotor
assembly
with
a
press
or
bearing
puller
L
I
EE037
Fig
EE
3I
Pulling
out
of
roar
bearing
EE
16
6
Remove
diode
cover
fIXing
screw
and
remove
diode
cover
Disconnect
three
stator
coil
lead
wires
from
diode
terminal
with
a
soldering
iron
7
Remove
A
tenninaJ
nut
and
diode
installation
nut
and
remove
diode
assembly
CD
AJ
f
e
ecA
O
1
Diode
assembly
o
2
Diode
cover
o
EE039
Fig
EE
32
Removing
diode
088embly
Note
Use
care
in
assembly
to
on
it
handling
diode
an
undue
st
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
Remove
alternator
from
car
and
connect
a
circuit
tester
between
F
tenninal
and
E
terminal
When
the
resistance
is
approxi
mately
5il
the
condition
of
brush
and
fIeld
coil
is
satisfactory
When
no
continuity
exists
in
brush
or
fIeld
coil
or
when
resistance
differs
significantly
between
those
parts
dis
assemble
and
inspect
A
o
E
O
1
ld
Q
EE040
Fig
EE
33
Inspecting
alternator
Page 186 of 537

Engine
Electrical
System
ALTERNATOR
TEST
Before
conducting
an
alternator
test
make
sure
th
tthe
battery
is
fully
charged
A
30
V
olt
voltmeter
and
suitable
test
probes
3re
necessary
for
the
test
Set
up
a
test
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE45
and
test
auernator
in
the
manner
indica
ted
in
the
flow
chart
below
1
Disconnect
connectors
at
alternator
2
Connect
A
terminal
to
F
terminal
3
Connect
one
test
probe
from
voltmeter
positive
terminal
to
A
terminal
Connect
the
other
test
probe
to
ground
Make
sure
that
voltmeter
registers
battery
voltage
4
Turn
on
headlights
and
switch
to
High
Beam
5
Start
engine
6
Increase
engine
speed
gradually
until
it
is
approximately
1
100
rpm
and
take
the
voltmeter
reading
Measured
value
Below
12
5
Volts
Alternator
is
in
trouble
remove
and
check
it
for
condition
Measured
value
Over
12
5
Volts
Alternator
is
in
good
condition
Notes
a
Do
Dot
run
engine
at
the
speed
of
more
than
1
100
rpm
while
test
is
being
conducted
on
alternator
b
Do
not
race
engine
i
9
l
IV
I
Battery
EE052
Voltmeter
Fig
EE
45
Testing
alternator
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Nominal
rating
V
A
LT138
IB
LTl35
36B
For
air
conditioner
1235
12
38
Negative
Negative
1
000
1
000
28
2
500
30
2
500
35
5
000
38
5
000
2
25
2
25
More
than
7
5
0
295
More
than
7
5
0
295
255
to
345
255
to
345
9
0
to
12
2
9
0
to
12
2
More
than
30
1
181
More
than
30
1
181
EE
19
Type
Ground
polarity
Minimum
revolution
when
generating
14V
with
no
load
rpm
Hot
output
current
Nrpm
Pulley
ratio
Brush
Length
Spring
pressure
mm
in
gr
oz
Slip
ring
outer
diameter
mm
in
Page 190 of 537
ADJUSTMENT
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
When
regulating
voltage
as
meas
ured
above
deviates
from
rated
value
adjust
regulator
in
accordance
with
the
following
instructions
I
Inspect
contact
surface
and
if
rough
lightly
polish
with
fine
emery
paper
1
500
or
600
2
Measure
each
gap
and
adjust
if
necessary
Adjust
core
gap
and
point
gap
in
that
order
No
adjustment
is
required
for
yoke
gap
3
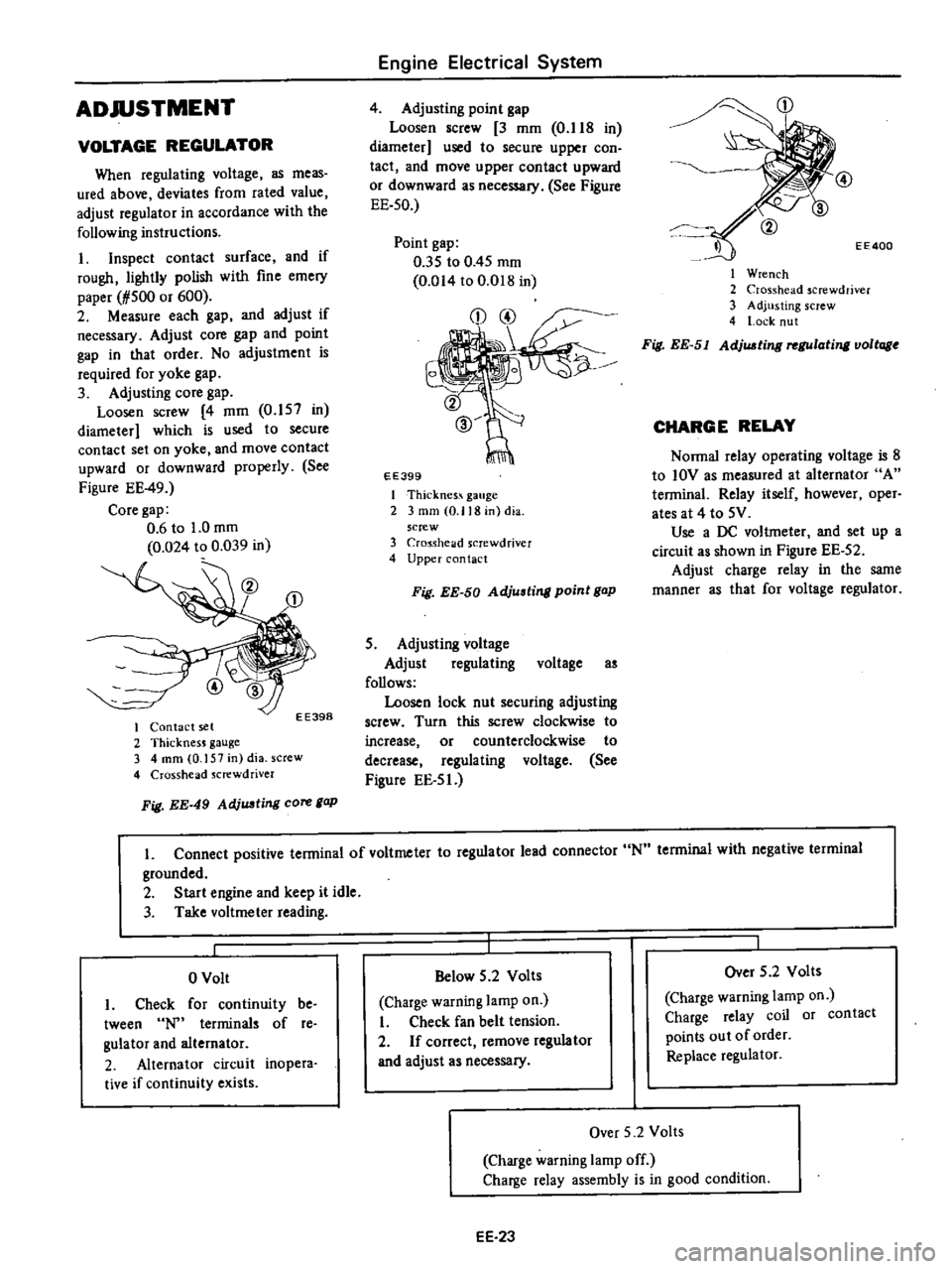
Adjusting
core
gap
Loosen
screw
4
mm
0
157
in
diameter
which
is
used
to
secure
contact
set
on
yoke
and
move
contact
upward
or
downward
properly
See
Figure
EE
49
Core
gap
0
6
to
1
0
mm
0
024
to
0
039
in
EE398
I
Contact
set
2
ThicknesJ
gauge
3
4
mm
0
157
in
dia
screw
4
Crosshead
Jcrewdriver
Fig
EE
49
AdjUJJting
core
gap
Engine
Electrical
System
4
Adjusting
point
gap
Loosen
screw
3
mm
O
lIS
in
diameter
used
to
secure
upper
con
tact
and
move
upper
contact
upward
or
downward
as
necessary
See
Figure
EE
50
Point
gap
035
to
0
45
mm
0
014
to
O
D1S
in
EE399
I
Thicknes
gauge
2
3
mm
0
118
in
dia
screw
3
Cro
Sshelld
screwdriver
4
Upper
contact
Fig
EE
50
Adjusting
point
gap
5
Adjusting
voltage
Adjust
regulating
voltage
as
follows
Loosen
lock
nut
securing
adjusting
screw
Turn
this
screw
clockwise
to
increase
or
counterclockwise
to
decrease
regulating
voltage
See
Figure
EE
5
J
CD
EE400
I
Wrench
2
Crosshead
screwdriver
3
Adjusting
screw
4
l
ock
nut
Fig
EE
51
AdjUJJting
rel
Ulating
voltage
CHARGE
RELAY
Nonna
relay
operating
voltage
is
S
to
IOV
as
measured
at
alternator
A
tenninal
Relay
itself
however
oper
ates
at
4
to
5V
Use
a
DC
voltmeter
and
set
up
a
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
52
Adjust
charge
relay
in
the
same
manner
as
that
for
voltage
regulator
L
Connect
positive
tenninal
of
voltmeter
to
regulator
lead
connector
N
tenninal
with
negative
terminal
grounded
2
Start
engine
and
keep
it
idle
3
Take
voltmeter
reading
o
Volt
I
Check
for
continuity
be
tween
terminals
of
re
gulator
and
alternator
2
Alternator
circuit
inopera
tive
if
continuity
exists
Below
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
on
I
Check
fan
belt
tension
2
If
correct
remove
regulator
and
adjust
as
necessary
Over
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
on
Charge
relay
coil
or
contact
points
out
of
order
Replace
regulator
Over
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
off
Charge
relay
assembly
is
in
good
condition
EE
23
Page 198 of 537
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CAP
AND
ROTOR
HEAD
Cap
and
rotor
head
should
be
in
spected
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Schedule
Remove
cap
and
clean
all
dust
and
carbon
deposits
from
cap
and
rotor
If
cap
is
cracked
or
is
leaking
replace
with
a
De
one
CONTACT
POINT
Contact
point
should
be
replaced
in
accordance
with
the
Maintenance
Schedule
Standard
point
gap
is
0
45
to
0
55
mm
O
OIS
to
0
022
in
In
case
size
is
off
the
standard
adjustment
is
made
by
loosening
point
screws
Gap
gauge
is
required
for
adjustment
When
point
surface
is
rough
take
off
any
irregularities
with
fine
sand
paper
of
No
500
or
600
or
with
oil
stone
When
wear
on
contact
points
is
noticeable
replace
points
together
with
contact
arm
To
replace
proceed
as
follows
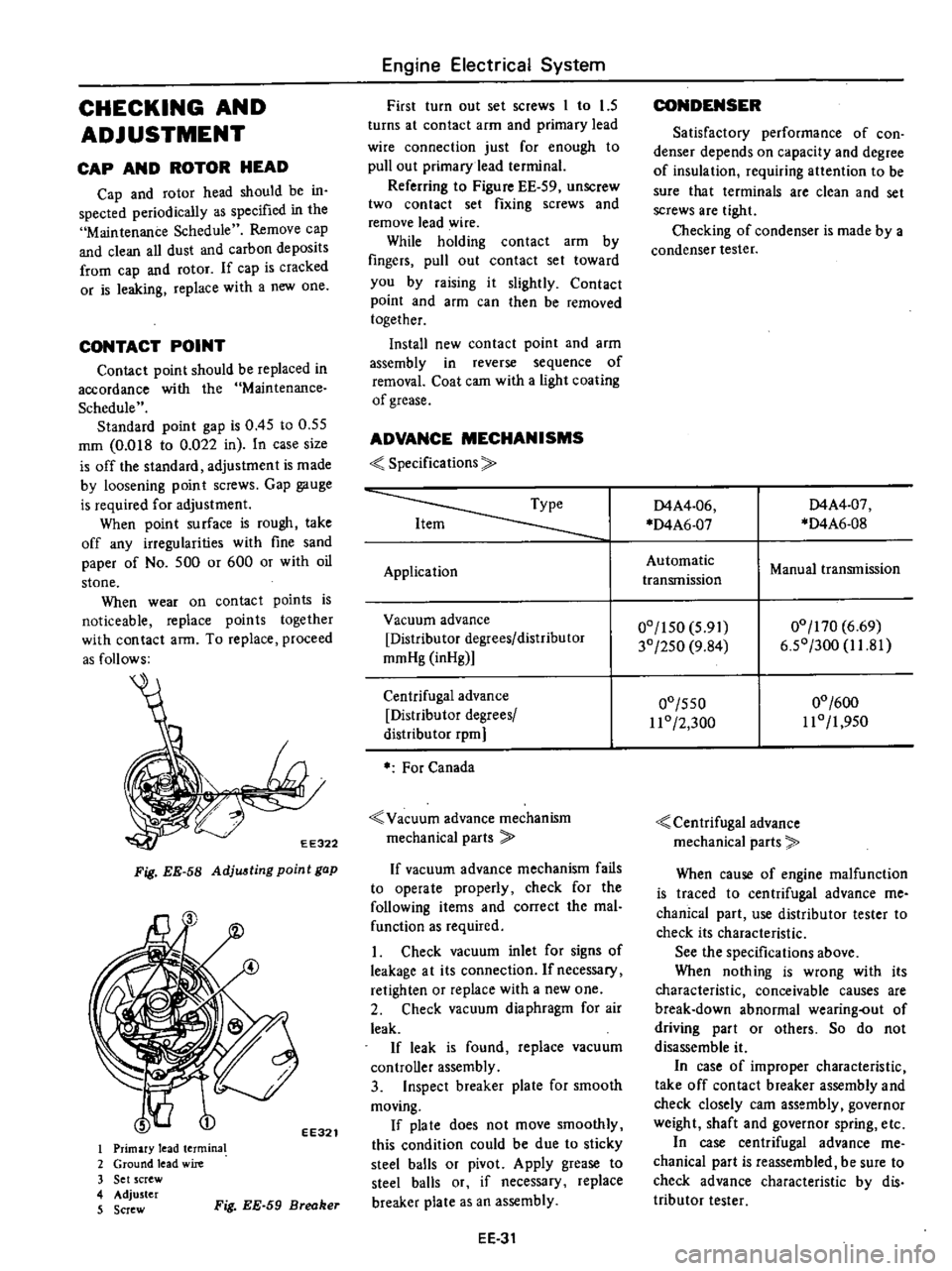
EE322
Fig
EE
58
Adju
ting
point
gap
EE321
I
Primary
lead
termina
2
Ground
lead
wire
3
Set
screw
4
Adjuster
5
Screw
Fig
EE
59
Breaker
Engine
Electrical
System
First
turn
out
set
screws
1
to
1
5
turns
at
contact
arm
and
primary
lead
wire
connection
just
for
enough
to
pull
out
primary
lead
terminal
Referring
to
Figure
EE
59
unSCrew
two
contact
set
fixing
screws
and
remove
lead
wire
While
holding
contact
arm
by
fingers
pull
out
contact
set
toward
you
by
raising
it
slightly
Contact
point
and
afm
can
then
be
removed
together
Install
new
contact
point
and
arm
assembly
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
Coat
cam
with
a
light
coating
of
grease
ADVANCE
MECHANISMS
Specifications
Application
Vacuum
advance
Distributor
degrees
distributor
mmHg
inHg
Centrifugal
advance
Distributor
degrees
distribu
tor
rpm
For
Canada
Vacuum
advance
mechanism
mechanical
parts
If
vacuum
advance
mechanism
fails
to
operate
properly
check
for
the
following
items
and
correct
the
mal
function
as
required
1
Check
vacuum
inlet
for
signs
of
leakage
at
its
connection
Ifnecessacy
retighten
or
replace
with
a
new
one
2
Check
vacuum
diaphragm
for
air
leak
If
leak
is
found
replace
vacuum
controller
assembly
3
Inspect
breaker
plate
for
smooth
moving
If
pia
te
does
not
move
smoothly
this
condition
could
be
due
to
sticky
steel
balls
or
pivot
Apply
grease
to
steel
balls
or
if
necessary
replace
breaker
plate
as
an
assembly
EE
31
CONDENSER
Satisfactory
performance
of
con
denser
depends
on
capacity
and
degree
of
insulation
requiring
attention
to
be
sure
that
terminals
are
clean
and
set
screws
are
tight
Checking
of
condenser
is
made
by
a
condenser
tester
D4A4
06
D4A6
07
D4A4
07
D4A6
0S
Automatic
transmission
Manual
transmission
00
150
5
91
30
250
9
S4
00
170
6
69
6
50
300
1I
S1
00
550
11
0
2
300
00
600
110
1
950
Centrifugal
advance
mechanical
parts
When
cause
of
engine
malfunction
is
traced
to
centrifugal
advance
me
chanical
part
use
distributor
tester
to
check
its
characteristic
See
the
specifications
above
When
nothing
is
wrong
with
its
characteristic
conceivable
causes
are
break
down
abnormal
wearing
out
of
driving
part
or
others
So
do
not
disassemble
it
In
case
of
improper
characteristic
take
off
contact
breaker
assembly
and
check
closely
cam
assembly
governor
weight
shaft
and
governor
spring
etc
In
case
centrifugal
advance
me
chanical
part
is
reassembled
be
sure
to
check
advance
characteristic
by
dis
tributor
tester
Page 204 of 537
Engine
Electrical
System
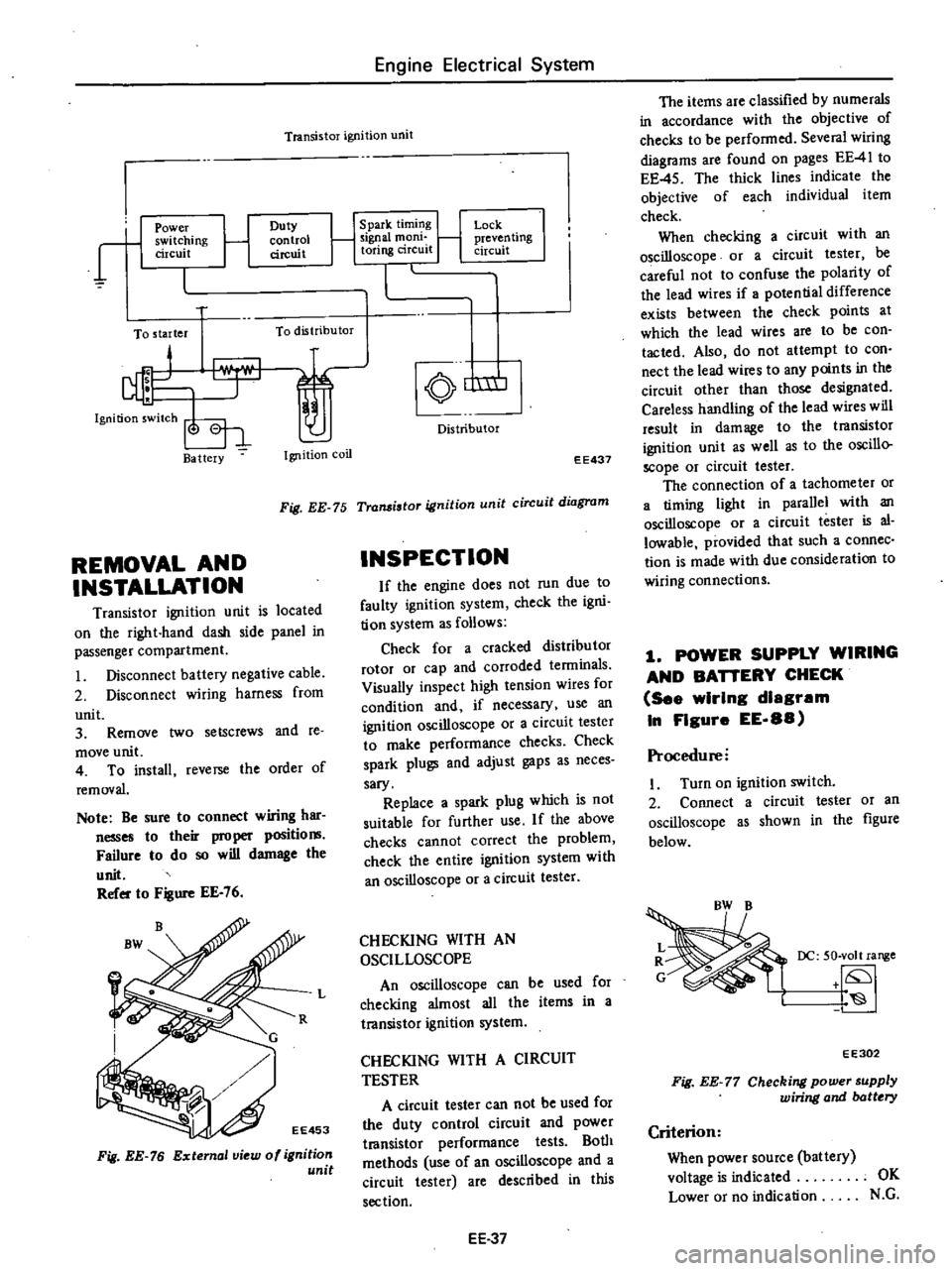
Transistor
ignition
unit
r
1
Power
switching
circuit
Duty
control
circuit
To
starter
To
distributor
Ba
ttery
Ignition
coil
1
Spark
timing
1
Signal
mom
toring
circuit
Lock
j
preven
ling
circuit
nm
Distributor
EE437
Fig
EE
75
Transistor
ignition
unit
circuit
diagram
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Transistor
ignition
unit
is
located
on
the
right
hand
dash
side
panel
in
passenger
compartment
Disconnect
battery
negative
cable
2
Disconnect
wiring
harness
from
unit
3
Remove
two
setscrews
and
te
move
unit
4
To
install
reverse
the
order
of
removal
Note
Be
sure
to
connect
wiring
har
nesses
to
their
proper
positio
Failure
to
do
so
will
damage
the
unit
Refer
to
Figure
EE
76
Fig
EE
76
External
view
of
ignition
unit
INSPECTION
If
the
engine
does
not
run
due
to
faulty
ignition
system
check
the
igni
tion
system
as
follows
Check
for
a
cracked
distributor
rotor
or
cap
and
corroded
tenninals
Visually
inspect
high
tension
wires
for
condition
and
if
necessary
use
an
ignition
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
to
make
performance
checks
Check
spark
plugs
and
adjust
gaps
as
neces
sary
Replace
a
spark
plug
which
is
not
suitable
for
further
use
If
the
above
checks
cannot
correct
the
problem
check
the
entire
ignition
system
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
L
CHECKING
WITH
AN
OSCILLOSCOPE
An
oscilloscope
can
be
used
for
checking
almost
all
the
items
in
a
transistor
ignition
system
CHECKING
WITH
A
CIRCUIT
TESTER
A
circuit
tester
can
not
be
used
for
the
duty
control
circuit
and
power
t18nsistor
performance
tests
Both
methods
use
of
an
oscilloscope
and
a
circuit
tester
are
described
in
this
section
EE
37
The
items
are
classified
by
numerals
in
accordance
with
the
objective
of
checks
to
be
performed
Several
wiring
diagrams
are
found
on
pages
EE
41
to
EE
45
The
thick
lines
indicate
the
objective
of
each
individual
item
check
When
checking
a
circuit
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
be
careful
not
to
confuse
the
polarity
of
the
lead
wires
if
potential
difference
exists
between
the
check
points
at
which
the
lead
wires
are
to
be
con
tacted
Also
do
not
attempt
to
con
nect
the
lead
wires
to
any
points
in
the
circuit
other
than
those
designated
Careless
handling
of
the
lead
wires
will
result
in
damage
to
the
transistor
ignition
unit
as
well
as
to
the
oscillo
scope
or
circuit
tester
The
connection
of
a
tachometer
or
a
timing
light
in
parallel
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
is
al
lowable
provided
that
such
a
connec
tion
is
made
with
due
consideration
to
wiring
connections
1
POWER
SUPPLY
WIRING
AND
BAnERY
CHECK
See
wIrIng
diagram
In
FIgure
EE
88
Procedure
I
Turn
on
ignition
switch
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
or
an
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
DC
50
volt
range
EE302
Fig
EE
77
Checking
power
supply
wiring
and
batt
ry
Criterion
When
power
source
battery
voltage
is
indicated
OK
Lower
or
no
indication
N
G
Page 205 of 537
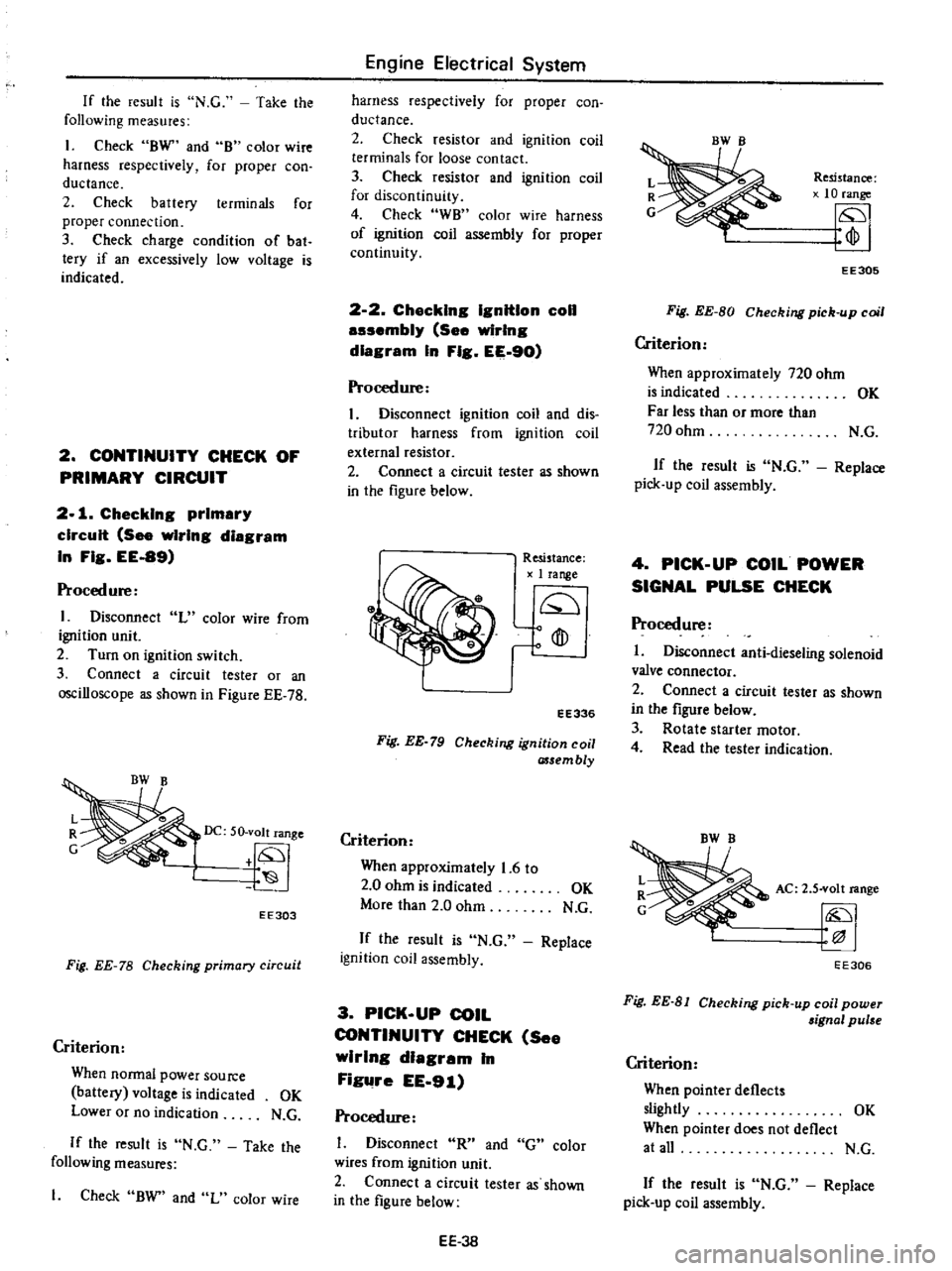
If
the
result
is
N
C
Take
the
following
measures
I
Check
BW
and
B
color
wire
harness
respectively
for
proper
con
ductance
2
Check
battery
terminals
for
proper
connection
3
Check
charge
condition
of
bat
tery
if
an
excessively
low
voltage
is
indicated
2
CONTINUITY
CHECK
OF
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
2
1
CheckIng
prImary
circuit
See
wiring
diagram
In
Fig
EE
89
Proced
ure
I
Disconnect
L
color
wire
from
ignition
unit
2
Turn
on
ignition
switch
3
C
ooneet
a
cireui
t
tester
or
an
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
78
DC
50
volt
range
tf
S
EE303
Fig
EE
78
Checking
primary
circuit
Criterion
When
Donnal
power
Source
battery
voltage
is
indicated
OK
Lower
or
no
indication
N
G
If
the
result
is
N
C
Take
the
following
measures
1
Check
BW
and
L
color
wire
Engine
Electrical
System
harness
respectively
for
proper
con
ductance
2
Check
resistor
and
ignition
coil
terminals
for
loose
contact
3
Check
resistor
and
ignition
coil
for
discontinuity
4
Check
WB
color
wire
harness
of
ignition
coil
assembly
for
proper
continuity
2
2
Chacklng
IgnitIon
coil
auembly
See
wiring
diagram
In
Fig
EE
90
Procedure
I
Disconnect
ignition
coil
and
dis
tributor
harness
from
ignition
coil
external
resistor
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
Resistance
1
range
Q
o
fD
ro
EE336
Fig
EE
79
Checking
ignition
coil
assembly
Criterion
When
approximately
1
6
to
2
0
ohm
is
indicated
OK
More
than
2
0
ohm
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
ignition
coil
assembly
3
PICK
UP
COIL
CONTINUITY
CHECK
See
wirIng
dIagram
In
Figure
EE
91
Procedure
Disconnect
R
and
G
color
wires
from
ignition
unit
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
EE
3B
Resistance
10
range
fp
EE305
Fig
EE
BO
Checking
pick
up
coil
Criterion
When
approximately
720
ohm
is
indicated
OK
Far
less
than
or
more
than
720
ohm
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly
4
PICK
UP
COIL
POWER
SIGNAL
PULSE
CHECK
Procedure
I
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
3
Rotate
starter
motor
4
Read
the
tester
indication
AC
2
S
volt
range
EE306
Fig
EE
81
Checking
pick
up
coil
power
aignal
pulse
Criterion
When
pointer
deflects
slightly
OK
When
pointer
does
not
deflect
at
all
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly