lock INFINITI QX4 2001 Factory User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2001, Model line: QX4, Model: INFINITI QX4 2001Pages: 2395, PDF Size: 43.2 MB
Page 31 of 2395

TCM FUNCTION=NBAT0013S03The function of the TCM is to:
IReceive input signals sent from various switches and sensors.
IDetermine required line pressure, shifting point, lock-up operation, and engine brake operation.
ISend required output signals to the respective solenoids.
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL OF TCMNBAT0013S04
Sensors and solenoid valves Function
InputPNP switch Detects select lever position and sends a signal to TCM.
Throttle position sensor Detects throttle valve position and sends a signal to TCM.
Closed throttle position switch Detects throttle valve's fully-closed position and sends a signal to TCM.
Wide open throttle position switchDetects a throttle valve position of greater than 1/2 of full throttle and sends
a signal to TCM.
Engine speed signal From ECM.
A/T fluid temperature sensor Detects transmission fluid temperature and sends a signal to TCM.
Revolution sensor Detects output shaft rpm and sends a signal to TCM.
Vehicle speed sensorUsed as an auxiliary vehicle speed sensor. Sends a signal when revolution
sensor (installed on transmission) malfunctions.
Overdrive control switchSends a signal, which prohibits a shift to ªD
4º (overdrive) position, to the
TCM.
ASCD control unitSends the cruise signal and ªD
4º (overdrive) cancellation signal from ASCD
control unit to TCM.
Turbine revolution sensor Sends an input shaft revolution signal.
Stop lamp switch Sends the lock-up release signal to the TCM at time of D
4(lock-up).
OutputShift solenoid valve A/BSelects shifting point suited to driving conditions in relation to a signal sent
from TCM.
Line pressure solenoid valveRegulates (or decreases) line pressure suited to driving conditions in rela-
tion to a signal sent from TCM.
Torque converter clutch solenoid
valveRegulates (or decreases) lock-up pressure suited to driving conditions in
relation to a signal sent from TCM.
Overrun clutch solenoid valveControls an ªengine brakeº effect suited to driving conditions in relation to a
signal sent from TCM.
O/D OFF indicator lamp Shows TCM faults, when A/T control components malfunction.
Control MechanismNBAT0180LINE PRESSURE CONTROLNBAT0180S01TCM has the various line pressure control characteristics to meet
the driving conditions.
An ON-OFF duty signal is sent to the line pressure solenoid valve
based on TCM characteristics.
Hydraulic pressure on the clutch and brake is electronically con-
trolled through the line pressure solenoid valve to accommodate
engine torque. This results in smooth shift operation.
OVERALL SYSTEM
Control System (Cont'd)
AT-26
Page 34 of 2395

Pilot pressure generated by the operation of shift solenoid valves
A and B is applied to the end face of shift valves A and B.
The drawing above shows the operation of shift valve B. When the
shift solenoid valve is ªONº, pilot pressure applied to the end face
of the shift valve overcomes spring force, moving the valve upward.
LOCK-UP CONTROLNBAT0180S03The torque converter clutch piston in the torque converter is locked
to eliminate torque converter slip to increase power transmission
efficiency. The solenoid valve is controlled by an ON-OFF duty
signal sent from the TCM. The signal is converted to oil pressure
signal which controls the torque converter clutch piston.
Conditions for Lock-up OperationNBAT0180S0301When vehicle is driven in 4th gear position, vehicle speed and
throttle opening are detected. If the detected values fall within the
lock-up zone memorized in the TCM, lock-up is performed.
Overdrive control switch ON OFF
Selector lever ªDº position
Gear position D
4D3
Vehicle speed sensor More than set value
Throttle position sensor Less than set opening
Closed throttle position switch OFF
A/T fluid temperature sensor More than 40ÉC (104ÉF)
SAT010J
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve ControlNBAT0180S0302The torque converter clutch solenoid valve is controlled by the
TCM. The plunger closes the drain circuit during the ªOFFº period,
and opens the circuit during the ªONº period. If the percentage of
OFF-time increases in one cycle, the pilot pressure drain time is
reduced and pilot pressure remains high.
The torque converter clutch piston is designed to slip to adjust the
ratio of ON-OFF, thereby reducing lock-up shock.
SAT011J
OFF-time INCREASING
"
Amount of drain DECREASING
"
Pilot pressure HIGH
"
Lock-up RELEASING
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
OVERALL SYSTEM
Control Mechanism (Cont'd)
AT-29
Page 35 of 2395
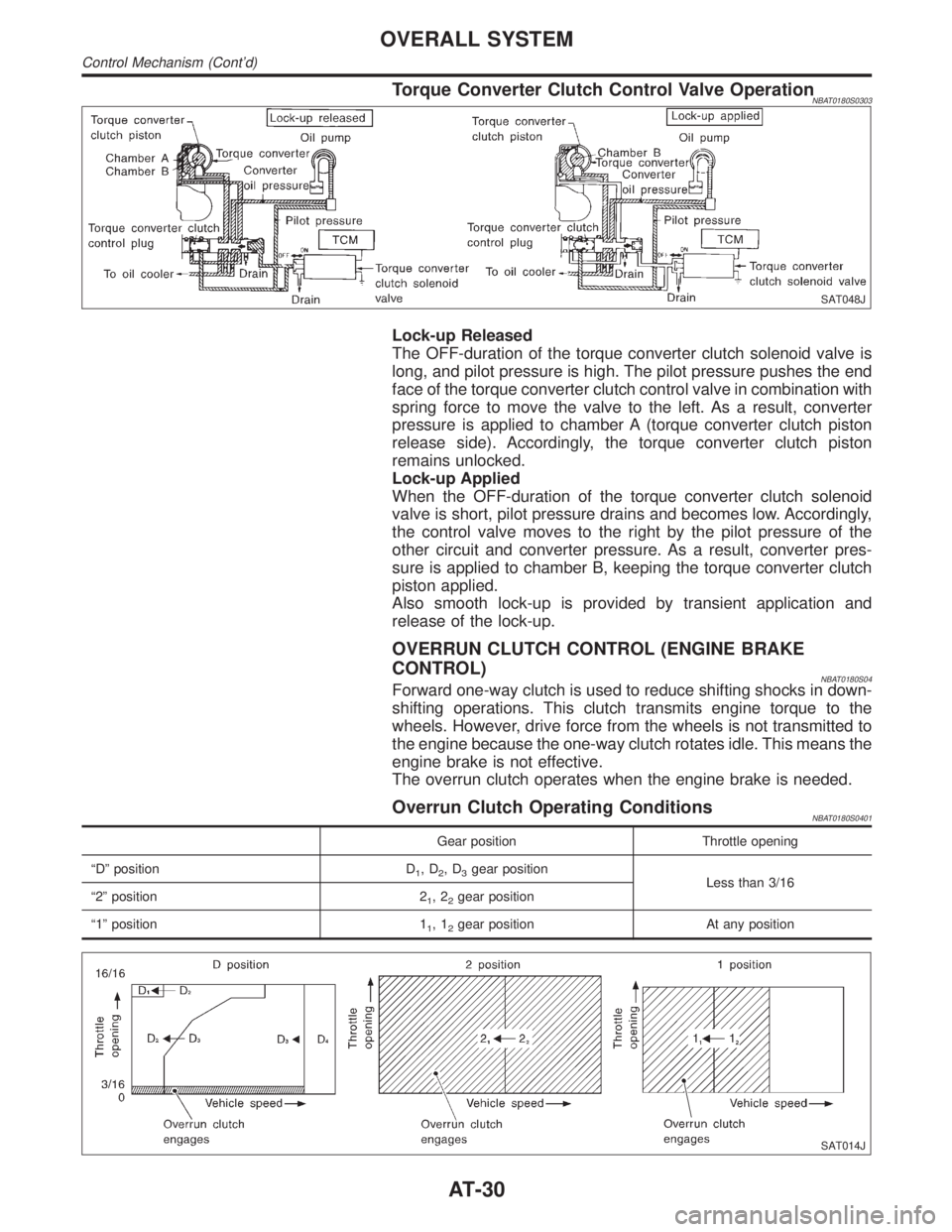
Torque Converter Clutch Control Valve OperationNBAT0180S0303
SAT048J
Lock-up Released
The OFF-duration of the torque converter clutch solenoid valve is
long, and pilot pressure is high. The pilot pressure pushes the end
face of the torque converter clutch control valve in combination with
spring force to move the valve to the left. As a result, converter
pressure is applied to chamber A (torque converter clutch piston
release side). Accordingly, the torque converter clutch piston
remains unlocked.
Lock-up Applied
When the OFF-duration of the torque converter clutch solenoid
valve is short, pilot pressure drains and becomes low. Accordingly,
the control valve moves to the right by the pilot pressure of the
other circuit and converter pressure. As a result, converter pres-
sure is applied to chamber B, keeping the torque converter clutch
piston applied.
Also smooth lock-up is provided by transient application and
release of the lock-up.
OVERRUN CLUTCH CONTROL (ENGINE BRAKE
CONTROL)
NBAT0180S04Forward one-way clutch is used to reduce shifting shocks in down-
shifting operations. This clutch transmits engine torque to the
wheels. However, drive force from the wheels is not transmitted to
the engine because the one-way clutch rotates idle. This means the
engine brake is not effective.
The overrun clutch operates when the engine brake is needed.
Overrun Clutch Operating ConditionsNBAT0180S0401
Gear position Throttle opening
ªDº position D
1,D2,D3gear position
Less than 3/16
ª2º position 2
1,22gear position
ª1º position 1
1,12gear position At any position
SAT014J
OVERALL SYSTEM
Control Mechanism (Cont'd)
AT-30
Page 36 of 2395

SAT015J
Overrun Clutch Solenoid Valve ControlNBAT0180S0402The overrun clutch solenoid valve is operated by an ON-OFF sig-
nal transmitted by the TCM to provide overrun clutch control
(engine brake control).
When this solenoid valve is ªONº, the pilot pressure drain port
closes. When it is ªOFFº, the drain port opens.
During the solenoid valve ªONº pilot pressure is applied to the end
face of the overrun clutch control valve.
SAT049J
Overrun Clutch Control Valve OperationNBAT0180S0403When the solenoid valve is ªONº, pilot pressure A is applied to the
overrun clutch control valve. This pushes up the overrun clutch
control valve. The line pressure is then shut off so that the clutch
does not engage.
When the solenoid valve is ªOFFº, pilot pressure A is not gener-
ated. At this point, the overrun clutch control valve moves down-
ward by spring force. As a result, overrun clutch operation pressure
is provided by the overrun clutch reducing valve. This causes the
overrun clutch to engage.
In the ª1º position, the overrun clutch control valve remains pushed
down so that the overrun clutch is engaged at all times.
Control ValveNBAT0181FUNCTION OF CONTROL VALVENBAT0181S01
Valve name Function
IPressure regulator valve
IPressure regulator plug
IPressure regulator sleeve plugRegulate oil discharged from the oil pump to provide optimum line pressure for all
driving conditions.
Pressure modifier valve Used as a signal supplementary valve to the pressure regulator valve. Regulates
pressure-modifier pressure (signal pressure) which controls optimum line pressure for
all driving conditions.
Modifier accumulator piston Smooths hydraulic pressure regulated by the pressure modifier valve to prevent pul-
sations.
Pilot valve Regulates line pressure to maintain a constant pilot pressure level which controls
lock-up mechanism, overrun clutch, 3-2 timing required for shifting.
Accumulator control valve
Accumulator control sleeveRegulate accumulator back-pressure to pressure suited to driving conditions.
Manual valve Directs line pressure to oil circuits corresponding to select positions.
Hydraulic pressure drains when the shift lever is in Neutral.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
OVERALL SYSTEM
Control Mechanism (Cont'd)
AT-31
Page 37 of 2395
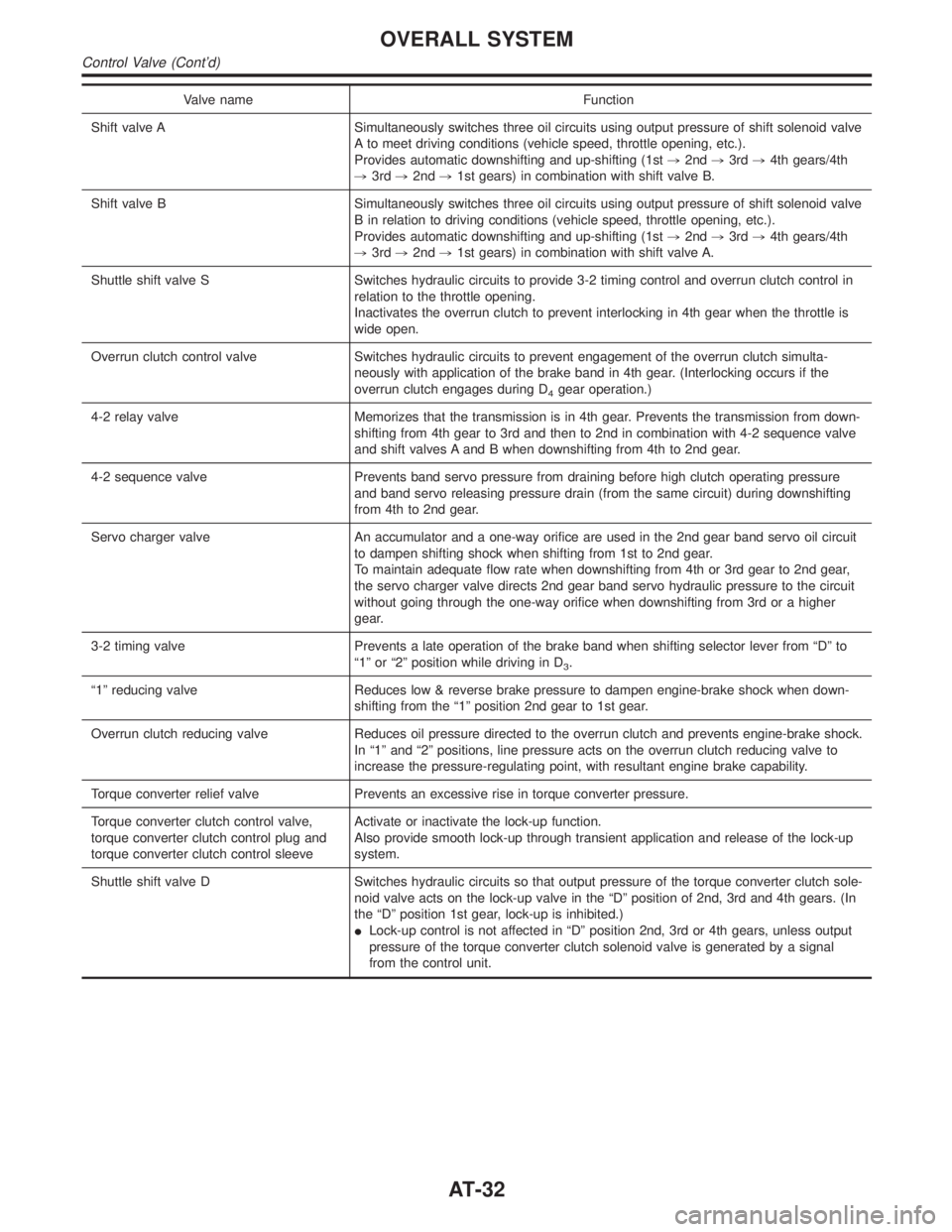
Valve name Function
Shift valve A Simultaneously switches three oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve
A to meet driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and up-shifting (1st,2nd,3rd,4th gears/4th
,3rd,2nd,1st gears) in combination with shift valve B.
Shift valve B Simultaneously switches three oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve
B in relation to driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and up-shifting (1st,2nd,3rd,4th gears/4th
,3rd,2nd,1st gears) in combination with shift valve A.
Shuttle shift valve S Switches hydraulic circuits to provide 3-2 timing control and overrun clutch control in
relation to the throttle opening.
Inactivates the overrun clutch to prevent interlocking in 4th gear when the throttle is
wide open.
Overrun clutch control valve Switches hydraulic circuits to prevent engagement of the overrun clutch simulta-
neously with application of the brake band in 4th gear. (Interlocking occurs if the
overrun clutch engages during D
4gear operation.)
4-2 relay valve Memorizes that the transmission is in 4th gear. Prevents the transmission from down-
shifting from 4th gear to 3rd and then to 2nd in combination with 4-2 sequence valve
and shift valves A and B when downshifting from 4th to 2nd gear.
4-2 sequence valve Prevents band servo pressure from draining before high clutch operating pressure
and band servo releasing pressure drain (from the same circuit) during downshifting
from 4th to 2nd gear.
Servo charger valve An accumulator and a one-way orifice are used in the 2nd gear band servo oil circuit
to dampen shifting shock when shifting from 1st to 2nd gear.
To maintain adequate flow rate when downshifting from 4th or 3rd gear to 2nd gear,
the servo charger valve directs 2nd gear band servo hydraulic pressure to the circuit
without going through the one-way orifice when downshifting from 3rd or a higher
gear.
3-2 timing valve Prevents a late operation of the brake band when shifting selector lever from ªDº to
ª1º or ª2º position while driving in D
3.
ª1º reducing valve Reduces low & reverse brake pressure to dampen engine-brake shock when down-
shifting from the ª1º position 2nd gear to 1st gear.
Overrun clutch reducing valve Reduces oil pressure directed to the overrun clutch and prevents engine-brake shock.
In ª1º and ª2º positions, line pressure acts on the overrun clutch reducing valve to
increase the pressure-regulating point, with resultant engine brake capability.
Torque converter relief valve Prevents an excessive rise in torque converter pressure.
Torque converter clutch control valve,
torque converter clutch control plug and
torque converter clutch control sleeveActivate or inactivate the lock-up function.
Also provide smooth lock-up through transient application and release of the lock-up
system.
Shuttle shift valve D Switches hydraulic circuits so that output pressure of the torque converter clutch sole-
noid valve acts on the lock-up valve in the ªDº position of 2nd, 3rd and 4th gears. (In
the ªDº position 1st gear, lock-up is inhibited.)
ILock-up control is not affected in ªDº position 2nd, 3rd or 4th gears, unless output
pressure of the torque converter clutch solenoid valve is generated by a signal
from the control unit.
OVERALL SYSTEM
Control Valve (Cont'd)
AT-32
Page 42 of 2395

SAT964I
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)=NBAT0183The MIL is located on the instrument panel.
1. The MIL will light up when the ignition switch is turned ON
without the engine running. This is a bulb check.
IIf the MIL does not light up, refer to EL-114, ªSchematicº.
(Or refer to EC-648, ªWiring Diagramº.)
2. When the engine is started, the MIL should go off.
If the MIL remains on, the on board diagnostic system has
detected an engine system malfunction. For detail, refer to
EC-59, ªIntroductionº.
CONSULT-IINBAT0184After performing ªSELF-DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE (WITH CON-
SULT-II)º (AT-37), place check marks for results on the ªDIAGNOS-
TIC WORKSHEETº, AT-55. Reference pages are provided follow-
ing the items.
NOTICE:
1) The CONSULT-II electrically displays shift timing and lock-up
timing (that is, operation timing of each solenoid).
Check for time difference between actual shift timing and the
CONSULT-II display. If the difference is noticeable, mechani-
cal parts (except solenoids, sensors, etc.) may be malfunction-
ing. Check mechanical parts using applicable diagnostic pro-
cedures.
2) Shift schedule (which implies gear position) displayed on
CONSULT-II and that indicated in Service Manual may differ
slightly. This occurs because of the following reasons:
IActual shift schedule has more or less tolerance or allowance,
IShift schedule indicated in Service Manual refers to the point
where shifts start, and
IGear position displayed on CONSULT-II indicates the point
where shifts are completed.
3) Shift solenoid valve ªAº or ªBº is displayed on CONSULT-II at
the start of shifting. Gear position is displayed upon completion
of shifting (which is computed by TCM).
4) Additional CONSULT-II information can be found in the Opera-
tion Manual supplied with the CONSULT-II unit.
SAT014K
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE (WITH CONSULT-II)NBAT0184S011. Turn on CONSULT-II and touch ªENGINEº for OBD-II detected
items or touch ªA/Tº for TCM self-diagnosis.
If A/T is not displayed, check TCM power supply and ground
circuit. Refer to AT-92. If result is NG, refer to EL-9, ªSche-
maticº.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
AT-37
Page 43 of 2395

SAT987J
2. Touch ªSELF-DIAG RESULTSº.
Display shows malfunction experienced since the last erasing
operation.
CONSULT-II performs REAL-TIME SELF-DIAGNOSIS.
Also, any malfunction detected while in this mode will be dis-
played at real time.
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULT TEST MODENBAT0184S02
Detected items
(Screen terms for CONSULT-II, ªSELF-DIAG
RESULTSº test mode)
Malfunction is detected when ...TCM self-diagnosis OBD-II (DTC)
Available by
O/D OFF
indicator lamp or
ªA/Tº on CONSULT-IIAvailable by
malfunction
indicator lamp*2,
ªENGINEº on CON-
SULT-II or GST ªA/Tº ªENGINEº
PNP switch circuitITCM does not receive the cor-
rect voltage signal (based on
the gear position) from the
switch.Ð P0705
ÐPNP SW/CIRC
Revolution sensorITCM does not receive the
proper voltage signal from the
sensor.X P0720
VHCL SPEED
SEN´A/TVEH SPD SEN/CIR
AT
Vehicle speed sensor (Meter)ITCM does not receive the
proper voltage signal from the
sensor.XÐ
VHCL SPEED
SEN´MTRÐ
A/T 1st gear functionIA/T cannot be shifted to the 1st
gear position even if electrical
circuit is good.Ð P0731*1
ÐA/T 1ST GR FNCTN
A/T 2nd gear functionIA/T cannot be shifted to the 2nd
gear position even if electrical
circuit is good.Ð P0732*1
ÐA/T 2ND GR FNCTN
A/T 3rd gear functionIA/T cannot be shifted to the 3rd
gear position even if electrical
circuit is good.Ð P0733*1
ÐA/T 3RD GR FNCTN
A/T 4th gear functionIA/T cannot be shifted to the 4th
gear position even if electrical
circuit is good.Ð P0734*1
ÐA/T 4TH GR FNCTN
A/T TCC S/V function (lock-up)IA/T cannot perform lock-up
even if electrical circuit is good.Ð P0744*1
Ð A/T TCC S/V FNCTN
Shift solenoid valve AITCM detects an improper volt-
age drop when it tries to operate
the solenoid valve.X P0750
SHIFT SOLENOID/V
ASFT SOL A/CIRC
Shift solenoid valve BITCM detects an improper volt-
age drop when it tries to operate
the solenoid valve.X P0755
SHIFT SOLENOID/V
BSFT SOL B/CIRC
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
CONSULT-II (Cont'd)
AT-38
Page 50 of 2395

SAT596J
SAT593J
13. CONSULT-II procedure ended.
If ªNGº appears on the screen, a malfunction may exist. Go to
ªDIAGNOSTIC PROCEDUREº.
DTC WORK SUPPORT MODENBAT0184S05
DTC work support item Description Check item
1ST GR FNCTN P0731Following items for ªA/T 1st gear function (P0731)º can be con-
firmed.
ISelf-diagnosis status (whether the diagnosis is being con-
ducted or not)
ISelf-diagnosis result (OK or NG)IShift solenoid valve A
IShift solenoid valve B
IEach clutch
IHydraulic control circuit
2ND GR FNCTN P0732Following items for ªA/T 2nd gear function (P0732)º can be con-
firmed.
ISelf-diagnosis status (whether the diagnosis is being con-
ducted or not)
ISelf-diagnosis result (OK or NG)IShift solenoid valve B
IEach clutch
IHydraulic control circuit
3RD GR FNCTN P0733Following items for ªA/T 3rd gear function (P0733)º can be con-
firmed.
ISelf-diagnosis status (whether the diagnosis is being con-
ducted or not)
ISelf-diagnosis result (OK or NG)IShift solenoid valve A
IEach clutch
IHydraulic control circuit
4TH GR FNCTN P0734Following items for ªA/T 4th gear function (P0734)º can be con-
firmed.
ISelf-diagnosis status (whether the diagnosis is being con-
ducted or not)
ISelf-diagnosis result (OK or NG)IShift solenoid valve A
IShift solenoid valve B
IOverrun clutch solenoid valve
ILine pressure solenoid valve
IEach clutch
IHydraulic control circuit
TCC S/V FNCTN P0744Following items for ªA/T TCC S/V function (lock-up) (P0744)º can
be confirmed.
ISelf-diagnosis status (whether the diagnosis is being con-
ducted or not)
ISelf-diagnosis result (OK or NG)ITorque converter clutch sole-
noid valve
IEach clutch
IHydraulic control circuit
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
CONSULT-II (Cont'd)
AT-45
Page 53 of 2395

2 JUDGEMENT PROCEDURE STEP 1
1. Turn ignition switch to ªOFFº position.
2. Push shift lock release button.
3. Move selector lever from ªPº to ªDº position.
4. Turn ignition switch to ªONº position. (Do not start engine.)
5. Depress and hold overdrive control switch in ªOFFº position (the O/D OFF indicator lamp will be ªONº) until directed to
release the switch. (If O/D OFF indicator lamp does not come on, go to step 5 on AT-257.)
6. Turn ignition switch to ªOFFº position.
SAT968I
7. Turn ignition switch to ªONº position (Do not start engine.).
8. Release the overdrive control switch (the O/D OFF indicator lamp will be ªOFFº).
9. Wait 2 seconds.
10. Move selector lever to ª2º position.
11. Depress and release the overdrive control switch (the O/D OFF indicator lamp will be ªONº).
12. Depress and hold the overdrive control switch (the O/D OFF indicator lamp will be ªOFFº) until directed to release the
switch.
SAT969I
©GO TO 3.
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Diagnostic Procedure Without CONSULT-II (Cont'd)
AT-48
Page 58 of 2395

SAT631IB
IntroductionNBAT0019
SAT632I
SEF234G
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, throttle
position sensor or PNP switch and provides shift control or lock-up
control via A/T solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal
sent from sensing elements used with the OBD-related parts of the
A/T system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is
capable of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can
store malfunctions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the
operation of the A/T system. The A/T system must be in good
operating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve
malfunction, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a problem that occurs intermit-
tently rather than continuously. Most intermittent problems are
caused by poor electric connections or improper wiring. In this
case, careful checking of suspected circuits may help prevent the
replacement of good parts.
A visual check only may not find the cause of the problems. A road
test with CONSULT-II (or GST) or a circuit tester connected should
be performed. Follow the ªWork Flowº. Refer to AT-57.
Before undertaking actual checks, take a few minutes to talk with
a customer who approaches with a driveability complaint. The cus-
tomer can supply good information about such problems, espe-
cially intermittent ones. Find out what symptoms are present and
under what conditions they occur. A ªDiagnostic Worksheetº like the
example (AT-55) should be used.
Start your diagnosis by looking for ªconventionalº problems first.
This will help troubleshoot driveability problems on an electronically
controlled engine vehicle.
Also check related Service bulletins.GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INTRODUCTION
Introduction
AT-53