ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 4251 of 6020
7A1-12 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
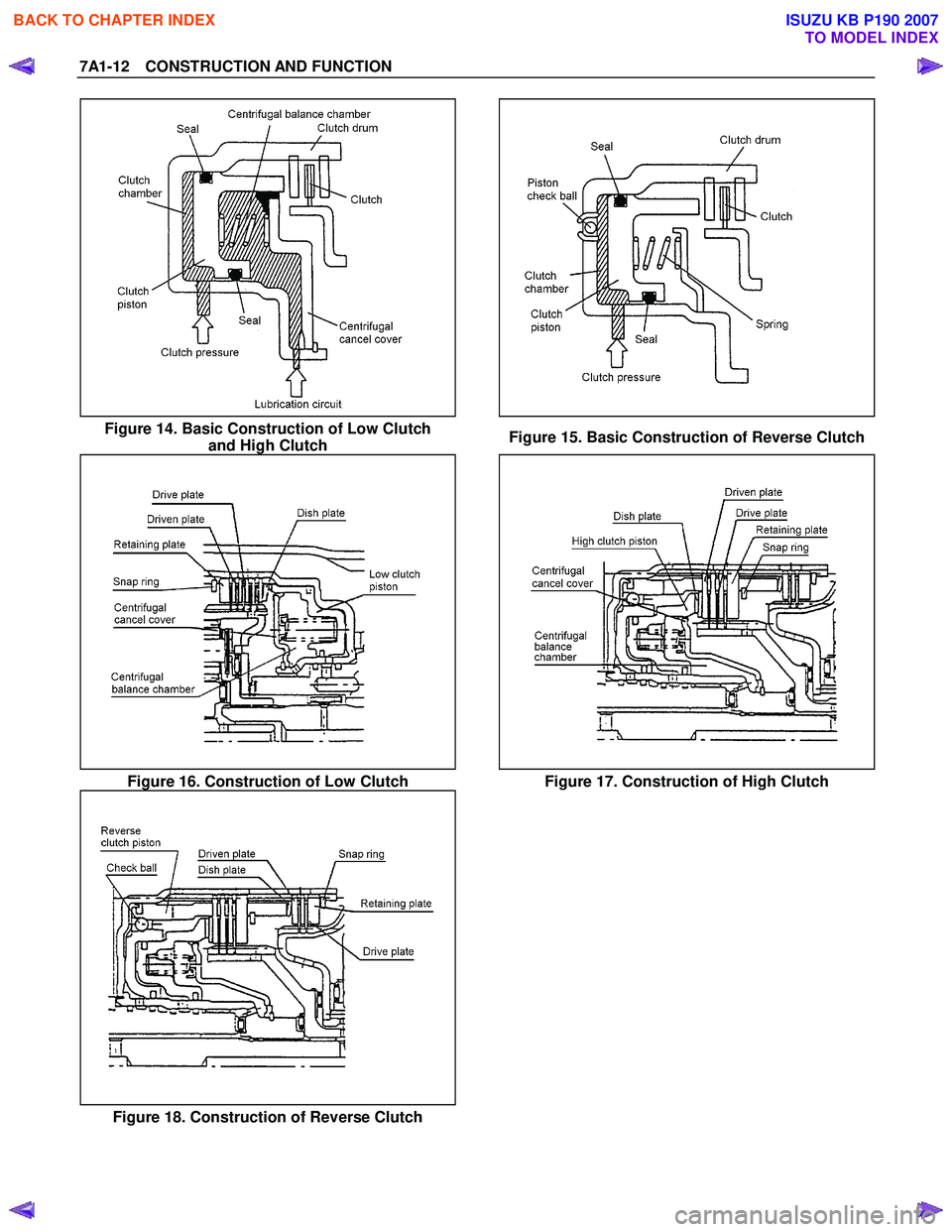
Figure 14. Basic Construction of Low Clutch and High Clutch Figure 15. Basic Construction of Reverse Clutch
Figure 16. Construction of Low Clutch Figure 17. Construction of High Clutch
Figure 18. Construction of Reverse Clutch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4252 of 6020
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-13
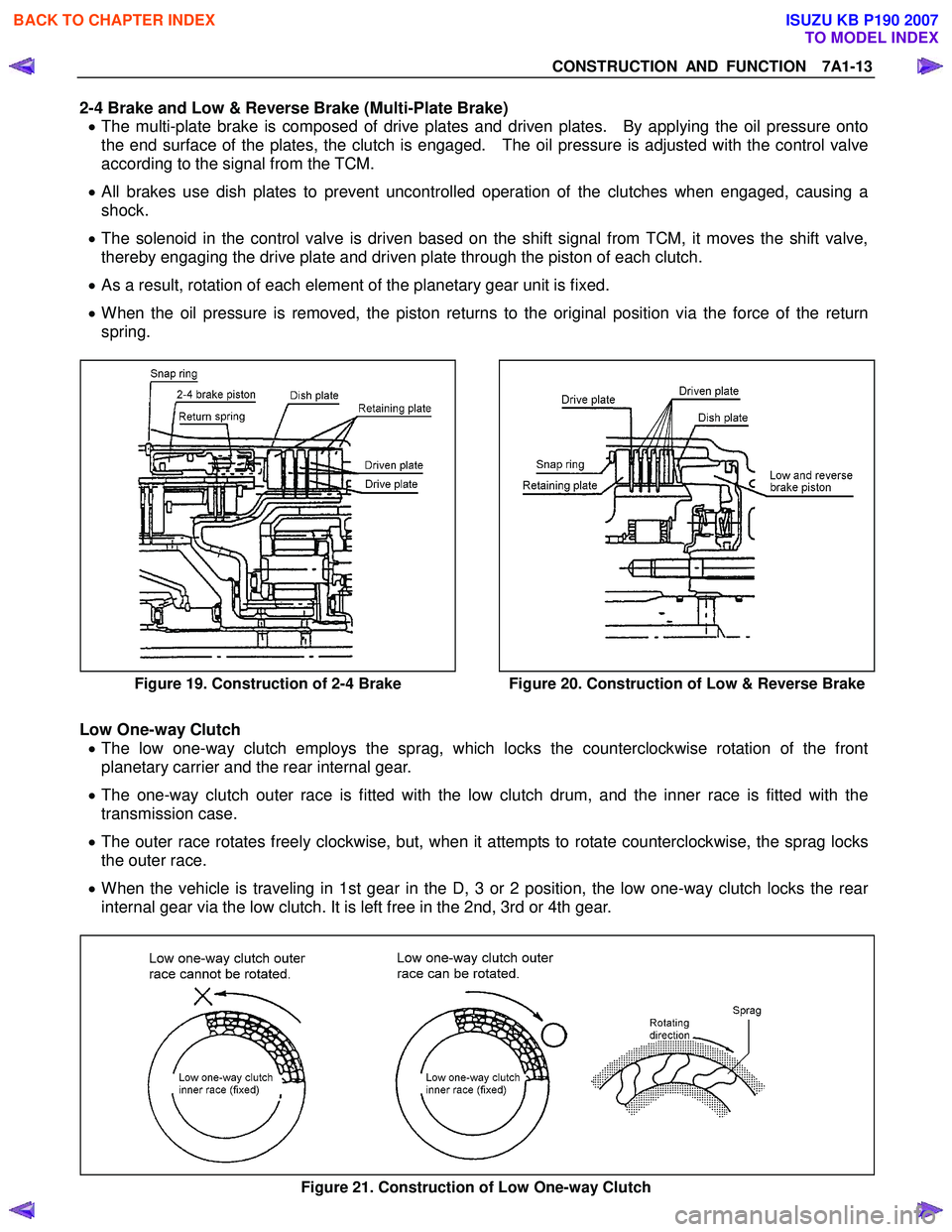
2-4 Brake and Low & Reverse Brake (Multi-Plate Brake) • The multi-plate brake is composed of drive plates and driven plates. By applying the oil pressure onto
the end surface of the plates, the clutch is engaged. The oil pressure is adjusted with the control valve
according to the signal from the TCM.
• All brakes use dish plates to prevent uncontrolled operation of the clutches when engaged, causing a
shock.
• The solenoid in the control valve is driven based on the shift signal from TCM, it moves the shift valve,
thereby engaging the drive plate and driven plate through the piston of each clutch.
• As a result, rotation of each element of the planetary gear unit is fixed.
• When the oil pressure is removed, the piston returns to the original position via the force of the return
spring.
Figure 19. Construction of 2-4 Brake
Figure 20. Construction of Low & Reverse Brake
Low One-way Clutch
• The low one-way clutch employs the sprag, which locks the counterclockwise rotation of the front
planetary carrier and the rear internal gear.
• The one-way clutch outer race is fitted with the low clutch drum, and the inner race is fitted with the
transmission case.
• The outer race rotates freely clockwise, but, when it attempts to rotate counterclockwise, the sprag locks
the outer race.
• When the vehicle is traveling in 1st gear in the D, 3 or 2 position, the low one-way clutch locks the rear
internal gear via the low clutch. It is left free in the 2nd, 3rd or 4th gear.
Figure 21. Construction of Low One-way Clutch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4253 of 6020

7A1-14 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
CONTROL VALVE
• Employing the direct electronic control (Direct Electronic Shift Control: DESC) for the clutch pressure has
simplified the oil pressure circuit, reduced the number of functional components and made the control
valve compact.
• The control valve body is divided into the upper body and the lower body. All solenoids, the oil pressure
switch and the ATF thermo sensor are installed to the lower body.
• Three-way valve type solenoids providing high responsibility are employed. Some of the solenoids are
switched between ON and OFF, and others repeat ON and OFF at 50Hz (duty cycle system).
Functionally, some supply output pressure when power is not supplied, and others drain the output
pressure.
• When the solenoid is driven based on the signal from the TCM, the oil pressure is changed.
Figure 22. Construction of Valve Body
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4254 of 6020
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-15
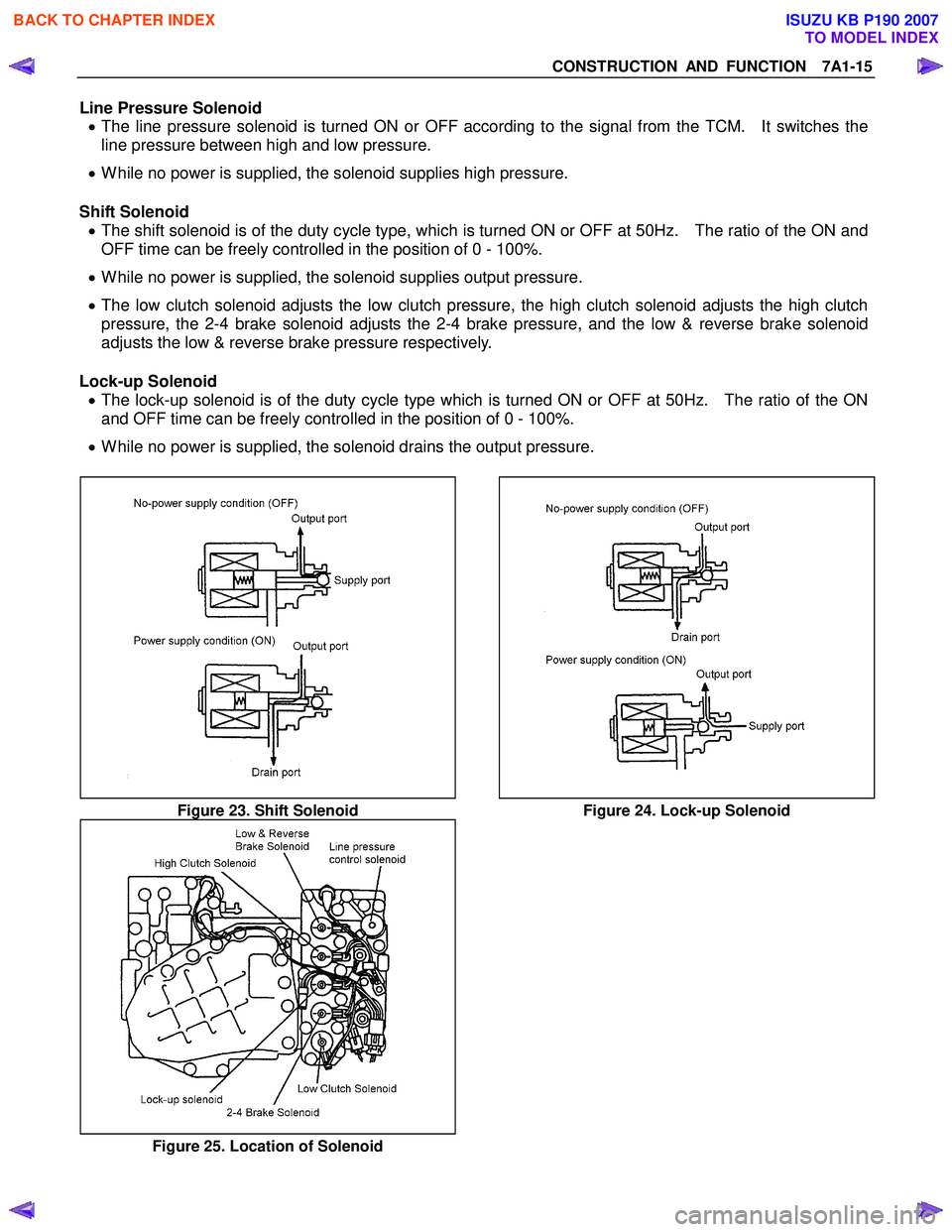
Line Pressure Solenoid • The line pressure solenoid is turned ON or OFF according to the signal from the TCM. It switches the
line pressure between high and low pressure.
• While no power is supplied, the solenoid supplies high pressure.
Shift Solenoid • The shift solenoid is of the duty cycle type, which is turned ON or OFF at 50Hz. The ratio of the ON and
OFF time can be freely controlled in the position of 0 - 100%.
• While no power is supplied, the solenoid supplies output pressure.
• The low clutch solenoid adjusts the low clutch pressure, the high clutch solenoid adjusts the high clutch
pressure, the 2-4 brake solenoid adjusts the 2-4 brake pressure, and the low & reverse brake solenoid
adjusts the low & reverse brake pressure respectively.
Lock-up Solenoid • The lock-up solenoid is of the duty cycle type which is turned ON or OFF at 50Hz. The ratio of the ON
and OFF time can be freely controlled in the position of 0 - 100%.
• While no power is supplied, the solenoid drains the output pressure.
Figure 23. Shift Solenoid Figure 24. Lock-up Solenoid
Figure 25. Location of Solenoid
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4255 of 6020
7A1-16 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
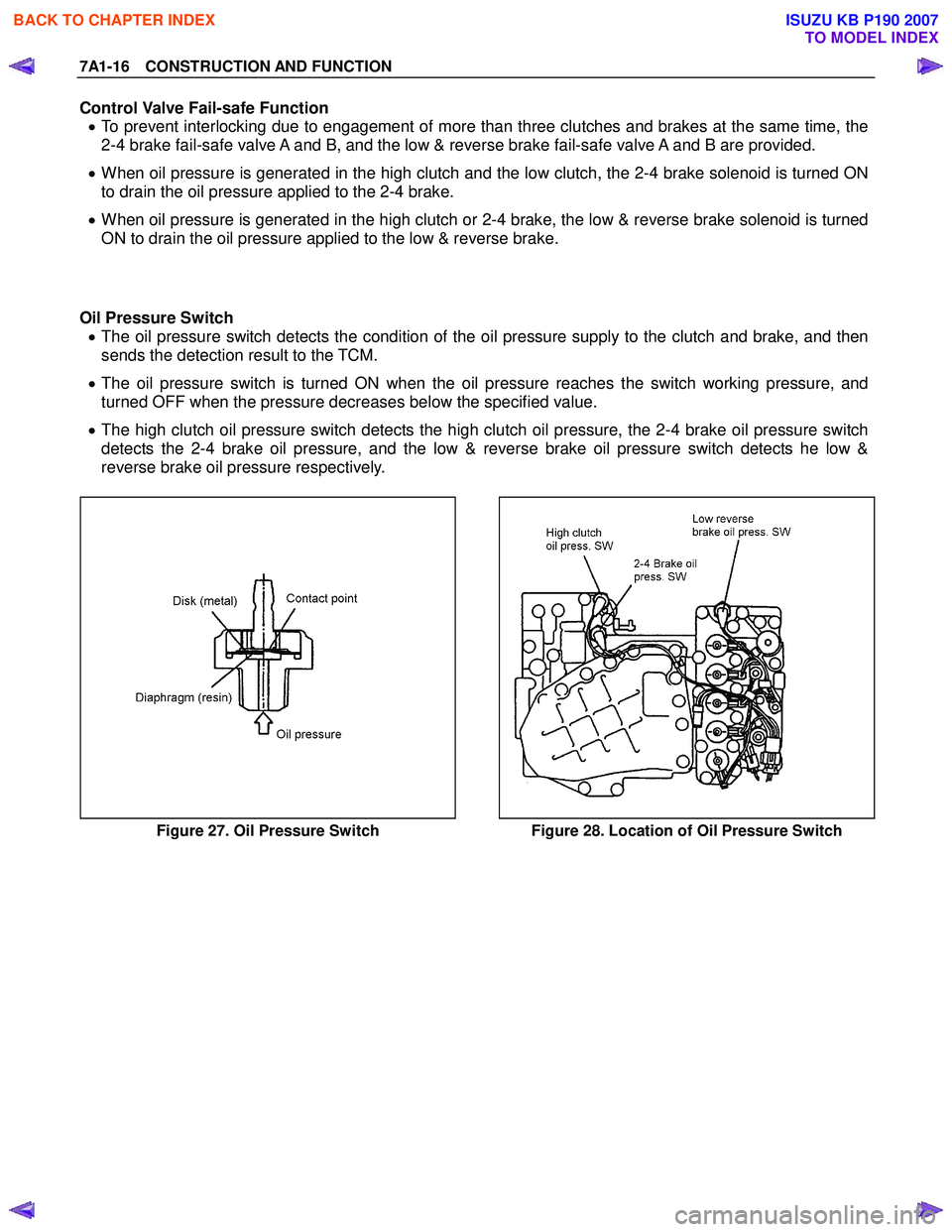
Control Valve Fail-safe Function • To prevent interlocking due to engagement of more than three clutches and brakes at the same time, the
2-4 brake fail-safe valve A and B, and the low & reverse brake fail-safe valve A and B are provided.
• When oil pressure is generated in the high clutch and the low clutch, the 2-4 brake solenoid is turned ON
to drain the oil pressure applied to the 2-4 brake.
• When oil pressure is generated in the high clutch or 2-4 brake, the low & reverse brake solenoid is turned
ON to drain the oil pressure applied to the low & reverse brake.
Oil Pressure Switch • The oil pressure switch detects the condition of the oil pressure supply to the clutch and brake, and then
sends the detection result to the TCM.
• The oil pressure switch is turned ON when the oil pressure reaches the switch working pressure, and
turned OFF when the pressure decreases below the specified value.
• The high clutch oil pressure switch detects the high clutch oil pressure, the 2-4 brake oil pressure switch
detects the 2-4 brake oil pressure, and the low & reverse brake oil pressure switch detects he low &
reverse brake oil pressure respectively.
Figure 27. Oil Pressure Switch Figure 28. Location of Oil Pressure Switch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4256 of 6020
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-17
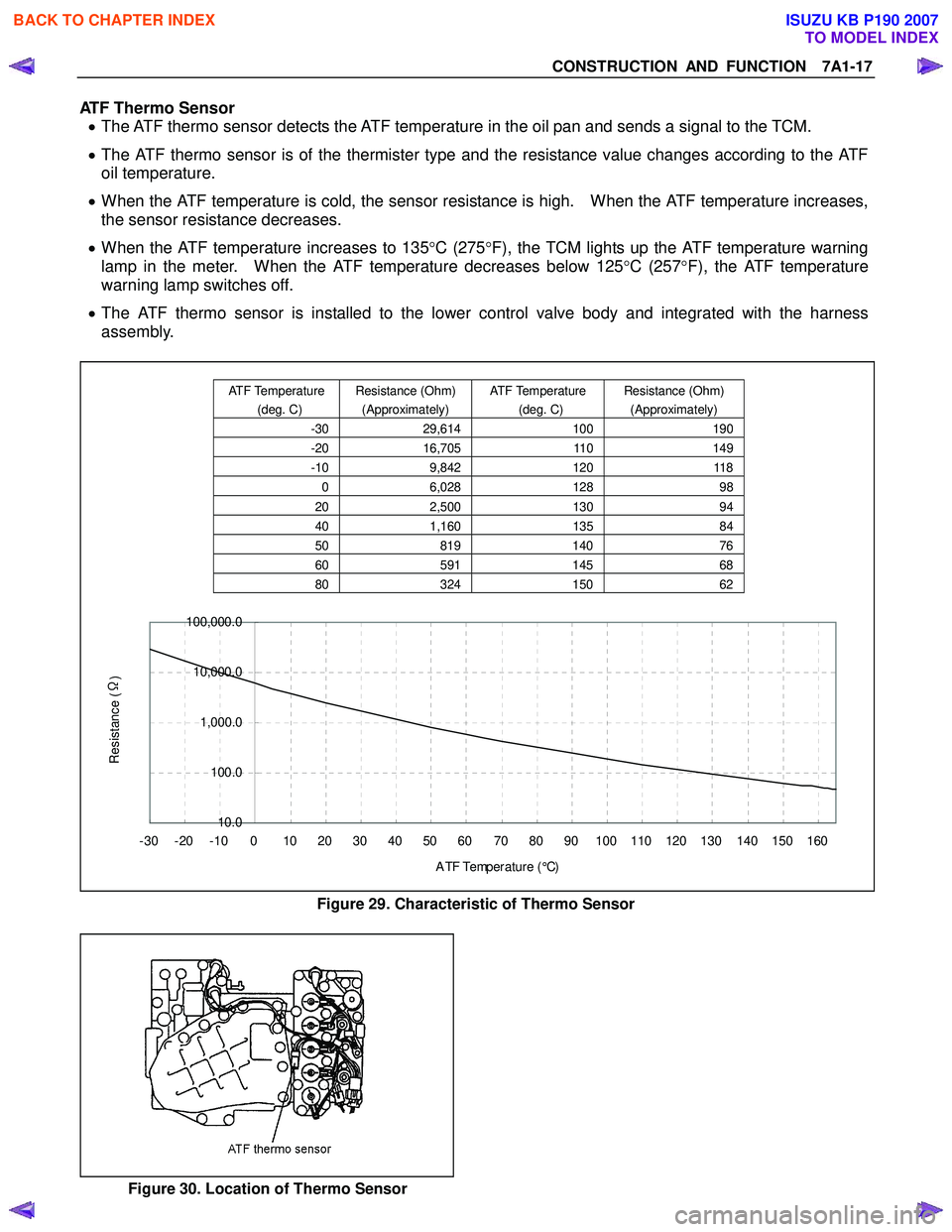
ATF Thermo Sensor • The ATF thermo sensor detects the ATF temperature in the oil pan and sends a signal to the TCM.
• The ATF thermo sensor is of the thermister type and the resistance value changes according to the ATF
oil temperature.
• When the ATF temperature is cold, the sensor resistance is high. When the ATF temperature increases,
the sensor resistance decreases.
• When the ATF temperature increases to 135 °C (275 °F), the TCM lights up the ATF temperature warning
lamp in the meter. When the ATF temperature decreases below 125 °C (257 °F), the ATF temperature
warning lamp switches off.
• The ATF thermo sensor is installed to the lower control valve body and integrated with the harness
assembly.
10.0
100.0
1,000.0
10,000.0
100,000.0
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 A TF Temp er a t ur e ( °C)
Resistance (Ω
)
Figure 29. Characteristic of Thermo Sensor
Figure 30. Location of Thermo Sensor
ATF Temperature
(deg. C) Resistance (Ohm)
(Approximately) ATF Temperature
(deg. C) Resistance (Ohm)
(Approximately)
-30 29,614 100190
-20 16,705 110149
-10 9,842 120118
0 6,028 128 98
20 2,500 130 94
40 1,160 135 84
50 819 140 76
60 591 14568
80 324 15062
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4257 of 6020

7A1-18 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
Terminal Assembly Pin No. Connected to Connected TCMPin No.
6 Line Pressure Solenoid B23
12 Low & Reverse Brake Oil Pressure Switch B12
5 Low & Reverse Brake Duty Solenoid B6
11 Ground Return B22
4 Lock-up Duty Solenoid B17
10 High Clutch Duty Solenoid B8
3 Low Clutch Duty Solenoid B9
9 2-4 Brake Duty Solenoid B7
2 Oil Thermo Sensor B4
8 Oil Thermo Sensor Ground B14
1 High Clutch Oil Pressure Switch B20
7 2-4 Brake Oil Pressure Switch B1
123456
891011127
Terminal AssemblyInhibitor Switch
Figure 31. Pin Assignment Figure 32. Location of Terminal Assembly
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4258 of 6020
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-19
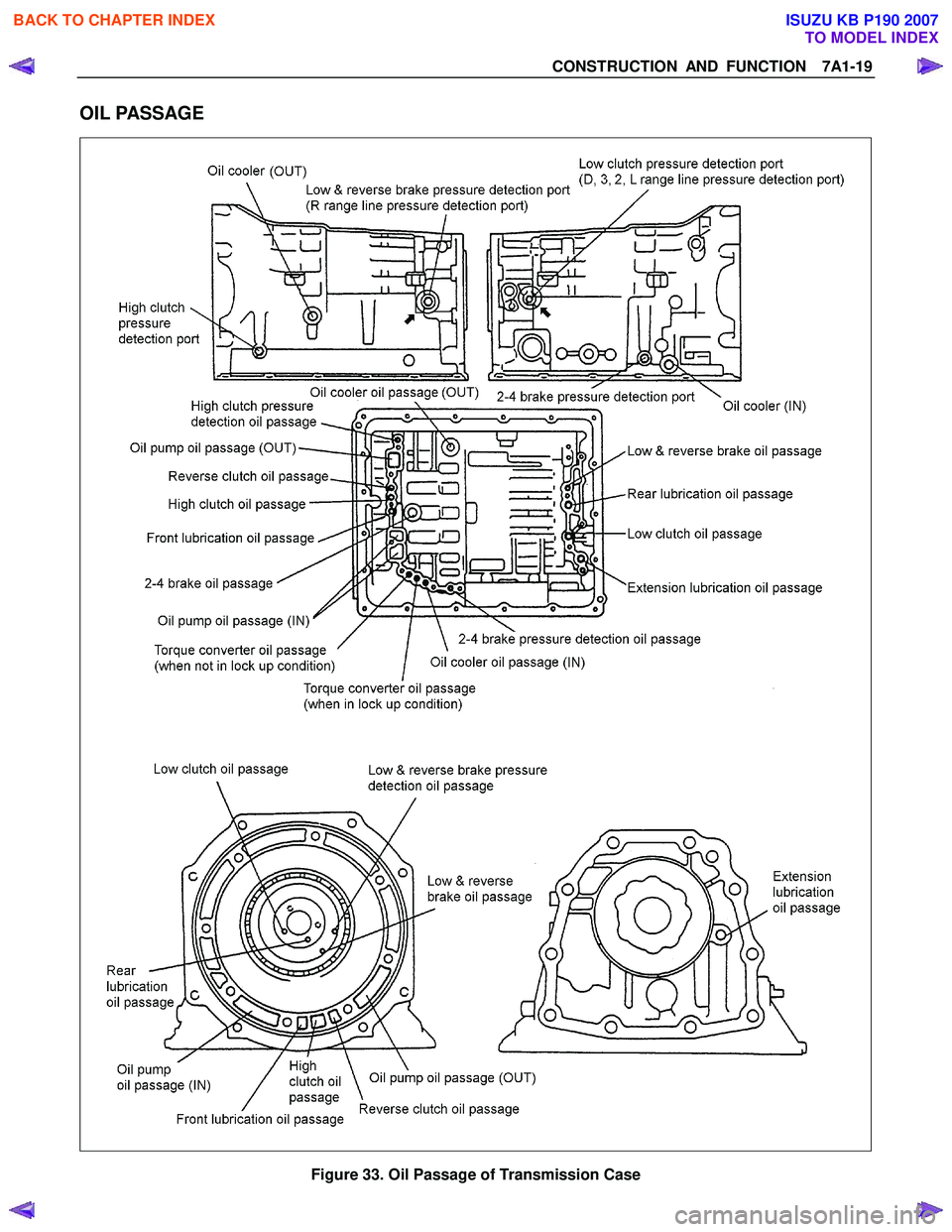
OIL PASSAGE
Figure 33. Oil Passage of Transmission Case
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4259 of 6020
7A1-20 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
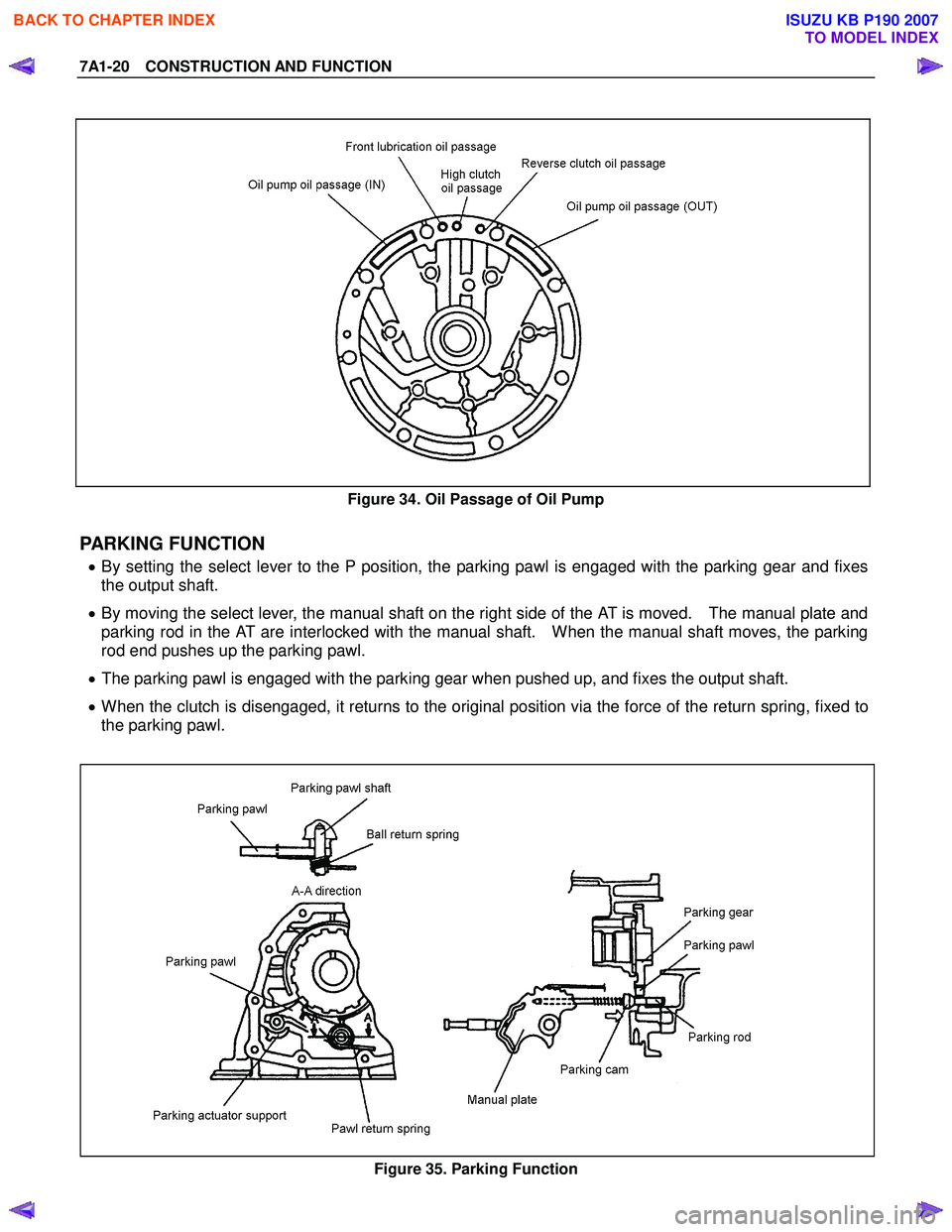
Figure 34. Oil Passage of Oil Pump
PARKING FUNCTION
• By setting the select lever to the P position, the parking pawl is engaged with the parking gear and fixes
the output shaft.
• By moving the select lever, the manual shaft on the right side of the AT is moved. The manual plate and
parking rod in the AT are interlocked with the manual shaft. When the manual shaft moves, the parking
rod end pushes up the parking pawl.
• The parking pawl is engaged with the parking gear when pushed up, and fixes the output shaft.
• When the clutch is disengaged, it returns to the original position via the force of the return spring, fixed to
the parking pawl.
Figure 35. Parking Function
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4260 of 6020

CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-21
INHIBITOR SWITCH
• The inhibitor switch is installed on the right side of the transmission main unit to detect the select lever
position.
• The inhibitor switch is connected with the starter SW circuit. The engine cannot be started when the
select lever is at any position other than the P and N position.
• By moving the select lever, the combination of the inhibitor switch pins is changed. The current position of
TCM is detected based on the combination of the pins.
10 7 3 2 4 8 5 1 9 6
P
R
N
D
3
2
L
6345
10987
21
Terminal Assembly Inhibitor Switch
Figure 36. Pin Assignment Figure 37. Location of Inhibitor Switch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007