ignition ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2173 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–3
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-139
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor High
Input ......................................................... 6E-140
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0122 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR LOW
INPUT ......................................................... 6E-143
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-143
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-143
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Low Input ....................... 6E-144
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0123 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR HIGH
INPUT ...................................................... 6E-147
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-147
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-147
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123 Throttle Position Sensor High Input ...................... 6E-148
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0131 O
2 SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW VOLTAGE
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1) ................................. 6E-150
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-150
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-150
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131 O
2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
6E-160
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0132 O
2
SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH VOLTAGE (BANK 1
SENSOR 1) ................................................ 6E-155
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-155
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-155
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0132 O
2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 1) .................................... 6E-156
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0134 O
2 SENSOR NO ACTIVITY DEFECTED
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1) ................................. 6E-159
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-159
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-160
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0134 O
2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank 1 Sensor 1) .................................... 6E-160
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135 O
2 SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1) ................................. 6E-163
Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-163
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-164
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0135 O
2 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1) 6E-164
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0201 INJECTOR 1 CONTROL CIRCUIT ............. 6E-167
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0202 INJECTOR 2 CONTROL CIRCUIT ............. 6E-167
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0203 INJECTOR 3 CONTROL CIRCUIT ............. 6E-167
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0204 INJECTOR 4 CONTROL CIRCUIT ............. 6E-167
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-167
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-168
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0201 Injector 1 Control Circuit .......................... 6E-168
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0202 Injector 2 Control Circuit .......................... 6E-168
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0203 Injector 3 Control Circuit .......................... 6E-168
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0204 Injector 4 Control Circuit .......................... 6E-168
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0325 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) MODULE CIRCUIT 6E-174
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-174
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-174
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0325 Knock
Sensor Module Circuit ............................. 6E-174
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT ............... 6E-177
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-177
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-177
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit ............................... 6E-178
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0336 CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE (58X) . 6E-180
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0337 CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT (58X) ...................... 6E-180
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-180
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-181
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit
Range/performance (58x) ........................ 6E-181
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0337 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low
Input (58x) ............................................... 6E-181
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0351 IGNITION 1 CONTROL CIRCUIT ............... 6E-186
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0352 IGNITION 2 CONTROL CIRCUIT ............... 6E-186
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-186
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-186
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351 Ignition 1 Control Circuit .......................... 6E-187
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0352 Ignition 2 Control Circuit .......................... 6E-187
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2175 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–5
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN ..... 6E-233
HARD START SYMPTOM ............................ 6E-236
ROUGH, UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT IDLE, STALLING SYMPTOM ............................... 6E-239
SURGES AND/OR CHUGS SYMPTOM ...... 6E-242
HESITATION, SAG, STUMBLE SYMPTOM 6E-245
CUTS OUT, MISSES SYMPTOM ................. 6E-248
LACK OF POWER, SLUGGISH OR SPONGY SYMPTOM ................................................. 6E-251
DETONATION/SPARK KNOCK SYMPTOM 6E-254
POOR FUEL ECONOMY SYMPTOM .......... 6E-256
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS OR ODORS SYMPTOM ................................... 6E-258
DIESELING, RUN-ON SYMPTOM ............... 6E-261
BACKFIRE SYMPTOM ................................. 6E-262
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE PROCEDURE ....... 6E-264
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) .......... 6E-264
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR 6E-264
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR .................................................... 6E-265
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR 6E-265
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR .................................................... 6E-266
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) ...... 6E-266
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE .............. 6E-267
KNOCK SENSOR ......................................... 6E-268
POWER STEERING PRESSURE (PSP) SWITCH ..................................................... 6E-268
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S) ......... 6E-269
EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVE SOLENOID 6E-269
FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF .......................... 6E-270
FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY ............................... 6E-270
FUEL INJECTOR .......................................... 6E-271
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR ................ 6E-273
IGNITION COIL ............................................ 6E-275
SPARK PLUGS ............................................ 6E-275
SPARK PLUG CABLES ................................ 6E-277
EMISSION CONTROL ; *CO ADJUSTER (W/O
CATALYSTIC CONVERTER) .................. 6E-277
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS ......................... 6E-279
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2176 of 6020

6E–6 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ABBREVIATIONS CHARTS
AbbreviationsAppellation
A/C Air Conditioner
A/T Automatic Transmission
ACC Accessory
BLK Black
BLU Blue
BRN Brown
CEL Check Engine Lamp
CKP Crankshaft Position
DLC Data Link Connector
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code
DVM Digital Volt Meter
ECM Engine Control Module
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature
EEPROM Electrically Erasable & Programmable Read Only Memory
EVAP Evaporative Emission
EVRV Electric Vacuum Regulating Valve
EXH Exhaust
FT Fuel Temperature
GND Ground
GRY Gray
HOS2 Heated Oxygen Sensor
IAC Idel Air Control
IAT Intake Air Temperature
IG Ignition
ITP Intake Throttle Position
KS Knock Sensor
M/T Manual Transmission
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure
MIL Malfunction Indicator Lamp
OBD On-Board Diagnostic
ORN Orange
OT Oil Temperature
PNK Pink
RED Red
SW Switch
TB Throttle Body
TEMP Temperature
TP Throttle Position
VCC Voltage Constant Control
VSS Vehicle Speed Sensor
WHT White
YEL Yellow
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2178 of 6020

6E–8 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
1234
(1)
(2) Injector #1 Cylinder
Injector #2 Cylinder (3)
(4) Injector #3 Cylinder
Injector #4 Cylinder (Under the ECM)
(1) Ignition Coil Module Assembly
(1) Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2198 of 6020

6E–28 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CONNECTOR LIST
No.Connector face No.Connector face
B-24
Green Meter-B C-122
CO Adjuster
B-58
Black Check connector E-6
Fuel injector
B-62
White Ignition switch (IGSUB : G1) E-7
Fuel injector
B-63
White Ignition switch (IGSUB : G2) E-8
Fuel injector
B-68
Immobilizer E-9
Fuel injector
C-2
Silver Engine room-RH ground E-18
Ignition coil
C-56
ECM E-60
ECM
C-107
White J/B E2 E-72
Engine earth-A
C-108
White J/B E1 E-74
Engine earth-B
C-121
IAT sensor E-77
O
2 sensor
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2214 of 6020

6E–44 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Connector J2 Port: View Looking Into ECM Case
1
17 16
32
PIN32
PIN1
PIN17
PIN16
Pin
No. B/
Box No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
J2-1 J2-1 Intake Air Temp. (IAT) Sensor Ground GRN Continuity
with
ground -
- - Disconnect ΩJ2-1 GND
J2-2 J2-2 Battery Power Supply RED/ WHT10-14V
Connect DC V J2-2 GND
J2-3 J2-3 Ignition Power Supply BLU/ YELLess than
1V 10-14V
Connect DC V J2-3 GND
J2-4 J2-4 To Data Link Connector No. 6 BLU -
-- - -- - -
J2-5 J2-5 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-6 J2-6 Oxygen Sensor (Ground) PNK Continuity
with
ground -
- - Connect ΩJ2-6 GND
J2-7 J2-7 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-8 J2-8 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-9 J2-9 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-10 J2-10 CO Adjust Signal (W/O Catalystic
Converter) YEL -
-- - -- - -
J2-11 J2-11 Fuel Pump Relay GRN/ WHT10-14V
While relay
is activated; 10-14V
Relay is not
activated;
Less than 1V10-14V Connect DC V J2-11 GND
J2-12 J2-12 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-13 J2-13 A/C Compressor Relay GRY/
RED Less than
1V A/C comp. is operated: Less than 1V
A/C comp. is not operated: 10-14V Connect DC V J2-13 GND
J2-14 J2-14 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-15 J2-15 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-16 J2-16 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-17 J2-17 CO Adjust (W/O Catalystic Converter) RED -
-- - -- - -
J2-18 J2-18 Battery Power Supply RED/ WHT10-14V
Connect DC V J2-18 GND
J2-19 J2-19 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-20 J2-20 Power Steering Pressure Switch GRN/
YEL Less than
1V
Pressure switch is turned on: Less than 1VPressure switch is turned off: 10-14VConnect DC V J2-20 GND
J2-21 J2-21 Oxygen Sensor BLU Less than 1VApprox.
0.4V Wave form D or 0.1 -
0.9V Connect DC V J2-21 J2-6
J2-22 J2-22 Intake Air Temp. (IAT) Sensor (Signal) YEL/
GRN Less than
1V
20℃: Approx. 2.9V / 40 ℃: Approx. 1.8V V
/ 60 ℃: Approx. 1.1V / 80 ℃: Approx. 0.6VConnect DC V J2-22 33
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2216 of 6020
6E–46 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
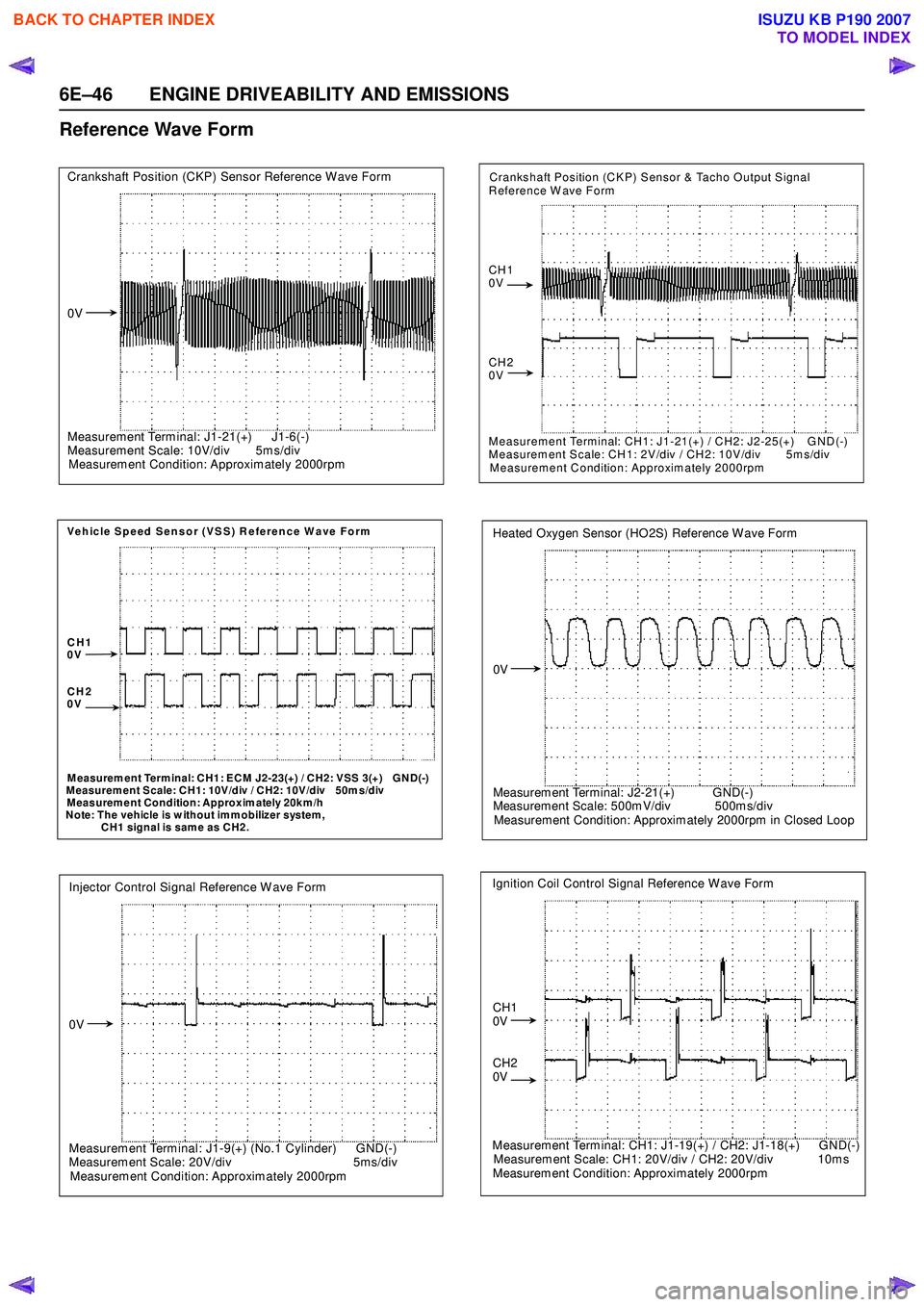
Reference Wave Form
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Reference W ave Form
0V
Measurem ent Term inal: J1-21(+) J1-6(-)
Measurem ent Scale: 10V/div 5m s/div
Measurem ent Condition: Approxim ately 2000rpm
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Reference Wave Form
CH1
0V
CH2
0V
M easurem ent Term inal: CH1: ECM J2-23(+) / CH2: VSS 3(+) GND(-)
M easurem ent Scale: CH1: 10V/div / CH2: 10V/div 50m s/div
Measurem ent Condition: Approxim ately 20km /h
Note: The vehicle is w ithout imm obilizer system,
CH1 signal is same as CH2.
Injector Control Signal Reference W ave Form
0V
Measurem ent Term inal: J1-9(+) (No.1 Cylinder) GND(-)
Measurement Scale: 20V/div 5ms/div
Measurem ent Condition: Approximately 2000rpm
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor & Tacho Output Signal
Reference W ave Form
CH1
0V
CH2
0V
Measurement Terminal: CH1: J1-21(+) / CH2: J2-25(+) GND(-)
Measurement Scale: CH1: 2V/div / CH2: 10V/div 5ms/div
Measurement Condition: Approximately 2000rpm
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Reference Wave Form
0V
Measurem ent Terminal: J2-21(+) GND(-)
Measurem ent Scale: 500m V/div 500m s/div
Measurement Condition: Approxim ately 2000rpm in Closed Loop
Ignition Coil Control Signal Reference Wave Form
CH1
0V
CH2
0V
Measurement Terminal: CH1: J1-19(+) / CH2: J1-18(+) GND(-)
Measurem ent Scale: CH1: 20V/div / CH2: 20V/div 10m s
Measurement Condition: Approximately 2000rpm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2218 of 6020
6E–48 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND
SENSORS
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located on the
intake manifold. The ECM controls the following.
• Fuel metering system
• Ignition timing
• On-board diagnostics for electrical functions.
The ECM constantly observes the information from vari-
ous sensors. The ECM controls the systems that affect
vehicle performance. And it performs the diagnostic
function of the system.
The function can recognize operational problems, and
warn to the driver through the check engine lamp, and
store diagnostic trouble code (DTC). DTCs identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in marking repairs.
The input / output devices in the ECM include analog to
digital converts, signal buffers, counters and drivers.
The ECM controls most components with electronic
switches which complete a ground circuit when turned
on.
Inputs (Operating condition read):
• Battery voltage
• Electrical ignition
• Exhaust oxygen content
• Intake manifold pressure
• Intake air temperature
• Engine coolant temperature
• Crankshaft position • Knock signal
• Throttle position
• Vehicle speed
• Power steering pressure
• Air conditioning request on or off
Outputs (Systems controlled):
• Ignition control
• Fuel control
• Idle air control
• Fuel pump
• EVAP canister purge
• Air conditioning
• Diagnostics functions
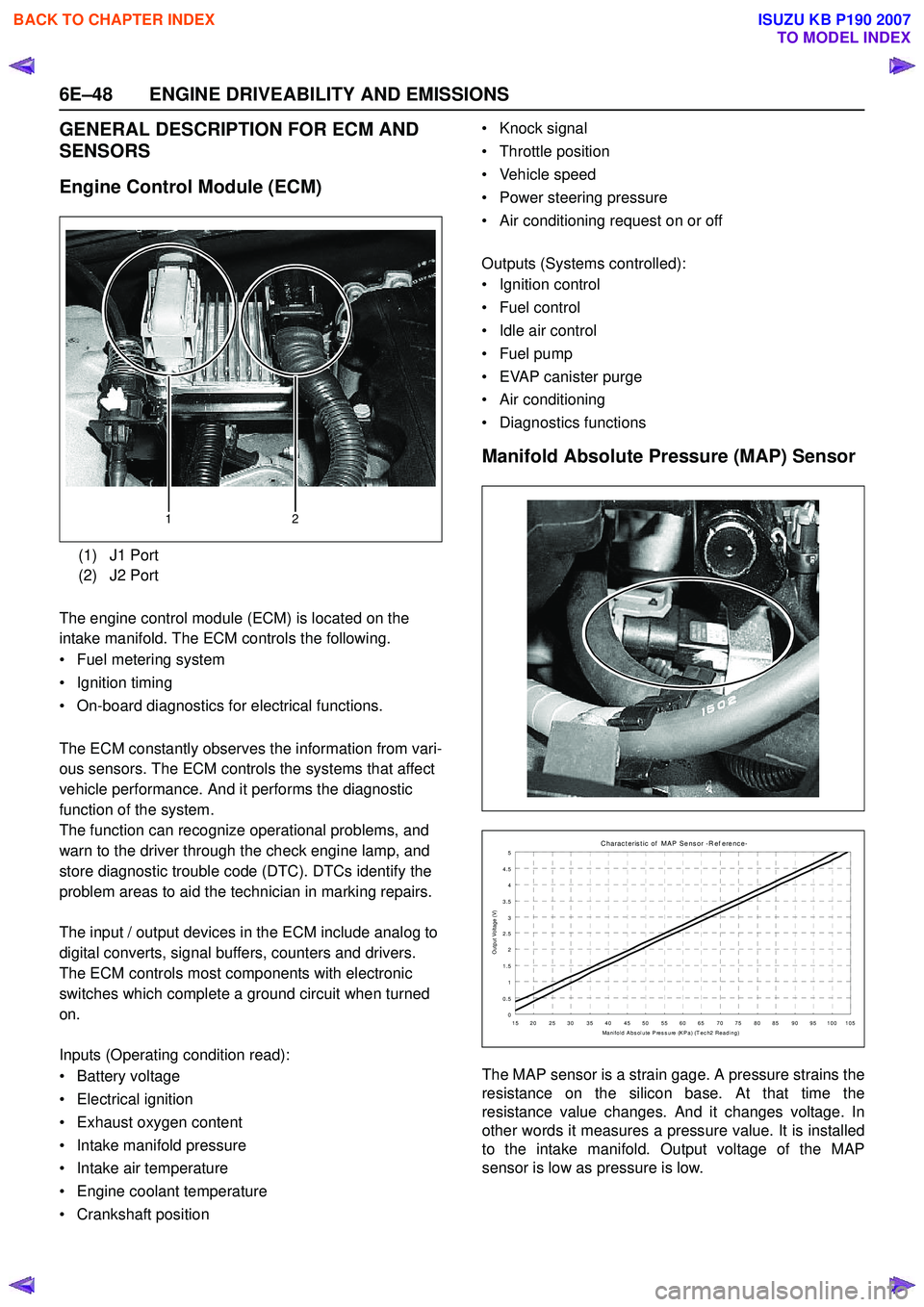
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The MAP sensor is a strain gage. A pressure strains the
resistance on the silicon base. At that time the
resistance value changes. And it changes voltage. In
other words it measures a pressure value. It is installed
to the intake manifold. Output voltage of the MAP
sensor is low as pressure is low.
(1) J1 Port
(2) J2 Port
12
C harac t eris t ic of MAP Sens or -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5 1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 Manifold Abs olute Press ure (KPa) (T ec h2 Reading)
Output Voltage (V)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2219 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–49
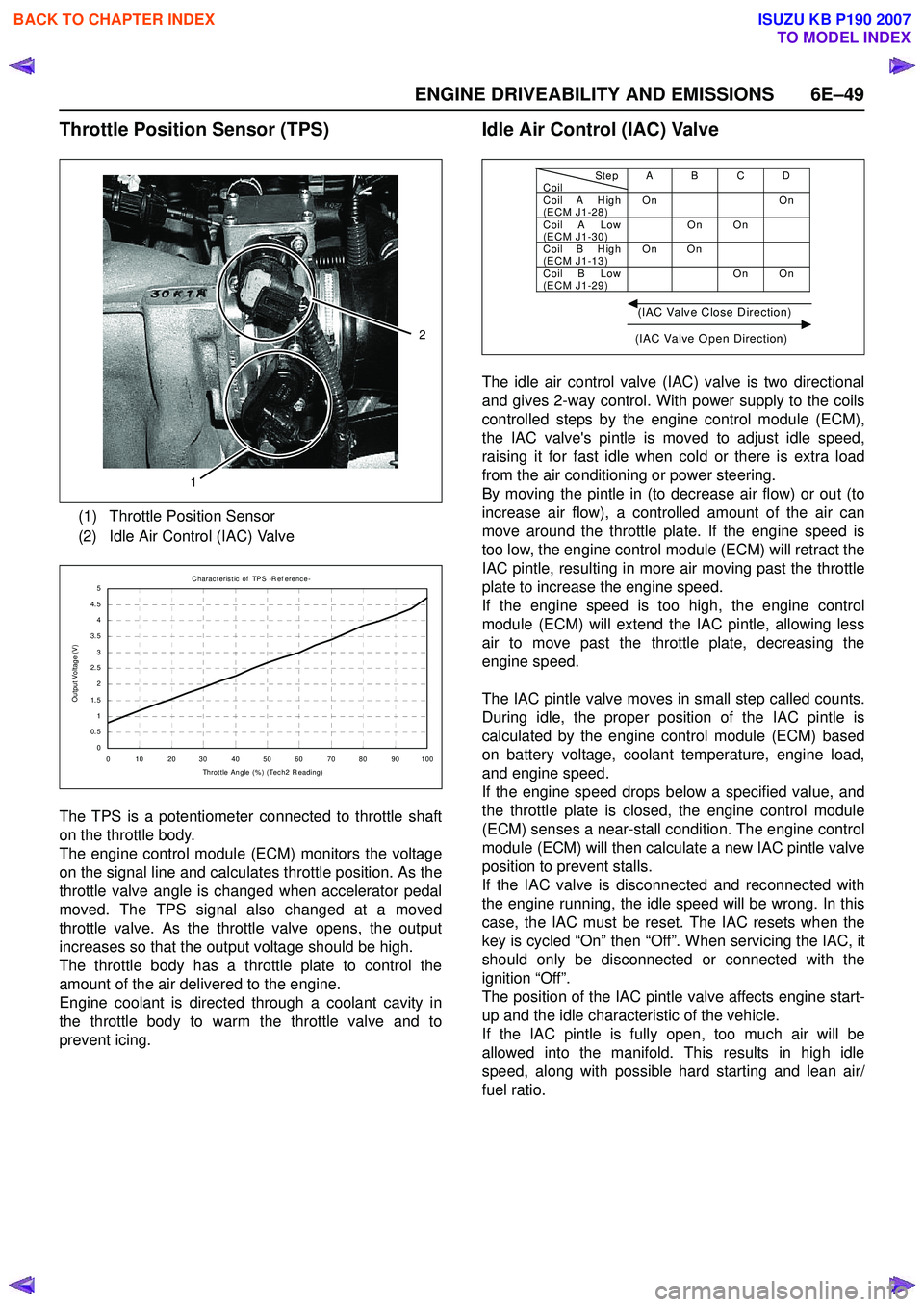
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is a potentiometer connected to throttle shaft
on the throttle body.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the voltage
on the signal line and calculates throttle position. As the
throttle valve angle is changed when accelerator pedal
moved. The TPS signal also changed at a moved
throttle valve. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that the output voltage should be high.
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of the air delivered to the engine.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The idle air control valve (IAC) valve is two directional
and gives 2-way control. With power supply to the coils
controlled steps by the engine control module (ECM),
the IAC valve's pintle is moved to adjust idle speed,
raising it for fast idle when cold or there is extra load
from the air conditioning or power steering.
By moving the pintle in (to decrease air flow) or out (to
increase air flow), a controlled amount of the air can
move around the throttle plate. If the engine speed is
too low, the engine control module (ECM) will retract the
IAC pintle, resulting in more air moving past the throttle
plate to increase the engine speed.
If the engine speed is too high, the engine control
module (ECM) will extend the IAC pintle, allowing less
air to move past the throttle plate, decreasing the
engine speed.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small step called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the engine control module (ECM) based
on battery voltage, coolant temperature, engine load,
and engine speed.
If the engine speed drops below a specified value, and
the throttle plate is closed, the engine control module
(ECM) senses a near-stall condition. The engine control
module (ECM) will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve
position to prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with
the engine running, the idle speed will be wrong. In this
case, the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the
key is cycled “On” then “Off”. When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “Off”.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-
up and the idle characteristic of the vehicle.
If the IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be
allowed into the manifold. This results in high idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and lean air/
fuel ratio.
(1) Throttle Position Sensor
(2) Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
1
2
C harac teris t ic of TPS -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5
1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
0 10 2030 405060 7080 90100 Throt t le Angle (% ) (Tec h2 R eading)
Output Voltage (V)
StepCoilAB CDCoil A H igh
(ECM J1-28) On On
Coil A Low
(ECM J1-30) On On
Coil B H igh
(ECM J1-13) On On
Coil B Low
(ECM J1-29) On On
(IAC Valve Close Direction)
(IAC Valve Open Direction)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2220 of 6020
6E–50 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
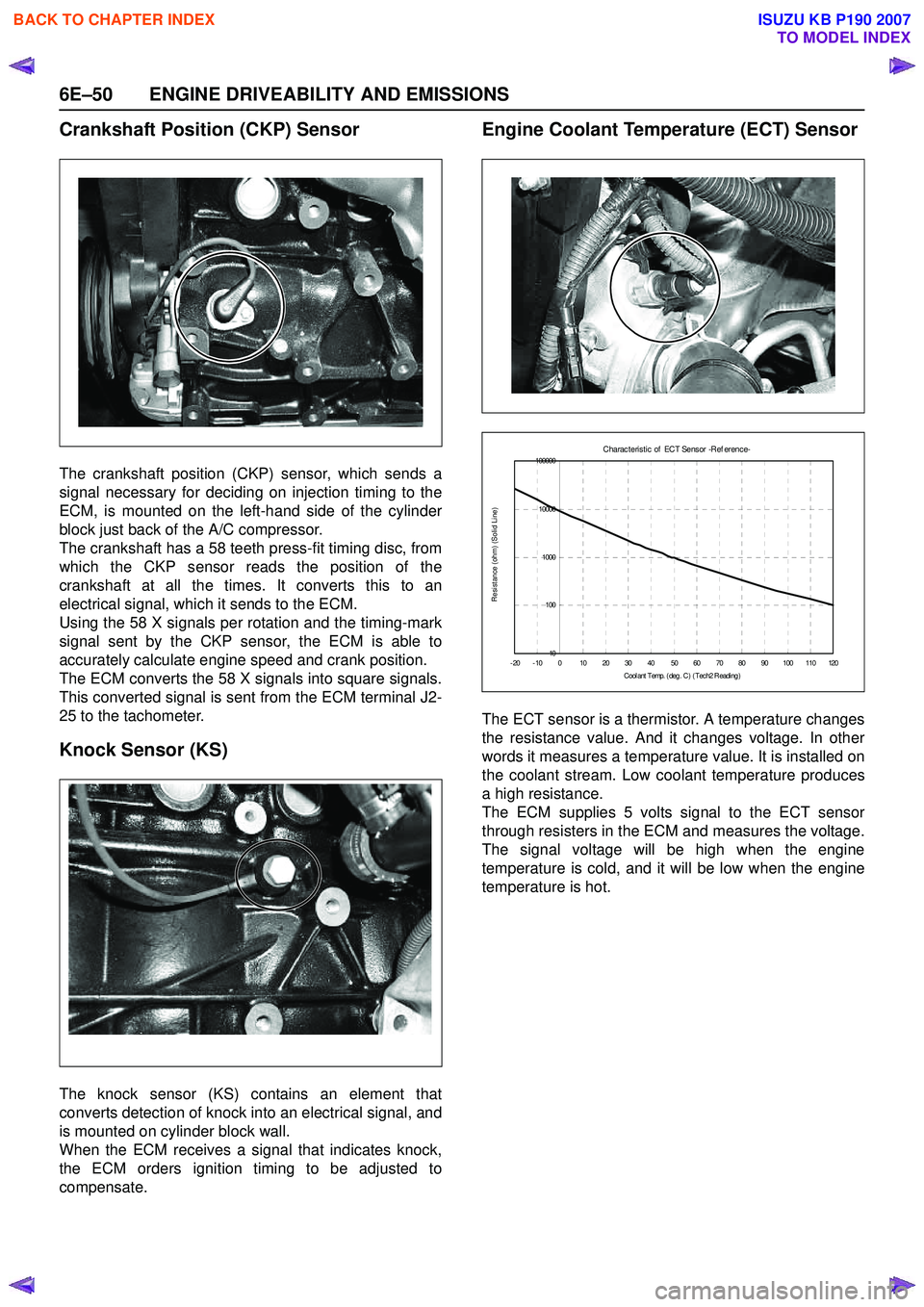
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor, which sends a
signal necessary for deciding on injection timing to the
ECM, is mounted on the left-hand side of the cylinder
block just back of the A/C compressor.
The crankshaft has a 58 teeth press-fit timing disc, from
which the CKP sensor reads the position of the
crankshaft at all the times. It converts this to an
electrical signal, which it sends to the ECM.
Using the 58 X signals per rotation and the timing-mark
signal sent by the CKP sensor, the ECM is able to
accurately calculate engine speed and crank position.
The ECM converts the 58 X signals into square signals.
This converted signal is sent from the ECM terminal J2-
25 to the tachometer.
Knock Sensor (KS)
The knock sensor (KS) contains an element that
converts detection of knock into an electrical signal, and
is mounted on cylinder block wall.
When the ECM receives a signal that indicates knock,
the ECM orders ignition timing to be adjusted to
compensate.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The ECT sensor is a thermistor. A temperature changes
the resistance value. And it changes voltage. In other
words it measures a temperature value. It is installed on
the coolant stream. Low coolant temperature produces
a high resistance.
The ECM supplies 5 volts signal to the ECT sensor
through resisters in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the engine
temperature is cold, and it will be low when the engine
temperature is hot.
C harac t eris t ic of ECT Sens or -R ef erenc e-
10
100
1000
10000
100000
-20-100 10203040 5060708090100110120 C ool ant T emp. ( deg . C ) ( Tec h2 R eadi ng )
Resistance (ohm) (Solid Line)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007