Interior JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2628 of 3039

Supplemental Restraint System - B-Pillar Side Impact Sensor
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details. Published: 11-May-2011
1. Make the air bag supplemental restraint system (SRS) safe.
Refer to: Standard Workshop Practices (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
2. WARNING: To avoid accidental deployment and possible personal injury,
the backup power supply must be depleted before repairing or replacing
any air bag supplementary restraints system (SRS) components. To
deplete the backup power supply energy, disconnect the battery ground
cable and wait for one minute. Failure to follow this instruction may
result in personal injury.
Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
3. Refer to: B-Pillar Lower Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
Installation
4. Torque: 12 Nm
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. If a new component has been installed, configure using Jaguar approved
diagnostic equipment.
Page 2653 of 3039

Supplemental Restraint System - Passenger Air Bag Module
Removal and Installation Published: 11-May-2011
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
2. Refer to: Steering Wheel (211-04 Steering Column, Removal and Installation).
3. Refer to: Driver Side Register (412-01 Climate Control, Removal and Installation).
4. Refer to: Information and Entertainment Display (415-01A Information and Entertainment System, Removal and Installation).
5. Refer to: Instrument Panel Speaker (415-01A Information and Entertainment System, Removal and Installation).
6. Refer to: A-Pillar Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
7. Refer to: Audio and Climate Control Assembly (415-01A Information and Entertainment System, Removal and Installation). 211-326
Locking Tool, Clockspring Special Tool(s)
Page 2673 of 3039

Supplemental Restraint System - Side Air Curtain Module
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
All vehicles Published: 19-May-2011
1. Make the air bag supplemental restraint system (SRS) safe.
Refer to: Standard Workshop Practices (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
2. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
3. Refer to: Interior Rear View Mirror (501-09 Rear View Mirrors, Removal and Installation).
4. Refer to: Overhead Console (501-12 Instrument Panel and Console, Removal and Installation).
5. Refer to: Sun Visor (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
6. Refer to: A-Pillar Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
7. Refer to: B-Pillar Upper Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
8. Refer to: C-Pillar Lower Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
9. Torque: 2 Nm
Page 2710 of 3039
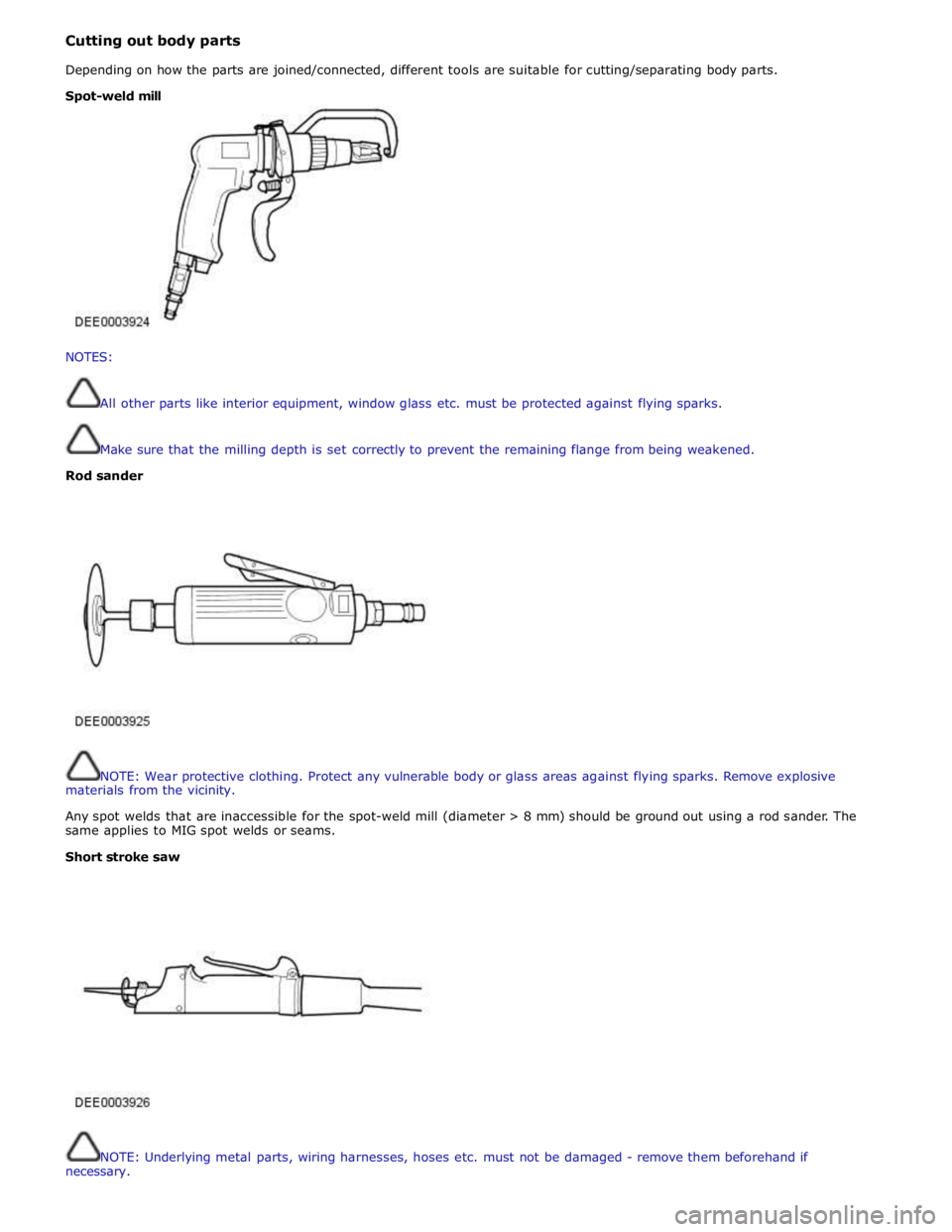
Cutting out body parts
Depending on how the parts are joined/connected, different tools are suitable for cutting/separating body parts.
NOTES:
All other parts like interior equipment, window glass etc. must be protected against flying sparks.
Make sure that the milling depth is set correctly to prevent the remaining flange from being weakened.
Rod sander
NOTE: Wear protective clothing. Protect any vulnerable body or glass areas against flying sparks. Remove explosive
materials from the vicinity.
Any spot welds that are inaccessible for the spot-weld mill (diameter > 8 mm) should be ground out using a rod sander. The
same applies to MIG spot welds or seams.
Short stroke saw
NOTE: Underlying metal parts, wiring harnesses, hoses etc. must not be damaged - remove them beforehand if
necessary. Spot-weld mill
Page 2718 of 3039

Part N-umber
Body Repairs - Corrosion Protection - Corrosion Protection
Description and Operation
General Published: 11-May-2011
The corrosion protection provided in production must be carefully maintained and/or reproduced during and after body repair
work. It is only then that the long-term warranty against penetrative corrosion damage can be assured.
Only Jaguar original bodywork components and Jaguar approved repair materials, (sealer, paint etc.), are to be used for
bodywork repairs.
Jaguar Original Parts
All Jaguar bodywork components have a cathodic base coating. Individual bodywork components are zinc plated on one or both
sides, (in different areas depending on vehicle model).
Together with elastic paint coating, this guarantees an optimum, highly resistant protection against corrosion caused by the
impact of small objects such as gravel.
NOTE: If possible, the individual protective layers, (zinc, cathodic base coat), on Jaguar bodywork components must not
be damaged or destroyed by sanding or other mechanical operations.
If hairline cracks at "bodywork connection areas" appear after reshaping work, (e.g. at door hinges), it must be ensured that
the corrosion protection provided in production is recreated. The complete paint covering must be re-created if necessary. The
same applies to reshaping work on heavily profiled bodywork components, (e.g. floor pan). Renew or touch-up the paint
coating, sealing beads and underbody protection as necessary.
After repair, any interior surfaces which are no longer visible or accessible must be primed before cavity wax is applied. To be
certain of an even coating on inner surfaces, careful application of spray, (twice, with drying time in-between), must be carried
out throughout the whole cavity.
If bodywork panels are strongly heated during repair work, this will invariably result in damage to or even destruction of the
applied corrosion protection material. The effectiveness of the cavity protection material is reduced if heating occurs.
Reworking of the affected areas is therefore vital.
Welded areas should be made good before corrosion protection is applied.
The corrosion protection measures to be taken when bodywork components are renewed are described on the following pages.
Corrosion Protection of New Components
All new components must be inspected for transport or storage damage such as scratches or dents. The following operations
may be necessary, depending on the extent of damage:
Undamaged New Component
Do not grind the cathodic primer.
Thoroughly clean with silicone remover and rub dry.
Slightly Damaged New Component
Sand out scratches.
Finely sand the surrounding surface.
Thoroughly clean with silicone remover and rub dry.
Apply corrosion protection primer to bare areas.
Damaged New Components (bumps and dents)
Beat out the dented area and sand down to bare metal.
Page 2731 of 3039

Seam Sealer
A heat cured, PVC based sealant is applied to specific joint seams during factory assembly. This material is not suitable for
service use and during repair and should be substituted by an approved seam sealer.
NOTE: Where seams are inaccessible following the reassembly or fitting of components, ensure that a paste-type seam
sealer is applied to such seams. Certain seams also become inaccessible after the completion of panel repairs. In such
instances apply seam sealer and paint before final assembly.
Apply seam sealers after the application of primer and before the application of top coat. The sealer must form a continuous
bead, with the profile of the bead dependent on the type of seam. If the seam sealer is applied with a brush take particular
care to maintain the required coverage of the seam.
Ensure that all accessible repair seams are sealed following a repair. Damage to a vehicle often flexes areas of the body
remote from the impact. As a result the seam sealer in these areas may be disturbed by subsequent straightening and repair
operations. Check all seams in the vicinity of the area undergoing repair for evidence of cracked seam sealer, then clean out as
required and apply fresh seam sealer using the following procedure:
Clean the affected seam and re-treat any exposed metal areas with a suitable etch phosphate primer.
Treat affected area with an etch-acid primer.
Apply appropriate seam sealer as necessary.
apply appropriate colour coat (and under body sealer as applicable).
Provided access is adequate, apply seam sealer to both sides of a repair joint. Where access is limited to one side only, (e.g.
box section), treat the affected box member with cavity wax.
Cavity Wax
After repairs, always re-treat these areas with an approved cavity wax. In addition, treat all interior surfaces which have been
disturbed during repairs whether they have been treated in production or not. This includes all box members, cavities and door
interiors.
Before wax injection, ensure that the cavity to be treated is free from any contamination or foreign matter. Where necessary,
clear out any debris.
Ensure that cavity wax is applied after the final paint process and before refitting any trim components.
During application ensure that the wax covers all flanges and seam areas and that it is adequately applied to all repaired
areas of both new and existing panels.
It should be noted that new panel assemblies and complete body shells are supplied without wax injection treatment. Ensure
that such treatment is carried out after repairs.
Effective cavity wax protection is vital. Always observe the following points:
Complete all paint refinish operations before wax application.
Check the spray pattern of injection equipment.
Mask all areas not to be waxed.
Remove body fixings, such as seat belt retractors, if contamination is at all likely.
Move door glasses to fully closed position before treating door interiors.
Treat body areas normally covered by trim before refitting items.
Check that body and door drain holes are clear after the protective wax has dried.
Keep all equipment clean, especially wax injection nozzles.
Page 2732 of 3039

Part N-umber
Body Repairs - Water Leaks - Water Leaks
Description and Operation
General Published: 11-May-2011
If water leaks occur after bodywork repairs, the cause can be established using the checks described below. A
systematic and logical procedure is required to locate water leaks. Before beginning extensive checks, a thorough visual
inspection must be carried out.
Visual Inspection
- The following characteristics may indicate existing leaks:
- Check the clearance and accurate fit of ancillary components such as the hood, tailgate, liftgate, doors, and so
on.
- Check for correct fit and possible damage to sealing elements such as blanking plugs, rubber door seals, and so
on.
- Check water drain holes for unhindered flow.
Various tests can be used to provide further information on possible leaks:
- Water test
- Washer test
- Road test
- Chalk (powder) test
Practical execution of tests and checks
Water test
NOTE: Never aim a jet of water directly at a rubber seal.
Carry out the water test with a second person present (in the passenger compartment).
Use variable washer nozzles (concentrated water jet to fine spray mist).
Start in the lower section and spray the whole area, working upwards in stages.
Washer test
Further tests can be carried out in the washer system.
Some leaks originate here, or only occur here.
The relevant passenger compartment should be checked using a torch during the wash procedure.
Road test
If no leaks are located during the tests above, road tests should be carried out on wet roads.
Road tests under various conditions:
- At various speeds.
- On various road surfaces (asphalt to cobbles).
- With loaded or unloaded vehicle.
- Driving through puddles (splash water).
Chalk test (powder test)
In this test, the clamping load and the bearing surface of the seal are checked.
Performing the test:
- Dust the door seal with powder or coat with chalk.
- Coat the bearing surface of the seal with a thin film of Vaseline.
- Slowly close the door and open it again.
- Check the width and continuity of the imprint on the door seal.
Other test equipment
Other equipment such as stethoscopes, UV lamps, special mirrors or ultrasound measuring instruments can be used to
locate leaks.
Rectifying the leak using recommended tools, auxiliary equipment and materials
Tools and auxiliary equipment:
- Dry, absorbent cloths
- Variable washer nozzle
- Torch, fluorescent tube
- Mirror
- Compressed air
- Seal lip installer
- Wet/dry vacuum cleaner
- Sealing compound compressor
- Remover for interior trim
- Cutter blade or pocket knife
- Wedge (wood or plastic)
- Hot air blower
- Special mirror for concealed leaks
Page 2735 of 3039

Side windows
In the case of side windows, the same problems can arise as for a windscreen. The same corrective actions must therefore be
used.
Door seal
Diagnosis:
- Water ingress in the lower part of the interior door trim or in the rocker panel area.
Cause:
- The water shield fitted behind the interior door trim exists to drain off water that has entered the door via the
drainage holes, either downwards or outwards. If the water shield seal is damaged or has been fitted incorrectly,
then water can get into the passenger compartment.
- In addition to this, the drainage holes can become clogged with leaves, dirt or excess cavity protection agents.
Water gathers in the door and ingresses into the passenger compartment.
- Check water shield for damage or correct fitting.
- If the water shield needs to be re-bonded, then approved seam sealer should be used.
- Before the water shield is installed, the drainage holes must be checked for unhindered flow.
Door seals
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water into the rocker panel area
Cause:
- Insufficient clamping load between seal and door.
Corrective action:
NOTE: When adjusting the clamping load, the profile alignment of the relevant components must always be taken
into consideration.
NOTE: Do not realign the flange too far in the direction of the door, as this can reduce the bearing surface of the
seal to the door.
- Check clamping load:
- The easiest way to check the clamping load of a seal to the respective bearing surface is by means of a paper
strip test. This consists of trapping strips of paper at various points between the door and the seal, and fully
closing the door. If it is possible to pull out the paper with no great resistance, then the clamping load is too
low.
- Adjust the clamping load:
- The clamping load is normally adjusted using the striker. When doing so, the edge alignment from the door to
the side panel, or from the front door to the rear door must be taken into account.
- Another setting method is to realign the panel flange for the seal mounting. The clamping load is increased by
moving the flange towards the door.
- Check the bearing surface:
- Apply chalk evenly to the surface of the seal. Evenly coat the bearing surface of the door with Vaseline.
- Close the door fully, the lock must engage. Open the door. The imprint of the chalk (bearing surface) can be
identified in the film of Vaseline.
- The bearing surface should be at least 5mm across at all points.
Other causes:
- The door seal must completely seal the door where it meets the bodywork.
- Water can ingress directly or indirectly into the interior of the vehicle if the seal is damaged at any point.
Corrective action:
- A damaged or worn door seal must always be renewed in full.
- When renewing the seal, the following must be taken into account:
- Always fit the seal first in the area of the narrow radii (corner points).
- Next, secure the seal to the flange evenly by tapping lightly with a rubber hammer. The installed seal must not
be kinked at any point.
NOTE: The prescribed length of a seal must not be shortened.
Other cause:
- The door seal is attached to the welded flange all the way round. If this welded flange is uneven or damaged at
any point (usually in areas with small radii) then this point could be subject to leaks.
- A stretched seal carrier can also cause a leak.
- In both cases, water gets into the vehicle interior under the seal carrier.
Corrective action:
- Align the deformed welded flange using a hammer and anvil block, prevent and, if necessary, repair any paint
damage.
Sliding roof/tilting roof
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water at sliding roof aperture
Cause:
- The sliding roof/tilting roof is installed in a water trap. The water drains off via the water trap, water drain holes
and drain hoses. The drain hoses lead downwards on both sides via the A-pillar and B-pillar.
- The drain holes or drain hoses can become clogged with leaves, dirt, underbody protection and so on.
Corrective action:
Page 2736 of 3039

NOTE: In the case of a sliding or tilting roof, the external rubber seal and the lock actuator or latch mechanism
must be checked first of all.
- Check the water trap for leaks.
- Check the drain hoses for leaks and for correct connection to the water trap.
- Check the drainage system for unhindered flow, and blow out with compressed air if necessary.
- Check the external seal and the correct adjustment of the sliding roof.
Liftgate
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water into rear headlining area and luggage area.
Cause:
- The leak problems of the tailgate and liftgate correspond to those of the doors.
- In addition to this, the area to be sealed is much bigger. The routing holes for cables and hoses must also be
sealed.
- The rubber grommets for the routing holes must be checked for damage and correct seating (fully unhooked).
- The mounting points of the liftgate hinges may leak.
Corrective action:
- Check the rubber grommets and renew if necessary.
- Check the hinge mounting points, and re-seal with sealing compound if necessary.
Forced air extraction
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water into side luggage compartment area
Cause:
- The forced air extraction for the vehicle interior is located in the quarter panel lower extension.
- The rubber flap of the forced air extraction must be able to move freely.
Corrective action:
- Remove the forced air extraction.
- Check the seal area between the bodywork and housing, as well as the rubber flap.
- Renew seal if necessary.
Rear window
Diagnosis:
- Ingress of water into the luggage compartment area
Cause:
- Rear window leaking.
- Check for leak in the same way as for leaking windscreen.
Page 2829 of 3039

(414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
6. Disconnect the generator electrical connectors.
7. Remove the windshield glass.
For additional information, refer to: Windshield Glass (501-11 Glass, Frames and Mechanisms, Removal and Installation).
8. Remove the rear window glass.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Window Glass (501-11 Glass, Frames and Mechanisms, Removal and Installation).
9. Remove the roof opening panel frame.
For additional information, refer to: Roof Opening Panel Frame (501-17 Roof Opening Panel, Removal and Installation).
10. Remove the driver and passenger side front scuff plate trim panels.
For additional information, refer to: Front Scuff Plate Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
11. Remove the driver and passenger side rear scuff plate trim panels.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Scuff Plate Trim Panel (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
12. Remove the driver and passenger side air curtain modules.
For additional information, refer to: Side Air Curtain Module (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation).
13. Remove the rear seat backrest.
14. Remove the driver and passenger side rear safety belt retractors.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Safety Belt Retractor (501-20A Safety Belt System, Removal and Installation).
15. Remove the rear center safety belt retractor.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Center Safety Belt Retractor (501-20A Safety Belt System, Removal and Installation).
16. Remove the driver and passenger side RF filters.
17. Remove the diversity antenna module.
18. Remove the antenna.
For additional information, refer to: Navigation System Antenna (419-07 Navigation System, Removal and Installation).
19. Release and position the roof wiring harnesses to one side
20. Position the roof opening panel front and rear drain hoses to one side.
21. Remove the driver and passenger side roof mouldings.
22. Drill out the spot welds.
www.JagDocs.com