Can bus JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 53 of 3039

Bus Topology of a
communication
network Coast Clutch Solenoid CCS Camshaft Position CMP Indicates camshaft position Carbon dioxide CO² Colorless gas with a density of approximately 1.5 times that of air Carbon monoxide CO Poisonous gas produced as the result of incomplete combustion Chlorofluorocarbon CFC Catalytic converter
In-line exhaust system device used to reduce the level of engine exhaust
emissions Celsius C
SI term for the Centigrade scale, with freezing point at zero and boiling point at 100 degrees Compact Disc CD Cylinder Head Temperature
Sensor CHT Sensor A sensor for measuring the temperature of the cylinder head Central Junction Box CJB Crankshaft Position CKP Indicates crankshaft position Clutch Pedal Position CPP Indicates clutch pedal position Controller Area Network CAN
A communication system which allows control modules to be linked together Constant Velocity CV Cubic centimeter cm³ Central Security Module CSM Electronic module to support security system functionality Data Link Connector DLC
Connector providing access and/or control of the vehicle information, operating conditions, and diagnostic information Driver Door Module DDM Electronic module to support driver door functionality Driver Seat Module DSM Electronic module to support driver seat functionality Daytime Running Lamps DRL Deutsche Institut fur Normung DIN German standards regulation body Diagnostic Trouble Code DTC
An alpha/numeric identifier for a fault condition identified by the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system Direct current dc
Current which flows in one direction only, though it may have appreciable pulsations in its magnitude Domestic Data Bus D2B Digital Versatile Disc DVD Electronic Automatic Temperature Control EATC
Exhaust Gas Recirculation EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation Temperature Sensor EGRT Sensing EGR function based on temperature change Electronic Brake Force
Distribution EBD
Engine Control Module ECM Electronic module to support engine functionality Electronic Crash Sensor ECS Sensor to measure severity of impact Engine Coolant Temperature ECT Engine Oil Pressure EOP European On-Board Diagnostic EOBD Electronic Pressure Control EPC Electrically Erasable
Programmable Read-Only Memory EEPROM
Erasable Programmable
Read-Only Memory EPROM
Evaporative Emission EVAP
System designed to prevent fuel vapor from escaping into the atmosphere. Typically includes a charcoal filled canister to absorb fuel vapor Flash Electrically Erasable
Programmable Read-Only Memory FEEPROM
Front Electronic Module FEM Flash Erasable Programmable
Read-Only Memory FEPROM
Frequency Modulation FM Fuel Pump Driver Module FPDM Fuel Rail Pressure FRP Generic Electronic Module GEM Ground GND
Electrical conductor used as a common return for an electrical circuit or
circuits, and with a relative zero potential Global Positioning System GPS Global System for Mobile
Communication GSM
Gross Vehicle Weight GVW Heated Oxygen Sensor HO2S Electrically heated oxygen sensor which induces fuelling corrections
Page 60 of 3039

Have a suitable fire extinguisher available when using welding or heating equipment.
First Aid
Apart from meeting any legal requirements it is desirable for someone in the workshop to be trained in First Aid procedures.
Splashes in the eye should be flushed carefully with clean water for at least ten minutes.
Soiled skin should be washed with soap and water.
Individuals affected by inhalation of gases, fumes etc. should be removed to fresh air immediately. If effects persist, consult a
doctor.
If liquids are swallowed inadvertently, consult a doctor giving the information on the container or label. Do not induce vomiting
unless this action is indicated on the label.
Fluoroelastomer
See Viton.
Foams - Polyurethane
See also Fire.
Used in sound and noise insulation. Cured foams used in seat and trim cushioning.
Follow manufacturer's instructions.
Unreacted components are irritating and may be harmful to the skin and eyes. Wear gloves and goggles.
Individuals with chronic respiratory diseases, asthma, bronchial medical problems, or histories of allergic diseases should not
work in or near uncured materials.
The components, vapors or spray mists can cause direct irritation, sensitivity reactions and may be toxic or harmful.
Vapors and spray mists must not be inhaled. These materials must be applied with adequate ventilation and respiratory
protection. Do not remove the respirator immediately after spraying, wait until the vapor/mists have cleared.
Burning of the uncured components and the cured foams can generate toxic and harmful fumes. Smoking, naked flames or the
use of electrical equipment during foaming operations and until vapors/mists have cleared should not be allowed. Any heat
cutting of cured foams or partially cured foams should be conducted with extraction ventilation.
Freon
See Air Conditioning Refrigerant.
Fuels
See also, Fire, Legal Aspects, Chemicals and Solvents.
Avoid skin contact with fuel where possible. Should contact occur, wash the affected skin with soap and water.
Gasoline (Petrol)
Highly flammable - observe No Smoking policy.
Swallowing can result in mouth and throat irritation and absorption from the stomach can result in drowsiness and
unconsciousness. Small amounts can be fatal to children. Aspiration of liquid into the lungs e.g. through vomiting, is a very
serious hazard.
Gasoline dries the skin and can cause irritation and dermatitis on prolonged or repeated contact. Liquid in the eye causes
severe pain.
Motor gasoline may contain appreciable quantities of benzene, which is toxic upon inhalation, and the concentration of
gasoline vapors must be kept very low. High concentrations will cause eye, nose and throat irritation, nausea, headache,
depression and symptoms of drunkenness. Very high concentrations will result in rapid loss of consciousness.
Ensure there is adequate ventilation when handling and using gasoline. Great care must be taken to avoid the serious
consequences of inhalation in the event of vapor build up arising from spillages in confined spaces.
Special precautions apply to cleaning and maintenance operations on gasoline storage tanks.
Gasoline should not be used as a cleaning agent. It must not be siphoned by mouth. See First Aid.
Gas - oil (Diesel Fuel)
See warnings and cautions in relevant manual sections.
Combustible.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 64 of 3039

Viton
In common with many other manufacturers' vehicles, some components installed to the Jaguar range have 'O' rings, seals or
gaskets which contain a material known as 'Viton'.
Viton is a fluoroelastomer, that is a synthetic rubber type which contains Fluorine. It is commonly used for 'O' rings, gaskets
and seals of all types. Although Viton is the most well known fluoroelastomer, there are others, including Fluorel and
Tecmoflon.
When used under design conditions fluoroelastomers are perfectly safe. If, however, they are exposed to temperatures in
excess of 400º C, the material will not burn, but will decompose, and one of the products formed is hydrofluoric acid.
This acid is extremely corrosive and may be absorbed directly, through contact, into the body.
'O' rings, seals or gaskets which have been exposed to very high temperatures will appear charred or as a black sticky
substance.
DO NOT, under any circumstances touch them or the attached components.
Enquiries should be made to determine whether Viton or any other fluoroelastomer has been used in the affected 'O' ring, seal
or gasket. If they are of natural rubber or nitrile there is no hazard. If in doubt, be cautious and assume that the material may
be Viton or any fluoroelastomer.
If Viton or any other fluoroelastomers have been used, the affected area should be decontaminated before the commencement
of work.
Disposable heavy duty plastic gloves should be worn at all times, and the affected area washed down using wire wool and a
limewater (calcium hydroxide) solution to neutralize the acid before disposing of the decomposed Viton residue and final
cleaning of the area. After use, the plastic gloves should be discarded carefully and safely.
Welding
See also Fire, Electric Shock, Gas Cylinders.
Welding processes include Resistance Welding (Spot Welding), Arc Welding and Gas Welding (and cutting).
Resistance Welding (Spot Welding)
This process may cause particles of molten metal to be emitted at a high velocity, and the eyes and skin must be protected.
Arc Welding
This process emits a high level of ultraviolet radiation which may cause arc-eye and skin burns to the operator and to other
persons nearby. Gas-shielded welding processes are particularly hazardous in this respect. Personal protection must be worn,
and screens used to shield other people.
CONTACT LENS WEARERS ARE ADVISED TO REVERT TO ORDINARY SPECTACLES WHEN ARC WELDING as the arc spectrum is
believed to emit microwaves which dry out the fluid between the lens and the eye. This may result in blindness when the lens
is removed from the eye.
Metal spatter will also occur, and appropriate eye and skin protection is necessary.
The heat of the welding arc will produce fumes and gases from the metals being welded, the rods and from any applied
coatings or contamination on the surfaces being worked on. These gases and fumes may be toxic and inhalation of these
should be avoided. The use of extraction ventilation to remove the fumes from the working area may be necessary particularly
in cases where the general ventilation is poor, or where considerable welding work is anticipated. In extreme cases or confined
spaces where adequate ventilation cannot be provided, air-fed respirators may be necessary.
Gas Welding (and Cutting)
Oxy-acetylene torches may be used for welding and cutting, and special care must be taken to prevent leakage of these gases,
with consequent risk of fire and explosion.
The process will produce metal spatter and eye and skin protection is necessary.
The flame is bright, and eye protection should be used, but the ultraviolet emission is much less than that from arc welding,
and lighter filters may be used.
The process itself produces few toxic fumes, but such fumes and gases may be produced from coatings on the work,
particularly during cutting away of damaged body parts, and inhalation of the fumes should be avoided.
In brazing, toxic fumes may be produced from the metals in the brazing rod, and a severe hazard may arise if brazing rods
containing cadmium are used. In this event particular care must be taken to avoid inhalation of fumes and expert advice may
be required.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS MUST BE TAKEN BEFORE ANY WELDING OR CUTTING TAKES PLACE ON VESSELS WHICH HAVE
CONTAINED COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS, E.G. BOILING OR STEAMING OUT OF FUEL TANKS.
Warning Symbols on Vehicles
Decals showing warning symbols will be found on various vehicle components.
Page 71 of 3039
General Information - Solvents, Sealants and Adhesives
Description and Operation Published: 11-May-2011
WARNING: Always handle all solvents, sealers and adhesives with extreme care. Some contain chemicals or give off
fumes which can be dangerous to health. Always follow the manufacturers instructions. If in doubt about any substance,
particularly a solvent, DO NOT use it.
CAUTION: If in doubt about the suitability of any proprietary solvent or sealer for a particular application, contact the
manufacturer of the product for information regarding storage, handling and application.
The Solvents, Sealers and Adhesives subsection refers to some commonly used chemicals and materials, hazards associated
with their use, and safety measures to be taken.
Adhesives and Sealers
Highly flammable, flammable, combustible – observe No Smoking policy.
Generally should be stored in No Smoking' areas. Cleanliness and tidiness in use should be observed e.g. disposable paper
covering benches; should be dispensed from applicators where possible; containers, including secondary containers, should be
labelled appropriately.
Solvent - based Adhesives/Sealers - See Solvents
Follow manufacturer's instructions.
Water - based Adhesives/Sealers
Those based on polymer emulsions and rubber latexes may contain small amounts of volatile toxic and harmful chemicals. Skin
and eye contact should be avoided and adequate ventilation provided during use.
Hot Melt Adhesives
In the solid state, they are safe. In the molten state they may cause burns and health hazards may arise from the inhalation
of toxic fumes.
Use appropriate protective clothing and a thermostatically controlled heater with a thermal cut - out and adequate extraction.
Resin - based Adhesives/Sealers e.g. Epoxide and Formaldehyde Resin - based
Mixing should be carried out in well ventilated areas, as harmful or toxic volatile chemicals may be released.
Skin contact with uncured resins and hardeners can result in irritation, dermatitis, and absorption of toxic or harmful chemicals
through the skin. Splashes can damage the eyes.
Provide adequate ventilation and avoid skin and eye contact.
Anaerobic, Cyanoacrylate (Super - glues) and other Acrylic Adhesives Many are irritant, sensitizing or harmful to the skin and/or respiratory tract. Some are eye irritants.
Skin and eye contact should be avoided and the manufacturer's instructions followed.
Cyanoacrylate adhesives (super-glues) MUST NOT contact the skin or eyes. If skin or eye tissue is bonded, cover with a clean
moist pad and seek immediate medical attention. Do not attempt to pull tissue apart. Use in well ventilated areas as vapors
can cause irritation to the nose and eyes.
For two - pack systems see Resin - based and Isocyanate Adhesives/Sealers.
Isocyanate (Polyurethane) Adhesives/Sealers
See also Resin - based Adhesives
Individuals suffering from asthma or respiratory allergies should not work with or near these materials as sensitivity reactions
can occur.
Over exposure is irritating to the eyes and respiratory system. Excessive concentrations may produce effects on the nervous
system including drowsiness. In extreme cases, loss of consciousness may result. Long term exposure to vapor concentrations
may result in adverse health effects.
Prolonged contact with the skin may lead to skin irritation and, in some cases, dermatitis.
Splashes entering the eye will cause discomfort and possible damage.
Any spraying should preferably be carried out in exhaust ventilated booths removing vapors and spray droplets from the
breathing zone.
Wear appropriate gloves, eye and respiratory protection.
Page 100 of 3039
11
Cutting of fingers or hand 12
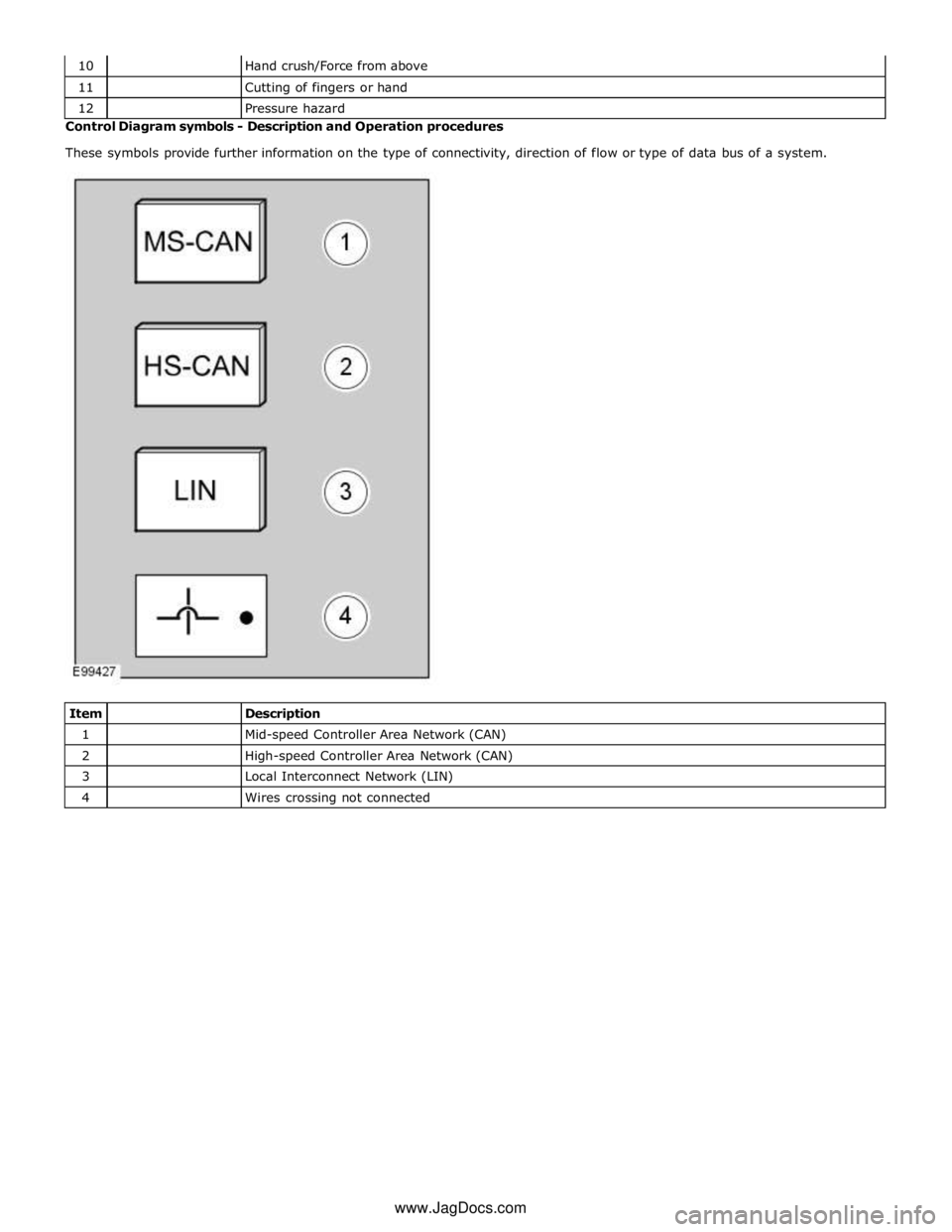
Pressure hazard Control Diagram symbols - Description and Operation procedures
These symbols provide further information on the type of connectivity, direction of flow or type of data bus of a system.
Item
Description 1
Mid-speed Controller Area Network (CAN) 2
High-speed Controller Area Network (CAN) 3
Local Interconnect Network (LIN) 4
Wires crossing not connected www.JagDocs.com
Page 104 of 3039

Avoid brake testing on busy roads where it can cause inconvenience or danger to other road users.
CAUTION: Brake testing which includes heavy brake applications should not be carried out with new brake pads/discs or
linings/drums until the components have bedded-in. New brake friction components will not reach full efficiency until the
bedding-in process is complete.
Test the brakes at several speeds within the normal operating range using both light and heavy pedal pressure. Note any
tendency to snatch, pull or drag, and any undue delay in application or release.
Allow the vehicle to coast and note any tendency to pull to one side, or evidence that the brakes are binding.
After stopping the vehicle (not immediately after a period of heavy braking), carefully check the brake temperature. A disc
which feels hot, or appreciably hotter than the others, indicates that the brake is binding.
After completion of the test, check for:
Oil, coolant, hydraulic, air and fuel leaks
Abnormal temperature of any moving components or assemblies, e.g. wheel hubs, transmission, axle etc., which might
indicate over tightness or lack of lubrication
Page 117 of 3039
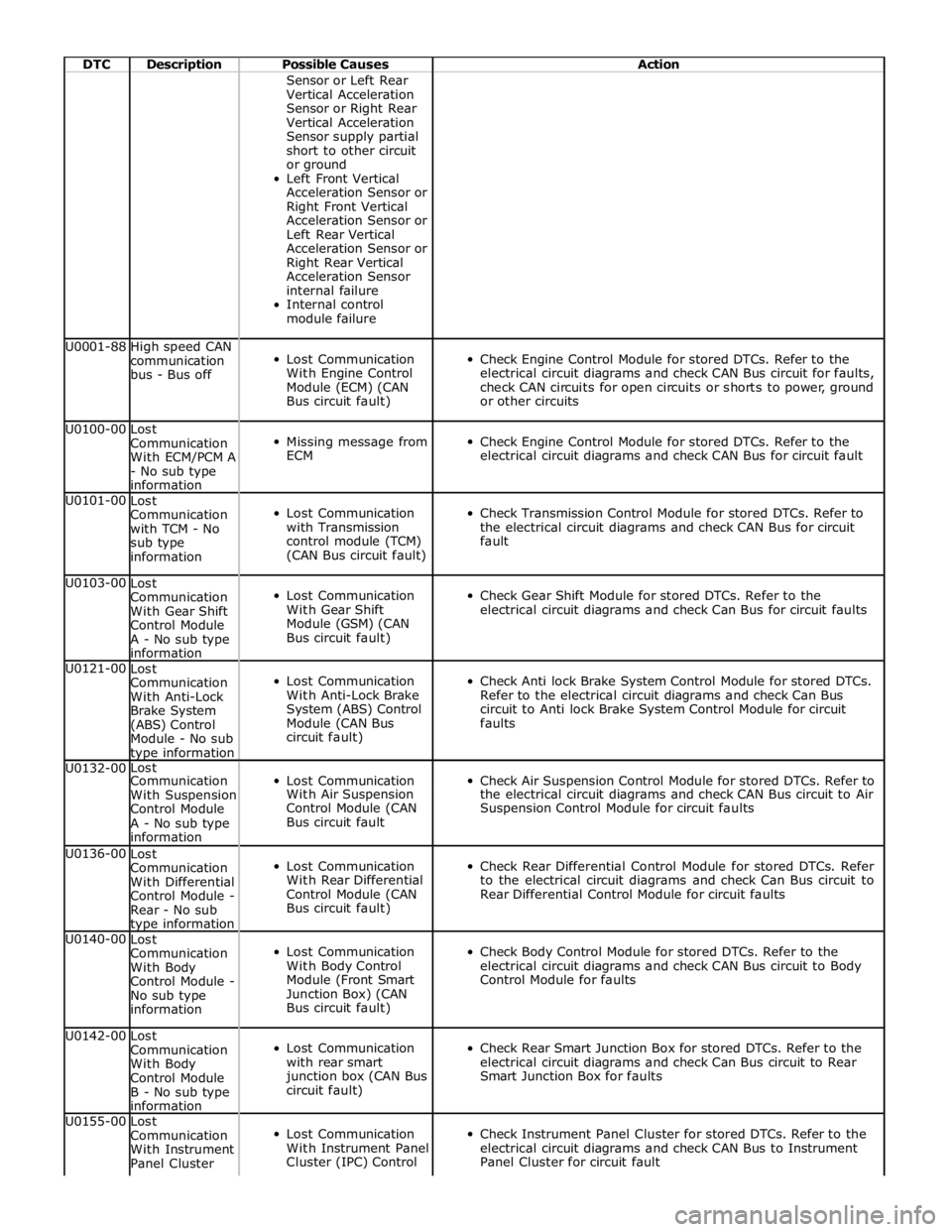
DTC Description Possible Causes Action Sensor or Left Rear
Vertical Acceleration
Sensor or Right Rear
Vertical Acceleration
Sensor supply partial
short to other circuit
or ground
Left Front Vertical
Acceleration Sensor or
Right Front Vertical
Acceleration Sensor or
Left Rear Vertical
Acceleration Sensor or
Right Rear Vertical
Acceleration Sensor
internal failure
Internal control
module failure U0001-88
High speed CAN
communication
bus - Bus off
Lost Communication
With Engine Control
Module (ECM) (CAN
Bus circuit fault)
Check Engine Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus circuit for faults,
check CAN circuits for open circuits or shorts to power, ground
or other circuits U0100-00
Lost
Communication
With ECM/PCM A
- No sub type
information
Missing message from
ECM
Check Engine Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus for circuit fault U0101-00
Lost
Communication
with TCM - No
sub type
information
Lost Communication
with Transmission
control module (TCM)
(CAN Bus circuit fault)
Check Transmission Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer to
the electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus for circuit
fault U0103-00
Lost
Communication
With Gear Shift
Control Module
A - No sub type
information
Lost Communication
With Gear Shift
Module (GSM) (CAN
Bus circuit fault)
Check Gear Shift Module for stored DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check Can Bus for circuit faults U0121-00
Lost
Communication
With Anti-Lock
Brake System
(ABS) Control
Module - No sub type information
Lost Communication
With Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) Control
Module (CAN Bus
circuit fault)
Check Anti lock Brake System Control Module for stored DTCs.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check Can Bus
circuit to Anti lock Brake System Control Module for circuit
faults U0132-00 Lost
Lost Communication
Check Air Suspension Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer to Communication With Suspension With Air Suspension the electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus circuit to Air Control Module Control Module (CAN Suspension Control Module for circuit faults A - No sub type Bus circuit fault information U0136-00
Lost
Communication
With Differential
Control Module -
Rear - No sub type information
Lost Communication
With Rear Differential
Control Module (CAN
Bus circuit fault)
Check Rear Differential Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer
to the electrical circuit diagrams and check Can Bus circuit to
Rear Differential Control Module for circuit faults U0140-00
Lost
Communication
With Body
Control Module -
No sub type
information
Lost Communication
With Body Control
Module (Front Smart
Junction Box) (CAN
Bus circuit fault)
Check Body Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus circuit to Body
Control Module for faults U0142-00
Lost
Communication
With Body
Control Module
B - No sub type
information
Lost Communication
with rear smart
junction box (CAN Bus
circuit fault)
Check Rear Smart Junction Box for stored DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check Can Bus circuit to Rear
Smart Junction Box for faults U0155-00
Lost
Communication
With Instrument
Panel Cluster
Lost Communication
With Instrument Panel
Cluster (IPC) Control
Check Instrument Panel Cluster for stored DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus to Instrument
Panel Cluster for circuit fault
Page 118 of 3039
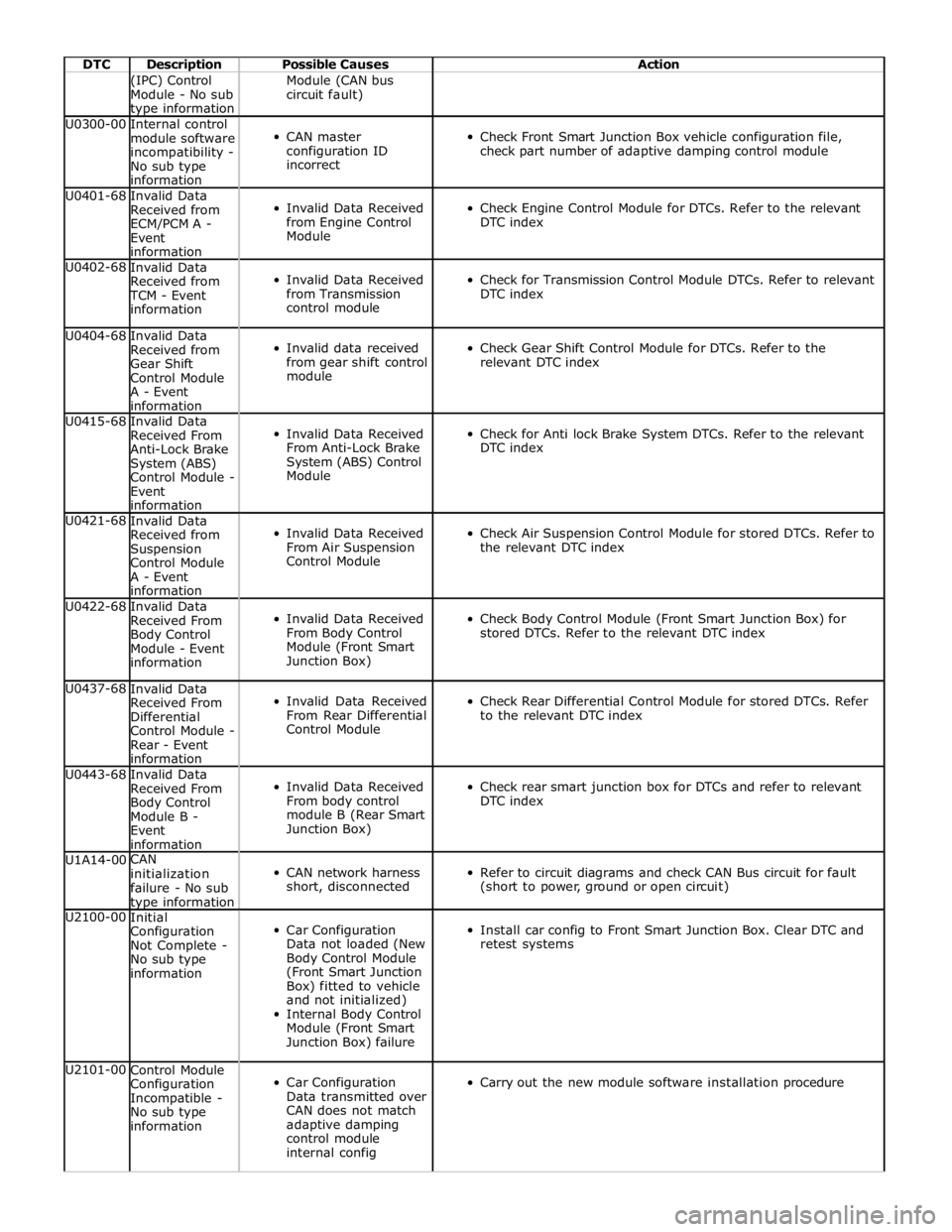
DTC Description Possible Causes Action (IPC) Control
Module - No sub
type information Module (CAN bus
circuit fault) U0300-00
Internal control
module software
incompatibility -
No sub type
information
CAN master
configuration ID
incorrect
Check Front Smart Junction Box vehicle configuration file,
check part number of adaptive damping control module U0401-68
Invalid Data
Received from
ECM/PCM A -
Event
information
Invalid Data Received
from Engine Control
Module
Check Engine Control Module for DTCs. Refer to the relevant
DTC index U0402-68
Invalid Data
Received from TCM - Event
information
Invalid Data Received
from Transmission
control module
Check for Transmission Control Module DTCs. Refer to relevant
DTC index U0404-68
Invalid Data
Received from
Gear Shift
Control Module
A - Event
information
Invalid data received
from gear shift control
module
Check Gear Shift Control Module for DTCs. Refer to the
relevant DTC index U0415-68
Invalid Data
Received From
Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS)
Control Module -
Event
information
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) Control
Module
Check for Anti lock Brake System DTCs. Refer to the relevant
DTC index U0421-68
Invalid Data
Received from
Suspension
Control Module
A - Event
information
Invalid Data Received
From Air Suspension
Control Module
Check Air Suspension Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer to
the relevant DTC index U0422-68
Invalid Data
Received From
Body Control
Module - Event
information
Invalid Data Received
From Body Control
Module (Front Smart
Junction Box)
Check Body Control Module (Front Smart Junction Box) for
stored DTCs. Refer to the relevant DTC index U0437-68
Invalid Data
Received From
Differential
Control Module -
Rear - Event
information
Invalid Data Received
From Rear Differential
Control Module
Check Rear Differential Control Module for stored DTCs. Refer
to the relevant DTC index U0443-68
Invalid Data
Received From
Body Control
Module B -
Event
information
Invalid Data Received
From body control
module B (Rear Smart
Junction Box)
Check rear smart junction box for DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC index U1A14-00 CAN
initialization
failure - No sub type information
CAN network harness
short, disconnected
Refer to circuit diagrams and check CAN Bus circuit for fault
(short to power, ground or open circuit) U2100-00
Initial
Configuration
Not Complete -
No sub type
information
Car Configuration
Data not loaded (New
Body Control Module
(Front Smart Junction
Box) fitted to vehicle
and not initialized)
Internal Body Control
Module (Front Smart
Junction Box) failure
Install car config to Front Smart Junction Box. Clear DTC and
retest systems U2101-00
Control Module
Configuration
Incompatible -
No sub type
information
Car Configuration
Data transmitted over
CAN does not match
adaptive damping
control module
internal config
Carry out the new module software installation procedure
Page 129 of 3039
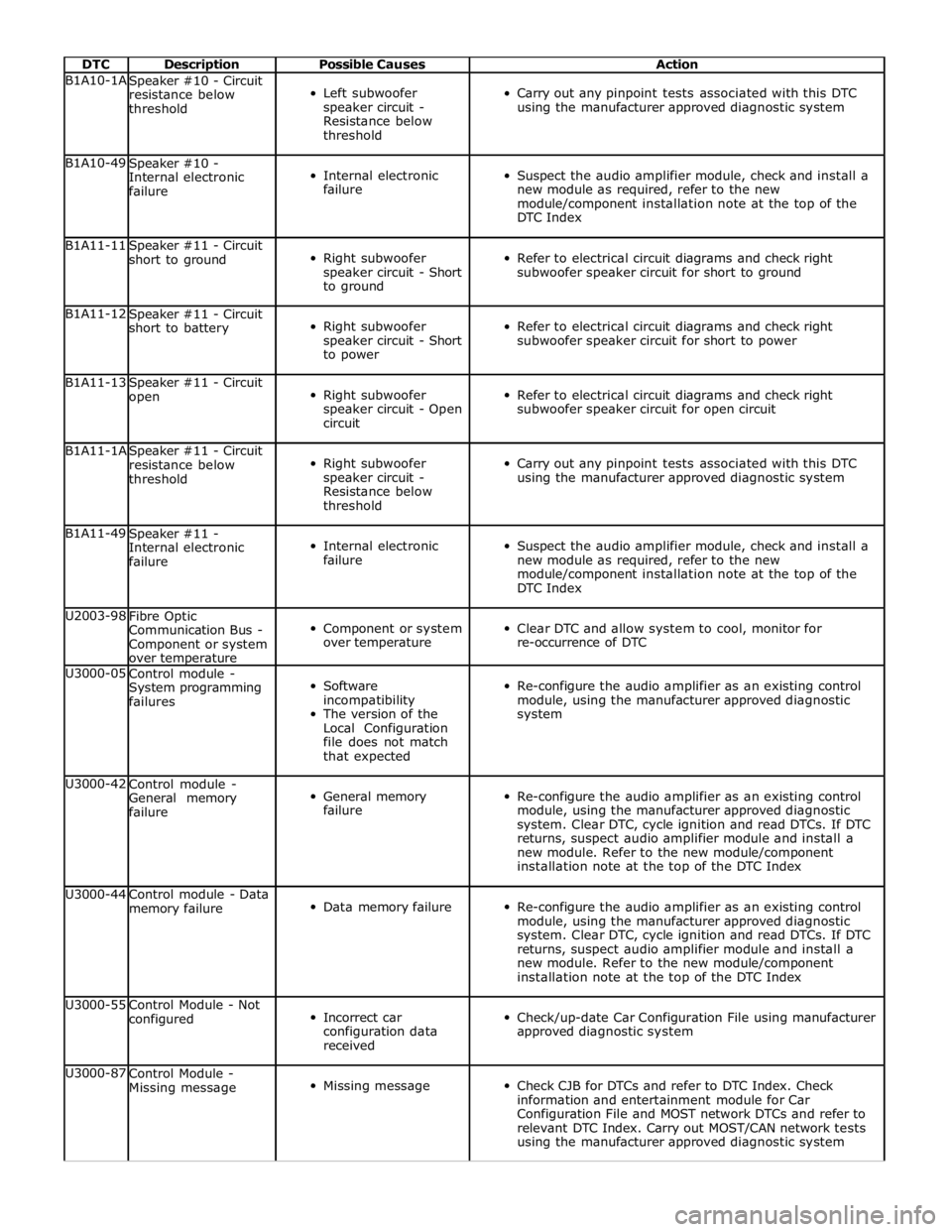
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1A10-1A
Speaker #10 - Circuit
resistance below
threshold
Left subwoofer
speaker circuit -
Resistance below
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system B1A10-49
Speaker #10 -
Internal electronic
failure
Internal electronic
failure
Suspect the audio amplifier module, check and install a
new module as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the
DTC Index B1A11-11
Speaker #11 - Circuit
short to ground
Right subwoofer
speaker circuit - Short
to ground
Refer to electrical circuit diagrams and check right
subwoofer speaker circuit for short to ground B1A11-12
Speaker #11 - Circuit
short to battery
Right subwoofer
speaker circuit - Short
to power
Refer to electrical circuit diagrams and check right
subwoofer speaker circuit for short to power B1A11-13
Speaker #11 - Circuit
open
Right subwoofer
speaker circuit - Open
circuit
Refer to electrical circuit diagrams and check right
subwoofer speaker circuit for open circuit B1A11-1A
Speaker #11 - Circuit
resistance below
threshold
Right subwoofer
speaker circuit -
Resistance below
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system B1A11-49
Speaker #11 -
Internal electronic
failure
Internal electronic
failure
Suspect the audio amplifier module, check and install a
new module as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the
DTC Index U2003-98
Fibre Optic
Communication Bus -
Component or system
over temperature
Component or system
over temperature
Clear DTC and allow system to cool, monitor for
re-occurrence of DTC U3000-05
Control module -
System programming
failures
Software
incompatibility
The version of the
Local Configuration
file does not match
that expected
Re-configure the audio amplifier as an existing control
module, using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system U3000-42
Control module -
General memory
failure
General memory
failure
Re-configure the audio amplifier as an existing control
module, using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Clear DTC, cycle ignition and read DTCs. If DTC
returns, suspect audio amplifier module and install a
new module. Refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index U3000-44
Control module - Data
memory failure
Data memory failure
Re-configure the audio amplifier as an existing control
module, using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Clear DTC, cycle ignition and read DTCs. If DTC
returns, suspect audio amplifier module and install a
new module. Refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index U3000-55
Control Module - Not
configured
Incorrect car
configuration data
received
Check/up-date Car Configuration File using manufacturer
approved diagnostic system U3000-87
Control Module -
Missing message
Missing message
Check CJB for DTCs and refer to DTC Index. Check
information and entertainment module for Car
Configuration File and MOST network DTCs and refer to
relevant DTC Index. Carry out MOST/CAN network tests
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system
Page 131 of 3039

Published: 17-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Blind Spot Monitoring System Module (SODL/SODR)
Description and Operation
Blind Spot Monitoring System Module (SODL/SODR)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal places,
and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'DTC Monitor' tab on the manufacturers
approved diagnostic system.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Blind Spot Monitoring System Module, for
additional Diagnosis and Testing information refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing Section.
For additional information, refer to: Warning Devices (413-09 Warning Devices, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B11C9-11
Driver Display Status
LED - Circuit short to
ground
Circuit short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
driver display status LED circuit for short to
ground B11C9-15
Driver Display Status
LED - Circuit short to
battery or open
Circuit short to power or
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
driver display status LED circuit for short to
ground B11D6-11
Driver Display Alert LED -
Circuit short to ground
Circuit short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
driver display status LED circuit for short to
ground B11D6-15
Driver Display Alert LED -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Circuit short to power or
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
driver display status LED circuit for short to
ground U0010-00
Medium Speed CAN
Communication Bus - No
sub type information
No sub type information
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
the power and ground connections to the module.
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, complete a CAN network integrity test.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check