engine JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.GPages: 521, PDF Size: 17.35 MB
Page 51 of 521
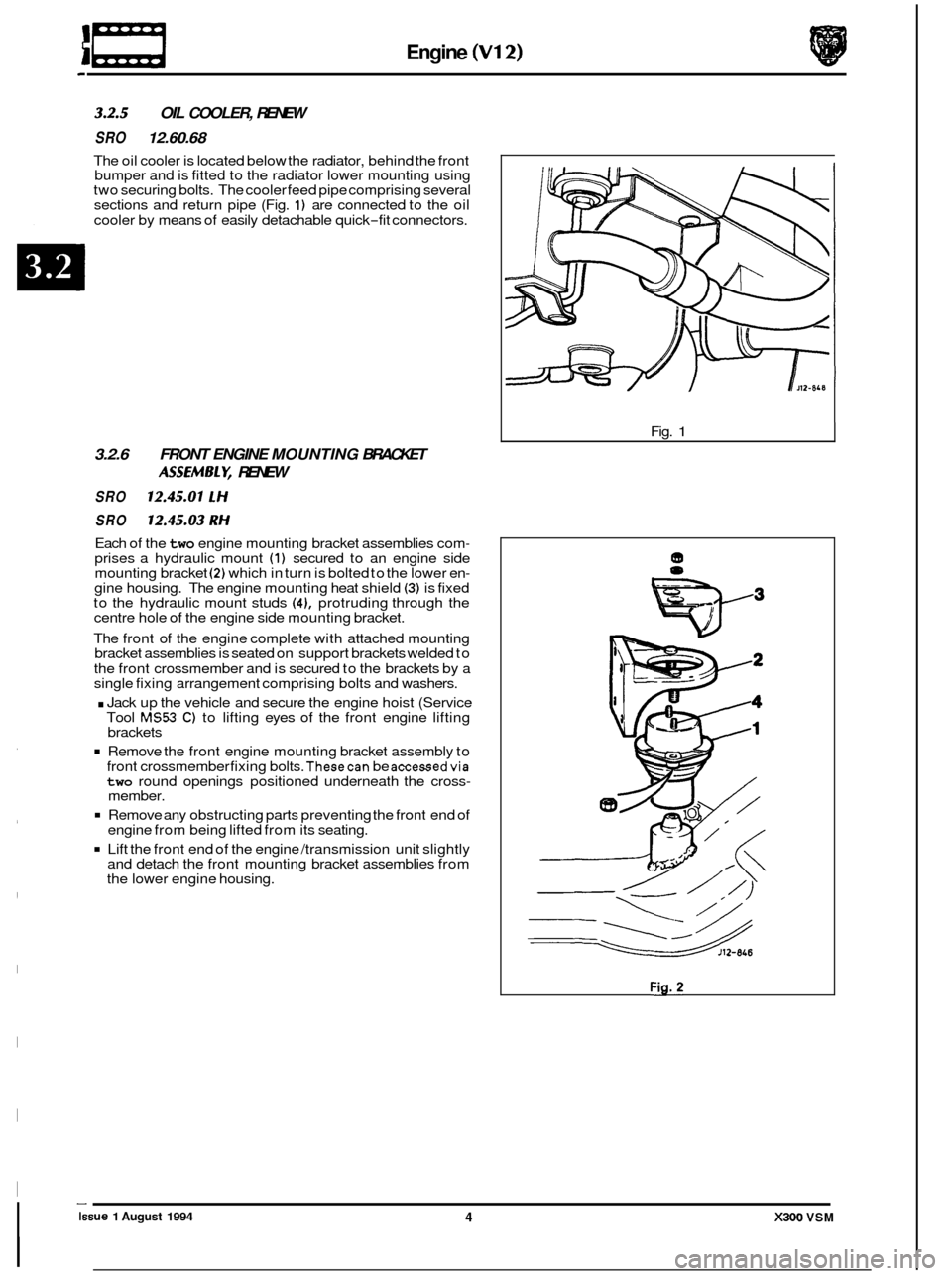
Engine (V12)
3.2.5 OIL COOLER, RENEW
SRO 12.60.68
The oil cooler is located below the radiator, behind the front
bumper and is fitted to the radiator lower mounting using
two securing bolts. The cooler feed pipe comprising several
sections and return pipe (Fig.
1) are connected to the oil
cooler by means of easily detachable quick
-fit connectors.
3.2.6 FRONT ENGINE MOUNTING BRACKET
SRO 12.45.01 LH
SRO 12.45.03 RH
Each of the two engine mounting bracket assemblies com- prises a hydraulic mount (1) secured to an engine side
mounting bracket (2) which in turn is bolted to the lower en- gine housing. The engine mounting heat shield (3) is fixed
to the hydraulic mount studs (41, protruding through the
centre hole of the engine side mounting bracket.
The front of the engine complete with attached mounting
bracket assemblies is seated on support brackets welded to
the front crossmember and is secured to the brackets by a
single fixing arrangement comprising bolts and washers.
. Jack up the vehicle and secure the engine hoist (Service
Tool MS53 C) to lifting eyes of the front engine lifting
brackets
Remove the front engine mounting bracket assembly to
front crossmember fixing bolts.
Thesecan be accessedvia two round openings positioned underneath the cross- member.
Remove any obstructing parts preventing the front end of
engine from being lifted from its seating.
Lift the front end of the engine /transmission unit slightly
and detach the front mounting bracket assemblies from
the lower engine housing.
ASSEMBLV, RENEW
Fig. 1
4 X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994
Page 52 of 521

Engine (V12)
3.2.7 REAR ENGINEMOUNTlNGASSEMBLY, RENEW
SRO
12.45.04
The rear engine mounting assembly (Fig. 1) comprises a
mounting bracket and spring assembly, secured to body un- derframe longitudinal members using nuts and washers.
With the aid of the engine hoist (Service Tool MS53 C) se- cured to the lifting eyes of the rear engine lifting brackets,
and a jack positioned underthe rear mounting brackettake
the weight of the engine.
. Undo and remove the mounting bracket and spring as-
sembly fixing arrangement.
rn Lower the jack and remove assembly.
Dismantle the assembly, clean all components and exam-
ine for any signs of wear or damage.
Renew components as necessary.
8 112-8'7
Fig. 1
I Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM 5
Page 54 of 521

Cooling System
SECTION CON TENTS
Sub-section Title SRO Page
I to IV ............ Preliminary Pages .................................................................... i
4.7.7 ............. Cooling System Description ........................................................... 7
4.1.7.7 ........... Cooling System Description. Major Components .......................................... 7
4.7.7.2 ........... Cooling System Description. Components for Climate Control System ........................ 7
4.7.1.3 ........... Cooling System Description. Components for Superchargwl Engine .......................... 7
4.7.7.4 ........... Cooling System Description. Operation .................................................. 7
4.7.2 ............. Cooling System Configuration .......................................................... 2
4.7.3 ............. Service Procedures ................................................................... 3
4.7.3.7 ........... Service Procedures. Safety Precautions .................................................. 3
4.7.3.2
........... Service Procedures. Working Practices .................................................. 3
4.7.3.3
........... Service Procedures. Coolant Change .................................................... 3
4.7.4.
............ Drain and Fill Procedures ............................................................. 4
4.7.4.7
........... Drain and Fill Procedures. Radiator, Drain ............................................... 4
4.7.4.2
........... Drain and Fill Procedures. Engine. Drain ................................................. 4
4.1.4.3
........... Drain and Fill Procedures. Radiator, Fill ................................................. 4
4.7.4.4
........... Drain and Fill Procedures. Complete System. Fill .......................................... 5
4.7.5 ............. Fault Diagnosis ...................................................................... 6
4.1.5.7 ........... Fault Diagnosis. Introduction ........................................................... 6
4.7.5.2 ........... Fault Diagnosis. Diagnostic Procedures .................................................. 6
Issue 1 August 19! X300 VSM i
Page 55 of 521
€3 Cooling System (AJ16)
Fixing
Fan cowl assembly to radiator
Header tank bracket to body
Header tank to body
Hose clip,
all except those shown below
Hose clip, bleed hose to radiator
Radiator drain plug
Radiator temperature switch
Lower
radiator cradle to body
Supercharger pump mounting
Supercharger pump to instrumounts
Supercharger radiator to body
Top radiator panel to body
1. SERVICE TOOLS & EQUIPMENT
No Jaguar service tools are required for working on the cooling system. Some normal workshop items will be required,
including
a pressure tester, hydrometer and thermometer.
Tightening Torque
(Nm)
8-9
7-1 0
2,5-3,5
2,5-3,5
1,5-2,5
1,5-2,5
13-17
7
-1 0
7-10
5-7
7-10
7
-10
Description UseS
To be issued
111. SERVICE MATERIALS
Notes
Iv: SZRVICE DATA
Application
Engine thermostat temperature rating
Coolant header cap pressure rating
Generator
/ water pump drive belt tension, new belt
Generator
/ water pump drive belt tension, service
tension
_____ ~~ Generator / water
pump drive belt tension measuring
point
Smcification
88OC
1,2 bar
Set to:
Run for one minute and allow belt to cool.
Reset to: (Burroughs method) 511 to
534 N;
Burroughs method: 51 1 to 534 N.
Clavis method: 167 to 173 Hz
Mid
-way between crankshaft and generator pulleys
(Burroughs method)
556 to 578
N;
(Clavis method) 174 to 180 Hz.
(Clavis method) 167 to 173
Hz
0
0
0
0
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 ii
Page 56 of 521

Cooling System (AJl6) m
4.1.1 COOLING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
4.1.1.1 Major Components
o Main engine crossflow radiator, incorporating a concentric tube cooler for the power steering fluid mounted in
the right
-hand radiator side tank. Vehicles with automatic transmission have a transmission fluid cooler
mounted in the left
-hand radiator side tank; for 4,O liter supercharged engines a six-plate cooler is fitted; other
vehicles have
a tube-type cooler. Adouble-action temperature switch, for controlling the radiator cooling fans,
is mounted in the left
-hand radiator side tank.
0 Two electrically operated radiator cooling fans, mounted behind the main radiator.
0 Coolant circulating pump, belt driven from the engine crankshaft.
0 Coolant header tank with pressure relief cap and coolant level probe.
o Engine thermostat.
4.1.1.2
0 Heater matrix.
o Electrically operated coolant circulating pump, mounted on the left-hand side of the engine bulkhead.
o Solenoid operated valve, located adjacent to the coolant circulating pump.
Components for Climate Control System
4.1.1.3 Components for Supercharged Engine
0 0 Supercharger crossflow radiator, mounted in front of the main radiator. The supercharger radiator is reverse- circuited, i.e. the coolant inlet is at the bottom of the radiator.
0 Electrically operated coolant circulating pump, located at the left-hand side of the main radiator.
4.1.1.4 Operation
The configuration of the cooling system for normally aspirated and supercharged (4,O liter) engines is shown in Sub- section 4.1.2.
The cooling system is pressurized, which allows the system to operate at a higher temperature without overheating.
The header tank is fitted with a pressure relief cap to protect the system against overpressure.
Under cold start conditions, coolant is forced by the engine driven water pump through the cylinder block and cylinder
head to the thermostat housing. The thermostat is closed to give rapid engine warm up, hence the coolant is returned
directly to the water pump inlet. When normal engine operating temperature is reached, the thermostat opens and
coolant is diverted through the radiator before returning to the water pump inlet. In vehicles fitted with
a supercharger,
coolant is circulated through the supercharger radiator and intercooler by the supercharger water pump. The super- charger cooling circuit uses the same coolant header tank as the main engine cooling system.
The radiator cooling fans operate in series and parallel under the control of the double
-action radiator mounted tem- perature switch. The fans are also controlled by the climate control system on vehicles fitted with air conditioning.
Under hot operating conditions, the fans may continue to operate after the engine has been switched off. The fans
stop automatically when the coolant temperature has been reduced sufficiently.
The system also provides the coolant supply for the climate control system, which is described in Section
14.
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 57 of 521
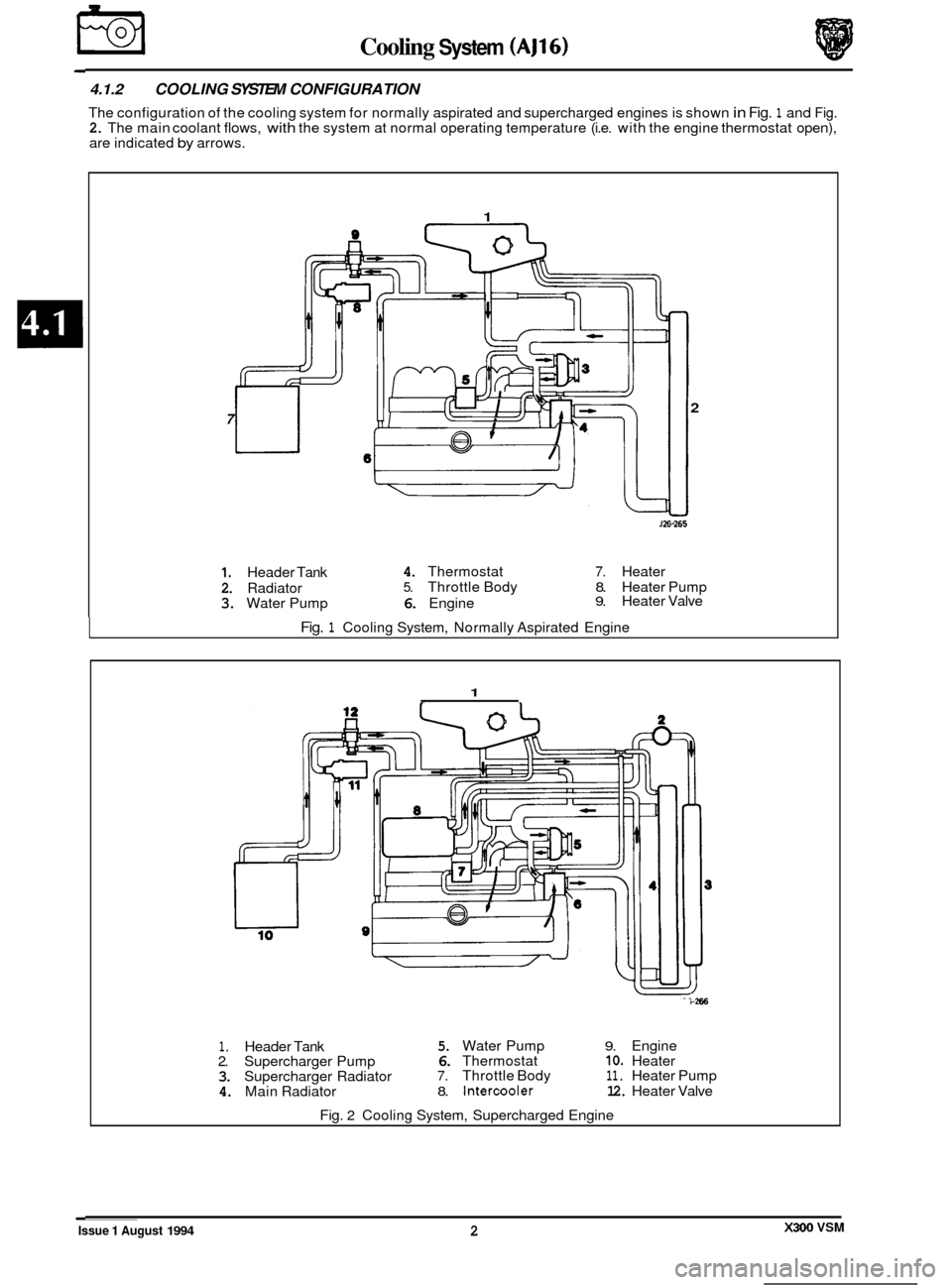
€3 Cooling System (AJ16)
4.1.2 COOLING SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
The configuration of the cooling system for normally aspirated and supercharged engines is shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. The main coolant flows, with the system at normal operating temperature (i.e. with the engine thermostat open),
are indicated by arrows.
1
2 7
J26-265
1. Header Tank 4. Thermostat 7. Heater
2. Radiator 5. Throttle Body 8. Heater Pump
3. Water Pump 6. Engine 9. Heater Valve
Fig. 1 Cooling System, Normally Aspirated Engine
1
i-266
1. Header Tank 5. Water Pump 9. Engine
2. Supercharger Pump 6. Thermostat IO. Heater
3. Supercharger Radiator 7. Throttle Body 11. Heater Pump
4. Main Radiator 8. Intercooler 12. Heater Valve
Fig.
2 Cooling System, Supercharged Engine
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM 2
Page 58 of 521

area washed to remove all traces of coolant.
CAUTION: To prevent the possibility of damage to the heater circuit pump and supercharger pump (where fitted),
the pumps should be electrically isolated if the ignition has to be turned ON while the cooling system is
drained.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE HEADER TANK PRESSURE CAP WHILE THE ENGINE IS HOT. IF THE CAP MUST
BE REMOVED, PROTECT THE HANDS AGAINST ESCAPING STEAM AND SLOWLY TURN THE CAP ANTI
- CLOCKWISE UNTIL THE EXCESS PRESSURE CAN ESCAPE. LEAVE THE CAP IN THIS POSITION UNTIL
ALL THE STEAM AND PRESSURE HAS ESCAPED AND THEN REMOVE THE CAP COMPLETELY.
WARNING: WHEN DRAINING THE COOLANT WITH THE ENGINE HOT, PROTECT THE HANDS AGAINST CONTACT
WITH HOT COOLANT.
WARNING: WHEN WORKING WITHIN THE ENGINE COMPARTMENT, KEEP CLEAR OF THE RADIATOR COOLING
FANS. THE FANS COULD START WITHOUT WARNING EVEN IF THE ENGINE IS NOT RUNNING.
4.1.3.2 Working Practices
Whenfilling thesystem with coolant,ensurethatthevehicle isstanding on a level surfaceandthatthecoolant is poured
in slowly so that airlocks are not introduced into the system. Airlocks can seriously affect the operation of the climate
control system and can cause damage to the heater circuit pump (and supercharger circuit pump if fitted).
Cooling System (AJ16)
4.1.3 SERVICE PROCEDURES
4.1.3.1 Safety Precautions
The anti-freeze specified in Appendix AI must be used wherever possible. It is designed to afford the maximum cor- rosion protection to all metals found in the engine cooling system, as well as having the frost protection properties
necessary during the winter months.
Should
it not be available, then anti-freeze conforming to Ford Motor Company specification ESLbM97B49-A may be
used. To provide optimum temperature and corrosion protection, the specified anti-freeze concentration must always
be used.
Once coolant has been drained from the system,
it must be discarded and not reused. Anti-freeze is harmful to the
environment. Used coolant must be disposed of safely and never poured down a drain connected to the public sewer.
CAUTION: Never fill or topup the system with water only.
CAUTION : Anti-freeze is harmful to paintwork. Coolant spillages must be wiped up immediately and the affected
Hose clips should always be positioned so that there is proper access for tightening and that the clip does not foul or
interfere with the operation of any components.
Drive belts must always be tensioned to the specified value and the tension checked
at the correct point on the belt.
This information is given in Subsection IV in the preliminary pages.
0
When tightening components, the torque figures given in Sukection II in the preliminary pages should always be
used for the fastenings listed.
4.1.3.3 Coolant Change
The coolant must be changed at intervals of four years. The system should be drained from the radiator drain plug,
flushed and filled with fresh coolant. Flushing should be carried out thoroughly to remove all the old coolant from the
engineand heater matrix. (The heatervalve isopen withthe ignition OFF). AfterfiIling,checkthecoolant concentration
with a hydrometer. For the specified anti-freeze and coolant concentration, see Appendix AI.
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 59 of 521
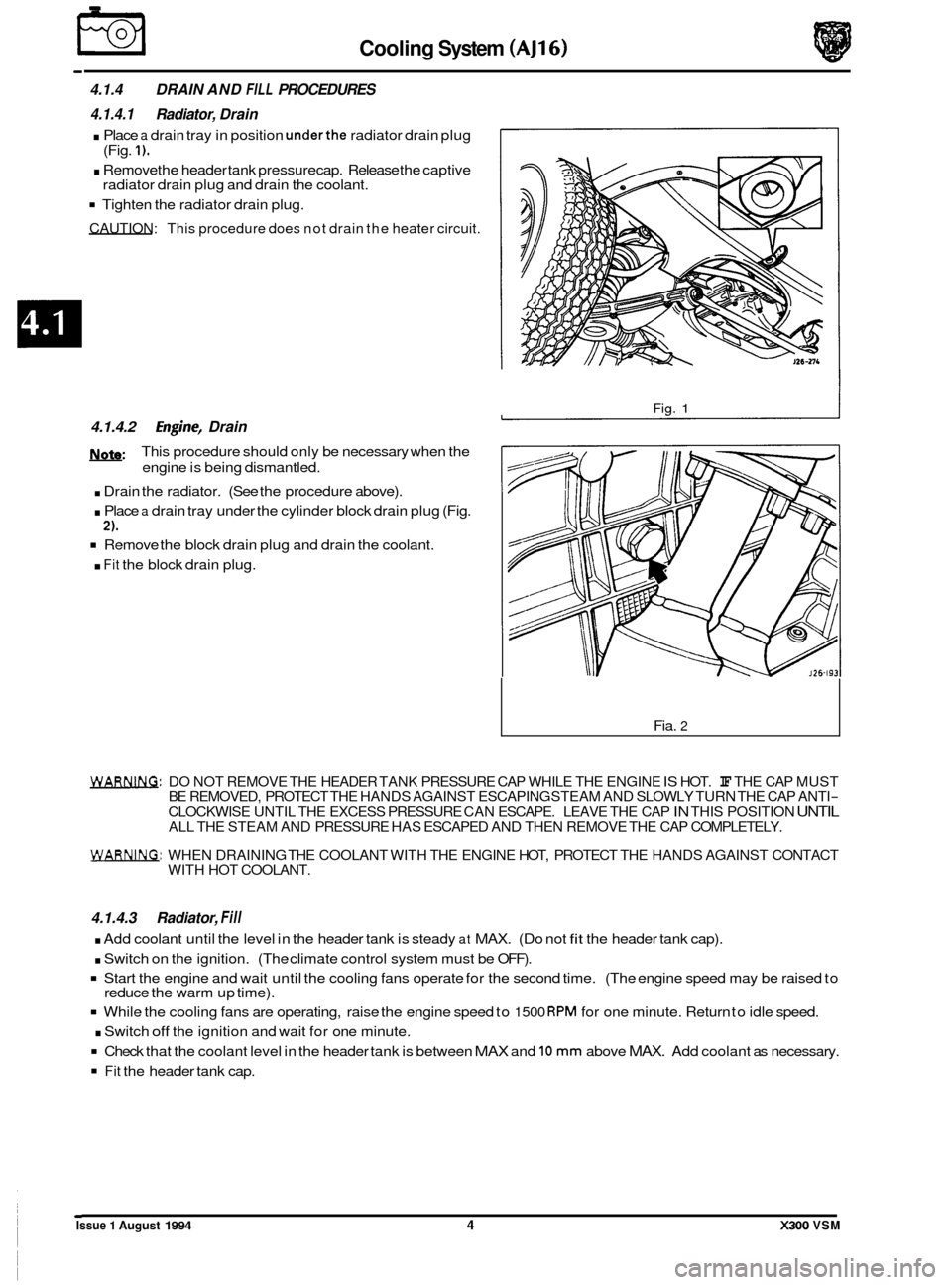
€3 Cooling System (AJ16)
4.1.4 DRAIN AND FILL PROCEDURES
4.1.4.1 Radiator, Drain
. Place a drain tray in position underthe radiator drain plug
. Remove the header tank pressure cap. Release the captive
Tighten the radiator drain plug.
CAUTION: This procedure does not drain the heater circuit.
(Fig. 1).
radiator drain plug and drain the coolant.
4.1.4.2 Engh-, Drain
m:
. Drain the radiator. (See the procedure above).
. Place a drain tray under the cylinder block drain plug (Fig.
Remove the block drain plug and drain the coolant.
. Fit the block drain plug.
This procedure
should only be necessary when the
engine is being dismantled.
2).
Fig. 1
Fia. 2
WAm. DO NOT REMOVE THE HEADER TANK PRESSURE CAP WHILE THE ENGINE IS HOT. IF THE CAP MUST
BE REMOVED, PROTECT THE HANDS AGAINST ESCAPING STEAM AND SLOWLY TURN THE CAP ANTI- CLOCKWISE UNTIL THE EXCESS PRESSURE CAN ESCAPE. LEAVE THE CAP IN THIS POSITION UNTIL ALL THE STEAM AND PRESSURE HAS ESCAPED AND THEN REMOVE THE CAP COMPLETELY.
WARNING: WHEN DRAINING THE COOLANT WITH THE ENGINE HOT, PROTECT THE HANDS AGAINST CONTACT
WITH HOT COOLANT.
4.1.4.3 Radiator, Fill
. Add coolant until the level in the header tank is steady at MAX. (Do not fit the header tank cap).
. Switch on the ignition. (The climate control system must be OFF).
Start the engine and wait until the cooling fans operate for the second time. (The engine speed may be raised to
While the cooling fans are operating, raise the engine speed to 1500 RPM for one minute. Return to idle speed.
. Switch off the ignition and wait for one minute.
Check that the coolant level in the header tank is between MAX and 10 mm above MAX. Add coolant as necessary.
Fit the header tank cap.
reduce
the warm up time).
Issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 60 of 521

.
0
0
Cooling System (AJ1
4.1.4.4 Complete System, Fill
. Add coolant until the level in the header tank is steady at MAX. (Do not fit the header tank cap).
m Switch on the ignition. (The climate control system must be OFF).
Start the engine and wait until the cooling fans operate for the second time. (The engine speed may be raised to
. While the cooling fans are operating, raise the engine speed to 1500 RPM for one minute. Return to idle speed.
. Turn the climate control system ON. Set the temperature to HI. Manually select a fan speed of approximately 50%.
. Run the engine for four minutes. Ensure that the climate control system outlet airtemperature is hot to very hot and
that there is no noise from the heater coolant circulating pump. (The engine speed may be raised to assist with heat- ing).
reduce the warm up time).
. Switch off the ignition and wait for one minute.
. Check that the coolant level in the header tank is between MAX and 10 mm above MAX. Add coolant as necessary.
Fit the header tank cap.
X300 VSM 5 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 62 of 521
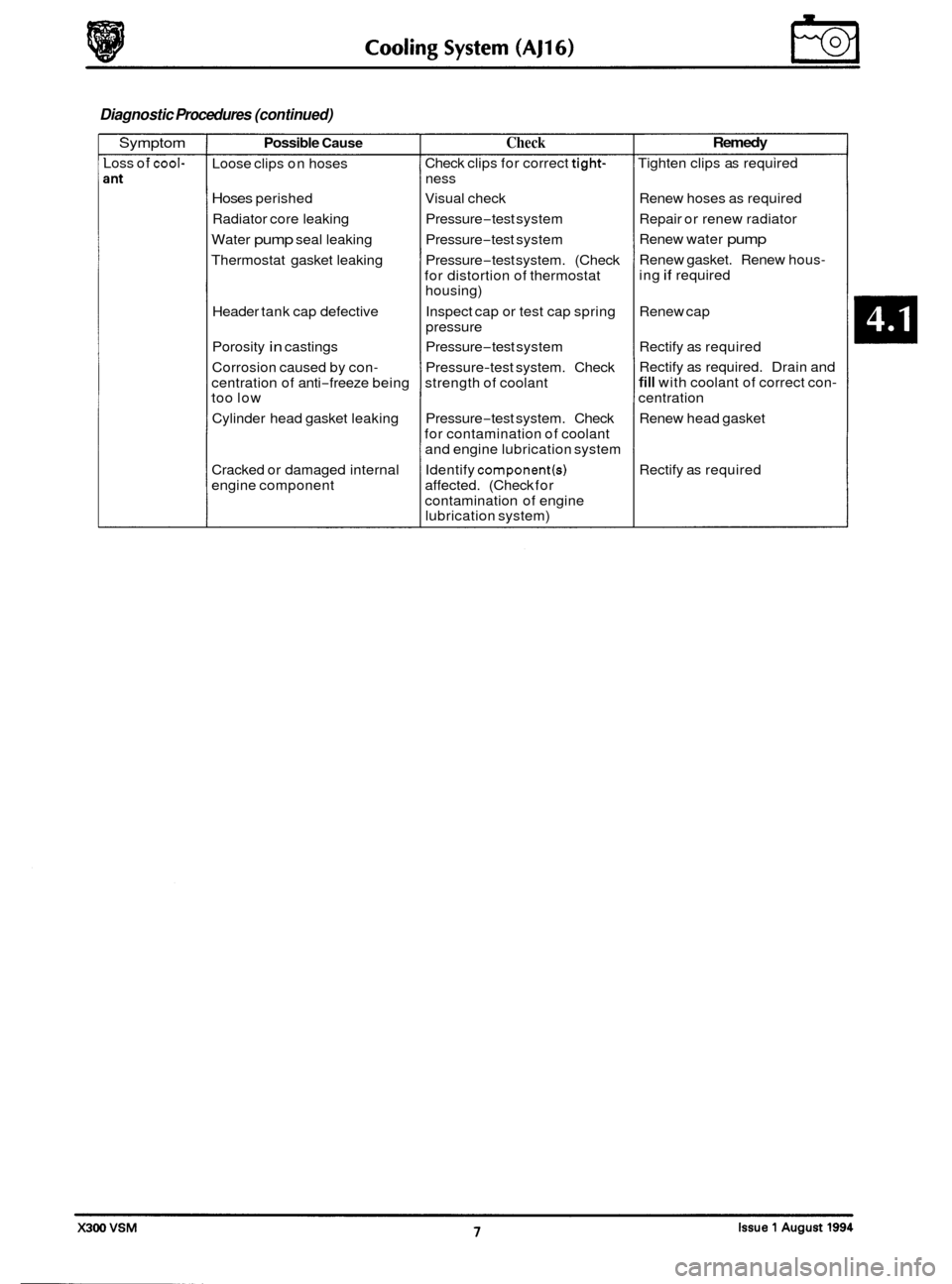
Diagnostic Procedures (continued)
Symptom
Loss of cool-
Possible Cause Check
Loose clips on hoses
Hoses perished Visual check
Radiator core leaking Pressure
-test system
Water
pump seal leaking Pressure-test system
Thermostat gasket leaking Pressure
-test system. (Check
for distortion of thermostat
housing)
Inspect cap or test cap spring
pressure
Pressure
-test system. Check
strength of coolant
Pressure
-test system. Check
for contamination of coolant
and engine lubrication system
Identify
component(s)
contamination of engine
lubrication system)
Check
clips for correct
tight-
ness
Header tank cap defective
Porosity
in castings Pressure-test system
Corrosion caused by con
-
centration of anti-freeze being
too low
Cylinder head gasket leaking
Cracked or damaged internal
engine component affected. (Check for
Remedy
Tighten clips as required
Renew hoses as required
Repair or renew radiator
Renew water
pump
Renew gasket. Renew hous-
ing if required
Renew cap
Rectify as required
Rectify as required. Drain and
fill with coolant of correct con-
centration
Renew head gasket
Rectify as required