engine JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1994 2.GPages: 521, PDF Size: 17.35 MB
Page 65 of 521
Lower radiator cradle to body
Radiator drain plug
1,5-2,5
Radiator temperature switch 13-17
Receiver drier to cooling fan assembly
Top radiator panel to body 7
-1 0
2,5-3,5
7-10
111. SERVICE
MATERIALS
Description USeS Notes
I to be issued I I I
0
SERVICE TOOLS & EQUIPMENT
No Jaguar service tools are required for working on the cooling system. Some normal workshop items will be required,
including a pressure tester, hydrometer and thermometer.
TORQUE TIGHTEN/ NG SPECI FICA TIONS
Fixing Tightening Torque
(Nm)
Electric fan assembly to body
Header tank bracket to body 7-10
7-10
Header tank to body
2,5-3,5
Hose clip, bleed hoses except those shown below 13-2.5
Hose clip, all main hoses 2,5-3,5
Hose clip, bleed hoses to header tank
Locator, fan cowl to radiator top panel 2.5-3,5
8,5-11,5
0
0
/U SERVICE
DATA
I Application
I Engine thermostat temperature rating
I Coolant header cap pressure rating
Water
pump / air injection pump drive belt tension
Drive belt tension measuring point
Specification I
88OC I
1.2 bar
Burroughs method: new belt 650
N. In service, if
tension falls below 320 N reset at 400 N
Clavis method: new belt 169 to 175 Hz. In service, if
tension falls below 127 Hz reset at 132 to 138 Hz.
Mid
-way between crankshaft and air injection pump
pulleys
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 ii
Page 66 of 521

Cooling System (V12
4.2.1 COOLING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION I
4.2.1.1 Major Components
o Engine crossflow radiator, incorporating a concentric tube cooler for the power steering fluid mounted in the
left
-hand radiator side tank. Vehicles with automatic transmission have a six-plate transmission fluid cooler
mounted in the right
-hand radiator side tank. A double-action temperature switch, for controlling the electric
radiator cooling fans, is mounted in the left
-hand radiator side tank.
0 Engine driven, viscous-coupled, radiator cooling fan
0 Two electrically operated radiator cooling fans, mounted in front of the radiator.
o Coolant circulating pump, belt driven from the engine crankshaft.
0 Coolant header tank with pressure relief cap and coolant level probe.
0 Two engine thermostats, one in each cylinder bank.
4.2.1.2
0 Heater matrix.
0 Electrically operated coolant circulating pump, mounted on the left-hand side of the engine bulkhead.
o Solenoid operated valve, located adjacent to the coolant circulating pump.
Components for Climate Control System
1
4.2.1.3 Operation
The configuration of the cooling system is shown in Sub-section 4.2.2.
The cooling system is pressurized, which allows the system to operate at a higher temperature without overheating.
The header tank is fitted with a pressure relief cap to protect the system against overpressure.
Under cold start conditions, coolant is forced by the engine driven water pump through each cylinder block and cylin
- der head to the thermostat housings. The thermostats are closed to give rapid engine warm up, hence the coolant is
returned via the engine cross pipe to the water pump inlet. When normal engine operating temperature is reached,
the thermostats open and coolant is diverted through the radiator before returning to the water pump inlet.
If the engine driven fan is unable to provide sufficient cooling, the electrically operated fans operate in series and paral
-
lel underthe control of the radiator mounted temperature switch. Under hot operating conditions, the electric fans may
continue to operate after the engine has been switched off. The fans stop automatically when the coolant temperature
has been reduced sufficiently.
The system also provides the coolant supply for the climate control system, which is described in Section 14.
I
I X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 67 of 521
Cooling System (VI 2)
0
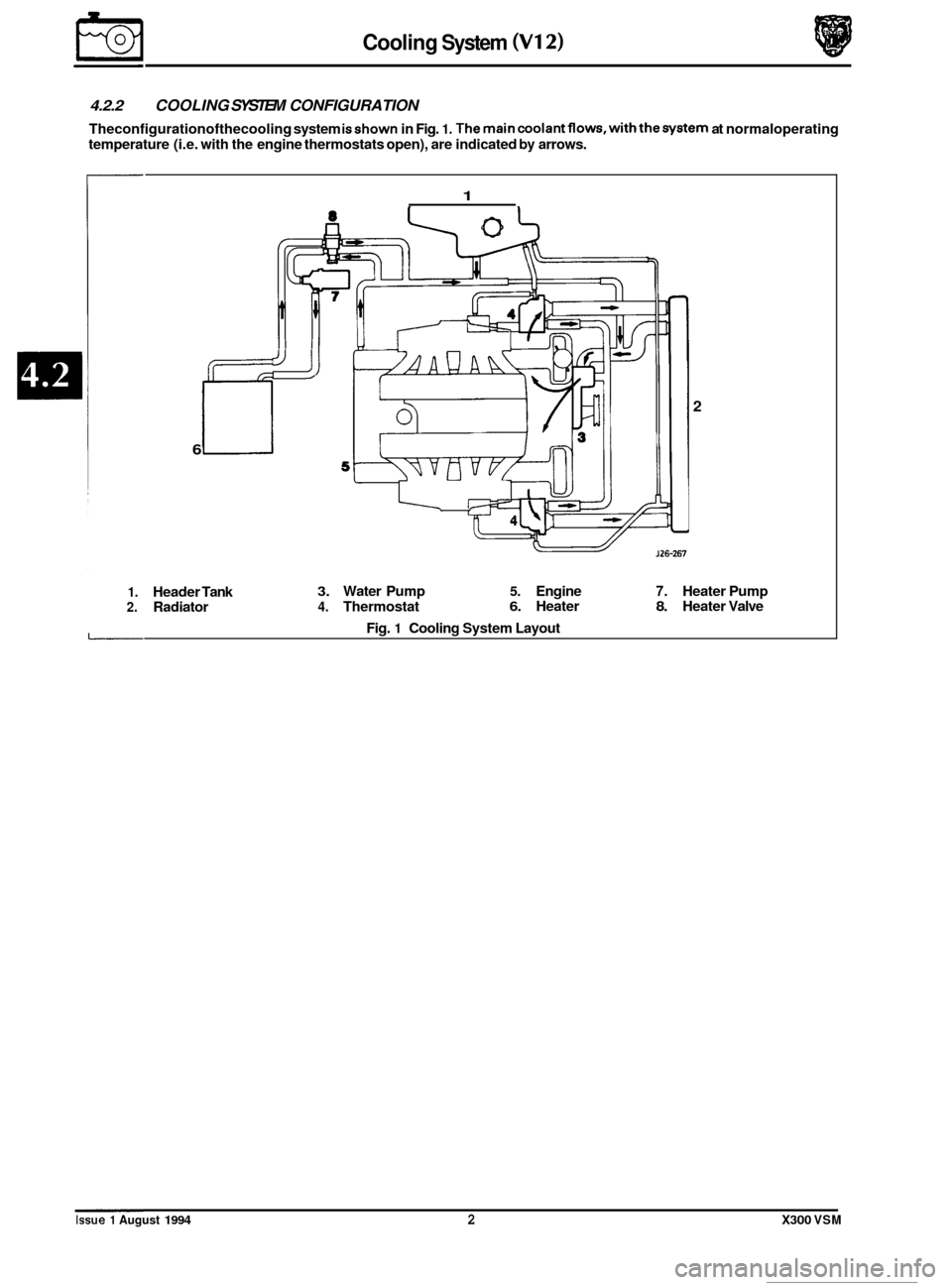
4.2.2 COOLING SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Theconfigurationofthecooling system isshown in Fig. 1. Themaincoolantflows,withthesystem at normaloperating
temperature (i.e. with the engine thermostats open), are indicated
by arrows.
6 rr
1
2
1. Header Tank 3. Water Pump 5. Engine 7. Heater Pump
2. Radiator 4. Thermostat 6. Heater 8. Heater Valve
Fig.
1 Cooling System Layout
Issue 1 August 1994 2 X300 VSM
Page 68 of 521

WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE HEADER TANK PRESSURE CAP WHILE THE ENGINE IS HOT. IF THE CAP MUST
BE REMOVED, PROTECT THE HANDS AGAINST ESCAPING STEAM AND SLOWLY TURN THE CAP ANTI- CLOCKWISE UNTIL THE EXCESS PRESSURE CAN ESCAPE. LEAVE THE CAP IN THIS POSITION UNTIL
ALL THE STEAM AND PRESSURE HAS ESCAPED AND THEN REMOVE THE CAP COMPLETELY.
WARNING: WHEN DRAINING THE COOLANT WITH THE ENGINE HOT, PROTECT THE HANDS AGAINST CONTACT
WITH HOT COOLANT.
WARNING
: WHEN WORKING WITHIN THE ENGINE COMPARTMENT, KEEP CLEAR OF THE ENGINE DRIVEN RADI- ATOR COOLING FAN WHEN THE ENGINE IS RUNNING.
4.2.3.2 Working Practices
Whenfilling thesystem with coolant,ensurethatthevehicle isstanding on a level surfaceand thatthecoolant is poured
in slowly so that airlocks are not introduced into the system. Airlocks can seriously affect the operation of the climate
control system and can cause damage to the heater circuit pump.
Hose clips should always be positioned
so that there is proper access for tightening and that the clip does not foul or
interfere with the operation of any components.
4.2.3 SERVICE PROCEDURES
4.2.3.1 Safety Precautions
The anti-freeze specified in Appendix A1 must be used wherever possible. It is designed to afford the maximum cor- rosion protection to all metals found in the engine cooling system, as well as having the frost protection properties
necessary during the winter months. Should it not be available, then anti-freeze conforming to Ford Motor Company
specification
ESBM97B49-A may be used. To provide optimum temperature and corrosion protection, the specified
anti-freeze concentration must always be used. Once coolant has been drained from the system, it must be discarded
and not reused. Anti-freeze is harmful to the environment. Always dispose of used coolant safely and never pour it down a drain connected to the public sewer.
CAUTION: Never fill or topup the system with water only.
CAUTION
: Anti-freeze is harmful to paintwork. Coolant spillages must be wiped up immediately and the affected
area washed to remove all traces of coolant.
CAUTION: To prevent the possibility of damage to the heater circuit
pump, the pump should be electrically isolated if the ignition has to be turned ON while the cooling system is drained.
The drive belt must always be tensioned to the specified value and the tension checked at the correct point on the belt.
This information is given in Sub-section IV in the preliminary pages.
When tightening components, the torque figures given in Sub
-section II in the preliminary pages should always be
used for the fastenings listed.
When fitting a replacement thermostat, ensure that the jiggle-pin is to the top of the thermostat housing.
4.2.3.3 Coolant Change
The coolant must be changed at intervals of four years. The system should be drained from the radiator drain plug,
flushed and filled with fresh coolant. Flushing should be carried out thoroughly to remove all the old coolant from the
engine and heater matrix. (The heatervalve isopen with the ignition OFF). AfterfilIing,checkthecoolant concentration
with a hydrometer. For specified anti-freeze and coolant concentration, see in Appendix Al.
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 69 of 521

€3 Cooling System (V12)
4.2.4 DRAIN AND FILL PROCEDURES
4.2.4.1 Radiator, Drain
. Place a drain tray in position under the radiator drain plug
. Remove the headertank pressure cap. Release thecaptive
Tighten the radiator drain plug.
(Fig.
1).
radiator drain
plug and drain the coolant.
CAUTION: This procedure does not drain the heater cir- cuit.
m: DO NOT REMOVE THE HEADER TANK PRES- SURE CAP WHILE THE ENGINE IS HOT. IF THE
CAP MUST BE REMOVED, PROTECT THE
HANDS AGAINST ESCAPING STEAM AND
SLOWLY TURN THE CAP
ANTI-CLOCKWISE UNTIL THE EXCESS PRESSURE CAN ESCAPE.
LEAVE THE CAP IN THIS POSITION UNTIL ALL
THE STEAM AND PRESSURE HAS ESCAPED
AND THEN REMOVE THE CAP COMPLETELY.
WARNING: WHEN DRAINING THE COOLANT
WITH THE
ENGINE HOT, PROTECT ME HANDS AGAINST
CONTACT WITH HOT COOLANT.
Fig. 1
4.2.4.2 Radiator, Fill
. Add coolant until the level in the header tank is steady at MAX. (Do not fit the header tank cap).
. Switch on the ignition. (The climate control system must be OFF).
. Start the engine and add coolant to the header tank if required to ensure that it does not empty.
. Run the engine until thetemperature gauge reads normal. (The enginespeed may be raised to reduce warm uptime).
. Switch off the ignition and wait for one minute.
Check that the coolant level in the header tank is between MAX and
10 mm above MAX. Add coolant as necessary.
. Fit the header tank cap.
4.2.4.3 Complete System, Fill
. Add coolant until the level in the header tank is steady at MAX. (Do not fit the header tank cap).
= Switch on the ignition. (The climate control system must be OFF).
. Start the engine and add coolant to the header tank if required to ensure that it does not empty.
. Run the engine until the temperature gauge reads normal, (The engine speed may be raised to reduce the warm up
. Turn the climate control system ON. Set the temperature to HI. Manually select a fan speed of approximately 50%.
. Run the engine for four minutes. Ensure that the climate control system outlet air temperature is hot to very hot and
that there is no noise from the heater coolant circulating pump. (The engine speed may be raised to assist with heat- ing).
time).
8 Switch
off the ignition and wait for one minute.
. Check that the coolant level in the header tank is between MAX and 10 mm above MAX. Add coolant as necessary.
. Fit the header tank cap.
4.2.4.4 System, Air Bleeding
After filling the system with coolant, any air present must be purged before effective cooling is possible. Provided the
correct fill procedure has been followed, purging of the system takes place automatically as follows:
The air entrained by the coolant, rises to the top of the radiator and to the highest point on each side of the engine (the
thermostat housings). While the thermostats are closed, the radiator is under reduced pressure due to the pump suc
- tion and air is bled through the jiggle-pins in each thermostat. Purged air is returnedvia the bleed system to the header
tank. When normal operating temperature is reached, the thermostats open and the system operates normally. ~~
Issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 71 of 521
rn Cooling System (VI 2)
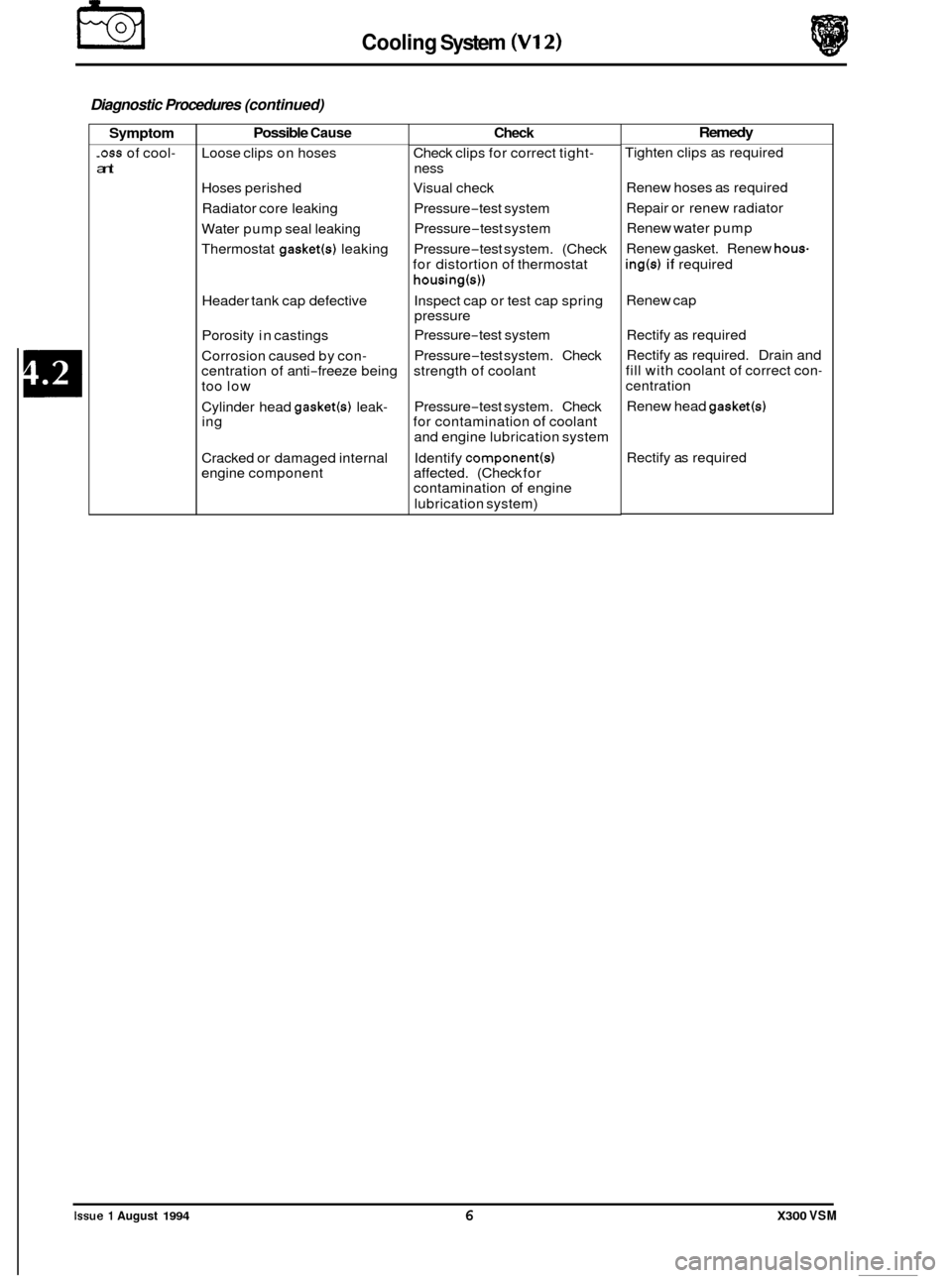
Diagnostic Procedures (continued)
Symptom
-0ss of cool-
ant
Possible Cause
Loose clips on hoses
Hoses perished
Radiator core leaking
Water pump seal leaking
Thermostat
gasket(s) leaking
Header tank cap defective
Porosity in castings
Corrosion caused by con
- centration of anti-freeze being
too low
Cylinder head
gasket(4 leak- ing
Cracked or damaged internal
engine component
Check
Check clips for correct tight-
ness
Visual check
Pressure
-test system
Pressure
-test system
Pressure
-test system. (Check
for distortion of thermostat
housing(s))
Inspect cap or test cap spring
pressure
Pressure
-test system
Pressure
-test system. Check
strength of coolant
Pressure
-test system. Check
for contamination of coolant
and engine lubrication system
Identify
component(s) affected. (Check for
contamination of engine
lubrication system)
Remedy
Tighten clips as required
Renew hoses as required
Repair or renew radiator
Renew water pump
Renew gasket. Renew
hous-
ing(s) if required
Renew cap Rectify as required
Rectify as required. Drain and
fill with coolant of correct con
-
centration
Renew head
gasket(s)
Rectify as required
Issue 1 August 1994 6 X300 VSM
Page 74 of 521
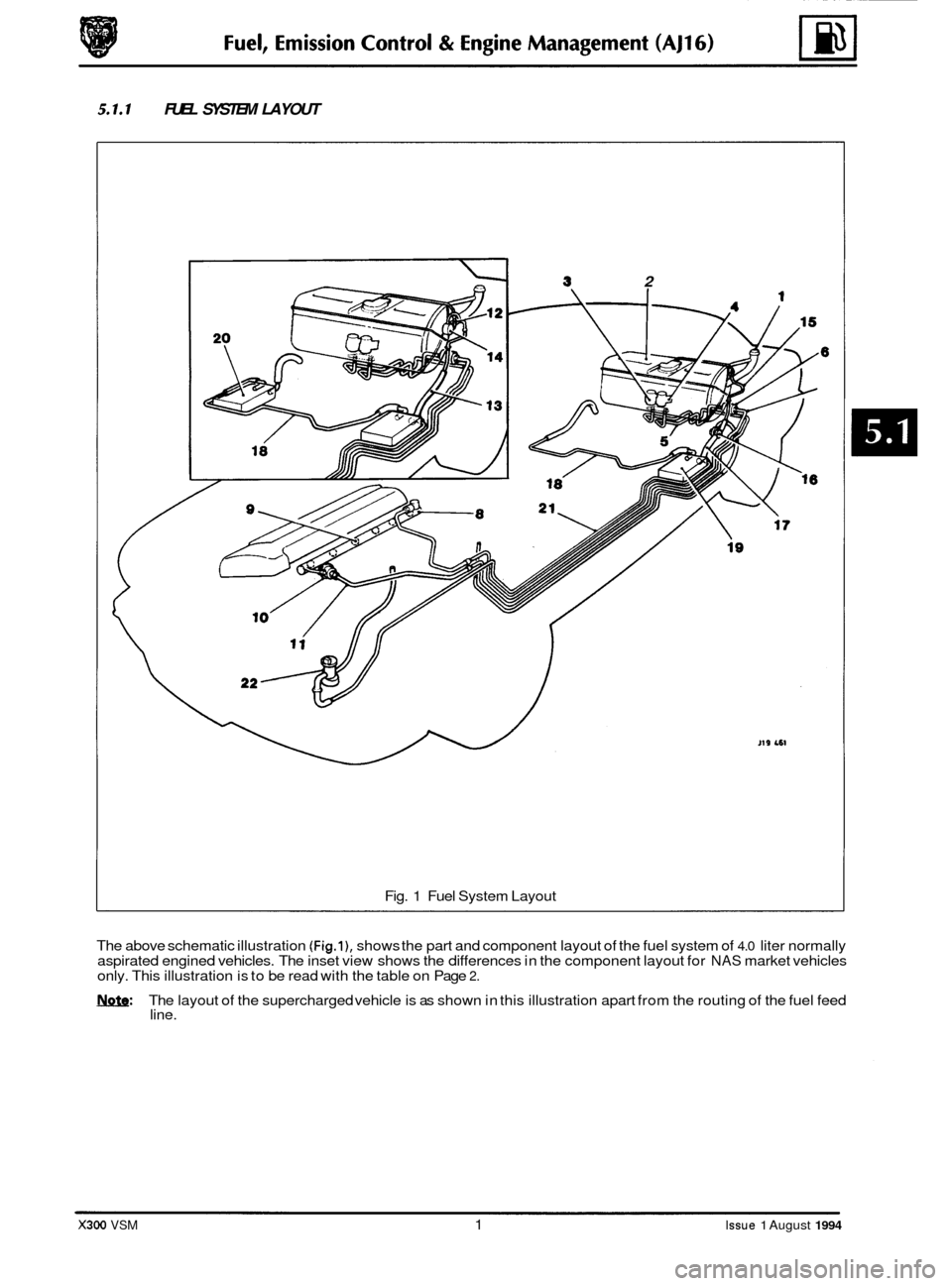
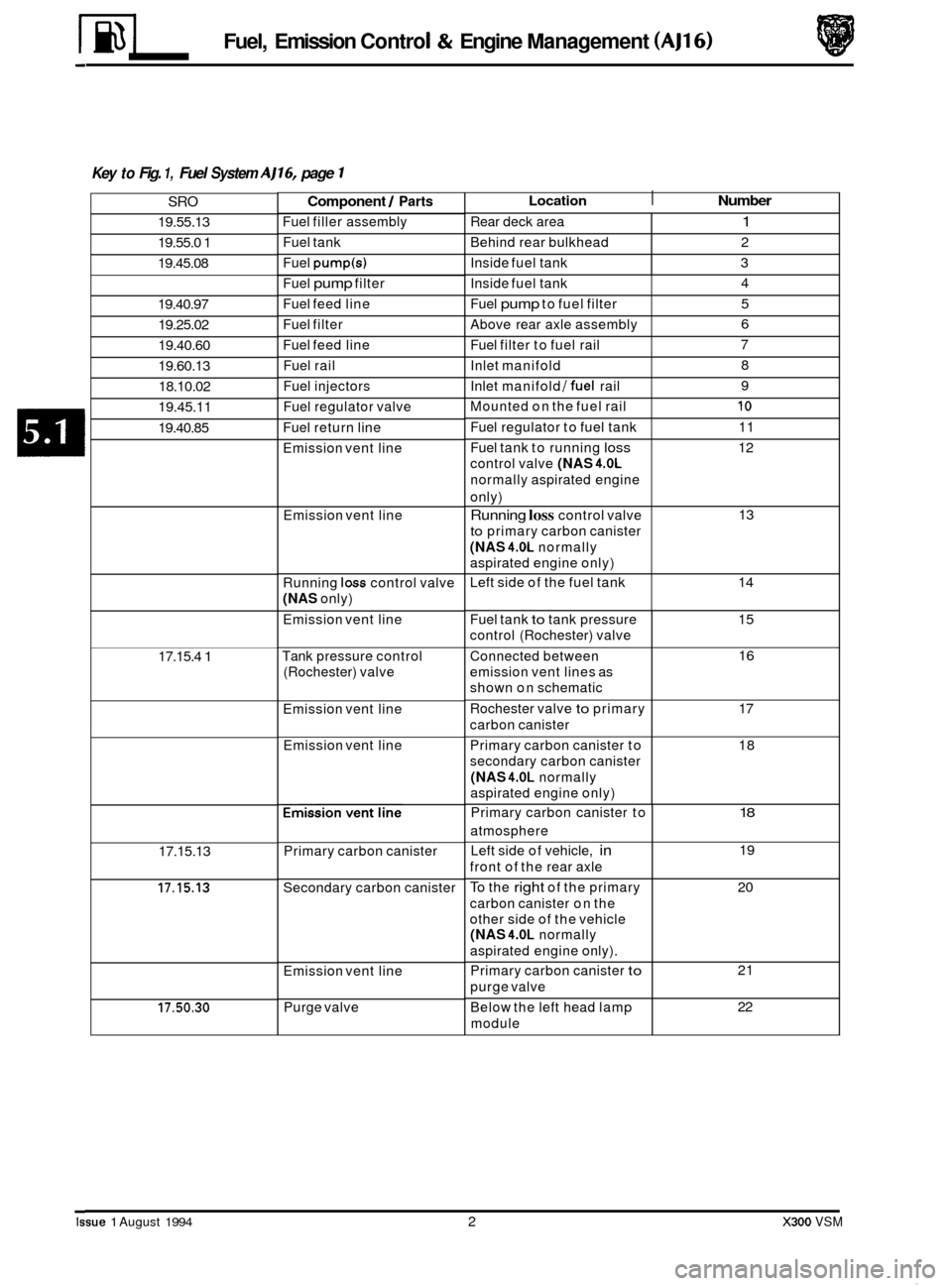
5.1.1 FUEL SYSTEM LAYOUT
0
9 2
Fig. 1 Fuel System Layout
The above schematic illustration
(Fig.l), shows the part and component layout of the fuel system of 4.0 liter normally
aspirated engined vehicles. The inset view shows the differences in the component layout for NAS market vehicles
only. This illustration is to be read with the table on Page 2.
M~Q: The layout of the supercharged vehicle is as shown in this illustration apart from the routing of the fuel feed
line.
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 75 of 521
Rear deck area
Behind rear bulkhead
Inside fuel tank 1
2
3
Inside fuel tank
Fuel
pump to fuel filter
Above rear axle assembly
Fuel filter to fuel rail
Inlet manifold
Inlet manifold
/fuel rail
Mounted on the fuel rail
Fuel regulator to fuel tank
Fuel tank to running
loss
control valve (NAS 4.0L
normally aspirated engine
only)
Running loss control valve
to primary carbon canister
(NAS 4.0L normally
aspirated engine only)
Left side of the fuel tank
4
5
6
7 8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Fuel tank to tank pressure
control (Rochester) valve
Connected between
emission vent lines as
shown on schematic
Rochester valve
to primary
carbon canister
Primary carbon canister to
secondary carbon canister
(NAS 4.0L normally
aspirated engine only)
15
16
17
18
Primary carbon canister to
atmosphere
Left side of vehicle,
in
front of the rear axle
To the right of the primary
carbon canister on the
other side of the vehicle
(NAS 4.0L normally
aspirated engine only).
Primary carbon canister
to
purge valve
Below the left head lamp
module
18
19
20
21
22
m Fuel, Emission Contro & Engine Management (AJ16) - .
0
0
0
0
Key to Fig. 1, Fuel System AJ16, page 1
Location I Number Component / Parts
Fuel filler assembly
SRO
19.55.13
19.55.0 1
19.45.08
Fuel tank
Fuel
pump(s)
Fuel pump filter
Fuel feed line
Fuel filter
Fuel feed line
19.40.97
19.25.02
19.40.60
19.60.13 18.10.02
19.45.11
Fuel rail
Fuel injectors
Fuel regulator valve
19.40.85 Fuel return line
Emission vent line
Emission vent line
Running
loss control valve
(NAS only)
Emission vent line
Tank pressure control
(Rochester) valve
17.15.4 1
Emission vent line
Emission vent line
Emission vent line
Primary carbon canister
17.15.13
Secondary carbon canister 17.15.13
Emission vent line
Purge valve
17.50.30
Issue 1 August 1994 2 X300 VSM
Page 76 of 521

striker and the-fuel cap stowage magnet.
The fuel bowl, retained around the filler neck by a clip, containing a drain tube filter located over the mating drain tube,
is rubber moulded onto a steel armature and fitted to the BIW decking panel by five M5 nuts.
The fuel lid latching assembly fitted to the metal armature of the fuel bowl by an M5 nut, includes the locking pin and
the operating actuator.
The actuator operates from the central locking system driven by the security and locking control module
(SLCM).
The fuel tank, mounted across thevehicle behind the passenger compartment rear bulkhead, is held in position by two
retaining straps, tightened by two M5 fixing arrangements.
The fuel tank of AJ16 engined vehicles contains one fuel pump, supplying fuel to the normally aspirated engine and
two fuel pumps, supplyingfuel to the supercharged engine. They are regenerative turbine pumps supplied by
Nippon- Denso. Nominal operating pressure is 3 bar (3.7 bar for supercharged engine) above the manifold depression and
pump delivery is 90 litredhour minimum at 13.2 volts, 3 bar outlet pressure. The pump(s) draw a nominal current of 7 amperes at 13 volts, 3 bar outlet pressure, ambient temperatures. Built in to the pump assembly is a over-pressure
relief valve which blows at 4.5 - 8.5 bar.
Fuel is drawn by the pumps from the fuel tank and is then supplied to the fuel rail via a
70 micron filter and the fuel
feed line connected in series by fuel filter.
The amount of fuel being injected into the engine
is controlled by the fuel injectors combined with the engine control module (ECM). - Any excessive fuel flowing through the system, is returned to the fuel tankvia the fuel regulator valve mounted on the
fuel rail, the fuel return line and the check valve also located inside the tank.
The two filters prevent contaminants from entering the fuel rail and possible damage to the fuel injectors, the engine,
the pump and the underfloor filter.
The fuel pumps are switched on and off by relays controlled by the engine control module
(ECM).
The second fuel pump for the supercharged engine operates only in the higher speed range, switching on at 4000rpm and off at 3200rpm.
The fuel lines are made up of an assembly, combining steel under floor pipes and flexible conductive anti-permeation
tubing. In orderto perform speedy remove and refit operations, the underfloor steel lines are linked through the engine
bay bulkhead to the flexible tubing, leading to the fuel rail and the fuel regulator by using positive sealing, quick-fit
type connectors. The same type connectors, are used to connect the fuel feed and return line to the fuel tank.
Connectors used inside the engine bay are of different sizes tocorrespond with the difference in pipe diameter, whereas
the connectors for the feed and return lines at the fuel tank are the same size.
Except for the return line connector at the fuel tank, two release tools, one for each size of connector are required to
release all remaining connectors.
-~
Fuel, Emission Control & Engine Management (AJ16)
5.1.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
m: WORKING ON THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY RESULT IN FUEL AND FUEL VAPOUR BEING PRESENT IN THE
ATMOSPHERE. FUEL VAPOUR IS EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE, HENCE GREAT CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHllST WORKING ON THE FUEL SYSTEM. ADHERE STRICTLY TO THE FOLLOWING PRECAUTIONS:
DO NOT
SMOEIN THE WORK AREA.
DISPLAY 'NO SMOKING
' SIGNS AROUND THE AREA.
ENSURE THAT A
CO2 FIRE EXTINGUISHER IS CLOSE AT HAND.
ENSURE THAT DRY SAND
IS AVAILABLE TO SOAK UP ANY FUEL SPILLAGE.
EMPTY FUEL USING SUITABLE FIRE
PROOF EQUIPMENT INTO AN AUTHORIZED EXPLOSIOWROOF
CONTAINER.
DO NOT EMPTY FUEL
INTO A PIT.
ENSURE THAT WORKING AREA
IS WELL VENTILATED.
ENSURE THAT ANY WORK ON THE FUEL SYSTEM
IS ONLY CARRIED OUT BY EXPERIENCED AND WELL
QUALIFIED MAINTENANCE PERSONNEL.
The fuel filler assembly, supplied complete with serviceable lid, hinge and hinge spring, is fixed to the Body-in-White
(BIW) decking panel by two M5 nuts. Additional parts of the assembly comprise a adjustable rubber buffer, a snap-in
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 77 of 521
Fuel, Emission Control & Engine Management (AJl6)
0
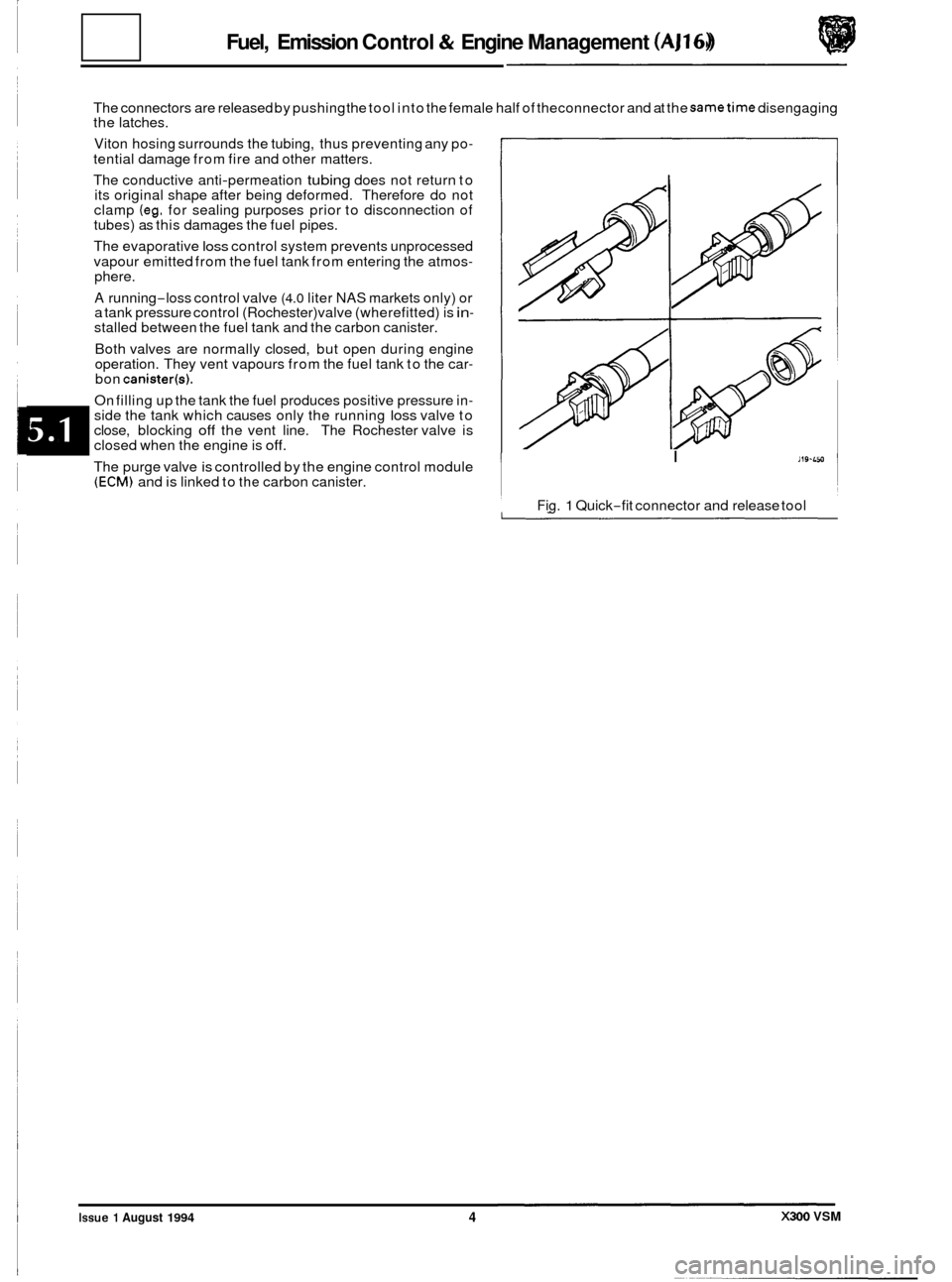
The connectors are released by pushing the tool in to the female half of theconnector and at the sametime disengaging
the latches.
Viton hosing surrounds the tubing, thus preventing any po
-
tential damage from fire and other matters.
The conductive anti
-permeation tubing does not return to
its original shape after being deformed. Therefore do not
clamp
(eg. for sealing purposes prior to disconnection of
tubes) as this damages the fuel pipes.
The evaporative
loss control system prevents unprocessed
vapour emitted from the fuel tank from entering the atmos
- phere.
A running-loss control valve (4.0 liter NAS markets only) or
a tank pressure control (Rochester) valve (wherefitted) is in- stalled between the fuel tank and the carbon canister.
Both valves are normally closed, but open during engine
operation. They vent vapours from the fuel tank to the car
- bon canisterb).
On filling up the tank the fuel produces positive pressure in- side the tank which causes only the running loss valve to
close, blocking off the vent line. The Rochester valve is
closed when the engine is off.
The purge valve is controlled by the engine control module (ECM) and is linked to the carbon canister.
I Jl9-LM
Fig. 1 Quick-fit connector and release tool
0
0
0
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 4