JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 1931 of 2198
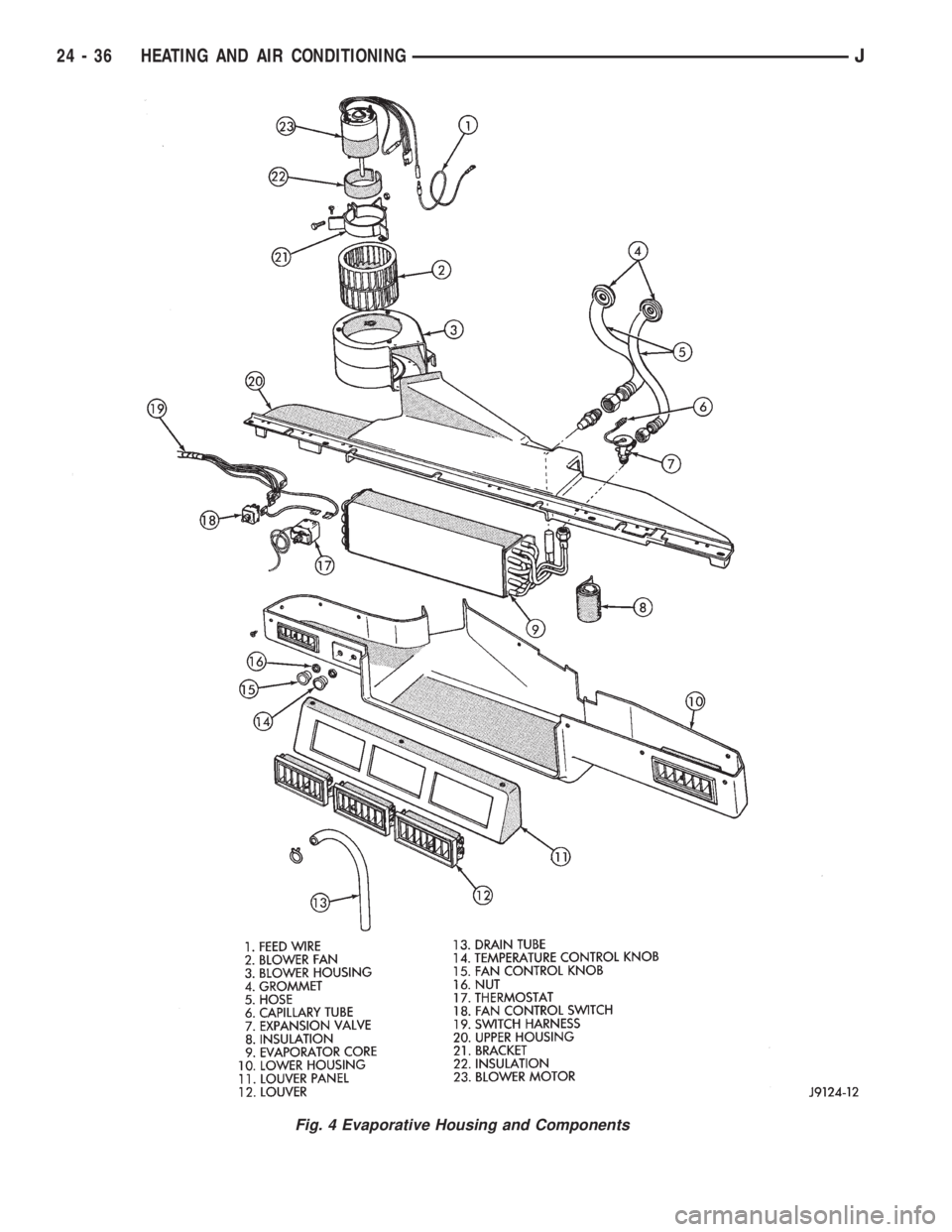
Fig. 4 Evaporative Housing and Components
24 - 36 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGJ
Page 1932 of 2198

TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION ................................................TORQUE
Compressor
Mounting Bolts ............................27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.)
Bracket Bolts ...............................27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.)
Shaft Nut ...............................14.4 Nzm (10.5 ft. lbs.)
JHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 37
Page 1933 of 2198

Page 1934 of 2198

EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION....... 7
EMISSION CONTROLS.................... 4GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
Catalytic Convertor......................... 1
DRB Scan Tool............................ 2
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System........ 1Service Reminder Indicator (SRI) Lamp.......... 1
Vacuum Hose Routing Schematics............. 2
Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label . 1
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of alphabetical designa-
tions is included in the Introduction section at the
beginning of this manual.
Information on the air cleaner housing and the air
cleaner element can be found in Group 14, Fuel Sys-
tems.
CATALYTIC CONVERTOR
Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake
Manifold for information.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
An EGR system is not used with the 2.5L 4 cylin-
der or the 4.0L 6 cylinder engine on any XJ or YJ
model.
SERVICE REMINDER INDICATOR (SRI) LAMP
The instrument panel mounted SRI lamp was for-
merly referred to as the emission maintenance re-
minder (EMR) lamp. It isnot usedon any XJ or YJ
model for the 1995 model year.
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
(VECI) LABEL
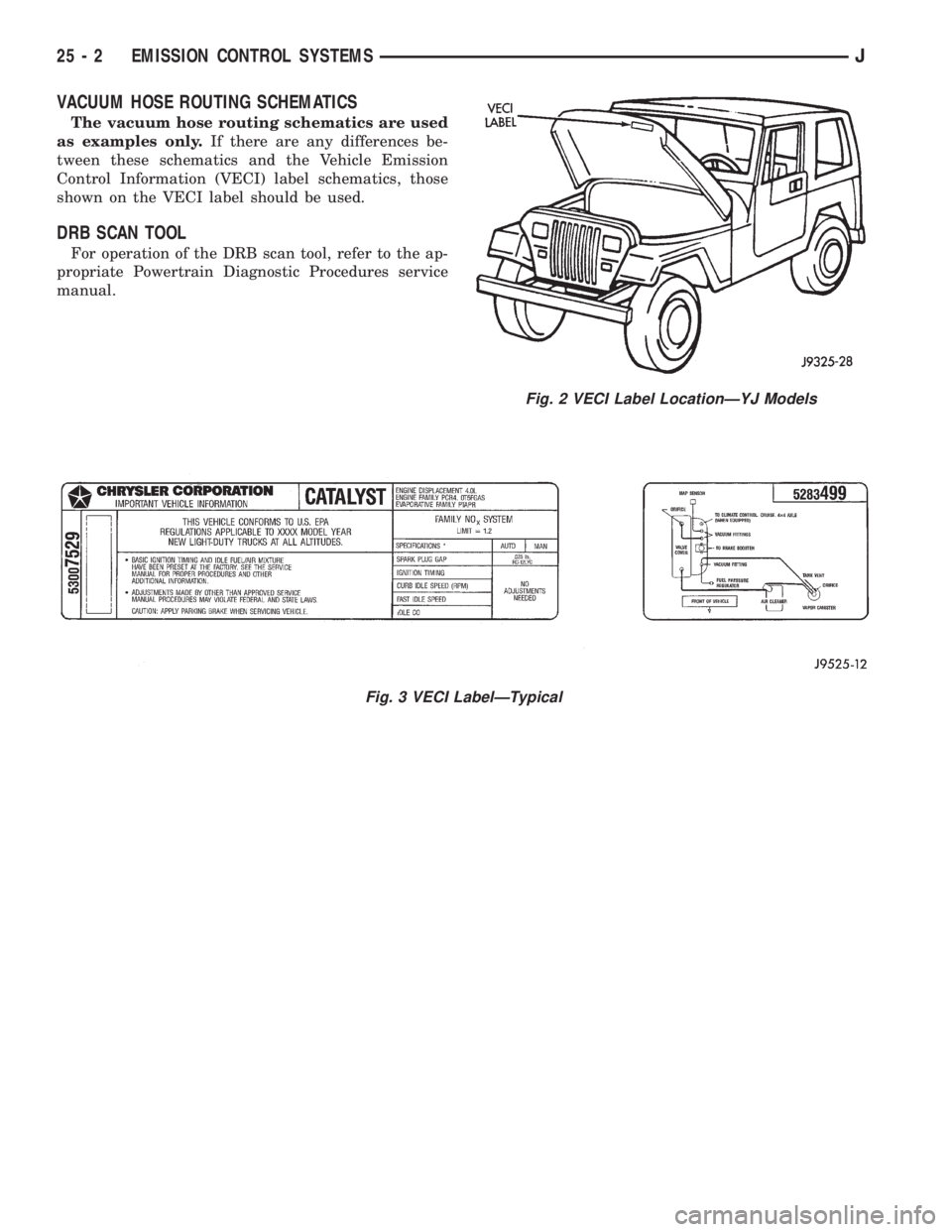
All vehicles are equipped with a combined VECI la-
bel. The label is located in the engine compartment
(Figs. 1 or 2). The label contains the following:
²Engine family and displacement
²Evaporative family
²Emission control system schematic²Certification application
²Engine timing specifications (if adjustable)
²Idle speeds (if adjustable)
²Spark plug and plug gap
The label also contains an engine vacuum sche-
matic. There are unique labels for vehicles built for
sale in the state of California and the country of
Canada. Canadian labels are written in both the En-
glish and French languages. These labels are perma-
nently attached and cannot be removed without
defacing information and destroying label.
The VECI label illustration (Fig. 3) is used as
an example only.Refer to the VECI label located in
the engine compartment (Figs. 1 or 2) for actual
emission information.
Fig. 1 VECI Label LocationÐXJ Models
JEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 1
Page 1935 of 2198
VACUUM HOSE ROUTING SCHEMATICS
The vacuum hose routing schematics are used
as examples only.If there are any differences be-
tween these schematics and the Vehicle Emission
Control Information (VECI) label schematics, those
shown on the VECI label should be used.
DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual.
Fig. 2 VECI Label LocationÐYJ Models
Fig. 3 VECI LabelÐTypical
25 - 2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSJ
Page 1936 of 2198
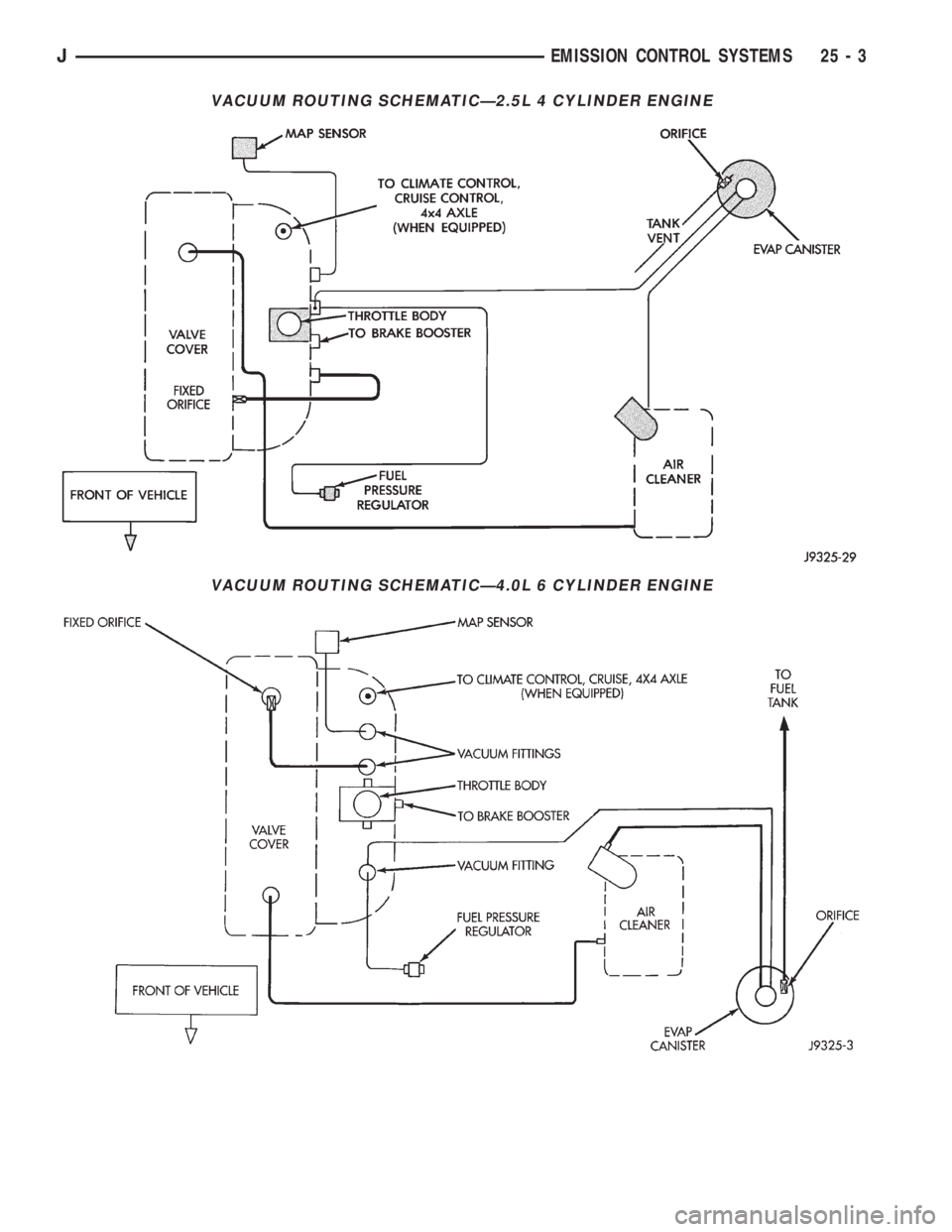
VACUUM ROUTING SCHEMATICÐ2.5L 4 CYLINDER ENGINE
VACUUM ROUTING SCHEMATICÐ4.0L 6 CYLINDER ENGINE
JEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 3
Page 1937 of 2198

EMISSION CONTROLS
INDEX
page page
Crankcase Ventilation System................. 5
EVAP (Evaporation) Control System............ 4
EVAP Canister............................ 4Fuel Tank Filler Tube Cap.................... 4
Oxygen (O2S) Sensor....................... 6
Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve................. 6
EVAP (EVAPORATION) CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The function of the EVAP control system is to pre-
vent the emissions of gasoline vapors from the fuel
tank into the atmosphere. When fuel evaporates in
the fuel tank, the vapors pass through vent hoses or
tubes to a carbon filled EVAP canister. They are tem-
porarily held in the canister until they can be drawn
into the intake manifold when the engine is running.
The EVAP canister is a feature on all models for
the storage of fuel vapors from the fuel tank.
The hoses used in this system are specially
manufactured. If replacement becomes neces-
sary, it is important to use only fuel resistant
hose.
EVAP CANISTER
A sealed, maintenance free, EVAP canister is used
on all vehicles. On XJ models, the EVAP canister is
located in the engine compartment on the passenger
side frame rail (Fig. 4). On YJ models, the EVAP can-
ister is located in the engine compartment on the
dash panel and below the brake master cylinder (Fig.
5). The EVAP canister is filled with granules of an
activated carbon mixture. Fuel vapors entering the
EVAP canister are absorbed by the charcoal granules.
CANISTER OPERATION
Vacuum is used to control and operate the
EVAP canister. No electrical circuitry is used to
control or operate the EVAP system.
The EVAP canister is equipped with a vacuum con-
trolled purge shutoff switch (orifice) (Figs. 4 or 5)
that controls canister purge operation. The switch is
open when manifold vacuum is applied to it. When
the engine is operating, the EVAP canister purge
function draws fresh air through the top of the can-
ister. This causes the stored vapors to be drawn out
of the canister and into the airstream in the air
cleaner snorkel (Fig. 6).
The air cleaner contains a venturi in the air
cleaner cover used as a purge line vacuum source
(Fig. 6). The venturi effect increases the speed of the
intake air flowing by the slots in the venturi wall.
This creates a low pressure area around the slots.
When the purge shutoff switch is open, vapors from
the canister are drawn through slots and into the air-
stream flowing through the venturi (Fig. 7). The va-
pors pass through the intake manifold into the
engine combustion chambers where they are con-
sumed during engine combustion.
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE CAP
The fuel tank filler tube cap (fuel tank cap) incor-
porates a two-way pressure/relief valve that is closed
to atmosphere during normal operating conditions.Fig. 4 EVAP Canister LocationÐXJ Models
Fig. 5 EVAP Canister LocationÐYJ Models
25 - 4 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSJ
Page 1938 of 2198

The relief valve used in fuel filler caps of all models
is calibrated at a pressure of 10 kPa (1.5 psi) or a
vacuum of 6 kPa (1.8 in. Hg). When the pressure or
vacuum is relieved, the valve returns to the normally
closed position.
CAUTION: The fuel filler cap must be removed prior
to disconnecting any fuel system component.
CRANKCASE VENTILATION SYSTEM
All 2.5L 4 cylinder and 4.0L 6 cylinder engines are
equipped with a Crankcase Ventilation (CCV) system(Figs. 8 or 9). The CCV system performs the same
function as a conventional PCV system, but does not
use a vacuum controlled valve.
On 4.0L 6 cylinder engines, a molded vacuum tube
connects manifold vacuum to top of cylinder head
(valve) cover at dash panel end. The vacuum tube
contains a fixed orifice of a calibrated size. It meters
the amount of crankcase vapors drawn out of the en-
gine.
On 2.5L 4 cylinder engines, a fitting on drivers side
of cylinder head (valve) cover contains the metered
orifice. It is connected to manifold vacuum.
A fresh air supply hose from the air cleaner is con-
nected to front of cylinder head cover on 4.0L en-
gines. It is connected to rear of cover on 2.5L
engines.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Manifold
vacuum draws the vapor/air mixture through the
fixed orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors
are then consumed during combustion.
Fig. 6 EVAP SystemÐTypical
Fig. 7 Air Cleaner VenturiÐTypical
Fig. 8 CCV SystemÐ2.5L EngineÐTypical
Fig. 9 CCV SystemÐ4.0L EngineÐTypical
JEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 5
Page 1939 of 2198
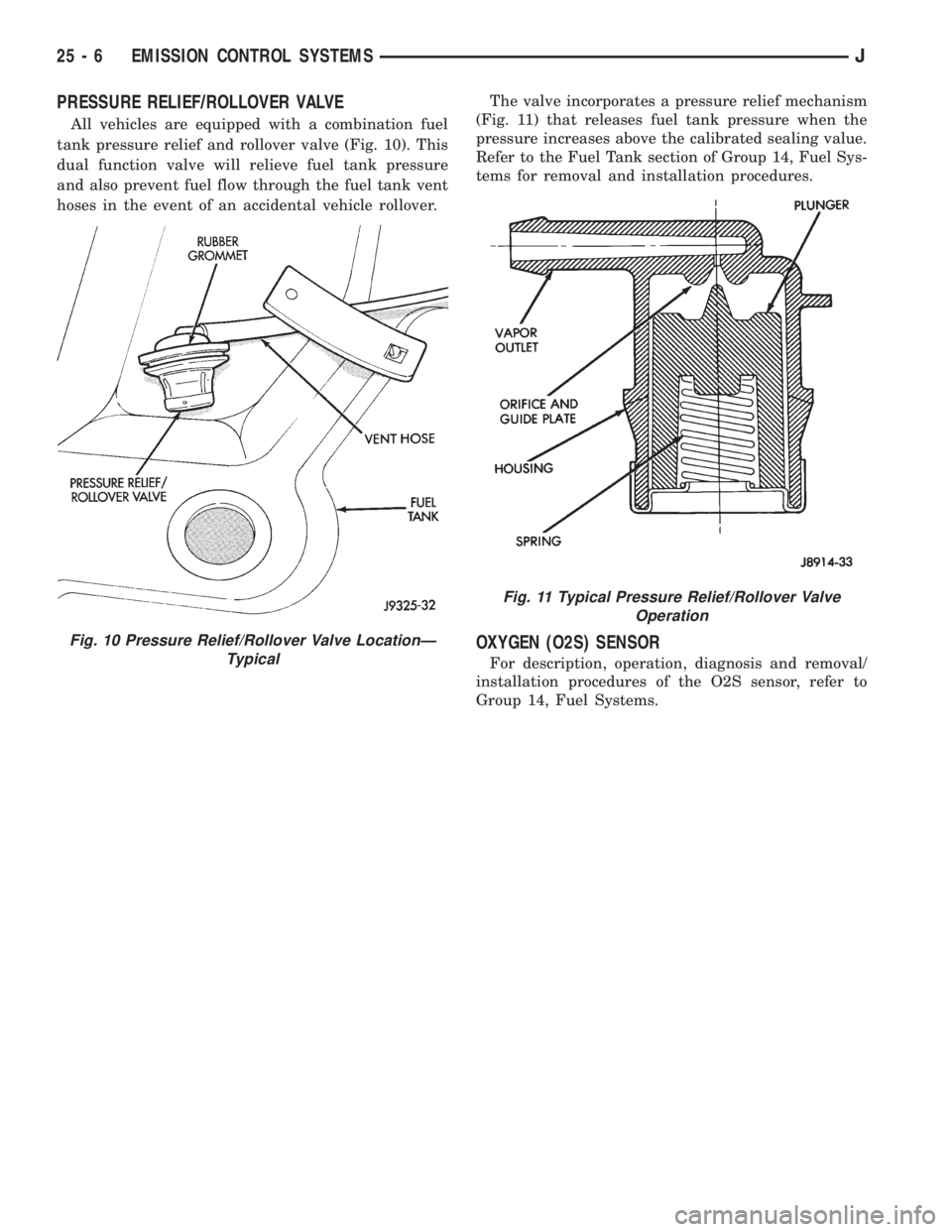
PRESSURE RELIEF/ROLLOVER VALVE
All vehicles are equipped with a combination fuel
tank pressure relief and rollover valve (Fig. 10). This
dual function valve will relieve fuel tank pressure
and also prevent fuel flow through the fuel tank vent
hoses in the event of an accidental vehicle rollover.The valve incorporates a pressure relief mechanism
(Fig. 11) that releases fuel tank pressure when the
pressure increases above the calibrated sealing value.
Refer to the Fuel Tank section of Group 14, Fuel Sys-
tems for removal and installation procedures.
OXYGEN (O2S) SENSOR
For description, operation, diagnosis and removal/
installation procedures of the O2S sensor, refer to
Group 14, Fuel Systems.
Fig. 10 Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve LocationÐ
Typical
Fig. 11 Typical Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve
Operation
25 - 6 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSJ
Page 1940 of 2198
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
INDEX
page page
Air Cleaner Element........................ 7
Coolant Temperature Sensor.................. 7
EVAP Canister............................ 7
Fuel Tank Filler Tube Cap.................... 7Oxygen (O2S) Sensor....................... 7
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).............. 7
Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve................. 7
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
For removal and installation procedures of both the
air cleaner housing and the air cleaner element, refer
to the Group 14, Fuel System.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
For description, operation, diagnosis and removal/
installation procedures of the engine coolant temper-
ature sensor, refer to Group 14, Fuel Systems.
EVAP CANISTER
On XJ models, the EVAP canister is located in the
engine compartment on the passenger side frame rail
(Fig. 1). On YJ models, the EVAP canister is located
in the engine compartment on the dash panel and be-
low the brake master cylinder (Fig. 2).
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
(1) Disconnect the vacuum lines at the EVAP can-
ister. Note location of lines before removal.(2) Remove canister retaining strap bolt.
(3) Remove canister from vehicle.
Reverse the procedure for installation.
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE CAP
If replacement of the fuel filler tube cap (fuel tank
cap) is necessary, it must be replaced with aniden-
tical capto be sure of correct system operation.
OXYGEN (O2S) SENSOR
For description, operation, diagnosis and removal/
installation procedures of the O2S sensor, refer to
Group 14, Fuel Systems.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
For removal and installation procedures, refer to
Group 14, Fuel Systems.
PRESSURE RELIEF/ROLLOVER VALVE
For removal and installation procedures, refer to
the Fuel Tank section of Group 14, Fuel Systems.
Fig. 1 EVAP CanisterÐXJ Models
Fig. 2 EVAP CanisterÐYJ Models
JEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 7