torque MAZDA 6 2002 Suplement Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 470 of 909
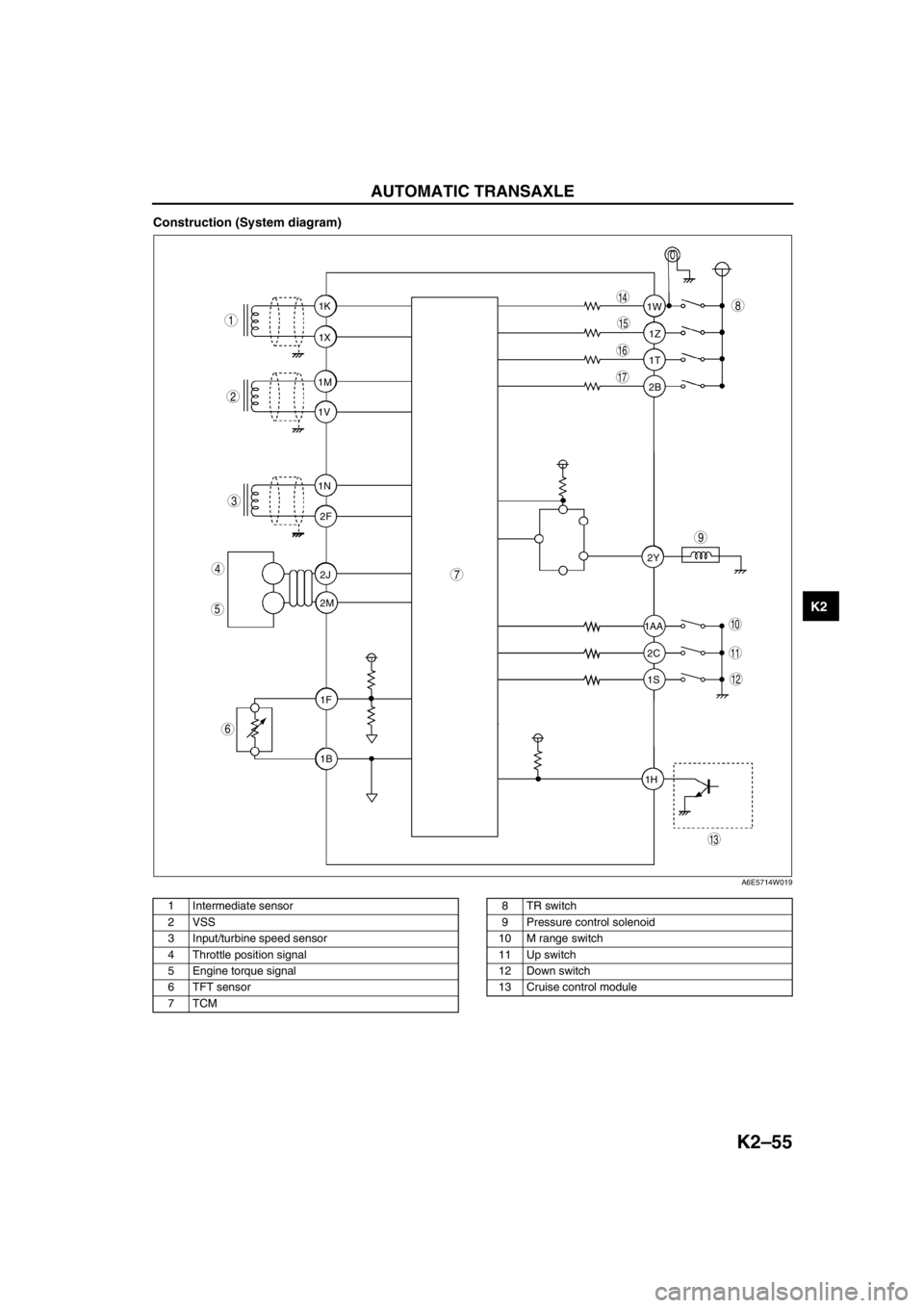
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–55
K2
Construction (System diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
1AA
2C 2Y
1S
1H2B 1K
1X
1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W019
1 Intermediate sensor
2 VSS
3 Input/turbine speed sensor
4 Throttle position signal
5 Engine torque signal
6 TFT sensor
7TCM8TR switch
9 Pressure control solenoid
10 M range switch
11 Up switch
12 Down switch
13 Cruise control module
Page 471 of 909
K2–56
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
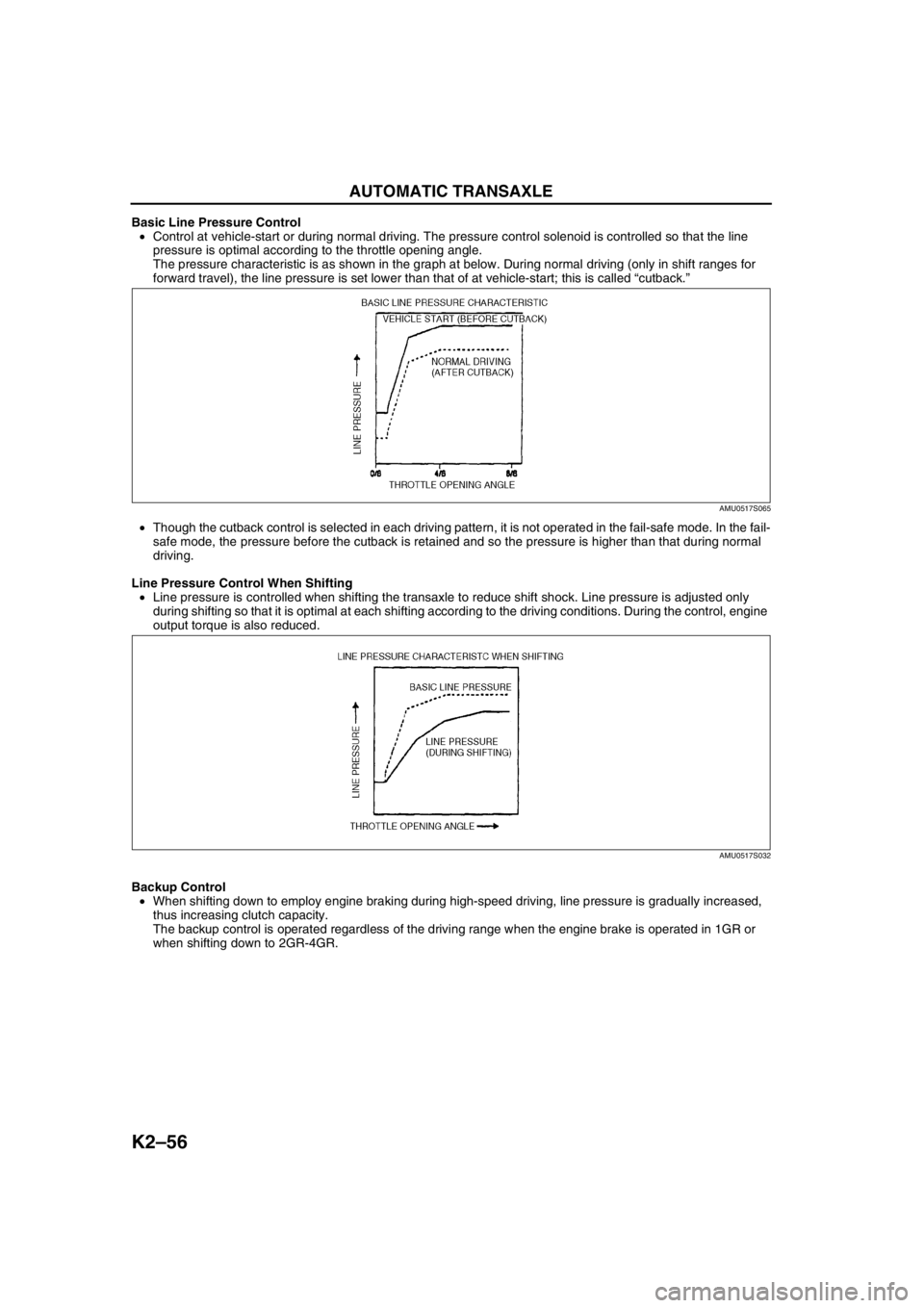
Basic Line Pressure Control
•Control at vehicle-start or during normal driving. The pressure control solenoid is controlled so that the line
pressure is optimal according to the throttle opening angle.
The pressure characteristic is as shown in the graph at below. During normal driving (only in shift ranges for
forward travel), the line pressure is set lower than that of at vehicle-start; this is called “cutback.”
•Though the cutback control is selected in each driving pattern, it is not operated in the fail-safe mode. In the fail-
safe mode, the pressure before the cutback is retained and so the pressure is higher than that during normal
driving.
Line Pressure Control When Shifting
•Line pressure is controlled when shifting the transaxle to reduce shift shock. Line pressure is adjusted only
during shifting so that it is optimal at each shifting according to the driving conditions. During the control, engine
output torque is also reduced.
Backup Control
•When shifting down to employ engine braking during high-speed driving, line pressure is gradually increased,
thus increasing clutch capacity.
The backup control is operated regardless of the driving range when the engine brake is operated in 1GR or
when shifting down to 2GR-4GR.
AMU0517S065
AMU0517S032
Page 473 of 909
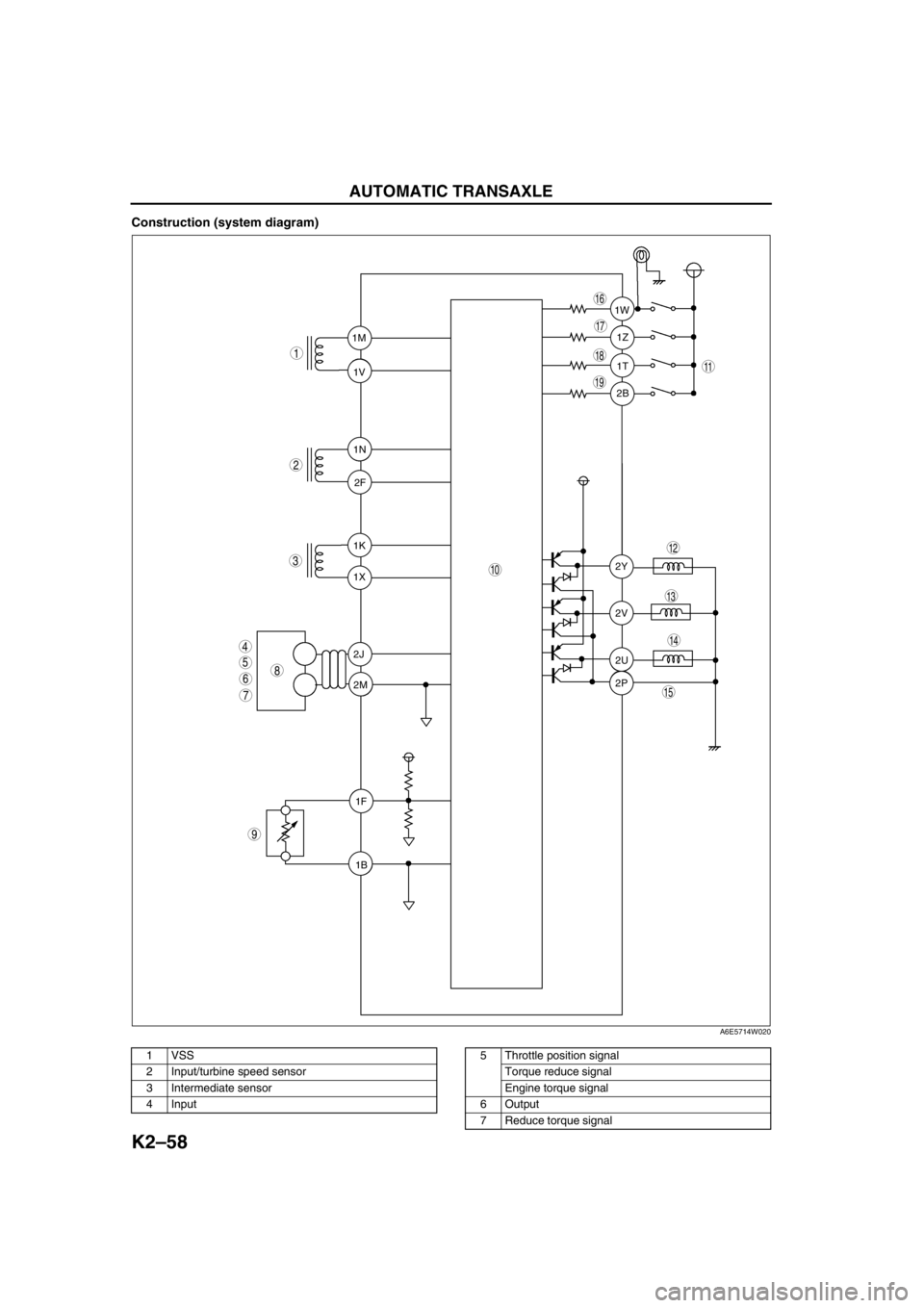
K2–58
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Construction (system diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
2B
2Y
2V
2U
2P 1K
1X 1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
19
18
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W020
1 VSS
2 Input/turbine speed sensor
3 Intermediate sensor
4 Input5 Throttle position signal
Torque reduce signal
Engine torque signal
6Output
7 Reduce torque signal
Page 474 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–59
K2
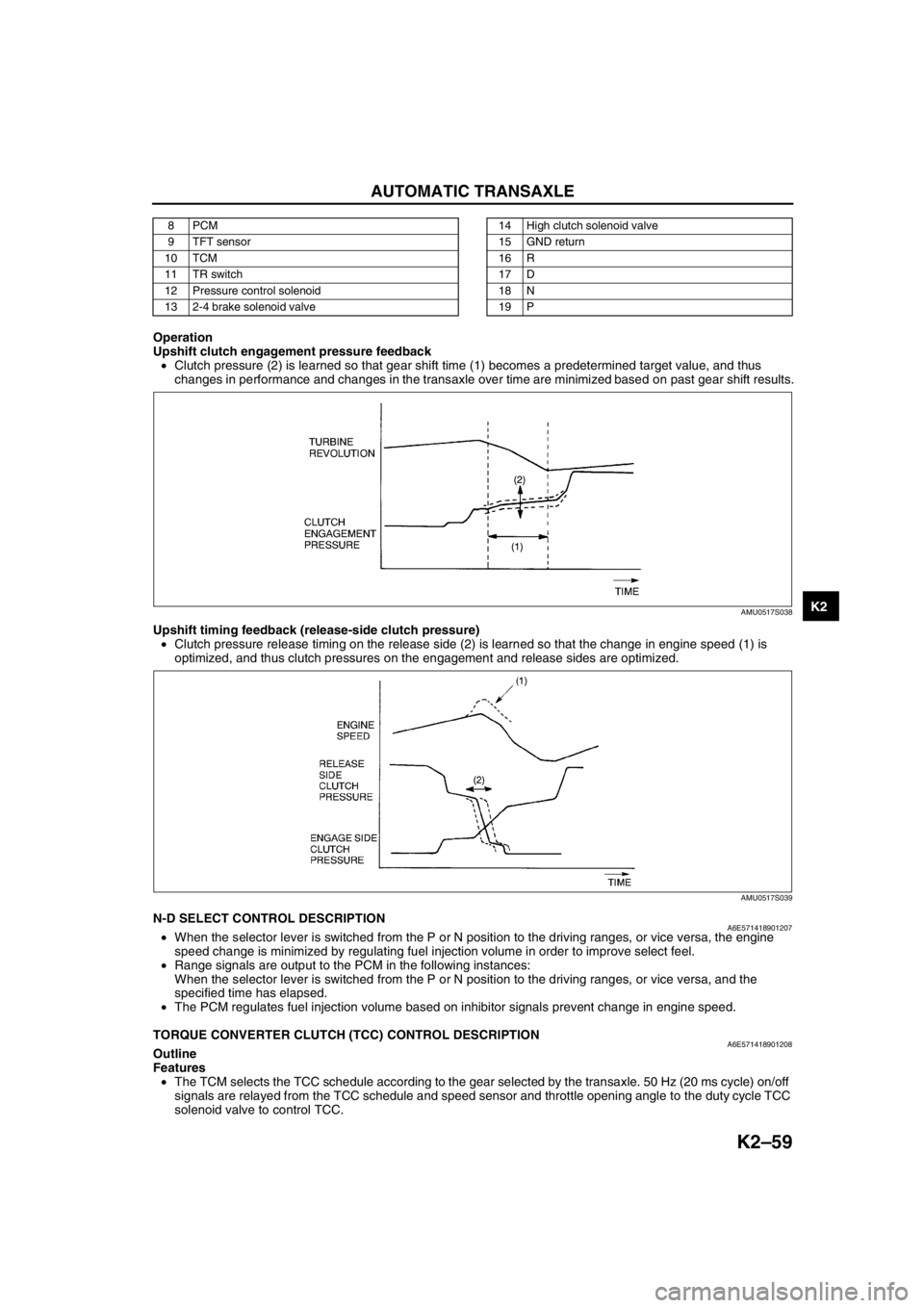
Operation
Upshift clutch engagement pressure feedback
•Clutch pressure (2) is learned so that gear shift time (1) becomes a predetermined target value, and thus
changes in performance and changes in the transaxle over time are minimized based on past gear shift results.
Upshift timing feedback (release-side clutch pressure)
•Clutch pressure release timing on the release side (2) is learned so that the change in engine speed (1) is
optimized, and thus clutch pressures on the engagement and release sides are optimized.
End Of SieN-D SELECT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901207•When the selector lever is switched from the P or N position to the driving ranges, or vice versa, the engine
speed change is minimized by regulating fuel injection volume in order to improve select feel.
•Range signals are output to the PCM in the following instances:
When the selector lever is switched from the P or N position to the driving ranges, or vice versa, and the
specified time has elapsed.
•The PCM regulates fuel injection volume based on inhibitor signals prevent change in engine speed.
End Of Sie
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901208Outline
Features
•The TCM selects the TCC schedule according to the gear selected by the transaxle. 50 Hz (20 ms cycle) on/off
signals are relayed from the TCC schedule and speed sensor and throttle opening angle to the duty cycle TCC
solenoid valve to control TCC.
8PCM
9 TFT sensor
10 TCM
11 TR switch
12 Pressure control solenoid
13 2-4 brake solenoid valve14 High clutch solenoid valve
15 GND return
16 R
17 D
18 N
19 P
AMU0517S038
AMU0517S039
Page 476 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–61
K2
Operation
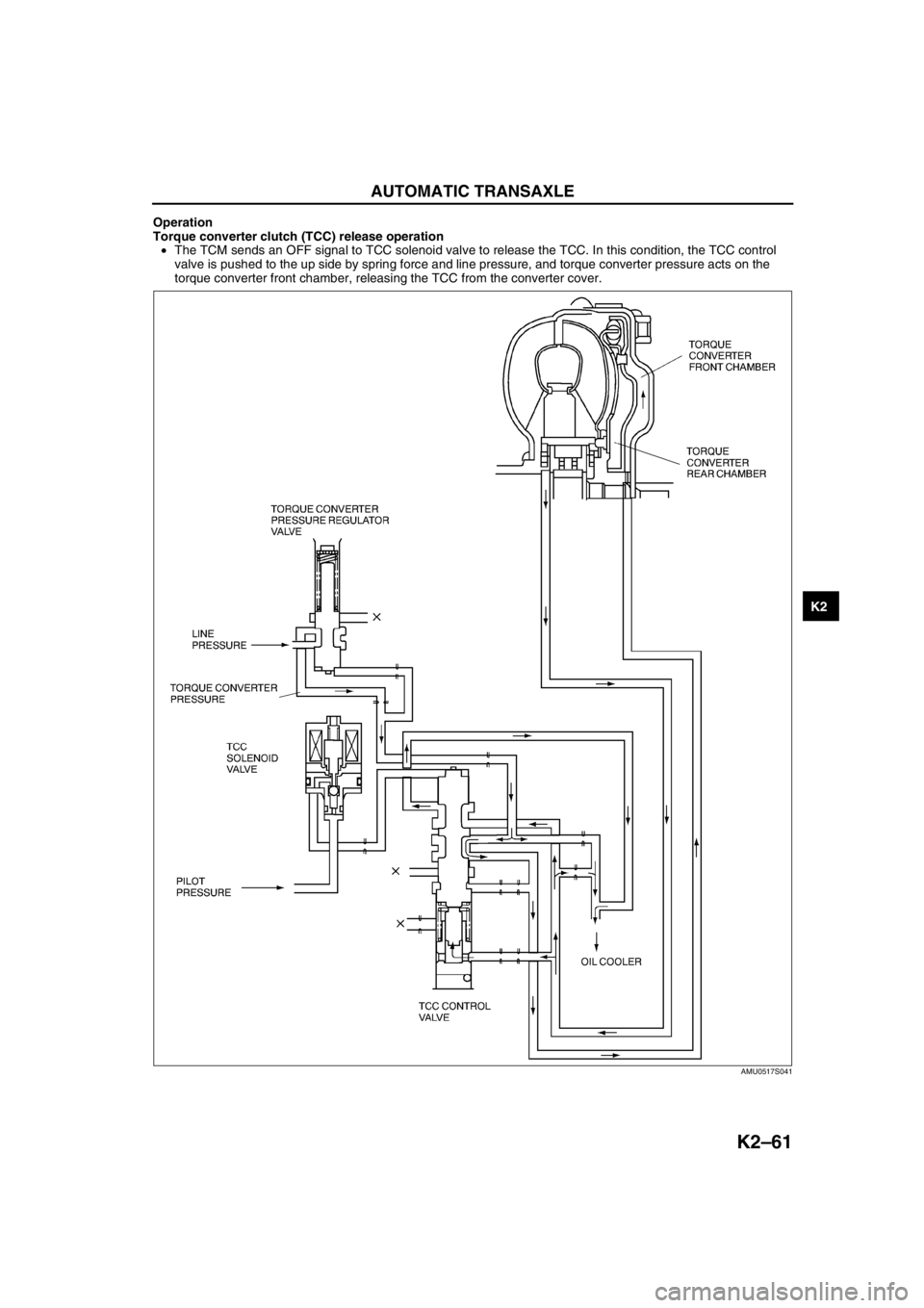
Torque converter clutch (TCC) release operation
•The TCM sends an OFF signal to TCC solenoid valve to release the TCC. In this condition, the TCC control
valve is pushed to the up side by spring force and line pressure, and torque converter pressure acts on the
torque converter front chamber, releasing the TCC from the converter cover.
AMU0517S041
Page 477 of 909
K2–62
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
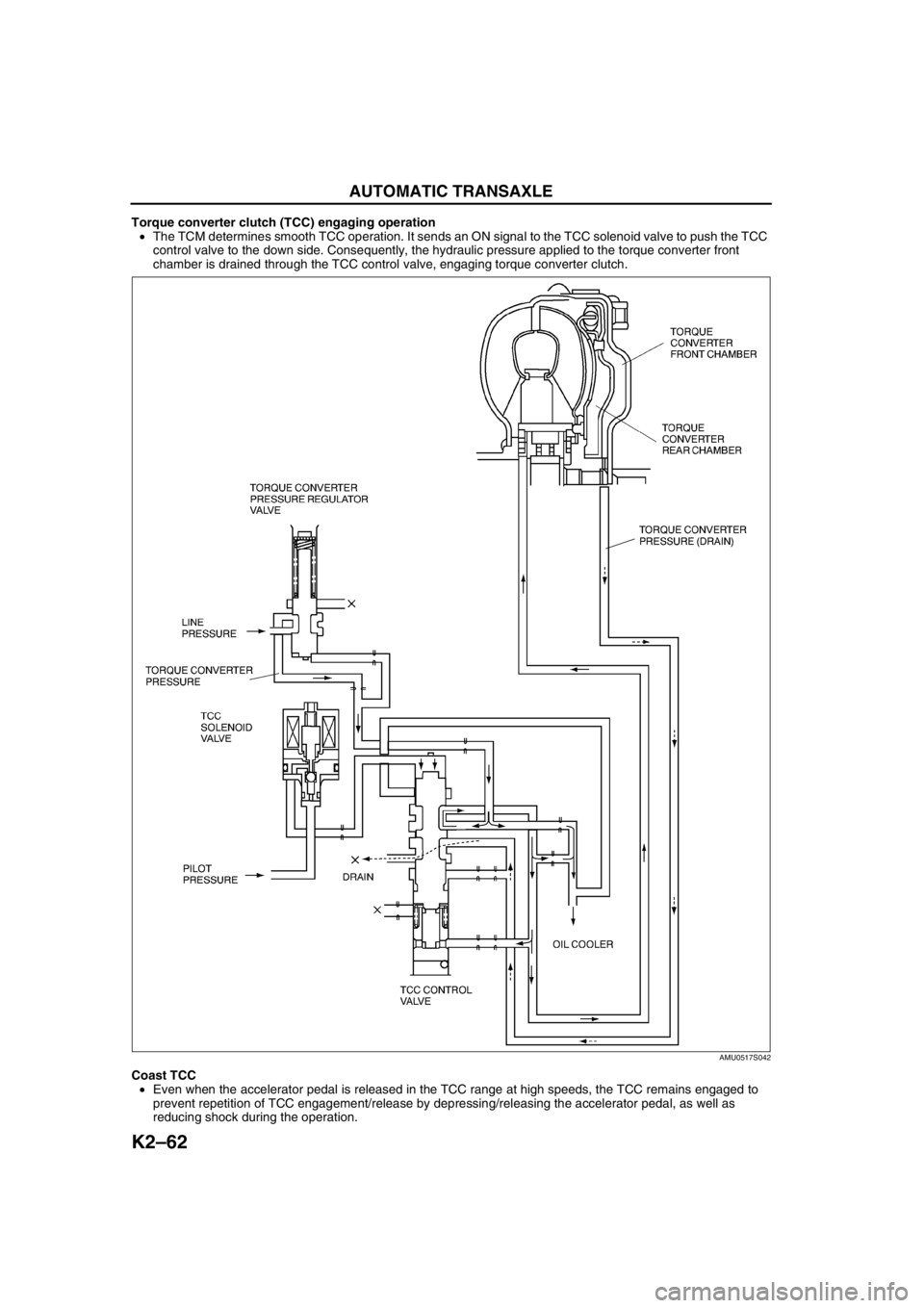
Torque converter clutch (TCC) engaging operation
•The TCM determines smooth TCC operation. It sends an ON signal to the TCC solenoid valve to push the TCC
control valve to the down side. Consequently, the hydraulic pressure applied to the torque converter front
chamber is drained through the TCC control valve, engaging torque converter clutch.
Coast TCC
•Even when the accelerator pedal is released in the TCC range at high speeds, the TCC remains engaged to
prevent repetition of TCC engagement/release by depressing/releasing the accelerator pedal, as well as
reducing shock during the operation.
AMU0517S042
Page 478 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–63
K2
Determination of Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Cancellation
The TCC control is canceled when any of the following condition are met:
•Engine coolant temperature is low.
•ATF temperature is low.
•Brake switch is on (when depressing the brake pedal).
•Accelerator depressing speed and accelerator opening angle are above the set value.
•Engine speed signal is below the set value.
•Failure is in the TCC control system detected by diagnosis function.
End Of Sie
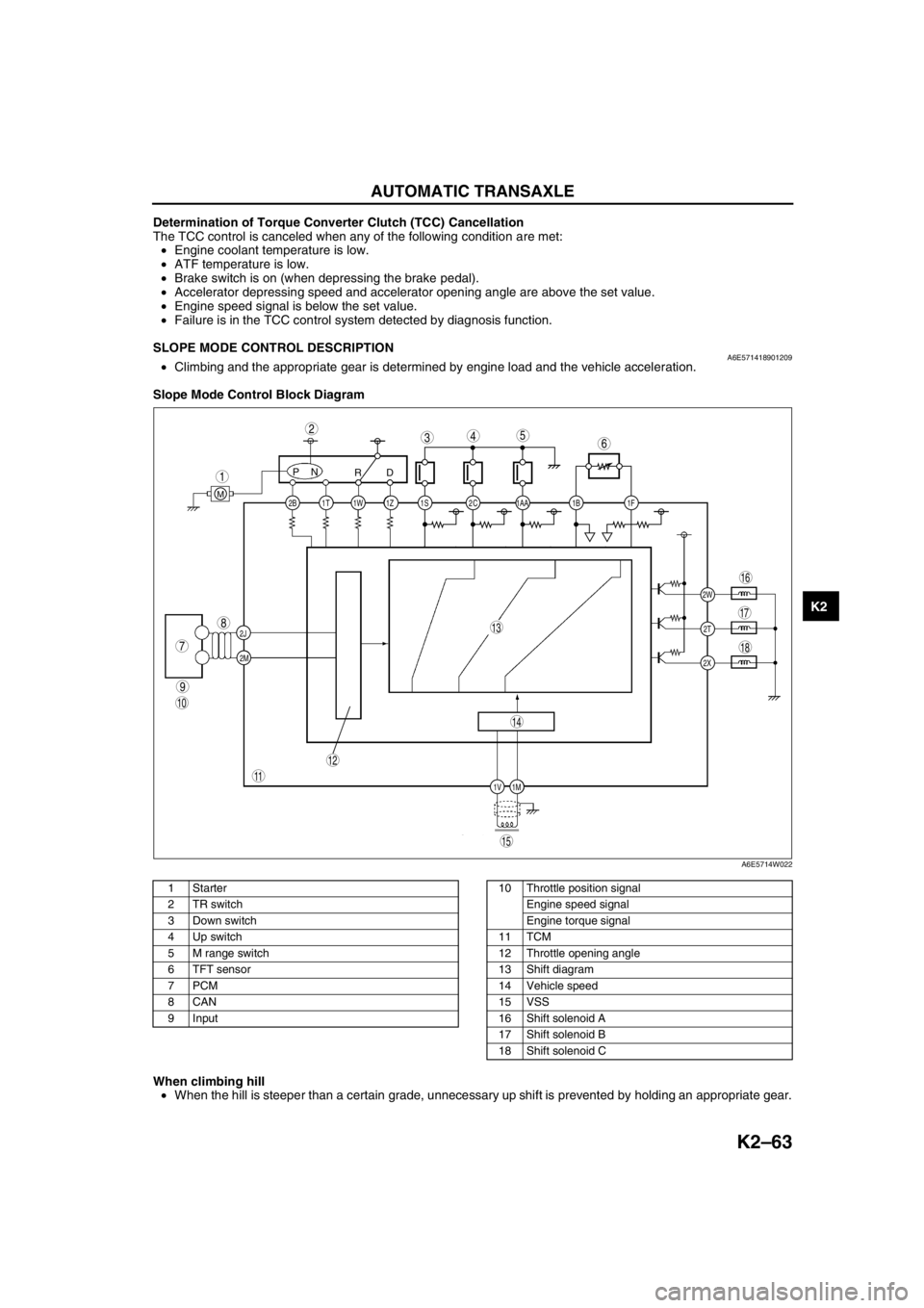
SLOPE MODE CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901209•Climbing and the appropriate gear is determined by engine load and the vehicle acceleration.
Slope Mode Control Block Diagram
.
When climbing hill
•When the hill is steeper than a certain grade, unnecessary up shift is prevented by holding an appropriate gear.
End Of Sie
2C 2B
2J
2M1AA 1S 1T 1Z1W 1B 1F
2W
1M 1V2T
2X
PN
RD
M
9
8
7
543
1
2
10
18
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W022
1Starter
2 TR switch
3 Down switch
4 Up switch
5 M range switch
6 TFT sensor
7PCM
8CAN
9 Input10 Throttle position signal
Engine speed signal
Engine torque signal
11 TCM
12 Throttle opening angle
13 Shift diagram
14 Vehicle speed
15 VSS
16 Shift solenoid A
17 Shift solenoid B
18 Shift solenoid C
Page 480 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–65
K2
Memory Function
•The memory function stores failure information detected in the failure detection function. Once failure
information is stored, the memory will not be cleared even when the ignition switch is turned off (LOCK
position) or the malfunction is repaired.
•The stored memory (failure information) can be cleared by using the WDS or disconnecting the negative
battery cable.
Failure Indication Function
•The failure indication function illuminates the AT warning lights when the failure detection function determines
there is a malfunction.
DTC Table
X : Available
CCM:Continuous monitor
Fail-safe Function
•In the fail-safe function, minimum vehicle drivability is obtained by changing the signals that are determined as
malfunctions by the failure detection function to the preset values, and limiting the TCM control.
DTC No. On-board diagnostic function MILAT warning
light
indicationDCMonitor
itemMemory
function
P0705 TR switch circuit malfunction (Power short circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0706 TR switch circuit malfunction (Open/ground short circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0711 TFT sensor malfunction (Stuck) X–2 CCM X
P0712 TFT sensor circuit malfunction (Short circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0713 TFT sensor circuit malfunction (Open circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0715 Input/turbine speed sensor circuit malfunction X X 2 CCM X
P0720 Vehicle speedometer sensor circuit malfunction X X 2 CCM X
P0740 TCC system X–2 CCM X
P0743 TCC solenoid valve malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0748 Pressure control solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0751 Shift solenoid A malfunction (Stuck off) X–2 CCM X
P0752 Shift solenoid A malfunction (Stuck on) X–2 CCM X
P0753 Shift solenoid A malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0756 Shift solenoid B malfunction (Stuck off) X–2 CCM X
P0757 Shift solenoid B malfunction (Stuck on) X–2 CCM X
P0758 Shift solenoid B malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0761 Shift solenoid C malfunction (Stuck off) X–2 CCM X
P0762 Shift solenoid C malfunction (Stuck on) X–2 CCM X
P0763 Shift solenoid C malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0768 Reduction timing solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0773 Neutral shift solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0778 2-4 brake solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0791 Intermediate sensor malfunction (Open/short) X X 2 CCM X
P0798 High clutch solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P1710 GND return malfunction–––Other X
U0073 CAN BUS OFF X X 1 CCM X
U0100 TCM cannot receive any signals from PCM X X 1 CCM X
DTC
No.On-board diagnostic function Detection condition Fail-safe TCC
P0705Transaxle range (TR) switch
circuit malfunction (power short
circuit)•Two or more range signals
are inputted from TR switch
for 5 seconds or more•TR switch priority
D > N > P > R
•Inhibits feedback control,
SLOPE mode, torque
reduction controlAvailable
P0706Transaxle range (TR) switch
circuit malfunction (open/ground
short circuit)•No range signal is inputted
from TR switch for 100
seconds or more•Inhibits feedback control,
SLOPE mode, torque
reduction controlAvailable
Page 481 of 909
K2–66
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
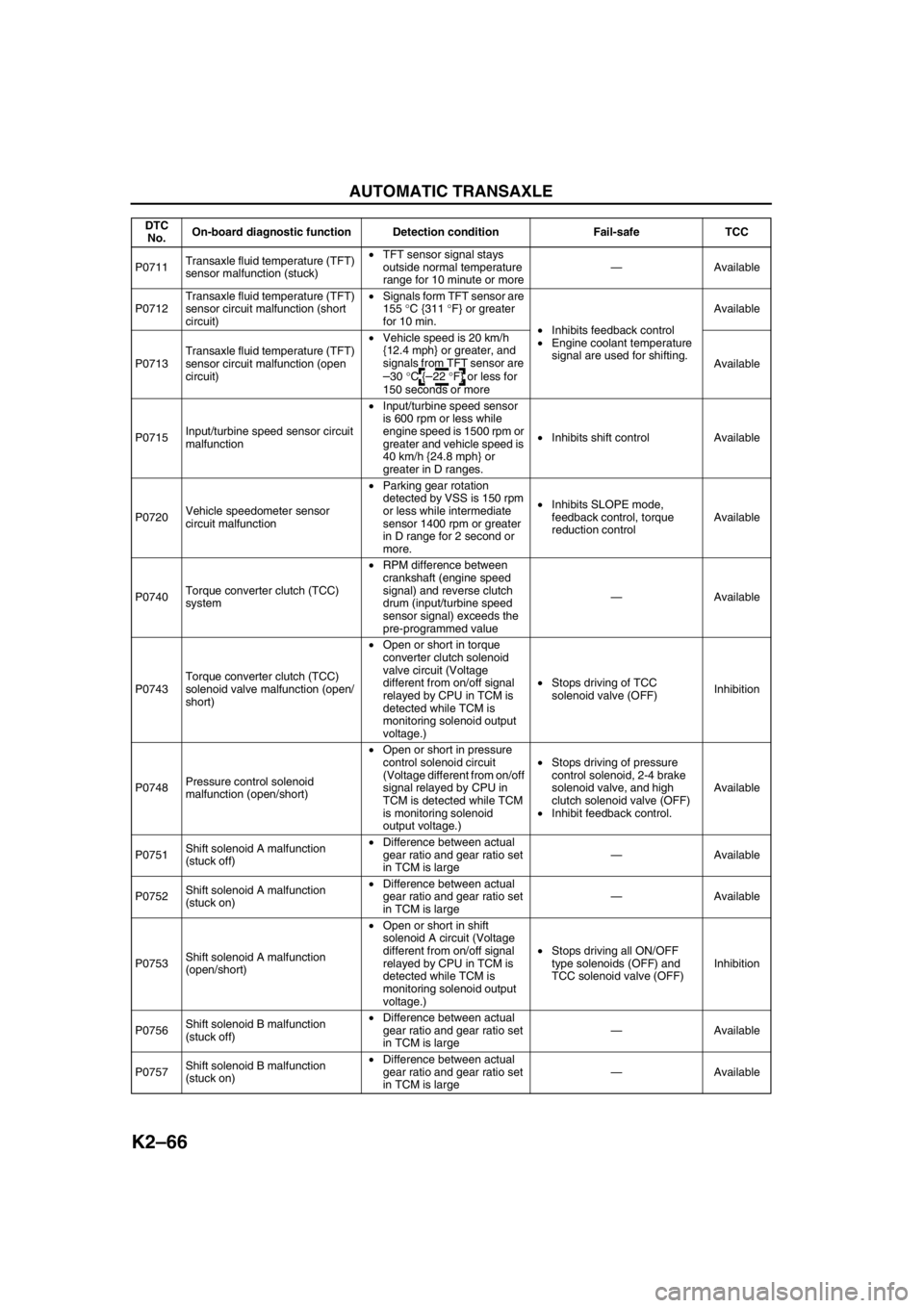
P0711Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT)
sensor malfunction (stuck)•TFT sensor signal stays
outside normal temperature
range for 10 minute or more—Available
P0712Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT)
sensor circuit malfunction (short
circuit)•Signals form TFT sensor are
155 °C {311 °F} or greater
for 10 min.
•Inhibits feedback control
•Engine coolant temperature
signal are used for shifting.Available
P0713Transaxle fluid temperature (TFT)
sensor circuit malfunction (open
circuit)•Vehicle speed is 20 km/h
{12.4 mph} or greater, and
signals from TFT sensor are
–30 °C {–22 °F} or less for
150 seconds or moreAvailable
P0715Input/turbine speed sensor circuit
malfunction•Input/turbine speed sensor
is 600 rpm or less while
engine speed is 1500 rpm or
greater and vehicle speed is
40 km/h {24.8 mph} or
greater in D ranges.•Inhibits shift control Available
P0720Vehicle speedometer sensor
circuit malfunction•Parking gear rotation
detected by VSS is 150 rpm
or less while intermediate
sensor 1400 rpm or greater
in D range for 2 second or
more.•Inhibits SLOPE mode,
feedback control, torque
reduction controlAvailable
P0740Torque converter clutch (TCC)
system•RPM difference between
crankshaft (engine speed
signal) and reverse clutch
drum (input/turbine speed
sensor signal) exceeds the
pre-programmed value—Available
P0743Torque converter clutch (TCC)
solenoid valve malfunction (open/
short)•Open or short in torque
converter clutch solenoid
valve circuit (Voltage
different from on/off signal
relayed by CPU in TCM is
detected while TCM is
monitoring solenoid output
voltage.)•Stops driving of TCC
solenoid valve (OFF)Inhibition
P0748Pressure control solenoid
malfunction (open/short)•Open or short in pressure
control solenoid circuit
(Voltage different from on/off
signal relayed by CPU in
TCM is detected while TCM
is monitoring solenoid
output voltage.)•Stops driving of pressure
control solenoid, 2-4 brake
solenoid valve, and high
clutch solenoid valve (OFF)
•Inhibit feedback control.Available
P0751Shift solenoid A malfunction
(stuck off)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0752Shift solenoid A malfunction
(stuck on)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0753Shift solenoid A malfunction
(open/short)•Open or short in shift
solenoid A circuit (Voltage
different from on/off signal
relayed by CPU in TCM is
detected while TCM is
monitoring solenoid output
voltage.)•Stops driving all ON/OFF
type solenoids (OFF) and
TCC solenoid valve (OFF)Inhibition
P0756Shift solenoid B malfunction
(stuck off)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0757Shift solenoid B malfunction
(stuck on)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available DTC
No.On-board diagnostic function Detection condition Fail-safe TCC
Page 482 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–67
K2
P0758Shift solenoid B malfunction
(open/short)•Open or short in shift
solenoid B circuit (Voltage
different from on/off signal
relayed by CPU in TCM is
detected while TCM is
monitoring solenoid output
voltage.)•Stops driving all ON/OFF
type solenoids (OFF) and
TCC solenoid valve (OFF)Inhibition
P0761Shift solenoid C malfunction
(stuck off)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0762Shift solenoid C malfunction
(stuck on)•Difference between actual
gear ratio and gear ratio set
in TCM is large—Available
P0763Shift solenoid C malfunction
(open/short)•Open or short in shift
solenoid C circuit (Voltage
different from on/off signal
relayed by CPU in TCM is
detected while TCM is
monitoring solenoid output
voltage.)•Stops driving all ON/OFF
type solenoids (OFF) and
TCC solenoid valve (OFF)Inhibition
P0768Reduction timing solenoid valve
malfunction (open/short)•Open or short in reduction
timing solenoid valve circuit
(Voltage different from on/off
signal relayed by CPU in
TCM is detected while TCM
is monitoring solenoid
output voltage.)•Stops driving of reduction
timing solenoid valve (OFF)Available
P0773Neutral shift solenoid valve
malfunction (open/short)•Open or short in neutral shift
solenoid valve circuit
(Voltage different from on/off
signal relayed by CPU in
TCM is detected while TCM
is monitoring solenoid
output voltage.)•Stops driving of neutral shift
solenoid valve (OFF)Available
P07782-4 brake solenoid valve
malfunction (open/short)•Open or short in 2-4 brake
solenoid valve circuit
(Voltage different from on/off
signal relayed by CPU in
TCM is detected while TCM
is monitoring solenoid
output voltage.)•Stops driving of pressure
control solenoid, 2-4 brake
solenoid valve, and high
clutch solenoid valve (OFF)
•Inhibit feedback control.Available
P0791Intermediate sensor malfunction
(open/short)•Rotation speed of output
gear (intermediate sensor)
is low when vehicle speed
and engine speed exceed
the pre programmed value•Inhibit feedback control
•Inhibits torque reduction
controlAvailable
P0798High clutch solenoid valve
malfunction (open/short)•Open or short in high clutch
solenoid valve circuit
(Voltage different from on/off
signal relayed by CPU in
TCM is detected while TCM
is monitoring solenoid
output voltage.)•Stops driving of pressure
control solenoid, 2-4 brake
solenoid valve, and high
clutch solenoid valve (OFF)
•Inhibit feedback control.Available
P1710 GND return malfunction•TCM detects open in GND
return signal of solenoid.—Available
U0073 CAN BUS OFF•CAN controller damaged.•Throttle valve opening angle
is fixed (4/8) at the time in
order to determine shift
•Maximizes line pressureInhibition
U0100TCM cannot receive any signals
from PCM•TCM cannot receive any
signals from PCM DTC
No.On-board diagnostic function Detection condition Fail-safe TCC