MAZDA 6 2002 Workshop Manual Suplement
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 761 of 909
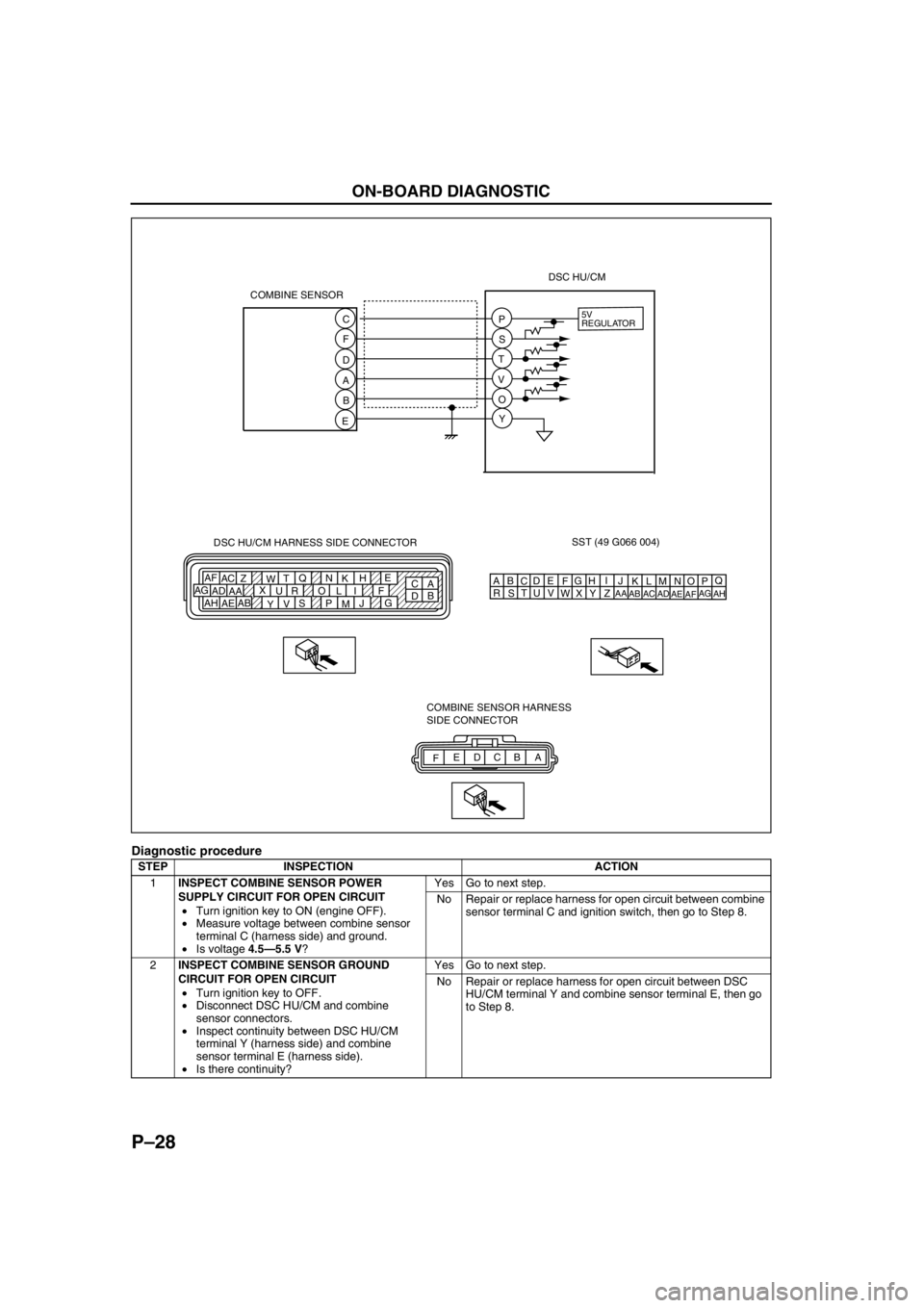
P–28
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
Diagnostic procedure
STEP INSPECTION ACTION
1INSPECT COMBINE SENSOR POWER
SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
•Turn ignition key to ON (engine OFF).
•Measure voltage between combine sensor
terminal C (harness side) and ground.
•Is voltage 4.5—5.5 V?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for open circuit between combine
sensor terminal C and ignition switch, then go to Step 8.
2INSPECT COMBINE SENSOR GROUND
CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
•Turn ignition key to OFF.
•Disconnect DSC HU/CM and combine
sensor connectors.
•Inspect continuity between DSC HU/CM
terminal Y (harness side) and combine
sensor terminal E (harness side).
•Is there continuity?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for open circuit between DSC
HU/CM terminal Y and combine sensor terminal E, then go
to Step 8.
SST (49 G066 004)
AQ
B
CDE
FG
HI
J DSC HU/CM HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
A
C E
H
K N Q
T
W Z AC AF
F I L O R U X
AA AD AG
G
J
M P S
V
Y AB
AE AHB
DKN
T
WZ
AC
AFLO
RU
XAA
ADAGMP
SV
YAB
AEAH 5V
REGULATOR
COMBINE SENSOR
FA B C D E COMBINE SENSOR HARNESS
SIDE CONNECTOR C
F
D
A
B
EP
S
T
V
O
YDSC HU/CM
Page 762 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
P–29
PEnd Of Sie
DTC U2511A6E697067650204
Diagnostic procedure
•Follow inspection procedures for CAN. (See T–39 MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION SYSTEM.)
End Of Sie
3INSPECT FORWARD-G SENSOR PART
SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
•Inspect continuity between DSC HU/CM
terminal V (harness side) and combine
sensor terminal A (harness side).
•Is there continuity?Yes Go to next step.
No Repair or replace harness for open circuit between DSC
HU/CM terminal V and combine sensor terminal A, then go
to Step 8.
4INSPECT FORWARD-G SENSOR PART
SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND
•Turn ignition key to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between DSC HU/CM
terminal V (harness side) and ground.
•Is there continuity?Yes Repair or replace harness for short to ground circuit
between DSC HU/CM terminal V and combine sensor
terminal A, then go to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
5INSPECT DIAGNOSIS SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR
SHORT FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
•Turn ignition key to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between DSC HU/CM
terminal S (harness side) and combine
sensor terminal F.
•Is there continuity?Yes Repair or replace harness for open circuit between DSC
HU/CM terminal S and combine sensor terminal F, then go
to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
6INSPECT DIAGNOSIS SIGNAL CIRCUIT FOR
SHORT TO GROUND
•Turn ignition key to OFF.
•Inspect continuity between DSC HU/CM
terminal S (harness side) and ground.
•Is there continuity?Yes Repair or replace harness for short to ground circuit
between DSC HU/CM terminal S and combine sensor
terminal F, then go to Step 8.
No Go to next step.
7INSPECT COMBINE SENSOR
•Inspect combine sensor.
•Is it okay?Yes Go to next step.
No Replace combine sensor, then go to next step.
8VERIFY TROUBLESHOOTING COMPLETED
•Clear DTC from memory.
•Is same DTC present?Yes Replace DSC HU/CM, then go to next step.
No Go to next step.
9VERIFY AFTER REPAIR PROCEDURE
•Is there any other DTC present?Yes Go to applicable DTC inspection.
No Troubleshooting completed. STEP INSPECTION ACTION
DTC U2511 CAN communication
DETECTION
CONDITION•Detects that the communication signals from 4WD CM is abnormal.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•4WD CM signals have communication error.
Page 763 of 909

R–1
R
RSUSPENSION
OUTLINE................................................................ R-2
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTION.......................... R-2
FEATURES .......................................................... R-2
SPECIFICATIONS ............................................... R-3
STRUCTURAL VIEW ...........................................R-4
REAR SUSPENSION............................................. R-5
SUSPENSION CONTROL SYSTEM ................... R-5
OUTLINE................................................................ R-7
SUPPLEMENTAL SERVICE INFORMATION .....R-7
WHEEL ALIGNMENT............................................. R-8
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT (WGN).................R-8
REAR WHEEL ALIGNMENT (WGN) ................... R-9
REAR SUSPENSION........................................... R-11
SUSPENSION CONTROL SYSTEM
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION (WGN) ...............R-11
REAR SHOCK ABSORBER
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION (WGN) ................ R-11
REAR SHOCK ABSORBER DISPOSAL
(WGN) .............................................................R-12
REAR STABILIZER
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION (4WD)................. R-13
TRAILING LINK REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
(4WD) .............................................................. R-14
REAR CROSSMEMBER
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION (4WD)................. R-16 FEATURES
SERVICE
Page 764 of 909

R–2
OUTLINE
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTIONA6E740201013201•The construction and operation of suspension system is essentially carried over from that of the current
Mazda6 (GG), except for the following features. (See Mazda6 Training Manual 3359-1*-02C.)
End Of Sie
FEATURESA6E740201013202Improved Handling Stability and Riding Comfort
•Wheel alignment has been set for WGN models.
•Rear stabilizer outer diameters are as follows:
WGN (2WD): 18 mm {0.71 in}
WGN (4WD): 21 mm {0.83 in}
•The suspension control system has been adopted as follows:
WGN (2WD): as an option
WGN (4WD): all models
End Of Sie
OUTLINE
Page 765 of 909

OUTLINE
R–3
R
SPECIFICATIONSA6E740201013203
*1: Engine coolant and engine oil are at specified level. Fuel is full. Spare tire, jack and tools are in designated position.
*
2: Difference between left and right must not exceed 1 °30'.*3: Distance between wheel center and fender brim is following. 4SD and 5HB front: 402 mm {15.82 in} (reference
value) 4SD and 5HB rear: 401 mm {15.78 in} (reference value), WGN (2WD) front: 405 mm {15.94 in}
(reference value) WGN (2WD) rear: 407 mm {16.02 in} (reference value)
Bold frames: New specifications
End Of Sie
Item Specification
New Mazda6 Current
Mazda6
GG (4SD, 5HB) GY (WGN 2WD) GY (WGN 4WD) GG (4SD, 5HB)
Engine type LF, MZR-CD
(RF Turbo) L8, LF, L3,
MZR-CD (RF Turbo) L3 L8, LF, L3
Fr o nt
suspension Type High-mount double wishbone (with double-pivoted lower arm(s))
Spring type Coil spring
Shock absorber type
Cylindrical, double-acting
(Low-pressure gas charged with rebound spring)
Stabilizer Type Torsion bar
Diameter (mm {in}) 23 {0.91}
Wheel
alignment
(Unloaded)*
1
Total toe-in (mm {in}) Tire: 2
±4 {0.08 ±0.16}, Rim inner: 1 ±3 {0.04 ±0.12}
(degree) 0 °11 ′±0°22 ′
Maximum
steering
angle inner
18 inch wheel specification vehicles: 36
°±3°
Except for above: 39 °±3°
outer 18 inch wheel specification vehicles: 30
°±3°
Except for above: 31 °±3°
Caster
angle*
2
(reference
value) normal 3
°47 ′±1° 3°40 ′±1° 3°35 ′±1° 3°47 ′±1°
elevated*33 °42' ±1° 3°35 ′±1° —3 °42' ±1 °
Camber
angle*
2
(reference
value) normal –0
°17 ′±1° –0°15 ′±1° –0°08 ′±1° –0°17 ′±1°
elevated*3–0 °10' ±1° –0°08 ′±1° —–0 °10' ±1°
Steering
axis
inclination
(reference
value) normal 5
°28 ′ 5°24 ′ 5°16 ′ 5°28 ′
elevated
*35 °18' 5 °16 ′ —5 °18'
Rear
suspension Type E-type multi-link
Spring type Coil spring
Stabilizer
Type Torsion bar
Diameter (mm {in})
4SD: 19 {0.75}
5HB: 18 {0.71}18 {0.71} 21 {0.83}
4SD: 19 {0.75}
5HB: 18 {0.71}
Shock absorber type Cylindrical,
double-acting
(Low-pressure gas charged) Cylindrical,
double-acting
(Low-pressure gas charged)/
(High-pressure
gas charged) Cylindrical,
double-acting
(High-pressure gas charged) Cylindrical,
double-acting
(Low-pressure gas charged)
Wheel
alignment
(Unloaded)*
1
Total toe-in (mm {in}) Tire: 2
±4 {0.08 ±0.16}, Rim inner: 1 ±3 {0.04 ±0.12}
(degree) 0 °11 ′±0°22 ′
Camber
angle*
2
normal –1 °13 ′±1° –1°06 ′±1° –1°03 ′±1° –1°13 ′±1°
elevated
*3–1 °05 ′±1° –0°58 ′±1° —–1 °05 ′±1°
Thrust angle (degree) 0 °±0°48 ′
Page 766 of 909
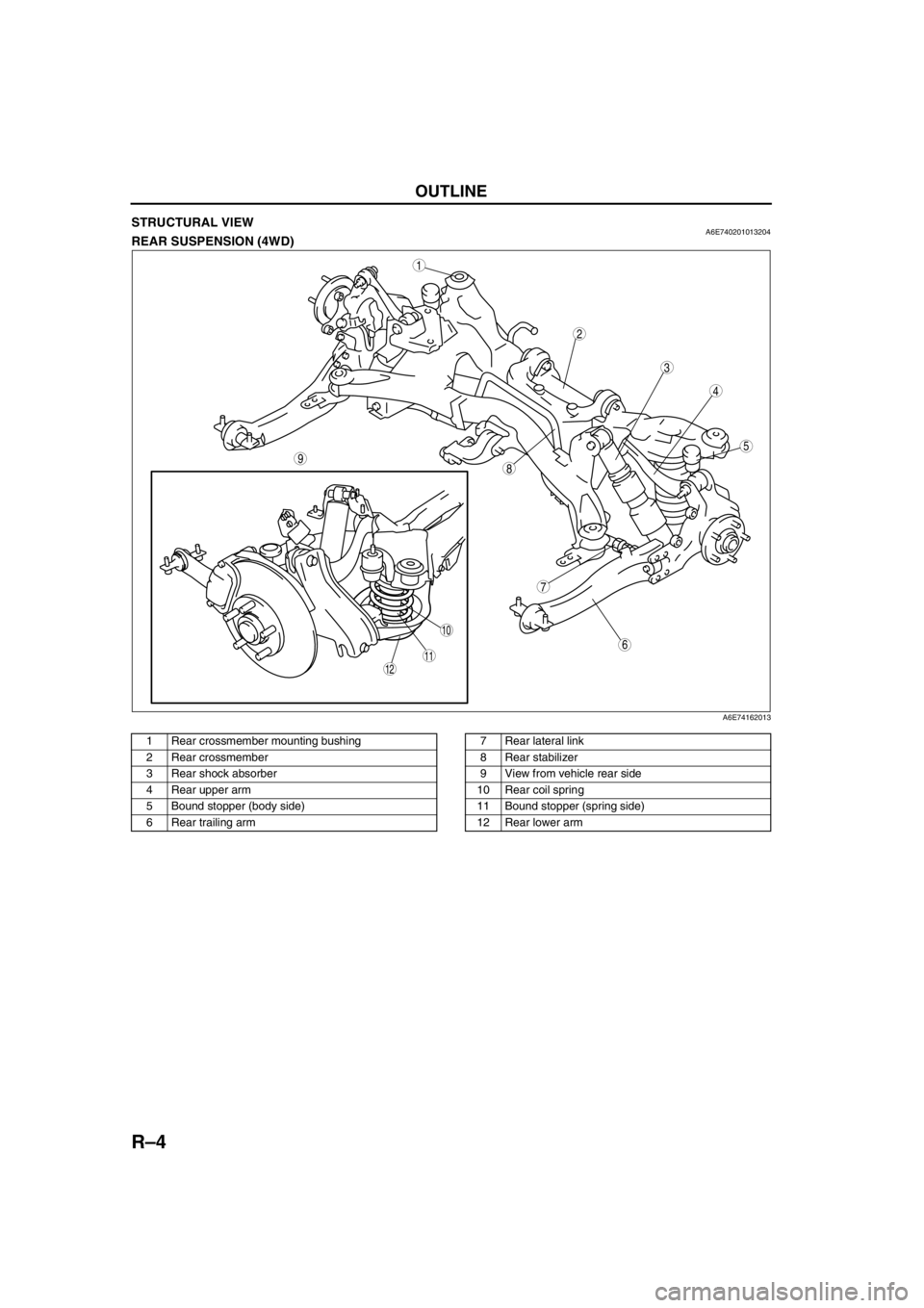
R–4
OUTLINE
STRUCTURAL VIEWA6E740201013204REAR SUSPENSION (4WD)
.
End Of Sie
98
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
116
12
A6E74162013
1 Rear crossmember mounting bushing
2 Rear crossmember
3 Rear shock absorber
4 Rear upper arm
5 Bound stopper (body side)
6 Rear trailing arm7 Rear lateral link
8 Rear stabilizer
9 View from vehicle rear side
10 Rear coil spring
11 Bound stopper (spring side)
12 Rear lower arm
Page 767 of 909
REAR SUSPENSION
R–5
R
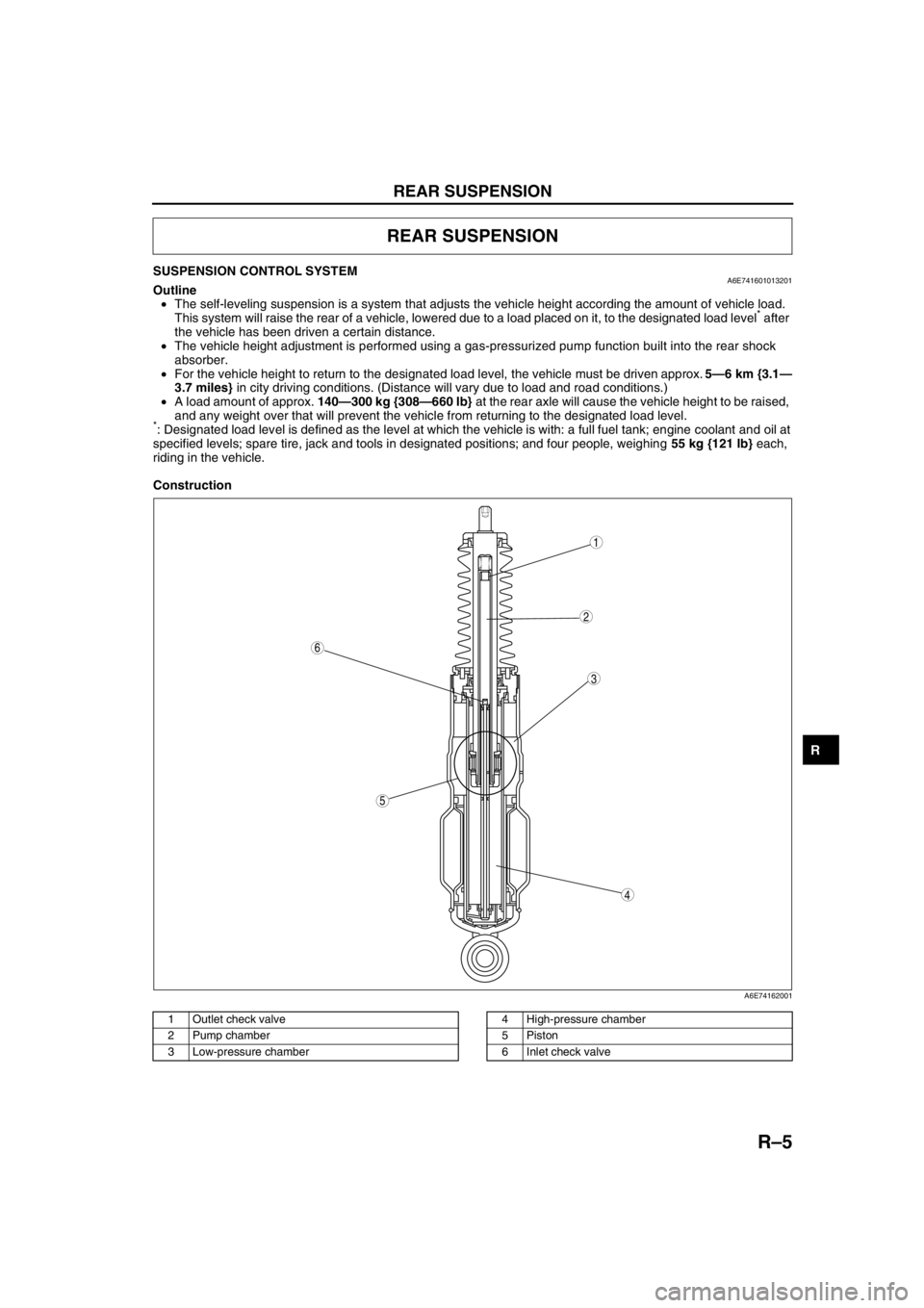
SUSPENSION CONTROL SYSTEMA6E741601013201Outline
•The self-leveling suspension is a system that adjusts the vehicle height according the amount of vehicle load.
This system will raise the rear of a vehicle, lowered due to a load placed on it, to the designated load level
* after
the vehicle has been driven a certain distance.
•The vehicle height adjustment is performed using a gas-pressurized pump function built into the rear shock
absorber.
•For the vehicle height to return to the designated load level, the vehicle must be driven approx. 5—6 km {3.1—
3.7 miles} in city driving conditions. (Distance will vary due to load and road conditions.)
•A load amount of approx. 140—300 kg {308—660 lb} at the rear axle will cause the vehicle height to be raised,
and any weight over that will prevent the vehicle from returning to the designated load level.
*: Designated load level is defined as the level at which the vehicle is with: a full fuel tank; engine coolant and oil at
specified levels; spare tire, jack and tools in designated positions; and four people, weighing 55 kg {121 lb} each,
riding in the vehicle.
Construction
.
REAR SUSPENSION
5
4
3
6
1
2
A6E74162001
1 Outlet check valve
2 Pump chamber
3 Low-pressure chamber4 High-pressure chamber
5Piston
6 Inlet check valve
Page 768 of 909
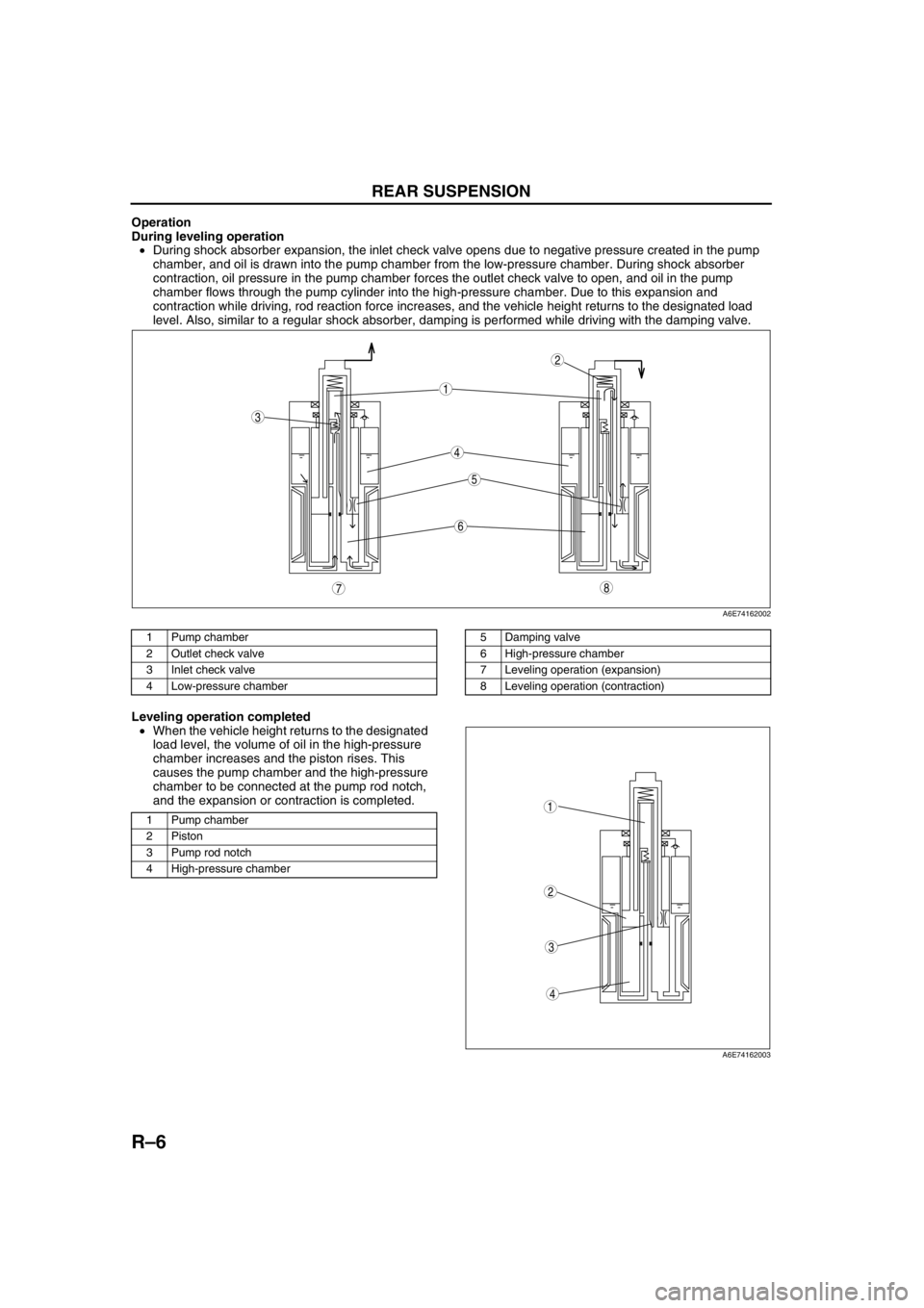
R–6
REAR SUSPENSION
Operation
During leveling operation
•During shock absorber expansion, the inlet check valve opens due to negative pressure created in the pump
chamber, and oil is drawn into the pump chamber from the low-pressure chamber. During shock absorber
contraction, oil pressure in the pump chamber forces the outlet check valve to open, and oil in the pump
chamber flows through the pump cylinder into the high-pressure chamber. Due to this expansion and
contraction while driving, rod reaction force increases, and the vehicle height returns to the designated load
level. Also, similar to a regular shock absorber, damping is performed while driving with the damping valve.
.
Leveling operation completed
•When the vehicle height returns to the designated
load level, the volume of oil in the high-pressure
chamber increases and the piston rises. This
causes the pump chamber and the high-pressure
chamber to be connected at the pump rod notch,
and the expansion or contraction is completed.
.
87
5
4
3
6
1
2
A6E74162002
1 Pump chamber
2 Outlet check valve
3 Inlet check valve
4 Low-pressure chamber5 Damping valve
6 High-pressure chamber
7 Leveling operation (expansion)
8 Leveling operation (contraction)
1 Pump chamber
2Piston
3 Pump rod notch
4 High-pressure chamber
4
3
1
2
A6E74162003
Page 769 of 909
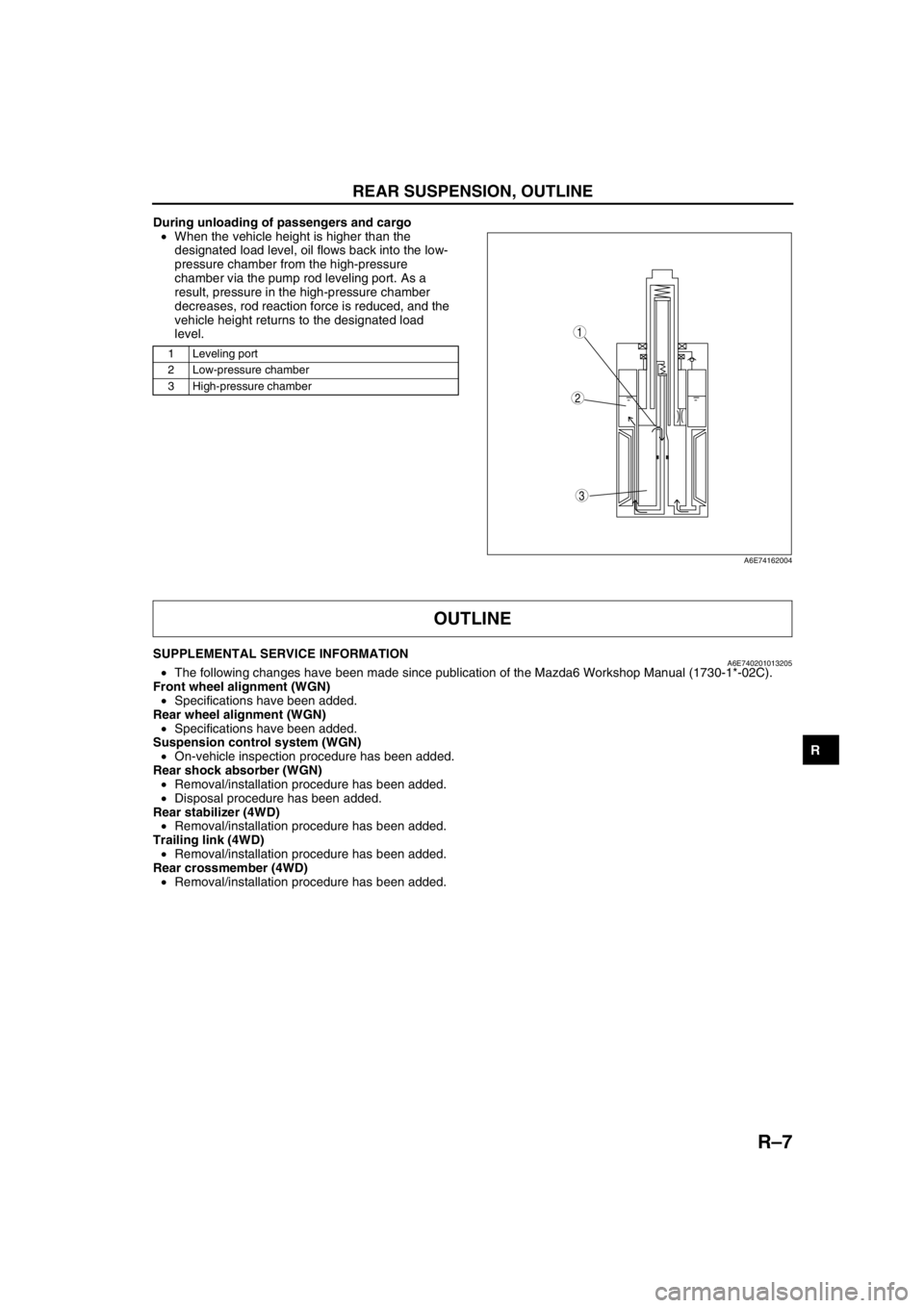
REAR SUSPENSION, OUTLINE
R–7
R
During unloading of passengers and cargo
•When the vehicle height is higher than the
designated load level, oil flows back into the low-
pressure chamber from the high-pressure
chamber via the pump rod leveling port. As a
result, pressure in the high-pressure chamber
decreases, rod reaction force is reduced, and the
vehicle height returns to the designated load
level.
.
End Of Sie
SUPPLEMENTAL SERVICE INFORMATIONA6E740201013205•The following changes have been made since publication of the Mazda6 Workshop Manual (1730-1*-02C).
Front wheel alignment (WGN)
•Specifications have been added.
Rear wheel alignment (WGN)
•Specifications have been added.
Suspension control system (WGN)
•On-vehicle inspection procedure has been added.
Rear shock absorber (WGN)
•Removal/installation procedure has been added.
•Disposal procedure has been added.
Rear stabilizer (4WD)
•Removal/installation procedure has been added.
Trailing link (4WD)
•Removal/installation procedure has been added.
Rear crossmember (4WD)
•Removal/installation procedure has been added.
End Of Sie
1 Leveling port
2 Low-pressure chamber
3 High-pressure chamber
3
1
2
A6E74162004
OUTLINE
Page 770 of 909
R–8
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT (WGN)A6E741201015201Specification (Unloaded)*1
2WD
*
1: Engine coolant and engine oil are at specified level. Spare tire, jack and tools are in designated position.
*2: Difference between left and right must not exceed 1 °30'.*3: Distance between wheel center and fender brim is 405 mm {15.94 in} (reference value).
4WD
*
1: Engine coolant and engine oil are at specified level. Spare tire, jack and tools are in designated position.
*2: Difference between left and right must not exceed 1 °30'.
Maximum Steering Angle Adjustment 1. Loosen the tie-rod end locknuts.
2. Remove the steering gear boot clamp.
3. Turn the tie rods to equalize the length L.
Maximum left/right difference3 mm {0.12 in}
4. Turn the tie rods equally to provide the correct maximum steering angle.
5. Tighten the tie-rod end locknuts.
Tightening torque68.6—98.0 N·m {7.00—9.99 kgf·m, 50.6—72.2 ft·lbf}
6. Verify that the boot is not twisted, and install the boot clamp.
7. Adjust the toe-in after adjusting the steering angle.
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Item Fuel gauge indication
Empty 1/4 1/2 3/4 Full
Maximum steering angle Inner
18 inch wheel specification vehicles: 36
°±3°
Except for above: 39 °±3°
Outer 18 inch wheel specification vehicles: 30
°±3°
Except for above: 31 °±3°
Total toe-in (mm {in}) Tire: 2
±4 {0.08 ±0.16}, Rim inner: 1 ±3 {0.04 ±0.12}
(degree) 0 °11 ′±0°22 ′
Caster angle
*2
(Reference value) normal 3
°30' ±1 ° 3°32' ±1 ° 3°34' ±1° 3°37' ±1° 3°40' ±1 °
elevated*33 °25' ±1 ° 3°27' ±1 ° 3°29' ±1° 3°32' ±1° 3°35' ±1 °
Camber angle
*2
(Reference value) normal -0
°14' ±1 ° -0°15' ±1°
elevated*3-0 °07' ±1 ° -0°08' ±1°
Steering axis inclination
(Reference value) normal 5
°24'
elevated
*35 °15' 5 °16'
Item Fuel gauge indication
Empty 1/4 1/2 3/4 Full
Maximum steering angle Inner 39
°±3°
Outer 31 °±3°
Total toe-in (mm {in}) Tire: 2
±4 {0.08 ±0.16}, Rim inner: 1 ±3 {0.04 ±0.12}
(degree) 0 °11 ′±0°22 ′
Caster angle*
2 (reference value) 3
°25' ±1 ° 3°27' ±1 ° 3°29' ±1 ° 3°32' ±1 ° 3°35' ±1 °
Camber angle*
2(reference value) -0
°07' ±1 ° -0°08' ±1°
Steering axis inclination (reference value) 5 °15' 5 °16'
LEFT AND RIGHT DIFFERENCE
L
LESS THAN 3 mm {0.12 in}
A6E7412W002