check engine MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 332 of 1146
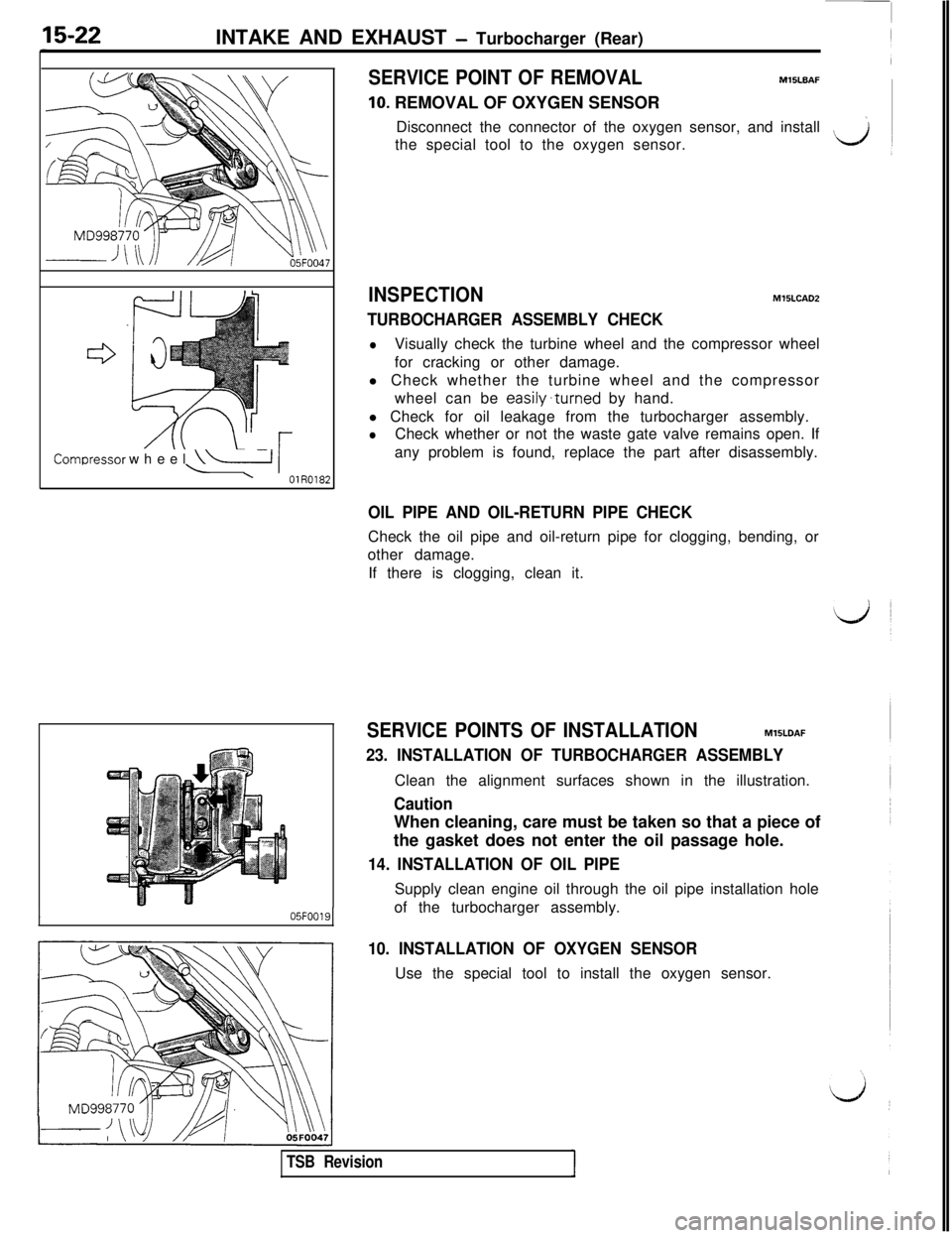
INTAKE AND EXHAUST - Turbocharger (Rear)
0
Comrxessorwheel \u ~i, rOlR0182
I05FOO19
SERVICE POINT OF REMOVALM15LBAF
10. REMOVAL OF OXYGEN SENSOR
Disconnect the connector of the oxygen sensor, and install
’the special tool to the oxygen sensor.
d,
INSPECTION
TURBOCHARGER ASSEMBLY CHECK
M15LCADZ
lVisually check the turbine wheel and the compressor wheel
for cracking or other damage.
l Check whether the turbine wheel and the compressor
wheel can be
easily.turned by hand.
l Check for oil leakage from the turbocharger assembly.
lCheck whether or not the waste gate valve remains open. If
any problem is found, replace the part after disassembly.
OIL PIPE AND OIL-RETURN PIPE CHECKCheck the oil pipe and oil-return pipe for clogging, bending, or
other damage.
If there is clogging, clean it.
SERVICE POINTS OF INSTALLATIONMlBLDAF
23. INSTALLATION OF TURBOCHARGER ASSEMBLYClean the alignment surfaces shown in the illustration.
CautionWhen cleaning, care must be taken so that a piece of
the gasket does not enter the oil passage hole.
14. INSTALLATION OF OIL PIPESupply clean engine oil through the oil pipe installation hole
of the turbocharger assembly.
10. INSTALLATION OF OXYGEN SENSORUse the special tool to install the oxygen sensor.
TSB Revision
Page 345 of 1146

17-1
EMISSIONCONTROL
.~
CATALYTIC CONVERTER............................:...Inspection
............................................................Removal and Installation
................................
CONTENTSM17.U. -
CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ComponentsLocation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Crankcase Ventilation System Inspection
._..Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve
. . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM................................................................Air Conditioner Switch
....................................Air Flow Sensor, Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor and Intake Air
Temperature Sensor
........................................Canister
............................................................Components Location
....................................
FuelFiller CapInspection................................OverfillLimiter (Two-way Valve)
....................Purge Control Solenoid Valve
........................Purge Control System Inspection
............................................................Purge Control Valve
........................
PurgePort VacuumCheck................................14
14
14
6
10
10
10
6
10
10
9
7
8
9
9EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR)
SYSTEM. . . . . ..____._.._........__........_____.........................Air-FuelRatio Control (MPI) System. . . . . . . .
Components Location
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .EGR Control Solenoid Valve
. . . . . . . .EGR Valve
EGR Valve Control Vacuum Check
SPECIFICATIONS................................................General Specifications
....................................Service Specifications
....................................
TROUBLESHOOTING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..______...............
VACUUM HOSES................................................Inspection
............................................................Installation
........................................................VacuumHosesRouting
....................................
11
14
11
13
12
13
13
12
2
2
22
Page 346 of 1146

17-2EMISSION CONTROL - Specifications / Troubleshooting
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONSMl’ICA- -\
Items
Crankcase emission control systemSpecifications
Closed type with positive crankcase ventilationvalve
Evaporative emission control systemCanister storage type
Canister
Charcoal type
Purge control solenoid valve
ON/OFF solenoid valve
Exhaust emission control system
Exhaust gas recirculation system
EGR valveVacuum-activated diaphragm type
EGR temperature sensor
EGR control solenoid valve
Catalytic converter
Monolith type
Location
Under floor
Turbocharger outlet (front bank and rear bank,)
and under floor
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONSMl7CB-.
ItemsSpecifications
Purge control solenoid valve coil resistance
036 - 44 [at 20°C (68”F)I\
EGR temperature sensor resistancekfl60 - 83 [at 50°C (I 22”F)]
11 - 14 [at 100°C (212”F)l
EGR control solenoid valve coil resistance1236 - 44 [at 20°C (68”F)lI
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom
Engine will not start
or hard to start
Rough idle or engine
stalls
Probable cause
Vacuum hose disconnected or damaged
The EGR valve is not closed
Malfunction of the purge control solenoid valve
The EGR valve is not closed
Vacuum hose disconnected or damaged
Malfunction of the positive crankcase ventilationvalveRemedy
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Replace
Malfunction of the purge control systemCheck the system; if there is a
problem, check its component parts
Engine hesitates or3oor acceleration
Zxcessive oil:onsumptron
Malfunction of the exhaust gas recirculation
system
Positive crankcase ventilation line cloggedCheck the system; if there is a
problem, check its component parts
Check positive crankcase
ventila-tion system
Ioor fuel mileageMalfunction of the exhaust gas recirculation
systemTSB RevisionCheck the system; if there is a
problem, check its component parts
d
Page 349 of 1146
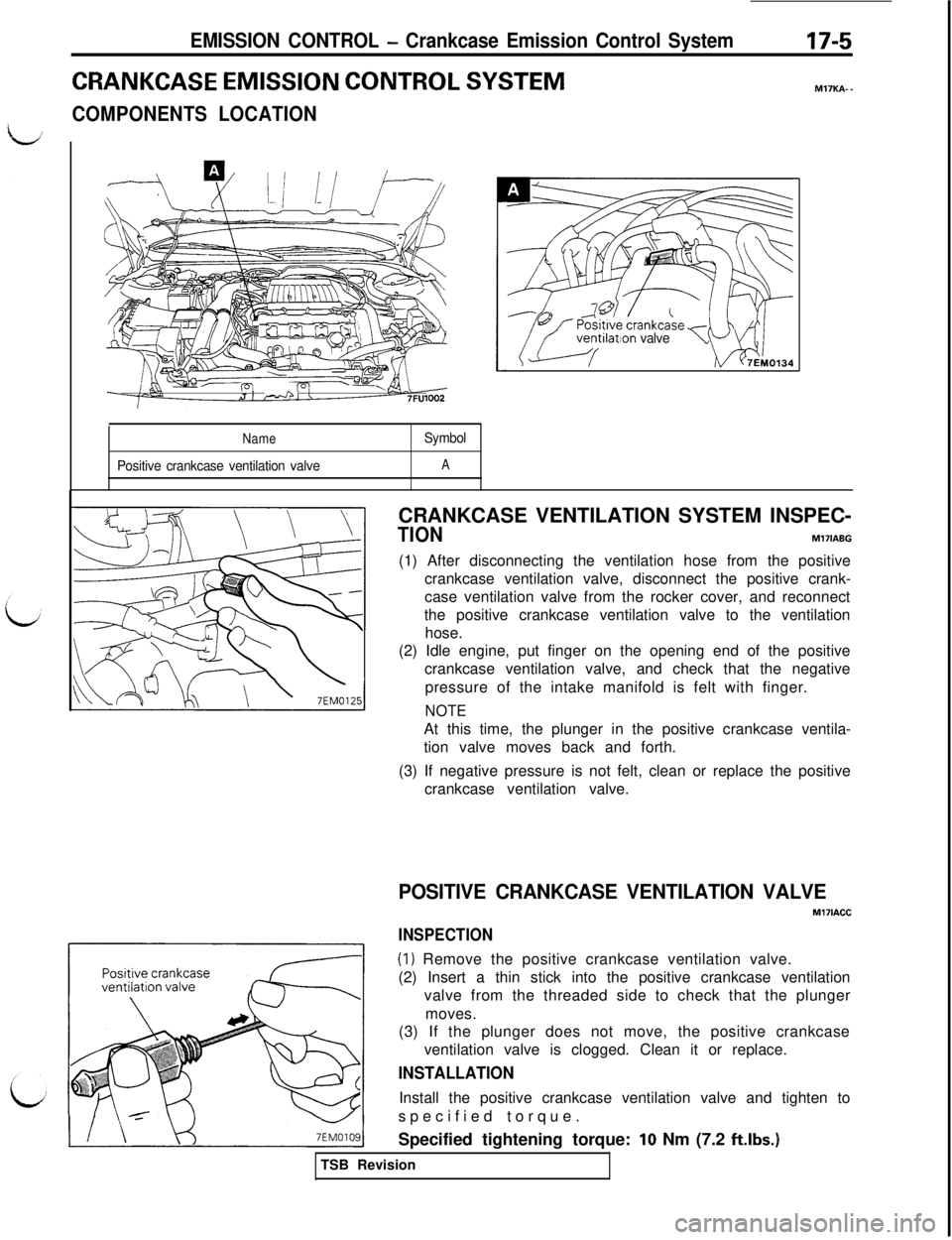
EMISSION CONTROL - Crankcase Emission Control System17-5
CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
COMPONENTS LOCATIONJ
Ir--‘-l7FU1002
Name
Positive crankcase ventilation valveSymbolA
i{
ventilation valve\”
------rLYJ7EM0134M17KA--
CRANKCASE VENTILATION SYSTEM INSPEC-
TIONM171ABG(1) After disconnecting the ventilation hose from the positive
crankcase ventilation valve, disconnect the positive crank-
case ventilation valve from the rocker cover, and reconnect
the positive crankcase ventilation valve to the ventilation
hose.
(2) Idle engine, put finger on the opening end of the positive
crankcase ventilation valve, and check that the negative
pressure of the intake manifold is felt with finger.
NOTEAt this time, the plunger in the positive crankcase ventila-
tion valve moves back and forth.
(3) If negative pressure is not felt, clean or replace the positive
crankcase ventilation valve.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION VALVEMl7lACC
INSPECTION
(1) Remove the positive crankcase ventilation valve.
(2) Insert a thin stick into the positive crankcase ventilation
valve from the threaded side to check that the plunger
moves.
(3) If the plunger does not move, the positive crankcase
ventilation valve is clogged. Clean it or replace.
INSTALLATIONInstall the positive crankcase ventilation valve and tighten to
specified torque.
Specified tightening torque:
10 Nm (7.2 ft.lbs.1TSB Revision
Page 351 of 1146
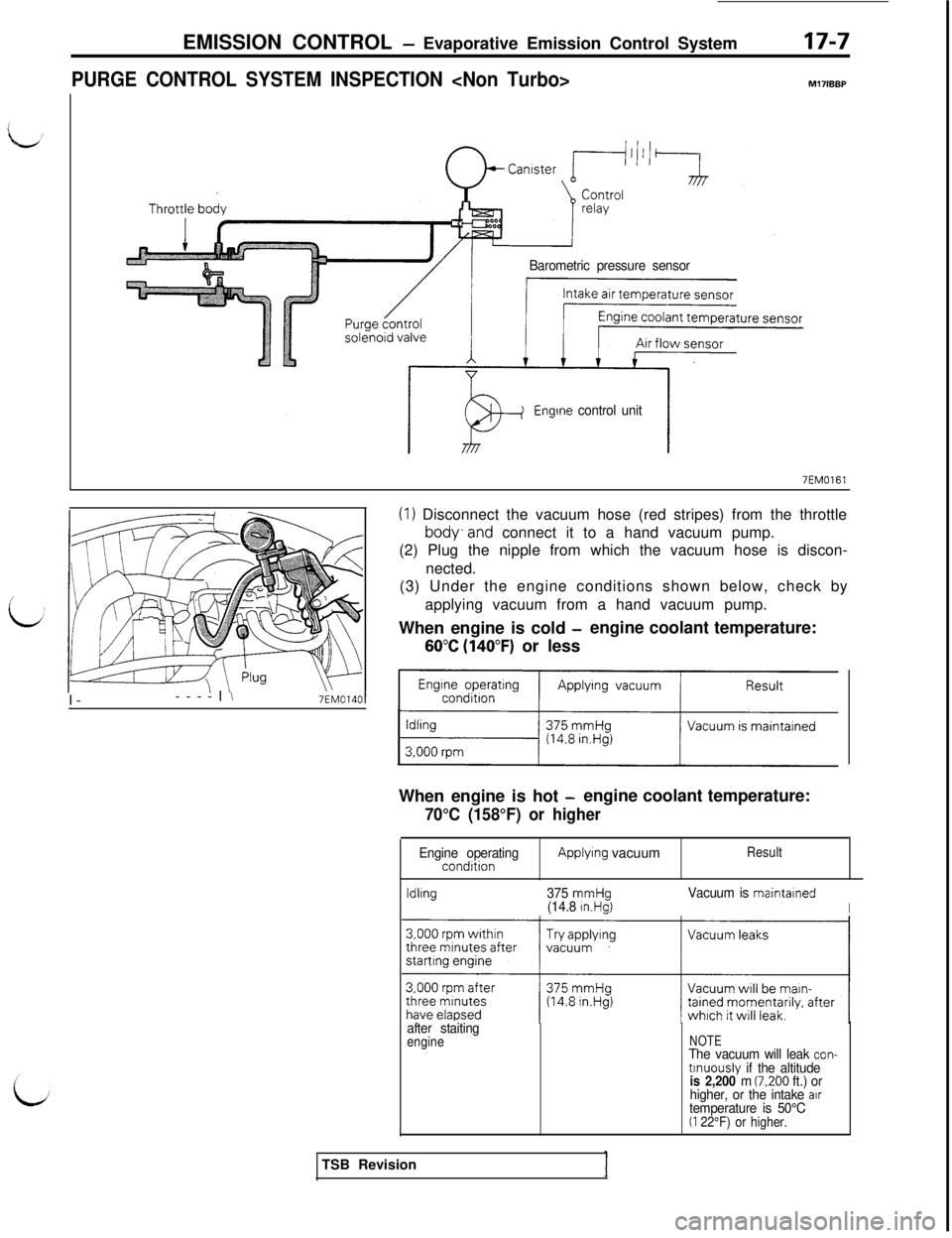
EMISSION CONTROL - Evaporative Emission Control System17-7
PURGE CONTROL SYSTEM INSPECTION
Barometric pressure sensor
Engine control unit
7EM0161I-----I
\7EM0140t
(1) Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripes) from the throttle
body,and connect it to a hand vacuum pump.
(2) Plug the nipple from which the vacuum hose is discon-
nected.
(3) Under the engine conditions shown below, check by
applying vacuum from a hand vacuum pump.
When engine is cold
-engine coolant temperature:
60°C (140°F) or less
When engine is hot
-engine coolant temperature:
70°C (158°F) or higher
Engine operatingcondttionApplying vacuumResult
ldllng375 mmHg(14.8 In.Hg)Vacuum is maintalned
I
after staitingengineNOTEThe vacuum will leak con-tenuously if the altitudeis 2,200 m (7.200 ft.) or
higher, or the intake airtemperature is 50°C(I 22°F) or higher.TSB Revision
Page 352 of 1146
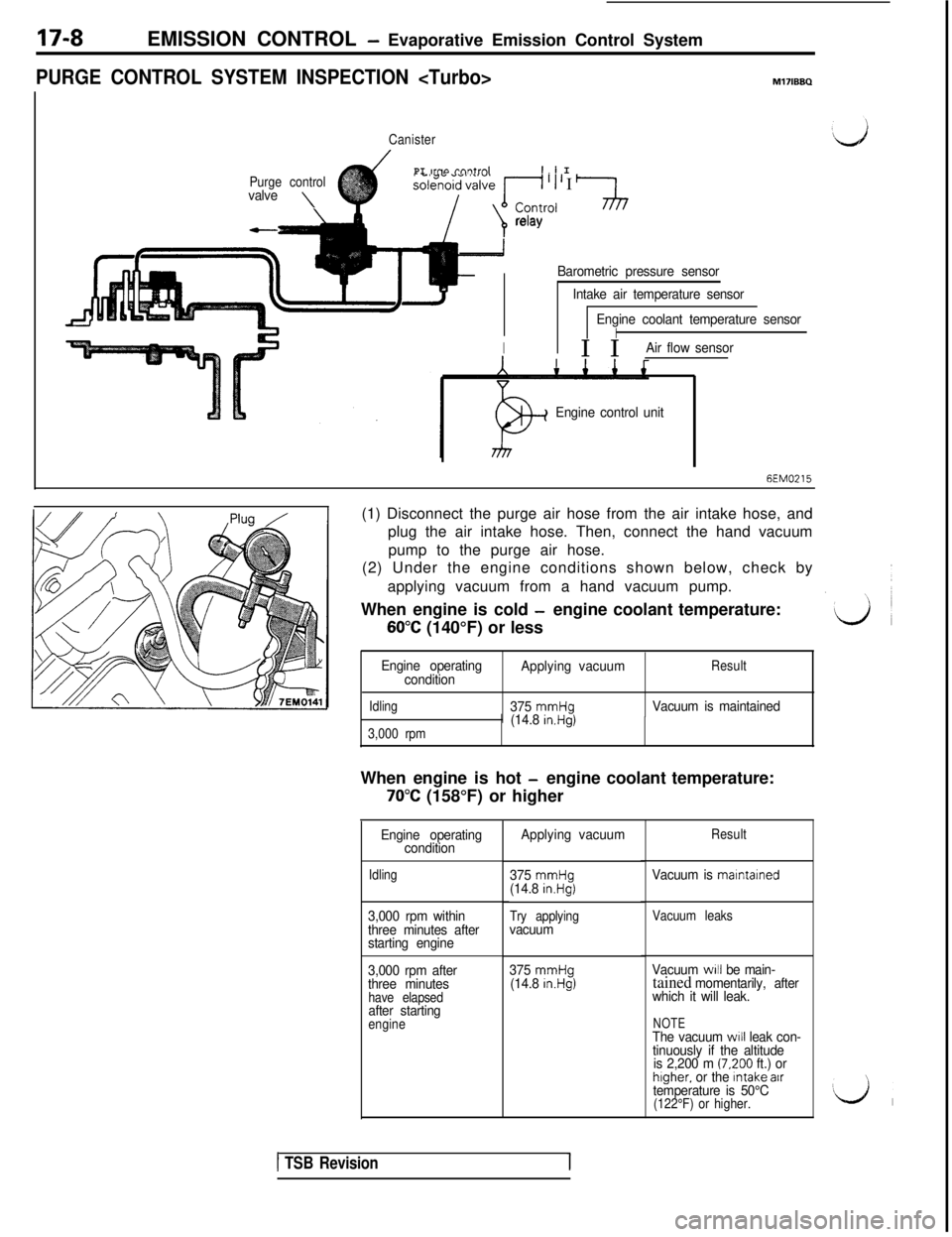
17-8EMISSION CONTROL - Evaporative Emission Control System
PURGE CONTROL SYSTEM INSPECTION
Canister
Purge control
valve\
PI IrnQ rnntrnlI.1 I
kXffo~~~~r~~ ’ I I-J
relay
Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
II1 I IAir flow sensor
Engine control unit
6EM0215(1) Disconnect the purge air hose from the air intake hose, and
plug the air intake hose. Then, connect the hand vacuum
pump to the purge air hose.
(2) Under the engine conditions shown below, check by
applying vacuum from a hand vacuum pump.
When engine is cold
-engine coolant temperature:
60°C (140°F) or less
Engine operating
conditionApplying vacuumResult
Idling
375 mmHgVacuum is maintained
3,000 rpm(14.8 in.Hg)When engine is hot
-engine coolant temperature:
70°C (158°F) or higher
Engine operating
condition
Idling
3,000 rpm within
three minutes after
starting engine
3,000 rpm after
three minutes
have elapsedafter startingengine
Applying vacuum
375
mmHg(14.8 in.Hg)
Try applyingvacuum
375
mmHg(14.8 in.Hg)
Result
Vacuum is marntained
Vacuum leaks
Vacuum WIII be main-tained momentarily, after
which it will leak.
NOTEThe vacuum WIII leak con-
tinuously if the altitude
is 2,200 m
(7,200 ft.) orhrgher. or the Intake arrtemperature is 50°C(122°F) or higher.
1 TSB Revision
Page 353 of 1146
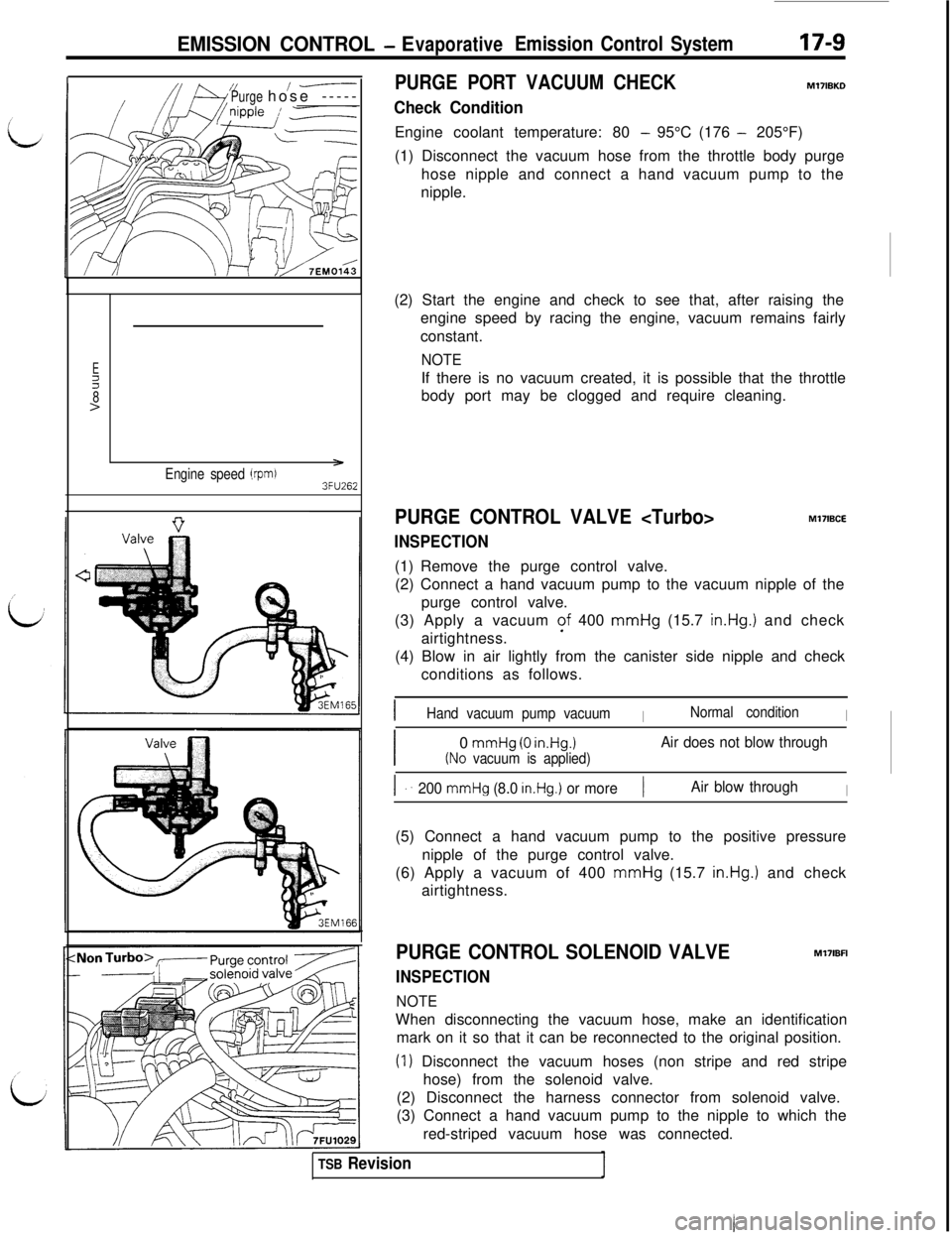
EMISSION CONTROL - EvaporativeEmission Control System
Purge/-----hose -----PURGE PORT VACUUM CHECK
Check Condition
17-9
M17lBKDEngine coolant temperature: 80
- 95°C (176 - 205°F)
(1) Disconnect the vacuum hose from the throttle body purge
hose nipple and connect a hand vacuum pump to the
nipple.
Ez8>
Engine speed (rprd3FU262(2) Start the engine and check to see that, after raising the
engine speed by racing the engine, vacuum remains fairly
constant.
NOTEIf there is no vacuum created, it is possible that the throttle
body port may be clogged and require cleaning.
PURGE CONTROL VALVE
INSPECTIONMl7IBCE
(1) Remove the purge control valve.
(2) Connect a hand vacuum pump to the vacuum nipple of the
purge control valve.
(3) Apply a vacuum of 400 mmHg (15.7
in.Hg.1 and check
airtightness.
(4) Blow in air lightly from the canister side nipple and check
conditions as follows.
IHand vacuum pump vacuumINormal conditionI
I0
mmHg (0 in.Hg.1Air does not blow through
(No vacuum is applied)
I ..200 mmHg (8.0 in.Hg.) or more1Air blow throughI(5) Connect a hand vacuum pump to the positive pressure
nipple of the purge control valve.
(6) Apply a vacuum of 400 mmHg (15.7
in.Hg.1 and check
airtightness.
PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE
INSPECTION
NOTEMl7lBFI
When disconnecting the vacuum hose, make an identification
mark on it so that it can be reconnected to the original position.
(I) Disconnect the vacuum hoses (non stripe and red stripe
hose) from the solenoid valve.
(2) Disconnect the harness connector from solenoid valve.
(3) Connect a hand vacuum pump to the nipple to which the
red-striped vacuum hose was connected.
TSB Revision
Page 354 of 1146

17-10EMISSION CONTROL - Evaporative Emission Control System
I-6EM13i(4) Apply a vacuum and check for airtightness when voltage
applied directly to the purge control solenoid valve and
when the voltage is discontinued.
Battery voltageResultNon-Turbo When applied
Vacuum leaks
When discontinuedVacuum is maintained
TurboWhen applied
When discontinued
Vacuum is maintained
Vacuum leaks
(5) Measure the resistance between the terminals of the
solenoid valve.
Standard value: 36
- 44 R [at 20°C (68”F)]
AIR FLOW SENSOR, ENGINE COOLANT TEMPER-ATURE SENSOR AND INTAKE AIR TEMPERA-
TURE SENSORM17lBGFTo inspect these parts, refer to GROUP 13
- MPI System
Components.
AIR CONDITIONER SWITCHMl7IBHF
To inspect the air conditioner switch, refer to GROUP 55
- Air
Conditioner Switch.
OVERFILL LIMITER (TWO-WAY VALVE)M17IBEFTo inspect the overfill limiter (two-way valve), refer to GROUP
13
- Fuel Tank.
CANISTERM17lBIFTo inspect the canister, refer to GROUP 13
- Fuel Line and
Vapor Line.
FUEL FILLER CAP INSPECTIONM17IBJBCheck the gasket of the fuel filler cap, and the filler cap itself,
for damage or deformation; replace the cap if necessary.
TSB Revision
Page 356 of 1146
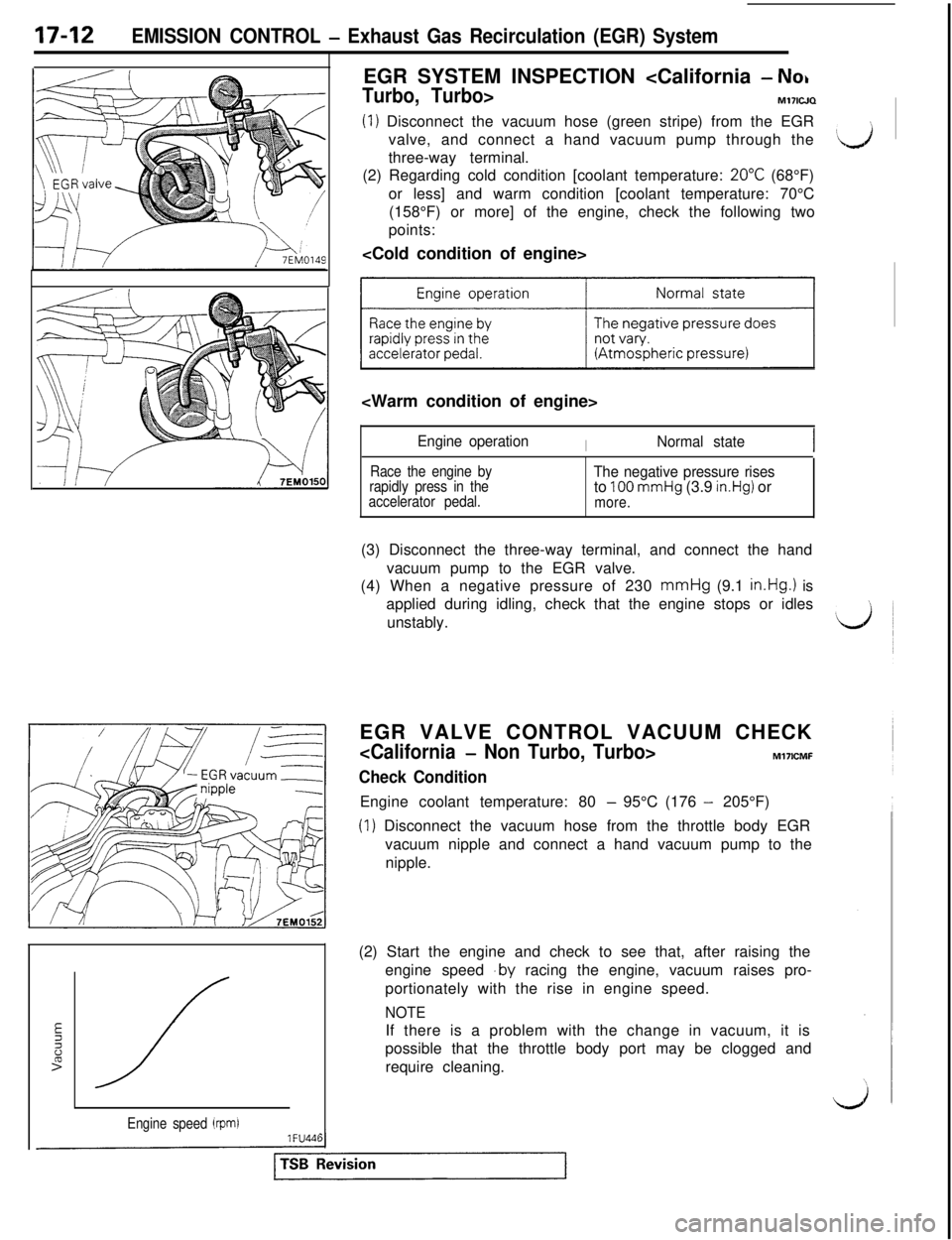
17-12EMISSION CONTROL - Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
Engine speed (rpm)1 FU44lEGR SYSTEM INSPECTION
Turbo, Turbo>M171WQ
(1) Disconnect the vacuum hose (green stripe) from the EGR
valve, and connect a hand vacuum pump through the
three-way terminal.
(2) Regarding cold condition [coolant temperature:
20°C (68°F)
or less] and warm condition [coolant temperature: 70°C
(158°F) or more] of the engine, check the following two
points:
~1
Engine operationINormal state
Race the engine by
rapidly press in the
accelerator pedal.The negative pressure risesto 100 mmHg (3.9 in.Hg) ormore.(3) Disconnect the three-way terminal, and connect the hand
vacuum pump to the EGR valve.
(4) When a negative pressure of 230 mmHg (9.1
in.Hg.1 is
applied during idling, check that the engine stops or idles
unstably.
EGR VALVE CONTROL VACUUM CHECK
Check ConditionEngine coolant temperature: 80
- 95°C (176 - 205°F)
(1) Disconnect the vacuum hose from the throttle body EGR
vacuum nipple and connect a hand vacuum pump to the
nipple.
(2) Start the engine and check to see that, after raising the
engine speed
.by racing the engine, vacuum raises pro-
portionately with the rise in engine speed.
NOTEIf there is a problem with the change in vacuum, it is
possible that the throttle body port may be clogged and
require cleaning.
Page 358 of 1146
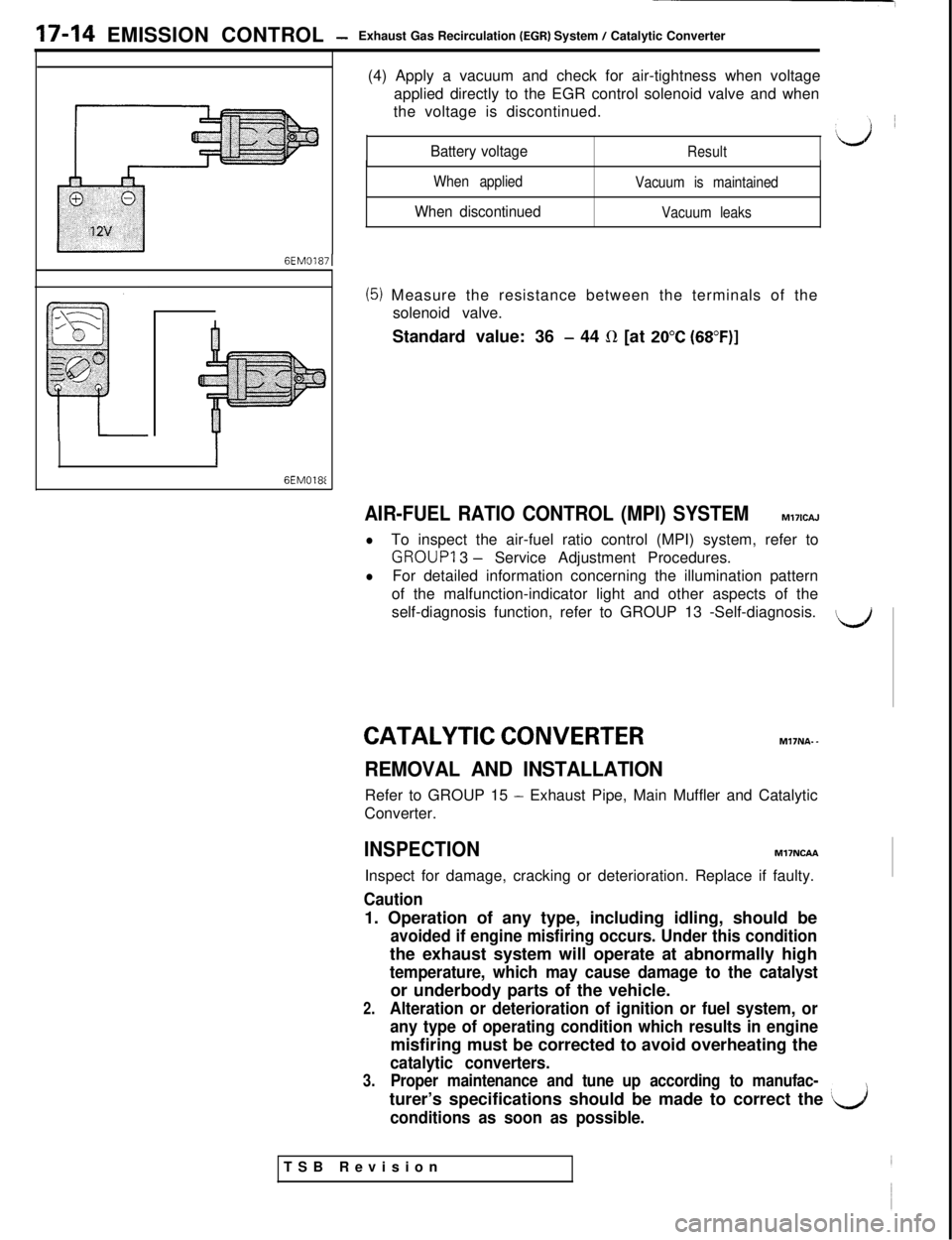
17-14 EMISSION CONTROL -Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System / Catalytic Converter
6EM01871
6EM0181(4) Apply a vacuum and check for air-tightness when voltage
applied directly to the EGR control solenoid valve and when
the voltage is discontinued.
Battery voltageResult
When applied
When discontinued
Vacuum is maintained
Vacuum leaks
(5) Measure the resistance between the terminals of the
solenoid valve.
Standard value: 36
- 44 R [at 20°C (68”F)]
AIR-FUEL RATIO CONTROL (MPI) SYSTEMM17ICAJ
lTo inspect the air-fuel ratio control (MPI) system, refer to
GROUP1 3 - Service Adjustment Procedures.
lFor detailed information concerning the illumination pattern
of the malfunction-indicator light and other aspects of the
self-diagnosis function, refer to GROUP 13 -Self-diagnosis.
\.J
CATALYTIC CONVERTERMl7N& -
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONRefer to GROUP 15
- Exhaust Pipe, Main Muffler and Catalytic
Converter.
INSPECTIONMl7NCAA
Inspect for damage, cracking or deterioration. Replace if faulty.
Caution1. Operation of any type, including idling, should be
avoided if engine misfiring occurs. Under this conditionthe exhaust system will operate at abnormally high
temperature, which may cause damage to the catalystor underbody parts of the vehicle.
2.Alteration or deterioration of ignition or fuel system, or
any type of operating condition which results in enginemisfiring must be corrected to avoid overheating the
catalytic converters.
3.Proper maintenance and tune up according to manufac-turer’s specifications should be made to correct the
‘bi
conditions as soon as possible.TSB Revision