NISSAN PATROL 2000 Electronic Repair Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2000, Model line: PATROL, Model: NISSAN PATROL 2000Pages: 1033, PDF Size: 30.71 MB
Page 251 of 1033
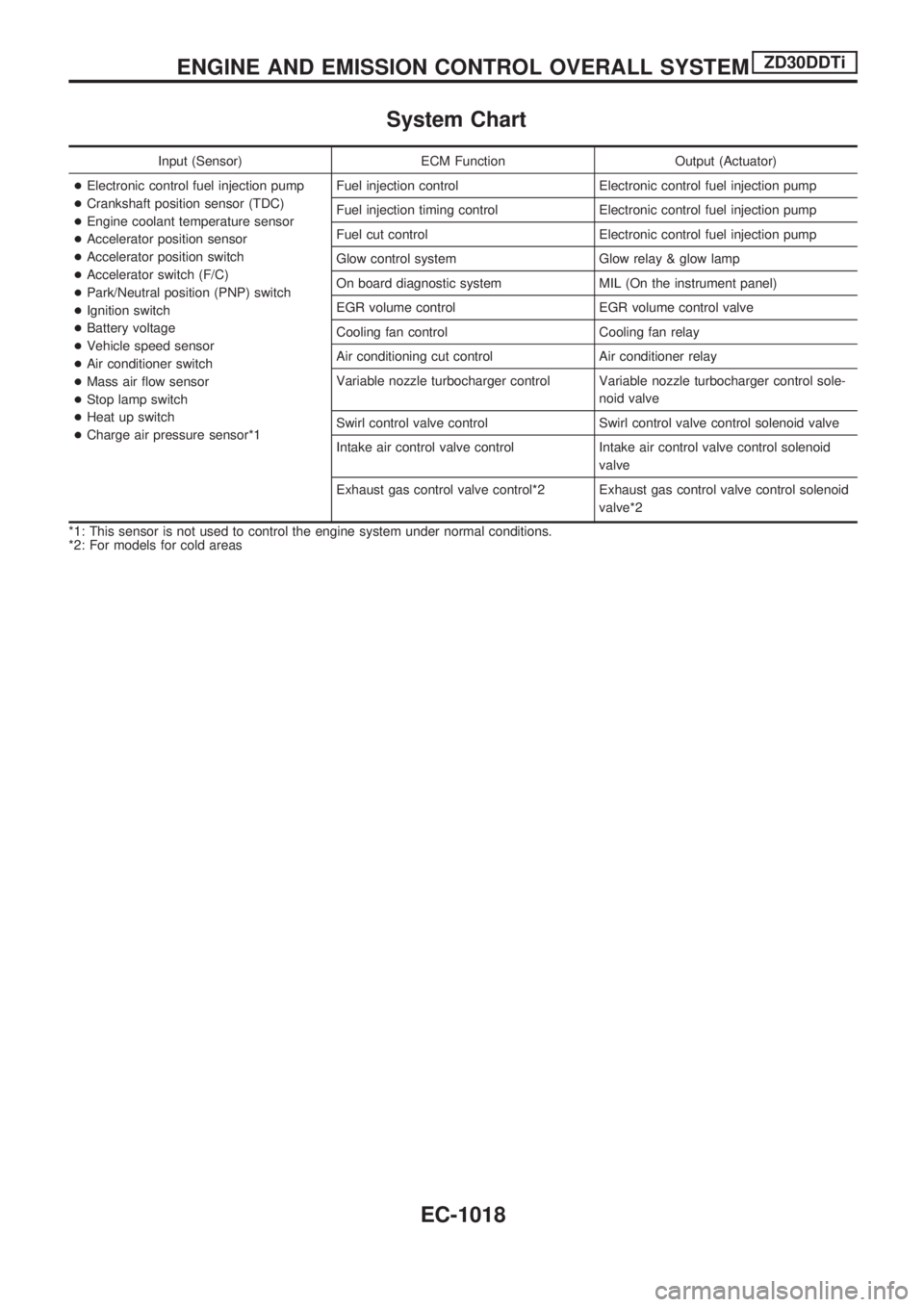
System Chart
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
+Electronic control fuel injection pump
+Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
+Engine coolant temperature sensor
+Accelerator position sensor
+Accelerator position switch
+Accelerator switch (F/C)
+Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch
+Ignition switch
+Battery voltage
+Vehicle speed sensor
+Air conditioner switch
+Mass air flow sensor
+Stop lamp switch
+Heat up switch
+Charge air pressure sensor*1Fuel injection control Electronic control fuel injection pump
Fuel injection timing control Electronic control fuel injection pump
Fuel cut control Electronic control fuel injection pump
Glow control system Glow relay & glow lamp
On board diagnostic system MIL (On the instrument panel)
EGR volume control EGR volume control valve
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
Variable nozzle turbocharger control Variable nozzle turbocharger control sole-
noid valve
Swirl control valve control Swirl control valve control solenoid valve
Intake air control valve control Intake air control valve control solenoid
valve
Exhaust gas control valve control*2 Exhaust gas control valve control solenoid
valve*2
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: For models for cold areas
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMZD30DDTi
EC-1018
Page 252 of 1033
Fuel Injection Control System
DESCRIPTION
System description
Three types of fuel injection control are provided to accommodate engine operating conditions; normal
control, idle control and start control. The ECM determines the appropriate fuel injection control. Under each
control, the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance.
Pulse signals are exchanged between ECM and electronic control fuel injection pump (control unit is built-
in). The fuel injection pump control unit performs duty control on the spill valve (built into the fuel injection
pump) according to the input signals to compensate the amount of fuel injected to the preset value.
Start control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection con-
trol (start control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Ignition switch Start signal
When the ECM receives a start signal from the ignition switch,
the ECM adapts the fuel injection system for the start control.
The amount of fuel injected at engine starting is a preset program
value in the ECM. The program is determined by the engine
speed and engine coolant temperature.
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the lower the
coolant temperature becomes, the greater the amount of fuel
injected. The ECM ends the start control when the engine speed
reaches the specific value, and shifts the control to the normal
or idle control.
Idle control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection con-
trol (Idle control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch Gear position
Battery Battery voltage
Accelerator position switch Idle position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner signal
Heat up switch Heat up switch signal
When the ECM determines that the engine speed is at idle, the fuel injection system is adapted for the idle
control. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected corresponding to changes in load applied to the
engine to keep engine speed constant. The ECM also provides the system with a fast idle control in response
to the engine coolant temperature and heat up switch signal.
SEF648S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
EC-1019
Page 253 of 1033

Normal control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Fuel injection con-
trol (Normal con-
trol)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is
determined according to sensor signals. The crankshaft position
sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position
sensor detects accelerator position. These sensors send signals
to the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between
various engine speeds and accelerator positions, are stored in
the ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the
optimal amount of fuel to be injected using the sensor signals in
comparison with the map.
Maximum amount control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Fuel injection con-
trol (Maximum
amount control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
The maximum injection amount is controlled to an optimum by the engine speed, intake air amount, engine
coolant temperature, and accelerator opening in accordance with the driving conditions.
This prevents the oversupply of the injection amount caused by decreased air density at a high altitude or
during a system failure.
Deceleration control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Accelerator switch (F/C) Accelerator positionFuel injection con-
trol (Deceleration
control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
The ECM sends a fuel cut signal to the electronic control fuel injection pump during deceleration for better
fuel efficiency. The ECM determines the time of deceleration according to signals from the accelerator switch
(F/C) and crankshaft position sensor (TDC).
SEF649S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
Fuel Injection Control System (Cont'd)
EC-1020
Page 254 of 1033
Fuel Injection Timing Control System
DESCRIPTION
The target fuel injection timing in accordance with the engine speed and the fuel injection amount are
recorded as a map in the ECM beforehand. The ECM and the injection pump control unit exchange signals
and perform feedback control for optimum injection timing in accordance with the map.
Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTION
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner ªONº signal
Air conditioner cut
controlAir conditioner relay Accelerator position sensorAccelerator valve opening
angle
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
System description
This system improves acceleration when the air conditioner is used.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the air conditioner is turned off for a few seconds.
When engine coolant temperature becomes excessively high, the air conditioner is turned off. This contin-
ues until the engine coolant temperature returns to normal.
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)
DESCRIPTION
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Fuel cut controlElectronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch Neutral position
Accelerator position switch or Accelerator
switch (F/C)Accelerator position
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
If the engine speed is above 2,700 rpm with no load (for example, in neutral and engine speed over 2,700
rpm) fuel will be cut off after some time. The exact time when the fuel is cut off varies based on engine speed.
Fuel cut will operate until the engine speed reaches 1,500 rpm, then fuel cut is cancelled.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control listed under ªFuel Injection Control Systemº,
EC-1019.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
EC-1021
Page 255 of 1033
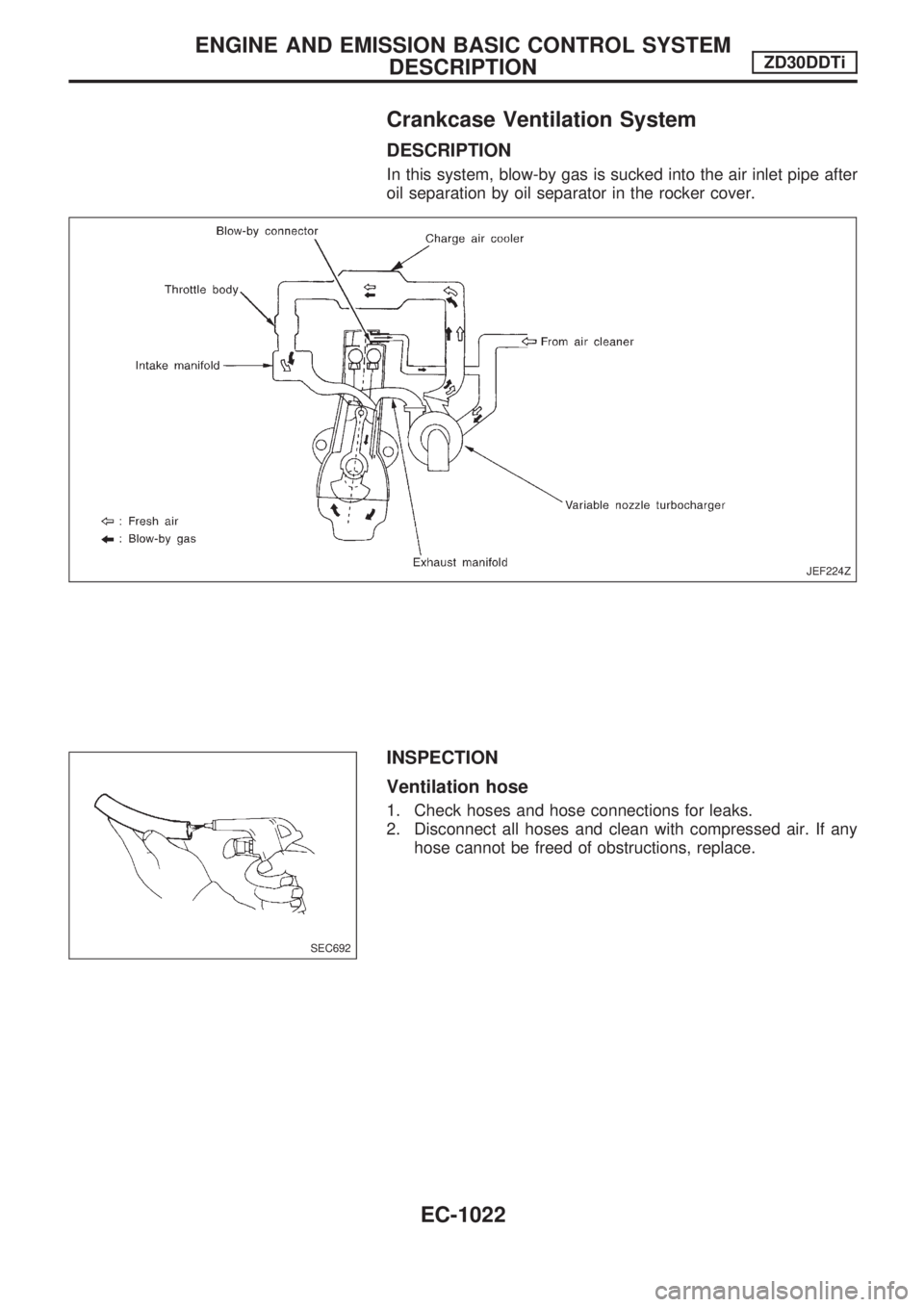
Crankcase Ventilation System
DESCRIPTION
In this system, blow-by gas is sucked into the air inlet pipe after
oil separation by oil separator in the rocker cover.
INSPECTION
Ventilation hose
1. Check hoses and hose connections for leaks.
2. Disconnect all hoses and clean with compressed air. If any
hose cannot be freed of obstructions, replace.
JEF224Z
SEC692
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
EC-1022
Page 256 of 1033

Injection Tube and Injection Nozzle
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAUTION:
+Do not disassemble injection nozzle assembly. If NG,
replace injection nozzle assembly.
+Plug flare nut with a cap or rag so that no dust enters the
nozzle. Cover nozzle tip for protection of needle.
Injection tube
Removal
1. Mark the cylinder Nos. to the injection tubes, then disconnect
them.
+Marking should be made at proper locations and by the
proper method, so that they are not erased by fuel, etc.
2. Remove the clamps, then disconnect the tubes one by one.
+Avoid letting leaked fuel get on the interior walls of the
engine compartment.
Take special care to prevent fuel from getting on the engine
mount insulator.
JEF237Z
JEF238Z
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREZD30DDTi
EC-1023
Page 257 of 1033

Installation
+Install the injection tubes, referring to the markings made
during removal.
+Install the injection tubes in the order of No. 3, No. 4, No. 1,
and No. 2.
Injection nozzle oil seal
Removal
Using a tool such as a flat-bladed screwdriver, pry the flange of
the seal, then remove it.
Installation
After the injection nozzle assembly is installed, push the seal
from the cylinder head side until it contacts the flange.
+Replace the oil seal with new one when the injection
nozzle assembly is removed. (It is not necessary to
replace the oil seal when only injection tubes are
removed.)
Spill tube
Installation
+After the spill tube is installed, check the airtightness of
the spill tube.
+After the bolts are tightened, the joint of the spill tube gasket
might be broken. However, this will not affect function.
Injection nozzle assembly
Removal
1. Remove the nozzle support, then pull out the injection nozzle
assembly by turning it clockwise/counterclockwise.
2. Using a tool such as a flat-head screwdriver, remove the
copper washer inside the cylinder head.
CAUTION:
Do not disassemble the injection nozzle.
Installation
1. Insert the nozzle gasket to the cylinder head hole.
2. Attach the O-ring to the mounting groove of the nozzle side,
then insert it in the cylinder head.
TEST AND ADJUSTMENT
WARNING:
When using nozzle tester, be careful not to allow diesel fuel
sprayed from nozzle to contact your hands or body, and
make sure your eyes are properly protected with goggles.
JEF248Z
JEF249Z
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREZD30DDTi
Injection Tube and Injection Nozzle (Cont'd)
EC-1024
Page 258 of 1033

Inspection for spill tube airtightness
Before the rocker cover is installed, perform the inspection as
follows.
1. Connect the handy vacuum pump to the spill hose.
2. Check that the airtightness is maintained after the negative
pressure shown below is applied.
Standard:
þ53.3 to þ66.7 kPa (þ533 to þ667 mbar, þ400 to
þ500 mmHg, þ15.75 to þ19.69 inHg)
Air bleeding of fuel piping
After the repair, bleed air in the piping by pumping the priming
pump up and down until it becomes heavy.
Injection pressure test
1. Install injection nozzle assembly to injection nozzle tester
and bleed air from flare nut.
2. Pump the tester handle slowly (one time per second) and
watch the pressure gauge.
3. Read the pressure gauge when the injection pressure just
starts dropping.
Initial injection pressure:
Used
19,026 kPa (190.3 bar, 194 kg/cm
2, 2,759 psi)
New
19,516 - 20,497 kPa (195.2 - 205.0 bar, 199 - 209
kg/cm
2, 2,830 - 2,972 psi)
Limit
16,182 kPa (161.8 bar, 165 kg/cm
2, 2,346 psi)
+The injection nozzle assembly has a 2-stage pressure injec-
tion function. However, the judgement should be made at the
first stage of the valve opening pressure.
JEF250Z
SEF251Z
JEF348Y
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREZD30DDTi
Injection Tube and Injection Nozzle (Cont'd)
EC-1025
Page 259 of 1033

Spray pattern test
1. Check spray pattern by pumping tester handle one full stroke
per second.
NG spray pattern:
Does not inject straight and strong (B in the fig-
ure).
Fuel drips (C in the figure).
Does not inject evenly (D in the figure).
2. If the spray pattern is not correct, replace injection nozzle
assembly.
Electronic Control Fuel Injection Pump
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAUTION:
When removing or installing the timing chain as incidental work of the fuel injection pump removal/
installation, always secure the internal mechanism of the idler gear with bolts before removing or
installing the fuel injection pump sprocket. Do not refer to the procedure for ªTIMING CHAINº in EM
section based on No. 1 cylinder compression top dead center. (Unless otherwise specified.)
JEF349Y
JEF259Z
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREZD30DDTi
Injection Tube and Injection Nozzle (Cont'd)
EC-1026
Page 260 of 1033

REMOVAL
1. Remove the following:
+Engine coolant draining
+Charge air cooler
+Air inlet pipe
+Throttle body
+Rocker cover
+Oil level gauge guide
+EGR guide tube
+EGR volume control solenoid valve
+Fuel hose
+Injection tube
+Radiator upper hose
+Radiator shroud
+Cooling fan
+Drive belt
+Vacuum pipe
+Vacuum pump
2. Move the power steering pump.
3. Remove the harness connector from the fuel injection pump.
+After pulling the connector stopper all the way back, remove
the connector.
+When the stopper is pulled all the way back, the interlocked-
connector will come off.
As for installation, when the connector is pushed all the way
forward until the stopper locks, the interlocked-connector is
inserted.
4. Remove the fuel injection pump rear bracket.
5. Remove the chain cover.
+Remove the installation bolts A, B, and C shown in the fig-
ure (left).
CAUTION:
During chain cover removal, seal the opening to prevent
foreign objects from getting into the engine.
6. Fix the internal mechanism of the idler gear (scissors gear
structure).
a. Remove the plug on the front side of the gear case.
b. While turning the crankshaft pulley clockwise, check the
tightening bolt hole of the idler gear internal mechanism
through the plug hole.
+Conduct the visual check using a mirror.
+When checking, note that there are 2 other holes (with no
thread) beside the tightening bolt hole on the idler gear.
JEF260Z
JEF261Z
JEF262Z
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREZD30DDTi
Electronic Control Fuel Injection Pump (Cont'd)
EC-1027