NISSAN PULSAR 1987 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1987, Model line: PULSAR, Model: NISSAN PULSAR 1987Pages: 238, PDF Size: 28.91 MB
Page 171 of 238
Rear Suspension 171
Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) When installing the stabilizer bar to the
knuckle assembly bushes, ensu re that the thicker bush
is installed to the front of the knuckle assembly. Install
the rear bush, washers and nut but do not tighten at
this stage. (2) Install the stabil izer bar mounting
brackets,
ensuring that the end with the large bevel is facing the
front of the vehicle. Tighte n the retaining bolts to the
specified torque. (3) Using a new gasket, install the intermediate
exhaust pipe to the catalytic converter, ensuring that
the earth wire terminal is installed, and tighten the
bolts securely. Install the exhaust mounting
retaining
bolt. (4) Install the rear wheels and lower the
vehicle
to the ground. With the wei ght of the vehicle on the
road wheels, tighten the stabilizer bar retaining nuts to
the specified torque.
8. REAR WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Specialized equipment is required to measure the
rear wheel alignment. It is therefore recommended
that the vehicle be referred to a specialist suspension
workshop or an authorized dealer for measurement
and adjustment. The suspension components should
be inspected and renewed as necessary prior to having
the wheel alignment checked. If any suspension com-
ponents are renewed, the re ar wheel toe out may be
temporarily adjusted as described below.
TO INSPECT
Examine the tread of the tires. Excessive or
uneven wear will indicate misalignment or damaged
or worn components. Refer to the Tire Wear Trouble
Shooting Chart in the Wheels and Tires section for
possible causes and renew the faulty components.
Badly worn tires should be renewed prior to
having the wheel alignment checked.
TO CHECK AND ADJUST TOE OUT
NOTE: The following procedures are only a
temporary measure. Th e vehicle should be
referred to a specialis t suspension work-
shop or authorized dealer for accurate
measurement and adjustment.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level floor and
bounce the vehicle several tim es to settle the suspen-
sion. (2) Move the vehicle forward approximately 5
meters, with the front wheels straight ahead, to settle
the tires and suspension to the normal running
position.
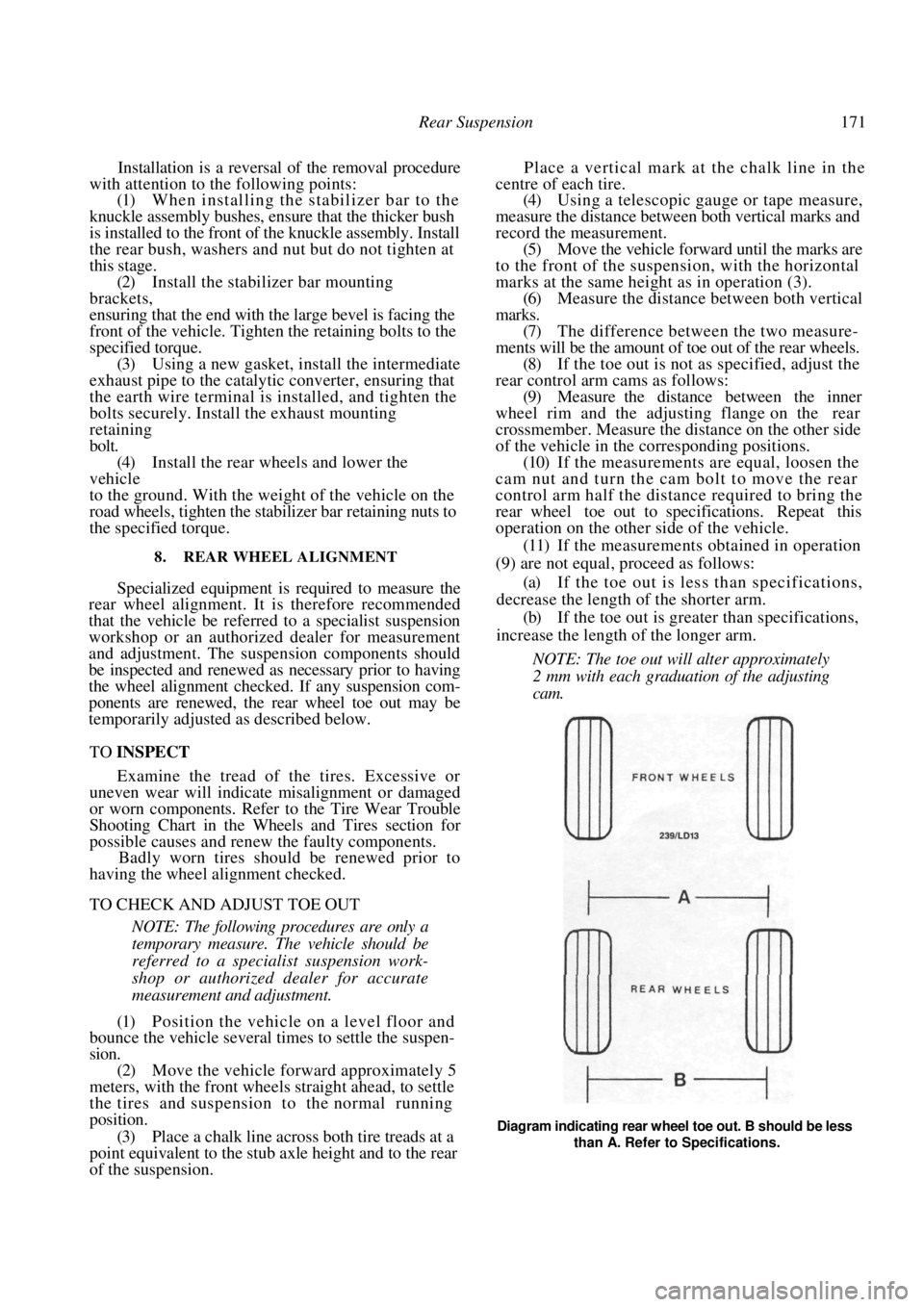
(3) Place a chalk line across both tire treads at a
point equivalent to the stub axle height and to the rear
of the suspension. Place a vertical mark at the chalk line in the
centre of each tire.
(4) Using a telescopic gauge or tape measure,
measure the distance between both vertical marks and
record the measurement. (5) Move the vehicle forward until the marks are
to the front of the suspen sion, with the horizontal
marks at the same height as in operation (3). (6) Measure the distance between both vertical
marks. (7) The difference between the two measure-
ments will be the amount of toe out of the rear wheels. (8) If the toe out is not as specified, adjust the
rear control arm cams as follows: (9) Measure the distance between the inner
wheel rim and the adjusting flange on the rear
crossmember. Measure the distance on the other side
of the vehicle in the corresponding positions. (10) If the measurements are equal, loosen the
cam nut and turn the cam bolt to move the rear
control arm half the distance required to bring the
rear wheel toe out to specifications. Repeat this
operation on the other side of the vehicle.
(11) If the measurements obtained in operation
(9) are not equal, proceed as follows:
(a) If the toe out is less than specifications,
decrease the length of the shorter arm.
(b) If the toe out is greater than specifications,
increase the length of the longer arm.
NOTE: The toe out will alter approximately
2 mm with each graduation of the adjusting
cam.
Diagram indicating rear wheel toe out. B should be less than A. Refer to Specifications.
Page 172 of 238

172
BRAKES
SPECIFICATIONS
Type:
Except Pulsar/Vector GL from
July 1989 and Astra models ... Four wheel disc
Pulsar/Vector GL from
July 1989 and Astra models —
Front...............................................................Disc
Rear..............................................................Drum
Operation:
Footbrake ............... Vacuum assisted diagonally
split dual hydraulic
Handbrake................ Mechanical on rear wheels
Fluid type ...........................................................Dot 4
Master cylinder:
Make ........................................................ Girlock
Bore diameter —
Large .................................................... 25.40 mm
Small .................................................... 20.64 mm
Front disc brakes:
Caliper bore diameter ........................... 48.1 mm
Disc diameter ........................................ 240 mm
Disc thickness, minimum ......................... 16 mm
Disc runout, maximum ......................... 0.07 mm
Disc pad thickness, minimum ....................2 mm
Rear disc pads:
Caliper bore diameter ......................... 30.16 mm
Disc diameter ........................................ 234 mm
Disc thickness, minimum ...........................9 mm
Disc runout, maximum .......................... 0.07 mm
Disc pad thickness, minimum ....................2 mm
Rear drum brakes:
Wheel cylinder bore diameter ............ 15.87 mm
Drum diameter, maximum ............... 204.50 mm
Drum out of round, maximum.............. 0.03 mm
Drum runout, maximum ........................ 0.05 mm
Brake lining wear limit ........................... 1.5 mm
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
Brake pedal bracket to body........................... 11 Nm
Brake pedal pivot bolt ..................................... 11 Nm
Brake servo unit to body................................. I I N m
Brake servo unit to master cylinder ............... 11 Nm
Pressure differential piston plug ...................... 12 Nm
Proportioning valve plug................................. 27 Nm
Caliper anchor plate bolts ............................... 52 Nm
Caliper guide bolts .......................................... 31 Nm
Brake hose to caliper....................................... 34 Nm
Handbrake cable bracket bolt ......................... 49 Nm
Handbrake lever to body ................................ 11 Nm
Cable clamp to body....................................... 11 Nm
Cam lever nut.................................................. 49 Nm
1. BRAKES TROUBLE SHOOTING
BRAKE PEDAL HARD
(1) Seized caliper piston or wheel cylinder: Over-
haul the caliper or wheel cylinder.
(2) Seized master cylinder piston: Overhaul the
master cylinder. (3) Seized pedal pivot: Rectify or renew the
pedal pivot shaft and bushes. (4) Restricted brake line: Remove the restriction
or renew the brake line.
(5) Vacuum servo system inoperative: Check
and repair the servo system.
NOTE: The vacuum servo system can be
checked as follows: With the engine
switched off, pump the brake pedal several
times to deplete any vacuum in the system.
With the engine still switched off, press
down firmly on the brake pedal and hold it
there noting the position and pressure re-
quired. Start the engine. If the servo unit is
operating correctly, the brake pedal will sink
slightly and the pressure required to hold it
may reduce. If the pedal does not sink
slightly when the engine is started, check the
vacuum supply to the servo unit. If vacuum
is reaching the brake servo unit, the unit can
be considered inoperative.
BRAKE DRAG
(1) Clogged master cylinder ports: Clean the
master cylinder and the fluid reservoir. Renew the
brake fluid. (2) Seized caliper piston or wheel cylinder: Over-
haul the caliper or wheel cylinder.
(3) Seized handbrake linkage: Free up or renew
the linkage.
Page 173 of 238
Brakes 173
Inspect the handbrake cable for chafing or fraying.
(4) Seized handbrake cables: Renew the hand-
brake cables.
NOTE: Raise the vehicle and spin the
wheels one at a time to check for binding. If
the wheels are not binding, have an assistant
apply and release the brakes. Check if the
brakes release immediately. A clogged mas-
ter cylinder port will cause binding on the
two wheels fed by that particular circuit
from the master cylinder. Open the bleeder
valve on one of the o ffending wheels to check
if pressure build up is the cause of the
binding. A seized handbrake cable will usu-
ally cause binding on a rear wheel. Discon-
nect the handbrake cable and check if the
wheel will then turn freely.
LOW SPONGY BRAKE PEDAL
(1) Incorrectly adjusted brake shoes: Check and
adjust the brake shoes.
(2) Insufficient fluid in the system: Check for
leaks, replenish the fluid to the specified level and
bleed the hydraulic system.
(3) Air in the brake hydraulic system: Bleed the
hydraulic system. (4) Master cylinder faulty: Repair or renew as
necessary.
NOTE: A spongy brake pedal in most cases
is caused by air in the hydraulic system. For
air to enter the system one or more of the
sealing rubbers or brake lines must be
sucking in air. Always rectify the cause of
the trouble before bleeding the hydraulic
system. Faulty components usually show up
as fluid leakage.
BRAKES LOCK ON APPLICATION
(1) Gummy linings or brake pads due to oil or
fluid contamination: Renew the linings or brake pads
and rectify the source of contamination. (2) Scored or eccentric brake drum or warped
disc: Check and machine or renew the drum or disc as
necessary.
(3) Incorrect or distorted linings or disc pads:
Check and renew as necessary. (4) Brake servo unit faulty: Repair or renew the
brake servo unit. (5) Broken or stretched brake shoe return
springs: Check and renew th e faulty brake springs.
(6) Faulty brake pressure proportioning valve:
Renew the brake pressure proportioning valve.
NOTE: If this condition arises, remove all
the wheels and check the condition of the
friction material for oil contamination and
excessive wear. Check the shoe return
springs for stretching by comparing their
free length with new sp rings. An eccentric-
brake drum or warped disc will be indicated
by pulsating of the brake pedal when the
brakes are lightly applied.
BRAKE PEDAL PULSATES
(1) Eccentric brake drums or warped disc: Check
and machine or renew the drum or disc as required.
(2) Loose or worn hub bearings: Renew the hub
bearings as necessary.
NOTE: Brake drums or discs that are run-
ning out must be machined. This job is best
entrusted to a brake specialist who will also
be able to determine if a new disc or drum
needs to be installed.
BRAKE FADE
(1) Incorrect shoe adjustment: Check and adjust
the shoe to drum clearance. (2) Eccentric brake drum: Check and machine or
renew the brake drum.
Check the brake hoses for deterioration, chafing and
leaks.
Page 174 of 238

174 Brakes
(3) Linings saturated with hydraulic fluid: Re-
new the linings in sets. (4) Incorrect linings installed: Check and install
the recommended linings in sets.
NOTE: In most cases brake fade is caused
by overuse of the footbrake, which in turn
causes a build up of heat at the friction
material and drums or disc. Once this
excessive build up of heat is allowed to
dissipate the brakes should again function
normally.
BRAKES OVERHEAT
(1) Incorrect shoe adjustment: Check and adjust
the shoe to drum clearance.
(2) Broken shoe return springs: Renew any
faulty springs.
(3) Faulty handbrake cables or incorrect adjust-
ment: Check and renew or adjust the cables. (4) Frozen wheel cylinder or caliper pistons:
Overhaul the cylinders or calipers. (5) Obstructed or damaged hydraulic hose or
line: Remove the obstruction or renew the hydraulic
hose or line.
(6) Obstructed master cylinder compensating
port: Clean the compensating port. (7) Blocked vent in the master cylinder reservoir
cap; Check and remove the obstruction in the vent. (8) Overuse of footbrake: Revise driving habits.
NOTE: To check for brake binding raise the
vehicle and spin each wheel in turn by hand.
If it is found that one wheel cylinder or
caliper piston is sti cking it is advisable to
overhaul all the wheel cylinders and calipers.
BRAKE FAILURE
(1) Faulty master cylinder: Remove and over-
haul the master cylinder. (2) Loss of fluid due to a leaking wheel cylinder:
Overhaul or renew the wheel cylinders and bleed the
hydraulic system.
(3) Loss of fluid due to a leaking caliper: Over-
haul or renew the caliper assemblies and bleed the
hydraulic system. (4) Loss of fluid due to a fractured pipe or faulty
union: Renew the faulty components as necessary and
bleed the hydraulic system. (5) Air in the hydraulic system: Locate the
source of the air leak, rectify the problem and bleed
the hydraulic system. (6) Water in the hydraulic fluid: Drain, flush,
refill and bleed the hydraulic system.
NOTE: To locate the source of a fluid leak,
fill the master cylinder reservoir with fluid
and check for obvious signs of external
leakage while an assistant pumps the brake
pedal.
Check the brake pipe unions for leaks.
BRAKE NOISE
(1) Brakes squeal on application: Glazed friction
material or missing or da maged disc pad anti-squeal
shims. (2) Grinding noise on application: Friction ma-
terial worn out. Check the friction material and
discs/drums. Renew the brake pads/shoes and ma-
chine or renew the brake discs/drums as necessary.
Inspect the brake discs for scoring and wear.
2. DESCRIPTION
The brakes are operated by hydraulic pressure in
two independent circuits by means of a tandem dual
circuit master cylinder coupled to a brake servo unit
mounted on the bulkhead between the brake pedal
and master cylinder.
The brake circuits are sp lit diagonally. The left
hand front and right hand rear brakes are connected
to the primary circuit, and the right hand front and
left hand rear brakes are connected to the secondary
circuit. Should a malfunction occur in one circuit, the
remaining circuit is capable of stopping the vehicle.
Page 175 of 238

Brakes 175
A pressure proportioning valve is incorporated in
each circuit to prevent premature locking of the rear
wheels during severe braking.
The four wheel hydraulically operated brakes
utilize disc brakes on each front wheel and disc brakes
or leading and trailing drum brake shoes on each rear
wheel.
The front disc brakes comprise a disc attached to
the hub assembly and a caliper bolted to the steering
knuckle.
The rear disc brakes comprise a disc and hub
assembly attached to the rear stub axle and a caliper
and anchor plate bolted to the backing plate.
The front and rear calipers are of the sliding type.
As pad wear takes place, the caliper piston is allowed
to slide outwards through the seal to take up a new
position in the caliper bore. Elastic deformation of the
seal takes place when the brakes are applied, which
returns the piston slightly when the brakes are re-
leased. Thus a constant clearance is maintained
between the pads and the disc when the brakes are in
the off position.
The disc brakes do not require periodical adjust-
ment in service to compensate for pad wear as they
are self adjusting.
The leading and trailing shoe drum brakes on the
rear wheels use a double ended wheel cylinder to
operate both brake shoes at the top. The lower end of
each brake shoe abuts a fixed anchor point. The brake
shoes are automatically adju sted when the brakes are
operated.
The handbrake operates the rear brakes via a
cable arrangement.
3. MASTER CYLINDER
Special Equipment Required:
To Install New Seals — Suitable machined drift
TO REMOVE
(1) Depress the brake pedal several times to
deplete the vacuum from the system.
(2) Raise the bonnet and install covers to
both
the front mudguards. Cover the areas of paintwork
beneath the master cylinder with absorbent cloth.
(3) Disconnect the wiring from the pressure
sensing switch. (4) Disconnect the brake pipes from the master
cylinder and plug the outlets and pipes to prevent the
loss of fluid and the ingress of dirt.
(5) Remove the nuts retaining the master cylin-
der to the brake servo unit and remove the master
cylinder from the vehicle.
TO DISMANTLE
(1) Remove the master cylinder as previously
described. (2) Remove the reservoir cap and diaphragm,
drain and discard the brake fluid from the reservoir. (3) Carefully remove the reservoir from the
master cylinder by pulling it from the reservoir
retainers by hand. Remove and discard the retainers
from the master cylinder. (4) Using internal snap ring pliers, remove the
snap ring from the primary reservoir port. (5) Remove the fast fill valve assembly and the
O ring from the port. Remove and discard the valve
washer from the fast fill valve.
(6) Remove the proportioning valve plugs and
the O rings. Discard the O rings. Withdraw the springs
and valve plungers from the master cylinder. Remove
and discard the seals from the valve plungers. (7) Remove the pressure sensing switch and
lever assembly from the master cylinder. {8) Remove the cylinder end plug from the
master cylinder. Remove and discard the O ring from
the plug.
(9) Carefully tap the front of the master cylinder
vertically on a block of wo od and remove the pressure
differential pistons from the master cylinder. Remove
and discard the O rings from the pistons. (10) Push the primary piston forward in the
cylinder with a blunt rod and while holding the
pressure, remove the stop pin from the master cylin-
der.
(11) The primary piston may now be withdrawn
from the cylinder bore. The secondary piston, retainer
and spring can also be withdrawn by carefully tapping
the master cylinder on a block of wood. (12) Prise the legs of the seal retainer upwards
and remove it from the primary piston. Remove the
seal and guide. Discard the seal and retainer.
NOTE: The secondary piston must no! be
dismantled by removing the screw. This
assembly has a factory p reset length and the
screw must not be altered in service.
(13) Remove the main seal and the guide from
the front of the secondary piston. Stretch the rear seal
from the groove and remove it from the piston. Take
Installed view of the master cylinder and servo unit. Air
duct removed for clarity. 1.8 liter model.
Page 176 of 238
176 Brakes
care not to damage the piston surfaces where the inner
diameter of the piston seals locate.
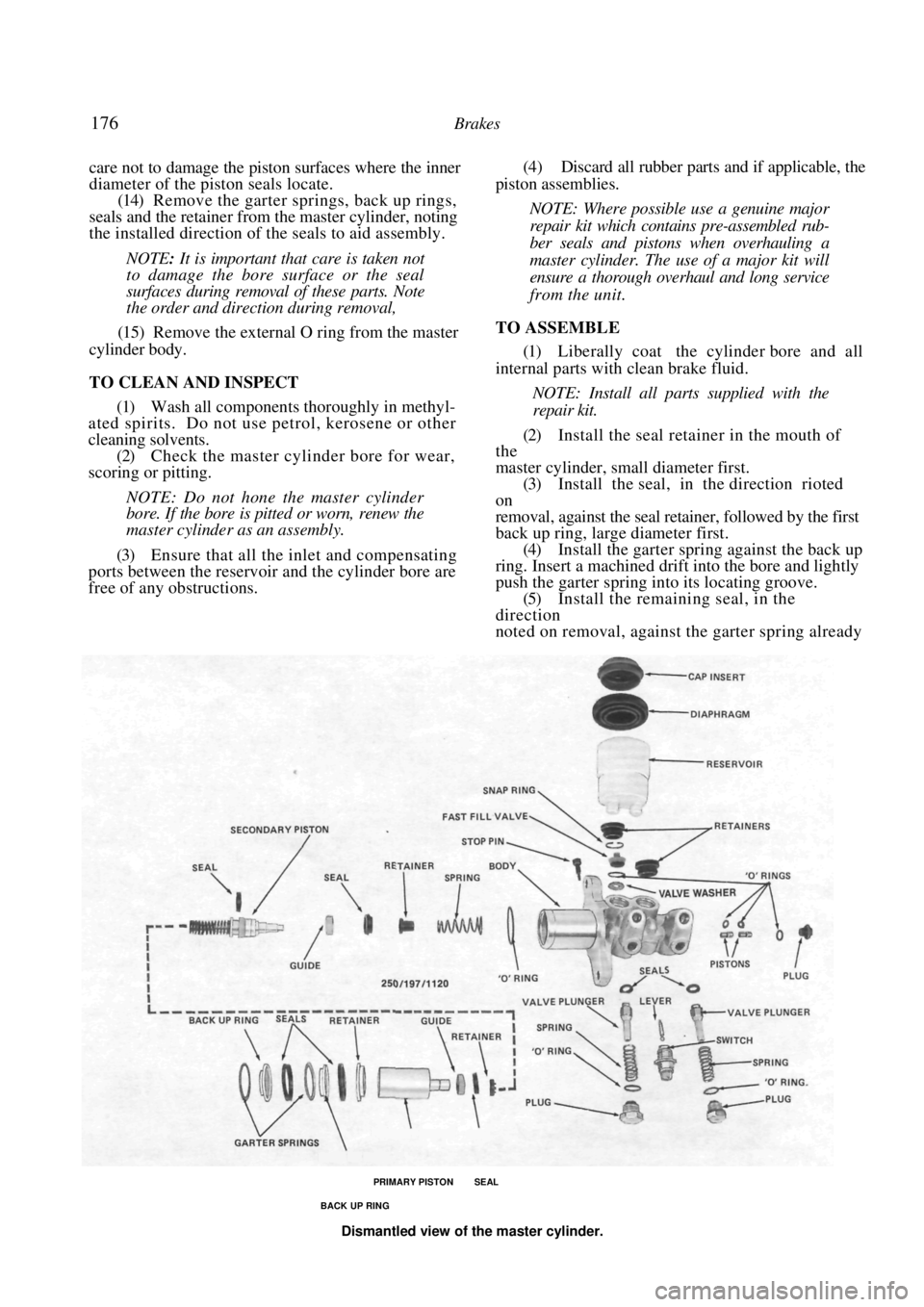
(14) Remove the garter springs, back up rings,
seals and the retainer from the master cylinder, noting
the installed direction of the seals to aid assembly.
NOTE: It is important that care is taken not
to damage the bore surface or the seal
surfaces during removal of these parts. Note
the order and direction during removal,
(15) Remove the external O ring from the master
cylinder body.
TO CLEAN AND INSPECT
(1) Wash all components thoroughly in methyl-
ated spirits. Do not use petrol, kerosene or other
cleaning solvents. (2) Check the master cyli nder bore for wear,
scoring or pitting.
NOTE: Do not hone the master cylinder
bore. If the bore is pitted or worn, renew the
master cylinder as an assembly.
(3) Ensure that all the inlet and compensating
ports between the reservoir and the cylinder bore are
free of any obstructions.
(4) Discard all rubber parts and if applicable, the
piston assemblies.
NOTE: Where possible use a genuine major
repair kit which contains pre-assembled rub-
ber seals and pistons when overhauling a
master cylinder. The use of a major kit will
ensure a thorough overhaul and long service
from the unit.
TO ASSEMBLE
(1) Liberally coat the cylinder bore and all
internal parts with clean brake fluid.
NOTE: Install all parts supplied with the
repair kit.
(2) Install the seal retainer in the mouth of
the
master cylinder, small diameter first.
(3) Install the seal, in the direction rioted
on
removal, against the seal retainer, followed by the first
back up ring, large diameter first. (4) Install the garter spring against the back up
ring. Insert a machined drift into the bore and lightly
push the garter spring into its locating groove. (5) Install the remaining seal, in the
direction
noted on removal, against the garter spring already
PRIMARY PISTON SEAL
BACK UP RING
Dismantled view of the master cylinder.
Page 177 of 238

Brakes 177
installed. Install the second back up ring, large
diam-
eter first.
(6) Install the second garter spring. Insert
a
machined drift into the bore and lightly push the
garter spring into its locating groove.
(7) Smear the secondary piston with clean brake
fluid. Ease the seal over the piston body into the
groove adjacent to the spring, ensuring that the seal lip
faces the spring and that the nylon spacer is against
the back of the seal. (8) Install the guide onto the secondary
piston,
large internal diameter first, followed by the main seal
with the lip facing away from the spring. (9) Lubricate the secondary piston assembly
with clean brake fluid and install the secondary spring
and retainer to the piston. Install the complete assem-
bly into the master cylinder bore. (10) Smear the primary piston with clean brake
fluid. Install the guide, large internal diameter first,
followed by the main seal with the lip facing towards
the small end of the piston.
(11) Install the retainer to the spigot on the front
end of the primary piston ensuring that the legs of the
retainer engage with the groove on the piston. (12) Lubricate the primary piston assembly with
clean brake fluid and install the assembly into the
master cylinder bore. With a blunt rod, push the
assembly down the bore sufficiently to preload the
pistons. While holding the preload, install the stop pin
and valve assemblies into
the master cylinder body and tighten securely. (13) Install a new O ring to the groove on the boss
of the mounting flange of the master cylinder.
(14) Install new O rings to th e pressure differential
pistons, smear them with cl ean brake fluid and install
them into the master cylinder body. (15) Install a new O ring to the pressure differen-
tial end plug, install the plug to the master
cylinder
body and tighten to the specified torque. (16) Using a blunt probe entered through the
sensing switch location hole, separate the pressure
differential pistons and install the switch actuating
lever between them. (17) Screw the sensing switch into its locating
hole until the detents on the switch body just contact
the locating hole facing (w ith the radial grooves).
Screw the switch assembly in a further half to one full
turn ensuring that the dete nts locate in the grooves.
(18) Install new valve seal s to the proportioning
valve plungers, with the serrations of the seals facing
away from the hexagons of the plungers.
(19) Install the new O rings to the
proportioning
valve plugs. (20) Install the valve springs over the stems of the
proportioning valves, insert the install the valve
plugs.
Tighten the plugs to the specified torque.
(21) Install a new O ring to the base of the fast fill
valve assembly. Install a new valve washer to the base
of the valve.
(22) Install the fast fill valve assembly in
the
primary reservoir port (nearest to the mounting flange
of the master cylinder) and install the snap ring
to
retain the assembly. Ensure that the snap ring is
correctly seated in the groove. (23) Smear the new reservoir retainers with clean
brake fluid and install them into the reservoir ports.
Carefully press the brake fluid reservoir into position,
ensuring that the outlet extensions are fully inserted in
the reservoir retainers. (24) Install the reservoir cap insert to the dia-
phragm and press the cap assembly onto the reservoir.
TO INSTAL
Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) Pour a small amount of clean brake fluid into
the reservoir and pump the master cylinder pistons
with a blunt rod until fluid begins to emerge from the
outlets. (2) Install the master cylinder to the brake servo
unit and loosely install the master cylinder retaining
nuts. (3) Connect the brake pipes to the master cylin-
der outlets, but do not tighten at this stage. (4) Securely tighten the nuts retaining the master
cylinder to the brake servo unit.
(5) Securely tighten the brake pipes and connect
the wiring to the pressure sensing switch.
(6) Fill the master cylinder reservoir with clean
brake fluid and bleed the brakes as described under
the Hydraulic System heading. (7) Check and if necessary adjust the brake
pedal height and free play as described under the
Brake Pedal heading.
4. BRAKE SERVO UNIT
TO CHECK OPERATION
(1) With the engine switched off, apply the
footbrake several times to exhaust all vacuum from
the system.
(2) Apply the footbrake and hold the brake pedal
fully depressed.
(3) Start the engine. If the servo unit is function-
ing satisfactorily a distinct downward movement of
the
brake pedal should be noticed. Should the pedal fail to move downward when the
engine has been started, the vacuum system can be
considered inoperative.
NOTE: If the pedal continues to fall away
there is a fault in the hydraulic system.
(4) Ensure that the brake pedal is fully released,
start the engine and run it at medium speed. Stop the
engine.
Page 178 of 238
178 Brakes
Let the vehicle stand for 1-2 minutes, press the
brake pedal two or three times and check its opera-
tion.
If there is no vacuum assistance, the vacuum
system has developed a leak or the one way check
valve is defective.
NOTE: Before removing the servo unit from
the vehicle for inspection, disconnect the
hose from the servo unit, start the engine
and check that the manifold vacuum is in
fact reaching the servo unit. Also test the one
way check valve as described below,
TO TEST ONE WAY CHECK VALVE
(1) Disconnect the hose and remove the check
valve from the servo unit.
(2) Check the valve for sticking. Suction on the
manifold side should allo w air to flow freely. Air
blown into the valve from the manifold side should
not be able to flow through the valve. (3) Install the valve and check the operation
of
the servo unit as previously described.
NOTE: Check that there are no air leaks at
the hose connections and that the hose clips
are tight. Also check that the hose is not
bulged or collapsed due to deterioration.
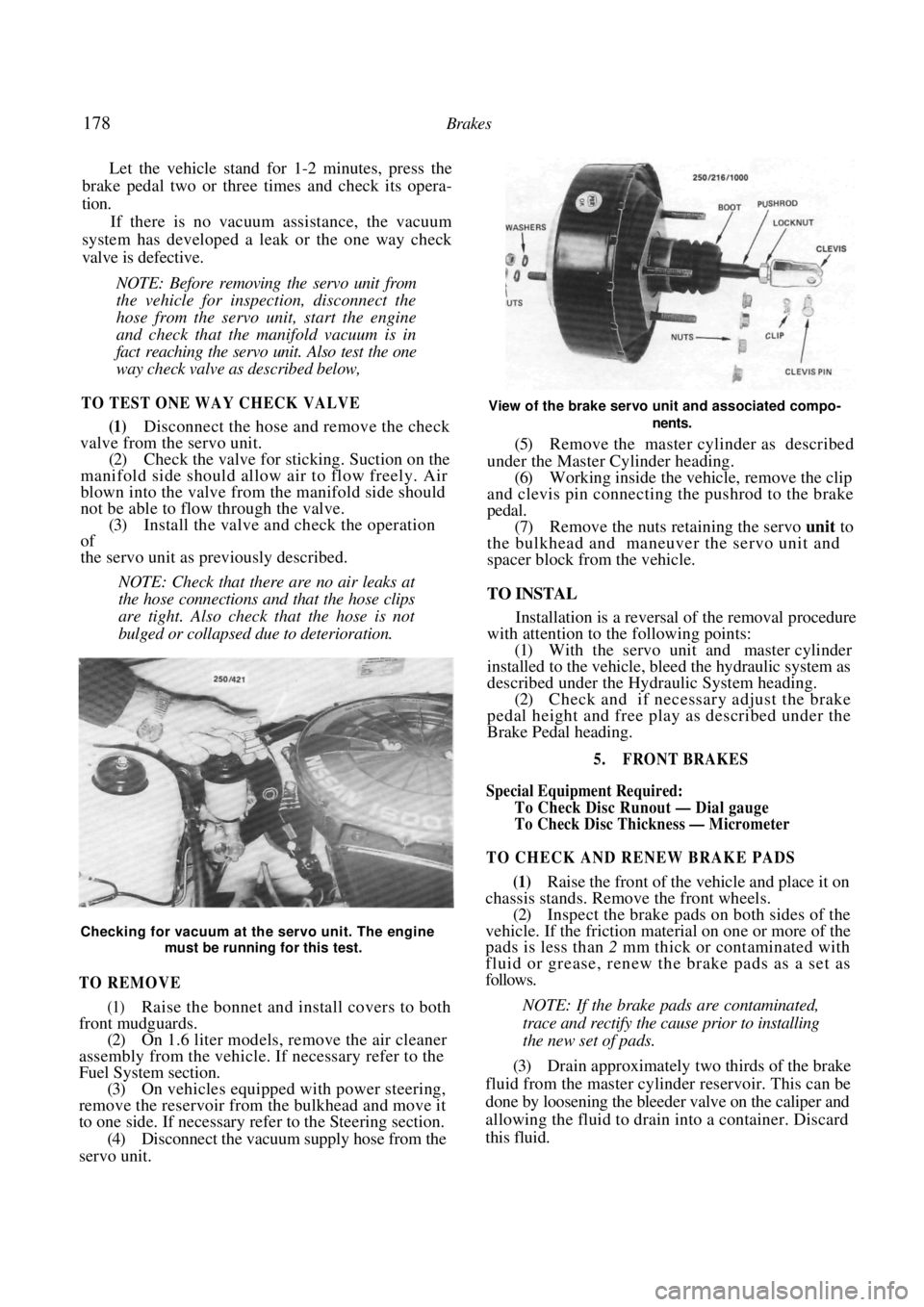
Checking for vacuum at the servo unit. The engine
must be running for this test.
TO REMOVE
(1) Raise the bonnet and install covers to both
front mudguards.
(2) On 1.6 liter models, remove the air cleaner
assembly from the vehicle. If necessary refer to the
Fuel System section.
(3) On vehicles equipped with power steering,
remove the reservoir from the bulkhead and move it
to one side. If necessary refer to the Steering section.
(4) Disconnect the vacuum supply hose from the
servo unit.
View of the brake servo unit and associated compo-
nents.
(5) Remove the master cylinder as described
under the Master Cylinder heading. (6) Working inside the vehicle, remove the clip
and clevis pin connecting the pushrod to the brake
pedal. (7) Remove the nuts retaining the servo unit to
the bulkhead and maneuver the servo unit and
spacer block from the vehicle.
TO INSTAL
Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) With the servo unit and master cylinder
installed to the vehicle, bleed the hydraulic system as
described under the Hydr aulic System heading.
(2) Check and if necessary adjust the brake
pedal height and free play as described under the
Brake Pedal heading.
5. FRONT BRAKES
Special Equipment Required:
To Check Disc Runout — Dial gauge
To Check Disc Thickness — Micrometer
TO CHECK AND RENEW BRAKE PADS
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the front wheels.
(2) Inspect the brake pads on both sides of the
vehicle. If the friction material on one or more of the
pads is less than 2 mm thick or contaminated with
fluid or grease, renew the brake pads as a set as
follows.
NOTE: If the brake pads are contaminated,
trace and rectify the cause prior to installing
the new set of pads.
(3) Drain approximately two thirds of the brake
fluid from the master cylinde r reservoir. This can be
done by loosening the bleeder valve on the caliper and
allowing the fluid to drai n into a container. Discard
this fluid.
Page 179 of 238
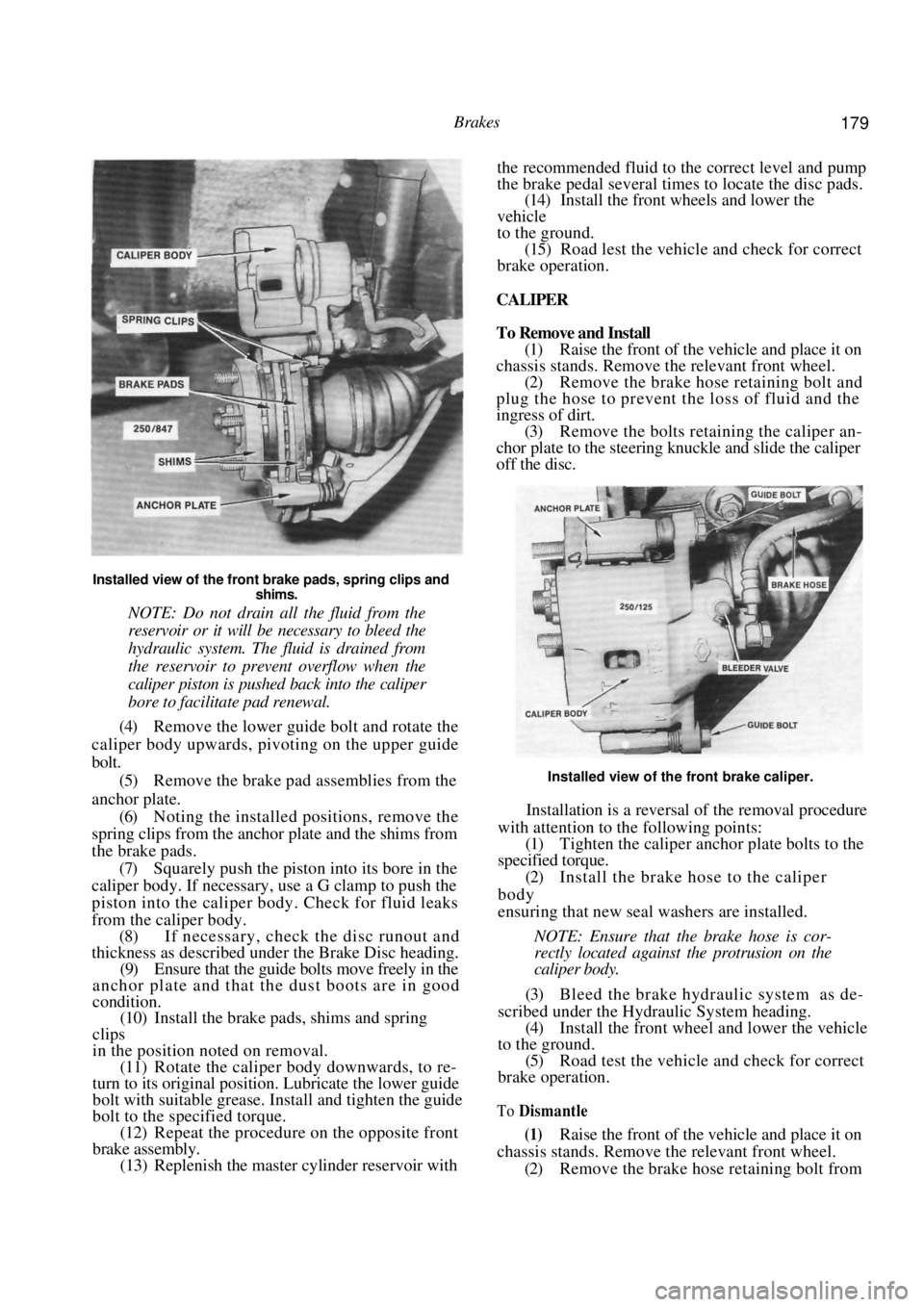
Brakes 179
Installed view of the front brake pads, spring clips and shims.
NOTE: Do not drain all the fluid from the
reservoir or it will be necessary to bleed the
hydraulic system. The fluid is drained from
the reservoir to prevent overflow when the
caliper piston is pushed back into the caliper
bore to facilitate pad renewal.
(4) Remove the lower guide bolt and rotate the
caliper body upwards, pivoting on the upper guide
bolt.
(5) Remove the brake pad assemblies from the
anchor plate. (6) Noting the installed positions, remove the
spring clips from the anchor plate and the shims from
the brake pads.
(7) Squarely push the piston into its bore in the
caliper body. If necessary, us e a G clamp to push the
piston into the caliper b ody. Check for fluid leaks
from the calip er body.
(8) If necessary, check the disc runout and
thickness as described under the Brake Disc heading.
(9) Ensure that the guide bolts move freely in the
anchor plate and that the dust boots are in good
condition. (10) Install the brake pads, shims and spring
clips
in the position noted on removal. (11) Rotate the caliper body downwards, to re-
turn to its original position. Lubricate the lower guide
bolt with suitable grease. In stall and tighten the guide
bolt to the specified torque. (12) Repeat the procedure on the opposite front
brake assembly. (13) Replenish the master cylinder reservoir with the recommended fluid to the correct level and pump
the brake pedal several times to locate the disc pads.
(14)
Install the front wheels and lower the
vehicle
to the ground. (15) Road lest the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
CALIPER
To Remove and Install
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant front wheel. (2) Remove the brake hose retaining bolt and
plug the hose to prevent the loss of fluid and the
ingress of dirt. (3) Remove the bolts retaining the caliper an-
chor plate to the steering knuckle and slide the caliper
off the disc.
Installed view of the front brake caliper.
Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) Tighten the caliper anch or plate bolts to the
specified torque.
(2) Install the brake hose to the caliper
body
ensuring that new seal washers are installed.
NOTE: Ensure that the brake hose is cor-
rectly located against the protrusion on the
caliper body.
(3) Bleed the brake hydraulic system as de-
scribed under the Hydraulic System heading. (4) Install the fron t wheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. (5) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
To Dismantle
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant front wheel.
(2) Remove the brake hose retaining bolt from
Page 180 of 238
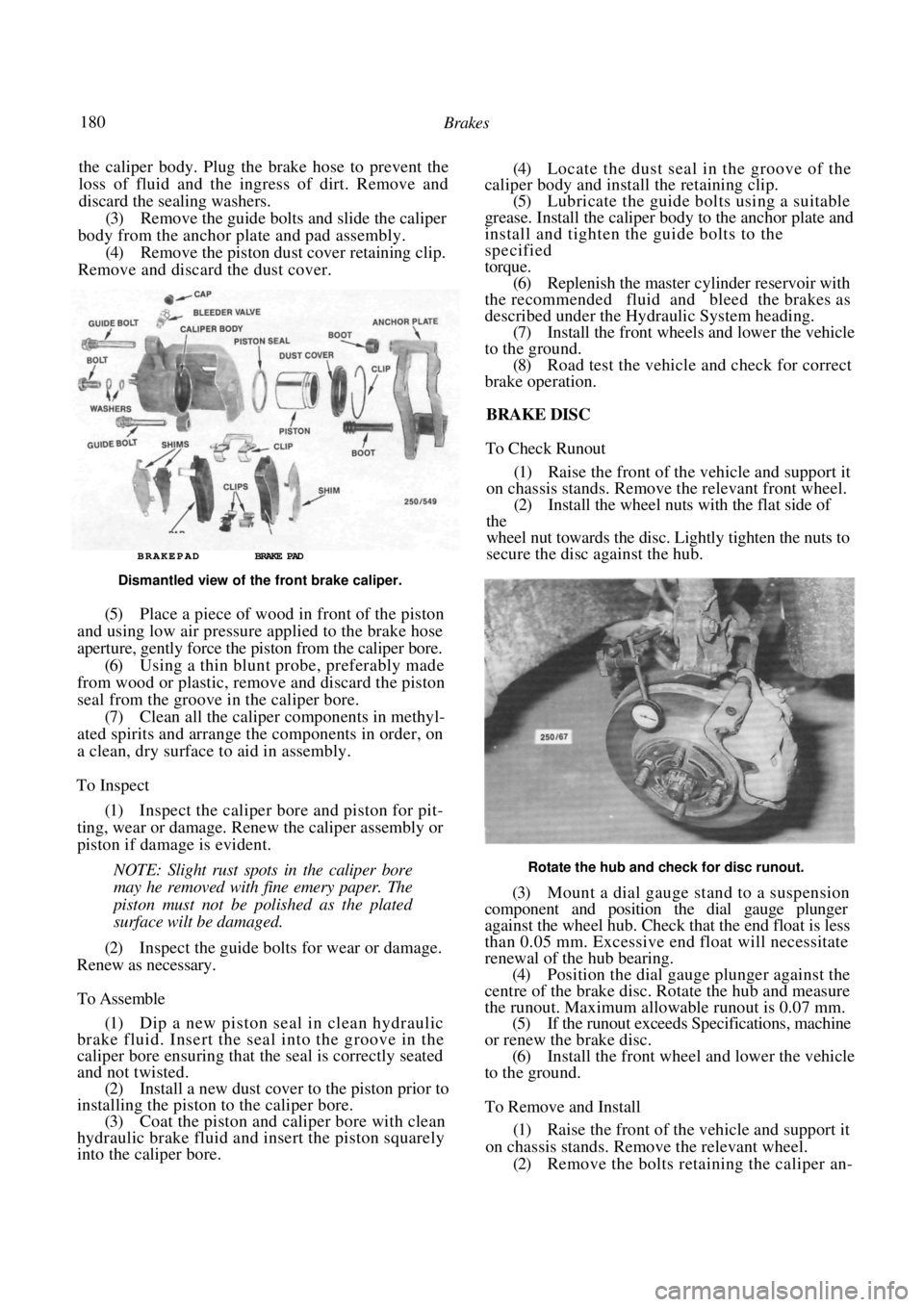
180 Brakes
the caliper body. Plug the brake hose to prevent the
loss of fluid and the ingress of dirt. Remove and
discard the sealing washers.
(3) Remove the guide bolts and slide the caliper
body from the anchor plate and pad assembly. (4) Remove the piston dust cover retaining clip.
Remove and discard the dust cover.
BRAKEPAD BRAKE PAD
Dismantled view of the front brake caliper.
(5) Place a piece of wood in front of the piston
and using low air pressure applied to the brake hose
aperture, gently force the piston from the caliper bore.
(6) Using a thin blunt probe, preferably made
from wood or plastic, remove and discard the piston
seal from the groove in the caliper bore. (7) Clean all the caliper components in methyl-
ated spirits and arrange the components in order, on
a clean, dry surface to aid in assembly.
To Inspect
(1) Inspect the caliper bore and piston for pit-
ting, wear or damage. Renew the caliper assembly or
piston if damage is evident.
NOTE: Slight rust spots in the caliper bore
may he removed with fine emery paper. The
piston must not be polished as the plated
surface wilt be damaged.
(2) Inspect the guide bolts for wear or damage.
Renew as necessary.
To Assemble
(1) Dip a new piston seal in clean hydraulic
brake fluid. Insert the seal into the groove in the
caliper bore ensuring that the seal is correctly seated
and not twisted.
(2) Install a new dust cover to the piston prior to
installing the piston to the caliper bore. (3) Coat the piston and caliper bore with clean
hydraulic brake fluid and insert the piston squarely
into the caliper bore.
(4) Locate the dust seal in the groove of the
caliper body and install the retaining clip.
(5) Lubricate the guide bolts using a suitable
grease. Install the caliper body to the anchor plate and
install and tighten the guide bolts to the
specified
torque. (6) Replenish the master cylinder reservoir with
the recommended fluid and bleed the brakes as
described under the Hydr aulic System heading.
(7) Install the front wheels and lower the vehicle
to the ground. (8) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
BRAKE DISC
To Check Runout
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove the relevant front wheel. (2) Install the wheel nuts with the flat side of
the
wheel nut towards the disc. Lightly tighten the nuts to
secure the disc against the hub.
Rotate the hub and check for disc runout.
(3) Mount a dial gauge stand to a suspension
component and position the dial gauge plunger
against the wheel hub. Check that the end float is less
than 0.05 mm. Excessive e nd float will necessitate
renewal of the hub bearing. (4) Position the dial gauge plunger against the
centre of the brake disc. Ro tate the hub and measure
the runout. Maximum allowable runout is 0.07 mm. (5) If the runout exceeds Specifications, machine
or renew the brake disc. (6) Install the fron t wheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground.
To Remove and Install
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove the relevant wheel. (2) Remove the bolts retaining the caliper an-